2,6-二甲基苯胺 | 87-62-7
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:10-12 °C(lit.)
-
沸点:216 °C
-
密度:0.984 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
-
闪点:196 °F
-
溶解度:13克/升
-
LogP:1.840
-
物理描述:2,6-xylidine appears as a liquid. Toxic by ingestion, inhalation and skin absorption. Slightly soluble in water. Used in pharmaceuticals, as dye intermediates and organic syntheses.
-
颜色/状态:Yellow liquid
-
气味:Characteristic odor
-
蒸汽密度:4.17 (NTP, 1992) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:0.125 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
自燃温度:520 °C
-
分解:When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of /nitrogen oxides/.
-
粘度:1.7 mPa.s (dynamic) at 50 °C
-
汽化热:Enthalpy of vaporization: 59.2 kJ/mol at 286-326 K
-
气味阈值:Odor threshold in air= 1.00X10+12 molecules/cc /Xylidines/
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.5610 at 20 °C/D
-
解离常数:pKa = 3.95 at 25 °C
-
保留指数:1136.2 ;1135.52 ;1136.26 ;1136.34 ;1137.15 ;1137.93 ;1143.41 ;1179 ;1140.7 ;1149 ;1131 ;1134 ;1143 ;1143 ;1146 ;1157 ;1173 ;1130
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):1.8
-
重原子数:9
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.25
-
拓扑面积:26
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:1
ADMET
安全信息
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:6.1
-
危险品标志:Xn,N
-
安全说明:S23,S25,S36/37,S61
-
危险类别码:R51/53,R20/21/22,R40,R37/38
-
WGK Germany:2
-
海关编码:29214910
-
危险品运输编号:UN 1711 6.1/PG 2
-
危险类别:6.1
-
RTECS号:ZE9275000
-
包装等级:II
-
储存条件:1. **储存注意事项**:储存于阴凉通风的库房中,远离火种和热源,并确保容器密封。应将储物与其他氧化剂、酸类、卤素和食用化学品分开存放,避免混合存储。配置相应的消防设备。储区需配备泄漏应急处理设备和合适的收容材料。 2. **包装与储存**:采用小开口钢桶、螺纹口玻璃瓶、铁盖压口玻璃或塑料瓶以及金属桶(罐),外加木板箱;安瓿瓶也应使用木板箱封装。储存于阴凉通风的仓库内,远离火种和热源,并防止阳光直射。保持容器密封,与氧化剂、酸类及食用化学品分开存放。搬运时轻装轻卸,以防包装和容器受损。
SDS
| 国标编号: | 61753 |
| CAS: | 87-62-7 |
| 中文名称: | 2,6-二甲(基)苯胺 |
| 英文名称: | 2,6-dimethylaniline;2,6-Xylidine |
| 别 名: | 1-氨基-2,6-二甲基苯 |
| 分子式: | C 8 H 11 N;(CH 3 ) 2 C 6 H 3 NH 2 |
| 分子量: | 121.18 |
| 熔 点: | 11.2℃ |
| 密 度: | 相对密度(水=1)0.98; |
| 蒸汽压: | 91℃ |
| 溶解性: | 不溶于水,溶于乙醇、乙醚 |
| 稳定性: | 稳定 |
| 外观与性状: | 无色液体 |
| 危险标记: | 14(毒害品) |
| 用 途: | 用于有机合成 |
2.对环境的影响:
一、健康危害
侵入途径:吸入、食入、经皮吸收。
健康危害:毒性与苯胺相似,形成高铁血红蛋白,造成组织缺氧,引起中枢神经系统,心血管系统和其它脏器损害。其中对中枢神经系统及肝脏损害较强,对血液作用较弱,也可引起皮炎。
急性中毒:病人出现恶心、呕吐、手指麻木、精神恍惚,唇、指端、耳廓发绀;重谨毒时皮肤、粘膜严重青紫,出现心悸、呼吸困难、抽搐等,甚至昏迷、休克。重笃者可出现溶血性黄疸、中毒性肝炎和中毒性肾损伤。
慢性中毒:患者有神经衰弱综合征表现,伴有轻度发绀、贫血和肝、脾肿大。
二、毒理学资料及环境行为
毒性:属中等毒类。
急性毒性:LD50840mg/kg(大鼠经口);707mg/kg(小鼠经口)
危险特性:遇明火、高热或与氧化剂接触,有引起燃烧的危险。受热分解放出有毒的氧化氮烟气。
燃烧(分解)产物:一氧化碳、二氧化碳、氧化氮。
3.现场应急监测方法:
4.实验室监测方法:
气相色谱法《空气中有害物质的测定方法》(第二版),杭士平主编
5.环境标准:
中国(TJ36-79)车间空气中有害物质的最高容许浓度 5mg/m3[皮]
6.应急处理处置方法:
一、泄漏应急处理
疏散泄漏污染区人员至安全区,禁止无关人员进入污染区,建议应急处理人员戴自给式呼吸器,穿化学防护服。不要直接接触泄漏物,在确保安全情况下堵漏。喷雾状水,减速少蒸发。用沙土或其它不燃性吸附剂混合吸收,然后收集运至废物处理场所处置。也可以用不燃性分散剂制成的乳液刷洗,经稀释的洗水放入废水系统。如大量泄漏,建围堤收容,然后收集、转移、回收或无害处理后废弃。
二、防护措施
呼吸系统防护:可能接触其蒸气时,佩带防毒面具。紧急事态抢救或逃生时,佩带正压自给式呼吸器。
眼睛防护:戴安全防护眼镜。
防护服:穿紧袖工作服,长统胶鞋。
手防护:戴橡皮手套。
其它:工作现场禁止吸烟、进食和饮水。及时换洗工作服。工作前后不饮酒,用温水洗澡。监测毒物。进行就业前和定期的体检。
三、急救措施
皮肤接触:立即脱去污染的衣着,用肥皂水及清水彻底冲洗。注意手、足和指甲等部位。
眼睛接触:立即提起眼睑,用大量流动清水或生理盐水冲洗。
吸入:迅速脱离现场至空气新鲜处。呼吸困难时给输氧。呼吸停止时,立即时进行人工呼吸。就医。
食入:误服者给漱口,饮水,洗胃后口服活性炭,再给以导泻。就医。
灭火方法:雾状水、泡沫、二氧化碳、干粉、砂土。
制备方法与用途
化学性质
2,6-二甲基苯胺为微黄色液体,沸点在216~217℃之间,熔点为10~12℃,折射率(20°C)为1.5590,相对密度为0.973。它不溶于水,能溶于醇、醚,并且可溶解于盐酸中。
用途
2,6-二甲基苯胺是多种农药和医药产品的中间体。在农药行业中,它可以用于生产高效杀菌剂如甲霜灵、呋霜灵、呋酰胺、甲呋酰胺、苯霜灵、杀毒矾以及除草剂异丁草胺、特瑞多(二甲草胺)和咪唑胺等;在医药行业,则可用于制造麻醉药如盐酸利多卡因、盐酸布比卡因、盐酸室安卡因、托卡铵、杜娟素等多种药物。此外,它也是生产兽药静松灵的重要原料。
用途
2,6-二甲基苯胺用作农药和医药中间体,可制造甲霜灵、呋霜灵及利多卡因等化合物。
用途
本产品是生产农药和医药的关键中间体,也可作为染料及其他化工产品的原材料。
生产方法
2,6-二甲基苯胺的主要合成路线包括间二甲苯氨解法、邻甲基苯胺烷基化法、苯胺甲基化法、间二甲苯双磺化硝化法和间二甲苯硝化还原法等。
生产方法
其制备方法有以下几种:
-
以间二甲苯为原料,采用混酸硝化与催化加氢相结合的方法。具体工艺是将间二甲苯冷却至0~5℃,分批加入冷却后的混酸(含56.5%硫酸、28%硝酸及15.5%水),第一次保持温度在17~25℃,3小时内加完;第二次则于相同温度范围内,在2小时内加完。最后滴加温度为25~30℃的溶液,并在该温度下搅拌30分钟。随后将硝化物用水洗涤并减压蒸馏得到粗品,再通过78~85℃/666.5Pa的馏分进行冷却结晶,最终获得2,6-二甲基硝基苯。
-
进行还原时,过去常用铁粉和稀盐酸逐步还原。具体操作为将铁粉逐步加入到2,6-二甲基硝基苯和稀盐酸溶液中,并在完成加料后回流30分钟。冷却后使用碳酸钠进行中和处理并用水蒸馏。分层后,油层干燥即得产品。现采用催化加氢方法代替铁粉还原,在催化剂存在下2,6-二甲基硝基苯催化加氢得到粗品,并经后续处理制备成品。
上述方法生产的产物还包括2,6-二甲基苯胺和2,4-二甲基苯胺,但在反应过程中2,6-二甲基苯胺占比较少。为此,国外广泛采用邻甲苯胺烷基化法生产2,6-二甲基苯胺。
2,6-二甲基苯胺的合成方法还有如下途径:
- 烷基化法:以邻甲苯胺和甲醇为原料,在催化剂存在的条件下,在一定压力下反应。此过程不仅产生主要产物2,6-二甲基苯胺,还伴有多种副产品的生成,其中包括与之结构相似、物理性质相近的2,3-二甲基苯胺。通过分离掉邻甲苯胺、三甲苯胺等其他副产品后,可得到98%的混合物作为起始原料(其中含有18%的2,3-二甲基苯胺)。进一步采用精密分馏技术,全塔理论板数超过80块,从而完全分离出这两种化合物,并最终获得高纯度的2,6-二甲基苯胺。
类别
有毒物品
毒性分级
中毒
急性毒性
口服 - 大鼠 LD50: 840 毫克/公斤;小鼠 LD50: 707 毫克/公斤
可燃性危险特性
遇明火可燃;与氧化剂反应;高温分解产生有毒氮氧化物烟雾
储运特性
应存放在通风、低温和干燥的库房中,并与酸类、氧化剂及食品添加剂分开存放
灭火剂
泡沫、二氧化碳、干粉或砂土等均可用于扑灭相关火灾。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 2,4,6-三甲基苯胺 2,4,6-trimethylaniline 88-05-1 C9H13N 135.209 2,6-二甲基苯肼 (2,6-dimethylphenyl)hydrazine 603-77-0 C8H12N2 136.197 —— 2,6-dimethyl-N-methylene benzamine 35203-02-2 C9H11N 133.193 —— N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)hydroxylamine 3096-63-7 C8H11NO 137.181 N,2,6-三甲基苯胺 N-methyl-2,6-dimethylaniline 767-71-5 C9H13N 135.209 1-氨基-3,5-二甲苯 3,5-dimethylaminoaniline 108-69-0 C8H11N 121.182 4-溴-2,6-二甲基苯胺 4-bromo-2,6-dimethylaniline 24596-19-8 C8H10BrN 200.078 —— 2,6-dimethyl-N-sulfinyl-benzenamine 17420-02-9 C8H9NOS 167.232 1,3-二甲基-2-叠氮基苯 2,6-dimethylphenylazide 26334-20-3 C8H9N3 147.18 —— N'-(2,6-methyl-phenyl)-N,N-dimethyl-formamidine —— C11H16N2 176.261 —— N,N'-ethane-1,2-diylidenebis(2,6-dimethylaniline) 49673-43-0 C18H20N2 264.37 - 1
- 2
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 2,4,6-三甲基苯胺 2,4,6-trimethylaniline 88-05-1 C9H13N 135.209 2,4-二甲基苯胺 2,4-Xylidine 95-68-1 C8H11N 121.182 邻甲苯胺 o-toluidine 95-53-4 C7H9N 107.155 2,6-二甲基-P-苯二胺 2,6-dimethylbenzene-1,4-diamine 7218-02-2 C8H12N2 136.197 2,6-二甲基苯肼 (2,6-dimethylphenyl)hydrazine 603-77-0 C8H12N2 136.197 —— 2,6-dimethyl-N-methylene benzamine 35203-02-2 C9H11N 133.193 1,3-二甲基-2-亚硝基苯 2,6-dimethylnitrosobenzene 19519-71-2 C8H9NO 135.166 N,2,6-三甲基苯胺 N-methyl-2,6-dimethylaniline 767-71-5 C9H13N 135.209 4-氨基-3,5-二甲基苯氰 4-amino-3,5-dimethylbenzonitrile 74896-24-5 C9H10N2 146.192 2-氨基-3-甲基苯甲醛 2-amino-3-methylbenzaldehyde 84902-24-9 C8H9NO 135.166 —— 2,6-dimethyl-4-ethylaniline 40813-99-8 C10H15N 149.236 4-氨基-3,5-二甲苯甲醛 4-amino-3,5-dimethylbenzaldehyde 56066-83-2 C9H11NO 149.192 4-碘-2,6-二甲基苯胺 4-iodo-2,6-dimethylaniline 4102-53-8 C8H10IN 247.079 4-氯-2,6-二甲基苯胺 4-chloro-2,6-dimethylaniline 24596-18-7 C8H10ClN 155.627 3,5-二甲基-4-氨基苯酚 3,5-dimethyl-4-aminophenol 3096-70-6 C8H11NO 137.181 4-溴-2,6-二甲基苯胺 4-bromo-2,6-dimethylaniline 24596-19-8 C8H10BrN 200.078 2,6-二甲苯基异氰酸酯 2,6-dimethylphenylisocyanate 28556-81-2 C9H9NO 147.177 —— 2,6-dimethyl-N-sulfinyl-benzenamine 17420-02-9 C8H9NOS 167.232 —— 2,6-xylyl isoselenocyanate 154592-61-7 C9H9NSe 210.137 2,6-二甲基异硫氰酸苯酯 2,6-dimethylphenylisothiocyanate 19241-16-8 C9H9NS 163.243 1,3-二甲基-2-叠氮基苯 2,6-dimethylphenylazide 26334-20-3 C8H9N3 147.18 —— (E)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)formamidine —— C9H12N2 148.208 —— N-ethyl-2,6-dimethylaniline 769-23-3 C10H15N 149.236 N-(2,6-二甲基苯)甲酰胺 2,6-dimethylformanilide 607-92-1 C9H11NO 149.192 2,6,N,N-四甲基苯胺 N,N,2,6-tetramethylaniline 769-06-2 C10H15N 149.236 N-(2,6-二甲基苯基)-羧基硫代酰胺 N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-carboxythioamide 20979-95-7 C9H11NS 165.259 —— 4-allyl-2,6-dimethylaniline 4494-83-1 C11H15N 161.247 4-异丙基-2,6-二甲基苯胺 2,6-dimethyl-4-isopropylaniline 42014-59-5 C11H17N 163.263 —— N-phenyl-2,6-dimethylaniline 4058-04-2 C14H15N 197.28 2,6-二甲基-N-(2-甲基苯基)苯胺 2,6-dimethyl-N-(o-tolyl)aniline 68014-57-3 C15H17N 211.307 双(2,6-二甲基苯)胺 bis(2,6-dimethylphenyl)amine 74443-35-9 C16H19N 225.334 4-(4-氨基-3,5-二甲基苄基)-2,6-二甲基苯胺 4,4'-methylenebis(2,6-dimethylaniline) 4073-98-7 C17H22N2 254.375 —— 2’,6’-dimethylazobenzene 17590-87-3 C14H14N2 210.279 4-(4-氨基苄基)-2,6-二甲基苯胺 4-[(4-aminophenyl)methyl]-2,6-xylidine 68434-48-0 C15H18N2 226.321 —— 4-benzyl-2,6-dimethylbenzenamine 16819-52-6 C15H17N 211.307 —— 1-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-2-phenyldiazene 10273-96-8 C14H14N2 210.279 —— (2,6-dimethyl) phenylguanidine 62577-35-9 C9H13N3 163.222 1,2-双(2,6-二甲基苯基)肼 2,2′,6,6′-(tetramethyldiphenyl)hydrazine 63615-06-5 C16H20N2 240.348 —— N-(2,6-Dimethylphenyl)ethylendiamin 71319-67-0 C10H16N2 164.25 —— 2,6-dimethylphenylimine of acetone 85384-97-0 C11H15N 161.247 二(2,6-二甲基苯基)二氮烯 2,2',6,6'-Tetramethyl-azobenzol 29418-31-3 C16H18N2 238.332 —— 2-(N-isopropylamino)-1,3-dimethylbenzene 61685-01-6 C11H17N 163.263 —— anti-2,2',6,6'-Tetramethylazobenzene 10228-76-9 C16H18N2 238.332 —— 1,3-bis(2,6-dimethylphenyl)carbodiimide 61110-94-9 C17H18N2 250.343 —— N-(2-propynyl)-2,6-dimethylbenzenamine 74248-48-9 C11H13N 159.231 —— 2-((2,6-dimethylphenyl)amino)acetonitrile 30123-97-8 C10H12N2 160.219 罗哌卡因杂质5 N-propyl-2,6-dimethylaniline 826-99-3 C11H17N 163.263 —— N-(4-methylphenyl)-2,6-dimethylaniline 24542-61-8 C15H17N 211.307 —— 2,6-dimethyl-4-(trifluoromethyl)aniline 144991-53-7 C9H10F3N 189.18 2-(2,6-二甲基苯胺基)乙醇 2-(2,6-dimethylphenylamino)ethanol 3046-95-5 C10H15NO 165.235 —— N-allyl-2,6-dimethylaniline 74248-47-8 C11H15N 161.247 (E)-3-(4-氨基-3,5-二甲基苯基)丙烯腈 (E)-3-(4-amino-3,5-dimethylphenyl)acrylonitrile 500292-94-4 C11H12N2 172.23 —— N1,N2-bis(2,6-dimethylphenyl)ethane-1,2-diamine 72991-60-7 C18H24N2 268.402 4-氨基-3,5-二甲基苯丙醇 3-(4-Amino-3,5-dimethyl-phenyl)-propan-1-ol 454476-59-6 C11H17NO 179.262 —— N,N'-ethane-1,2-diylidenebis(2,6-dimethylaniline) 49673-43-0 C18H20N2 264.37 —— N-[(1E,2E)-2-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)ethylidene]-2,6-dimethylphenylamine 134780-63-5 C18H20N2 264.37 —— N-tert-butyl-2,6-dimethylaniline —— C12H19N 177.29 —— ropivacaine 24053-84-7 C11H16N2 176.261 —— N'-(2,6-methyl-phenyl)-N,N-dimethyl-formamidine —— C11H16N2 176.261 3-溴-2,6-二甲基苯胺 3-bromo-2,6-dimethylaniline 53874-26-3 C8H10BrN 200.078 —— N-(2,6-dimethyl-phenyl)-propane-1,3-diamine 79429-47-3 C11H18N2 178.277 —— 4-amino-3,5-dimethylphenyl methyl sulphide 120578-20-3 C9H13NS 167.275 —— N-TMS-2,6-Dimethylaniline 69563-03-7 C11H19NSi 193.364 3-羟基-2,6-二甲苯胺 3-amino-2,4-dimethylphenol 100445-96-3 C8H11NO 137.181 —— N-butyl-2,6-dimethylphenylamine 41115-22-4 C12H19N 177.29 - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:Noelting; Forel, Chemische Berichte, 1885, vol. 18, p. 2677,2681摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:Formal arylation of NH3 to produce diphenylamines over supported Pd catalysts摘要:在Pd/Al2O3存在下,可以通过以尿素为氮源、环己酮为芳基化源进行无受体形式芳基化合成各种二苯胺。DOI:10.1039/c7cc06737b
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:Synthesis of 2-benzoylpyrrole derivatives via C–H functionalization adjacent to nitrogen of pyrrole摘要:A direct transition-metal-free synthesis of 2-benzoylpyrrole derivatives from free (N-H) pyrroles and benzaldehyde has been developed. The benzoylation reaction at the 2 or 5-position of pyrrole proceeded well under the alkali metalation system and with 2,6-dimethylaniline as the additive in moderate to good yields. This strategy offers a simple, efficient approach to synthesis of the 2-benzoylpyrrole derivatives. (C) 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.DOI:10.1016/j.tetlet.2015.04.118
文献信息
-
Compositions for Treatment of Cystic Fibrosis and Other Chronic Diseases申请人:Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated公开号:US20150231142A1公开(公告)日:2015-08-20The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising an inhibitor of epithelial sodium channel activity in combination with at least one ABC Transporter modulator compound of Formula A, Formula B, Formula C, or Formula D. The invention also relates to pharmaceutical formulations thereof, and to methods of using such compositions in the treatment of CFTR mediated diseases, particularly cystic fibrosis using the pharmaceutical combination compositions.
-
Cobalt(II)-Catalyzed Isocyanide Insertion Reaction with Sulfonyl Azides in Alcohols: Synthesis of Sulfonyl Isoureas作者:Tian Jiang、Zheng-Yang Gu、Ling Yin、Shun-Yi Wang、Shun-Jun JiDOI:10.1021/acs.joc.7b01127日期:2017.8.4A Co(II)-catalyzed isocyanide insertion reaction with sulfonyl azides in alcohols to form sulfonyl isoureas via nitrene intermediate has been developed. This protocol provides a new, environmentally friendly, and simple strategy for the synthesis of sulfonyl isourea derivatives by employing a range of substrates under mild conditions.
-
Metal-Free Cascade Formation of Intermolecular C–N Bonds Accessing Substituted Isoindolinones under Cathodic Reduction作者:Zirong Zou、Genuo Cai、Weihao Chen、Canlin Zou、Yamei Li、Hongting Wu、Lu Chen、Jinhui Hu、Yibiao Li、Yubing HuangDOI:10.1021/acs.joc.1c01845日期:2021.11.5An electrochemical protocol for the construction of substituted isoindolinones via reduction/amidation of 2-carboxybenzaldehydes and amines has been realized. Under metal-free and external-reductant-free electrolytic conditions, the reaction achieves the cascade formation of intermolecular C–N bonds and provides a series of isoindolinones in moderate to good yields. The deuterium-labeling experiment
-
Syntheses and antimicrobial activities of five-membered heterocycles having a phenylazo substituent.作者:KUNIYOSHI TANAKA、KEIZO MATSUO、AI NAKANISHI、MISAKO JO、HIRONORI SHIOTA、MIKIKO YAMAGUCHI、SAKIKO YOSHINO、KEIKO KAWAGUCHIDOI:10.1248/cpb.32.3291日期:——Several five-membered heterocycles having a phenylazo substituent, 3-phenylazotetronic acids (2a-n), 3-phenylazotetramic acids (4a-i), 4-phenylazo-5-isoxazolinones (6a-g, 8a-f) and 5-phenylazo-4-thiazolidinones (10a-f, 12a-e), were synthesized and tested for antimicrobial activities. Tetronic acid and tetramic acid derivatives (2 and 4) inhibited the growth of gram-positive bacteria. 5-Isoxazolinone and 4-thiazolidinone derivatives (8 and 10) showed inhibitory activities against fungi as well as bacteria.
-
Facile, Catalytic Dehydrocoupling of Phosphines Using β‐Diketiminate Iron(II) Complexes作者:Andrew K. King、Antoine Buchard、Mary F. Mahon、Ruth L. WebsterDOI:10.1002/chem.201503399日期:2015.11.2Catalytic dehydrocoupling of primary and secondary phosphines has been achieved for the first time using an iron pre‐catalyst. The reaction proceeds under mild reaction conditions and is successful with a range of diarylphosphines. A proton acceptor is not needed for the transformation to take place, but addition of 1‐hexene does allow for turnover at 50 °C. The catalytic system developed also facilitates
表征谱图
-
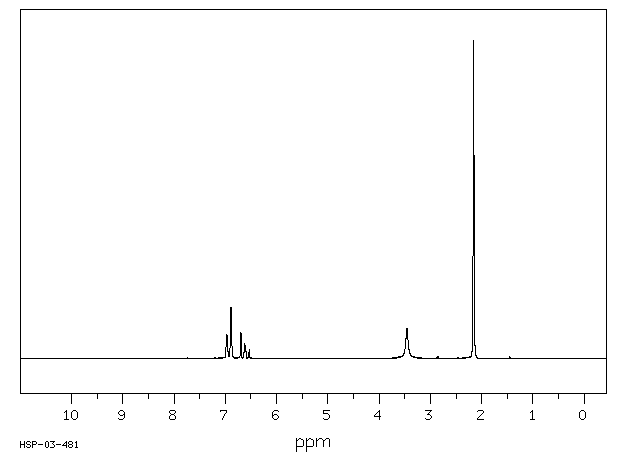
氢谱1HNMR
-
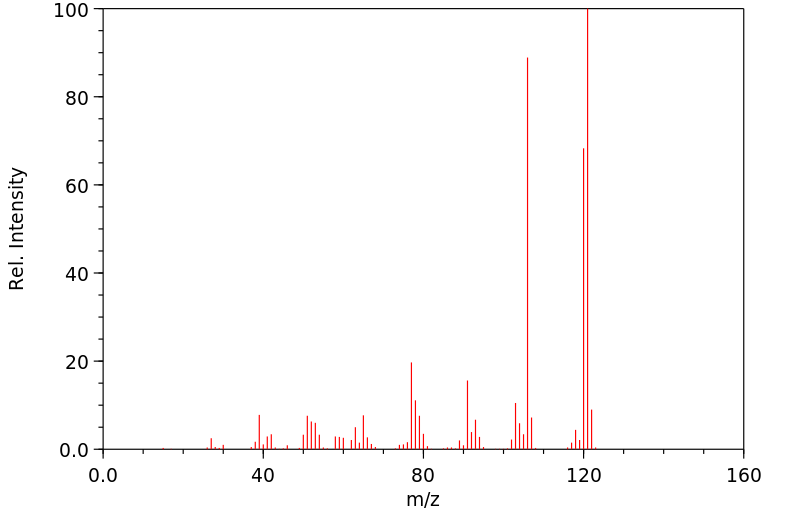
质谱MS
-
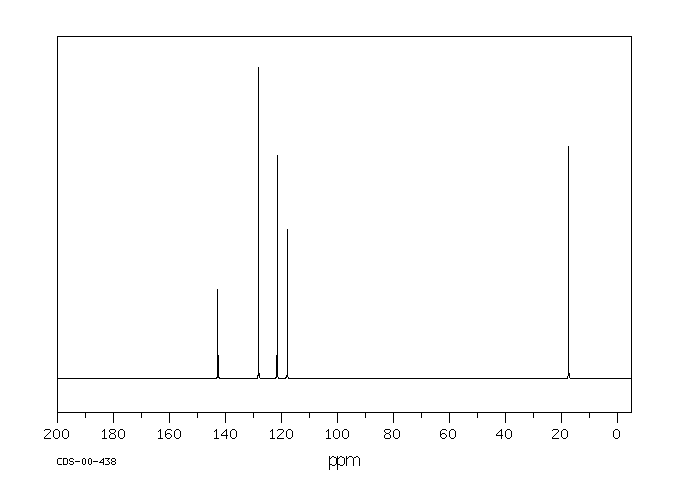
碳谱13CNMR
-
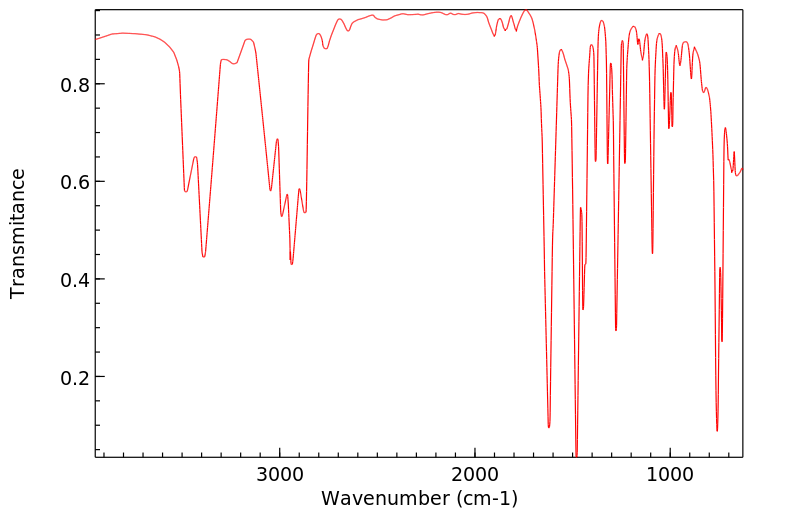
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息