棕榈酸 | 57-10-3
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:61-62.5 °C(lit.)
-
沸点:351.5 °C
-
密度:0.852 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
-
闪点:>230 °F
-
溶解度:在氯仿中的溶解度为0.5 M,澄清,无色
-
介电常数:2.3(71℃)
-
LogP:7.170
-
物理描述:Solid
-
颜色/状态:White crystalline scales
-
气味:Virtually odorless; slight characteristic odor
-
味道:Slight characteristic taste
-
蒸汽压力:3.8X10-7 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
水溶性:-6.81
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
分解:When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
-
粘度:7.80 mPa.sec (cP) at 70 °C
-
燃烧热:-10,030.6 kJ/mol
-
汽化热:96.28 kJ/mole at 200 °C
-
表面张力:28.2 mN/m (dyn/cm) at 70 °C
-
气味阈值:Odor Threshold Low: 10.0 [mmHg]; Odor threshold (detection) = 10 ppm
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.4309 at 70 °C
-
解离常数:pKa = 4.75 (est)
-
碰撞截面:195 Ų [M+Na]+ [CCS Type: DT, Method: single field calibrated with Agilent tune mix (Agilent)]
-
保留指数:1942 ;1972 ;1968 ;1981 ;1951 ;1951 ;1979 ;1956 ;1954 ;1965 ;1962 ;1938 ;1938 ;1952 ;1952 ;1941 ;1952 ;1941 ;1950 ;1939 ;1942 ;1942 ;1943 ;1938.97 ;2001 ;2000 ;1956 ;1966 ;1950 ;1951 ;1956 ;1956 ;1973 ;1973 ;1975 ;1961 ;1963 ;1974 ;1957 ;1976 ;1962 ;1978 ;1962 ;1965 ;1957 ;2009 ;1965 ;1938 ;1940 ;1960 ;1940 ;1951 ;1956 ;1973 ;1953 ;1951 ;1943 ;1949 ;1951 ;1968 ;1968 ;1963 ;1968 ;1943 ;1968 ;1937 ;1951 ;1940 ;1944 ;1981 ;1968 ;1967 ;1937 ;1937 ;1949 ;1935 ;1955 ;1997 ;1940 ;1978 ;1960 ;1949 ;1948 ;1948 ;1970 ;1959.6 ;1950 ;1942.2 ;1946 ;1945 ;1976 ;1980 ;1970 ;1937 ;1937 ;1965 ;1983 ;1956 ;1944 ;1953 ;1946 ;1936 ;1942 ;1958 ;1946 ;1941 ;1944 ;1966.1 ;1973 ;1981 ;1964 ;1947 ;1957 ;1944 ;1950 ;1943 ;1944 ;1945 ;1973 ;1980 ;1973 ;336.7 ;336.7 ;336.9 ;325.15
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):6.4
-
重原子数:18
-
可旋转键数:14
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.937
-
拓扑面积:37.3
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:2
ADMET
安全信息
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险品标志:Xi
-
安全说明:S26,S37/39
-
危险类别码:R36/38
-
WGK Germany:-
-
海关编码:2915709000
-
危险品运输编号:NONH for all modes of transport
-
RTECS号:RT4550000
-
危险性防范说明:P261,P301+P312,P302+P352,P304+P340,P305+P351+P338
-
危险性描述:H302,H315,H319,H335
-
储存条件:1. 内衬塑料袋的硬纸箱或编织袋包装,应储存在阴凉、干燥、通风的地方,并远离火源和氧化剂。 2. 硬纸箱或编织袋内衬塑料袋包装,每箱(或袋)净重25kg或50kg。同样需要储存在阴凉、干燥、通风的地方,并远离火源和氧化剂。按照一般化学品规定进行贮存和运输。
SDS
| 第一部分:化学品名称 |
| 化学品中文名称: | 十六酸;棕榈酸 |
| 化学品英文名称: | Hexadecanoic acid;Palmitic acid |
| 中文俗名或商品名: | |
| Synonyms: | |
| CAS No.: | 57-10-3 |
| 分子式: | C 16 H 32 O 2 |
| 分子量: | 256.42 |
| 第二部分:成分/组成信息 |
| 纯化学品 混合物 | |||
| 化学品名称:十六酸;棕榈酸 | |||
|
| 第三部分:危险性概述 |
| 危险性类别: | |
| 侵入途径: | 吸入 食入 经皮吸收 |
| 健康危害: | 具刺激性。未见工业使用中对人损害的报道,无致癌性。 |
| 环境危害: | |
| 燃爆危险: | 本品可燃,具刺激性。 |
| 第四部分:急救措施 |
| 皮肤接触: | 用肥皂水及清水彻底冲洗。就医。 |
| 眼睛接触: | 拉开眼睑,用流动清水冲洗15分钟。就医。 |
| 吸入: | 脱离现场至空气新鲜处。就医。 |
| 食入: | 误服者,饮适量温水,催吐。就医。 |
| 第五部分:消防措施 |
| 危险特性: | 遇高热、明火或氧化剂,有引起燃烧的危险。 |
| 有害燃烧产物: | 一氧化碳、二氧化碳。 |
| 灭火方法及灭火剂: | 消防人员须戴好防毒面具,在安全距离以外,在上风向灭火。灭火剂:雾状水、抗溶性泡沫、二氧化碳、干粉。 |
| 消防员的个体防护: | |
| 禁止使用的灭火剂: | |
| 闪点(℃): | |
| 自燃温度(℃): | |
| 爆炸下限[%(V/V)]: | |
| 爆炸上限[%(V/V)]: | |
| 最小点火能(mJ): | |
| 爆燃点: | |
| 爆速: | |
| 最大燃爆压力(MPa): | |
| 建规火险分级: |
| 第六部分:泄漏应急处理 |
| 应急处理: | 小心扫起,避免扬尘,置于袋中转移至安全场所。也可以用大量水冲洗,经稀释的污水放入废水系统。如大量泄漏,收集回收或无害处理后废弃。 |
| 第七部分:操作处置与储存 |
| 操作注意事项: | 密闭操作,提供充分的局部排风。防止粉尘释放到车间空气中。操作人员必须经过专门培训,严格遵守操作规程。建议操作人员佩戴防尘面具(全面罩),穿橡胶耐酸碱服,戴橡胶耐酸碱手套。远离火种、热源,工作场所严禁吸烟。使用防爆型的通风系统和设备。避免产生粉尘。避免与碱类、氧化剂、还原剂接触。配备相应品种和数量的消防器材及泄漏应急处理设备。倒空的容器可能残留有害物。 |
| 储存注意事项: | 储存于阴凉、通风的库房。远离火种、热源。防止阳光直射。包装密封。应与碱类、氧化剂、还原剂分开存放,切忌混储。配备相应品种和数量的消防器材。储区应备有合适的材料收容泄漏物。 |
| 第八部分:接触控制/个体防护 |
| 最高容许浓度: | 中 国 MAC:未制订标准前苏联 MAC:未制订标准美国TLV—TWA:未制订标准 |
| 监测方法: | |
| 工程控制: | 提供良好的自然通风条件。 |
| 呼吸系统防护: | 一般不需特殊防护。 |
| 眼睛防护: | 一般不需特殊防护。 |
| 身体防护: | 穿工作服。 |
| 手防护: | 一般不需特殊防护。 |
| 其他防护: | 工作后,淋浴更衣。 |
| 第九部分:理化特性 |
| 外观与性状: | 白色带珠光的鳞片。 |
| pH: | |
| 熔点(℃): | 63~64 |
| 沸点(℃): | 351.5 |
| 相对密度(水=1): | 0.8414(80℃) |
| 相对蒸气密度(空气=1): | |
| 饱和蒸气压(kPa): | |
| 燃烧热(kJ/mol): | |
| 临界温度(℃): | |
| 临界压力(MPa): | |
| 辛醇/水分配系数的对数值: | |
| 闪点(℃): | |
| 引燃温度(℃): | |
| 爆炸上限%(V/V): | |
| 爆炸下限%(V/V): | |
| 分子式: | C 16 H 32 O 2 |
| 分子量: | 256.42 |
| 蒸发速率: | |
| 粘性: | |
| 溶解性: | 不溶于水,微溶于石油醚,溶于乙醇,易溶于乙醚、氯仿、冰醋酸。 |
| 主要用途: | 用于制造蜡烛、肥皂、金属皂、润滑脂、合成洗涤剂、软化剂等。 |
| 第十部分:稳定性和反应活性 |
| 稳定性: | 在常温常压下 稳定 |
| 禁配物: | 碱类、氧化剂、还原剂。 |
| 避免接触的条件: | |
| 聚合危害: | 不能出现 |
| 分解产物: | 一氧化碳、二氧化碳。 |
| 第十一部分:毒理学资料 |
| 急性毒性: | 无毒 |
| 急性中毒: | |
| 慢性中毒: | |
| 亚急性和慢性毒性: | |
| 刺激性: | 人经皮:75mg/3天,间歇染毒,轻度刺激。 致敏性: |
| 致敏性: | |
| 致突变性: | |
| 致畸性: | |
| 致癌性: |
| 第十二部分:生态学资料 |
| 生态毒理毒性: | |
| 生物降解性: | |
| 非生物降解性: | |
| 生物富集或生物积累性: |
| 第十三部分:废弃处置 |
| 废弃物性质: | |
| 废弃处置方法: | 建议用控制焚烧法或安全掩埋法处置。在能利用的地方重复使用容器或在规定场所掩埋。 |
| 废弃注意事项: |
| 第十四部分:运输信息 |
| |
| 危险货物编号: | |
| UN编号: | |
| 包装标志: | |
| 包装类别: | |
| 包装方法: | |
| 运输注意事项: | 储存于阴凉、通风仓间内。远离火种、热源。保持容器密封。防止阳光曝晒。应与氧化剂、碱类分开存放。搬运时要轻装轻卸,防止包装及容器损坏。 |
| RETCS号: | |
| IMDG规则页码: |
| 第十五部分:法规信息 |
| 国内化学品安全管理法规: | 化学危险物品安全管理条例 (1987年2月17日国务院发布),化学危险物品安全管理条例实施细则 (化劳发[1992] 677号),工作场所安全使用化学品规定 ([1996]劳部发423号)等法规,针对化学危险品的安全使用、生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应规定。 |
| 国际化学品安全管理法规: |
| 第十六部分:其他信息 |
| 参考文献: | 1.周国泰,化学危险品安全技术全书,化学工业出版社,1997 2.国家环保局有毒化学品管理办公室、北京化工研究院合编,化学品毒性法规环境数据手册,中国环境科学出版社.1992 3.Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety,CHEMINFO Database.1998 4.Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety, RTECS Database, 1989 |
| 填表时间: | 年月日 |
| 填表部门: | |
| 数据审核单位: | |
| 修改说明: | |
| 其他信息: | 6 |
| MSDS修改日期: | 年月日 |
制备方法与用途
棕榈酸,即十六酸,是自然界中分布最广的脂肪酸之一。常温下呈白色晶体状,不溶于水,但溶于醚、氯仿、丙酮等有机溶剂。它广泛存在于各种油脂中,如桕脂、棕榈油、漆脂、棉籽油、大豆油、花生油、玉米胚芽油、鱼油、乳脂、牛、羊、猪脂肪等。同时,它还与高级饱和一元醇形成的酯(即天然蜡)广泛存在于许多种动植物体中。
应用棕榈酸的简单酯主要用于塑料工业。其碱金属盐溶于水,有去污作用,是香皂和肥皂的主要成分之一。其他金属盐不溶于水,用于润滑剂、制药工业、化妆品以及防水剂和杀菌剂等。棕榈酸主要来源于油脂,通过将油脂皂化、酸化后分离而得。
用途主要用作表面活性剂,用作非离子型时,可用于聚氧乙烯山梨糖醇酐单棕榈酸酯和山梨糖醇酐单棕榈酸酯,前者制成亲油性乳化剂而应用于化妆品和医药,后者可用在化妆品、医药、食品的乳化剂,颜料墨水的分散剂,也用作消泡剂;用作阴离子型时,制成棕榈酸钠而用于脂肪酸肥皂的原料,塑料乳化剂等;棕榈酸锌用作化妆品、塑料的稳定剂;除用作表面活性剂外,还用作棕榈酸异丙酯、甲酯、丁酯、胺化合物、氯化物等的原料;其中棕榈酸异丙酯是化妆品油相原料,可用于制唇膏、各种膏霜、发油、发膏等;其他如棕榈酸甲酯可用作润滑油添加剂、表面活性剂原料;PVC的增滑剂等;蜡烛、肥皂、润滑脂、合成洗涤剂、软化剂等的原料;用作香料,是我国GB2760-1996规定允许使用的食用香料;也用作食品消泡剂。
生产工艺- 直接从棕榈树果中提取;
- 以牛油(含50%棕榈酸)、木蜡(含77%)为原料,在高温(250℃)、高压(50.67×10^5 Pa)下水解,可制得多种脂肪酸的混合物,再进行水解及碱性处理,即可制得本品。
- 以油酸为原料,在350℃下碱熔,双键发生异构,与羧基处于共轭位置,进一步催化氧化,可分解为棕榈酸。
天然脂肪酸无毒。可安全用于食品(FDA,§172.860,2000)。
食品添加剂最大允许使用量和最大允许残留量标准 用途一种靶向细胞膜的饱和脂肪酸。用于气相分析标准物质,测定水的硬度和钙、镁、钡、铅、汞、锌。有机合成,制造各种棕榈酸金属盐和防水剂。
生产方法自然界中广泛存在,几乎所有的油脂中都有含量不等的软脂酸组分。我国特产的乌桕油中,软脂酸的含量可高达60%以上,而棕榈树果实的棕榈油中含量大约为40%,但菜油中的含量则不足2%。将乌桕油或棕榈油水解、分馏、压榨分离不饱和脂肪酸后,经重结晶即制得棕榈酸。市售品棕榈酸一般熔点为57.5-62.5℃。
生产方法:用米糠油、椰子油、棕榈仁油等的混合脂肪酸经真空分馏而得。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 辛酸 Octanoic acid 124-07-2 C8H16O2 144.214 月桂酸 laurate 143-07-7 C12H24O2 200.321 肉豆蔻酸 n-tetradecanoic acid 544-63-8 C14H28O2 228.375 硬脂酸 stearic acid 57-11-4 C18H36O2 284.483 —— 16-iodohexadecanoic acid 2536-36-9 C16H31IO2 382.325 12-溴十二烷酸 12-bromododecanoic acid 73367-80-3 C12H23BrO2 279.217 —— 11-oxo-hexadecanoic acid 2388-81-0 C16H30O3 270.412 11-羟基十六烷酸 11-hydroxyhexadecanoic acid 502-75-0 C16H32O3 272.428 棕榈酸甲酯 hexadecanoic acid methyl ester 112-39-0 C17H34O2 270.456 油酸 cis-Octadecenoic acid 112-80-1 C18H34O2 282.467 反油酸 Elaidic acid 112-79-8 C18H34O2 282.467 —— 9-hexadecenoic acid 2091-29-4 C16H30O2 254.413 —— 7-decynoic acid 54373-85-2 C10H16O2 168.236 —— 5-oxohexadecanoic acid 70444-63-2 C16H30O3 270.412 紫胶桐酸 9,10,16-trihydroxyhexadecanoic acid 6949-98-0 C16H32O5 304.427 (Z,Z)-9,12-十八烷二烯酸二聚物 linoleic acid 60-33-3 C18H32O2 280.451 3,12-二羟基十六烷酸 3,12-dihydroxy-hexadecanoic acid 66675-73-8 C16H32O4 288.428 棕榈酸乙酯 Ethyl palmitate 628-97-7 C18H36O2 284.483 硬脂酸乙酯 stearic acid ethyl ester 111-61-5 C20H40O2 312.536 十六酸乙烯酯 vinyl palmitate 693-38-9 C18H34O2 282.467 油酸甲酯 Methyl oleate 112-62-9 C19H36O2 296.494 十六(烷)酸十八(烷)酯 octadecyl hexadecanoate 2598-99-4 C34H68O2 508.913 三十烷基棕榈酸酯 triacontyl hexadecanoate 6027-71-0 C46H92O2 677.235 —— 2-iodopalmitic acid 101434-56-4 C16H31IO2 382.325 月桂醇棕榈酸酯 dodecyl hexadecanoic acid ester 42232-29-1 C28H56O2 424.751 —— hexadeca-6,10,14-trienoic acid 4444-12-6 C16H26O2 250.381 乙基9-癸烯酸酯 ethyl 9-decenoate 67233-91-4 C12H22O2 198.305 2-溴十六烷酸 2-bromopalmitic acid 18263-25-7 C16H31BrO2 335.325 1-十六烷醇 1-Hexadecanol 36653-82-4 C16H34O 242.445 十六醛 Hexadecanal 629-80-1 C16H32O 240.429 - 1
- 2
- 3
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 二十酸 Arachidic acid 506-30-9 C20H40O2 312.536 壬二酸 azelaic acid 123-99-9 C9H16O4 188.224 辛二酸 Suberic acid 505-48-6 C8H14O4 174.197 肉豆蔻酸 n-tetradecanoic acid 544-63-8 C14H28O2 228.375 月桂酸 laurate 143-07-7 C12H24O2 200.321 16-羟基棕榈酸 16-hydroxyhexadecanoic acid 506-13-8 C16H32O3 272.428 十五烷酸 palmitic acid 1002-84-2 C15H30O2 242.402 软脂-(羧基-14C)酸 1-(14)C-palmitic acid 765-07-1 C16H32O2 258.418 硬脂酸 stearic acid 57-11-4 C18H36O2 284.483 木焦油酸 n-Tetracosanoic acid 557-59-5 C24H48O2 368.644 —— 15-oxohexadecanoic acid 39115-09-8 C16H30O3 270.412 己酸 hexanoic acid 142-62-1 C6H12O2 116.16 —— 15-Hydroxypalmitic acid —— C16H32O3 272.428 —— (R)-15-hydroxyhexadecanoic acid 212012-94-7 C16H32O3 272.428 —— ω-3-hydroxypalmitic acid 59642-39-6 C16H32O3 272.428 —— ω-2-hydroxypalmitic acid —— C16H32O3 272.428 11-羟基十六烷酸 11-hydroxyhexadecanoic acid 502-75-0 C16H32O3 272.428 10-羟基十六烷酸 10-hydroxypalmitic acid 23048-75-1 C16H32O3 272.428 9-羟基十六酸 9-hydroxyhexadecanoic acid 17833-52-2 C16H32O3 272.428 12-羟基十六烷酸 12-hydroxyhexadecanoic acid 83646-62-2 C16H32O3 272.428 —— (12R)-12-hydroxyhexadecanoic acid 938159-92-3 C16H32O3 272.428 棕榈酸甲酯 hexadecanoic acid methyl ester 112-39-0 C17H34O2 270.456 硬酯酸甲酯C18 Methyl stearate 112-61-8 C19H38O2 298.51 花生酸甲酯 Methyl arachidate 1120-28-1 C21H42O2 326.563 月桂酸甲酯 methyl laurate 111-82-0 C13H26O2 214.348 三十酸甲酯C30 methyl 1-triacontanoate 629-83-4 C31H62O2 466.832 —— triacontanedioic acid dimethyl ester 24397-43-1 C32H62O4 510.842 —— peroxypalmitic acid 7311-29-7 C16H32O3 272.428 棕榈油酸 Palmitoleic acid 373-49-9 C16H30O2 254.413 油酸 cis-Octadecenoic acid 112-80-1 C18H34O2 282.467 (±)-2-甲基硬脂酸 2-methyl-octadecanoic acid 7217-83-6 C19H38O2 298.51 —— 15-hydroxyhexadecanoic acid methyl ester 55823-13-7 C17H34O3 286.455 —— (-) (R)-2-methyloctadecanoic acid 75879-20-8 C19H38O2 298.51 —— (R)-3-methyl-nonadecanoic acid 60787-52-2 C20H40O2 312.536 —— β-Methylstearinsaeure 52304-07-1 C19H38O2 298.51 2-甲基十六烷酸 2-methylpalmitic acid 27147-71-3 C17H34O2 270.456 月桂酸甲酯 methyl 11-dodecenoate 29972-79-0 C13H24O2 212.332 2-羟基十六烷酸 2-hydroxypalmitic acid 764-67-0 C16H32O3 272.428 (R)-2-羟基棕榈酸 (R)-(-)-2-hydroxyhexadecanoic acid 16452-51-0 C16H32O3 272.428 羟基癸酸 DL-2-hydroxydecanoic acid 5393-81-7 C10H20O3 188.267 (Z,Z)-9,12-十八烷二烯酸二聚物 linoleic acid 60-33-3 C18H32O2 280.451 戊二酸 1,5-pentanedioic acid 110-94-1 C5H8O4 132.116 —— (R)-3-hydroxyhexadecanoic acid 20595-04-4 C16H32O3 272.428 —— (R)-3-hydroxyoctadecanoic acid 14531-43-2 C18H36O3 300.482 外消旋-3-羟基十八烷酸 3-hydroxyoctadecanoic acid 17773-30-7 C18H36O3 300.482 —— (+)-11-hydroxy-hexadecanoic acid methyl ester 60368-18-5 C17H34O3 286.455 —— 13-hydroxyhexadecanoic acid methyl ester 58763-58-9 C17H34O3 286.455 —— 14-hydroxyhexadecanoic acid methyl ester 86233-90-1 C17H34O3 286.455 —— 2-oxohexadecanoic acid 2570-24-3 C16H30O3 270.412 3-羟基十六酸 β-hydroxypalmitic acid 2398-34-7 C16H32O3 272.428 甲基11-羟基十六烷酸酯 11-hydroxyhexadecanoic acid methyl ester 60368-18-5 C17H34O3 286.455 —— methyl 10-hydroxyhexadecanoate 56247-30-4 C17H34O3 286.455 —— 2-oxoheptadecanoic acid 73506-86-2 C17H32O3 284.439 棕榈酸乙酯 Ethyl palmitate 628-97-7 C18H36O2 284.483 硬脂酸乙酯 stearic acid ethyl ester 111-61-5 C20H40O2 312.536 Γ-十八碳三烯酸 (9Z,12Z,15Z)-octadeca-9-12,15-trienoic acid 463-40-1 C18H30O2 278.435 十六烷酸丙酯 propyl palmitate 2239-78-3 C19H38O2 298.51 十六酸乙烯酯 vinyl palmitate 693-38-9 C18H34O2 282.467 氯代棕榈油甲酯 chloromethyl palmitate 61413-69-2 C17H33ClO2 304.901 丁酸 butyric acid 107-92-6 C4H8O2 88.1063 油酸甲酯 Methyl oleate 112-62-9 C19H36O2 296.494 反油酸甲酯 octadec-9-enoic acid methyl ester 2462-84-2 C19H36O2 296.494 —— methyl 9-pentadecenoate 25915-47-3 C16H30O2 254.413 —— 1,19-nonadec-9-enedioic acid dimethyl ester 57568-16-8 C21H38O4 354.53 二甲基十八碳-9-烯二酸酯 dimethyl 9-octadecen-1,18-dioate 13481-97-5 C20H36O4 340.503 —— 9-eicosenoic acid methyl ester 10340-21-3 C21H40O2 324.547 2-十四烷基棕榈酸 2-tetradecylhexadecanoic acid 66880-77-1 C30H60O2 452.805 十六烷酸丁基酯 butyl palmitate 111-06-8 C20H40O2 312.536 C16-18脂肪酸C12-18烷醇酯 Cetyl palmitate 540-10-3 C32H64O2 480.859 十六碳烷基十四烷酸酯 tetradecanoic acid hexadecyl ester 2599-01-1 C30H60O2 452.805 棕榈酸正壬酯 nonyl palmitate 42232-26-8 C25H50O2 382.671 十六烷酸癸酯 decyl palmitate 42232-27-9 C26H52O2 396.698 十六(烷)酸十八(烷)酯 octadecyl hexadecanoate 2598-99-4 C34H68O2 508.913 十六(烷)酸十四(烷)酯 myristyl palmitate 4536-26-9 C30H60O2 452.805 月桂醇棕榈酸酯 dodecyl hexadecanoic acid ester 42232-29-1 C28H56O2 424.751 —— undecyl hexadecanoate 42232-28-0 C27H54O2 410.725 棕榈酸辛酯 octyl palmitate 16958-85-3 C24H48O2 368.644 棕榈酸戊酯 n-pentyl-palmitate 31148-31-9 C21H42O2 326.563 棕榈酸二十二烷醇酯 n-docosanyl hexadecanoate 42232-33-7 C38H76O2 565.02 —— tetratriacontyl hexadecanoate 84461-48-3 C50H100O2 733.343 三十烷基棕榈酸酯 triacontyl hexadecanoate 6027-71-0 C46H92O2 677.235 氧杂环十七烷-2-酮 15-hexadecanolide 109-29-5 C16H30O2 254.413 棕榈酸庚酯 heptyl palmitate 26718-83-2 C23H46O2 354.617 —— 2-iodopalmitic acid 101434-56-4 C16H31IO2 382.325 棕榈酸己酯 hexyl hexadecanoate 42232-25-7 C22H44O2 340.59 硬脂酸十八醇脂 octadecanoic acid, octadecyl ester 2778-96-3 C36H72O2 536.966 —— 15-(hexadecanoyloxy)pentadecanoic acid —— C31H60O4 496.815 2-溴十六烷酸 2-bromopalmitic acid 18263-25-7 C16H31BrO2 335.325 —— hexane-1,6-diyl dihexadecanoate 23130-50-9 C38H74O4 595.003 2-溴十五酸 2-bromo-pentadecanoic acid 82144-78-3 C15H29BrO2 321.298 2-氯十六烷酸 α-chloro-palmitic acid 19117-92-1 C16H31ClO2 290.874 硬脂烷醛 n-Octadecanal 638-66-4 C18H36O 268.483 1-十六烷醇 1-Hexadecanol 36653-82-4 C16H34O 242.445 十六醛 Hexadecanal 629-80-1 C16H32O 240.429 1-十五醇 pentadecanol 629-76-5 C15H32O 228.418 十五醛 n-pentadecanal 2765-11-9 C15H30O 226.403 —— α-tetradecylacrylic acid 6818-50-4 C17H32O2 268.44 乙二醇棕榈酸酯 2-hydroxyethyl hexadecanoate 4219-49-2 C18H36O3 300.482 —— 1,5-di(hexadecanoyloxy)pentane 26933-79-9 C37H72O4 580.976 - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Reduction of Fatty Acid Methyl Esters to Fatty Alcohols To Improve Volatility for Isotopic Analysis without Extraneous Carbon摘要:在基于色谱的高精度化合物特异性或位点特异性同位素分析中,衍生化基团中的碳无法与分析物碳区分。我们报告了一种将脂肪酸甲酯还原为脂肪醇的方法,以促进高质量的色谱分离,且没有添加外源性碳,随后进行高精度的位点特异性同位素分析。棕榈酸甲酯在一次反应中被LiAlH4定量还原为1-十六醇。1-十六醇的气相热解会产生一系列单不饱和醇和类似于棕榈酸甲酯裂解中发现的α-烯烃,以及一个额外的峰,对应热解脱水产物1-十六烯。对这些碎片进行碳同位素分析的精度达到SD(δ13C) < 0.4‰。对极低富集 [1-13C]-1-十六醇(δ13C = −4.00‰)的位点特异性分析结果显示C1位点没有混淆的证据,且同位素比符合预期。热解产物1-十六烯在同位素上相较于1-十六醇呈现富集,这可能导致其他热解产物的轻微耗尽,但可以通过常规校准加以考虑。该程序具有通用性,可扩展至中等分子量、低挥发性分析物的化合物特异性和位点特异性分析,这些分析物含有酸基团,否则将被含有外源性碳的甲基、乙基、乙酰基或三甲基硅基团阻碍。DOI:10.1021/ac9802527
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:酯碱水解的简单方法摘要:通过使用二氯甲烷/甲醇(9:1)作为溶剂,已经开发出一种非常温和,快速的方法,可在非水条件下有效地进行酯的碱性水解。该方法可在室温下几分钟内方便地由相应的酯和氢氧化钠提供羧酸和醇。提出了合理的反应机理。DOI:10.1016/j.tetlet.2007.09.074
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:9-癸烯醇的合成方法摘要:本发明公开了一种9‑癸烯醇的合成方法,包括以下步骤:将1,10‑癸二醇、高级脂肪酸和催化剂搅拌混合后升温至340℃~360℃,得混合底料;将1,10‑癸二醇以滴加的方式向保温于340℃~360℃的混合底料进行连续进料,以精馏的方式实现连续出料;将所得的出料进行常压精馏,收集99±0.5℃馏分;剩余物料减压精馏,收集110±0.5℃/30mm Hg馏分,得9‑癸烯醇。在上述减压精馏的釜底液中混入1,10‑癸二醇,所得的混合料替代用于连续进料的1,10‑癸二醇,可继续进行循环反应。公开号:CN105330516B
文献信息
-
[EN] TARGETED DELIVERY AND PRODRUG DESIGNS FOR PLATINUM-ACRIDINE ANTI-CANCER COMPOUNDS AND METHODS THEREOF<br/>[FR] ADMINISTRATION CIBLÉE ET CONCEPTIONS DE PROMÉDICAMENTS POUR COMPOSÉS ANTICANCÉREUX À BASE DE PLATINE ET D'ACRIDINE ET MÉTHODES ASSOCIÉES申请人:WAKE FOREST SCHOOL OF MEDICINE公开号:WO2013033430A1公开(公告)日:2013-03-07Acridine containing cispiaiin compounds have been disclosed that show greater efficacy against cancer than other cisplatin compounds. Methods of delivery of those more effective eisp!aiin compounds to the nucleus in cancer ceils is disclosed using one or more amino acids, one or more sugars, one or more polymeric ethers, C i^aikylene-phenyl-NH-C(0)-R.15, folic acid, av03 iniegriii RGD binding peptide, tamoxifen, endoxifen, epidermal growth factor receptor, antibody conjugates, kinase inhibitors, diazoles, triazol.es, oxazoies, erlotinib, and/or mixtures thereof; wherein R]§ is a peptide.
-
[EN] ACC INHIBITORS AND USES THEREOF<br/>[FR] INHIBITEURS DE L'ACC ET UTILISATIONS ASSOCIÉES
-
Compositions for Treatment of Cystic Fibrosis and Other Chronic Diseases申请人:Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated公开号:US20150231142A1公开(公告)日:2015-08-20The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising an inhibitor of epithelial sodium channel activity in combination with at least one ABC Transporter modulator compound of Formula A, Formula B, Formula C, or Formula D. The invention also relates to pharmaceutical formulations thereof, and to methods of using such compositions in the treatment of CFTR mediated diseases, particularly cystic fibrosis using the pharmaceutical combination compositions.
-
[EN] COMPOUNDS FOR THE TREATMENT OF AMYLOID-ASSOCIATED DISEASES<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS POUR LE TRAITEMENT DE MALADIES ASSOCIÉES À LA SUBSTANCE AMYLOÏDE申请人:REMYND NV公开号:WO2016083490A1公开(公告)日:2016-06-02This invention provides novel compounds of formulae (I) or (II) or a stereoisomer, enantiomer, racemic, or tautomer thereof, (I) (II) wherein the substituents are as defined in the specification. The present invention also relates to the novel compounds for use as a medicine, more in particular for the prevention or treatment of amyloid-related diseases, more specifically certain neurological disorders, such as disorders collectively known as tauopathies, disorders characterized by cytotoxic α-synuclein amyloidogenesis. The present invention also relates to the use of said novel compounds for the manufacture of medicaments useful for treating such amyloid-related diseases. The present invention further relates to pharmaceutical compositions including said novel compounds and to methods for the preparation of said novel compounds.这项发明提供了式(I)或(II)或其立体异构体、对映异构体、消旋体或互变异构体的新化合物,其中取代基如规范中所定义。本发明还涉及用作药物的这些新化合物,更具体地用于预防或治疗与淀粉样蛋白相关的疾病,更具体地说是某些神经系统疾病,如被统称为tau病变的疾病,以及由细胞毒性α-突触核蛋白淀粉生成所特征化的疾病。本发明还涉及利用这些新化合物制备对治疗此类淀粉样蛋白相关疾病有用的药物。本发明还涉及包括这些新化合物的药物组合物以及这些新化合物的制备方法。
-
[EN] IMPROVED SYNTHETIC METHODS OF MAKING (2H-1,2,3-TRIAZOL-2-YL)PHENYL COMPOUNDS AS OREXIN RECEPTOR MODULATORS<br/>[FR] PROCÉDÉS SYNTHÉTIQUES AMÉLIORÉS POUR LA FABRICATION DE COMPOSÉS DE (2H-1,2,3-TRIAZOL-2-YL)PHÉNYLE UTILISÉS COMME MODULATEURS DES RÉCEPTEURS DE L'OREXINE申请人:JANSSEN PHARMACEUTICA NV公开号:WO2021023843A1公开(公告)日:2021-02-11Processes for preparing (((3aR,6aS)-5-(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)hexahydropyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrrol-2(1H)-yl)(2-fluoro-6-(2H-l,2,3-triazol-2- yl)phenyl)methanone are described, which are useful for commercial manufacturing. Said compound is an orexin receptor modulator and may be useful in pharmaceutical compositions and methods for the treatment of diseased states, disorders, and conditions mediated by orexin activity, such as insomnia and depression.
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
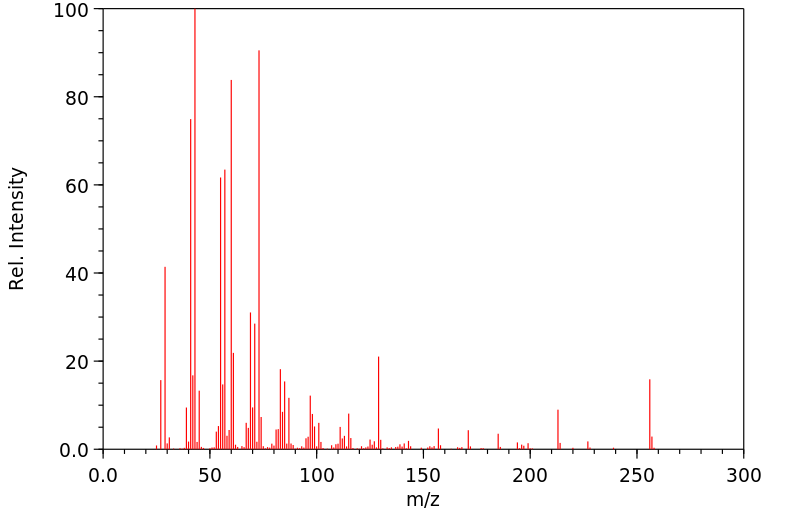
质谱MS
-
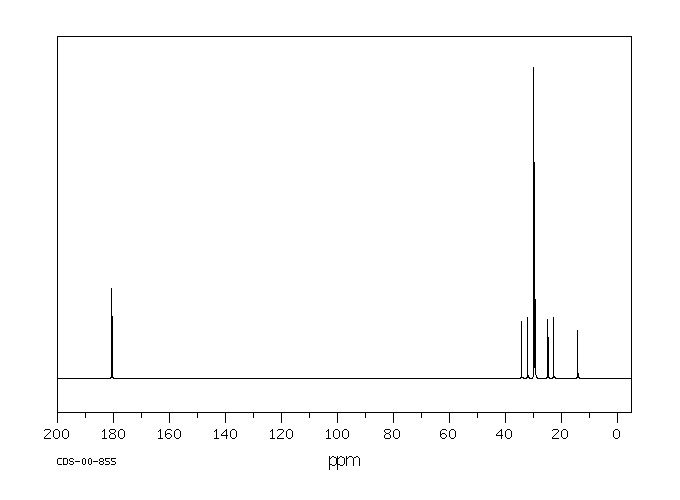
碳谱13CNMR
-
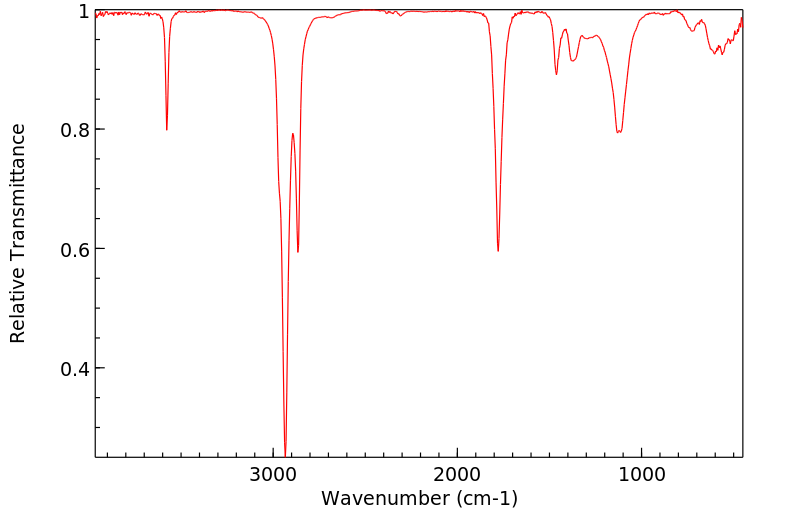
红外IR
-
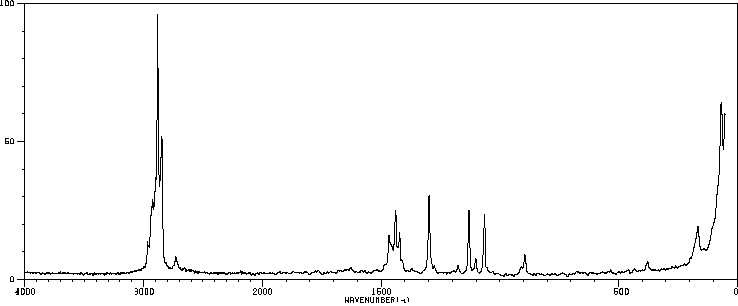
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息