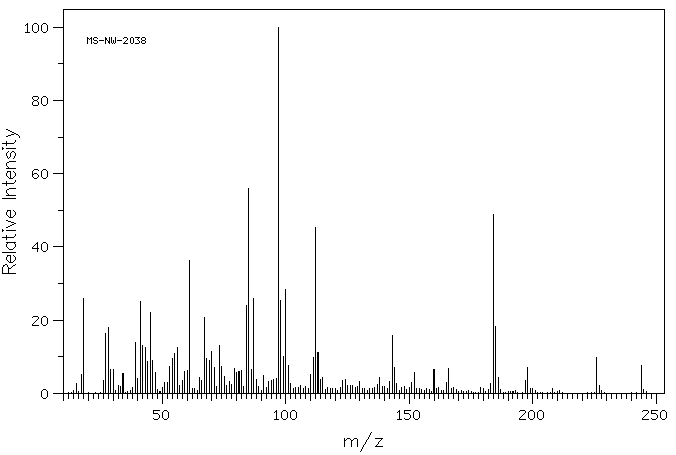
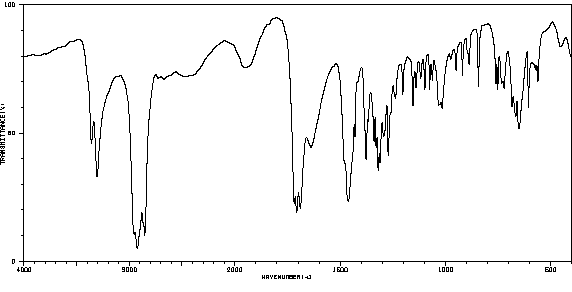
代谢
Biotin is excreted in the urine as biotin, bisnorbiotin, biotin sulfoxide, biotin sulfone, bisnorbiotin methyl ketone and tetranobiotin-1-sulfoxide.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)