N,N-二甲基甲酰胺 | 68-12-2
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:-61 °C (lit.)
-
比旋光度:0.94 º
-
沸点:153 °C (lit.)
-
密度:0.944 g/mL (lit.)
-
蒸气密度:2.5 (vs air)
-
闪点:136 °F
-
溶解度:水:混溶
-
最大波长(λmax):λ: 270 nm Amax: 1.00λ: 275 nm Amax: 0.30λ: 295 nm Amax: 0.10λ: 310 nm Amax: 0.05λ: 340-400 nm Amax: 0.01
-
暴露限值:NIOSH REL: TWA 10 ppm (30 mg/m3), IDLH 500 ppm; OSHA PEL: TWA 10 ppm; ACGIH TLV: TWA 10 ppm (adopted).
-
介电常数:36.710000000000001
-
LogP:-1.010
-
物理描述:N,n-dimethylformamide appears as a water-white liquid with a faint fishy odor. Flash point 136°F. Slightly less dense than water. Vapors heavier than air. Toxic by inhalation or skin absorption. May irritate eyes.
-
颜色/状态:Colorless to very slightly yellow liquid
-
气味:Fishy odor
-
蒸汽密度:2.51 (NTP, 1992) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:3.87 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
亨利常数:7.39e-08 atm-m3/mole
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
N,N-二甲基甲酰胺是一种非质子型极性溶剂,对多种有机化合物和无机化合物具有良好的溶解能力。在无碱、酸、水存在的条件下,它表现出良好的化学稳定性。
-
化学性质方面,在无酸、碱、水存在的情况下,即使加热到沸点也相对稳定。但在酸的作用下会分解成甲酸和二甲胺盐;而在碱的作用下,则会分解为甲酸盐和二甲胺。
-
受紫外线照射时,N,N-二甲基甲酰胺会分解生成二甲胺与甲醛;加热至约350℃时,它会进一步分解成二甲胺和一氧化碳。此溶剂还能与盐酸形成稳定的等摩尔加合物,其熔点为40℃,沸点为110℃。同样地,N,N-二甲基甲酰胺也能与二氧化硫三氯化物(SO3)生成结晶性加合物,熔点为138℃,沸点为145℃。这些加合物在电子密度高的芳香环上能引入CHO基团,这称为Vilsmeier反应。此外,在室温下,五氧化二磷不溶于N,N-二甲基甲酰胺;但在40℃以上形成络合物后,即使在常温也能溶解而不沉淀。与钠加热时会发生剧烈反应并释放氢气,而在0℃左右的温度下,它也能够与三乙基铝发生强烈反应,并且还能与格氏试剂(Grignard reagent)反应。此外,在与酰氯及酸酐作用后能生成二甲酰胺衍生物。
-
N,N-二甲基甲酰胺属于低毒类物质。动物实验表明,大量连续投给可导致体重减轻并影响造血功能;对眼、皮肤和黏膜有强烈刺激性,液态或蒸气被皮肤吸收还能引起肝脏损伤。吸入高浓度蒸汽会引发急性中毒症状如严重刺激、全身痉挛、疼痛性便秘及恶心呕吐等。长期接触可能导致慢性中毒表现如皮肤和黏膜刺激、恶心、呕吐、胸闷、头痛、全身不适、食欲减退、胃痛、肝肿大及肝功能异常,尿胆素原和尿胆素亦会增加。在使用过程中应确保平均蒸汽浓度不超过29.9mg/m³;59.8mg/m³的环境下即可出现中毒症状(损害中枢神经系统)。根据大鼠和小鼠经口毒性实验,LD₅₀为3000~7000mg/kg。嗅觉阈值为0.14mg/m³,TJ 36-79规定车间空气中最高容许浓度为10mg/m³。
-
稳定性:稳定。
-
聚合危害:不会发生聚合。
-
-
自燃温度:440 °C
-
分解:Temperatures >350 °C may cause decomposition to form dimethylamine and carbon dioxide, with pressure developing in closed containers.
-
粘度:0.802 cP at 25 °C
-
腐蚀性:Pure dimethylformamide is essentially noncorrosive to metals. However, copper, tin and their alloys should be avoided.
-
燃烧热:1921 kJ/mole at 25 °C
-
汽化热:47.6 kJ/mole at 25 °C
-
表面张力:36.42 dyne/cm at 25 °C
-
电离电位:9.12 eV
-
聚合:Methylene diisocyanate polymerized violently on contact with dimethyl formamide.
-
气味阈值:300 mg/cu m (odor low) 300 mg/cu m (odor high)
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.42083 at 25 °C/D
-
解离常数:pKa = -0.30 (conjugate acid)
-
保留指数:756.3;752;745;747;750;753;742.1;742;736.3;746;751;746;735;738
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-1
-
重原子数:5
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.666
-
拓扑面积:20.3
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:1
ADMET
安全信息
-
职业暴露等级:A
-
职业暴露限值:TWA: 10 ppm (30 mg/m3) [skin]
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:3
-
立即威胁生命和健康浓度:500 ppm
-
危险品标志:T
-
安全说明:S45,S53
-
危险类别码:R20/21,R36,R61
-
WGK Germany:1
-
海关编码:2924191000
-
危险品运输编号:UN 2265 3/PG 3
-
危险类别:3
-
RTECS号:LQ2100000
-
包装等级:III
-
危险标志:GHS02,GHS07,GHS08
-
危险性描述:H226,H312 + H332,H319,H360D
-
危险性防范说明:P201,P210,P261,P280,P308 + P313,P370 + P378
-
储存条件:储存注意事项 应将物品储存在阴凉、通风的库房中,库温不宜超过37℃。远离火种、热源,并保持容器密封。与氧化剂、还原剂、卤素等分开存放,切忌混储。使用防爆型照明和通风设施,并禁止使用易产生火花的机械设备和工具。储存区应配备泄漏应急处理设备和合适的收容材料。
SDS
| 国标编号: | 33627 |
| CAS: | 68-12-2 |
| 中文名称: | N,N-二甲基甲酰胺 |
| 英文名称: | N,N-dimethylformamide;DMF |
| 别 名: | 甲酰二甲胺 |
| 分子式: | C 3 H 7 NO;(CH 3 ) 2 NCH(O) |
| 分子量: | 73.10 |
| 熔 点: | -61℃ 沸点:152.8℃ |
| 密 度: | 相对密度(水=1)0.94; |
| 蒸汽压: | 58℃ |
| 溶解性: | 与水混溶,可混溶于多数有机溶剂 |
| 稳定性: | 稳定 |
| 外观与性状: | 无色液体,有微弱的特殊臭味 |
| 危险标记: | 7(易燃液体) |
| 用 途: | 主要用作工业溶剂,医药工业上用于生产维生素、激素,也用于制造杀虫脒 |
2.对环境的影响:
一、健康危害
侵入途径:吸入、食入、经皮吸收。
健康危害:急性中毒:主要有眼和上呼吸道刺激症状、头痛、焦虑、恶心、呕吐、腹痛、便秘等。肝损害一般在中毒数日后出现,肝脏肿大,肝区痛,可出现黄疸。经皮肤吸收中毒者,皮肤出现水泡、水肿、粘糙,局部麻木、瘙痒、灼痛。
慢性影响:有皮肤、粘膜刺激,神经衰弱综合征,血压偏低。尚有恶心、呕吐、胸闷、食欲不振、胃痛、便秘及肝功能变化。
二、毒理学资料及环境行为
毒性:低毒类。
急性毒性:LD 50 400mg/kg(大鼠经口);4720mg/kg(兔经皮);LC 50 9400mg/m 3 ,2小时(小鼠吸入);人吸入30~60ppm,消化道症状,肝功可异常,有黄疸,尿胆原增加,蛋白尿;人吸入10~20ppm(有时30ppm),头痛,食欲不振,恶心,肝功和心电图正常。
亚急性和慢性毒性:大鼠吸入2500mg/m 3 ,6小时/天,5天,80%死亡,肝肺有病变;人吸入5.1~49mg/m 3 ×3年,神衰症候群,血压偏低,肝功能变化。
危险特性:易燃,遇高热、明火或与氧化剂接触,有引起燃烧爆炸的危险。能与浓硫酸、发烟硝酸猛烈反应,甚至发生爆炸。与卤化物(如四氯化碳)能发生剧烈反应。
燃烧(分解)产物:一氧化碳、二氧化碳、氧化氮。
3.现场应急监测方法:
气体检测管法
气体速测管(德国德尔格公司产品)
4.实验室监测方法:
气相色谱法《作业环境空气中有毒物质检测方法》陈安之主编
色谱/质谱法《水和有害废物的监测分析方法》周文敏等编译
5.环境标准:
| 中国(TJ36-70) | 车间空气中有害物质的最高容许浓度 | 10mg/m 3 [皮] |
| 前苏联(1975) | 居民区大气中有害物最大允许浓度 | 0.03mg/m 3 (最大值、昼夜均值) |
| 前苏联(1975) | 水体中有害物质最高允许浓度 | 10mg/L |
| 嗅觉阈浓度 | 0.14mg/m 3 |
6.应急处理处置方法:
一、泄漏应急处理
迅速撤离泄漏污染区人员至安全区,并进行隔离,严格限制出入。切断火源。建议应急处理人员戴自给正压式呼吸器,穿消防防护服。尽可能切断泄漏源。防止进入下水道、排洪沟等限制性空间。小量泄漏:用砂土或其它不燃材料吸附或吸收。也可以用大量水冲洗,洗水稀释后放入废水系统。大量泄漏:构筑围堤或挖坑收容;用泡沫覆盖,降低蒸气灾害。用防爆泵转移至槽车或专用收集器内,回收或运至废物处理场所处置。
废弃物处置方法:用焚烧法。废料溶于易燃溶剂后,再焚烧。焚烧炉排出的气体要通过碱洗涤器除去有害成分,从纤维沉降槽和聚氯乙烯反应器的洁净溶剂中回收N,N-二甲基甲酰胺。
二、防护措施
呼吸系统防护:空气中浓度超标时,佩戴过滤式防毒面具(半面罩)。
眼睛防护:戴化学安全防护眼镜。
身体防护:穿化学防护服。
手防护:戴橡胶手套。
其它:工作现场严禁吸烟。工作毕,淋浴更衣。
三、急救措施
皮肤接触:脱去被污染的衣着,用大量流动清水冲洗,至少15分钟。就医。
眼睛接触:立即提起眼睑,用大量流动清水或生理盐水彻底冲洗至少15分钟。就医。
吸入:迅速脱离现场至空气新鲜处。保持呼吸道通畅。如呼吸困难,给输氧。如呼吸停止,立即进行人工呼吸。就医。
食入:饮足量温水,催吐,就医。
灭火方法:灭火剂:雾状水、抗溶性泡沫、干粉、二氧化碳、砂土。尽可能将容器从火场移至空旷处。喷水保持火场容器冷却,直至灭火结束。
制备方法与用途
根据提供的信息,二甲基甲酰胺(DMF)是一种重要的有机溶剂和化工原料。下面总结了其主要用途、生产方法以及安全注意事项:
主要用途- 合成工业:在多种有机合成反应中作为溶剂或催化剂使用。
- 农药与医药行业:用于生产多种农药品种及药物。
- 塑料加工与纤维制造:用作聚合物的溶解剂和纤维生产的湿纺丝溶剂。
- 精细化工:如肽类化合物合成、光学分析等领域。
- 分离技术:在石油化学工业中作为气体吸收剂,用于芳烃萃取等过程。
- 甲酸甲酯-二甲胺法:通过甲酸与甲醇反应生成甲酸甲酯,再与二甲胺进行气相反应制备DMF。
- 二甲胺-一氧化碳法:在甲醇钠的催化作用下直接以二甲胺和一氧化碳为原料合成DMF。
- 羰基合成法:首先由CO和甲醇通过羰基合成生成甲酸甲酯,然后与二甲胺反应制备DMF。
- 三氯乙醛法:采用三氯乙醛与二甲胺进行反应。
- 毒性:属有毒物质,长期接触可引起中毒症状;急性摄入可能造成严重伤害甚至死亡。
- 易燃性:遇火源或高温下燃烧,并产生有毒氮氧化物烟雾。
- 储存与运输:应避免阳光直射、保持良好通风环境,远离明火及强氧化剂存放。
综上所述,二甲基甲酰胺是一种多功能的化学物质,在化工生产中具有广泛应用。然而,因其毒性及易燃性特点,在实际操作过程中需要严格遵守相关安全规范以确保人员健康与安全生产。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 N-甲基甲酰胺 N-Methylformamide 123-39-7 C2H5NO 59.0678 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 N-甲酰基-N-甲基甲酰胺 N-Methyl-diformamid 18197-25-6 C3H5NO2 87.0782 N-甲基甲酰胺 N-Methylformamide 123-39-7 C2H5NO 59.0678 N-乙基-N-甲基-甲酰胺 N-ethyl-N-methylformamide 28860-25-5 C4H9NO 87.1216 N,N-二甲基脲 1,1-Dimethylurea 598-94-7 C3H8N2O 88.1093 N-羟基甲基-N-甲基甲酰胺 N-formyl-N-hydroxy-methyl-methylamine 20546-32-1 C3H7NO2 89.0941
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:The Action of Elementary Fluorine upon Organic Compounds. XXII. The Fluorination of Some Amides, Nitriles and of Methyl Thiocyanate1摘要:DOI:10.1021/ja01523a031
-
作为产物:描述:4-甲基噻唑 生成 N,N-二甲基甲酰胺参考文献:名称:PYRAZINE DERIVATIVE AND APPLICATION THEREOF IN INHIBITING SHP2摘要:本发明涉及吡嗪衍生物,其在抑制SHP2中的应用,以及具有化学式(I)的化合物或其药用可接受的盐、酯、异构体、溶剂合物、前药或同位素标记。化合物的化学式(I)结构如下。本发明提供的新型吡嗪衍生物具有出色的抑制SHP2活性,并可用于预防和/或治疗非受体蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶介导或依赖的疾病或紊乱。公开号:EP3936502A1
-
作为试剂:描述:5-溴吲哚-3-乙酸 在 indium(III) chloride 、 草酰氯 、 dimethyl sulfide borane 、 caesium carbonate 、 N,N-二甲基甲酰胺 作用下, 以 四氢呋喃 、 二氯甲烷 、 甲苯 为溶剂, 反应 28.5h, 生成 9-bromo-5,6,7,12-tetrahydropyrido[3',2':2,3]azepino[4,5-b]indole参考文献:名称:1-azakenpaullone 的高效合成,一种用于细胞再生的糖原合成酶激酶-3β 的选择性抑制剂摘要:1-Azakenpaullone 是一种糖原合成酶激酶 3β 的选择性抑制剂,通过执行两步方案合成,该方案以三氯化铟介导的分子内环化和温和的反应条件为特色。简洁的合成表明合成效率显着提高并减少了废物的排放。我们期望本研究能够促进1-azakenpaullone及其类似物在细胞再生和再生医学中的应用。DOI:10.1039/d4nj00434e
文献信息
-
Cyclopropyl derivative lipoxygenase inhibitors申请人:Abbott Laboratories公开号:US05037853A1公开(公告)日:1991-08-06Certain carbocyclic aryl- and heterocyclic aryl-substituted cyclopropyl N-hydroxyureas, N-hydoroxycarboxamides, and N-acyl-N-hydroxyamides inhibit 5- and/or 12-lipoxygenase and are useful in the treatment of inflammatory disease states.某些含环丙基N-羟基脲、N-羟基羧酰胺和N-酰基-N-羟基酰胺的碳环芳基和杂环芳基取代物抑制5-和/或12-脂氧合酶,在治疗炎症性疾病状态中具有用处。
-
BENZOTHIOPHENE INHIBITORS OF RHO KINASE申请人:Kahraman Mehmet公开号:US20080021026A1公开(公告)日:2008-01-24The present invention relates to compounds and methods which may be useful as inhibitors of Rho kinase for the treatment or prevention of disease.本发明涉及化合物和方法,这些化合物和方法可能作为Rho激酶的抑制剂在治疗或预防疾病方面有用。
-
Fmoc-Based Synthesis of Peptide Thioesters for Native Chemical Ligation Employing a <i>tert</i>-Butyl Thiol Linker作者:Richard Raz、Jörg RademannDOI:10.1021/ol1029723日期:2011.4.1toward secondary amines in basic milieu, in contrast to other alkyl and aryl thioesters. Exploiting this enhanced stability, peptide thioesters were synthesized in a direct manner, applying a tert-butyl thiol linker for Fmoc-based solid-phase peptide synthesis.
-
Compositions for Treatment of Cystic Fibrosis and Other Chronic Diseases申请人:Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated公开号:US20150231142A1公开(公告)日:2015-08-20The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising an inhibitor of epithelial sodium channel activity in combination with at least one ABC Transporter modulator compound of Formula A, Formula B, Formula C, or Formula D. The invention also relates to pharmaceutical formulations thereof, and to methods of using such compositions in the treatment of CFTR mediated diseases, particularly cystic fibrosis using the pharmaceutical combination compositions.
-
[EN] COMPOUNDS FOR THE TREATMENT OF AMYLOID-ASSOCIATED DISEASES<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS POUR LE TRAITEMENT DE MALADIES ASSOCIÉES À LA SUBSTANCE AMYLOÏDE申请人:REMYND NV公开号:WO2016083490A1公开(公告)日:2016-06-02This invention provides novel compounds of formulae (I) or (II) or a stereoisomer, enantiomer, racemic, or tautomer thereof, (I) (II) wherein the substituents are as defined in the specification. The present invention also relates to the novel compounds for use as a medicine, more in particular for the prevention or treatment of amyloid-related diseases, more specifically certain neurological disorders, such as disorders collectively known as tauopathies, disorders characterized by cytotoxic α-synuclein amyloidogenesis. The present invention also relates to the use of said novel compounds for the manufacture of medicaments useful for treating such amyloid-related diseases. The present invention further relates to pharmaceutical compositions including said novel compounds and to methods for the preparation of said novel compounds.这项发明提供了式(I)或(II)或其立体异构体、对映异构体、消旋体或互变异构体的新化合物,其中取代基如规范中所定义。本发明还涉及用作药物的这些新化合物,更具体地用于预防或治疗与淀粉样蛋白相关的疾病,更具体地说是某些神经系统疾病,如被统称为tau病变的疾病,以及由细胞毒性α-突触核蛋白淀粉生成所特征化的疾病。本发明还涉及利用这些新化合物制备对治疗此类淀粉样蛋白相关疾病有用的药物。本发明还涉及包括这些新化合物的药物组合物以及这些新化合物的制备方法。
表征谱图
-
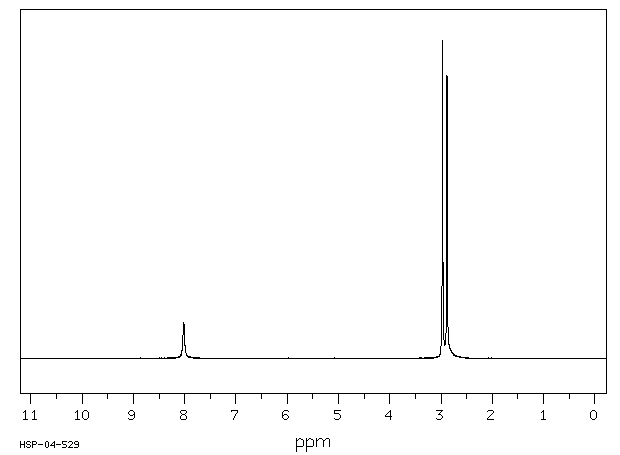
氢谱1HNMR
-
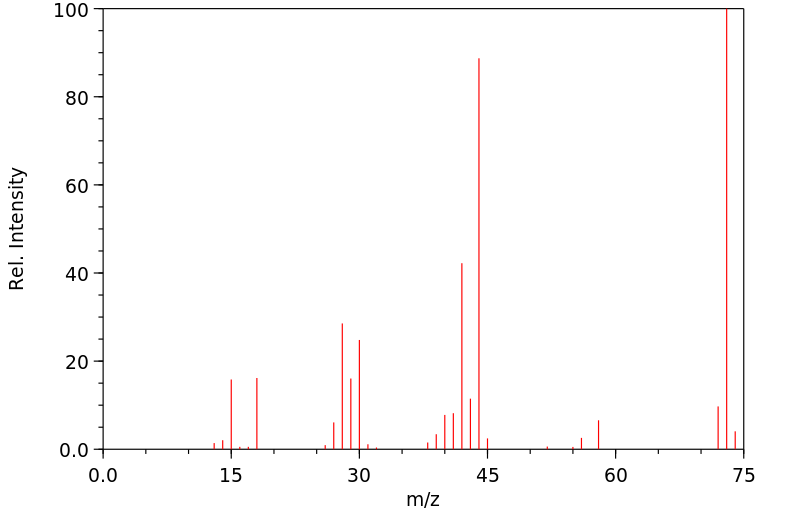
质谱MS
-
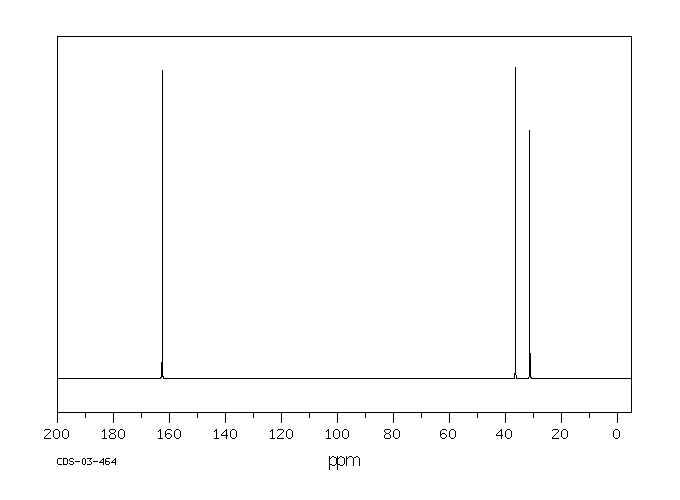
碳谱13CNMR
-
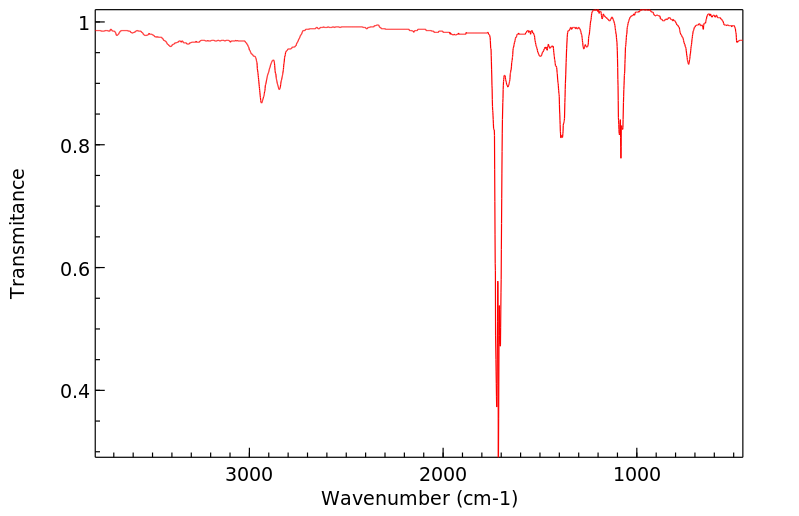
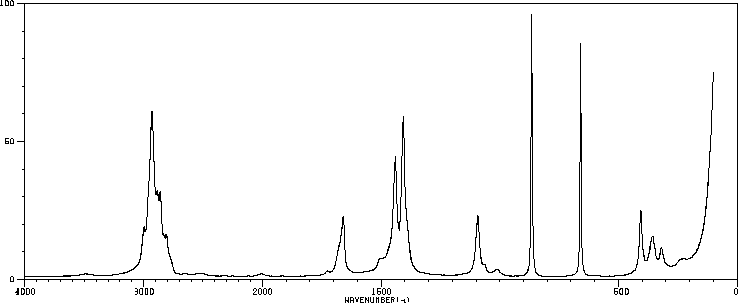
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息