苯乙烯 | 100-42-5
中文名称
苯乙烯
中文别名
苏合香烯;乙烯苯;乙烯基苯;肉桂烯;苯基乙烯;斯替林
英文名称
styrene
英文别名
ethenyl-benzene;phenylethylene;vinylbenzene;stryene
CAS
100-42-5
化学式
C8H8
mdl
MFCD00008612
分子量
104.152
InChiKey
PPBRXRYQALVLMV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:-31 °C (lit.)
-
沸点:145-146 °C (lit.)
-
密度:0.906 g/mL at 25 °C
-
蒸气密度:3.6 (vs air)
-
闪点:88 °F
-
溶解度:0.24克/升
-
介电常数:2.4(25℃)
-
暴露限值:TLV-TWA 50 ppm (~212 mg/m3) (ACGIH and NIOSH), 100 ppm (~425 mg/m3) (OSHA and MSHA); ceiling 200 ppm, peak 600 ppm/5 min/3 h (OSHA); STEL 100 ppm (~425 mg/m3) (ACGIH).
-
LogP:2.96 at 25℃
-
物理描述:Styrene monomer, stabilized appears as a clear colorless to dark liquid with an aromatic odor. Vapors heavier than air and irritating to the eyes and mucous membranes. Subject to polymerization. If the polymerization takes place inside a closed container, the container may rupture violently. Less dense than water and insoluble in water. Used to make plastics, paints, and synthetic rubber.
-
颜色/状态:Colorless to yellowish, oily liquid
-
气味:Characteristic, sweet, balsamic, almost floral odor that is extremely penetrating
-
蒸汽密度:3.6 (Air = 1)
-
蒸汽压力:6.40 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
亨利常数:Henry's Law constant = 0.00275 atm cu m/mole at 25 °C
-
大气OH速率常数:5.80e-11 cm3/molecule*sec
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
在热、光或过氧化物作用下容易发生聚合,通常需加入81mg/m3的丁基邻苯二酚作阻聚剂。在酸性催化剂或离子催化剂存在下也易发生聚合。使用铂、镍等作为催化剂在温和条件下加氢可得到乙苯,若加氢过量则生成乙基环己烷;氧化铬作为催化剂时,会生成苯甲酸。
-
苯乙烯有毒,其毒性比苯弱。该物质具有引人发笑的臭味,在空气中浓度为25×10-6时即可察觉,而在50×10-6时则会感到不快。不过,即使在这样低浓度下也无毒害作用,随着浓度升高刺激性增强,可刺激皮肤和呼吸道;高浓度时有麻醉作用。苯乙烯不会造成慢性中毒,因其在生物体内易被氧化成苯甲酸、苯基甘醇、苯乙醇酸等化合物,并进一步转化为马尿酸或葡萄糖酸酯排出体外。空气中最高容许浓度为420mg/m3。生产设备应密闭以防跑冒滴漏,操作时需佩戴个人防护用具;有呼吸系统疾病、肝脏病、肾脏病或血液病者不宜从事此类工作。
-
苯乙烯可刺激皮肤和黏膜并具有麻醉作用,对血液和肝有一定损害作用。吸入1%的蒸气数分钟后会失去知觉。与苯不同的是,苯乙烯不会引起慢性中毒,车间空气中最高容许浓度为40mg/m3。吸入其蒸气会导致中毒,在空气中的允许浓度不应超过0.1mg/L。
-
稳定性:稳定
-
禁配物:强氧化剂、酸类、卤素等
-
避免接触条件:受热
-
聚合危害:聚合
-
-
自燃温度:914 °F (490 °C)
-
分解:Hazardous decomposition products formed under fire conditions - Carbon oxides.
-
粘度:0.696 cP at 25 °C
-
腐蚀性:Styrene will corrode copper and copper alloys
-
燃烧热:-4,395.63 kJ/mol at 25 °C
-
汽化热:10.50 kcal/mol at 25 °C
-
表面张力:32.3 dynes/cm at 20 °C
-
电离电位:8.40 eV
-
聚合:Polymerizes slowly at room temperature and readily at temp > 65 °C.
-
气味阈值:Odor Threshold Low: 0.01 [mmHg]; Odor Threshold High: 1.9 [mmHg]; Detection odor threshold from AIHA (mean = 0.14 ppm)
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.5440 at 25 °C
-
保留指数:914 ;870 ;874 ;880.3 ;871 ;900.02 ;871 ;876 ;872 ;886 ;888 ;878 ;874.35 ;871 ;873 ;875 ;873 ;873 ;885 ;885 ;885 ;880 ;884 ;884 ;885 ;885 ;877.8 ;886 ;880 ;893 ;885 ;890.5 ;897.3 ;873 ;874.4 ;874.4 ;874.4 ;874.7 ;874.7 ;874.9 ;878 ;885 ;878 ;896 ;879 ;895 ;871 ;877 ;878 ;872 ;872 ;881 ;878 ;895 ;878 ;876 ;883.8 ;873 ;870 ;875 ;881 ;882.7 ;873.29 ;875 ;877 ;875 ;880 ;883 ;887 ;872 ;884 ;885 ;885 ;885 ;871 ;871 ;877 ;875 ;873 ;880 ;875 ;878 ;887 ;890 ;878 ;880 ;883 ;866 ;863 ;862 ;871 ;879 ;868 ;875 ;876 ;880 ;886 ;879 ;869 ;868 ;882 ;900 ;900 ;884
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):2.9
-
重原子数:8
-
可旋转键数:1
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:0
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:0
ADMET
代谢
最近通过LC-ESI-MS在小鼠尿液中识别出了苯乙烯的新代谢物,三种异构的烯基苯基硫酸(2-、3-和4-VPMA)。在这项研究中,4-VPMA以及2-和3-VPMA的微量也在接触苯乙烯蒸汽浓度为23至244 mg/立方米的手工层压工人尿液中被发现。这些轮班结束时的样本中4-VPMA的浓度为4.59±3.64 ng/mL(平均值±标准差;n=10),而工作轮班后次日早晨发现的浓度为2.14±2.07 ng/mL(平均值±标准差;n=10)。在次日早晨的样本中,4-VPMA与苯基乙二酸浓度之间发现了强烈的相关性(R=0.959),而在轮班结束和次日早晨样本中4-VPMA与扁桃酸之间的相关性要弱得多。4-VPMA的排泄仅占吸收的苯乙烯剂量的约3.5 x 10(-4)%。尽管代谢产率非常低,但VPMAs的形成清楚地表明了苯乙烯环氧化反应的发生和程度,这一反应被认为是具有毒理学相关性的代谢途径。
New metabolites of styrene, three isomeric vinylphenylmercapturic acids (2-, 3-, and 4-VPMA), were recently identified by LC-ESI-MS in the urine of mice. In this study, 4-VPMA together with traces of 2- and 3-VPMA were found also in the urine of hand-lamination workers, which were exposed to styrene vapors at concentrations ranging from 23 to 244 mg/cu m. Concentrations of 4-VPMA in these end-of-shift samples were 4.59+/-3.64 ng/mL (mean+/-S.D.; n=10), those found next morning after the work-shift were 2.14+/-2.07 ng/mL (mean+/-S.D.; n=10). Strong correlation (R=0.959) was found in the next-morning samples between concentrations of 4-VPMA and phenylglyoxylic acid, whereas correlations found between 4-VPMA and mandelic acid in both end-of-shift and next-morning samples were much weaker. The excretion of 4-VPMA accounted for only about 3.5 x 10(-4)% of the absorbed dose of styrene. Despite very low metabolic yield, formation of VPMAs clearly indicates occurrence and extent of styrene ring oxidation considered to be a toxicologically relevant metabolic pathway.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
人类P450 2A13是最有效的酶,用于催化尼古丁的代谢和4-(甲基硝基氨基)-1-(3-吡啶基)-1-丁酮(NNK)的代谢激活。可以想象,P450 2A13也在代谢空气污染物中的化学物质,因为这种酶在呼吸道中高度表达。在这项研究中,作者们调查了P450 2A13可能代谢萘、苯乙烯和甲苯的可能性,这些物质不仅包含在空气污染物中,也包含在烟草烟雾中,尽管已知它们是由P450 1A2或2E1代谢的。他们发现,P450 2A13催化萘生成1-和2-萘酚的内在清除率(kcat/ Km)(分别是3.1-和2.2倍)高于P450 1A2,并且比P450 2E1更有效地催化苯乙烯生成7,8-环氧苯乙烯和甲苯生成苯甲醇。P450 2A13与P450 2E1的底物特异性重叠得到了证实,因为P450 2A13催化氯佐辛6-羟基化(kcat/ Km值高8倍)和对硝基苯酚2-羟基化(kcat/ Km值高19倍),这些都是P450 2E1的标志活性。因此,作者们发现P450 2A13代谢多种环境化学物质,并且具有P450 1A2和2E1的底物特异性重叠,这表明P450 2A13在呼吸道中与环境化学物质的局部代谢有关,这些化学物质与毒性或致癌性有关。
Human P450 2A13 is the most efficient enzyme for catalyzing the metabolism of nicotine and metabolic activation of 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone (NNK). It is conceivable that P450 2A13 also metabolizes chemicals in air pollutants because this enzyme is highly expressed in the respiratory tract. In this study, /the authors/ investigated the possibility that P450 2A13 can metabolize naphthalene, styrene, and toluene, which are included in air pollutants as well as tobacco smoke, although they were known to be metabolized by P450 1A2 or 2E1. /They/ found that P450 2A13 catalyzed 1- and 2-naphthol formations from naphthalene with higher intrinsic clearances (kcat/ Km) (3.1- and 2.2-fold, respectively) than P450 1A2 and also more efficiently catalyzed the styrene 7,8-oxide formation from styrene and the benzylalcohol formation from toluene than P450 2E1. The overlapping substrate specificity of P450 2A13 with P450 2E1 was supported by the finding that P450 2A13 catalyzed chlorzoxazone 6-hydroxylation (8-fold higher value of kcat/ Km) and p-nitrophenol 2-hydroxylation (19-fold higher value of kcat/ Km), which are marker activities of P450 2E1. Thus, /the authors/ found that P450 2A13 metabolizes diverse environmental chemicals and has overlapping substrate specificities of P450 1A2 and 2E1, suggesting that P450 2A13 plays important roles in the local metabolism of environmental chemicals in the respiratory tract related to toxicity or carcinogenicity.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
当前研究旨在探讨细胞色素P450(CYP450)激活和电敏感的瞬态受体电位锚蛋白1受体(TRPA1)在介导对苯乙烯和萘的感官刺激反应中的作用。为此,通过气测计测量C57Bl/6J雌性小鼠在15分钟暴露期间的每次呼气开始时的刹停时间来衡量这些蒸气的感官刺激。在预先给予CYP450抑制剂美替拉酮的动物中,对75 ppm苯乙烯和7 ppm萘的感官刺激反应减少了三倍或更多,这为代谢激活在这些蒸气反应中的作用提供了证据。在TRPA1-/-敲除小鼠中,对苯乙烯(75 ppm)和萘(7.6 ppm)的感官刺激反应几乎不存在,这表明这个受体在介导反应中起着关键作用。因此,这些结果支持了苯乙烯和萘蒸气通过TRPA1检测其CYP450代谢物来启动感官刺激反应的假设。
The current study was aimed at examining the role of cytochrome P450 (CYP450) activation and the electrophile-sensitive transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 receptor (TRPA1) in mediating the sensory irritation response to styrene and naphthalene. Toward this end, the sensory irritation to these vapors was measured in female C57Bl/6J mice during 15-min exposure via plethysmographic measurement of the duration of braking at the onset of each expiration. The sensory irritation response to 75 ppm styrene and 7 ppm naphthalene was diminished threefold or more in animals pretreated with the CYP450 inhibitor metyrapone, providing evidence of the role of metabolic activation in the response to these vapors. The sensory irritation response to styrene (75 ppm) and naphthalene (7.6 ppm) was virtually absent in TRPA1-/- knockout mice, indicating the critical role of this receptor in mediating the response. Thus, these results support the hypothesis that styrene and naphthalene vapors initiate the sensory irritation response through TRPA1 detection of their CYP450 metabolites.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
CYP2E1已被确定为参与人类苯乙烯代谢的主要细胞色素P450同种型。CYP2E1在人类中表现出多态性,不同的基因型至少部分与酶活性个体表达水平的不同有关。研究者们研究了CYP2E1的遗传多态性和表型是否调节尿液中苯乙烯代谢物的水平,以及它们是否可用于评估职业暴露于苯乙烯的风险。选择了暴露于苯乙烯(平均浓度为362.7 mg/m³)的49名男性工人和一个对照组。采集尿液、血液和颊拭子样本以确定尿生物指标(苯乙酸和扁桃酸),使用RT-PCR在血液中定量CYP2E1的mRNA,并分析颊拭子中CYP2E1酶的不同多态性。研究者们发现,携带CYP2E1*5B杂合子等位基因(cl/c2)的个体与野生型纯合子(c1/c1)相比,酶的mRNA表达降低,苯乙烯代谢物的排泄也减少,这表明在这种多态性存在时,酶的可诱导性降低。结果显示,CYP2E1表型(通过血液样本中特定mRNA的表达测量)和CYP2E1*5B等位基因基因型的组合效应,可能解释尿液中苯乙烯代谢物排泄的可变性。
The CYP2E1 has been identified as the main cytochrome P450 isoform involved in human styrene metabolism. CYP2E1 presents polymorphism in humans and the different genotypes may, at least partly, be related to the different levels of individual expression of enzyme activity. /Investigators/ studied whether the genetic polymorphisms and phenotype of CYP2E1 modulate the level of urinary styrene metabolites and if they can be used for assessing risks of occupational exposure to styrene. A population of 49 male workers exposed to styrene (average level 362.7 mg/cu m) and a control group were selected. Samples of urine, blood and buccal swab were taken to determine the urinary biological indicators (phenylglyoxylic acid and mandelic acid), to quantify mRNA of CYP2E1 in blood using RT-PCR and to analyze different polymorphisms of enzyme CYP2E1 from buccal swab. /Investigators/ found decreased expression of mRNA of the enzyme, as well as decreased excretion of the styrene metabolites in individuals carrying the CYP2E1*5B heterozygote allele (cl/c2) with respect to the wild-type homozygote (c1/c1), which indicates a reduction in the inducibility of the enzyme in the presence of this polymorphism. The results show that the combined effect of both the CYP2E1 phenotype, measured by the expression of the specific mRNA in blood samples, and the CYP2E1*5B allele genotype, may explain the variability of urinary excretion of the styrene metabolites.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
Styrene has known human metabolites that include Styrene 7,8-oxide.
来源:NORMAN Suspect List Exchange
毒理性
识别和使用:苯乙烯是一种从无色到淡黄色的油性液体。它用于制造塑料、合成橡胶和树脂,并作为绝缘体。它还用作冰淇淋和糖果的风味增强剂。人体研究:人类通过吸入800 ppm(3.4 mg/L)苯乙烯3小时,会立即出现眼睛和喉咙刺激、鼻粘液分泌增加、金属味、嗜睡和眩晕。测试结束后,注意到轻微的肌肉无力,伴随惰性和抑郁。长期接触苯乙烯会导致皮肤起泡和皮炎的发展,这被认为是由皮肤脱脂引起的。报道了肝脏(例如,血清胆酸增加和血浆酶活性增强)和生殖系统(例如,女性工人出生频率降低和自发流产频率增加)的影响。流行病学研究发现,苯乙烯工人的淋巴造血癌症(白血病或淋巴瘤或所有)的死亡率和发病率增加,有胰腺和食道肿瘤的提示性证据。尽管苯乙烯-7,8-氧化物是苯乙烯的主要和活性环氧化物代谢物,但目前还没有足够的人类研究。苯乙烯在光氧化时与臭氧和二氧化氮反应形成对人体眼睛刺激性高的产物,如形成烟雾。此外,当苯乙烯废物与溴或氯废物混合并在阳光下反应时,形成了一种强烈的催泪剂。动物研究:动物急性暴露于苯乙烯会导致皮肤和呼吸道刺激以及中枢神经系统效应。液态苯乙烯是一种皮肤刺激物,直接接触会导致红斑。苯乙烯在兔眼中引起了中度的结膜炎和轻微的、短暂的角膜损伤。兔子的眼球震颤得到证实,在苯乙烯暴露期间,旋转性眼球震颤的方向发生了反转。吸入10000 ppm苯乙烯的大鼠和豚鼠在几分钟内昏迷,并在30至60分钟的暴露后死亡。在2500 ppm暴露的动物表现出无力 and 意识模糊,随后是不协调、震颤和昏迷;在8小时内死亡。吸入160 ppm的小鼠在3分钟内的呼吸频率降低了50%;吸入250 ppm两次各6小时或500 ppm单次6小时的小鼠发展为严重的中央小叶肝坏死。吸入125 ppm苯乙烯的小鼠,每天6小时,连续4天,肝脏重量增加。当大鼠在饮用水中给予0、125或250 ppm商业级苯乙烯三代时,没有检测到与处理相关的繁殖变化。长期化学致癌生物检测表明,苯乙烯在几种小鼠品系中引起了肺癌,在大鼠中引起了乳腺癌,苯乙烯-7,8-氧化物在大鼠和小鼠中引起了前胃肿瘤,在小鼠中引起了肝癌。苯乙烯在存在代谢激活的情况下诱导了沙门氏菌typhimurium TA1535和TA100的逆向突变。它对TA1537、TA1538或TA98没有诱变性。苯乙烯在没有代谢激活的情况下,对各种沙门氏菌typhimurium菌株的点测试没有诱变性。即使在代谢激活的情况下,它也没有诱导裂殖酵母Schizosaccharomyces pombe的前向突变。在雄性小鼠的宿主介导试验中,1000 mg/kg苯乙烯增加了酿酒酵母D4菌株的基因转换频率。苯乙烯在人类和其他脊椎动物中的内分泌干扰活性似乎可以忽略不计。生态毒性研究:在聚苯乙烯杯中繁殖的Ceriodaphnia dubia后代数量减少。苯乙烯在2.3至23 mg/L的浓度下刺激了端足类动物Pontoporeia affinis的游泳活动。较高的苯乙烯水平(35和46 mg/L)导致端足类动物停止游泳数天,然后恢复大于正常的活动。
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: Styrene is a colorless to yellowish, oily liquid. It is used in the manufacture of plastics, synthetic rubber, and resins, and as an insulator. It is also used as a flavoring agent for ice cream and candy. HUMAN STUDIES: Humans acutely exposed to styrene by inhalation to 800 ppm (3.4 mg/L) for 3 hr experience immediate eye and throat irritation, increased nasal mucous secretion, metallic taste, drowsiness, and vertigo. After test termination, slight muscular weakness, accompanied by inertia and depression were noted. Long-term contact with styrene results in blistering of the skin and development of dermatitis, which is thought to result from defatting of the skin. Effects on the liver (e.g., increased serum bile acid and enhanced activity of plasma enzymes) and reproductive system (e.g., decreased frequency of births and increased frequency of spontaneous abortions in female workers) have been reported. Epidemiologic studies found styrene workers had increased mortality or incidences of lymphohematopoietic cancers (leukaemia or lymphoma or all), with suggestive evidence for pancreatic and esophageal tumors. No adequate human studies are available for styrene-7,8-oxide although this is the primary and active epoxide metabolite of styrene. Both are genotoxic and form DNA adducts in humans. Products having high irritancy to the human eye are formed when styrene is photo-oxidized with ozone and nitrogen dioxide as in formation of smog. Also, a potent lacrimator has been formed when styrene wastes became mixed with bromine or chlorine wastes and reacted under the influence of sunlight. ANIMAL STUDIES: Acute exposure of animals to styrene causes irritation of the skin and respiratory tract, and central nervous system effects. Liquid styrene is a skin irritant which, on direct contact, causes erythema. Styrene in the rabbit eye caused moderate conjunctival irritation and slight, transient corneal injury. Nystagmus was demonstrated in rabbits, and during styrene exposure the directions of the rotatory nystagmus reversed. Rats and guinea pigs that inhaled 10,000 ppm styrene became comatose within minutes and died after 30 to 60 minutes of exposure. Animals exposed at 2500 ppm showed weakness and stupor, followed by incoordination, tremor, and coma; death followed within 8 hours. A 50% reduction in respiratory rate occurred in mice that inhaled 160 ppm for 3 minutes; mice that inhaled 250 ppm for two 6-hr periods or 500 ppm for a single 6-hr period developed severe centrilobular hepatic necrosis. Mice inhaling 125 ppm styrene, 6 hrs/day for 4 days developed increased liver weight. When rats were given 0, 125, or 250 ppm commercial grade styrene in their drinking water for three generations, no treatment-related changes in reproduction could be detected. Long-term chemical carcinogenesis bioassays showed that styrene caused lung cancers in several strains of mice and mammary cancers in rats and styrene-7,8-oxide caused tumors of the forestomach in rats and mice and of the liver in mice. Styrene induced reverse mutations in Salmonella typhimurium TA1535 and TA100 in presence of metabolic activation. It was not mutagenic to TA1537, TA1538 or TA98. Styrene was not mutagenic in spot test with various strains of Salmonella typhimurium without metabolic activation. It did not induce forward mutations in Schizosaccharomyces pombe, even with metabolic activation. In host-mediated assay using male mice, 1000 mg/kg styrene increased gene conversion frequency in Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain D4. The endocrine disruptor activity of styrene in humans and other vertebrates appears to be negligible. ECOTOXICITY STUDIES: Offspring numbers were reduced in Ceriodaphnia dubia bred in polystyrene cups. The swimming activity of the amphipod, Pontoporeia affinis, was stimulated by styrene at concentrations between 2.3 and 23 mg/L. Higher styrene levels (35 and 46 mg/L) caused amphipods to cease swimming for several days, then resume greater than normal activity.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
Styrene 7,8-oxide, a metabolite of styrene, can form DNA adducts by binding to deoxyguanosine. It is also mutagenic and causes increased frequency of sister chromatid exchange, chromosomal aberrations, micronucleated cells, and DNA strand breaks. (L1831)
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
苯乙烯基于有限的人类致癌性研究证据、充分的实验动物致癌性研究证据以及对致癌机制的支持性数据,合理预期为人类致癌物。
Styrene is reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen based on limited evidence of carcinogenicity from studies in humans, sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity from studies in experimental animals, and supporting data on mechanisms of carcinogenesis.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
Evaluation: There is limited evidence in humans for the carcinogenicity of styrene. There is limited evidence in experimental animals for the carcinogenicity of styrene. Styrene is possibly carcinogenic to humans (Group 2B).
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
A4;不能分类为人类致癌物。/苯乙烯,单体/
A4; Not classifiable as a human carcinogen. /Styrene, monomer/
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
人体吸收苯乙烯可以通过所有途径进行,但主要通过呼吸道。
The absorption of styrene in humans proceeds by all routes, but mainly through the respiratory tract.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
苯乙烯蒸汽通过肺部吸收;与相应的肺部吸收相比,在空气中接触浓度高达2.5克/立方米(600 ppm)的苯乙烯时,其经皮吸收是微不足道的(大约2%)。通过手部皮肤吸收液态苯乙烯的速率为9-15毫克/平方厘米/小时,而水溶液(66-269毫克/升)的吸收速率为40-180微克/平方厘米/小时。苯乙烯可溶于血液,并已在脂肪组织中找到。在17名工人中的13人的皮下脂肪样本中发现了苯乙烯,这是在空气中最近职业接触超过4.2毫克/立方米(1 ppm)苯乙烯后长达3天内的结果。在空气中接触420毫克/立方米(100 ppm)苯乙烯后,呼出气中的苯乙烯会迅速减少。
Styrene vapors are absorbed through lung; percutaneous absorption of styrene during exposure to concentrations up to 2.5 g/cu M (600 ppm) in air is insignificant (about 2%) as compared with the respective pulmonary absorption. The percutaneous absorption of liquid styrene through skin of hand is 9-15 mg/sq cm/hr and that of aqueous solution (66-269 mg/L) is 40-180 ug/sq cm/hr. Styrene is soluble in blood and has been found in fat tissue. It was found in SC fat samples from 13/17 workers for as long as 3 days after most recent occupational exposure to more than 4.2 mg/cu M (1 ppm) styrene in air. It is rapidly depleted in breath following exposure to 420 mg/cu M (100 ppm) in air.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
在给予20毫克/公斤的口服剂量的14C标记的苯乙烯后,研究了雄性和雌性大鼠在不同时间间隔的组织分布和排泄。含最高浓度的是肾脏,其次是肝脏和胰腺。主要的排泄途径是通过肾脏,24小时内90%的剂量出现在尿液中。从粪便中回收的剂量不到2%。
The tissue distribution and excretion of an oral dose of 20 mg/kg of (14)C-labeled styrene was studied in both male and female rats at various time intervals after admin. Organ with highest concn was kidney, followed by liver and pancreas. Principal route of excretion was by way of the kidneys, with 90% of dose appearing in urine within 24 hr. Less than 2% of the dose was recovered from the feces.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
已观察到,苯乙烯会穿过胎盘。
Styrene, it has been observed, crosses the placenta.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
安全信息
-
职业暴露等级:A
-
职业暴露限值:TWA: 50 ppm (215 mg/m3), STEL: 100 ppm (425 mg/m3)
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:3
-
立即威胁生命和健康浓度:700 ppm
-
危险品标志:Xn
-
安全说明:S16,S23,S26,S36,S36/37,S45,S7
-
危险类别码:R10,R36/38,R20
-
WGK Germany:2
-
海关编码:2902500000
-
危险品运输编号:UN 2055 3/PG 3
-
危险类别:3
-
RTECS号:WL3675000
-
包装等级:III
-
储存条件:1. 储存注意事项:通常商品会添加阻聚剂。储存时应选择阴凉、通风的库房,并远离火源和热源,库温不宜超过37℃。包装要求密封,避免与空气接触。应将该物品与氧化剂和酸类分开存放,严禁混储。不宜大量或长期储存。使用防爆型照明和通风设施,禁止使用可能产生火花的机械设备和工具。储存区需配备泄漏应急处理设备及合适的收容材料。 2. 采用镀锌铁桶包装,并在包装时加入阻聚剂。贮存时应低温(25℃以下)或冷藏保存,以防聚合变质。避免火源,不得直接日晒。储存期限为一个月。按易燃有毒物品的规定进行运输和存储。
SDS
| 第一部分:化学品名称 |
| 化学品中文名称: | 不饱和聚酯树脂 |
| 化学品英文名称: | Unsaturated polyester resin |
| 中文俗名或商品名: | |
| Synonyms: | |
| CAS No.: | 100-42-5 |
| 分子式: | 无资料 |
| 分子量: | 无资料 |
| 第二部分:成分/组成信息 |
| 纯化学品 混合物 | |||
| 化学品名称:不饱和聚酯树脂 | |||
|
| 第三部分:危险性概述 |
| 危险性类别: | |
| 侵入途径: | 吸入、食入、皮肤接触 |
| 健康危害: | 对眼和上呼吸道粘膜有刺激和麻醉作用。急性中毒:高浓度时,立即引起眼及上呼吸道粘膜的刺激,出现眼痛、流泪、流涕、喷嚏、咽痛、咳嗽等,继之头痛、头晕、恶心、呕吐、全身乏力等;严重者可有眩晕、步态蹒跚。眼部受苯乙烯液体污染时,可致灼伤。慢性影响:常见神经衰弱综合征,有头痛、乏力、恶心、食欲减退、腹胀、忧郁、健忘、指颤等。对呼吸道有刺激作用,长期接触有时引起阻塞性肺部病变。皮肤粗糙、皲裂和增 |
| 环境危害: | 对环境有严重危害,对水体、土壤和大气可造成污染。 |
| 燃爆危险: | 本品易燃,为可疑致癌物,具刺激性。 |
| 第四部分:急救措施 |
| 皮肤接触: | 脱去污染的衣着,用肥皂水和清水彻底冲洗皮肤。 |
| 眼睛接触: | 立即提起眼睑,用大量流动清水或生理盐水彻底冲洗至少15分钟。就医。 |
| 吸入: | 迅速脱离现场至空气新鲜处。保持呼吸道通畅。如呼吸困难,给输氧。如呼吸停止,立即进行人工呼吸。就医。 |
| 食入: | 饮足量温水,催吐。就医。 |
| 第五部分:消防措施 |
| 危险特性: | 其蒸气与空气可形成爆炸性混合物,遇明火、高热或与氧化剂接触,有引起燃烧爆炸的危险。遇酸性催化剂如路易斯催化剂、齐格勒催化剂、硫酸、氯化铁、氯化铝等都能产生猛烈聚合,放出大量热量。其蒸气比空气重,能在较低处扩散到相当远的地方,遇火源会着火回燃。 |
| 有害燃烧产物: | 一氧化碳、二氧化碳。 |
| 灭火方法及灭火剂: | 尽可能将容器从火场移至空旷处。喷水保持火场容器冷却,直至灭火结束。灭火剂:泡沫、干粉、二氧化碳、砂土。用水灭火无效。遇大火,消防人员须在有防护掩蔽处操作。 |
| 消防员的个体防护: | |
| 禁止使用的灭火剂: | |
| 闪点(℃): | 32.2 |
| 自燃温度(℃): | |
| 爆炸下限[%(V/V)]: | 1.1 |
| 爆炸上限[%(V/V)]: | 6.1 |
| 最小点火能(mJ): | |
| 爆燃点: | |
| 爆速: | |
| 最大燃爆压力(MPa): | |
| 建规火险分级: |
| 第六部分:泄漏应急处理 |
| 应急处理: | 迅速撤离泄漏污染区人员至安全区,并进行隔离,严格限制出入。切断火源。建议应急处理人员戴自给正压式呼吸器,穿防毒服。尽可能切断泄漏源。防止流入下水道、排洪沟等限制性空间。小量泄漏:用活性炭或其它惰性材料吸收。也可以用不燃性分散剂制成的乳液刷洗,洗液稀释后放入废水系统。大量泄漏:构筑围堤或挖坑收容。用泡沫覆盖,降低蒸气灾害。用防爆泵转移至槽车或专用收集器内,回收或运至废物处理场所处置。 |
| 第七部分:操作处置与储存 |
| 操作注意事项: | 密闭操作,加强通风。操作人员必须经过专门培训,严格遵守操作规程。建议操作人员佩戴过滤式防毒面具(半面罩),戴化学安全防护眼镜,穿防毒物渗透工作服,戴橡胶耐油手套。远离火种、热源,工作场所严禁吸烟。使用防爆型的通风系统和设备。防止蒸气泄漏到工作场所空气中。避免与氧化剂、酸类接触。灌装时应控制流速,且有接地装置,防止静电积聚。搬运时要轻装轻卸,防止包装及容器损坏。配备相应品种和数量的消防器材及泄漏应急处理设备。倒空的容器可能残留有害物。 |
| 储存注意事项: | 通常商品加有阻聚剂。储存于阴凉、通风的库房。远离火种、热源。库温不宜超过30℃。包装要求密封,不可与空气接触。应与氧化剂、酸类分开存放,切忌混储。不宜大量储存或久存。采用防爆型照明、通风设施。禁止使用易产生火花的机械设备和工具。储区应备有泄漏应急处理设备和合适的收容材料。 |
| 第八部分:接触控制/个体防护 |
| 最高容许浓度: | |
| 监测方法: | |
| 工程控制: | 生产过程密闭,加强通风。 |
| 呼吸系统防护: | 空气中浓度超标时,建议佩戴过滤式防毒面具(半面罩)。紧急事态抢救或撤离时,建议佩戴隔离式呼吸器。 |
| 眼睛防护: | 化学安全防护眼镜。 |
| 身体防护: | 穿防毒物渗透工作服。 |
| 手防护: | 防化学品手套 |
| 其他防护: | 工作现场禁止吸烟、进食和饮水。工作完毕,淋浴更衣。保持良好的卫生习惯。 |
| 第九部分:理化特性 |
| 外观与性状: | 无色透明油状液体,尖锐苯乙烯气味 |
| pH: | |
| 熔点(℃): | |
| 沸点(℃): | 145 |
| 相对密度(水=1): | |
| 相对蒸气密度(空气=1): | 3.6 |
| 饱和蒸气压(kPa): | |
| 燃烧热(kJ/mol): | |
| 临界温度(℃): | |
| 临界压力(MPa): | |
| 辛醇/水分配系数的对数值: | |
| 闪点(℃): | 32.2 |
| 引燃温度(℃): | |
| 爆炸上限%(V/V): | 6.1 |
| 爆炸下限%(V/V): | 1.1 |
| 分子式: | 无资料 |
| 分子量: | 无资料 |
| 蒸发速率: | |
| 粘性: | |
| 溶解性: | 微溶于水 |
| 主要用途: |
| 第十部分:稳定性和反应活性 |
| 稳定性: | 在常温常压下 |
| 禁配物: | 强氧化剂、酸类。 |
| 避免接触的条件: | 光照、空气。 |
| 聚合危害: | |
| 分解产物: |
| 第十一部分:毒理学资料 |
| 急性毒性: | |
| 急性中毒: | |
| 慢性中毒: | |
| 亚急性和慢性毒性: | |
| 刺激性: | |
| 致敏性: | |
| 致突变性: | |
| 致畸性: | |
| 致癌性: |
| 第十二部分:生态学资料 |
| 生态毒理毒性: | |
| 生物降解性: | |
| 非生物降解性: | |
| 生物富集或生物积累性: |
| 第十三部分:废弃处置 |
| 废弃物性质: | |
| 废弃处置方法: | |
| 废弃注意事项: |
| 第十四部分:运输信息 |
| |
| 危险货物编号: | |
| UN编号: | |
| 包装标志: | |
| 包装类别: | |
| 包装方法: | |
| 运输注意事项: | |
| RETCS号: | |
| IMDG规则页码: |
| 第十五部分:法规信息 |
| 国内化学品安全管理法规: | |
| 国际化学品安全管理法规: |
| 第十六部分:其他信息 |
| 参考文献: | 1.周国泰,化学危险品安全技术全书,化学工业出版社,1997 2.国家环保局有毒化学品管理办公室、北京化工研究院合编,化学品毒性法规环境数据手册,中国环境科学出版社.1992 3.Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety,CHEMINFO Database.1998 4.Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety, RTECS Database, 1989 |
| 填表时间: | 年月日 |
| 填表部门: | |
| 数据审核单位: | |
| 修改说明: | |
| 其他信息: | |
| MSDS修改日期: | 年月日 |
制备方法与用途
苯乙烯的基本信息
生产方法
主要通过乙苯脱氢制得:
主要用途 化学性质 危害性与安全处理-
健康危害:
- 对人眼和上呼吸道有刺激作用。
- 短期暴露可引起呼吸困难、头痛等;长期接触可能导致神经衰弱综合征。
-
急救措施:
- 如果吸入,应迅速转移至空气新鲜处并保持安静。
- 若眼睛接触到,立即用大量清水冲洗至少15分钟,并就医。
- 灭火方法:使用干粉、干砂、二氧化碳或泡沫等灭火剂进行灭火。
- 短时间接触容许浓度(STEL):420毫克/立方米
- 时间加权平均容许浓度(TWA):210毫克/立方米
注意:以上信息仅供参考,具体使用时请遵循相关的安全操作规程和国家标准。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 Alpha-甲基苯乙烯 1-ethenyl-4-methylbenzene 622-97-9 C9H10 118.178 —— 2-phenylvinyl iodide 101349-79-5 C8H7I 230.048 —— E-styryl iodide 42599-24-6 C8H7I 230.048 —— (Z)-styryl iodide 57918-63-5 C8H7I 230.048 氯乙烯基苯 1-(2-chlorovinyl)benzene 622-25-3 C8H7Cl 138.597 [(Z)-2-溴乙烯基]苯 [(E)-2-bromoethenyl]benzene 588-72-7 C8H7Br 183.048 —— (Z)-β-bromostyrene 1335-06-4 C8H7Br 183.048 β-溴苯乙烯 bromostyrene 103-64-0 C8H7Br 183.048 3-甲基苯乙烯 3-methylstyrene 100-80-1 C9H10 118.178 反式-1,2-二苯乙烯 (E)-1,2-diphenyl-ethene 103-30-0 C14H12 180.249 二苯乙烯 stilbene 588-59-0 C14H12 180.249 —— buta-1,3-dien-1-ylbenzene 1515-78-2 C10H10 130.189 2-甲基苯乙烯 1-methyl-2-vinyl-benzene 611-15-4 C9H10 118.178 Β-苯乙烯甲醚 1-(2-methoxyvinyl)benzene 4747-15-3 C9H10O 134.178 反式肉桂醛 (E)-3-phenylpropenal 14371-10-9 C9H8O 132.162 肉桂醛 3-phenyl-propenal 104-55-2 C9H8O 132.162 肉桂醇 3-Phenylpropenol 104-54-1 C9H10O 134.178 3-苯基丙-2-烯-1-醇 (2E)-3-phenyl-2-propen-1-ol 4407-36-7 C9H10O 134.178 —— 2,2-dibromostyrene 31780-26-4 C8H6Br2 261.944 4-氯苯乙烯 para-chlorostyrene 1073-67-2 C8H7Cl 138.597 —— (E)-(2-phenylethenyl)mercury chloride 16187-31-8 C8H7ClHg 339.187 1,2-二乙烯基苯 1,2-divinylbenzene 91-14-5 C10H10 130.189 对溴苯乙烯 1-bromo-4-ethenyl-benzene 2039-82-9 C8H7Br 183.048 甲苯 toluene 108-88-3 C7H8 92.1405 alpha- 溴苯乙烯 1-bromovinylbenzene 98-81-7 C8H7Br 183.048 2-苯基-1-丙烯 isopropenylbenzene 98-83-9 C9H10 118.178 4-氯甲基苯乙烯 4-Vinylbenzyl chloride 1592-20-7 C9H9Cl 152.623 —— β-styryldimethylsilane 119873-75-5 C10H14Si 162.307 —— (E)-(2-azidovinyl)benzene 18756-03-1 C8H7N3 145.164 —— (Z,Z)-bis(phenylethenyl)telluride 105654-27-1 C16H14Te 333.887 —— (Z)-2-phenylethenyl azide 20544-50-7 C8H7N3 145.164 —— dichloro(E-2-phenylethen-1-yl)borane 6688-97-7 C8H7BCl2 184.861 反式-BETA-苯乙烯硼酸 (E)-styrylboronic acid 6783-05-7 C8H9BO2 147.969 [(E)-2-苯基乙烯基]硼酸 Dihydroxy-styryl-boran 4363-35-3 C8H9BO2 147.969 三甲基-[(E)-2-苯乙烯基]硅烷 1-(trimethylsilyl)-2-phenylethene 19372-00-0 C11H16Si 176.334 —— (E)-2-phenylethenyl(trimethyl)stannane 50849-52-0 C11H16Sn 266.958 对二甲苯 para-xylene 106-42-3 C8H10 106.167 3-氯苯乙烯 3-Chlorostyrene 2039-85-2 C8H7Cl 138.597 3-溴苯乙烯 3-bromostyrene 2039-86-3 C8H7Br 183.048 - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— <1-13C>-2-Phenylaethen 61415-37-0 C8H8 105.141 Alpha-甲基苯乙烯 1-ethenyl-4-methylbenzene 622-97-9 C9H10 118.178 对二乙烯苯 1,4-Divinylbenzene 105-06-6 C10H10 130.189 —— E-styryl iodide 42599-24-6 C8H7I 230.048 —— (Z)-(2-fluorovinyl)benzene 20405-78-1 C8H7F 122.142 —— (E)-(2-fluorovinyl)benzene 20405-77-0 C8H7F 122.142 丙-1,2-二烯基苯 1-phenylpropadiene 2327-99-3 C9H8 116.163 —— (E)-β-chlorostyrene 4110-77-4 C8H7Cl 138.597 —— (Z)-β-chlorostyrene 4604-28-8 C8H7Cl 138.597 氯乙烯基苯 1-(2-chlorovinyl)benzene 622-25-3 C8H7Cl 138.597 甲基苯乙烯 1-propenylbenzene 873-66-5 C9H10 118.178 顺-β-甲基苯乙烯 cis-1-phenyl-1-propylene 766-90-5 C9H10 118.178 1-丙烯基苯 1-phenylpropene 637-50-3 C9H10 118.178 —— phenylketene 3496-32-0 C8H6O 118.135 —— (E)-styrene-β-d 6911-81-5 C8H8 105.144 β-溴苯乙烯 bromostyrene 103-64-0 C8H7Br 183.048 —— (Z)-β-bromostyrene 1335-06-4 C8H7Br 183.048 [(Z)-2-溴乙烯基]苯 [(E)-2-bromoethenyl]benzene 588-72-7 C8H7Br 183.048 3-甲基苯乙烯 3-methylstyrene 100-80-1 C9H10 118.178 反式-1,2-二苯乙烯 (E)-1,2-diphenyl-ethene 103-30-0 C14H12 180.249 二苯乙烯 stilbene 588-59-0 C14H12 180.249 顺式-二苯乙烯 cis-stilben 645-49-8 C14H12 180.249 —— buta-1,3-dien-1-ylbenzene 1515-78-2 C10H10 130.189 1-苯-1,3-丁二烯 (E)-1-Phenyl-1,3-butadiene 16939-57-4 C10H10 130.189 —— (E)-β-(methylthio)styrene 15436-06-3 C9H10S 150.244 2-甲基苯乙烯 1-methyl-2-vinyl-benzene 611-15-4 C9H10 118.178 (2,2-二氯乙烯基)苯 (2,2-dichlorovinyl)benzene 698-88-4 C8H6Cl2 173.042 —— 1-(3-phenyl-1,2-propadienyl)benzene —— C15H12 192.26 (Z)-1-丁烯基苯 (Z)-but-1-en-1-ylbenzene 1560-09-4 C10H12 132.205 反式-1-苯基-1-丁烯 (E)-1-phenyl-1-butene 1005-64-7 C10H12 132.205 (2,2-二氟乙烯基)苯 2',2'-difluorostyrene 405-42-5 C8H6F2 140.132 —— 1-phenylbut-1-ene 824-90-8 C10H12 132.205 —— cinnamylamine 4360-51-4 C9H11N 133.193 反式肉桂醛 (E)-3-phenylpropenal 14371-10-9 C9H8O 132.162 肉桂醛 3-phenyl-propenal 104-55-2 C9H8O 132.162 (肉)桂腈 cinnamonitrile 4360-47-8 C9H7N 129.161 肉桂腈 cinnamic nitrile 1885-38-7 C9H7N 129.161 3-苯基丙-2-烯腈 (Z)-cinnamonitrile 24840-05-9 C9H7N 129.161 2-甲基-1-苯基丙烯 (2-methyl-1-propenyl)-benzene 768-49-0 C10H12 132.205 苯乙烯-β,β-d2 styrene-d2 934-85-0 C8H8 106.136 (Z)-肉桂醇 (Z)-cinnamyl alcohol 4510-34-3 C9H10O 134.178 3-苯基丙-2-烯-1-醇 (2E)-3-phenyl-2-propen-1-ol 4407-36-7 C9H10O 134.178 肉桂醇 3-Phenylpropenol 104-54-1 C9H10O 134.178 肉桂基氯 cinnamyl chloride 2687-12-9 C9H9Cl 152.623 肉桂基氯 Cinnamyl chloride 21087-29-6 C9H9Cl 152.623 4-氟苯乙烯 4-Fluorostyrene 405-99-2 C8H7F 122.142 4-乙烯苯胺 4-Vinylaniline 1520-21-4 C8H9N 119.166 —— 4-Deutero-styrol 10473-16-2 C8H8 105.144 —— (1E)-1,4-pentadienylbenzene 55666-17-6 C11H12 144.216 —— 1-phenyl-1-iodoethylene 51246-20-9 C8H7I 230.048 1,2-二乙烯基苯 1,2-divinylbenzene 91-14-5 C10H10 130.189 1,4-二苯基-1,3丁二烯 1,4-Diphenyl-1E,3E-butadiene 538-81-8 C16H14 206.287 1-氟乙烯基苯 α-fluorostyrene 696-31-1 C8H7F 122.142 (1-氯乙烯基)苯 1-chlorostyrene 618-34-8 C8H7Cl 138.597 1,4-二苯基1,3-丁二烯 1,4-diphenylbutadiene 886-65-7 C16H14 206.287 4-羟基苯乙烯 4-Vinylphenol 2628-17-3 C8H8O 120.151 1-[(1E,3Z)-4-苯基-1,3-丁二烯基]苯 (1Z,3E)-1,4-diphenylbuta-1,3-diene 5808-05-9 C16H14 206.287 对溴苯乙烯 1-bromo-4-ethenyl-benzene 2039-82-9 C8H7Br 183.048 甲苯 toluene 108-88-3 C7H8 92.1405 2-苯基-1-丙烯 isopropenylbenzene 98-83-9 C9H10 118.178 alpha- 溴苯乙烯 1-bromovinylbenzene 98-81-7 C8H7Br 183.048 —— 4-methylstilbene 4714-21-0 C15H14 194.276 1-甲基-4-((e)-苯乙烯)-苯 E-1-methyl-4-styryl-benzene 1860-17-9 C15H14 194.276 —— (Z)-4-methylstilbene 1657-45-0 C15H14 194.276 苯乙烯-Alpha-d1 α-deuteriostyrene 1193-80-2 C8H8 105.144 —— 3-methyl-1-phenyl-1-butene —— C11H14 146.232 —— (E)-(3-methylbut-1-en-1-yl)benzene —— C11H14 146.232 苯,1,3-戊二烯基- 1-phenylpenta-1,3-diene 1608-27-1 C11H12 144.216 4-氯甲基苯乙烯 4-Vinylbenzyl chloride 1592-20-7 C9H9Cl 152.623 —— (Z)-3-methyl-1-phenylbut-1-ene 15325-56-1 C11H14 146.232 —— (1E,3E)-1-phenyl-1,3-pentadiene 3909-96-4 C11H12 144.216 1,5-二苯基-1,4-戊二烯 (E,E)-1,5-diphenyl-1,4-pentadiene 26057-47-6 C17H16 220.314 —— bis(2-phenylethenyl) sulfide 2848-29-5 C16H14S 238.353 反,反-1,4-均二苯乙烯 1,4-Distyrylbenzene 1608-41-9 C22H18 282.385 —— 1,4-distyrylbenzene 1608-30-6 C22H18 282.385 —— 4,4'-distyrylstilbene 64496-23-7 C30H24 384.521 —— (E)-(3-methoxyprop-1-en-1-yl)benzene 22688-03-5 C10H12O 148.205 —— (cis,cis)-1,4-distyrylbenzene 1608-40-8 C22H18 282.385 —— (E)-1-styryl-4-vinylbenzene —— C16H14 206.287 —— 4,4'-Distyryl-stilben 21850-31-7 C30H24 384.521 —— (E)-(2-azidovinyl)benzene 18756-03-1 C8H7N3 145.164 —— (Z)-2-phenylethenyl azide 20544-50-7 C8H7N3 145.164 —— (3E)-4-phenyl-3-buten-1-ol 770-36-5 C10H12O 148.205 —— β-azidostyrene 16722-99-9 C8H7N3 145.164 —— (E)-ethoxystyrene 20565-86-0 C10H12O 148.205 (E)-4-苯基-3-丁烯腈 (E)-4-phenyl-3-butenenitrile 20068-10-4 C10H9N 143.188 [(1E)-4-溴-1-丁烯-1-基]苯 (E)-(4-bromobut-1-en-1-yl)benzene 7515-41-5 C10H11Br 211.101 —— 4-phenylbut-3-enenitrile 16170-45-9 C10H9N 143.188 1,6-二苯基-1,3,5-己三烯 1,6-diphenyl-hexa-1,3,5-triene 1720-32-7 C18H16 232.325 —— (E)-1-phenyl-1,5-hexadiene 56644-04-3 C12H14 158.243 —— ((1E,4E)-hexa-1,4-dien-1-yl)benzene 21502-38-5 C12H14 158.243 肉桂基甲基硫醚 Cinnamyl Methyl Sulfide 10276-15-0 C10H12S 164.271 —— dichloro(styryl)phosphine 17391-53-6 C8H7Cl2P 205.023 —— β-styryldichlorophosphine 33818-05-2 C8H7Cl2P 205.023 —— β-tert-butylstyrene 25338-51-6 C12H16 160.259 —— (E)-1-tert-butyl-2-phenylethene 3846-66-0 C12H16 160.259 —— 1,6-diphenyl-hexa-1,5-diene 4439-45-6 C18H18 234.341 —— (1E,5E)-1,6-diphenyl-1,5-hexadiene 58463-02-8 C18H18 234.341 —— (E)-1-phenyl-1-hexene 6111-82-6 C12H16 160.259 - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:The Mn-catalyzed paired electrochemical facile oxychlorination of styrenes via the oxygen reduction reaction摘要:报告了一种通过锰催化剂以可控模式生成氯自由基的电化学方法,并使用廉价的MgCl2作为氯源。DOI:10.1039/c9cc06746a
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:A general and efficient aldehyde decarbonylation reaction by using a palladium catalyst摘要:通过使用Pd(OAc)2,开发了一种简便的醛脱羰反应。多种底物可进行脱羰处理,无需使用任何外源配体或CO清除剂。DOI:10.1039/c2cc31144e
-
作为试剂:描述:1,1-二苯乙烯 、 O,O-二甲基硫代磷酸 在 苯乙烯 、 ammonium peroxydisulfate 、 1-methyl-2(1H)-quinoxalinone 作用下, 以 水 、 二甲基亚砜 为溶剂, 以17%的产率得到参考文献:名称:烯烃的多组分杂芳基硫代磷酸化用于获得 β-硫代磷酸化喹喔啉酮摘要:在此,我们提出了 (NH4)2S2O8 介导的芳基烯烃与喹喔啉酮和 P(O)SH 化合物的双官能化反应。该方法能够以 37-79% 的产率合成各种含硫代磷酸酯的喹喔啉-2(1H)-酮衍生物(46 个实例)。该反应与一系列官能团兼容,并且很容易适应大规模合成。初步研究表明硫代磷酸酯自由基参与了这些转化。DOI:10.1002/adsc.202301517
文献信息
-
Highly Regio- and Enantioselective Alkoxycarbonylative Amination of Terminal Allenes Catalyzed by a Spiroketal-Based Diphosphine/Pd(II) Complex作者:Jiawang Liu、Zhaobin Han、Xiaoming Wang、Zheng Wang、Kuiling DingDOI:10.1021/jacs.5b07764日期:2015.12.16An enantioselective alkoxycarbonylation-amination cascade process of terminal allenes with CO, methanol, and arylamines has been developed. It proceeds under mild conditions (room temperature, ambient pressure CO) via oxidative Pd(II) catalysis using an aromatic spiroketal-based diphosphine (SKP) as a chiral ligand and a Cu(II) salt as an oxidant and affords a wide range of α-methylene-β-arylamino
-
2‐Pyridyl Sulfoxide: A Versatile and Removable Directing Group for the Pd <sup>II</sup> ‐Catalyzed Direct CH Olefination of Arenes作者:Alfonso García‐Rubia、M. Ángeles Fernández‐Ibáñez、Ramón Gómez Arrayás、Juan Carlos CarreteroDOI:10.1002/chem.201003633日期:2011.3.21Removable and versatile: The 2‐pyridylsulfinyl group has proved to be an efficient directing group in the PdII‐catalyzed aryl ortho CH olefination. This catalyst system enables the sequential double olefination to give asymmetrically di‐ortho‐functionalized arenes. The sulfinyl directing group can be easily cleaved, providing access to 1,3‐disubstituted arenes, or transformed into a thiol group.
-
Alternate Heme Ligation Steers Activity and Selectivity in Engineered Cytochrome P450-Catalyzed Carbene-Transfer Reactions作者:Kai Chen、Shuo-Qing Zhang、Oliver F. Brandenberg、Xin Hong、Frances H. ArnoldDOI:10.1021/jacs.8b09613日期:2018.12.5platform of engineered cytochrome P450 enzymes to carry out carbene-transfer reactions using a lactone-based carbene precursor. By simply altering the heme-ligating residue, we obtained two enzymes that catalyze olefin cyclopropanation (Ser) or S-H bond insertion (Cys). Both enzymes exhibit high catalytic efficiency and stereoselectivity, thus enabling facile access to structurally diverse spiro[2.4]lactones
-
Electrochemical sulfonylation of thiols with sulfonyl hydrazides: a metal- and oxidant-free protocol for the synthesis of thiosulfonates作者:Zu-Yu Mo、Toreshettahally R. Swaroop、Wei Tong、Yu-Zhen Zhang、Hai-Tao Tang、Ying-Ming Pan、Hong-Bin Sun、Zhen-Feng ChenDOI:10.1039/c8gc02143k日期:——
We have developed a new metal- and oxidant-free method for the synthesis of anticancer thiosulfonates
via sulfonylation of thiols. -
Direct Dearomatization of Pyridines via an Energy-Transfer-Catalyzed Intramolecular [4+2] Cycloaddition作者:Jiajia Ma、Felix Strieth-Kalthoff、Toryn Dalton、Matthias Freitag、J. Luca Schwarz、Klaus Bergander、Constantin Daniliuc、Frank GloriusDOI:10.1016/j.chempr.2019.10.016日期:2019.11The catalytic dearomatization of pyridines, accessing medicinally relevant N-heterocycles, is of high interest. Currently direct, dearomative strategies rely generally on reduction or nucleophilic addition, thus limiting the architecture of the dearomatized products to a six-membered ring. We herein introduce a catalytic, dearomative cycloaddition reaction with pyridines using photoinduced energy transfer吡啶的催化脱芳香化作用,获得医学上相关的氮-杂环,引起了人们的极大兴趣。当前直接的脱芳香化策略通常依赖于还原或亲核加成,从而将脱芳香化产物的结构限制为六元环。我们在本文中介绍了使用光诱导的能量转移催化作用与吡啶进行的催化脱芳香环加成反应,从而推进脱芳香化方法,并增加了吡啶脱芳香化产物的拓扑结构。这种空前的方法具有高收率,广泛的底物范围(44个例子),出色的官能团耐受性和简便的可扩展性。此外,采用了可回收且可持续的聚合物固定化光催化剂。计算和实验研究支持一种机制,其中肉桂基部分通过可见光介导的能量转移催化被提升为其相应的激发三线态,然后向吡啶进行区域选择性和脱芳香性的[4 + 2]环加成。这项工作证明了可见光催化对实现热挑战性有机转化的贡献。
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
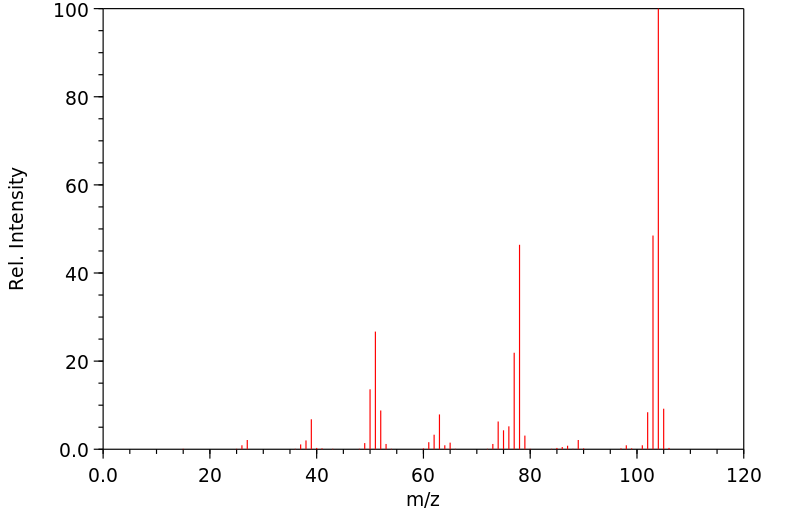
质谱MS
-
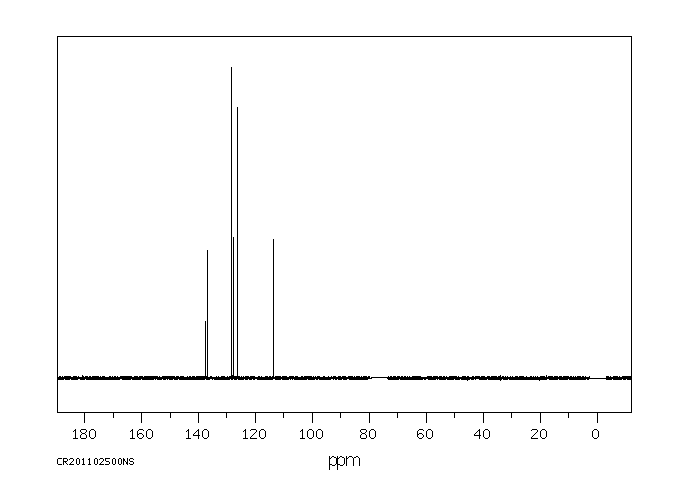
碳谱13CNMR
-
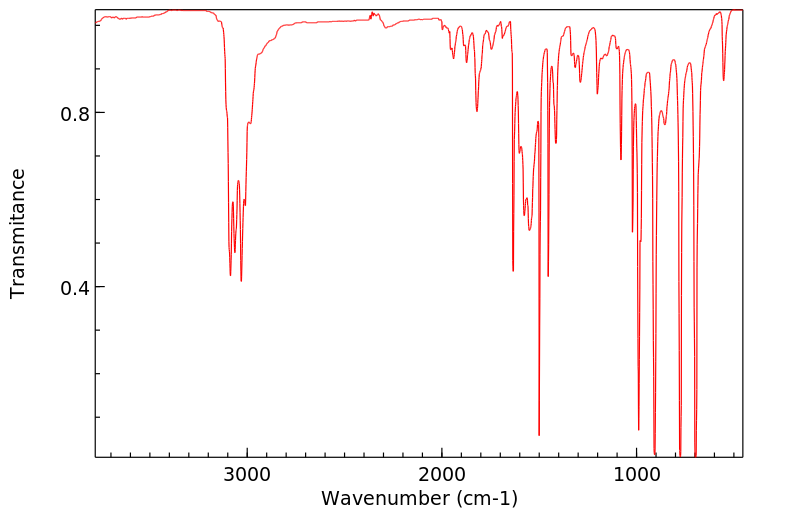
红外IR
-
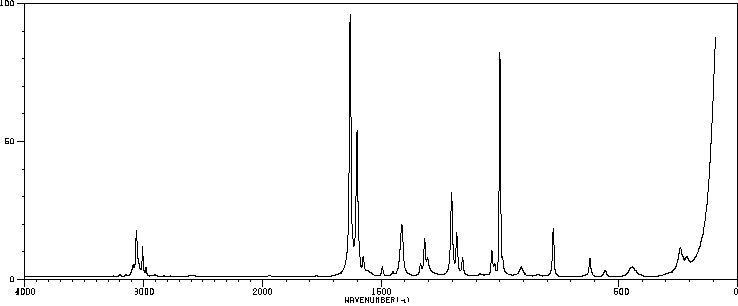
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(βS)-β-氨基-4-(4-羟基苯氧基)-3,5-二碘苯甲丙醇
(S,S)-邻甲苯基-DIPAMP
(S)-(-)-7'-〔4(S)-(苄基)恶唑-2-基]-7-二(3,5-二-叔丁基苯基)膦基-2,2',3,3'-四氢-1,1-螺二氢茚
(S)-盐酸沙丁胺醇
(S)-3-(叔丁基)-4-(2,6-二甲氧基苯基)-2,3-二氢苯并[d][1,3]氧磷杂环戊二烯
(S)-2,2'-双[双(3,5-三氟甲基苯基)膦基]-4,4',6,6'-四甲氧基联苯
(S)-1-[3,5-双(三氟甲基)苯基]-3-[1-(二甲基氨基)-3-甲基丁烷-2-基]硫脲
(R)富马酸托特罗定
(R)-(-)-盐酸尼古地平
(R)-(-)-4,12-双(二苯基膦基)[2.2]对环芳烷(1,5环辛二烯)铑(I)四氟硼酸盐
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[((6-甲基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[(4-叔丁基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[(3-甲基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-4,7-双(3,5-二-叔丁基苯基)膦基-7“-[(吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2”,3,3'-四氢1,1'-螺二茚满
(R)-3-(叔丁基)-4-(2,6-二苯氧基苯基)-2,3-二氢苯并[d][1,3]氧杂磷杂环戊烯
(R)-2-[((二苯基膦基)甲基]吡咯烷
(R)-1-[3,5-双(三氟甲基)苯基]-3-[1-(二甲基氨基)-3-甲基丁烷-2-基]硫脲
(N-(4-甲氧基苯基)-N-甲基-3-(1-哌啶基)丙-2-烯酰胺)
(5-溴-2-羟基苯基)-4-氯苯甲酮
(5-溴-2-氯苯基)(4-羟基苯基)甲酮
(5-氧代-3-苯基-2,5-二氢-1,2,3,4-oxatriazol-3-鎓)
(4S,5R)-4-甲基-5-苯基-1,2,3-氧代噻唑烷-2,2-二氧化物-3-羧酸叔丁酯
(4S,4''S)-2,2''-亚环戊基双[4,5-二氢-4-(苯甲基)恶唑]
(4-溴苯基)-[2-氟-4-[6-[甲基(丙-2-烯基)氨基]己氧基]苯基]甲酮
(4-丁氧基苯甲基)三苯基溴化磷
(3aR,8aR)-(-)-4,4,8,8-四(3,5-二甲基苯基)四氢-2,2-二甲基-6-苯基-1,3-二氧戊环[4,5-e]二恶唑磷
(3aR,6aS)-5-氧代六氢环戊基[c]吡咯-2(1H)-羧酸酯
(2Z)-3-[[(4-氯苯基)氨基]-2-氰基丙烯酸乙酯
(2S,3S,5S)-5-(叔丁氧基甲酰氨基)-2-(N-5-噻唑基-甲氧羰基)氨基-1,6-二苯基-3-羟基己烷
(2S,2''S,3S,3''S)-3,3''-二叔丁基-4,4''-双(2,6-二甲氧基苯基)-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-2,2''-联苯并[d][1,3]氧杂磷杂戊环
(2S)-(-)-2-{[[[[3,5-双(氟代甲基)苯基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基}-N-(二苯基甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-[[[[[((1S,2S)-2-氨基环己基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基]-N-(二苯甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-[[[[[[((1R,2R)-2-氨基环己基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基]-N-(二苯甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2-硝基苯基)磷酸三酰胺
(2,6-二氯苯基)乙酰氯
(2,3-二甲氧基-5-甲基苯基)硼酸
(1S,2S,3S,5S)-5-叠氮基-3-(苯基甲氧基)-2-[(苯基甲氧基)甲基]环戊醇
(1S,2S,3R,5R)-2-(苄氧基)甲基-6-氧杂双环[3.1.0]己-3-醇
(1-(4-氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(3-溴苯基)环丁基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2-氯苯基)环丁基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2-氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2,6-二氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(-)-去甲基西布曲明
龙蒿油
龙胆酸钠
龙胆酸叔丁酯
龙胆酸
龙胆紫-d6
龙胆紫