环己烷 | 110-82-7
中文名称
环己烷
中文别名
六氢代苯;六氢化苯
英文名称
cyclohexane
英文别名
c-hexane
CAS
110-82-7
化学式
C6H12
mdl
MFCD00003814
分子量
84.1613
InChiKey
XDTMQSROBMDMFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:4-7 °C (lit.)
-
沸点:80.7 °C (lit.)
-
密度:0.779 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
-
蒸气密度:2.9 (vs air)
-
闪点:-1 °F
-
溶解度:可与乙醇混溶(加热)
-
最大波长(λmax):λ: 210 nm Amax: ≤1.00λ: 220 nm Amax: ≤0.50λ: 230 nm Amax: ≤0.20λ: 235 nm Amax: ≤0.10λ: 240 nm Amax: ≤0.08λ: 250 nm Amax: ≤0.03λ: 255 nm Amax: ≤0.01
-
介电常数:2.0(20℃)
-
暴露限值:TLV-TWA 300 ppm (~1050 mg/m3) (ACGIH, OSHA, and NIOSH); IDLH 10,000 ppm (NIOSH).
-
LogP:3.44 at 20℃
-
物理描述:Cyclohexane appears as a clear colorless liquid with a petroleum-like odor. Used to make nylon, as a solvent, paint remover, and to make other chemicals. Flash point -4°F. Density 6.5 lb / gal (less than water) and insoluble in water. Vapors heavier than air.
-
颜色/状态:Colorless mobile liquid
-
气味:Solvent odor; pungent when impure
-
蒸汽密度:2.9 (NTP, 1992) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:96.9 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
亨利常数:0.15 atm-m3/mole
-
大气OH速率常数:7.49e-12 cm3/molecule*sec
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
自燃温度:473 °F (245 °C)
-
分解:When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and fumes.
-
粘度:0.977 mPa.s at 20 °C
-
燃烧热:-3919.6 kJ/mole at 25 °C
-
汽化热:33.059 kJ/mol at 25 °C; 29.977 kJ/mol at the boiling point
-
表面张力:Liquid surface tension: 24.98mN/m at 20 °C
-
电离电位:9.88 eV
-
气味阈值:The reported odor threshold is approximately 25 ppm.
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.42662 at 20 °C/D
-
相对蒸发率:Evaporation time (Ether = 1): 2.6
-
保留指数:655.8;647.56;648.22;654.6;665;648.9;651.2;651.24;651;651.09;651.14;651;668;662;662;656.4;657.3;660.8;647.36;650.41;652.19;662;650;660.1;661.2;661.9;662.3;662.9;664.1;665.7;681;676;656.8;662.2;663.35;668;657.8;649;650;672;688.3;697.9;658;655.7;649;660.6;660.6;665.6;665.6;663;664;658;663;668;676;671.1;674;658.7;660.9;663.2;665.5;673.6;658;685;656;658;660;663;665;668;663.7;664.2;675;661;669;683;650;661;661;661;661;662;657;657.2;659.1;659.6;661.3;662.1;663.6;664.7;666.1;667.4;668.8;670.3;669.2;663;668;674;662;664;667;667;676;675;676;658;651;666;663;668;673;680;685;661;662.9;653.9;677;657.7;658.1;663.2;700;654.7;664;662;657;666;648.95;659.9;658;649.4;660.5;657;660;666;666;654;649;663.3;649;664;650;658;664;666;663;677;645;661;669;675;661;665;664;651;659;675;675
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):3.4
-
重原子数:6
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:1.0
-
拓扑面积:0
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:0
ADMET
代谢
四种已知的或怀疑的环己烷代谢物(环己醇、环己酮、1,4-环己二醇和1,4-环己二酮)也进行了对肾脏影响的研究。这些化合物以每日0.5克/公斤的剂量给药(每周5次腹腔注射,持续两周)。只有环己醇增加了β-2-微球蛋白,这表明这种代谢物是环己烷对肾脏影响的负责物质。
Four known or suspected metabolites of cyclohexane (cyclohexanol, cyclohexanone, 1,4-cyclohexanediol and 1,4-cyclohexanedione) were also studied for kidney effects. These compounds were administered at a daily dose of 0.5 g/kg (5 I.P. injections per week for two weeks). Only cyclohexanol increased beta-2-microglobulin which suggests that this metabolite is responsible for the kidney effects of cyclohexane.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
环己烷的处置和代谢已经在三种物种中进行了研究;大鼠、兔和人类。现有数据表明,环己烷可以通过口服和吸入途径被吸收,但通过皮肤途径没有足够的数据。在检查的组织中没有明显的生物滞留证据。在暴露于环己烷2周的大鼠大脑中没有发现环己烷。已知环己烷会经历氧化代谢,产生环己醇(主要代谢物)、环己酮,以及可能的其他氧化产物(1,2-或1,4-二羟基环己烷及其相应的酮类似物)。醇类产物可以形成第二阶段结合物(硫酸盐和葡萄糖苷酸)。
The disposition and metabolism of cyclohexane have been investigated in three species; rat, rabbit and man. The available data indicate that cyclohexane can be absorbed via the oral and inhalation routes but no adequate data exist via the dermal route. There is no clear evidence of bioretention in the tissue examined. No cyclohexane was found in the brain of rats exposed to cyclohexane for 2 weeks. Cyclohexane is known to undergo oxidative metabolism to yield cyclohexanol (major metabolite), cyclohexanone, and possibly other oxidative products (1,2- or 1,4-dihydroxycyclohexane and its corresponding ketone analogs). The alcohol products can form phase 2 conjugates (sulfates and glucuronide).
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
环己烷(CH)和环己醇(CH-ol)是重要的溶剂和化学中间体,它们的代谢和毒物动力学在志愿者中进行了研究,这些志愿者在浓度为1010和236 mg/cu m的环己烷和环己醇中分别进行了8小时的吸入暴露(职业暴露限值:CH,1050 mg/cu m;CH-ol,200 mg/cu m)。吸收的母化合物剂量中,尿液中环己醇和1,2-和1,4-环己二醇(CH-diol)的产率分别为环己烷暴露后的0.5%、23.4%和11.3%,环己醇暴露后的1.1%、19.1%和8.4%,这是通过涉及水解葡萄糖苷酸结合物的气相色谱法确定的。环己烷和环己醇的代谢模式与实验室先前研究的环己酮(CH-one)非常相似。对于所有三种化合物,环己醇的峰值排泄发生在暴露期结束时,之后迅速下降。1,2-和1,4-CH-diol的排泄曲线在暴露后0-6小时内达到最大值,随后的消除半衰期为14-18小时。环己烷化合物从生物体中消除的限速步骤是CH-diol的肾清除率...
The metabolism and toxicokinetics of cyclohexane (CH) and cyclohexanol (CH-ol), important solvents and chemical intermediates, were studied in volunteers after 8-hr periods of inhalation exposure at concentrations of 1010 and 236 mg/cu m, respectively (occupational exposure limits: CH, 1050 mg/cu m; CH-ol, 200 mg/cu m)). Of the dose of absorbed parent compounds, the yields of urinary CH-ol and 1,2- and 1,4-cyclohexanediol (CH-diol) were 0.5%, 23.4%, and 11.3%, respectively, after exposure to CH and 1.1%, 19.1%, and 8.4%, respectively, after exposure to CH-ol as determined by a gas chromatography method involving hydrolysis of glucuronide conjugates. The metabolic patterns of CH and CH-ol were very similar to that of cyclohexanone (CH-one) studied in the laboratory previously. For all three compounds, peak excretion of CH-ol occurred at the end of the exposure period, after which it decayed rapidly. Excretion curves of 1,2- and 1,4-CH-diol reached maximal values within 0-6 hr postexposure, with subsequent elimination half-lives being 14-18 hr. The rate-limiting step in the elimination of CH compounds from the organism is renal clearance of CH-diols...
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
These compounds /including cyclohexane/ ... are metabolized mostly into cyclohexanol glucuronide.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
挥发性烃主要通过肺部吸收,也可能在吞咽后通过吸吮进入体内。
Volatile hydrocarbons are absorbed mainly through the lungs, and may also enter the body after ingestion via aspiration. (A600)
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
环己烷是一种无色、高度易燃的液体,在石油中以0.5-1.0%的浓度自然存在。它具有刺激性的石油样气味,被用作清漆、树脂和合成橡胶的有机溶剂;油漆和清漆去除剂;提取精油;制造野营炉的固体燃料;在杀菌剂配方中;在甾体类药物的再结晶中;以及在分析化学中用于分子量测定。它也是制造己二酸、苯、环己基氯、硝基环己烷、环己醇和环己酮的化学中间体。在美国,环己烷目前没有注册为农药使用,但批准的农药用途可能会定期更改,因此必须咨询联邦、州和地方当局以获取当前批准的用途。从一般人群接触环己烷的研究中发现,由于五位母亲居住在化学制造厂或工业用户设施附近,她们暴露于环境污染物,其中八位母亲中有五位母亲的乳汁中含有了环己烷(浓度未确定)。人类接触和毒性:现有数据表明,环己烷可以通过口服和吸入途径吸收,但通过皮肤途径没有足够的数据。过度接触环己烷的潜在症状包括眼睛、皮肤和呼吸系统的刺激;嗜睡;皮炎;麻醉和昏迷,尽管环己烷通常具有较低的急性毒性。在吸入86或860 mg/m³环己烷4小时的人类暴露研究中,没有显著的治疗相关效果。职业暴露于5至211 ppm的环己烷,平均为1.2年,对周围神经系统没有不利影响。在人类中没有报告全身性中毒。环己烷已知会经过氧化代谢产生环己醇(主要代谢物)、环己酮,以及可能的其他氧化产物(1,2-或1,4-二羟基环己烷及其相应的酮类似物)。动物研究:高蒸汽浓度在兔子上产生了惊厥。兔子口服毒性剂量导致严重腹泻、循环衰竭和死亡,没有明显的中枢神经系统抑制或麻醉。尸检显示普遍的血管损伤,但对血细胞生成没有影响。大鼠和小鼠暴露于0、500、2000或7000 ppm的环己烷蒸汽,每天6小时,每周5天,共14周。在暴露期间,暴露于7000 ppm的小鼠表现出毒性的临床迹象,包括过度活跃、转圈、跳跃/跳跃、过度梳理、后腿踢动、站立在前腿上,偶尔翻转行为。在另一项研究中,暴露于7000 ppm的雄性和雌性小鼠在循环红细胞质量(红细胞、血红蛋白、血细胞比容)和血浆蛋白浓度(仅限雄性)的测量中略有增加。暴露于7000 ppm的雄性大鼠和雄性和雌性小鼠的相对肝脏重量显著增加,7000 ppm的雄性小鼠在暴露期结束时的绝对肝脏重量也显著增加。在第三项研究中,雌性大鼠每周5天,连续2周腹膜内给药0.375、0.75或1.5 g/kg的环己烷。1.5 g/kg的高剂量环己烷导致肾脏近端小管功能障碍,导致β-2-微球蛋白增加。β-2-微球蛋白的增加归因于代谢物环己醇。在测试环己烷对繁殖和发育的影响时,暴露于7000 ppm的P1和F1雌性的平均体重、总体平均体重增加和总体平均食物效率显著降低。暴露于2000 ppm或7000 ppm环己烷的成年大鼠在暴露期间的实验室内对声音刺激的反应减弱或没有反应。7000 ppm的F1和F2幼崽从哺乳第7天开始,在整个25天哺乳期的剩余时间内平均体重显著降低。在多达5种Salmonella typhimurium菌株(TA1535、TA1537、TA97、TA98和TA100)有或没有代谢激活的情况下,环己烷在剂量为0.01、0.033、0.10、0.33、1.0、3.3和10 mg/板的测试中呈阴性。生态毒性研究:环己烷抑制了小球藻的生长11-13天,但延长了指数生长期,并将生长产量提高了2.5倍,与对照组相比。在24小时和96小时暴露于包括环己烷在内的七种环脂肪烃后,测定了条纹鲈及其主要食物生物——湾虾,Crangon franciscorum的急性毒性。条纹鲈和湾虾的96小时LC50分别为3.2至9.3 uL/L和1.0至6.2 uL/L。
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: Cyclohexane is a colorless, highly flammable liquid occurring naturally in petroleum at concentrations of 0.5-1.0%. It has a pungent petroleum-like odor and is used as an organic solvent for lacquers, resins, and synthetic rubber; paint and varnish remover; extraction of essential oils; manufacturing of solid fuel for camp stoves; in fungicidal formulations; in recrystallization of steroids; and in analytical chemistry for molecular weight determinations. It is also a chemical intermediate in the manufacturing of adipic acid, benzene, cyclohexyl chloride, nitrocyclohexane, cyclohexanol and cyclohexanone. Not registered for current pesticide use in the U.S., but approved pesticide uses may change periodically and so federal, state and local authorities must be consulted for currently approved uses. Studies from the exposure of the general population to cyclohexane revealed that human milk from five of eight mothers contained cyclohexane (concentrations not determined) from the mothers' exposure to environmental pollutants since they resided near chemical manufacturing plants or industrial user facilities. HUMAN EXPOSURE AND TOXICITY: The available data indicate that cyclohexane can be absorbed via oral and inhalation routes but no adequate data exist via the dermal route. Potential symptoms of overexposure to cyclohexane are irritation of eyes, skin and respiratory system; drowsiness; dermatitis; narcosis and coma although cyclohexane generally has low acute toxicity. In humans exposed via inhalation for 4 hours to 86 or 860 mg/cu m cyclohexane, there were no significant treatment-related effects. Occupational exposure to 5 to 211 ppm cyclohexane for a median of 1.2 years, had no adverse effects on the peripheral nervous system. There have been no systemic poisonings reported in man. Cyclohexane is known to undergo oxidative metabolism to yield cyclohexanol (major metabolite), cyclohexanone, and possibly other oxidative products (1,2- or 1,4-dihydroxycyclohexane and its corresponding ketone analogs). ANIMAL STUDIES: High vapor concentrations have produced convulsions in rabbits. Toxic oral doses in rabbits led to severe diarrhea, circulatory collapse and death, without prominent central nervous depression or anesthesia. Autopsy revealed generalized vascular damage but no effects on blood formation. Rats and mice, were exposed to 0, 500, 2000, or 7000 ppm of cyclohexane vapor 6 hr/day, 5 days/week for 14 weeks. During exposure sessions, mice exposed to 7000 ppm exhibited clinical signs of toxicity which included hyperactivity, circling, jumping/hopping, excessive grooming, kicking of rear legs, standing on front legs, and occasional flipping behavior. In another study, male and female mice exposed to 7000 ppm had slight increases in measures of circulating erythrocyte mass (red blood cells, hemoglobin, hematocrit) and plasma protein concentration (males only). Male rats and male and female mice exposed to 7000 ppm had significantly increased relative liver weights, and 7000 ppm male mice also had significantly increased absolute liver weights at the end of the exposure period. In the third study, female rats were administered cyclohexane intraperitoneally at a dose of 0.375, 0.75, or 1.5 g/kg, 5 days a week for 2 weeks. The high dose of 1.5 g/kg of cyclohexane caused a proximal tubular dysfunction of the kidney which resulted in an increase in beta-2-microglobulin. The increase in beta-2-microglobulin was attributed to the metabolite cyclohexanol. When testing the effect of cyclohexane on reproduction and development, there were statistically significant reductions in mean body weight, overall mean body weight gain, and overall mean food efficiency for P1 and F1 females exposed to 7000 ppm. Adult rats exposed to 2000 ppm or 7000 ppm cyclohexane exhibited diminished response or no response to a sound stimulus while in the chambers during exposure. Mean pup weight was statistically significantly reduced from lactation day 7 throughout the remainder of the 25-day lactation period for both F1 and F2 7000 ppm litters. Cyclohexane was negative for mutagenicity at doses of 0.01, 0.033, 0.10, 0.33, 1.0, 3.3, and 10 mg/plate in as many as 5 Salmonella typhimurium strains (TA1535, TA1537, TA97, TA98, and TA100) with or without metabolic activation. ECOTOXICITY STUDIES: Cyclohexane inhibited growth of Chlorella for 11-13 days, but prolonged the exponential growth phase and increased the growth yield 2.5 fold compared with the control. Acute toxicities after 24 and 96 hr exposures to seven alicyclic hexanes including cyclohexane were determined for striped bass and one of their major food organisms, the bay shrimp, Crangon franciscorum. The 96 hr LC50 for striped bass and bay shrimp ranged from 3.2 to 9.3 uL/L and from 1.0 to 6.2 uL/L, respectively.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
石油馏分是中枢神经系统抑制剂,会导致肺部损伤。
Petroleum distillates are central nervous system depressants and cause pulmonary damage. (A600)
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
环己烷存在于汽油中,对人类可能具有致癌性(2B组)。
Cyclohexane is found in gasoline, which is possibly carcinogenic to humans (Group 2B). (L135)
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
石油馏分是有害的吸入物质,可能导致肺部损伤、中枢神经系统抑制以及心脏效果,如心律不齐。它们还可能影响血液、免疫系统、肝脏和肾脏。(A600,L1297)
Petroleum distillates are aspiration hazards and may cause pulmonary damage, central nervous system depression, and cardiac effects such as cardiac arrhythmias. They may also affect the blood, immune system, liver, and kidney. (A600, L1297)
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
该物质可以通过吸入其蒸汽和摄入进入人体。
The substance can be absorbed into the body by inhalation of its vapour and by ingestion.
来源:ILO-WHO International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs)
吸收、分配和排泄
Studies from the exposure of the general population to cyclohexane revealed that human milk from five of eight mothers contained cyclohexane (concentrations not determined). /It was/ suggested that the cyclohexane in the milk resulted from the mothers' exposure to environmental pollutants since they resided near chemical manufacturing plants or industrial user facilities.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
环己烷暴露并未影响大脑的新陈代谢、RNA、谷胱甘肽以及谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶的活性。然而,随着环己烷剂量的增加,大脑偶氮还原酶活性显著降低,并且在恢复期之后仍然远低于对照组水平。已知混合功能氧化酶系统的激活能够抑制偶氮还原。结果表明,尽管与脂肪组织相比,大脑中增加的血液循环有助于环己烷从大脑中排出,但激活肝脏混合功能氧化酶系统是整体降低体内环己烷浓度的主要途径。
...Measures of brain metabolism, RNA, glutathione, and glutathione peroxidase activity were not affected by cyclohexane exposure. However, the cyclohexane dose increased, brain azoreductase activity decreased significantly and was still well below control levels after a recovery period. Activation of the mixed-function oxidase system has been found to inhibit azo reduction. /The results suggest/ that although increased blood circulation in the brain compared to fatty tissue enhances cyclohexane elimination from the brain, the activation of a liver mixed-function oxidase system is the primary vehicle for decreasing the cyclohexane concentration in the body as a whole.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
在大约72小时后,给成年雄性Fischer 344大鼠单次静脉注射10 mg/kg的(14)C-环己烷或单次口服200 mg/kg后,脂肪组织中的放射性浓度是血液中的16倍。在较高的口服剂量(1,000或2,000 mg/kg)下,脂肪组织与血液中放射性活性的比率大约为45。尽管脂肪组织中的放射性主要是由环己烷(79-84%)组成,但在肌肉、肝脏和皮肤中,只有2-18%的(14)C被确认为环己烷。环己烷、环己醇和环己酮都存在于所有组织中...
Seventy-two hours after a single intravenous dose of 10 mg/kg [(14)C]cyclohexane or a single oral dose of 200 mg/kg to adult male Fischer 344 rats, the concentration of radioactivity in adipose was 16 times greater than that in blood. At higher oral doses (1,000 or 2,000 mg/kg), the adipose tissue-to-blood ratio of radioactivity approximately 45. Although radioactivity in adipose tissues was primarily cyclohexane (79-84%), in muscle, liver and skin, only 2-18% of the (14)C was identified as cyclohexane. Cyclohexane, cyclohexanol, and cyclohexanone were present in all tissues...
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
环己烷消除主要有两条途径:(1) 未代谢的环己烷存在于呼出的气体中,(2) 氧化产物,例如自由态或结合态的环己醇,存在于尿液中。环己烷暴露的生物监测包括测量肺泡气样本中的环己烷或尿液中的环己醇(自由态或结合态)。
There are two major pathways in the elimination of cyclohexane: (1) cyclohexane (unmetabolized) is present in expired air, and (2) oxidative products e.g., cyclohexanol as free or bound, are present in the urine. Biomonitoring of cyclohexane exposure include the measurement of cyclohexane in alveolar air specimens or cyclohexanol (free or bound) in the urine.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
安全信息
-
职业暴露等级:A
-
职业暴露限值:TWA: 300 ppm (1050 mg/m3)
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:3
-
立即威胁生命和健康浓度:1,300 ppm [10% LEL]
-
危险品标志:F
-
安全说明:S16,S25,S33,S60,S61,S62,S9
-
危险类别码:R67,R38,R50/53,R11,R65
-
WGK Germany:2
-
海关编码:2902110000
-
危险品运输编号:UN 1145
-
危险类别:3
-
RTECS号:GU6300000
-
包装等级:II
-
危险标志:GHS02,GHS07,GHS08,GHS09
-
危险性描述:H225,H304,H315,H336,H410
-
危险性防范说明:P210,P301 + P310,P331,P370 + P378,P403 + P235
-
储存条件:储存时应注意以下事项: - 储存在阴凉、通风良好的库房中。 - 远离火源和热源,库温不宜超过29℃。 - 保持容器密封。 - 应与氧化剂分开存放,切忌混储。 - 使用防爆型照明和通风设施。 - 禁止使用易产生火花的机械设备和工具。 - 储存区应配备泄漏应急处理设备和合适的收容材料。
SDS
| 国标编号: | 31004 |
| CAS: | 110-82-7 |
| 中文名称: | 环己烷 |
| 英文名称: | cyclohexane;hexahydrobenzene |
| 别 名: | 六氢化苯 |
| 分子式: | C 6 H 12 ;CH 2 (CH 2 ) 4 CH 2 |
| 分子量: | 84.16 |
| 熔 点: | 6.5℃ 沸点:80.7℃ |
| 密 度: | 相对密度(水=1)0.78; |
| 蒸汽压: | -16.5℃ |
| 溶解性: | 不溶于水,溶于乙醇、乙醚、苯、丙酮等多数有机溶剂 |
| 稳定性: | 稳定 |
| 外观与性状: | 无色液体,有刺激性气味 |
| 危险标记: | 7(易燃液体) |
| 用 途: | 用作一般溶剂、色谱分析标准物质及用于有机合成 |
2.对环境的影响:
一、健康危害
侵入途径:吸入、食入、经皮吸收。
健康危害:对眼和上呼吸道有轻度刺激作用。持续吸入可引起头晕、恶心、倦睡和其它一些麻醉症状。液体污染皮肤可引起痒感。
二、毒理学资料及环境行为
毒性:属低毒类。有刺激和麻醉作用。
急性毒性:LD 50 12705mg/kg(大鼠经口)
刺激性:家兔经皮:1548mg(2天),间歇,皮肤刺激。
亚急性和慢性毒性:家兔分别吸入65g/m 3 ,6小时/天,2周;44g/m 3 ,6小时/天,2周;32g/m 3 ,6小时/天,5周,分别出现3/4,1/4,3/4死亡。表现有足爪节律性痉挛、麻醉、暂时轻瘫、流涎、结膜刺激等症状。
致突变性:DNA损伤:大肠杆菌10µmol/L。
危险特性:极易燃,其蒸气与空气可形成爆炸性混合物。遇明火、高热极易燃烧爆炸。与氧化剂接触发生强烈反应,甚至引起燃烧。在火场中,受热的容器有爆炸危险。其蒸气比空气重,能在较低处扩散到相当远的地方,遇明火会引着回燃。
燃烧(分解)产物:一氧化碳、二氧化碳。
3.现场应急监测方法:
气体检测管法
4.实验室监测方法:
气相色谱法《空气中有害物质的测定方法》(第二版),杭士平编
5.环境标准:
| 中国(TJ36-79) | 车间空气中有害物质的最高容许浓度 | 100mg/m 3 |
| 前苏联(1977) | 居民区大气中有害物最大允许浓度 | 1.4mg/m 3 (最大值、昼夜均值) |
| 前苏联(1975) | 水体中有害物质最高允许浓度 | 0.1mg/L |
| 前苏联(1975) | 污水排放标准 | 100mg/L |
| 嗅觉阈浓度 | 1.4mg/m 3 |
6.应急处理处置方法:
一、泄漏应急处理
迅速撤离泄漏污染区人员至安全区,并进行隔离,严格限制出入。切断火源。建议应急处理人员戴自给正压式呼吸器,穿消防防护服。尽可能切断泄漏源。防止进入下水道、排洪沟等限制性空间。小量泄漏:用活性炭或其它惰性材料吸收。也可以用不燃性分散剂制成的乳液刷洗,洗液稀释后放入废水系统。大量泄漏:构筑围堤或挖坑收容;用泡沫覆盖,降低蒸气灾害。用防爆泵转移至槽车或专用收集器内,回收或运至废物处理场所处置。
废弃物处置方法:用焚烧法。
二、防护措施
呼吸系统防护:一般不需要特殊防护,高浓度接触时可佩戴自吸过滤式防毒面具(半面罩)。
眼睛防护:空气中浓度超标时,戴安全防护眼镜。
身体防护:穿防静电工作服。
手防护:戴防苯耐油手套。
其它:工作现场严禁吸烟。避免长期反复接触。
三、急救措施
皮肤接触:脱去被污染的衣着,用肥皂水和清水彻底冲洗皮肤。
眼睛接触:提起眼睑,用流动清水或生理盐水冲洗。就医。
吸入:迅速脱离现场至空气新鲜处。保持呼吸道通畅。如呼吸困难,给输氧。如呼吸停止,立即进行人工呼吸。就医。
食入:饮足量温水,催吐,就医。
灭火方法:喷水冷却容器,可能的话将容器从火场移至空旷处。处在火场中的容器若已变色或从安全泄压装置中产生声音,必须马上撤离。灭火剂:泡沫、干粉、二氧化碳、砂土。用水灭火无效。
制备方法与用途
概述
环己烷(英文名称:Cyclohexane)是一种有汽油气味的无色流动液体,不溶于水,可与乙醇、乙醚、丙酮、苯等多种有机溶剂混溶,在甲醇中的溶解度为100份甲醇可溶解57份环己烷(25℃)。它易挥发和燃烧,闪点18℃,蒸气与空气形成爆炸性混合物,爆炸极限1.3~8.3%(体积)。对酸、碱比较稳定,与中等浓度的硝酸或混酸在低温下不发生反应,与稀硝酸在100℃以上的封管中发生硝化反应,生成硝基环己烷。在铂或钯催化下,350℃以上发生脱氢反应生成苯。与氧化铝、硫化钼、钴、镍、铝一起于高温下发生异构化,生成甲基戊烷。与三氯化铝在温和条件下则异构化为甲基环戊烷。
化学性质环己烷易挥发和极易燃烧,蒸气与空气形成爆炸性混合物, 爆炸极限1.3~8.3%(体积)。遇明火、高热极易燃烧爆炸。与氧化剂接触发生强烈反应,甚至引起燃烧。在火场中燃烧产生刺激烟雾。库房应通风低温干燥,并与氧化剂、酸类分开存放。
用途环己烷主要用于制造环己醇、环己酮,在涂料工业中广泛用作溶剂;用于有机合成;作为萃取溶剂和色素稀释剂;用作纤维醚类、脂肪类、油类、蜡、沥青、树脂及橡胶的溶剂;有机和重结晶介质;涂料和清漆的去除剂等。还可用作尼龙6和尼龙66的原料,聚合反应稀释剂、油漆脱膜剂、清净剂、己二酸萃取剂和粘结剂等。
生产方法目前几乎所有环己烷都是通过纯苯加氢制得,仅菲利浦(Phillips)公司用富环已烷馏分进行分馏方法生产。苯加氢制环己烷的方法很多,通常分为液相法和气相法两种,其中以液相法居多。
毒性ADI未规定(FAO/WHO,2001)。
急性毒性与刺激数据- 口服- 大鼠 LD50: 12705 毫克/公斤
- 口服- 小鼠 LD50: 813 毫克/ 公斤
- 皮肤- 兔子 1548 毫克/ 2 天
环己烷的含量可以通过以下步骤测定:
- 载气:氦;流速 (100±0.5)ml/min。
- 流量:4μl。
- 滞留时间 0.84min。然后按峰面积求取含量。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 正己烷 hexane 110-54-3 C6H14 86.1772 正庚烷 n-heptane 142-82-5 C7H16 100.204 环辛烷 Cyclooctan 292-64-8 C8H16 112.215 环庚烷 cycloheptane 291-64-5 C7H14 98.1882 环癸烷 cyclodecane 293-96-9 C10H20 140.269 正十六烷 Hexadecane 544-76-3 C16H34 226.446 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 正己烷 hexane 110-54-3 C6H14 86.1772 正庚烷 n-heptane 142-82-5 C7H16 100.204 正戊烷 pentane 109-66-0 C5H12 72.1503 十一烷 Undecan 1120-21-4 C11H24 156.312 环庚烷 cycloheptane 291-64-5 C7H14 98.1882 正辛烷 octane 111-65-9 C8H18 114.231 环十二烷 cyclododecane 294-62-2 C12H24 168.323 环戊烷 Cyclopentane 287-92-3 C5H10 70.1344
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:Dichlorides of Cyclohexane摘要:DOI:10.1021/ja01155a107
-
作为产物:描述:(benzyloxy)benzene 在 磷酸 、 5 % platinum on carbon 、 氢气 作用下, 以 水 为溶剂, 199.84 ℃ 、2.0 MPa 条件下, 反应 6.0h, 生成 环己烷参考文献:名称:木质素模型单体和二聚体模型在贵金属催化剂上的加氢脱氧摘要:系统地研究了反应条件(温度,酸度)对负载的Pt,Pd和Ru催化剂对木质素模型化合物水相加氢脱氧(HDO)的催化性能的影响。苯酚的转化是通过芳香环的氢化而产生的,从而得到环己酮,然后将其转化为环己醇和环己烷。尽管对于Pt和Pd基催化剂,芳环加氢速率较高,但对于Ru / C,环己酮中极性C = O部分的加氢速率更快。贵金属催化剂上苯酚到环己烷的完全HDO只能在布朗斯台德酸助催化剂存在下实现。在愈创木酚转化中,在Pt / C上0.5小时内即可实现有效的脱甲氧基化和环氢化。在酸性条件下 在4小时内,转化率为75%,对环己烷的选择性接近90%。为了深入了解在HDO条件下裂解木质素中芳族单元之间共价键的可能性,研究了二聚模型物质(如二苯醚,苄基苯醚,二苯甲烷和联苯)的反应性。尽管在贵金属催化剂的存在下,二聚氧桥接的模型化合物(例如苄基苯基醚和二苯醚)可以很容易地转化为单体形式,但未观察到二苯基甲烷和联DOI:10.1016/j.cattod.2013.12.011
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:Alicyclic Studies. XIII.1 Preparation and Reactions of 1,1'-Dicycloalkenyls*摘要:DOI:10.1021/jo01362a026
文献信息
-
<i>N</i>-Ammonium Ylide Mediators for Electrochemical C–H Oxidation作者:Masato Saito、Yu Kawamata、Michael Meanwell、Rafael Navratil、Debora Chiodi、Ethan Carlson、Pengfei Hu、Longrui Chen、Sagar Udyavara、Cian Kingston、Mayank Tanwar、Sameer Tyagi、Bruce P. McKillican、Moses G. Gichinga、Michael A. Schmidt、Martin D. Eastgate、Massimiliano Lamberto、Chi He、Tianhua Tang、Christian A. Malapit、Matthew S. Sigman、Shelley D. Minteer、Matthew Neurock、Phil S. BaranDOI:10.1021/jacs.1c03780日期:2021.5.26taking a first-principles approach guided by computation, these new mediators were identified and rapidly expanded into a library using ubiquitous building blocks and trivial synthesis techniques. The ylide-based approach to C–H oxidation exhibits tunable selectivity that is often exclusive to this class of oxidants and can be applied to real-world problems in the agricultural and pharmaceutical sectors强 C(sp 3 )-H 键的位点特异性氧化在有机合成中具有无可争议的效用。从简化对代谢物的获取和先导化合物的后期多样化到截断逆合成计划,学术界和工业界都越来越需要新的试剂和方法来实现这种转变。当前化学试剂的一个主要缺点是在结构和反应性方面缺乏多样性,这阻碍了用于快速筛选的组合方法的使用。在这方面,定向进化仍然最有希望在各种复杂环境中实现复杂的 C-H 氧化。在此,我们提出了一个设计合理的平台,该平台使用N-铵叶立德作为电化学驱动的氧化剂,用于位点特异性、化学选择性 C(sp 3 )-H 氧化。通过采用以计算为指导的第一性原理方法,这些新的介质被识别出来,并使用无处不在的构建块和简单的合成技术迅速扩展到一个库中。基于叶立德的 C-H 氧化方法表现出可调的选择性,这通常是此类氧化剂独有的,可应用于农业和制药领域的实际问题。
-
Facile Approach for C(sp3)–H Bond Thioetherification of Isochroman作者:Chun Cai、Jie Feng、Guoping Lu、Meifang LvDOI:10.1055/s-0034-1380125日期:——An unprecedented C–S formation protocol via the direct oxidative C(sp 3 )–H bond thioesterification of isochroman under metal-free conditions was developed. A series of isochroman derivatives could be afforded efficiently by the green, simple, and atom-economical method.
-
Designed To React: Terminal Copper Nitrenes and Their Application in Catalytic C−H Aminations作者:Julian Moegling、Alexander Hoffmann、Fabian Thomas、Nicole Orth、Patricia Liebhäuser、Ulrich Herber、Robert Rampmaier、Julia Stanek、Gerhard Fink、Ivana Ivanović-Burmazović、Sonja Herres-PawlisDOI:10.1002/anie.201713171日期:2018.7.16Heteroscorpionate ligands of the bis(pyrazolyl)methane family have been applied in the stabilisation of terminal copper tosyl nitrenes. These species are highly active intermediates in the copper‐catalysed direct C−H amination and nitrene transfer. Novel perfluoroalkyl‐pyrazolyl‐ and pyridinyl‐containing ligands were synthesized to coordinate to a reactive copper nitrene centre. Four distinct copper
-
Silica–Dendrimer Core–Shell Microspheres with Encapsulated Ultrasmall Palladium Nanoparticles: Efficient and Easily Recyclable Heterogeneous Nanocatalysts作者:Ankush V. Biradar、Archana A. Biradar、Tewodros AsefaDOI:10.1021/la203066d日期:2011.12.6We report the synthesis, characterization, and catalytic properties of novel monodisperse SiO2@Pd-PAMAM core–shell microspheres containing SiO2 microsphere cores and PAMAM dendrimer-encapsulated Pd nanoparticle (Pd-PAMAM) shells. First, SiO2 microspheres, which were prepared by the Stöber method, were functionalized with vinyl groups by grafting their surfaces with vinyltriethoxysilane (VTS). The vinyl我们报道了新型的单分散SiO 2 @ Pd-PAMAM核-壳微球的合成,表征和催化性能,其中SiO 2 @ Pd-PAMAM核-壳微球包含SiO 2微球核和PAMAM树枝状聚合物包裹的Pd纳米粒子(Pd-PAMAM)壳。首先,将通过Stöber方法制得的SiO 2微球通过乙烯基三乙氧基硅烷(VTS)接枝其表面而被乙烯基官能化。然后将乙烯基基团通过使用转化为环氧化物米氯过氧苯甲酸。用胺封端的G4聚(酰胺基胺)(PAMAM)树状聚合物处理后,SiO 2负载的环氧化物发生开环反应,得到SiO 2@PAMAM核-壳微球。通过使Pd(II)离子与树枝状聚合物核心中的胺基络合,然后用NaBH 4将其还原为Pd(0),来合成SiO 2负载的PAMAM树状聚合物核心中的Pd纳米粒子。这产生了SiO 2 @ Pd-PAMAM核-壳微球。通过跟踪FTIR光谱,元素分析和热重曲线上的重量损失,可以监测材料中不同
-
Nitrogen-enriched porous carbon supported Pd-nanoparticles as an efficient catalyst for the transfer hydrogenation of alkenes作者:Jie Li、Xin Zhou、Ning-Zhao Shang、Cheng Feng、Shu-Tao Gao、Chun WangDOI:10.1039/c8nj03656j日期:——g-C3N4 as a nitrogen source and a self-sacrificial template. The prepared Pd@NPC exhibited superior catalytic activity and chemoselectivity for the catalytic transfer hydrogenation of alkenes under mild conditions with formic acid as a hydrogen donor. Moreover, the catalyst displays high structure stability, and can be reused for five runs without any significant decrease of its catalytic activity and
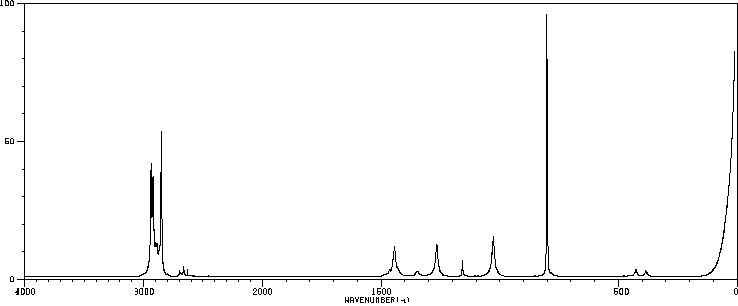
表征谱图
-
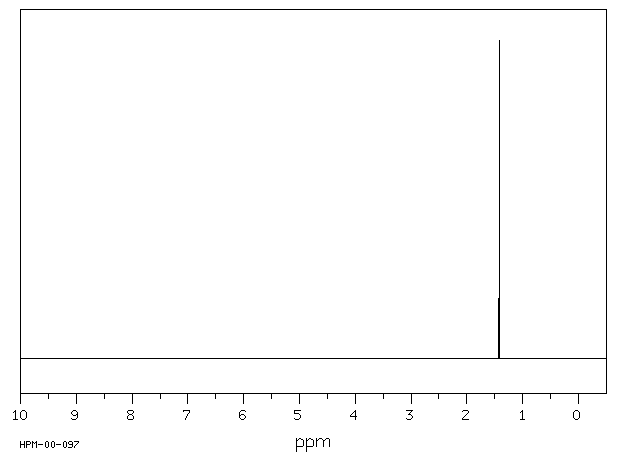
氢谱1HNMR
-
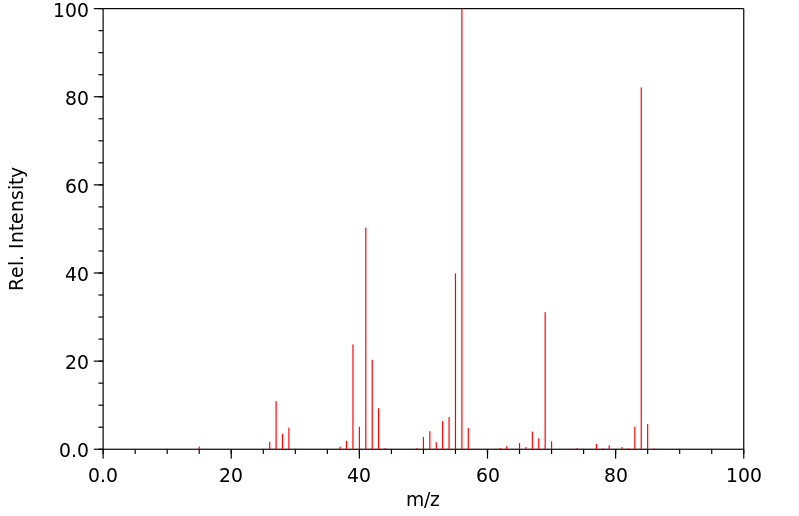
质谱MS
-
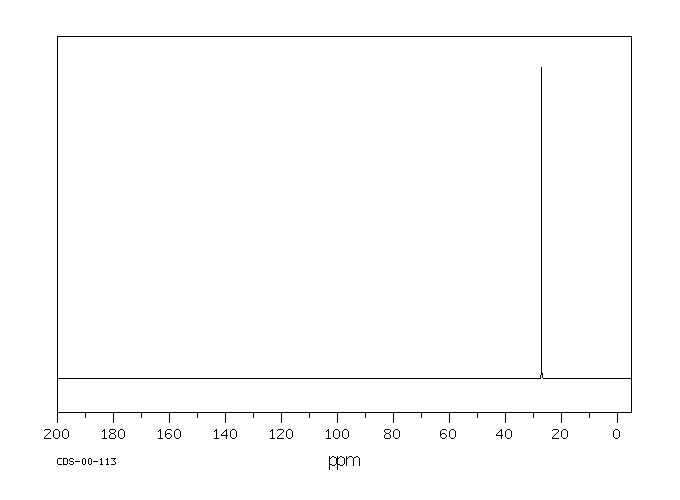
碳谱13CNMR
-
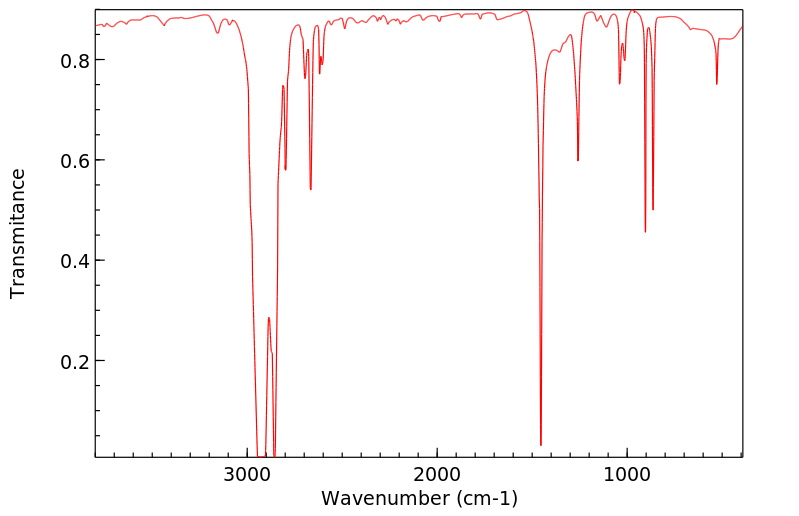
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
顺式-1-乙基-3-甲基环己烷
顺式-1-乙基-2-甲基环丙烷
顺式-1,3-二甲基环庚烷
顺式-1,2-二甲基环丙烷
顺式-1,2-二乙基环戊烷
顺式-1,2-二(1-甲基乙基)环丙烷
顺式-1,2-二(1-甲基乙基)环丙烷
顺式,反式,反式-1,2,4-三甲基环己烷
Copper, ethyl-
辛烷-d18
辛基环戊烷
辛基环丙烷
联苯肼酯
联环戊基
羰基双(环茂二烯基)钛
矿油精
癸烷,2,8-二甲基-
癸烷
decyl radical
癸基环戊烷
異十八烷
甲烷-d3
甲烷-d2
甲烷-d1
甲烷-D4
甲烷-3H
甲烷-13C,d4
甲烷-13C
甲烷
甲基自由基
甲基环辛烷
甲基环癸烷
甲基环戊烷
甲基环己烷-Me-d3
甲基环己烷
甲基环十一烷
甲基环丙烷
甲基环丁烷.
甲基丙烷-2-d
环辛烷-D16
环辛烷
环癸烷
环戊烷-D9
环戊烷-D10
环戊烷-13C1
环戊烷,三(2-辛基十二基)-
环戊烷
环戊基甲基自由基
环戊基环庚烷
环戊基环己烷