反式肉桂醛 | 14371-10-9
中文名称
反式肉桂醛
中文别名
桂皮醛;3-苯基-2-丙烯醛;反-3-苯丙烯醛;反-肉桂醛;3-苯丙烯醛;桂醛;TRANS-肉桂醛
英文名称
(E)-3-phenylpropenal
英文别名
trans-cinnamaldehyde;Cinnamaldehyde;(E)-cinnamaldehyde;(2E)-3-phenylprop-2-enal;cinnamic aldehyde;3-phenylacrylaldehyde;(E)-3-phenylprop-2-enal
CAS
14371-10-9
化学式
C9H8O
mdl
MFCD00007000
分子量
132.162
InChiKey
KJPRLNWUNMBNBZ-QPJJXVBHSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:−9-−4 °C(lit.)
-
沸点:250-252 °C(lit.)
-
密度:1.05 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
-
蒸气密度:4.6 (vs air)
-
闪点:160 °F
-
溶解度:可溶于氯仿(少量)、DMSO(少量)、甲醇(少量)
-
介电常数:16.899999999999999
-
LogP:1.820
-
物理描述:Cinnamaldehyde is a yellow oily liquid with a cinnamon odor and sweet taste. (NTP, 1992)
-
颜色/状态:Yellowish oily liquid
-
气味:PUNGENT, SPICY NOTE
-
味道:BURNING TASTE
-
蒸汽密度:VAPOR DENSITY: 4.6 (AIR= 1)
-
蒸汽压力:2.89X10-2 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
大气OH速率常数:4.80e-11 cm3/molecule*sec
-
气味阈值:50-750 ppb
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.618-1.623 at 20 °C/D
-
碰撞截面:134.25 Ų [M+H]+ [CCS Type: DT, Method: stepped-field]
-
保留指数:1227;1243;1257;1235.1;1222;1224;1228;1256;1256;1266;1235;1240;1239;1224;1240;1225
-
稳定性/保质期:
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):1.9
-
重原子数:10
-
可旋转键数:2
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:17.1
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:1
ADMET
代谢
研究了反式-[3-14C]肉桂醛在雄性和雌性Fischer 344大鼠以及CD1小鼠体内的代谢情况,通过腹腔注射给予2和250 mg/kg体重的剂量,以及雄性通过口服灌胃给予250 mg/kg的剂量。在两种物种中,给药剂量的约94%在72小时内通过排泄物回收,其中大部分(75-81%)出现在0-24小时的尿液中。在给药后72小时,体内残留的剂量不到2%。尿液中的代谢物通过色谱特性进行鉴定。在两种物种中,主要的尿液代谢物是马尿酸,伴随着3-羟基-3-苯基丙酸、苯甲酸和苯甲酰葡萄糖苷。肉桂酸与甘氨酸形成的结合物仅在鼠标体内大量生成。肉桂醛的氧化代谢基本上遵循肉桂酸的代谢途径,通过类似于脂肪酸的β-氧化。除了肉桂酸和肉桂醛共有的代谢物外,大鼠0-24小时尿液中7%的14C归因于两个新的代谢物,而在小鼠中是三个新的代谢物,其他研究工作已经表明这些新的代谢物来自于肉桂醛代谢的第二条途径,涉及与谷胱甘肽的结合。在大鼠和小鼠中,肉桂醛的排泄模式和代谢轮廓不会因性别、剂量大小和给药途径而有系统地受到影响。数据讨论了其与反式肉桂醛安全性评估的相关性,特别是从高剂量到低剂量的毒性数据外推的有效性或无效性。/反式肉桂醛/
The metabolism of trans-[3-14C]cinnamaldehyde was investigated in male and female Fischer 344 rats and CD1 mice at doses of 2 and 250 mg/kg bw given by ip injection and in males at 250 mg/kg by oral gavage. Some 94% of the administered dose was recovered in the excreta in 72 hr in both species with most (75-81%) present in the 0-24-hr urine. Less than 2% of the administered dose was found in the carcasses at 72 hr after dosing. Urinary metabolites were identified by their chromatographic characteristics. In both species the major urinary metabolite was hippuric acid accompanied by 3-hydroxy-3-phenylpropionic acid, benzoic acid and benzoyl glucuronide. The glycine conjugate of cinnamic acid was formed to a considerable extent only in the mouse. The oxidative metabolism of cinnamaldehyde essentially follows that of cinnamic acid, by beta-oxidation analogous to that of fatty acids. Apart from the metabolites common to cinnamic acid and cinnamaldehyde, 7% of 0-24-hr urinary 14C was accounted for by two new metabolites in the rat and three in the mouse, which have been shown in other work to arise from a second pathway of cinnamaldehyde metabolism involving conjugation with glutathione. The excretion pattern and metabolic profile of cinnamaldehyde in rats and mice are not systematically affected by sex, dose size and route of administration. The data are discussed in terms of their relevance to the safety evaluation of trans-cinnamaldehyde, particularly the validity or otherwise of extrapolation of toxicity data from high to low dose. /trans-Cinnamaldehyde/
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
为了评估肉桂醛和肉桂醇在人类皮肤中的代谢程度,并为皮肤中的醇脱氢酶(ADH)和醛脱氢酶(ALDH)在此类代谢中的作用提供证据……研究了肉桂醇和醛在人类皮肤匀浆和亚细胞组分中的代谢程度……研究在有和无ADH/细胞色素P450抑制剂4-甲基吡唑和细胞质ALDH抑制剂双硫仑的情况下进行。观察到在各个亚细胞组分中对肉桂醇和肉桂醛的不同代谢:皮肤细胞质被认为是肉桂化合物代谢的主要场所。在整体皮肤匀浆和细胞质组分中,使用4-甲基吡唑和双硫仑观察到显著的代谢抑制……这项研究已经证明,位于特定亚细胞隔室内的皮肤ADH和ALDH活性在皮肤中激活和解毒CAlc和CAld方面起着重要作用……
To evaluate the extent of cinnamaldehyde and cinnamic alcohol metabolism in human skin and provide evidence for the role of cutaneous alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) and aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) in such metabolism ... the extent of cinnamic alcohol and aldehyde metabolism was investigated in human skin homogenates and sub-cellular fractions ... Studies were conducted in the presence and absence of the ADH/cytochrome P450 inhibitor 4-methylpyrazole and the cytosolic ALDH inhibitor, disulfiram. Differential metabolism of cinnamic alcohol and cinnamaldehyde was observed in various subcellular fractions: skin cytosol was seen to be the major site of cinnamic compound metabolism. Significant metabolic inhibition was observed using 4-methylpyrazole and disulfiram in whole skin homogenates and cytosolic fractions only ... This study has demonstrated that cutaneous ADH and ALDH activities, located within defined subcellular compartments, play important roles in the activation and detoxification of CAlc and CAld in skin ...
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
Cinnamaldehyde administered intraperitoneally to a rabbit was excreted in the urine as cinnamic acid, cinnamoylglycine, benzoic acid and hippuric acid.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
Identification of 2 sulfur containing urinary metabolites of cinnamic aldehyde in rat which are 3-S-(N-acetylcysteinyl)-3-phenylpropyl alcohol and 3-S-(N-acetylcysteinyl)-3-phenylpropionic acid.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
Cinnamaldehyde is a known human metabolite of cinnarizine.
来源:NORMAN Suspect List Exchange
毒理性
Cinnamaldehyde is an allergen. The physiologic effect of cinnamaldehyde is by means of increased histamine release and cell-mediated immunity.
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
对人类不具有致癌性(未被国际癌症研究机构IARC列名)。
No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC).
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
过敏反应。
Allergic reaction.
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
吸入;皮肤接触;吞食
Inhalation; dermal; ingestion
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
肉桂醛过敏可能在不同患者中导致各种症状,从严重的过敏性反应到哮喘、腹部症状、湿疹或头痛等。
The specific symptoms that can result from cinnamic aldehyde allergy can vary considerably amongst patients from a severe anaphylactic reaction to asthma, abdominal symptoms, eczema or headaches. (L2140)
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
吸收、分配和排泄
肉桂醛通过皮肤的吸收率为52%,并且已经证明能够从肠道快速吸收。
Cinnamaldehyde is 52% absorbed through the skin and shown to be rapidly absorbed from the gut.
来源:DrugBank
吸收、分配和排泄
Cinnamaldehyde is metabolized and excreted primarily in the urine and, to a minor extent, in the feces. After oral or intraperitoneal administration to rats and mice, 69–98% of the dose of cinnamaldehyde was recovered in the urine and feces within 24 h.
来源:DrugBank
吸收、分配和排泄
丁香醛(CNMA)的生物利用度在F344雄性大鼠中进行了研究。大鼠通过口服灌胃的方式给予CNMA玉米油悬浮液,分别使用微囊化或纯化学物质,剂量为50、250和500毫克/千克。在任何剂量下,两种配方的CNMA血液浓度曲线或尿中马尿酸排泄速率都没有发现差异。两种配方在250和500毫克/千克的剂量下都显示出低生物利用度(<20%)。无论使用哪种配方,口服灌胃CNMA都显著增加了尿中马尿酸的排泄。大约75%的CNMA剂量被代谢成马尿酸并从尿液中回收。在50小时的尿液中回收的马尿酸总量与CNMA剂量密切相关。数据表明,CNMA从微囊中完全释放,并且CNMA的微囊化不影响其生物利用度或代谢...
The bioavailability of microencapsulated cinnamaldehyde (CNMA) was investigated in male F344 rats. Rats were gavaged with CNMA in corn oil using either microencapsulated or the neat chemical at doses of 50, 250, and 500 mg/kg. No differences between the two formulations at any of the doses were found in either CNMA blood concentration profiles or in the rate of urinary hippuric acid excretion. Both formulations showed a low bioavailability (< 20%) at 250 and 500 mg/kg. Regardless of the formulation used, oral gavage of CNMA significantly increased the urinary excretion of hippuric acid. About 75% of the dose of CNMA was metabolized to hippuric acid and recovered in the urine. The total amount of hippuric acid recovered in a 50-hr urinary collection correlated well with the CNMA dose. The data suggest that there was complete release of CNMA from the microcapsules and that microencapsulation of CNMA does not affect its bioavailability or its metabolism ...
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
/Cinnamaldehyde is/ presumably oxidized in vivo to cinnamic acid, which is excreted in urine as benzoic and hippuric acids.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
安全信息
-
危险品标志:Xn,Xi
-
安全说明:S24,S26,S36/37,S37/39
-
危险类别码:R36/37/38,R21,R43
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:29122990,29122900
-
RTECS号:GD6476000
-
包装等级:I; II; III
-
危险标志:GHS07
-
危险性描述:H315,H317,H319,H335
-
危险性防范说明:P261,P280,P305 + P351 + P338
-
储存条件:铝桶或玻璃瓶进行密封包装,并应储存在阴凉且避光的地方,储存温度需保持在4°C以下。
SDS
模块 1. 化学品
1.1 产品标识符
: 反式肉桂醛
产品名称
1.2 鉴别的其他方法
无数据资料
1.3 有关的确定了的物质或混合物的用途和建议不适合的用途
仅用于研发。不作为药品、家庭或其它用途。
模块 2. 危险性概述
2.1 GHS-分类
易燃液体 (类别 4)
皮肤刺激 (类别 2)
眼睛刺激 (类别 2A)
皮肤过敏 (类别 1)
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触) (类别 3)
2.2 GHS 标记要素,包括预防性的陈述
象形图
警示词 警告
危险申明
H227 可燃液体
H315 造成皮肤刺激。
H317 可能导致皮肤过敏反应。
H319 造成严重眼刺激。
H335 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
警告申明
预防措施
P210 远离热源、火花、明火和热表面。- 禁止吸烟。
P261 避免吸入粉尘/烟/气体/烟雾/蒸气/喷雾.
P264 操作后彻底清洁皮肤。
P271 只能在室外或通风良好之处使用。
P272 禁止将污染的工作服带出作业场所。
P280 戴防护手套/穿防护服/戴护目镜/戴面罩.
事故响应
P302 + P352 如果皮肤接触:用大量肥皂和水清洗。
P304 + P340 如吸入: 将患者移到新鲜空气处休息,并保持呼吸舒畅的姿势。
P305 + P351 + P338 如与眼睛接触,用水缓慢温和地冲洗几分钟。如戴隐形眼镜并可方便地取
出,取出隐形眼镜,然后继续冲洗.
P312 如感觉不适,呼救中毒控制中心或医生.
P321 具体处置(见本标签上提供的急救指导)。
P333 + P313 如出现皮肤刺激或皮疹:求医/就诊。
P337 + P313 如仍觉眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
P362 脱掉沾污的衣服,清洗后方可再用。
P370 + P378 火灾时: 用干的砂子,干的化学品或耐醇性的泡沫来灭火。
安全储存
P403 + P233 存放于通风良的地方。 保持容器密闭。
P403 + P235 保持低温,存放于通风良好处。
P405 存放处须加锁。
废弃处置
P501 将内容物/ 容器处理到得到批准的废物处理厂。
2.3 其它危害物 - 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
3.1 物 质
: C9H8O
分子式
: 132.16 g/mol
分子量
组分 浓度或浓度范围
trans-Cinnamaldehyde
<=100%
化学文摘登记号(CAS 14371-10-9
No.)
模块 4. 急救措施
4.1 必要的急救措施描述
一般的建议
请教医生。 向到现场的医生出示此安全技术说明书。
吸入
如果吸入,请将患者移到新鲜空气处。 如呼吸停止,进行人工呼吸。 请教医生。
皮肤接触
用肥皂和大量的水冲洗。 请教医生。
眼睛接触
用大量水彻底冲洗至少15分钟并请教医生。
食入
禁止催吐。 切勿给失去知觉者通过口喂任何东西。 用水漱口。 请教医生。
4.2 主要症状和影响,急性和迟发效应
咳嗽, 呼吸短促, 头痛, 恶心, 呕吐, 据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
4.3 及时的医疗处理和所需的特殊处理的说明和指示
无数据资料
模块 5. 消防措施
5.1 灭火介质
灭火方法及灭火剂
用水雾,抗乙醇泡沫,干粉或二氧化碳灭火。
5.2 源于此物质或混合物的特别的危害
碳氧化物
5.3 给消防员的建议
如必要的话,戴自给式呼吸器去救火。
5.4 进一步信息
用水喷雾冷却未打开的容器。
模块 6. 泄露应急处理
6.1 作业人员防护措施、防护装备和应急处置程序
使用个人防护用品。 避免吸入蒸气、烟雾或气体。 保证充分的通风。 移去所有火源。
人员疏散到安全区域。 谨防蒸气积累达到可爆炸的浓度。蒸气能在低洼处积聚。
6.2 环境保护措施
如能确保安全,可采取措施防止进一步的泄漏或溢出。 不要让产品进入下水道。
6.3 泄漏化学品的收容、清除方法及所使用的处置材料
围堵溢出,用防电真空清洁器或湿刷子将溢出物收集起来,并放置到容器中去,根据当地规定处理(见第13部
分)。 放入合适的封闭的容器中待处理。
6.4 参考其他部分
丢弃处理请参阅第13节。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
7.1 安全操作的注意事项
避免接触皮肤和眼睛。 避免吸入蒸气和烟雾。
切勿靠近火源。-严禁烟火。采取措施防止静电积聚。
7.2 安全储存的条件,包括任何不兼容性
贮存在阴凉处。 使容器保持密闭,储存在干燥通风处。
打开了的容器必须仔细重新封口并保持竖放位置以防止泄漏。
充气保存 对空气敏感。
7.3 特定用途
无数据资料
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
8.1 容许浓度
最高容许浓度
没有已知的国家规定的暴露极限。
8.2 暴露控制
适当的技术控制
根据良好的工业卫生和安全规范进行操作。 休息前和工作结束时洗手。
个体防护设备
眼/面保护
面罩與安全眼鏡请使用经官方标准如NIOSH (美国) 或 EN 166(欧盟) 检测与批准的设备防护眼部。
皮肤保护
戴手套取 手套在使用前必须受检查。
请使用合适的方法脱除手套(不要接触手套外部表面),避免任何皮肤部位接触此产品.
使用后请将被污染过的手套根据相关法律法规和有效的实验室规章程序谨慎处理. 请清洗并吹干双手
所选择的保护手套必须符合EU的89/686/EEC规定和从它衍生出来的EN 376标准。
完全接触
物料: 丁基橡胶
最小的层厚度 0.3 mm
溶剂渗透时间: 480 min
测试过的物质ButojECt® (KCL 897 / Z677647, 规格 M)
飞溅保护
物料: 丁腈橡胶
最小的层厚度 0.4 mm
溶剂渗透时间: 30 min
测试过的物质Camatril® (KCL 730 / Z677442, 规格 M)
, 测试方法 EN374
如果以溶剂形式应用或与其它物质混合应用,或在不同于EN
374规定的条件下应用,请与EC批准的手套的供应商联系。
这个推荐只是建议性的,并且务必让熟悉我们客户计划使用的特定情况的工业卫生学专家评估确认才可.
这不应该解释为在提供对任何特定使用情况方法的批准.
身体保护
全套防化学试剂工作服, 防护设备的类型必须根据特定工作场所中的危险物的浓度和数量来选择。
呼吸系统防护
如危险性评测显示需要使用空气净化的防毒面具,请使用全面罩式多功能防毒面具(US)或ABEK型
(EN
14387)防毒面具筒作为工程控制的候补。如果防毒面具是保护的唯一方式,则使用全面罩式送风防
毒面具。 呼吸器使用经过测试并通过政府标准如NIOSH(US)或CEN(EU)的呼吸器和零件。
模块 9. 理化特性
9.1 基本的理化特性的信息
a) 外观与性状
形状: 液体
b) 气味
无数据资料
c) 气味阈值
无数据资料
d) pH值
无数据资料
e) 熔点/凝固点
熔点/凝固点: -7.5 °C
f) 沸点、初沸点和沸程
248 °C 在 1,013 hPa
g) 闪点
71 °C - 闭杯
h) 蒸发速率
无数据资料
i) 易燃性(固体,气体)
无数据资料
j) 高的/低的燃烧性或爆炸性限度 无数据资料
k) 蒸气压
无数据资料
l) 蒸汽密度
4.56 - (空气= 1.0)
m) 密度/相对密度
1.050 g/cm3
n) 水溶性
无数据资料
o) n-辛醇/水分配系数
辛醇--水的分配系数的对数值: 1.9
p) 自燃温度
无数据资料
q) 分解温度
无数据资料
r) 粘度
无数据资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应活性
10.1 反应性
无数据资料
10.2 稳定性
无数据资料
10.3 危险反应
无数据资料
10.4 应避免的条件
热,火焰和火花。
10.5 不相容的物质
强氧化剂, 强碱
10.6 危险的分解产物
其它分解产物 - 无数据资料
模块 11. 毒理学资料
11.1 毒理学影响的信息
急性毒性
无数据资料
皮肤刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
眼睛刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
呼吸道或皮肤过敏
可能引起皮肤过敏性反应。
生殖细胞致突变性
细胞突变性-体外试验 - 仓鼠 - 成纤维细胞
细胞发生分析
细胞突变性-体外试验 - 仓鼠 - 成纤维细胞
形态变形
细胞突变性-体外试验 - 仓鼠 - 子宫
姐妹染色单体互换
细胞突变性-体内试验 - 小鼠 - 经口
微核测试
细胞突变性-体内试验 - 大鼠 - 经口
微核测试
致癌性
IARC:
此产品中没有大于或等于 0。1%含量的组分被 IARC鉴别为可能的或肯定的人类致癌物。
生殖毒性
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触)
吸入 - 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
特异性靶器官系统毒性(反复接触)
无数据资料
吸入危险
无数据资料
潜在的健康影响
吸入 吸入可能有害。 引起呼吸道刺激。
摄入 如服入是有害的。
皮肤 通过皮肤吸收可能有害。 造成皮肤刺激。
眼睛 造成严重眼刺激。
接触后的征兆和症状
咳嗽, 呼吸短促, 头痛, 恶心, 呕吐, 据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
附加说明
化学物质毒性作用登记: GD6476000
模块 12. 生态学资料
12.1 生态毒性
无数据资料
12.2 持久性和降解性
无数据资料
12.3 潜在的生物累积性
无数据资料
12.4 土壤中的迁移性
无数据资料
12.5 PBT 和 vPvB的结果评价
无数据资料
12.6 其它不良影响
无数据资料
模块 13. 废弃处置
13.1 废物处理方法
产品
此易爆炸产品可以在备有燃烧后处理和洗刷作用的化学焚化炉中燃烧
将剩余的和不可回收的溶液交给有许可证的公司处理。
受污染的容器和包装
按未用产品处置。
模块 14. 运输信息
14.1 联合国危险货物编号
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.2 联合国运输名称
欧洲陆运危规: 非危险货物
国际海运危规: 非危险货物
国际空运危规: 非危险货物
14.3 运输危险类别
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.4 包裹组
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.5 环境危险
欧洲陆运危规: 否 国际海运危规 国际空运危规: 否
海洋污染物(是/否): 否
14.6 对使用者的特别提醒
无数据资料
模块 15 - 法规信息
N/A
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
制备方法与用途
食品添加剂最大允许使用量与残留量标准
桂醛
化学性质
添加剂中文名称: 桂醛
允许使用该种添加剂的食品中文名称: 经表面处理的鲜水果
添加剂功能: 防腐剂
最大允许使用量(g/kg): 按生产需要适量使用
最大允许残留量(g/kg): 残留量≤0.3mg/kg
| Target | Value |
|---|---|
| TRPA1 |
淡黄色油状液体,熔点-7.5℃,沸点253℃(部分分解),127℃(2.13kPa),相对密度1.0497(20/4℃),折光率1.6195,闪点71℃。溶于醇、氯仿,微溶于水。具有特殊的肉桂芳香气味,能随水蒸汽挥发。肉桂醛是我国产桂皮油和锡兰桂油的主要成分,含量约55-85%,天然品和合成品都是反式结构。
用途重要的合成香料,主要用于调制素馨、铃兰、玫瑰等日用香精,也用于食品香料,赋予食品肉桂香味。除了在调味品类、肉桂、甜酒中使用外,还广泛应用于苹果、樱桃等水果香精。肉桂醛在食品中的用量分别为:清凉饮料为10ppm,冰淇淋类为8ppm,糖果为700ppm,点心类为200ppm,口香糖为5000ppm,调味品为20ppm,肉类为60ppm。肉桂醛也是医药的中间体。
用途 生产方法将肉桂油、桂皮油等天然油与亚硫酸氢钠加成,再经精馏而得该品。合成的方法是由苯甲醛和乙醛在稀碱的作用下发生交叉羟醛缩合反应制得。具体步骤如下:在反应锅内加入133kg苯甲醛,400kg水,并于20℃条件下加入10kg 40-50%氢氧化钠、66.6kg乙醛。然后加入40-50kg苯,搅拌反应5小时后分层,取苯层中和,减压蒸馏,收集130℃(2.67kPa)的馏分,得到肉桂醛约55-60kg。同时回收苯甲醛80kg(8.0/1.33kg)。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 反式-肉桂醛 cinnamaldehyde 57194-69-1 C9H8O 132.162 肉桂醛 3-phenyl-propenal 104-55-2 C9H8O 132.162 甲基苯乙烯 1-propenylbenzene 873-66-5 C9H10 118.178 顺-β-甲基苯乙烯 cis-1-phenyl-1-propylene 766-90-5 C9H10 118.178 —— cinnamoyl fluoride 38986-89-9 C9H7FO 150.152 3-苯基-2-丙烯酰氯 Cinnamoyl chloride 17082-09-6 C9H7ClO 166.607 肉桂酸 (E)-3-phenylacrylic acid 140-10-3 C9H8O2 148.161 肉桂酰氯 cinnamoyl chloride 102-92-1 C9H7ClO 166.607 1-苯-1,3-丁二烯 (E)-1-Phenyl-1,3-butadiene 16939-57-4 C10H10 130.189 肉桂基胺 (E)-cinnamylamine 4360-51-4 C9H11N 133.193 —— trans-cinnamyl iodide 82859-39-0 C9H9I 244.075 肉桂腈 cinnamic nitrile 1885-38-7 C9H7N 129.161 (肉)桂腈 cinnamonitrile 4360-47-8 C9H7N 129.161 (Z)-肉桂醇 (Z)-cinnamyl alcohol 4510-34-3 C9H10O 134.178 3-苯基丙-2-烯-1-醇 (2E)-3-phenyl-2-propen-1-ol 4407-36-7 C9H10O 134.178 肉桂醇 3-Phenylpropenol 104-54-1 C9H10O 134.178 肉桂基氯 Cinnamyl chloride 21087-29-6 C9H9Cl 152.623 —— Cinnamyl bromide 4392-24-9 C9H9Br 197.074 —— 4-chlorocinnamaldehyde 1075-77-0 C9H7ClO 166.607 1,4-二苯基-1,3丁二烯 1,4-Diphenyl-1E,3E-butadiene 538-81-8 C16H14 206.287 —— (Z)-2-chloro-3-phenyl-2-propenal 33603-89-3 C9H7ClO 166.607 α-溴代肉桂醛 α-bromocinnamaldehyde 5443-49-2 C9H7BrO 211.058 —— (2Z)-2-bromo-3-phenyl-2-propenal 33603-90-6 C9H7BrO 211.058 —— (E)-2-bromo-3-phenylprop-2-enal 99686-39-2 C9H7BrO 211.058 —— Methyl cinnamate 103-26-4 C10H10O2 162.188 —— (E)-(3-methoxyprop-1-en-1-yl)benzene 22688-03-5 C10H12O 148.205 —— cinnamaldehyde oxime 59336-59-3 C9H9NO 147.177 N-肉桂亚基羟胺 (1E,2E)-cinnamaldehyde oxime 13372-81-1 C9H9NO 147.177 —— (E)-3-phenyl-thioacrylic acid S-methyl ester 79909-76-5 C10H10OS 178.255 —— trans-3-Diazo-1-phenyl-propen 22553-93-1 C9H8N2 144.176 —— (E)-1-(3,3-dichloroprop-1-en-1-yl)benzene 29268-75-5 C9H8Cl2 187.069 苯乙烯 styrene 100-42-5 C8H8 104.152 —— (E)-(3-ethoxy-1-propen-1-yl)benzene —— C11H14O 162.232 —— (E)-1-phenyl-1-hexene 6111-82-6 C12H16 160.259 —— (hexa-1,3-dien-1-yl)benzene 41635-77-2 C12H14 158.243 —— (E)-(3-(allyloxy)prop-1-en-1-yl)benzene 80586-92-1 C12H14O 174.243 —— (E)-N,N-dimethyl-3-phenylprop-2-en-1-amine 42817-44-7 C11H15N 161.247 —— 5-phenylpenta-2,4-dienol —— C11H12O 160.216 反式-肉桂酸乙酯 ethyl cinnamate 4192-77-2 C11H12O2 176.215 肉桂酸乙酯 ethyl 3-phenyl-2-propenoate 103-36-6 C11H12O2 176.215 2-丙烯酰胺,N,N-二甲基-3-苯基-,(2E)- (E)-N,N-dimethylcinnamamide 17431-39-9 C11H13NO 175.23 —— (E)-cinnamyl azide —— C9H9N3 159.191 —— ethyl (E)-1-phenylbut-1-en-3-ol 36004-04-3 C10H12O 148.205 —— (E)-(3-isopropoxyprop-1-en-1-yl)benzene 14289-95-3 C12H16O 176.258 乙酸肉桂酯 Cinnamyl acetate 21040-45-9 C11H12O2 176.215 —— phenylketene 3496-32-0 C8H6O 118.135 —— [(E)-3-nitroprop-1-enyl]benzene 62753-09-7 C9H9NO2 163.176 —— N,N-dimethyl-N'-(3-phenyl-allylidene)-hydrazine 15023-38-8 C11H14N2 174.246 —— cinnamaldehyde N,N-dimethylhydrazone 67068-24-0 C11H14N2 174.246 —— (E)-cinnamaldehyde dimethylacetal 4364-06-1 C11H14O2 178.231 1-叔丁基-4-苯基-1-氮杂-1,3-丁二烯 1-tert-butyl-4-phenyl-1-aza-1,3-butadiene 136809-07-9 C13H17N 187.285 反式-桂皮酸酐 cinnamic anhydride 21947-71-7 C18H14O3 278.307 —— (E)-2-(3-phenylallylidene)malononitrile 41109-96-0 C12H8N2 180.209 —— (1E,3E)-1-chloro-4-(4-phenylbuta-1,3-dien-1-yl)benzene 37985-13-0 C16H13Cl 240.732 —— (E)-cinnamyloxytrimethylsilane 109283-53-6 C12H18OSi 206.36 β-溴苯乙烯 bromostyrene 103-64-0 C8H7Br 183.048 —— (Z)-β-bromostyrene 1335-06-4 C8H7Br 183.048 [(Z)-2-溴乙烯基]苯 [(E)-2-bromoethenyl]benzene 588-72-7 C8H7Br 183.048 2-羟基-4-苯基-3-丁烯腈 2-hydroxy-4-phenyl-3-butenenitrile 61912-03-6 C10H9NO 159.188 —— (+/-)-3-chloro-3-methoxy-1t-phenyl-propene-(1) —— C10H11ClO 182.65 - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 反式-肉桂醛 cinnamaldehyde 57194-69-1 C9H8O 132.162 甲基苯乙烯 1-propenylbenzene 873-66-5 C9H10 118.178 1-丙烯基苯 1-phenylpropene 637-50-3 C9H10 118.178 反-肉桂酰胺 cinnamamide 22031-64-7 C9H9NO 147.177 苄叉丙酮 (E)-benzalacetone 1896-62-4 C10H10O 146.189 苄叉丙酮 1-Phenylbut-1-en-3-one 122-57-6 C10H10O 146.189 反式-alpha-甲基肉桂醛 α-methyl-trans-cinnamaldehyde 15174-47-7 C10H10O 146.189 —— cinnamoyl fluoride 38986-89-9 C9H7FO 150.152 肉桂酸 Cinnamic acid 621-82-9 C9H8O2 148.161 肉桂酸 (E)-3-phenylacrylic acid 140-10-3 C9H8O2 148.161 別桂皮酸 cis-cinnamic acid 102-94-3 C9H8O2 148.161 —— thiolocinnamic acid —— C9H8OS 164.228 3-苯基-2-丙烯酰氯 Cinnamoyl chloride 17082-09-6 C9H7ClO 166.607 1-苯-1,3-丁二烯 (E)-1-Phenyl-1,3-butadiene 16939-57-4 C10H10 130.189 —— buta-1,3-dien-1-ylbenzene 1515-78-2 C10H10 130.189 —— trans-cinnamyl iodide 82859-39-0 C9H9I 244.075 肉桂基胺 (E)-cinnamylamine 4360-51-4 C9H11N 133.193 肉桂腈 cinnamic nitrile 1885-38-7 C9H7N 129.161 —— (E)-but-1-en-3-yn-1-ylbenzene —— C10H8 128.174 肉桂醇 3-Phenylpropenol 104-54-1 C9H10O 134.178 3-苯基丙-2-烯-1-醇 (2E)-3-phenyl-2-propen-1-ol 4407-36-7 C9H10O 134.178 —— 1-phenylbut-1-en-3-yne 5622-76-4 C10H8 128.174 —— (E)-1-phenylpenta-1,4-dien-3-one 73291-51-7 C11H10O 158.2 —— Cinnamyl bromide 4392-24-9 C9H9Br 197.074 肉桂基氯 Cinnamyl chloride 21087-29-6 C9H9Cl 152.623 —— (Z)-2-iodo-3-phenylacrylaldehyde 116544-98-0 C9H7IO 258.058 —— (dibenzylidene)acetone 115587-57-0 C17H14O 234.298 联甲基苯乙烯酮 dibenzylideneacetone 35225-79-7 C17H14O 234.298 1,4-二苯基-1,3丁二烯 1,4-Diphenyl-1E,3E-butadiene 538-81-8 C16H14 206.287 1-[(1E,3Z)-4-苯基-1,3-丁二烯基]苯 (1Z,3E)-1,4-diphenylbuta-1,3-diene 5808-05-9 C16H14 206.287 —— (3E)-1,4-diphenyl-1,3-butadiene 72777-78-7 C16H14 206.287 1,4-二苯基1,3-丁二烯 1,4-diphenylbutadiene 886-65-7 C16H14 206.287 —— (E)-cinnamaldehyde-2-d 17537-30-3 C9H8O 133.154 —— (2E, 4E)-5-phenylpenta-2,4-dienal 13466-40-5 C11H10O 158.2 5-苯基戊-2,4-二烯醛 5-phenylpenta-2,4-dienal 13466-40-5 C11H10O 158.2 —— trans-cinnamaldehyde chlorimin —— C9H8ClN 165.622 —— (1E,3E)-1-phenyl-1,3-pentadiene 3909-96-4 C11H12 144.216 —— 1-phenyl-1,3-pentadiene —— C11H12 144.216 —— (2Z)-2-bromo-3-phenyl-2-propenal 33603-90-6 C9H7BrO 211.058 1-苯基戊-1-烯-3-酮 1-phenyl-pent-1-en-3-one 3152-68-9 C11H12O 160.216 α-溴代肉桂醛 α-bromocinnamaldehyde 5443-49-2 C9H7BrO 211.058 —— (1E)-1-phenylpent-1-en-3-one 3152-68-9 C11H12O 160.216 α-氯代肉桂醛 α-chloro-cinnamaldehyde 18365-42-9 C9H7ClO 166.607 —— (E)-2-bromo-3-phenylprop-2-enal 99686-39-2 C9H7BrO 211.058 —— (Z)-2-chloro-3-phenyl-2-propenal 33603-89-3 C9H7ClO 166.607 —— (3E)-4-phenyl-3-buten-1-ol 770-36-5 C10H12O 148.205 (E)-N-羟基-3-苯基丙烯酰胺 trans-cinnamohydroxamic acid 29900-75-2 C9H9NO2 163.176 (E)-N-羟基-3-苯基丙-2-烯酰胺 N-hydroxycinnamamide 3669-32-7 C9H9NO2 163.176 —— 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1-aza-1,3-butadiene 196703-82-9 C10H11N 145.204 —— N-((2E)-3-phenylprop-2-enylidene)methanamine 116910-43-1 C10H11N 145.204 —— Methyl cinnamate 103-26-4 C10H10O2 162.188 α-甲基肉桂醛 3-(2-methylphenyl)prop-2-en-1-al 4549-82-0 C10H10O 146.189 肉桂酸甲酯 methyl cinnamate 103-26-4 C10H10O2 162.188 —— (E)-1-bromo-4-phenylbut-3-en-2-one —— C10H9BrO 225.085 —— (E)-cinnamoyl cyanide 6047-90-1 C10H7NO 157.172 —— ((1E,3E)-4-bromobuta-1,3-dienyl)benzene 188802-38-2 C10H9Br 209.085 —— [(1E,3Z)-4-bromobuta-1,3-dien-1-yl]benzene —— C10H9Br 209.085 N-甲基肉桂基胺 (E)-N-methylcinnamylamine 83554-67-0 C10H13N 147.22 —— [(1E,3E)-4-chlorobuta-1,3-dien-1-yl]benzene 18685-02-4 C10H9Cl 164.634 —— [(1E,3Z)-4-chlorobuta-1,3-dien-1-yl]benzene —— C10H9Cl 164.634 (E)-4-苯基-3-丁烯胺 (E)-4-phenylbut-3-en-1-amine 7515-38-0 C10H13N 147.22 N-肉桂亚基羟胺 (1E,2E)-cinnamaldehyde oxime 13372-81-1 C9H9NO 147.177 —— cinnamaldehyde oxime 59336-59-3 C9H9NO 147.177 —— (1E,2Z)-3-phenylacrylaldehyde oxime 13372-81-1 C9H9NO 147.177 —— ((E)-3-phenylallylidene)hydrazine 1031850-23-3 C9H10N2 146.192 —— (E)-1-chloro-4-phenylbut-3-en-2-one 88981-42-4 C10H9ClO 180.634 —— ((1E,3E)-hexa-1,3,5-trien-1-yl)benzene —— C12H12 156.227 —— (E)-pent-1-en-3-yn-1-ylbenzene 54157-31-2 C11H10 142.2 —— (E)-3-phenyl-thioacrylic acid S-methyl ester 79909-76-5 C10H10OS 178.255 —— trans-3-Diazo-1-phenyl-propen 22553-93-1 C9H8N2 144.176 —— (E)-1-(3,3-dichloroprop-1-en-1-yl)benzene 29268-75-5 C9H8Cl2 187.069 —— N-(E)-cinnamyl-hydroxylamine 113038-82-7 C9H11NO 149.192 —— 3t-phenyl-acrylonitrile N-oxide 93970-65-1 C9H7NO 145.161 —— 1,6-diphenyl-1,3,5-hexatriene 17329-15-6 C18H16 232.325 1,6-二苯基-1,3,5-己三烯 1,6-diphenyl-hexa-1,3,5-triene 1720-32-7 C18H16 232.325 —— 1,6-diphenylhexa-(1E,3Z,5E)-triene 1720-32-7 C18H16 232.325 —— (E)-1-phenyl-1,5-hexadiene 56644-04-3 C12H14 158.243 —— (1E,4E)-1-phenyl-1,4-hexadien-3-one 91897-73-3 C12H12O 172.227 反式-5-苯基-4-戊烯醛 (E)-5-phenylpent-4-enal 36884-75-0 C11H12O 160.216 —— (E)-1-phenylhexa-1,4,5-trien-3-one 1321942-08-8 C12H10O 170.211 —— (E)-(4-bromobut-1-en-3-yn-1-yl)benzene —— C10H7Br 207.07 苯乙烯 styrene 100-42-5 C8H8 104.152 —— (E)-(4-methylpenta-1,3-dien-1-yl)benzene 39491-73-1 C12H14 158.243 —— 7-phenyl-hepta-2,4,6-trienal 6460-63-5 C13H12O 184.238 —— (2E,4E,6E)-7-phenylhepta-2,4,6-trienal 32410-52-9 C13H12O 184.238 —— (E)-1-phenylhexa-1,5-dien-3-one 100840-13-9 C12H12O 172.227 (2E)-N-乙基-3-苯基-2-丙烯-1-胺 ethyl-(3-phenylallyl)amine 188049-29-8 C11H15N 161.247 —— (2E,4E)-5-phenylpenta-2,4-dienenitrile 14164-31-9 C11H9N 155.199 —— 5-phenylpenta-2,4-dienenitrile 110729-75-4 C11H9N 155.199 —— ((1E,3E)-hexa-1,3-dien-1-yl)benzene 39491-62-8 C12H14 158.243 —— (1E,3Z)-1-phenylhexa-1,3-diene 39491-61-7 C12H14 158.243 —— (2E,4E)-5-phenylpenta-2,4-dien-1-amine 77629-16-4 C11H13N 159.231 —— trans-cinnamaldehyde ethylimine 69375-96-8 C11H13N 159.231 —— (E,E,E,E)-9-Phenyl-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenal —— C15H14O 210.276 —— (2E,4E,6E,8E,10E)-11-Phenylundeca-2,4,6,8,10-pentaenal 5462-94-2 C17H16O 236.313 —— (E)-(3-(allyloxy)prop-1-en-1-yl)benzene 80586-92-1 C12H14O 174.243 —— cinnamyl formate 23510-72-7 C10H10O2 162.188 —— α-(hydroxymethyl)cinnamaldehyde 951024-70-7 C10H10O2 162.188 —— (E)-N,N-dimethyl-3-phenylprop-2-en-1-amine 42817-44-7 C11H15N 161.247 —— (E,E)-1-(4-methylphenyl)-4-phenylbuta-1,3-diene 37985-11-8 C17H16 220.314 - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:一锅铜(I)催化合成3,5-二取代异恶唑摘要:通过便利的一锅三步程序,利用原位生成的腈氧化物和末端乙炔之间的区域选择性铜(I)催化的环加成反应,以方便的一锅三步程序以高收率获得了3,5-二取代的异恶唑。大多数官能团不干扰反应,该反应可以在水性溶剂中进行而无需氧气的保护。由于所有试剂都以化学计量的形式使用,因此副产物的形成得以最小化。DOI:10.1021/jo050163b
-
作为产物:描述:(E)-1-phenyl-3-phenylselanylprop-2-en-1-ol 在 硫酸 、 silica gel 作用下, 以 二氯甲烷 为溶剂, 反应 24.0h, 以90%的产率得到反式肉桂醛参考文献:名称:β-Phenylseone α,β-不饱和醛,高效的三碳同源试剂。1,3-羰基转座摘要:摘要 容易得到的 β-苯基硒基 α,β-不饱和醛与格氏试剂和正丁基锂反应生成 1,2-加成产物,在硅胶存在下酸水解得到不含硒的 α,β -具有 1,3-羰基转位的不饱和羰基化合物。DOI:10.1080/00397919108021067
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:Ku, Bonchul; Oh, Dong Young, Synthetic Communications, 1989, vol. 19, # 3and4, p. 433 - 438摘要:DOI:
文献信息
-
Fe(0)-Mediated Synthesis of Tri- and Tetra-Substituted Olefins from Carbonyls: An Environmentally Friendly Alternative to Cr(II)作者:J. R. Falck、Romain Bejot、Deb K. Barma、Anish Bandyopadhyay、Suju Joseph、Charles MioskowskiDOI:10.1021/jo061445u日期:2006.10.1carbonyls by activated polyhalides. In many instances, Fe(0) was equivalent or superior to Cr(II). Notably, Fe(0), but not Cr(II), proved compatible with a wide range of functionality, inter alia, unprotected phenol, aryl nitro, carboxylic acid, and alkyl nitrile. A surprising reversal of stereoselectivity for aldehydes versus ketones was observed using both metals. The resultant α-halo-α,β-unsaturated or α
-
Preparation of functionalized cyclobutenones and phenolic compounds from α-diazo β-ketophosphonates作者:Rindra Andriamiadanarivo、Bernard Pujol、Bernard Chantegrel、Christian Deshayes、Alain DoutheauDOI:10.1016/s0040-4039(00)61512-5日期:1993.12When heated in refluxing benzene or toluene, α-diazo β-ketophosphonates 2, prepared in three steps from aldehydes or ketones, gave rise to functionalized cyclobutenones 4 or phenolic compounds 5. These products are formed by electrocyclisation respectively of a vinyl or dienylketene, resulting from a Wolff rearrangement.
-
A “one-pot” multicomponent approach to polysubstituted 4-aminopyridines作者:Jiaan Shao、Wanwan Yu、Zhanying Shao、Yongping YuDOI:10.1039/c2cc17850h日期:——A novel and facile domino reaction has been developed to synthesize a variety of polysubstituted 4-aminopyridines from α-azidovinylketones, aldehydes and methylamine derivatives in reasonably good yields under mild conditions. Additionally, a possible mechanism is proposed.
-
<i>α</i>-Alkylation of<i>α</i>,<i>β</i>-Unsaturated Aldehyde Dimethylhydrazones Accompanied with the Double Bond Migration to<i>β</i>,<i>γ</i>作者:Masakazu Yamashita、Kaoru Matsumiya、Ken-ichi NakanoDOI:10.1246/bcsj.66.1759日期:1993.6Lithiated α,β-unsaturated aldehyde N,N-dimethylhydrazones reacted with alkyl halides accompanied by double bond migration to give α-alkylated β,γ-unsaturated aldehyde N,N-dimethylhydrazones in satisfactory yields. This reaction was found to be caused at the first step by deprotonation from a γ-carbon atom by lithium diisopropylamide. In the case of hydrazones with two kinds of γ-protons, deprotonation from the less hindered γ-carbon occurred selectively. Using this reaction, a novel sesquiterpene, 2,5,9-trimethyl-2-vinyl-4,8-decadienal, which has a vinyl group at the α-position, was synthesized in a good yield.
-
4' SUBSTITUTED COMPOUNDS HAVING 5-HT6 RECEPTOR AFFINITY申请人:Dunn Robert公开号:US20080318941A1公开(公告)日:2008-12-25The present disclosure provides compounds having affinity for the 5-HT 6 receptor which are of the formula (I): wherein R 1 , R 2 , R 5 , R 6 , B, D, E, G, Q, x and n are as defined herein. The disclosure also relates to methods of preparing such compounds, compositions containing such compounds, and methods of use thereof.本公开提供了具有亲和力的化合物,其对5-HT 6 受体具有亲和力,其化学式为(I): 其中R1、R2、R5、R6、B、D、E、G、Q、x和n如本文所定义。本公开还涉及制备这种化合物的方法、含有这种化合物的组合物以及使用这些化合物的方法。
表征谱图
-
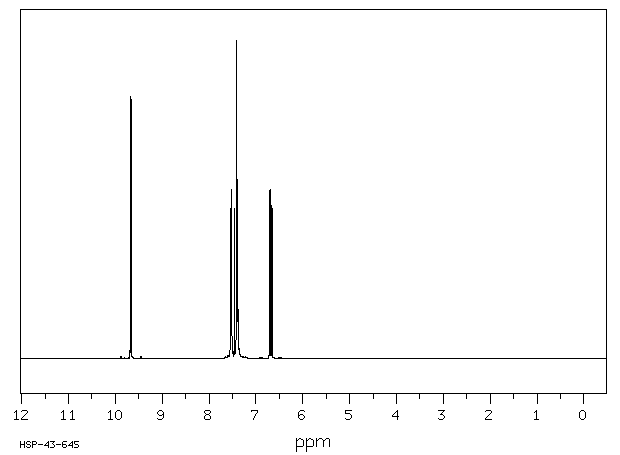
氢谱1HNMR
-
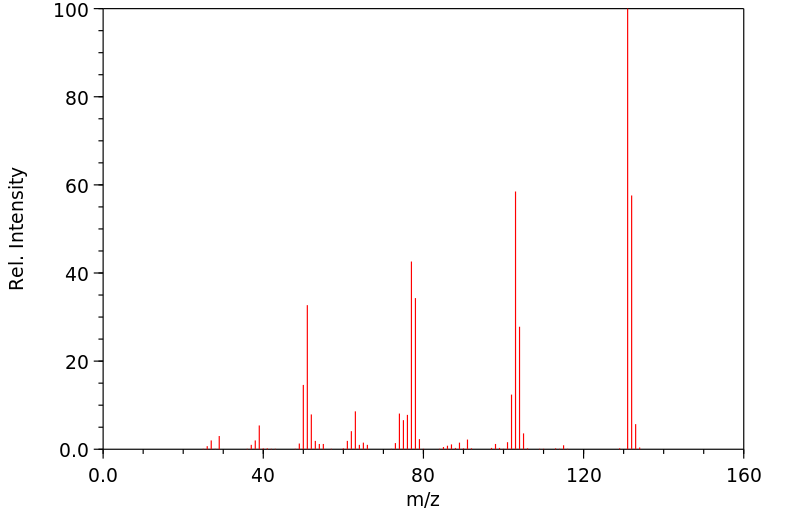
质谱MS
-
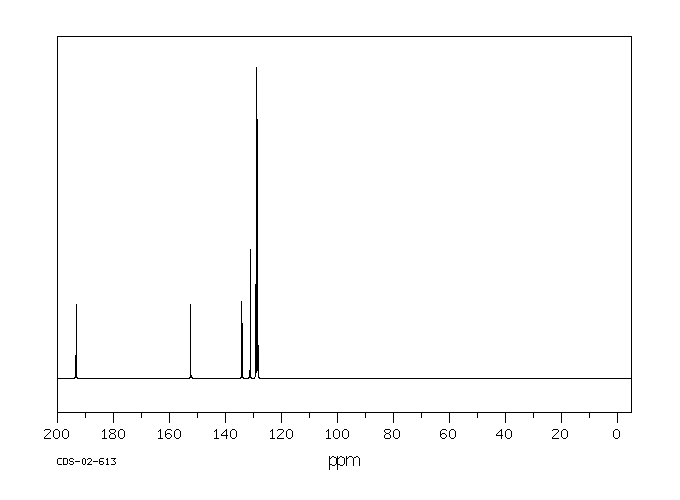
碳谱13CNMR
-
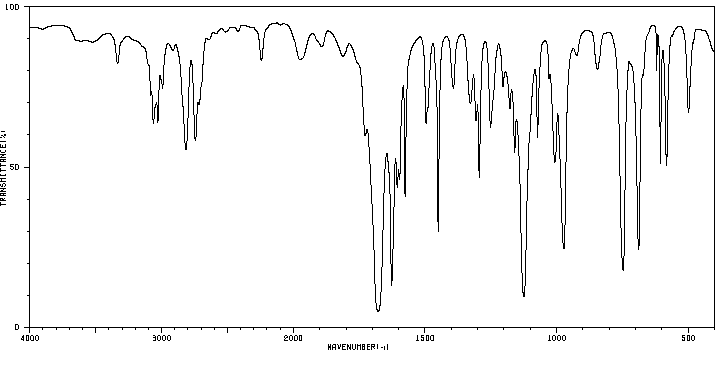
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
间三氟甲基肉桂醛
间三氟甲基肉桂醛
邻硝基肉桂醛
邻氯肉桂醛
邻氟肉桂醛
茚-2-甲醛
苯甲酸,2-[[2-羟基-3-(2,3,6,7-四氢-3,7-二甲基-2,6-二羰基-1H-嘌呤-1-基)丙基][3-(三氟甲基)苯基]氨基]-
肉桂醛
甲位戊基桂醛
对硝基肉桂醛
对甲基肉桂醛
对氟肉桂醛
反式肉桂醛
反式-肉桂醛
反式-alpha-甲基肉桂醛
反-4-氟肉桂醛
反-4-(二乙胺基)肉桂醛
厄洛替尼杂质46
亚苄基丙二醛
丁醛,4-氯-2-[氯(4-甲基苯基)亚甲基]-
α-甲基肉桂醛
α-甲基肉桂醛
α-溴代肉桂醛
α-氯代肉桂醛
α-己基肉桂醛
alpha-乙基肉桂醛
N-乙酰基-3-氨基-3-苯基-2-丙烯醛
8-溴-6-氯-2H-苯并吡喃-3-甲醛
6-羟基苯并吡喃-3-甲醛
6,8-二溴-2H-色烯-3-甲醛
5-甲氧基-2H-色烯-3-甲醛
5-氯-2-(氯苯基亚甲基)戊醛
4-羟基肉桂醛
4-硝基肉桂醛
4-甲氧基肉桂醛
4-甲氧基肉桂醛
4-溴肉桂醛
4-氯肉桂醛
4-叔-丁基-2-甲基肉桂醛
4-二甲基氨基肉桂醛
4-三氟甲氧基桂皮醛
3-苯基戊-2-烯醛
3-苯基壬-2-烯-4-炔醛
3-苯基-3-苯基硫代-2-丙烯醛
3-甲基-1H-茚-2-甲醛
3-溴肉桂醛
3-溴-3-苯基丙-2-烯醛
3-溴-3-(4-氯苯基)丙烯醛
3-氯肉桂醛
3-氯-3-苯基丙烯醛