异丙苯 | 98-82-8
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:−96 °C(lit.)
-
沸点:152-154 °C(lit.)
-
密度:0.864 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
-
蒸气密度:4.1 (vs air)
-
闪点:115 °F
-
溶解度:0.05g/l
-
介电常数:2.4(20℃)
-
暴露限值:Flammable liquid; flash point (closed cup) 36°C (97°F) (NFPA 1986), 39°C (102°F) (Merck 1996), 35.5°C (96°F) (Meyer 1989); vapor pressure 8 torr at 20°C (68°F); vapor density 4.1 (air=1); the vapor is heavier than air and may travel a considerable distance to a nearby ignition source and flash back; autoignition temperature 425°C (797°F); fire- extinguishing agent: dry chemical, foam, or CO2; use a water spray to keep fire- exposed containers cool and to disperse the vapors。Cumene forms explosive mixtures in the air within the range 0.9–6.5% by volume in air. Cumene may form peroxide on prolonged exposure to air. It should be tested for peroxides before it is subjected to distillation or evaporation。.
-
LogP:3.55 at 20℃
-
物理描述:Cumene appears as a clear colorless liquid with an aromatic odor. Flash point 115°F. Less dense than water and insoluble in water. Vapors heavier than air. May be moderately toxic by inhalation, ingestion and skin absorption.
-
颜色/状态:Colorless liquid
-
气味:Gasoline-like odor
-
蒸汽密度:4.1 (Air = 1)
-
蒸汽压力:4.5 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
亨利常数:Henry's Law constant = 1.15X10-2 atm-cu m/mol at 25 °C
-
大气OH速率常数:6.50e-12 cm3/molecule*sec
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
自燃温度:420 °C
-
分解:Hazardous decomposition products: Toxic gases and vapors (such as carbon monoxide) may be released.
-
粘度:0.737 mPa.sec at 25 °C
-
汽化热:45.13 kJ/mol at 25 °C
-
表面张力:27.69 mN/m at 25 °C
-
电离电位:8.75 eV
-
气味阈值:Odor Threshold Low: 0.008 [mmHg]; Odor Threshold High: 0.13 [mmHg]; Detection odor threshold from AIHA (mean = 0.032 ppm)
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.4915
-
保留指数:914.3 ;906.9 ;910.8 ;936.1 ;907.2 ;907.9 ;910 ;913 ;909.43 ;909.62 ;910 ;923 ;909.07 ;905.1 ;906 ;910.7 ;911.3 ;909 ;911 ;909.1 ;909.82 ;912.2 ;930 ;930 ;935.1 ;942.5 ;912 ;909 ;909 ;919 ;919 ;919.2 ;919.5 ;920.1 ;920.7 ;919 ;920 ;920 ;920 ;920 ;920 ;920 ;916 ;919 ;919 ;920 ;922 ;909.3 ;909.8 ;911.3 ;921 ;915 ;929 ;920 ;926 ;932 ;909 ;920.4 ;925.6 ;931.8 ;915.5 ;922 ;927 ;930 ;932 ;929 ;932 ;935 ;937 ;940 ;910.1 ;910.1 ;910.1 ;910.1 ;910.1 ;910.1 ;916 ;912 ;915 ;932 ;920 ;908.4 ;915 ;910 ;922.1 ;915.8 ;927.7 ;911.6 ;909 ;920 ;919 ;912.8 ;956 ;912 ;908 ;910.7 ;917.8 ;926.5 ;914 ;925 ;914 ;923 ;911 ;920 ;918 ;919 ;920 ;920 ;920 ;914 ;908 ;919 ;918.9 ;908 ;926 ;912 ;920 ;920 ;925 ;926 ;916 ;906 ;905 ;925 ;938 ;961 ;906 ;913 ;915 ;921 ;905 ;910 ;903 ;917 ;919 ;916 ;929 ;929 ;925
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):3.7
-
重原子数:9
-
可旋转键数:1
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.333
-
拓扑面积:0
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:0
ADMET
安全信息
-
职业暴露等级:A
-
职业暴露限值:TWA: 50 ppm (245 mg/m3) [skin]
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:3
-
立即威胁生命和健康浓度:900 ppm [10% LEL]
-
危险品标志:Xn,N
-
安全说明:S24,S37,S61,S62
-
危险类别码:R51/53,R10,R65,R37
-
WGK Germany:1
-
海关编码:2902700000
-
危险品运输编号:UN 1918 3/PG 3
-
危险类别:3
-
RTECS号:GR8575000
-
包装等级:III
-
储存条件:储存注意事项: - 储存于阴凉、通风的库房。 - 远离火种、热源,库温不宜超过37℃。 - 保持容器密封,并与氧化剂分开存放,切忌混储。 - 使用防爆型照明和通风设施,禁止使用易产生火花的机械设备和工具。 - 储区应备有泄漏应急处理设备和合适的收容材料。
制备方法与用途
化学性质
异丙苯是一种无色液体,不溶于水,但能溶于乙醇、乙醚、苯和四氯化碳。
用途
异丙苯主要用于生产苯酚和丙酮,也用作提高燃料油辛烷值的添加剂、合成香料和聚合引发剂的原料。此外,它还是制造苯酚的重要中间体,并且是除草剂异丙隆的中间体。绝大部分(98%以上)的异丙苯用于生产苯酚和丙酮,一小部分则用作添加剂、合成香料以及聚合反应引发剂等。该物质也可作为色谱分析标准物质或有机合成原料及发动机燃料辛烷值的提升剂。
生产方法
异丙苯由苯与丙烯进行烷基化反应制得。通常采用三氯化铝为催化剂,氯化氢为促进剂,在常压和95℃左右温度下反应。除了生成异丙苯外,还会产生二异丙苯、三异丙苯等多烷基副产物。为了减少副反应,可适当增加苯的比例(苯与丙烯的摩尔比约为3),使三氯化铝在反应液中的含量维持在3%-8%,并在较低的丙烯浓度下进行反应。通过将反应压力提高到0.5-0.6MPa,可以提高反应器的生产能力并减少尾气中苯的损失。反应后所得烷基化液体冷却、沉淀分离出固体(三氯化铝与多异丙苯络合物)循环使用。随后,经水解、中和及精馏步骤制得异丙苯。另一种气相法工艺则是将液态苯和丙烯通过载有磷酸的氧化铝或硅酸铝催化床层进行催化烷基化反应,其压力为1.5-40MPa,温度约250℃。目前工业上主要采用上述液相法生产异丙苯。
类别
易燃液体
毒性分级
中毒
急性毒性
口服 - 大鼠 LD₅₀: 1,400 毫克/公斤;小鼠 LD₅₀: 12,750 毫克/公斤
刺激数据
皮肤 - 兔子 100 毫克/24小时 中度;眼睛 - 兔子 500 毫克/24小时 轻度
爆炸物危险特性
与空气混合可爆
可燃性危险特性
遇明火、高温或氧化剂易燃,燃烧时产生刺激烟雾
储运特性
库房需通风并保持低温干燥;应与其他氧化剂分开存放
职业标准
时间加权平均容许浓度(TWA): 245 毫克/立方米;短时间接触容许浓度(STEL): 370 毫克/立方米
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 叔丁基苯 tert-butylbenzene 98-06-6 C10H14 134.221 4-异丙基甲苯 4-methylisopropylbenzene 99-87-6 C10H14 134.221 1,4-二异丙基苯 1,4-bis(1-methylethyl)benzene 100-18-5 C12H18 162.275 乙基苯 ethylbenzene 100-41-4 C8H10 106.167 β-溴代异丙基苯 1-bromo-2-phenylpropane 1459-00-3 C9H11Br 199.09 环丙基苯 cyclopropylbenzene 873-49-4 C9H10 118.178 仲丁基苯 2-butylbenzene 135-98-8 C10H14 134.221 2-苯基-1-丙醇 (RS)-2-phenyl-1-propanol 1123-85-9 C9H12O 136.194 1,3-二异丙基苯 1,3-diisopropylbenzene 99-62-7 C12H18 162.275 三異丙苯 1,3,5-triisopropyl benzene 717-74-8 C15H24 204.356 4-异丙基苯酚 4-Isopropylphenol 99-89-8 C9H12O 136.194 4-异丙基苯甲醇 cuminol 536-60-7 C10H14O 150.221 4-溴异丙苯 2-(4-bromophenyl)propane 586-61-8 C9H11Br 199.09 正丙基苯 Propylbenzene 103-65-1 C9H12 120.194 4-异丙基苯甲醛 (4-isopropylbenzaldehyde) 122-03-2 C10H12O 148.205 2-苯基-2-丙醇 1-methyl-1-phenylethyl alcohol 617-94-7 C9H12O 136.194 Alpha,Alpha-二甲基苄胺 2-phenyl-2-propylamine 585-32-0 C9H13N 135.209 叔戊基苯 tery-amylbenzene 2049-95-8 C11H16 148.248 烯丙苯 allylbenzene 300-57-2 C9H10 118.178 3-苯基丁醛 3-Phenylbutyraldehyde 16251-77-7 C10H12O 148.205 —— α,α-dimethylbenzyl iodide 54290-22-1 C9H11I 246.091 二异丙苯 1,2-diisopropylbenzene 577-55-9 C12H18 162.275 ALFA, ALFA-二甲基苄氯 Cumyl chloride 934-53-2 C9H11Cl 154.639 丁苯 1-butylbenzene 104-51-8 C10H14 134.221 m-氯枯烯 m-chlorocumene 7073-93-0 C9H11Cl 154.639 3-异丙基苯酚 3-isopropylhydroxybenzene 618-45-1 C9H12O 136.194 三甲基苯甲醇 p-cymene-8-ol 1197-01-9 C10H14O 150.221 4-异丙基苯甲醚 1-methoxy-4-(1-methylethyl)benzene 4132-48-3 C10H14O 150.221 2-碘异丙基苯 2-isopropyliodobenzene 19099-54-8 C9H11I 246.091 1,2-二苯基丙烷 1,2-diphenylpropane 5814-85-7 C15H16 196.292 异丙苯酚 2-(1-methylethyl)phenol 88-69-7 C9H12O 136.194 邻二乙苯 1,2-Diethylbenzene 135-01-3 C10H14 134.221 (R)-(+)-1-苯基乙醇 (R)-1-phenylethanol 1517-69-7 C8H10O 122.167 苏合香醇 1-Phenylethanol 98-85-1 C8H10O 122.167 2-异丙基苯硫酚 2-isopropylbenzenethiol 6262-87-9 C9H12S 152.26 苯乙酮 acetophenone 98-86-2 C8H8O 120.151 1-溴-2-异丙基苯 1-bromo-2-isopropylbenzene 7073-94-1 C9H11Br 199.09 - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 4-异丙基甲苯 4-methylisopropylbenzene 99-87-6 C10H14 134.221 叔丁基苯 tert-butylbenzene 98-06-6 C10H14 134.221 1,4-二异丙基苯 1,4-bis(1-methylethyl)benzene 100-18-5 C12H18 162.275 乙基苯 ethylbenzene 100-41-4 C8H10 106.167 —— p-tert.-Butyl-cumol 4132-49-4 C13H20 176.302 对二叔丁基苯 1,4-di-tert-butylbenzene 1012-72-2 C14H22 190.329 β-溴代异丙基苯 1-bromo-2-phenylpropane 1459-00-3 C9H11Br 199.09 仲丁基苯 2-butylbenzene 135-98-8 C10H14 134.221 P-伞花烃 m-cymene 535-77-3 C10H14 134.221 —— (1-chloropropan-2-yl)benzene 824-47-5 C9H11Cl 154.639 2-苯基丙醛 2-Phenylpropanal 93-53-8 C9H10O 134.178 2-苯基丙烷-1-硫醇 2-phenylpropane-1-thiol 34366-19-3 C9H12S 152.26 2-苯基-1-丙醇 (RS)-2-phenyl-1-propanol 1123-85-9 C9H12O 136.194 1,3-二异丙基苯 1,3-diisopropylbenzene 99-62-7 C12H18 162.275 4-异丙基苯乙醇 2-(4-isopropylphenyl)ethanol 10099-57-7 C11H16O 164.247 1-烯丙基-4-异丙基苯 1-allyl-4-isopropylbenzene 3897-64-1 C12H16 160.259 1-氯-4-丙-2-基苯 1-chloro-4-isopropylbenzene 2621-46-7 C9H11Cl 154.639 三異丙苯 1,3,5-triisopropyl benzene 717-74-8 C15H24 204.356 1-甲基-3,5-二(丙-2-基)苯 1-methyl-3,5-diisopropyl benzene 3055-14-9 C13H20 176.302 4-异丙基苯胺 4-Isopropylaniline 99-88-7 C9H13N 135.209 4-异丙基苯酚 4-Isopropylphenol 99-89-8 C9H12O 136.194 对异丙基苯硫酚 4-mercapto-cumene 4946-14-9 C9H12S 152.26 4-异丙基氟苯 1-fluoro-4-isopropylbenzene 403-39-4 C9H11F 138.185 邻-异丙基苯 2-isopropyltoluene 527-84-4 C10H14 134.221 1-碘-4-异丙苯 4-iodocumene 17356-09-1 C9H11I 246.091 4-溴异丙苯 2-(4-bromophenyl)propane 586-61-8 C9H11Br 199.09 4-异丙基苯乙烯 4-isopropylstyrene 2055-40-5 C11H14 146.232 4-异丙基苯甲醇 cuminol 536-60-7 C10H14O 150.221 正丙基苯 Propylbenzene 103-65-1 C9H12 120.194 4-异丙基苯甲醛 (4-isopropylbenzaldehyde) 122-03-2 C10H12O 148.205 4-异丙基苄氯 4-isopropylbenzyl chloride 2051-18-5 C10H13Cl 168.666 4-异丙基苯甲腈 p-Cyanocumen 13816-33-6 C10H11N 145.204 对异丙基溴苄 4-i-propylbenzyl bromide 73789-86-3 C10H13Br 213.117 —— 1-(β-bromo-isopropyl)-4-isopropyl-benzene 91560-81-5 C12H17Br 241.171 —— 1-sec-butyl-4-isopropyl-benzene 27702-09-6 C13H20 176.302 2-苯基-2-丙醇 1-methyl-1-phenylethyl alcohol 617-94-7 C9H12O 136.194 —— 1-(β-chloro-isopropyl)-4-isopropyl-benzene —— C12H17Cl 196.72 Alpha,Alpha-二甲基苄胺 2-phenyl-2-propylamine 585-32-0 C9H13N 135.209 1-异丙基-3-(2-甲基-2-丙基)苯 1-Isopropyl-3-tert.-butyl-benzol 20033-12-9 C13H20 176.302 4-(1-甲乙基)苯丙醛 3-(4'-isopropylphenyl)propanal 7775-00-0 C12H16O 176.258 叔戊基苯 tery-amylbenzene 2049-95-8 C11H16 148.248 2-氟丙烷-2-基苯 (2-fluoropropan-2-yl)benzene 74185-81-2 C9H11F 138.185 4-叔丁基苯酚 4-tert-butylphenol 98-54-4 C10H14O 150.221 —— 2-bromo-2-phenylpropane 3575-19-7 C9H11Br 199.09 异丙苯-D1 isopropylbenzene-d1 4019-54-9 C9H12 121.186 —— α,α-dimethylbenzyl iodide 54290-22-1 C9H11I 246.091 二异丙苯 1,2-diisopropylbenzene 577-55-9 C12H18 162.275 ALFA, ALFA-二甲基苄氯 Cumyl chloride 934-53-2 C9H11Cl 154.639 2-甲基-2-苯基丙烷-1-醇 2-methyl-2-phenyl-propan-1-ol 2173-69-5 C10H14O 150.221 —— 4-(4-isopropylphenyl)butanal 62518-63-2 C13H18O 190.285 m-氯枯烯 m-chlorocumene 7073-93-0 C9H11Cl 154.639 —— p-(methoxymethyl)-isopropylbenzene 73789-85-2 C11H16O 164.247 异丁基苯 1-phenyl-2-methylpropane 538-93-2 C10H14 134.221 3-异丙基苯酚 3-isopropylhydroxybenzene 618-45-1 C9H12O 136.194 —— 4-(4-Propan-2-ylphenyl)butan-1-ol 1082600-70-1 C13H20O 192.301 3-异丙基苯胺 3-Isopropylaniline 5369-16-4 C9H13N 135.209 (1-甲基戊基)-苯 2-phenylhexane 6031-02-3 C12H18 162.275 —— 1-(4-isopropylphenyl)ethanol 1475-10-1 C11H16O 164.247 —— m-Fluorcumol 2193-38-6 C9H11F 138.185 1-溴-3-异丙基苯 1-bromo-3-isopropylbenzene 5433-01-2 C9H11Br 199.09 1,2-二苯乙烷 1,1'-(1,2-ethanediyl)bisbenzene 103-29-7 C14H14 182.265 4'-异丙基苯乙酮 4-isopropylacetophenone 645-13-6 C11H14O 162.232 —— 1-benzyl-4-isopropylbenzene 886-58-8 C16H18 210.319 —— 2-isopropyltriphenylene —— C21H18 270.374 —— 5-(4-isopropylphenyl)pentanal 1310312-76-5 C14H20O 204.312 —— Dicumylmethan 25566-92-1 C19H24 252.4 —— 1-isopropyl-4-tert-pentyl-benzene 125340-91-2 C14H22 190.329 —— 4-isopropyl-N-methylaniline 6950-79-4 C10H15N 149.236 —— 3-isopropylbenzonitrile 40751-59-5 C10H11N 145.204 兔耳草醛 cyclamenaldehyde 103-95-7 C13H18O 190.285 —— 1-chloro-2-(4-isopropylphenyl)-2-methylpropane 105737-88-0 C13H19Cl 210.747 3-异丙基苯乙烯 3-isopropyl-styrene 19789-34-5 C11H14 146.232 —— 3-<4-Isopropyl-phenyl>-butanol-(1) 18846-82-7 C13H20O 192.301 2-碘异丙基苯 2-isopropyliodobenzene 19099-54-8 C9H11I 246.091 4-(4-异丙基苯基)-2-丁酮 4-(4-Isopropyl-phenyl)-butan-2-on 10528-64-0 C13H18O 190.285 —— 3-(4'-isopropylphenyl)-3-methylpropanal 54437-50-2 C13H18O 190.285 2-异丙基苯胺 2-isopropylaniline 643-28-7 C9H13N 135.209 —— 4-Isopropyl-stilben 20884-07-5 C17H18 222.33 异丙苯酚 2-(1-methylethyl)phenol 88-69-7 C9H12O 136.194 1-氯-2-丙-2-基苯 2-chlorocumene 2077-13-6 C9H11Cl 154.639 —— dicymyl ether 146689-61-4 C20H26O 282.426 —— 1-isopropyl-4-(phenylethynyl)benzene 29778-23-2 C17H16 220.314 苏合香醇 1-Phenylethanol 98-85-1 C8H10O 122.167 2,3-二甲基-2-苯基丁烷 2,3-dimethyl-2-phenylbutane 26356-11-6 C12H18 162.275 2-氟异丙基苯 1-fluoro-2-isopropylbenzene 2022-67-5 C9H11F 138.185 (1,1-二甲基丁基)苯 2-methyl-2-phenylpentane 1985-57-5 C12H18 162.275 2-异丙基苯硫酚 2-isopropylbenzenethiol 6262-87-9 C9H12S 152.26 1-异丙基-4-(三氟甲基)苯 4-(trifluoromethyl)cumene 32445-99-1 C10H11F3 188.193 苯乙酮 acetophenone 98-86-2 C8H8O 120.151 1-溴-2-异丙基苯 1-bromo-2-isopropylbenzene 7073-94-1 C9H11Br 199.09 - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Barnett; Sanders, Journal of the Chemical Society, 1933, p. 434,436摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:Gerhardt; Cahours, Annales de Chimie (Cachan, France), 1841, vol. <3> 1, p. 87摘要:DOI:
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:一种一锅法烯烃需氧环氧化制备环氧化物的方法摘要:一种一锅法烯烃需氧环氧化制备环氧化物的方法,属于有机合成技术领域。将烯烃、烷基芳烃类化合物、碱加入溶剂中,或直接将烯烃、烷基芳烃类化合物、碱三者混合,在空气或氧气氛围中,升温至70~160℃温度,反应1~48h,烯烃在烷基芳烃类化合物、碱和空气(或氧气)存在的条件下直接氧化为对应的环氧化物,收率高达99%。反应过程中,生成的烷基过氧化物原位生成、原位消耗,使其浓度保持在较低水平;而且生成的烷基过氧自由基也可以与烯烃反应,进一步生成其过氧化物,提高效率。本发明操作简单、条件温和、原料成本低、无需特殊的复杂设备,具有良好的工业应用前景。公开号:CN110590712B
文献信息
-
氢化反应方法申请人:郑州大学公开号:CN111099986B公开(公告)日:2023-02-03
-
Kinetics of C–H bond and alkene oxidation by trans-dioxoruthenium(<scp>VI</scp>) porphyrins作者:Clare Ho、Wa-Hung Leung、Chi-Ming CheDOI:10.1039/dt9910002933日期:——characterized, and the kinetics and mechanism of oxidation of the C–H bond and alkenes investigated. The complexes were selective towards tertiary C–H bonds in saturated alkanes but were almost inactive towards secondary C–H bonds. However, they were reactive towards aromatic hydrocarbons and the second-order rate constants (k2) for the oxidation of ethylbenzene and cumene by [Ru(tpp)O2](tpp = 5, 10, 15, 20-teA.合成并表征了一系列[Ru VI LO 2 ]配合物(H 2 L =对位取代的四苯基卟啉),并研究了C–H键和烯烃的氧化动力学和机理。该络合物对饱和烷烃中的C–H键具有选择性,但对C–H二级键几乎没有活性。但是,它们对芳烃有反应性,[Ru(tpp)O 2 ](tpp = 5,10,15,20-四苯基卟啉)氧化乙苯和枯烯的二级速率常数(k 2)为2.21。 ×10 –4和3.16×10 –4 dm 3 mol –1s –1分别。发现环己烯被[Ru(tpp)O 2 ]烯丙基氧化的动力学同位素效应(K H / K D)为11.7 。CH 2 Cl 2 -MeOH混合物中烯烃氧化的主要有机产物是环氧化物,[Ru(tpp)O 2 ]得到的单体产物为[Ru IV(tpp)O]·EtOH。或[Ru IV(tpp)(OH)2 ·] EtOH。与[Ru VI(oep)O 2 ](oep = 2,3,7,8
-
Metal-free photoinduced C(sp3)–H borylation of alkanes作者:Chao Shu、Adam Noble、Varinder K. AggarwalDOI:10.1038/s41586-020-2831-6日期:2020.10.29precious-metal catalysts for C-H bond cleavage and, as a result, display high selectivity for borylation of aromatic C(sp2)-H bonds over aliphatic C(sp3)-H bonds4. Here we report a mechanistically distinct, metal-free borylation using hydrogen atom transfer catalysis5, in which homolytic cleavage of C(sp3)-H bonds produces alkyl radicals that are borylated by direct reaction with a diboron reagent. The reaction硼酸及其衍生物是化学科学中最有用的试剂之一,其应用范围涵盖药物、农用化学品和功能材料。催化 CH 硼酸化是将这些和其他硼基团引入有机分子的有效方法,因为它可用于直接官能化原料化学品的 CH 键,而无需底物预活化1-3。这些反应传统上依赖贵金属催化剂进行 CH 键断裂,因此,与脂肪族 C(sp3)-H 键相比,芳族 C(sp2)-H 键的硼化显示出高选择性。在这里,我们报告了使用氢原子转移催化的机械上独特的无金属硼化反应 5,其中 C(sp3)-H 键的均裂产生的烷基自由基通过与二硼试剂直接反应而被硼化。该反应通过基于 N-烷氧基邻苯二甲酰亚胺的氧化剂和氯氢原子转移催化剂之间的紫光光诱导电子转移进行。不同寻常的是,更强的甲基 CH 键优先于较弱的二级、三级甚至苄基 CH 键被硼化。机理研究表明,高甲基选择性是形成氯自由基 - 硼酸盐复合物的结果,该复合物选择性地切割空间不受阻碍的 CH 键。通过使用光致氢原子转移策略,
-
Ambient Hydrogenation and Deuteration of Alkenes Using a Nanostructured Ni‐Core–Shell Catalyst作者:Jie Gao、Rui Ma、Lu Feng、Yuefeng Liu、Ralf Jackstell、Rajenahally V. Jagadeesh、Matthias BellerDOI:10.1002/anie.202105492日期:2021.8.16selective hydrogenation and deuteration of a variety of alkenes is presented. Key to success for these reactions is the use of a specific nickel-graphitic shell-based core–shell-structured catalyst, which is conveniently prepared by impregnation and subsequent calcination of nickel nitrate on carbon at 450 °C under argon. Applying this nanostructured catalyst, both terminal and internal alkenes, which
-
Chemoselective Hydrogenation of Olefins Using a Nanostructured Nickel Catalyst作者:Mara Klarner、Sandra Bieger、Markus Drechsler、Rhett KempeDOI:10.1002/zaac.202100124日期:2021.11.25pharmaceutical industry. Here, we report on a nanostructured nickel catalyst that enables the selective hydrogenation of purely aliphatic and functionalized olefins under mild conditions. The earth-abundant metal catalyst allows the selective hydrogenation of sterically protected olefins and further tolerates functional groups such as carbonyls, esters, ethers and nitriles. The characterization of our
表征谱图
-
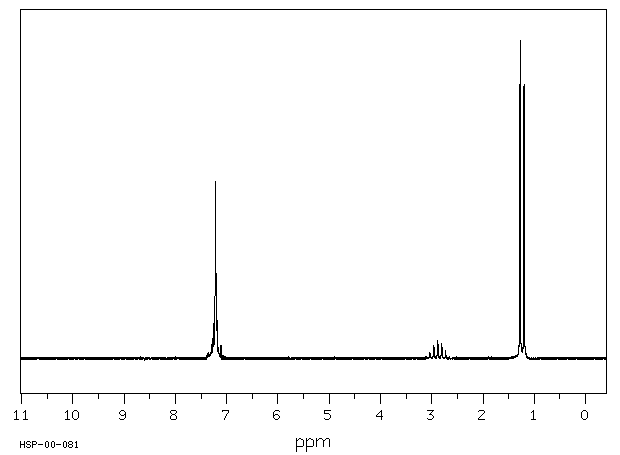
氢谱1HNMR
-
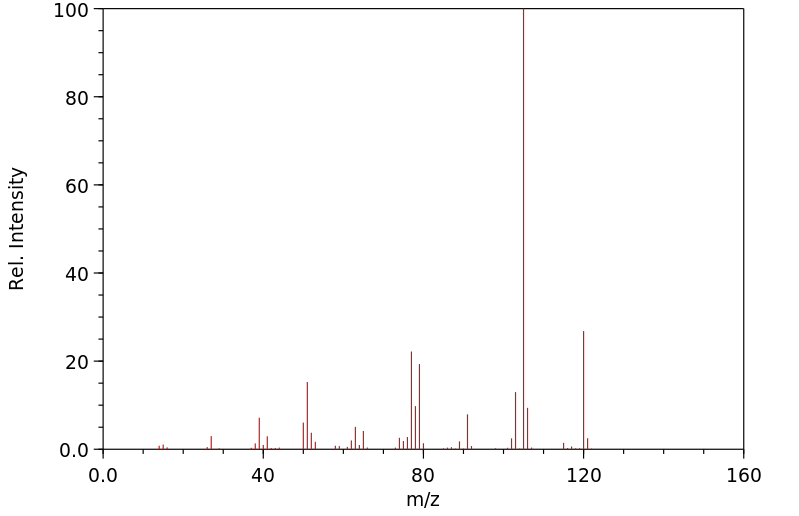
质谱MS
-
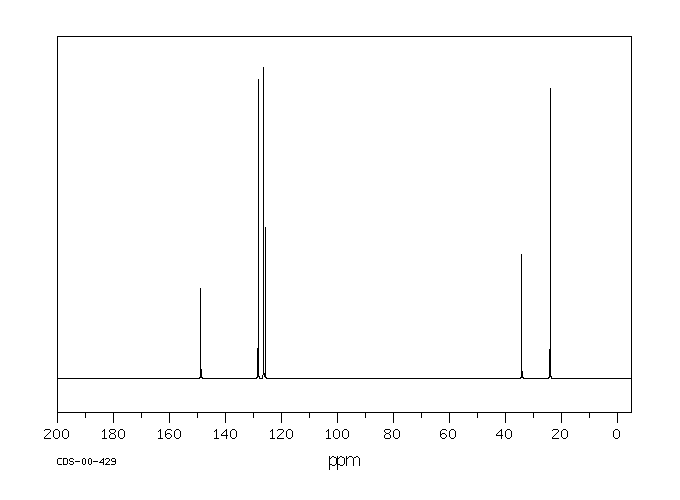
碳谱13CNMR
-
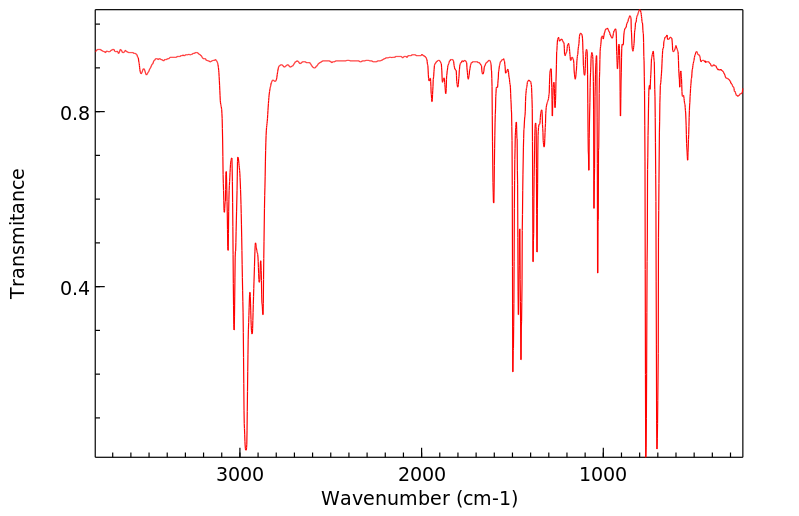
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息