硝基苯 | 98-95-3
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:5-6 °C (lit.)
-
沸点:210-211 °C (lit.)
-
密度:1.196 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
-
蒸气密度:4.2 (vs air)
-
闪点:190 °F
-
溶解度:1.90g/l
-
介电常数:35.7(20℃)
-
暴露限值:TLV-TWA 1 ppm (~5 mg/m3) (ACGIH, MSHA, and OSHA); IDLH 200 ppm (NIOSH).
-
LogP:1.86 at 24.5℃ and pH7.9
-
物理描述:Nitrobenzene appears as a pale yellow to dark brown liquid. Flash point 190°F. Very slightly soluble in water. Toxic by inhalation and by skin absorption. Combustion give toxic oxides of nitrogen. Density 10.0 lb /gal.
-
颜色/状态:Greenish-yellow crystals or yellow, oily liquid
-
气味:Odor of volatile oil almond
-
味道:Aqueous solutions are sweet tasting
-
蒸汽密度:4.3 (EPA, 1998) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:0.245 mm Hg at 25 °C (est)
-
亨利常数:2.40e-05 atm-m3/mole
-
大气OH速率常数:1.40e-13 cm3/molecule*sec
-
自燃温度:900 °F (482 °C)
-
分解:When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of /nitrogen oxides/.
-
粘度:1.863 mPa-s at 25 °C
-
燃烧热:-10,420 BTU/LB= -5,791 CAL/G= -242.5X10+5 J/KG
-
汽化热:55.01 kJ/mol at 25 °C
-
表面张力:46.34 mN/m at 20 °C
-
电离电位:9.92 eV
-
气味阈值:Odor detection in air: 1.46x10-2 mg/l /vapor/, purity not specified.
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.5562 at 20 °C
-
解离常数:pKa = 3.98 at 0 °C
-
保留指数:1049.2;1057.4;1058.3;1066.7;1068.5;1103;1103;1085;1114;1062;1076;1081;1046;1052;1059;1047;1056;1066;1076;1068;1073.8;1065;1062;1063.2;1046;1059;1062;1057.2;1057;1062.6;1046;1046
-
稳定性/保质期:
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):1.9
-
重原子数:9
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:45.8
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:2
ADMET
安全信息
-
职业暴露等级:B
-
职业暴露限值:TWA: 1 ppm (5 mg/m3) [skin]
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:6.1
-
立即威胁生命和健康浓度:200 ppm
-
安全说明:S16,S27,S28,S28A,S36/37,S45,S61,S7
-
危险品运输编号:UN 1662 6.1/PG 2
-
WGK Germany:2
-
海关编码:2904201000
-
危险类别:6.1
-
危险品标志:T,N
-
危险类别码:R51/53,R48/23/24,R40,R23/24/25,R62
-
RTECS号:DA6475000
-
包装等级:II
-
危险标志:GHS06,GHS08
-
危险性描述:H301 + H311 + H331,H351,H360F,H372,H412
-
危险性防范说明:P201,P280,P302 + P352 + P312,P304 + P340 + P312,P308 + P313
-
储存条件:储存时应注意以下事项:存放在阴凉通风的库房中,远离火源和热源,确保容器密封良好。与氧化剂、还原剂、碱类及食用化学品分开存放,严禁混合储存,并配备相应的消防设备。储区应配置泄漏应急处理设施以及合适的收容材料。
SDS
| 国标编号: | 61056 |
| CAS: | 98-95-3 |
| 中文名称: | 硝基苯 |
| 英文名称: | nitrobenzene;Oil of mirbane |
| 别 名: | 密斑油 |
| 分子式: | C 6 H 5 NO 2 |
| 分子量: | 123.11 |
| 熔 点: | 5.7℃ |
| 密 度: | 相对密度(水=1)1.20; |
| 蒸汽压: | 87.8℃ |
| 溶解性: | 不溶于水,溶于乙醇、乙醚、苯等多数有机溶剂 |
| 稳定性: | 稳定 |
| 外观与性状: | 淡黄色透明油状液体,有苦杏仁味 |
| 危险标记: | 14(剧毒品) |
| 用 途: | 用作溶剂,制造苯胺、染料等 |
2.对环境的影响: 一、健康危害 侵入途径:吸入、食入、经皮吸收。 健康危害:主要引起高铁血红蛋白血症。可引起溶血及肝损害。 急性中毒:有头痛、头晕、乏力、皮肤粘膜紫绀、手指麻木等症状;严重时可出现胸闷、呼吸困难、心悸,甚至心律紊乱、昏迷、抽搐、呼吸麻痹。有时中毒后出现溶血性贫血、黄疸、中毒性肝炎。 慢性中毒:可有神经衰弱综合征;慢性溶血时,可出现贫血、黄疸;还可引起中毒性肝炎。 二、毒理学资料及环境行为 急性毒性:LD50489mg/kg(大鼠经口);2100mg/kg(大鼠经皮);狗静脉150mg/kg,最小致死剂量;人(女性)经口200mg/kg,最小中毒剂量(血液毒性);人经口5mg/kg,最小中毒剂量(不悦感)。 致突变性:细胞遗传学分析:啤酒酵母菌10mmol/管。 生殖毒性:大鼠吸入最低中毒浓度(TCL0):5ppm(6小时),(90天,雄性),影响精子生成,影响睾丸、附睾和输精管。 污染来源:硝基苯是有机合成的原料,最重要的用途是生产苯胺染料,还是重要的有机溶剂。环境中的硝基苯主要来自化工厂、染料厂的废水废气,尤其是苯胺染料厂排出的污水中含有大量硝基苯。贮运过程中的意外事故,也会造成硝基苯的严重污染。 硝基苯在水中具有极高的稳定性。由于其密度大于水,进入水体的硝基苯会沉入水底,长时间保持不变。又由于其在水中有一定的溶解度,所以造成的水体污染会持续相当长的时间。硝基苯的沸点较高,自然条件下的蒸发速度较慢,与强氧化剂反应生成对机械震动很敏感的化合物,能与空气形成爆炸性混合物。倾翻在环境中的硝基苯,会散发出刺鼻的苦杏仁味。80℃以上其蒸气与空气的混合物具爆炸性,倾倒在水中的硝基苯,以黄绿色油状物沉在水底。当浓度为5mg/L时,被污染水体呈黄色,有苦杏仁味。当浓度达100mg/L时,水几乎是黑色,并分离出黑色沉淀。当浓度超过33mg/L时可造成鱼类及水生生物死亡。吸入、摄入或皮肤吸收均可引起人员中毒。中毒的典型症状是气短、眩晕、恶心、昏厥、神志不清、皮肤发蓝,最后会因呼吸衰竭而死亡。 危险特性:遇明火、高热或与氧化剂接触,有引起燃烧爆炸的危险。与硝酸反应强烈。 燃烧(分解)产物:一氧化碳、二氧化碳、氧化氮。 3.现场应急监测方法: 便携式气相色谱法《突发性环境污染事故应急监测与处理处置技术》万本太主编 4.实验室监测方法: 监测方法 来源 类别 气相色谱法 GB13194-91 水质 锌还原-盐酸萘乙二胺光度法 GB15501-95 空气 气相色谱法 《固体废弃物试验分析评价手册》中国环境监测总站等译 固体废弃物 还原-偶氮比色法 《水和废水监测分析方法》(第三版)国家环保局编 水和废水 5.环境标准: 中国 (TJ36-79) 车间空气中有害物质的最高容许浓度 5mg/m3[皮] 居住区大气中有害物质的最高容许浓度 0.01mg/m3(一次值) 中国(GB16297-1996) 大气污染物综合排放标准 ①最高允许排放浓度(mg/L) 16(表2);20(表1) ②最高允许排放速率(kg/h) 二级0.060~1.3(表2);0.05~1.1(表1) 三级0.080~1.7(表2);0.090~2.0(表1) ③无组织排放监控浓度限值(mg/m3) 0.040(表2);0.050(表1) 中国(GHZB1-1999) 地表水环境质量标准(I、II、III类水域特定值) 0.017mg/L 中国(GB8978-1996) 污水综合排放标准 一级:2.0mg/L 二级:3.0mg/L 三级:5.0mg/L 嗅觉阈浓度 5.12mg/m3 6.应急处理处置方法: 一、泄漏应急处理 迅速撤离泄漏污染区人员至安全区,并进行隔离,严格限制出入。切断火源。建议应急处理人员戴自给正压式呼吸器,穿防毒服。不要直接接触泄漏物。尽可能切断泄漏源。防止进入下水道、排洪沟等限制性空间。当硝基苯洒在地面时,立即用沙土、泥块阻断漏液的温延,配戴好面具、手套,将漏液或漏物收集在适当的容器内封存,用沙土或其它惰性材料吸收残液,转移到安全地带。立即仔细收集被污染土壤,转移到安全地带。当硝基苯倾倒在水面时,应迅速切断被污染水体的流动,以免污染扩散。中毒人员立即离开现场,到空气新鲜的地方,脱去被沾染的外衣,用大量的水冲洗皮肤,漱口,大量饮水,催吐,即送医院。着火时用大量水和干粉、泡沫、二氧化碳等灭火器灭火。接触硝基苯的人员严禁饮酒,以免加重加速毒性作用。沿地面加强通风,以驱赶硝基苯蒸气。 二、防护措施 呼吸系统防护:可能接触其蒸气时,佩戴过滤式防毒面具(半面罩)。紧急事态抢救或撤离时,建议佩戴自给式呼吸器。 眼睛防护:戴安全防护眼镜。 身体防护:穿透气型防毒服。 手防护:戴防苯耐油手套。 其它:工作现场禁止吸烟、进食和饮水。及时换洗工作服。工作前后不饮酒,用温水洗澡。注意检测毒物。实行就业前和定期的体检。 三、急救措施 皮肤接触:立即脱去被污染的衣着,用肥皂水和清水彻底冲洗皮肤。就医。 眼睛接触:提起眼睑,用流动清水或生理盐水冲洗。就医。 吸入:迅速脱离现场至空气新鲜处。保持呼吸道通畅。如呼吸困难,给输氧。如呼吸停止,立即进行人工呼吸。就医。 食入:饮足量温水,催吐,就医。 灭火方法:消防人员须佩戴防毒面具、穿全身消防服。喷水冷却容器,可能的话将容器从火场移至空旷处。灭火剂:雾状水、抗溶性泡沫、二氧化碳、砂土。
制备方法与用途
硝基苯是一种重要的有机化工原料,具有多种用途和生产工艺。以下是关于硝基苯的一些关键信息:
主要用途 生产方法-
传统间歇法硝化:
-
连续法硝化:
-
绝热硝化法:
- 可间歇或连续操作,通过利用反应产生的热量来浓缩硫酸。
- 存储条件:应存放在阴凉、干燥的库房中,避免接触火种和自燃物、氧化剂等易燃物质。
- 使用注意事项:在通风设施良好的环境中使用,并佩戴防毒面具,防止皮肤接触。
- 根据毒理学研究结果,硝基苯具有一定的毒性级别(中毒),需要谨慎处理。长期暴露可能导致头痛、贫血等症状。
- 通过合适的通风措施可以有效控制其浓度在安全范围内(如TLV-TWA为1PPM或5毫克/立方米)。
- 避免使用明火和高温,防止燃烧产生有毒氮氧化物烟雾。
- 在发生火灾时可采用泡沫、二氧化碳或砂土等灭火剂进行扑救,并保持库房内通风良好以降低危险性。
总之,硝基苯作为一种重要的化工原料,在生产和使用过程中需要严格遵守安全操作规程,确保人员健康及环境安全。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 硝基苯-15N 15N-nitrobenzene 3681-79-6 C6H5NO2 124.105 4-硝基苯胺 4-nitro-aniline 100-01-6 C6H6N2O2 138.126 对二硝基苯 para-dinitrobenzene 100-25-4 C6H4N2O4 168.109 4-硝基碘苯 4-Iodonitrobenzene 636-98-6 C6H4INO2 249.008 —— nitrobenzene-4-d 13122-36-6 C6H5NO2 124.103 4-硝基甲苯 1-methyl-4-nitrobenzene 99-99-0 C7H7NO2 137.138 间硝基苯胺 3-nitro-aniline 99-09-2 C6H6N2O2 138.126 1-溴-4-硝基苯 4-Bromonitrobenzene 586-78-7 C6H4BrNO2 202.007 对硝基氯苯 4-chlorobenzonitrile 100-00-5 C6H4ClNO2 157.556 对硝基苯酚 4-nitro-phenol 100-02-7 C6H5NO3 139.111 对氟硝基苯 4-Fluoronitrobenzene 350-46-9 C6H4FNO2 141.102 4-硝基苯肼 4-nitrophenylhydrazin 100-16-3 C6H7N3O2 153.14 2-硝基苯胺 2-nitro-aniline 88-74-4 C6H6N2O2 138.126 1,3-二硝基苯 1,3-Dinitrobenzene 99-65-0 C6H4N2O4 168.109 亚硝基苯 Nitrosobenzene 586-96-9 C6H5NO 107.112 —— p-nitro-N-nitroso aniline 40078-29-3 C6H5N3O3 167.124 苯基羟胺 N-Phenylhydroxylamine 100-65-2 C6H7NO 109.128 2-硝基萘 2-nitronaphthalene 581-89-5 C10H7NO2 173.171 N,N-二甲基对硝基苯胺 N,N-Dimethyl-4-nitroaniline 100-23-2 C8H10N2O2 166.18 3-硝基氯苯 3-Chloronitrobenzene 121-73-3 C6H4ClNO2 157.556 —— 4-nitrophenyl azide 1516-60-5 C6H4N4O2 164.123 1-碘-3-硝基苯 m-iodonitrobenzene 645-00-1 C6H4INO2 249.008 3-硝基甲苯 1-methyl-3-nitrobenzene 99-08-1 C7H7NO2 137.138 间氟硝基苯 3-fluoro-1-nitrobenzene 402-67-5 C6H4FNO2 141.102 间溴硝基苯 3-Bromonitrobenzene 585-79-5 C6H4BrNO2 202.007 对硝基苯甲醛 4-nitrobenzaldehdye 555-16-8 C7H5NO3 151.122 间硝基苯酚 meta-nitrophenol 554-84-7 C6H5NO3 139.111 对硝基苯甲醇 4-Nitrobenzyl alcohol 619-73-8 C7H7NO3 153.137 氯-(4-硝基苯基)汞 p-NO2-C6H4HgCl 20265-00-3 C6H4ClHgNO2 358.146 硝基氯苯 2-Chloronitrobenzene 88-73-3 C6H4ClNO2 157.556 3-硝基苯肼 3-nitrophenylhydrazine 619-27-2 C6H7N3O2 153.14 甲基硝基苯 1-methyl-2-nitrobenzene 88-72-2 C7H7NO2 137.138 —— nitrobenzene-d1 32488-51-0 C6H5NO2 124.103 1-氟-2-硝基苯 ortho-nitrofluorobenzene 1493-27-2 C6H4FNO2 141.102 2-硝基碘苯 o-nitroiodobenzene 609-73-4 C6H4INO2 249.008 1-溴-2-硝基苯 2-nitrophenyl bromide 577-19-5 C6H4BrNO2 202.007 1,2-二硝基苯 1,2-Dinitrobenzene 528-29-0 C6H4N2O4 168.109 4-硝基苯基硼酸 4-nitrophenylboronic acid 24067-17-2 C6H6BNO4 166.929 —— p-Iodoxynitrobenzene 16825-79-9 C6H4INO4 281.007 - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 硝基苯-15N 15N-nitrobenzene 3681-79-6 C6H5NO2 124.105 4-硝基苯胺 4-nitro-aniline 100-01-6 C6H6N2O2 138.126 对二硝基苯 para-dinitrobenzene 100-25-4 C6H4N2O4 168.109 4-硝基碘苯 4-Iodonitrobenzene 636-98-6 C6H4INO2 249.008 4-硝基甲苯 1-methyl-4-nitrobenzene 99-99-0 C7H7NO2 137.138 间硝基苯胺 3-nitro-aniline 99-09-2 C6H6N2O2 138.126 对硝基苯酚 4-nitro-phenol 100-02-7 C6H5NO3 139.111 1-溴-4-硝基苯 4-Bromonitrobenzene 586-78-7 C6H4BrNO2 202.007 对硝基氯苯 4-chlorobenzonitrile 100-00-5 C6H4ClNO2 157.556 —— 4-nitro<(18)O>phenol 20168-37-0 C6H5NO3 141.111 对氟硝基苯 4-Fluoronitrobenzene 350-46-9 C6H4FNO2 141.102 —— 1-[18F]fluoro-4-nitrobenzene 16447-86-2 C6H4FNO2 140.103 N-甲基对硝基苯胺 N-methyl(p-nitroaniline) 100-15-2 C7H8N2O2 152.153 1-硝基-3-亚硝基苯 1-nitro-3-nitrosobenzene 17122-21-3 C6H4N2O3 152.109 2-硝基苯胺 2-nitro-aniline 88-74-4 C6H6N2O2 138.126 1,3-二硝基苯 1,3-Dinitrobenzene 99-65-0 C6H4N2O4 168.109 亚硝基苯 Nitrosobenzene 586-96-9 C6H5NO 107.112 苯基羟胺 N-Phenylhydroxylamine 100-65-2 C6H7NO 109.128 2-硝基萘 2-nitronaphthalene 581-89-5 C10H7NO2 173.171 3-硝基氯苯 3-Chloronitrobenzene 121-73-3 C6H4ClNO2 157.556 4,4'-二硝基二苯胺 N,N-bis(p-nitrophenyl)amine 1821-27-8 C12H9N3O4 259.221 4-硝基二苯胺 4-nitrodiphenylamine 836-30-6 C12H10N2O2 214.224 4-氨基-4-硝基二苯胺 N-(4-nitrophenyl)-1,4-phenylenediamine 6149-34-4 C12H11N3O2 229.238 3-硝基甲苯 1-methyl-3-nitrobenzene 99-08-1 C7H7NO2 137.138 1-碘-3-硝基苯 m-iodonitrobenzene 645-00-1 C6H4INO2 249.008 间氟硝基苯 3-fluoro-1-nitrobenzene 402-67-5 C6H4FNO2 141.102 间溴硝基苯 3-Bromonitrobenzene 585-79-5 C6H4BrNO2 202.007 3-硝基苯硫酚 3-nitrothiophenol 3814-18-4 C6H5NO2S 155.177 N-乙基-对-硝基苯胺 N-Ethyl-4-nitroanilin 3665-80-3 C8H10N2O2 166.18 对乙基硝基苯 4-ethylnitrobenzene 100-12-9 C8H9NO2 151.165 1-(氯甲基)-4-硝基苯 4-nitrobenzyl chloride 100-14-1 C7H6ClNO2 171.583 间硝基苯酚 meta-nitrophenol 554-84-7 C6H5NO3 139.111 对硝基苯甲醛 4-nitrobenzaldehdye 555-16-8 C7H5NO3 151.122 对硝基溴化苄 1-bromomethyl-4-nitro-benzene 100-11-8 C7H6BrNO2 216.034 甲基硝基苯 1-methyl-2-nitrobenzene 88-72-2 C7H7NO2 137.138 硝苯酚 2-hydroxynitrobenzene 88-75-5 C6H5NO3 139.111 硝基氯苯 2-Chloronitrobenzene 88-73-3 C6H4ClNO2 157.556 —— nitrobenzene-d1 32488-51-0 C6H5NO2 124.103 4-亚硝基苯胺 4-nitrosoaniline 659-49-4 C6H6N2O 122.126 1-氟-2-硝基苯 ortho-nitrofluorobenzene 1493-27-2 C6H4FNO2 141.102 N-4-硝基苯基丙胺 N-propyl-p-nitroaniline 103796-64-1 C9H12N2O2 180.206 2-硝基碘苯 o-nitroiodobenzene 609-73-4 C6H4INO2 249.008 N-异丙基-4-硝基苯胺 N-isopropyl-p-nitroaniline 25186-43-0 C9H12N2O2 180.206 硝基联苯 1-phenyl-4-nitrobenzene 92-93-3 C12H9NO2 199.209 3,5-二氟硝基苯 1,3-difluoro-5-nitrobenzene 2265-94-3 C6H3F2NO2 159.092 1-溴-2-硝基苯 2-nitrophenyl bromide 577-19-5 C6H4BrNO2 202.007 4,4'-二硝基联苯 4,4'-dinitrobiphenyl 1528-74-1 C12H8N2O4 244.207 1,2-二硝基苯 1,2-Dinitrobenzene 528-29-0 C6H4N2O4 168.109 1,3-二溴-5-硝基苯 3,5-dibromonitrobenzene 6311-60-0 C6H3Br2NO2 280.903 对硝基异丙基苯 4-nitrocumene 1817-47-6 C9H11NO2 165.192 1-(二氯甲基)-4-硝基苯 1-dichloromethyl-4-nitrobenzene 619-78-3 C7H5Cl2NO2 206.028 对硝基苯乙腈 4-Nitrophenylacetonitrile 555-21-5 C8H6N2O2 162.148 alpha,alpha-二溴-4-硝基甲苯 1-dibromomethyl-4-nitro-benzene 619-75-0 C7H5Br2NO2 294.93 N-丁基-4-硝基苯胺 N-butyl-4-nitroaniline 58259-34-0 C10H14N2O2 194.233 - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Ricca, B., Gazzetta Chimica Italiana, 1927, vol. 57, p. 269 - 273摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:对乙酰基转移速率的去溶剂化评估:对酶催化的洞察摘要:酶通过各种物理有机机制极大地提高了反应速率。其中最具争议的问题之一是破产。为了对这种贡献进行定量评估,我们检查了乙酰基转移到氧二阴离子的过程。这是形成高能酰基磷酸酯的酶的模型反应。磷酸盐或膦酸盐与乙酸对硝基苯酯 (pNPA) 的水性反应显示出与使用单阴离子亲核试剂获得的布朗斯台德相关性以及其他更大的氧双阴离子(钼酸盐、砷酸盐和钒酸盐)的反应性的显着负偏差。这和其他数据表明去溶剂化对活化能有重要贡献。为了进一步研究这一点,我们研究了各种 DMSO(二甲亚砜)/H_2O 混合物对氯甲基膦酸酯反应的影响,和钼酸盐,关于与 pNPA 的反应。将 DMSO 浓度从 1% 增加到 90% (v/v) 会使这些反应中的每一个的二级速率常数增加 5000 多倍。这比对酚盐反应的增强作用大 1000 多倍对与中性亲核试剂(咪唑)反应的(抑制)作用超过 105 倍。对于氧二阴离子,外推到纯 DMSO 会产生约DOI:10.1021/ja993341p
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:环状二芳基碘盐在合成轴向手性天然产物类似物中的应用摘要:展示了环状二芳基碘鎓盐在生物活性天然产物类似物合成中的应用。轴向手性联芳基是通过环状二芳基碘鎓盐的对映选择性开环获得的。区域选择性硼化是通过八个步骤获得联苯酚关键中间体的两种对映体的关键。合成了 8,8”-氨基双黄酮,分析了其生物活性,并鉴定了优异构体。探讨了结构-活性关系。DOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.4c01308
文献信息
-
Novel processes for the preparation of adenosine compounds and intermediates thereto申请人:——公开号:US20030069423A1公开(公告)日:2003-04-10Novel processes for the preparation of adenosine compounds and intermediates thereto. The adenosine compounds prepared by the present processes may be useful as cardiovascular agents, more particularly as antihypertensive and anti-ischemic agents, as cardioprotective agents which ameliorate ischemic injury or myocardial infarct size consequent to myocardial ischemia, and as an antilipolytic agents which reduce plasma lipid levels, serum triglyceride levels, and plasma cholesterol levels. The present processes may offer improved yields, purity, ease of preparation and/or isolation of intermediates and final product, and more industrially useful reaction conditions and workability.
-
Cell adhesion-inhibiting antiinflammatory and immune-suppressive compounds申请人:Abbott Laboratories公开号:US20040116518A1公开(公告)日:2004-06-17The present invention relates to novel cinnamide compounds that are useful for treating inflammatory and immune diseases and cerebral vasospasm, to pharmaceutical compositions containing these compounds, and to methods of inhibiting inflammation or suppressing immune response in a mammal.本发明涉及新型肉桂酰胺化合物,用于治疗炎症和免疫性疾病以及脑血管痉挛,以及含有这些化合物的药物组合物,以及在哺乳动物中抑制炎症或抑制免疫反应的方法。
-
Compositions for Treatment of Cystic Fibrosis and Other Chronic Diseases申请人:Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated公开号:US20150231142A1公开(公告)日:2015-08-20The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising an inhibitor of epithelial sodium channel activity in combination with at least one ABC Transporter modulator compound of Formula A, Formula B, Formula C, or Formula D. The invention also relates to pharmaceutical formulations thereof, and to methods of using such compositions in the treatment of CFTR mediated diseases, particularly cystic fibrosis using the pharmaceutical combination compositions.
-
[EN] SUBSTITUTED BENZYLAMINE COMPOUNDS, THEIR USE IN MEDICINE, AND IN PARTICULAR THE TREATMENT OF HEPATITIS C VIRUS (HCV) INFECTION<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS DE BENZYLAMINE SUBSTITUÉS, LEUR UTILISATION EN MÉDECINE, EN PARTICULIER DANS LE TRAITEMENT D'UNE INFECTION PAR LE VIRUS DE L'HÉPATITE C (VHC)申请人:ASTEX THERAPEUTICS LTD公开号:WO2013064538A1公开(公告)日:2013-05-10The invention provides compounds of the formula (I): or a salt, N-oxide or tautomer thereof, wherein A is CH, CF or nitrogen; E is CH, CF or nitrogen; and R0 is hydrogen or C1-2 alkyl; R1a is selected from CONH2; CO2H; an optionally substituted acyclic C1-8 hydrocarbon group; and an optionally substituted monocyclic carbocyclic or heterocyclic group of 3 to 7 ring members, of which 0, 1, 2, 3 or 4 are heteroatom ring members selected from O, N and S; R2 is selected from hydrogen and a group R2a; R2a is selected from an optionally substituted acyclic d-8 hydrocarbon group; an optionally substituted monocyclic carbocyclic or heterocyclic group of 3 to 7 ring members, of which 0, 1 or 2 ring members are heteroatom ring members selected from O, N and S; and an optionally substituted bicyclic heterocyclic group of 9 or 10 ring members, of which 1 or 2 ring members are nitrogen atoms; wherein at least one of R1 and R2 is other than hydrogen; R3 is an optionally substituted 3- to 10-membered monocyclic or bicyclic carbocyclic or heterocyclic ring containing 0, 1, 2 or 3 heteroatom ring members selected from N, O and S; R4a is selected from halogen; cyano; C1-4 alkyl optionally substituted with one or more fluorine atoms; C1-4 alkoxy optionally substituted with one or more fluorine atoms; hydroxy-C1-4 alkyl; and C1-2 alkoxy-C1-4 alkyl; R5 is selected from hydrogen and a substituent R5a; and R5a is selected from C1-2 alkyl optionally substituted with one or more fluorine atoms; C1-3 alkoxy optionally substituted with one or more fluorine atoms; halogen; cyclopropyl; cyano; and amino, The compounds have activity against hepatitis C virus and can be used in the prevention or treatment of hepatitis C viral infections.该发明提供了以下式(I)的化合物,或其盐、N-氧化物或互变异构体,其中A为CH、CF或氮;E为CH、CF或氮;R0为氢或C1-2烷基;R1a选自CONH2;CO2H;一个可选择取代的非环状C1-8碳氢化合物基团;以及一个可选择取代的含有3至7个环成员的单环碳环或杂环基团,其中0、1、2、3或4个是从O、N和S中选择的杂原子环成员;R2选自氢和一个基团R2a;R2a选自一个可选择取代的非环状d-8碳氢化合物基团;一个可选择取代的含有3至7个环成员的单环碳环或杂环基团,其中0、1或2个环成员是从O、N和S中选择的杂原子环成员;以及一个可选择取代的含有9或10个环成员的双环杂环基团,其中1或2个环成员是氮原子;其中R1和R2中至少一个不是氢;R3选自一个可选择取代的含有0、1、2或3个从N、O和S中选择的杂原子环成员的3至10个成员的单环或双环碳环或杂环环;R4a选自卤素;氰基;C1-4烷基,可选择取代一个或多个氟原子;C1-4烷氧基,可选择取代一个或多个氟原子;羟基-C1-4烷基;和C1-2烷氧基-C1-4烷基;R5选自氢和一个取代基R5a;R5a选自C1-2烷基,可选择取代一个或多个氟原子;C1-3烷氧基,可选择取代一个或多个氟原子;卤素;环丙基;氰基;和氨基。这些化合物对丙型肝炎病毒具有活性,并可用于预防或治疗丙型肝炎病毒感染。
-
[EN] THIENOPYRIDONE DERIVATIVES AS AMP-ACTIVATED PROTEIN KINASE (AMPK) ACTIVATORS<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS DE THÉNOPYRIDONE COMME ACTIVATEURS DE LA PROTÉINE KINASE DÉPENDANTE DE L'AMP (AMPK)申请人:MERCK PATENT GMBH公开号:WO2009124636A1公开(公告)日:2009-10-15The present invention relates to compounds of formula (I) wherein R1, R2 and R3 are as defined in claim 1, including pharmaceutical compositions thereof and for their use in the treatment and/or prevention of diseases and disorders modulated by AMP agonists. The invention is also directed to intermediates and to a method of preparation of compounds of formula (I).本发明涉及式(I)的化合物,其中R1、R2和R3如权利要求1所定义,包括其药物组合物以及用于治疗和/或预防由AMP激动剂调节的疾病和紊乱的用途。该发明还涉及中间体和式(I)化合物的制备方法。
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
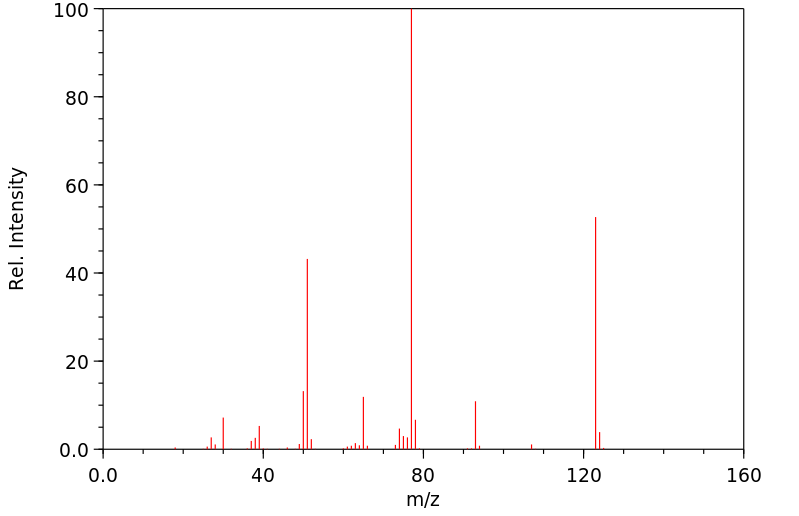
质谱MS
-
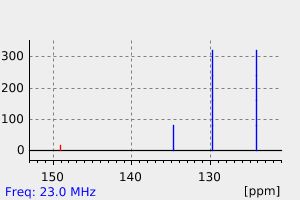
碳谱13CNMR
-
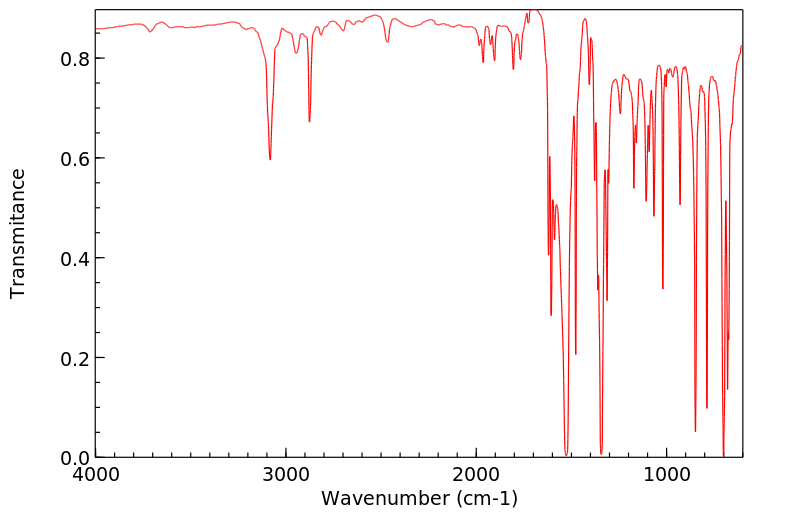
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息