代谢
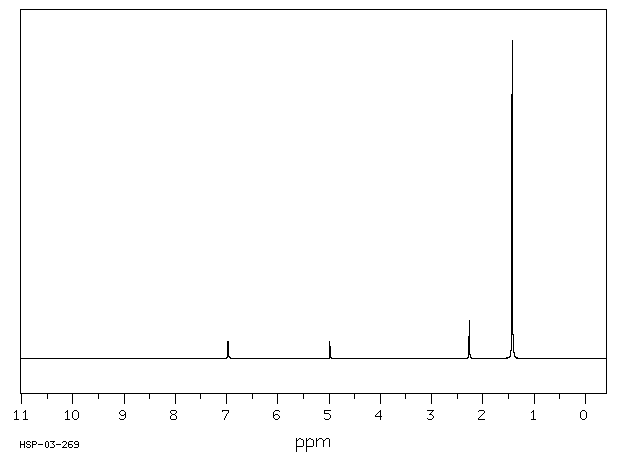
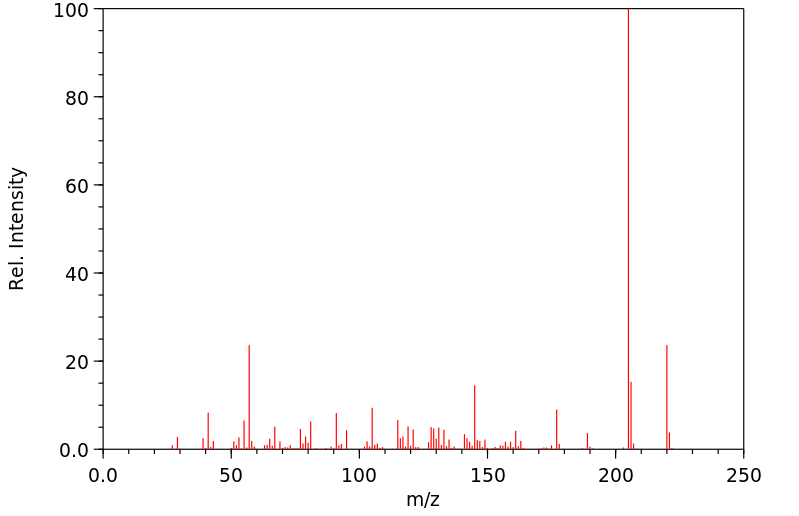
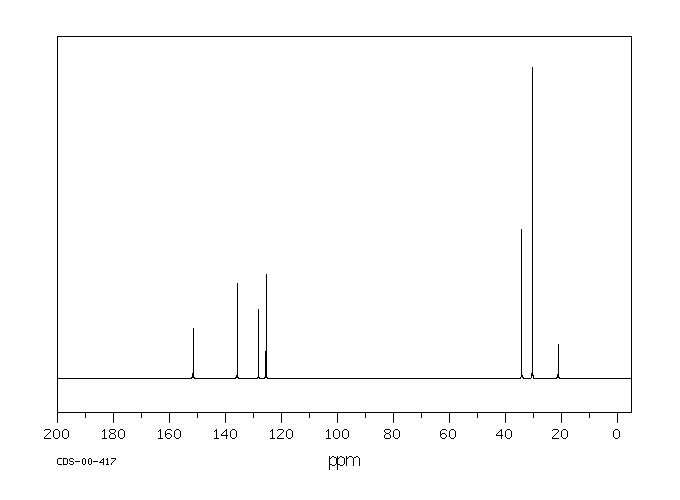
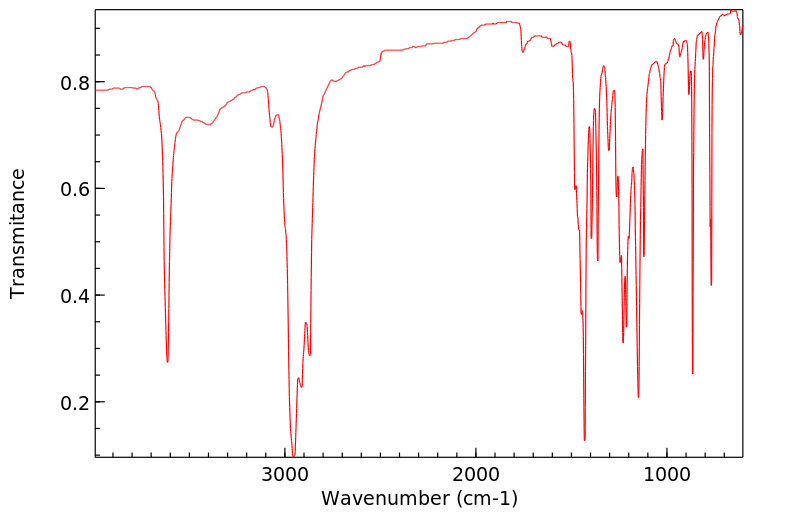
氧化代谢(第1相反应)通过微粒体单加氧酶系统介导是BHT降解的主要途径。在人类中, tert-丁基基团的氧化最为常见。没食子酸酯和2-叔丁基氢醌主要通过非氧化途径(甲基化或与硫酸和葡萄糖醛酸结合)进行代谢。尤其是BHT经常代谢为醌甲烷(QM),据认为QM是促进肿瘤形成的原因。QM的一个例子是2,6-二-叔丁基-4-亚甲基环己二烯酮(BHT-QM)。QM具有很强的亲电性,并且容易与蛋白质形成加合物。
Oxidative metabolism (phase 1 reactions) mediated by the microsomal monooxygenase system is the major route for BHT degradation. Oxidation of the tert-butyl groups is most common in man. Gallates and 2-tert-butylhydroquinone are mainly metabolized by non-oxidative pathways (methylation or conjugation with sulphate and glucuronic acid). (A15352). In particular BHT is frequently metabolized to quinone methides (QMs) which are thought to be responsible for promoting tumor formation. One example of a QM is 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-methylenecyclohexa-2,5-dienone (BHT-QM). QMs are strongly electrophilic and readily form adducts with proteins.
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)