1.1 产品标识符 :
2,4,6-三叔丁基苯酚 产品名称
1.2 鉴别的其他方法 无数据资料
1.3 有关的确定了的物质或混合物的用途和建议不适合的用途 仅供科研用途,不作为药物、家庭备用药或其它用途。
模块 2. 危险性概述 2.1 GHS分类 急性毒性, 经口 (类别4)
急性
水生毒性 (类别1)
2.2 GHS 标记要素,包括预防性的陈述 象形图
警示词 警告
危险申明
H302 吞咽有害。
H400 对
水生
生物毒性极大。
警告申明
预防
P264 操作后彻底清洁皮肤。
P270 使用本产品时不要进食、饮
水或吸烟。
P273 避免释放到环境中。
措施
P301 + P312 如果吞下去了: 如感觉不适,呼救解毒中心或看医生。
P330 漱口。
P391 收集溢出物。
处理
P501 将内容物/ 容器处理到得到批准的废物处理厂。
2.3 其它危害物 - 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息 3.1 物 质 :
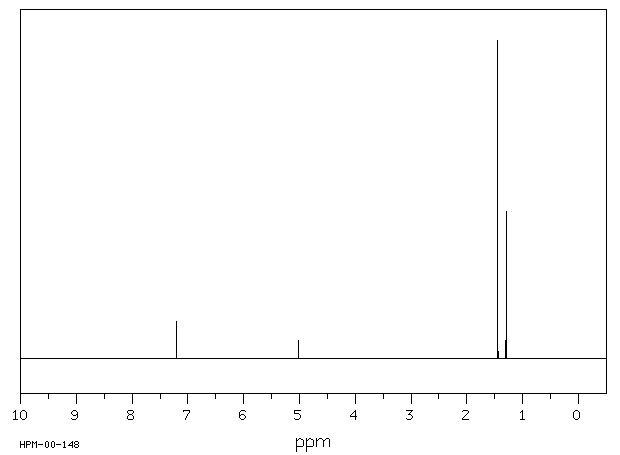
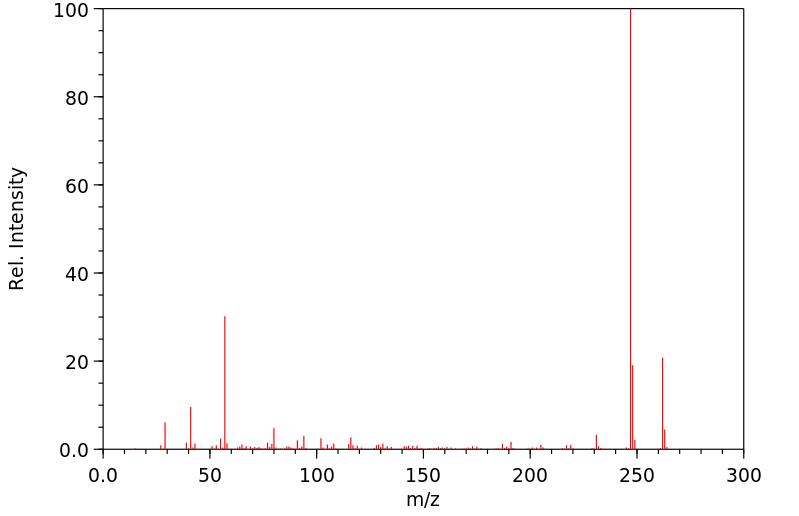
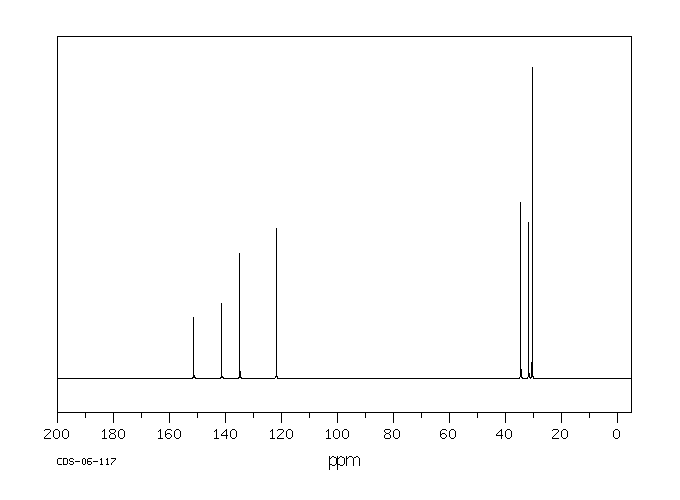
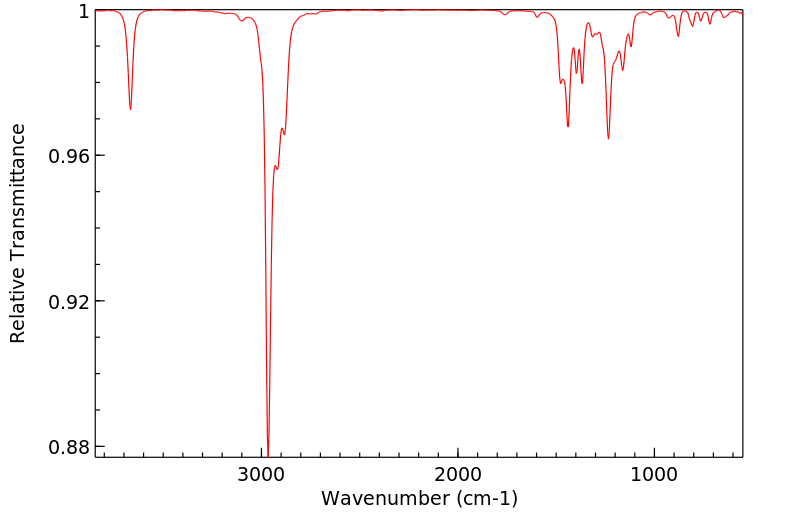
C18H30O 分子式
: 262.43 g/mol
分子量
组分 浓度或浓度范围
2,4,6-Tri-tert-butylphenol
-
CAS 号
732-26-3 EC-编号 211-989-5
模块 4. 急救措施 4.1 必要的急救措施描述 一般的建议
请教医生。 出示此安全技术说明书给到现场的医生看。
吸入
如果吸入,请将患者移到新鲜空气处。 如果停止了呼吸,给于人工呼吸。 请教医生。
皮肤接触
用肥皂和大量的
水冲洗。 请教医生。
眼睛接触
用
水冲洗眼睛作为预防措施。
食入
切勿给失去知觉者从嘴里喂食任何东西。 用
水漱口。 请教医生。
4.2 主要症状和影响,急性和迟发效应 4.3 及时的医疗处理和所需的特殊处理的说明和指示 无数据资料
模块 5. 消防措施 5.1 灭火介质 灭火方法及灭火剂
用
水雾,耐醇泡沫,干粉或
二氧化碳灭火。
5.2 源于此物质或混合物的特别的危害 碳氧化物
5.3 给消防员的建议 如必要的话,戴自给式呼吸器去救火。
5.4 进一步信息 无数据资料
模块 6. 泄露应急处理 6.1 人员的预防,防护设备和紧急处理程序 使用个人防护设备。 防止粉尘的生成。 防止吸入蒸汽、气雾或气体。 保证充分的通风。
将人员撤离到安全区域。 避免吸入粉尘。
6.2 环境保护措施 在确保安全的前提下,采取措施防止进一步的泄漏或溢出。 不要让产物进入下
水道。
防止排放到周围环境中。
6.3 抑制和清除溢出物的方法和材料 收集、处理泄漏物,不要产生灰尘。 扫掉和铲掉。 存放进适当的闭口容器中待处理。
6.4 参考其他部分 丢弃处理请参阅第13节。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存 7.1 安全操作的注意事项 避免接触皮肤和眼睛。 防止粉尘和气溶胶生成。
在有粉尘生成的地方,提供合适的排风设备。一般性的防火保护措施。
7.2 安全储存的条件,包括任何不兼容性 贮存在阴凉处。 容器保持紧闭,储存在干燥通风处。
7.3 特定用途 无数据资料
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护 8.1 容许浓度 最高容许浓度
没有已知的国家规定的暴露极限。
8.2 暴露控制 适当的技术控制
按照良好工业和安全规范操作。 休息前和工作结束时洗手。
个体防护设备
眼/面保护
带有防护边罩的安全眼镜符合 EN166要求请使用经官方标准如NIOSH (美国) 或 EN 166(欧盟)
检测与批准的设备防护眼部。
皮肤保护
戴手套取 手套在使用前必须受检查。
请使用合适的方法脱除手套(不要接触手套外部表面),避免任何皮肤部位接触此产品.
使用后请将被污染过的手套根据相关法律法规和有效的实验室规章程序谨慎处理. 请清洗并吹干双手
所选择的保护手套必须符合EU的89/686/E
EC规定和从它衍生出来的EN 376标准。
身体保护
全套防
化学试剂工作服, 防护设备的类型必须根据特定工作场所中的危险物的浓度和含量来选择。
呼吸系统防护
如须暴露于有害环境中,请使用P95型(美国)或P1型(欧盟 英国
143)防微粒呼吸器。如需更高级别防护,请使用OV/AG/P99型(美国)或ABEK-P2型 (欧盟 英国 143)
防毒罐。
呼吸器使用经过测试并通过政府标准如NIOSH(US)或CEN(EU)的呼吸器和零件。
模块 9. 理化特性 9.1 基本的理化特性的信息 a) 外观与性状
形状: 结晶
颜色: 黄色
b) 气味
无数据资料
c) 气味阈值
无数据资料
d) pH值
无数据资料
e) 熔点/凝固点
熔点/凝固点: 125 - 130 °C - lit.
f) 起始沸点和沸程
277 °C - lit.
g) 闪点
130.00 °C - 闭杯
h) 蒸发速率
无数据资料
i) 易燃性(固体,气体)
无数据资料
j) 高的/低的燃烧性或爆炸性限度 无数据资料
k) 蒸汽压
无数据资料
l) 蒸汽密度
无数据资料
m) 相对密度
无数据资料
n)
水溶性
无数据资料
o) n-
辛醇/
水分配系数
无数据资料
p) 自燃温度
无数据资料
q) 分解温度
无数据资料
r) 粘度
无数据资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应活性 10.1 反应性 无数据资料
10.2 稳定性 无数据资料
10.3 危险反应的可能性 无数据资料
10.4 应避免的条件 无数据资料
10.5 不兼容的材料 碱, 酰
氯, 酸酐, 氧化剂, 黄
铜,
铜 10.6 危险的分解产物 其它分解产物 - 无数据资料
模块 11. 毒理学资料 11.1 毒理学影响的信息 急性毒性
皮肤刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
眼睛刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
呼吸道或皮肤过敏
无数据资料
生殖细胞突变性
无数据资料
致癌性
IARC:
此产品中没有大于或等于 0。1%含量的组分被 IARC鉴别为可能的或肯定的人类致癌物。
生殖毒性
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触)
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(反复接触)
无数据资料
吸入危险
无数据资料
潜在的健康影响
吸入 吸入可能有害。 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
摄入 误吞对人体有害。
皮肤 如果通过皮肤吸收可能是有害的。 可能引起皮肤刺激。
眼睛 可能引起眼睛刺激。
附加说明
化学物质毒性作用登记: SN3570000
模块 12. 生态学资料 12.1 生态毒性 对鱼类的毒性 半数致死浓度(LC50) - Pimephales promelas (黑头软口鲦鱼) - 0.061 mg/l -
96.0 h
12.2 持久存留性和降解性 无数据资料
12.3 潜在的生物蓄积性 无数据资料
12.4 土壤中的迁移性 无数据资料
12.5 PBT 和 vPvB的结果评价 无数据资料
12.6 其它不利的影响 对
水生
生物毒性极大。
模块 13. 废弃处置 13.1 废物处理方法 产品
将剩余的和未回收的溶液交给处理公司。 联系专业的拥有废弃物处理执照的机构来处理此物质。
与易燃溶剂相溶或者相混合,在备有燃烧后处理和洗刷作用的
化学焚化炉中燃烧
受污染的容器和包装
作为未用过的产品弃置。
模块 14. 运输信息 14.1 联合国危险货物编号 欧洲陆运危规: 3077 国际海运危规: 3077 国际空运危规: 3077
14.2 联合国(UN)规定的名称 欧洲陆运危规: ENVIRONME
NTALLY HAZARDOUS SUBSTANCE, SOLID, N.O.S. (2,4,6-Tri-tert-
butylphenol)
国际海运危规: ENVIRONME
NTALLY HAZARDOUS SUBSTANCE, SOLID, N.O.S. (2,4,6-Tri-tert-
butylphenol)
国际空运危规: Environme
NTAlly hazardous subSTance, solid, n.o.s. (2,4,6-Tri-tert-butylphenol)
14.3 运输危险类别 欧洲陆运危规: 9 国际海运危规: 9 国际空运危规: 9
14.4 包裹组 欧洲陆运危规: III 国际海运危规: III 国际空运危规: III
14.5 环境危险 欧洲陆运危规: 是 国际海运危规 海运污染物: 是 国际空运危规: 是
14.6 对使用者的特别提醒 进一步信息
危险品独立包装,液体5升以上或固体5公斤以上,每个独立包装外和独立内包装合并后的外包装上都必须有EHS
标识 (根据欧洲 ADR 法规 2.2.9.1.10, IMDG 法规 2.10.3),
模块 15 - 法规信息 N/A
模块16 - 其他信息 N/A