4,4'-乙烯二(2,6-二叔-丁基苯酚) | 1516-94-5
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:174-175 °C
-
沸点:464.0±40.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:0.982±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted)
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):10.1
-
重原子数:32
-
可旋转键数:7
-
环数:2.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.6
-
拓扑面积:40.5
-
氢给体数:2
-
氢受体数:2
安全信息
-
海关编码:2907299090
SDS
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 2,6-二叔丁基-4-甲基苯酚 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-methyl-phenol 128-37-0 C15H24O 220.355 2,6-二叔丁基苯酚 2,6-di-t-butylphenol 128-39-2 C14H22O 206.328 3,5-二叔丁基-4-羟基苯甲醛 3,5-Di-t-butyl-4-hydroxybenzaldehyde 1620-98-0 C15H22O2 234.338 3,5-二叔丁基-4-羟基苄醇 3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxybenzyl alcohol 88-26-6 C15H24O2 236.354 —— 3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxy benzyl chloride 955-01-1 C15H23ClO 254.8 2,6-二叔丁基-4-溴甲基苯酚 4-(bromomethyl)-2,6-di-tert-butylphenol 2091-51-2 C15H23BrO 299.251 丙泊酚 2,6-diisopropylphenol 2078-54-8 C12H18O 178.274 抗氧剂 702 4,4'-Methylenebis(2,6-di-tert-butylphenol) 118-82-1 C29H44O2 424.667 4-[2-(4-羟基-3,5-二叔-丁基-苯基)乙烯基]-2,6-二叔-丁基-苯酚 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-[(E)-2-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)ethenyl]phenol 2950-01-8 C30H44O2 436.678 2,6-二叔丁基对(二甲氨甲基)苯酚 N,N-dimethyl-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxybenzyl)amine 88-27-7 C17H29NO 263.423
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:在过氧化氢与铜(II)反应中过氧自由基的化学证据。摘要:在CH 3 CN中,Cu(II)导致了氢过氧化物叔酸的两个前所未有的分解:4-氢过氧环己基2,5-二烯酮1和2的脱氧为中间过氧自由基R-OO的存在提供了化学支持。1'和2'。DOI:10.1016/s0040-4020(01)87222-7
-
作为产物:描述:2,6-二叔丁基-4-甲基苯酚 在 tris(2,2-bipyridine)ruthenium(II) hexafluorophosphate 、 1-(N-(difluoromethyl)-4-methylphenylsulfonamido)pyridin-1-ium trifluoromethanesulfonate 、 均三甲苯 作用下, 以 乙腈 为溶剂, 以25 %的产率得到4,4'-乙烯二(2,6-二叔-丁基苯酚)参考文献:名称:光氧化还原催化 1-((N-(二氟甲基)-4-甲基苯基)-磺酰胺基)吡啶-1-鎓三氟甲磺酸盐合成 N-CF2H 化合物摘要:NCF 2 H化合物广泛应用于已批准和实验药物中,但安装该部分的方法有限。提出了直接的N- (二氟甲基)磺酰胺化方案,使 NCF 2 H 化合物多样化,有利于药物发现。这种光氧化还原催化策略采用了一种具有广泛官能团耐受性的新型吡啶鎓试剂,并展示了连续流方案的有效适应。DOI:10.1002/anie.202304294
文献信息
-
Catalytic oxidation of 2,6-di-t-butyl-4-methylphenol by a supported iron complex作者:Narc�s Homs、Pilar Ram�rez de la Piscina、Francesc BorrullDOI:10.1039/c39880001075日期:——The catalytic oxidation of 2,6-di-t-butyl-4-methylphenol using a catalyst of K4[Fe(CN)6] supported on acid-modified τAl2O3 is reported.使用K的催化剂2,6-二-叔丁基-4-甲基苯酚的催化氧化4的[Fe(CN)6 ]负载在酸改性τAl 2 ö 3报道。
-
Metal ions and complexes in organic reactions. Part VII. Copper-promoted hydrogen transfer from aromatic donors to halides作者:R. G. R. Bacon、O. J. StewartDOI:10.1039/j39690000301日期:——substitution by the reductants, and (in the case of o-bromonitrobenzene) with a small amount of Ullmann-type coupling of the halide. Copper(I) oxide or the metal were the most effective of the copper species examined, and both dissolved during reaction. Unsaturated substituents, particularly o-NO2, greatly enhanced reducibility. α-Bromo-ketones readily underwent similar reduction. Fission occurred in the
-
Antioxidant synergism between butylated hydroxyanisole and butylated hydroxytoluene作者:Kanji OmuraDOI:10.1007/bf02577855日期:1995.12
Abstract Decay of the 2,6‐di‐
tert ‐butyl‐4‐methylphenoxy radical [butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT)‐radical] in the presence of butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA) was investigated in 1,2‐dimethoxyethane with or without triethylamine. BHT‐radical was conveniently generated by dissociation of its unstable dimer in solution. The products were BHT, 3,3′‐di‐tert ‐butyl‐5,5′‐dimethoxy‐2,2′‐dihydroxybiphenyl (BHA‐dimer), 2,6‐di‐tert ‐butyl‐p ‐quinone methide (QM), 1,2‐bis (3,5‐di‐tert ‐butyl‐4‐hydroxyphenyl)ethane, and 3,3′,5,5′‐tetra‐tert ‐butyl‐4,4′‐stilbenequinone. The reaction without added triethylamine gave larger quantities of the last two products and BHA (recovery), whereas the reaction with it provided larger quantities of the first two products. The marked difference in the product distribution can be accounted for by a series of reactions including reversible dehydrogenation of BHA with BHT‐radical, which generates 2‐tert ‐butyl‐4‐methoxyphenoxy radical (BHA‐radical) and BHT, reversible dimerization of BHA‐radical, which affords an intermediarybis (cyclohexadienone), and spontaneous and base‐catalyzed prototropic rearrangement of the intermediate into BHA‐dimer. Products of coupling between BHT‐radical and BHA‐radical were not obtained. BHA was found to undergo facile acid‐catalyzed addition to QM, providing two isomericbis (hydroxyphenyl)methanes. The results help to elucidate the mechanism of antioxidant synergism between BHA and BHT and may suggest that the synergism can be affected by base or acid.摘要 研究了 2,6-二叔丁基-4-甲基苯氧基自由基[丁基羟基甲苯(BHT)自由基]在丁基羟基苯甲醚(BHA)存在下,在含有或不含有三乙胺的 1,2-二甲氧基乙烷中的衰变情况。BHT 自由基是由其不稳定的二聚体在溶液中解离生成的。产物为 BHT、3,3′-二叔丁基-5,5′-二甲氧基-2,2′-二羟基联苯(BHA-二聚体)、2,6-二叔丁基对醌甲酰胺(QM)、1,2-双(3,5-二叔丁基-4-羟基苯基)乙烷和 3,3′,5,5′-四叔丁基-4,4′-二苯醌。在不添加三乙胺的反应中,后两种产物和 BHA(回收)的数量较多,而在添加三乙胺的反应中,前两种产物的数量较多。产物分布的明显差异可以通过一系列反应来解释,包括 BHA 与 BHT-自由基的可逆脱氢反应,生成 2-叔丁基-4-甲氧基苯氧基自由基(BHA-自由基)和 BHT;BHA-自由基的可逆二聚反应,生成中间体双(环己二烯酮);以及中间体自发和碱催化原向重排为 BHA-二聚体。BHT-radical 和 BHA-radical 之间的偶联产物没有得到。研究发现,BHA 可与 QM 发生简单的酸催化加成反应,生成两种异构体双(羟基苯基)甲烷。这些结果有助于阐明 BHA 和 BHT 的抗氧化协同作用机制,并可能表明协同作用会受到碱或酸的影响。 -
Optically active compound and photosensitive resin composition申请人:——公开号:US20030211421A1公开(公告)日:2003-11-13A photoactive compound is used in combination with a photosensitizer, represented by the following formula (1): A −[( J ) m −( X-Pro )] n (1) wherein A represents a hydrophobic unit comprising at least one kind of hydrophobic groups selected from a hydrocarbon group and a heterocyclic group, J represents a connecting group, X-Pro represents a hydrophilic group protected by a protective group Pro which is removable by light exposure, m represents 0 or 1, and n represents an integer of not less than 1. The protective group Pro may be removable by light exposure in association with the photosensitizer (especially, a photo acid generator), or may be a hydrophobic protective group. The hydrophilic group may be a hydroxyl group or a carboxyl group. The photoactive compound has high sensitivity to a light source of short wavelength beams, for resist application, therefore, the photoactive compound is advantageously used for forming a pattern with high resolution.
-
Electrolytic oxidative methyl-methyl coupling of cresol salts申请人:Monsanto Company公开号:US04101391A1公开(公告)日:1978-07-18Electrolytic oxidation of cresol salts substituted with non-interfering, blocking substituents at least at the 2,4,6-positions relative to the phenolic oxyanion where at least one of the substituents is the cresolic methyl leads to methyl-methyl coupled dehydrodimeric cresols.
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
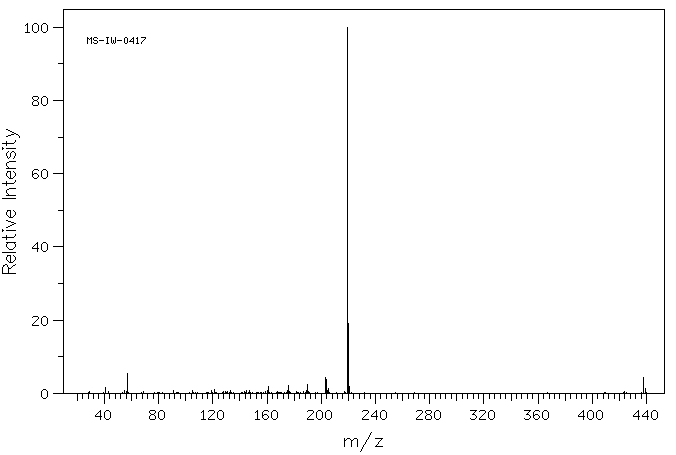
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
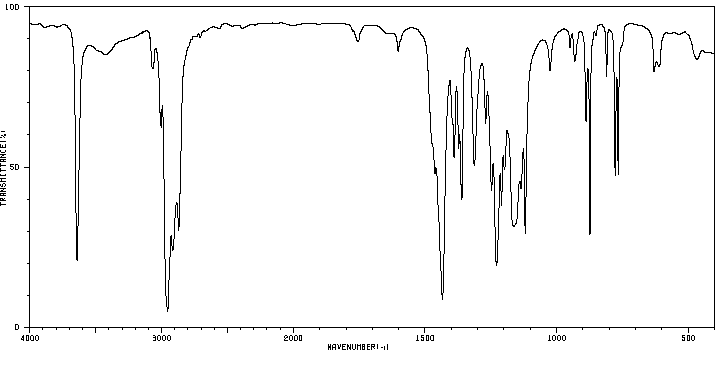
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息