对硝基氯苯 | 100-00-5
中文名称
对硝基氯苯
中文别名
4-硝基氯苯;4-氯硝基苯;1-氯-4-硝基苯;对硝基氯化苯;对氯硝基苯
英文名称
4-chlorobenzonitrile
英文别名
4-Chloronitrobenzene;1-chloro-4-nitrobenzene;p-chloronitrobenzene;4-nitrochlorobenzene;p-nitrochlorobenzene;para-chloronitrobenzene;4-nitro-1-chlorobenzene;4-CNB;p-CNB
CAS
100-00-5
化学式
C6H4ClNO2
mdl
MFCD00007285
分子量
157.556
InChiKey
CZGCEKJOLUNIFY-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:80-83 °C(lit.)
-
沸点:242 °C(lit.)
-
密度:1.298 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
-
蒸气密度:5.4 (vs air)
-
闪点:>230 °F
-
溶解度:溶于丙酮和酒精 (Weast, 1986)
-
暴露限值:Potential occupational carcinogen. NIOSH REL: IDLH 100; OSHA PEL: TWA 1.
-
物理描述:P-nitrochlorobenzene is a light yellow crystalline solid. Density 1.520 g / cm3. Melting point 83°C. Sweet odor. Very toxic by inhalation, ingestion, and skin absorption.
-
颜色/状态:Monoclinic prisms
-
气味:Sweet odor
-
蒸汽密度:5.44 (NTP, 1992) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:2.19X10-2 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
亨利常数:4.89e-06 atm-m3/mole
-
分解:...WHEN HEATED TO DECOMPOSITION IT EMITS VERYY TOXIC FUMES OF /NITROGEN OXIDES AND HYDROGEN CHLORIDE./
-
粘度:1.07X10-3 Pa-s at 356.65 deg K
-
汽化热:6.21X10+7 J/Kmol at 356.65 deg K
-
表面张力:3.71X10-2 N/m at 356.65 deg K
-
电离电位:9.96 eV
-
折光率:MAX ABSORPTION (METHANOL): 270.5 NM (LOG E= 4.03); SADTLER REF NUMBER: 4683 (IR, PRISM); 435 (IR, GRATING); INDEX OF REFRACTION: 1.5376 AT 100 °C/ALPHA
-
保留指数:1229.5;1187;1189;1221.4;1193
-
稳定性/保质期:
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):2.4
-
重原子数:10
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:45.8
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:2
ADMET
代谢
The major urinary metabolites were conjugated (glucuronide or sulfate) forms of nitrochlorophenol and N-acetylcysteine conjugate of nitrobenzene. Minor metabolites included aminochlorophenol and N-acetylated aminochlorophenol. Para-chloroaniline has also been identified as a metabolite in the urine of rabbits following oral administration of PNCB.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
p-Nitrochlorobenzene yields n-acetyl-s-(p-nitrophenyl)-l-cysteine, p-chloroaniline and 2-chloro-5-nitrophenol in rabbits.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
单氯硝基苯异构体的代谢在雄性Fischer-344大鼠的孤立肝细胞和肝亚细胞组分中进行比较。... 4-氯硝基苯代谢为4-氯乙酰苯胺、4-氯苯胺和S-(4-硝基苯基)谷胱甘肽,三者大约等量(90分钟内加入底物的10-15%)。使用肝微粒体的研究表明,将氯硝基苯还原为氯苯胺的反应受到SKF 525-A、美托拉宗和一氧化碳的抑制,这表明细胞色素P-450在此反应中发挥作用...
The metabolism of radiolabeled monochloronitrobenzene isomers was compared in isolated hepatocytes and hepatic subcellular fractions from male Fischer-344 rats. ... 4-Chloronitrobenzene was metabolized to 4-chloroacetanilide, 4-chloroaniline, and S-(4-nitrophenyl)glutathione in approximately equal amounts (10-15% of the added substrate in 90 min). Studies with hepatic microsomes showed that reduction of the chloronitrobenzenes to chloroanilines was inhibited by SKF 525-A, metyrapone, and carbon monoxide, suggesting that cytochrome P-450 played a role in the reaction...
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
被对氯硝基苯急性中毒的人体尿液中代谢物通过气相色谱-质谱法被鉴定出来。共鉴定出8种物质,分别是:大量N-乙酰-S-(4-硝基苯基)-半胱氨酸,相对大量的对氯苯胺、2-氯-5-硝基酚和对氯硝基苯热解产生的对氯甲酰苯胺,少量的2-氨基-5-氯酚和2,4-二氯苯胺,以及微量的对氯乙酰苯胺和4-氯-2-羟基乙酰苯胺。在尿液中检测到了这些物质。所有吸收的对氯硝基苯在排泄前都已被代谢,因为尿液中没有检测到母体化合物。
Urinary metabolites from human subjects acutely poisoned with p-chloro-nitrobenzene were identified with GLC-mass spectrometry. Eight substances /were identified/, namely, a very large amount of N-acetyl-S-(4-nitrophenyl)-cysteine, relatively large quantities of p-chloroaniline, 2-chloro-5-nitrophenol and p-chloroformanilide produced by pyrolysis of a substance originating from p-chloro-nitrobenzene, small amounts of 2-amino-5-chlorophenol and 2,4-dichloroaniline, and traces of p-chloroacetanilide and 4-chloro-2-hydroxyacetanilide, were detected in urine samples. All of the absorbed p-chloro-nitrobenzene was metabolized prior to excretion, as the parent cmpd was not found in the urine.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
1-氯-4-硝基苯通过皮肤、胃肠道的呼吸系统迅速吸收,并在脂肪、血细胞、骨骼肌、肝脏和肾脏中分布。大部分物质随尿液排出,随后通过粪便排出。1-氯-4-硝基苯在哺乳动物体内发生三种主要转化:硝基还原、氯离子在谷胱甘肽结合中的位移以及环羟基化。从工作人员意外接触到1-氯-4-硝基酚中,发现了大量的2-氯-5-硝基酚、N-乙酰-S-(4-硝基苯基)-L-半胱氨酸、4-氯苯胺和4-氯甲酰胺。雄性大鼠口服LD50为294或694毫克/千克体重,雌性大鼠为565或664毫克/千克体重。主要症状为发绀。在4小时的蒸气和微晶颗粒暴露期间,LC50水平无法达到16100毫克/立方米。雄性大鼠的皮肤LD50为750毫克/千克体重,雌性大鼠为1722毫克/千克体重;雄性兔子的LD50为3550毫克/千克体重,雌性兔子为2510毫克/千克体重。急性皮肤应用后,主要症状为发绀。在评估急性毒性时,必须考虑到1-氯-4-硝基苯是一种形成高铁血红蛋白的化学物质。人类接触的经验:所有可用的报告都与混合接触有关,经常与1-氯-2-硝基苯和/或硝基苯结合。在这种情况下,一个关键方面是1-氯-4-硝基苯通过皮肤和呼吸系统迅速吸收。急性中毒的症状包括高铁血红蛋白血症、呕吐、头痛,严重情况下会导致晕厥。关于皮肤刺激的研究报告在结果描述方面存在不足,尽管如此,1-氯-4-硝基苯被认为是轻微刺激兔子的皮肤(完整或刮伤)。由于关于皮肤致敏的有限且质量较差的信息,无法得出该化学物质是否具有致敏活性的结论。通过吸入重复剂量的毒性已经在老鼠身上进行了为期4周和13周的研究。在这两个研究中,没有达到NOAEC,LOAEC分别为5毫克/立方米(4周研究)和1.5 ppm(9.81毫克/立方米,13周研究),基于最敏感效果的血红蛋白血症(分别为3%和4%)。老鼠为期13周的吸入重复剂量毒性研究显示,组织病理损伤的无作用浓度为6 ppm(39.24毫克/立方米)。在两个物种中,靶器官被确定为肝脏、肾脏(仅限大鼠)、脾脏和血液。同样,在大鼠口服给药的重复剂量毒性研究中,发现了与血红蛋白血症一致的变化。1-氯-4-硝基苯在大肠杆菌中诱导反向突变。在哺乳动物细胞的体外(HPRT测试)和昆虫的体内,它不是致突变剂。小鼠淋巴瘤试验呈阳性。在体外,它诱导了高剂量的染色体畸变和姐妹染色单体交换;在大鼠肝细胞中没有报告未偶联DNA合成。该化学物质在体内小鼠骨髓中诱导了微核。在大鼠骨髓中,它没有在体内诱导染色体畸变。中国仓鼠骨髓细胞的体内SCE测试呈弱阳性。在老鼠的肝脏、肾脏和大脑中观察到DNA链断裂。因此,1-氯-4-硝基苯具有在体内表达低效力的致突变活性。在大鼠中进行的1-氯-4-硝基苯的慢性毒性/致癌性研究显示,睾丸间质细胞肿瘤的发生率增加,这些肿瘤在历史对照数据的范围内,并评估为与化合物无关。在另一项大鼠研究中,报告简要,没有发现肿瘤。在报告简要的老鼠研究中,发现了血管肿瘤(具体位置未指明)。总的来说,考虑到遗传毒性测试的结果和现有长期研究的局限性,不能排除致癌潜力。已经在大鼠和小鼠中通过口服给药研究了1-氯-4-硝基苯对繁殖的毒性。在大鼠的两代研究中,没有观察到对生育的影响,最高剂量组为5毫克/千克体重;然而,在这个剂量下,在睾丸中观察到了组织病理学效应。但是,由于低剂量和中等剂量组的睾丸没有进行组织病理学检查,因此无法确定NOAEL(雄性生殖器官毒性)。在小鼠中使用NTP连续繁殖方案进行了研究。NOAEL(生育)为125毫克/千克体重/天,LOAEL(后代一般毒性)为62.5毫克/千克体重/天。NOAEL(成人一般毒性)为125毫克/千克体重/天,但由于对两个较低组动物的评估非常有限,无法进行完整评估。关于大鼠和小鼠的生殖器官组织病理学评估的两种亚慢性吸入研究是可用的。在暴露于1-氯-4-硝基苯的大鼠中,观察到精子生成减少
1-Chloro-4-nitrobenzene is rapidly absorbed via skin, gastrointestinal tract or respiratory tract and distributed in the tissue predominantly in fat, blood cells, skeletal muscles, liver and kidney. Most of the substance was excreted with the urine followed by excretion with feces. 1-Chloro-4-nitrobenzene undergoes three major types of transformation in vivo in mammals: nitro-group reduction, displacement of the chloride in glutathione conjugation, and ring hydroxylation. From accidental exposure of workers to 1-chloro-4-nitrophenol, large amounts of 2-chloro-5- nitrophenol, N-acetyl-S-(4-nitrophenyl)-L-cysteine, 4-chloroaniline and 4-chloroformanilide were identified. The oral LD50 for 1-chloro-4-nitrobenzene in male rats is 294 or 694 mg/kg bw and in female rats 565 or 664 mg/kg bw. Cyanotic appearance was the predominant symptom. The ... LC50 level could not be reached up to 16100 mg/cu m during a 4-hrs exposure against vapor and microcrystalline particles. The LD50 (dermal) for male rats is 750 mg/kg bw and for female rats 1722 mg/kg bw; the LD50 for male rabbits is 3550 mg/kg bw and for female rabbits 2510 mg/kg bw after acute dermal application. Cyanotic appearance was the predominant symptom. For the evaluation of acute toxicity it has to be taken into account that 1-chloro-4-nitrobenzene is a methemoglobin forming chemical. Experience with human exposure: all available reports relate to mixed exposure, frequently in combination with 1-chloro-2-nitrobenzene and/or nitrobenzene. A critical aspect in this context is that 1-chloro-4-nitrobenzene is rapidly absorbed via skin and the respiratory tract. The signs of acute intoxication include methaemoglobinaemia, vomiting, headache and in severe cases collapse. The available study-reports on skin irritation have deficiencies with regard to the description of the results, nevertheless, 1-chloro-4-nitrobenzene is judged to be slightly irritating to the skin (intact or scarificed) of rabbits ... Due to the limited and poor quality information available regarding skin sensitization it cannot be concluded whether or not the chemical has a sensitizing activity. The repeated dose toxicity via inhalation has been examined in rats for a period of 4 weeks and 13 weeks. In both studies, NOAECs were not achieved, the LOAECs were 5 mg/cu m (4 week-study) and 1.5 ppm (9.81 mg/vu m, 13 week-study), respectively, based on methemoglobinemia (3 % and 4 %, respectively) as the most sensitive effect. ... The repeated dose toxicity via inhalation for a period of 13 weeks in mice revealed a NOAEC for histopathologic injury of 6 ppm (39.24 mg/cu m). As target organs liver, kidney (rat only), spleen and blood were identified in both species. Similarly, repeated dose toxicity by oral administration in rats ... revealed changes predominantly consistent with methemoglobinemia. ... 1-Chloro-4-nitrobenzene induced reverse mutations in bacteria. It was not mutagenic in mammalian cells in vitro (HPRT test) and in insects in vivo. A mouse lymphoma assay was positive. In vitro it induced chromosomal aberrations and sister chromatid exchanges at high doses; no UDS in rat hepatocytes was reported. The chemical induced micronuclei in mouse bone marrow in vivo at a toxic dose. In rat bone marrow it did not induce chromosomal aberrations in vivo. An in vivo SCE test was weakly positive in bone marrow cells of Chinese hamsters. DNA strand breaks were observed in liver, kidney and brain of mice. 1-Chloro-4-nitrobenzene is consequently capable of expressing mutagenic activity in vivo with low potency. A combined chronic toxicity/carcinogenicity study ... with 1-chloro-4-nitrobenzene in rats produced an increased incidence in interstitial cell tumours of the testes which were within the range of the historical control data and evaluated as not compound related. ... In another rat study ... reported in brief, no tumors were found. In the available study with mice ... reported in brief, vascular tumors (localization not specified) were found. ... Overall, taking into consideration the results of the genotoxicity tests and the limitations in the available long term studies, a carcinogenic potential cannot be ruled out. Toxicity to reproduction of 1-chloro-4-nitrobenzene has been examined in rats and mice by oral administration. In a two generation study with rats ... no impairment of fertility was observed up to 5 mg/kg bw (high dose group), nevertheless, at this dose histopathological effects in testes were observed. But the evaluation of the effect on the male reproductive tract is limited because the testes in the low and mid dose group were not examined histopathologically. Therefore a NOAEL (male reproductive organ toxicity) was not established. ... In mice a study was performed using the NTP continuous breeding protocol. The NOAEL (fertility) is 125 mg/kg bw/day, the LOAEL (offspring general toxicity) is 62.5 mg/kg bw/day. The NOAEL (adult general toxicity) is 125 mg/kg bw/day, but full evaluation is not possible because evaluation of the animals of the two lower groups were very limited. Two subchronic inhalation studies with rats and mice with histopathologic evaluations on reproductive organs are available. There was evidence of decreased spermatogenesis (24 ppm) and decrease in average estrous cycle length in rats exposed to 1-chloro-4-nitrobenzene (6 ppm and above). In female mice an increase in estrous cycle length was noted at the highest exposure group (24 ppm). Developmental toxicity of 1-chloro-4-nitrobenzene has been examined in rats and rabbits by oral administration ... a NOAEL for maternal toxicity was not achieved, the LOAEL(maternal toxicity) is 5 mg/kg bw/day; the NOAEL (developmental toxicity) is 15 mg/kg bw/day. The study with rabbits suffered from methodology deficiencies. Due to high mortality rate at the highest dose level, only two doses could be evaluated: the LOAEL (maternal toxicity) is 5 mg/kg bw/day and the LOAEL (developmental toxicity) is 5 mg/kg bw/day. Thus, in both species developmental toxicity occurred in the presence of maternal toxicity. There are indications of immunotoxic potency following single and repeated applications of 1-chloro-4- nitrobenzene. Concerning the toxicity of 1-chloro-4-nitrobenzene towards aquatic species reliable experimental results of tests with fish, daphnia, and algae are available. The acute toxicity determined for fish (Brachydanio rerio) was of 14.36 mg/L (96 hr LC50) and 2 mg/L (48 hr) for Leuciscus idus and for daphnia (Daphnia magna) of 2.7 mg/L (48 hr-EC50). In the growth rate tests with algae (Scenedesmus subspicatus) the values 4.9 mg/L (48 hr-ErC10) and 16 mg/L (48 hr- ErC50) were achieved while for Chlorella pyrenoidosa an effect value of 4.9 mg/L (96 hr-EC50) was found. The prolonged toxicity to fish (Brachydanio rerio) for the endpoint sub-lethal effects (feeding, malposition) was evaluated through a 14 days test and a NOEC value of 1.53 mg/l was determined. Two chronic tests with Daphnia (Daphnia magna) are available that were performed with analytical monitoring of the test substance concentration. In one test a 21 d-EC10 of 0.103 mg/L (effective concentration) was observed for the endpoint reproduction rate. The second test resulted in a 21d-NOEC of 0.19 mg/L (effective concentration) for the same endpoint. Calculating the geometric mean of these two values gives a NOEC of 0.14 mg/Ll. A PNECaqua = 2.8 g/L is derived from this value, using an assessment factor of 50.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
Evaluation: There is inadequate evidence in humans for the carcinogenicity of chloronitrobenzenes. There is inadequate evidence in experimental animals for the carcinogenicity of chloronitrobenzenes. Overall evaluation: Chloronitrobenzenes are not classifiable as to their carcinogenicity to humans (Group 3). /Chloronitrobenzenes/
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
A3; 已确认的动物致癌物,对人类的相关性未知。
A3; Confirmed animal carcinogen with unknown relevance to humans.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
国际癌症研究机构致癌物:对氯硝基苯
IARC Carcinogenic Agent:4-Chloronitrobenzene
来源:International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC)
毒理性
国际癌症研究机构(IARC)致癌物分类:2B组:可能对人类致癌
IARC Carcinogenic Classes:Group 2B: Possibly carcinogenic to humans
来源:International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC)
吸收、分配和排泄
Elimination of PNCB or its metabolites was essentially complete (95.5%) within 72 hours after a single oral dose of approximately 200 mg/kg to male rats.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
在人身上,对硝基氯苯可能通过肺部和皮肤被吸收...。
In humans, PNCB may be absorbed through the lungs and skin ... .
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
研究了剂量对大鼠皮肤吸收2-氯硝基苯和4-氯硝基苯的影响。将(14)C标记的2-氯硝基苯或4-氯硝基苯以相当于0、0.65、6.5或65 mg/kg剂量的应用率涂在雄性Fischer 344大鼠剃光的背上。收集24、48或72小时的尿液和粪便样本,并测定(14)C活性。收集乙醇阱中的挥发性呼出物并进行分析。72小时后,大鼠被处死,取下皮肤并分析(14)C活性。大约21-27%和43至45%的2-氯硝基苯和4-氯硝基苯剂量分别在72小时内通过尿液排出。大约11至15%的2-氯硝基苯剂量和5至12%的4-氯硝基苯剂量在72小时内被排出。4-氯硝基苯的粪便排出量显示出与剂量相关的增加,仅在将65 mg/kg剂量与0.65 mg/kg剂量比较时统计显著。大约27至32%的来自2-氯硝基苯的放射性活性和13至15%的来自4-氯硝基苯的(14)C活性在乙醇阱中回收。收集到的放射性活性的量不依赖于剂量,由未变化的2-氯硝基苯或4-氯硝基苯组成。...对所有的(14)C数据进行分析表明,2-氯硝基苯的皮肤吸收在整个剂量范围内是线性的。只有在应用0.65和6.5 mg/kg后,4-氯硝基苯的皮肤吸收才是线性的。/结果表明/,在使用的实验条件下,至少有33至40%和51至62%的施用的2-氯硝基苯和4-氯硝基苯剂量分别从大鼠的皮肤吸收。...2-氯硝基苯的皮肤吸收在0.65 mg/kg到65 mg/kg的剂量范围内是线性的。4-氯硝基苯的皮肤吸收基本上不受剂量的影响。
The effect of dose on the dermal absorption of 2-chloronitrobenzene and 4-chloronitrobenzene was studied in rats. (14)C labeled 2-chloronitrobenzene or 4-chloronitrobenzene was applied to the shaved backs of male Fischer 344 rats at an application rates equivalent to doses of 0, 0.65, 6.5 or 65 mg/kg. Urine and feces samples were collected for 24, 48 or 72 hr and assayed for (14)C activity. Exhaled volatiles were collected in ethanol traps and analyzed. After 72 hr, the rats were /sacrificed/ and their skin removed and analyzed for (14)C activity. Approx 21-27% and 43 to 45% of the 2-chloronitrobenzene and 4-chloronitrobenzene doses, respectively, were eliminated in the urine over 72 hr. Approx 11 to 15% of the 2-chloronitrobenzene dose and 5 to 12% of the 4-chloronitrobenzene dose were excreted over 72 hr. Fecal excretion of 4-chloronitrobenzene showed a dose related incr which was statistically significant only when comparing the 65 mg/kg dose with the 0.65 mg/kg dose. Approx 27 to 32% of 2-chloronitrobenzene derived radioactivity and 13 to 15% of the 4-chloronitrobenzene derived (14)C activity were recovered in the ethanol traps. The amt of collected radioactivity did not depend on dose and consisted of unchanged 2-chloronitrobenzene or 4-chloronitrobenzene. ... An analysis of all (14)C data indicated that the dermal absorption of 2-chloronitrobenzene ... was linear over the entire dose range. Dermal absorption of 4-chloronitrobenzene was linear only after application of 0.65 and 6.5 mg/kg. /Results indicate/ that under the experimental conditions used at least 33 to 40% and 51 to 62% of the applied 2-chloronitrobenzene and 4-chloronitrobenzene doses, respectively, are absorbed from the skin of rats. ... Dermal absorption of 2-chloronitrobenzene is linear over the dose range 0.65 mg/kg to 65 mg/kg. Dermal absorption of 4-chloronitrobenzene is essentially unaffected by dose.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
p-氯硝基苯在雄性Sprague-Dawley大鼠中进行了研究,通过腹腔注射0、30、100或333 mg/kg的p-硝基氯苯。从给药后1至169小时定期收集血液和尿液样本。在这些时间点测定了血浆中p-硝基氯苯的浓度。尿液样本用于分析p-硝基氯苯的代谢物。注射30和100 mg/kg剂量后的p-氯硝基苯血浆浓度随时间线性下降。而333 mg/kg p-氯硝基苯的下降是非线性的。根据第一正矩计算得出的p-氯硝基苯的平均滞留时间随剂量增加而增加。系统性的p-氯硝基苯清除率,定义为剂量与血浆浓度-时间曲线下面积的比率,随p-氯苯剂量的增加而降低。观察结果表明,p-氯硝基苯从血浆中的清除是非线性的。N-乙酰-5-(4-硝基苯基)-L-半胱氨酸是主要的尿液代谢物,约占每个给予的p-氯硝基苯剂量的30%,占总代谢物浓度的50%。每个p-氯硝基苯代谢物的估计速率常数随剂量增加而降低,且大于产生代谢物的速率常数。然而,N-乙酰-S-(4-硝基苯基)-L-半胱氨酸的消除速率与p-氯硝基苯成比例。
p-chloronitrobenzene was studied in male Sprague-Dawley rats injected ip with 0, 30, 100, or 333 mg/kg p-nitrochlorobenzene. Blood and urine samples were collected periodically from 1 to 169 hr after dosing. Plasma p-nitrochlorobenzene concn were determined at these times. The urine samples were analyzed for p-nitrochlorobenzene metabolites. The plasma concentrations of p-chloronitrobenzene following injection with the 30 and 100 mg/kg doses decreased linearly with time. The decrease following 333 mg/kg p-chloronitrobenzene was nonlinear. The mean residence time of p-chloronitrobenzene, determined from the first normal moment, increased with increasing dose. Systemic p-chloronitrobenzene clearance, defined as the ratio of the dose to the area under the plasma concn time curve, decreased with increasing p-chlorobenzene dose. The observations indicated that clearance of p-chloronitrobenzene from the plasma was nonlinear. N-acetyl-5-(4-nitrophenyl)-L-cysteine was the major urinary metabolite accounting for approx 30% of each administered p-chloronitrobenzene dose and 50% of the total metabolite concn. The rate constants for estimation of each p-chloronitrobenzene metabolite decr with increasing dose and were larger than those for production of the metabolites. The elimination rate of N-acetyl-S-(4-nitrophenyl)-L-cysteine, however, was proportional to p-chloronitrobenzene.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
在大鼠中,口服给药后至少有78%的化合物被吸收,而经皮应用后至少有62%的化合物被吸收。口服摄入化合物后72小时内,多达74%的剂量通过尿液排出,多达12%通过粪便排出。经皮应用后,72小时内45%的剂量通过尿液排出,12%通过粪便排出(多达30%的剂量在保护装置和乙醇阱中回收,收集挥发性物质)。在两种应用途径中,都显示在非常高剂量下,初始的尿液排泄速率会延迟,初始的粪便排泄会明显减少。这些在高剂量下的观察结果可能反映了从更大的胆汁排泄速率中的再吸收,提示涉及到肠肝循环,但没有迹象表明1-氯-4-硝基苯或其代谢物之一有积累。口服应用24小时后,化合物的最高浓度在脂肪中,其次是血细胞、骨骼肌、肝脏和肾脏。在72小时时,最高浓度在血细胞中,其次是脂肪、骨骼肌和肝脏。
In rats, following oral dosing at least 78 % and following dermal application at least 62 % of the applied compound were absorbed. 72 hours after oral uptake of the compound up to 74 % of the dose was excreted with the urine and up to 12 % with the feces. After dermal application 45 % of the dose was excreted in the urine and 12 % in the feces within 72 hrs (up to 30 % of the dose was recovered in the protective device and ethanol trap (collects volatiles)). In both application routes, it was shown that at very high doses the initial urinary excretion rate is delayed and the initial fecal excretion is markedly depressed. These observations at high doses may reflect the reabsorption from greater biliary excretion rates suggesting involvement of the enterohepatic cycle, but there are no signs of accumulation of 1-chloro-4-nitrobenzene or one of its metabolites. 24 hours post oral application the highest concentrations of the compound were found in the fat, followed by blood cells, skeletal muscles , liver and kidney. At 72 hours greatest concentration was found in the blood cells followed by fat, skeletal muscles and liver.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
安全信息
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:6.1
-
立即威胁生命和健康浓度:100 mg/m3
-
安全说明:S28,S28A,S36/37,S45,S61
-
危险品运输编号:UN 1578 6.1/PG 2
-
WGK Germany:2
-
海关编码:29049085
-
危险类别:6.1
-
危险品标志:T
-
危险类别码:R51/53,R40,R48/20/21/22,R23/24/25,R68
-
RTECS号:CZ1050000
-
包装等级:II
制备方法与用途
化学性质
对硝基氯苯为浅黄色结晶。它难溶于水(25℃时仅溶0.03%),微溶于冷乙醇,而能溶于热乙醇、乙醚、丙酮和苯等有机溶剂。
用途
它是制造偶氮染料及硫化染料、药物如非那西丁及扑热息痛、农药除草醚等的重要中间体。同时,对硝基氯苯也是橡胶防老剂4010的原料。此外,它还能用于制备有机合成染料和作为医药、农药及橡胶工业中的重要中间体。
生产方法
将硝酸与硫酸配制成混酸后,再与氯苯进行硝化反应,生成硝基氯苯(对位65%、邻位34%、间位1%)。随后分离硝基氯苯和废酸。分离后的硝基氯苯经过水洗、中和及干燥结晶处理后得到成品对硝基氯苯。而共融油则通过精馏、脱焦和结晶过程获得联产品——邻硝基氯苯。
类别
有毒物品,属于高毒级别。
急性毒性
口服-大鼠 LD50: 420 毫克/公斤;口服-小鼠 LD50: 440 毫克/公斤
可燃性危险特性
对硝基氯苯在明火下可燃,并在高温分解产生有毒的氮氧化物和氯化物烟雾。
储运特性
应存放在通风、低温且干燥的地方,与氧化剂及食品添加剂分开存放。
职业标准
时间加权平均容许浓度(TWA)为1毫克/立方米;短时间接触容许浓度(STEL)为3毫克/立方米。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 4-氯亚硝基苯 1-chloro-4-nitroso-benzene 932-98-9 C6H4ClNO 141.557 硝基苯 nitrobenzene 98-95-3 C6H5NO2 123.111 2-氯-5-硝基苯胺 2-chloro-5-nitroaniline 6283-25-6 C6H5ClN2O2 172.571 2-硝基-5-氯苯胺 5-Chloro-2-nitroaniline 1635-61-6 C6H5ClN2O2 172.571 4-硝基苯胺 4-nitro-aniline 100-01-6 C6H6N2O2 138.126 对二硝基苯 para-dinitrobenzene 100-25-4 C6H4N2O4 168.109 对硝基苯酚 4-nitro-phenol 100-02-7 C6H5NO3 139.111 4-硝基苯肼 4-nitrophenylhydrazin 100-16-3 C6H7N3O2 153.14 1-溴-4-硝基苯 4-Bromonitrobenzene 586-78-7 C6H4BrNO2 202.007 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 4-氯亚硝基苯 1-chloro-4-nitroso-benzene 932-98-9 C6H4ClNO 141.557 4-氯苯基羟胺 N-(4-chlorophenyl)hydroxylamine 823-86-9 C6H6ClNO 143.573 硝基苯 nitrobenzene 98-95-3 C6H5NO2 123.111 3,4-二氯硝基苯 3,4-dichloronitrobenzene 99-54-7 C6H3Cl2NO2 192.001 3-硝基氯苯 3-Chloronitrobenzene 121-73-3 C6H4ClNO2 157.556 2-硝基-5-氯苯胺 5-Chloro-2-nitroaniline 1635-61-6 C6H5ClN2O2 172.571 硝基氯苯 2-Chloronitrobenzene 88-73-3 C6H4ClNO2 157.556 1-氯-2-碘-4-硝基苯 1-chloro-2-iodo-4-nitrobenzene 74534-15-9 C6H3ClINO2 283.453 4-硝基苯胺 4-nitro-aniline 100-01-6 C6H6N2O2 138.126 —— 4-chloro-N-(4-nitrophenyl)aniline 20983-67-9 C12H9ClN2O2 248.669 4-氯-3-氟硝基苯 1-chloro-2-fluoro-4-nitrobenzene 350-31-2 C6H3ClFNO2 175.547 3-溴-4-氯硝基苯 3-bromo-4-chloronitrobenzene 16588-26-4 C6H3BrClNO2 236.452 2-氯-5-硝基苯硫醇 2-chloro-5-nitrobenzenethiol 89880-53-5 C6H4ClNO2S 189.622 5-氯-2-硝基甲苯 5-chloro-2-nitrotoluene 5367-28-2 C7H6ClNO2 171.583 2-硝基-5-氯苯酚 5-chloro-2-nitrophenol 611-07-4 C6H4ClNO3 173.556 1-氯-2,4-二硝基苯 1-chloro-2,4-dinitro-benzene 97-00-7 C6H3ClN2O4 202.554 4-硝基碘苯 4-Iodonitrobenzene 636-98-6 C6H4INO2 249.008 对氟硝基苯 4-Fluoronitrobenzene 350-46-9 C6H4FNO2 141.102 —— 1-[18F]fluoro-4-nitrobenzene 16447-86-2 C6H4FNO2 140.103 对硝基苯酚 4-nitro-phenol 100-02-7 C6H5NO3 139.111 4-硝基甲苯 1-methyl-4-nitrobenzene 99-99-0 C7H7NO2 137.138 4-硝基苯硫醇 para-nitrobenzenethiol 1849-36-1 C6H5NO2S 155.177 - 1
- 2
- 3
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:Blanksma; Fohr, Recueil des Travaux Chimiques des Pays-Bas, 1946, vol. 65, p. 706,709摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:“过碳酸钠” (SPC) 作为有机合成的过氧化氢来源摘要:“过碳酸钠”(SPC)是一种廉价、稳定、安全且可商购的材料,可用作有机合成的过氧化氢来源。环氧化、胺和硫化物氧化反应用固体试剂简单地进行,产率中等至极好。DOI:10.1246/cl.1986.665
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:Anion activation in the synthesis of ethers from oxygen anions and p-chloronitrobenzene摘要:DOI:10.1021/jo00166a017
文献信息
-
Efficient copper(I)-catalyzed C–S cross-coupling of thiols with aryl halides in an aqueous two-phase system作者:Xin-Yan Zhang、Xiao-Yan Zhang、Sheng-Rong GuoDOI:10.1080/17415993.2010.547197日期:2011.2.1A mild and convenient C–S bond formation reaction catalyzed by CuI/L-proline in an aqueous two-phase system was achieved, providing a simple method for the synthesis of aryl sulfides in good yields.
-
一种对硝基苯甲醚合成方法
-
N-ARYLAMIDINE-SUBSTITUTED TRIFLUOROETHYL SULFIDE DERIVATIVES AS ACARICIDES AND INSECTICIDES申请人:BAYER CROPSCIENCE AG公开号:US20140315898A1公开(公告)日:2014-10-23The present invention relates to novel N-arylamide-substituted trifluoroethyl sulfide derivatives of the formula (I) in which X 1 , X 2 , X 3 , X 4 , R 1 , R 2 , R 3 , n have the meanings given in the description—to their use as acaricides and insecticides for controlling animal pests and to processes and intermediates for their preparation
-
Npy antagonists, preparation and uses申请人:Botez Iuliana公开号:US20090233910A1公开(公告)日:2009-09-17The present invention concerns novel compounds, their preparation and their uses, therapeutic uses in particular. More specifically it concerns derivative compounds having at least two aromatic cycles, their preparation and their uses, in particular in the area of human or animal health. These compounds have an affinity for the biological receptors of neuropeptide Y, NPY, present in the central and peripheral nervous systems. The compounds of the invention are preferably NPY antagonists, and more particularly antagonists of sub-type NPY Y1, and can therefore be used for the therapeutic or prophylactic treatment of any disorder involving NPY. The present invention also concerns pharmaceutical compositions containing said compounds, their preparation and their uses, as well as treatment methods using said compounds.本发明涉及新颖化合物,它们的制备和用途,特别是在治疗方面的用途。更具体地说,它涉及至少具有两个芳香环的衍生化合物,它们的制备和用途,特别是在人类或动物健康领域。这些化合物对存在于中枢和外周神经系统中的神经肽Y(NPY)的生物受体具有亲和力。本发明的化合物优选为NPY拮抗剂,更具体地说是NPY Y1亚型的拮抗剂,因此可用于治疗或预防涉及NPY的任何疾病。本发明还涉及含有所述化合物的药物组合物,其制备和用途,以及使用所述化合物的治疗方法。
-
2-OXO-2- (2-PHENYL-5,6,7,8-TETRAHYDRO-INDOLIZIN-3-YL) -ACETAMIDE DERIVATIVES AND RELATED COMPOUNDS AS ANTIFUNGAL AGENTS申请人:Payne Lloyd James公开号:US20110009390A1公开(公告)日:2011-01-13The invention provides compounds of formula (I), and pharmaceutically and agriculturally acceptable salts thereof: wherein: R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, R8, A1, L1 and n are as defined herein. These compounds and their pharmaceutically acceptable salts are useful in the manufacture of medicaments for use in the prevention or treatment of a fungal disease. Compounds of formula (I), and agriculturally acceptable salts thereof, may also be used as agricultural fungicides.该发明提供了式(I)的化合物,以及其在药学和农业上可接受的盐:其中:R1、R2、R3、R4、R5、R6、R7、R8、A1、L1和n如本文所定义。这些化合物及其药学上可接受的盐在制造用于预防或治疗真菌病的药物方面是有用的。式(I)的化合物及其在农业上可接受的盐也可用作农业杀菌剂。
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
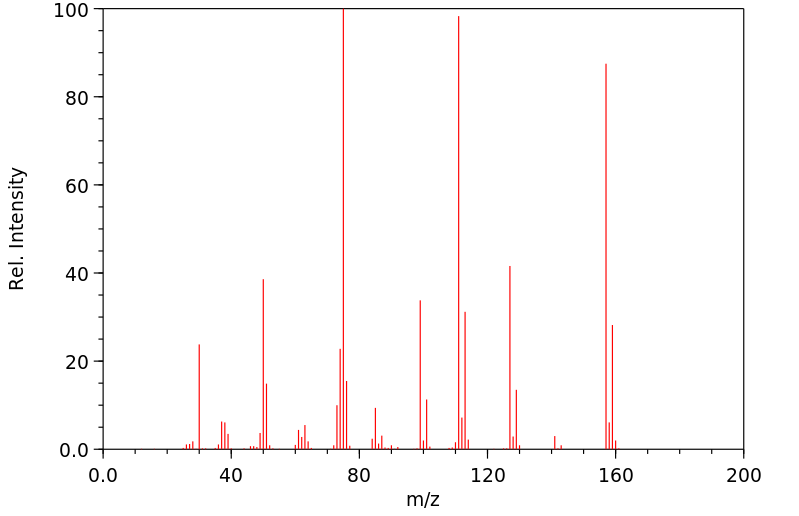
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
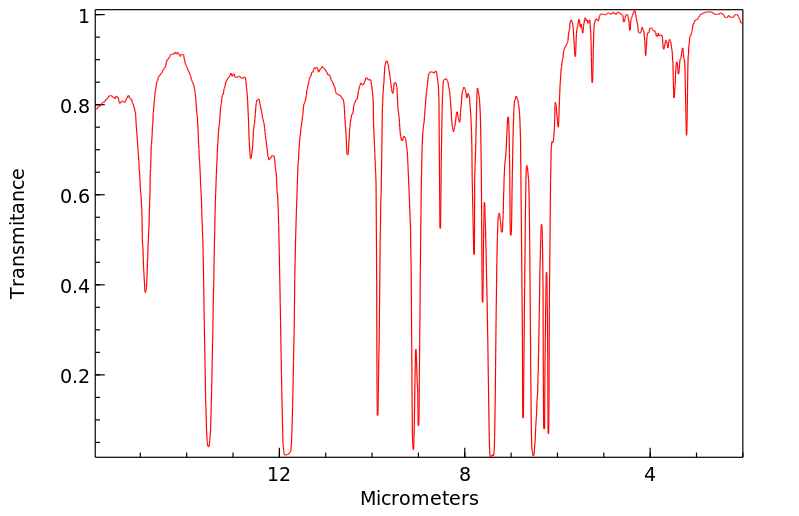
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(βS)-β-氨基-4-(4-羟基苯氧基)-3,5-二碘苯甲丙醇
(S,S)-邻甲苯基-DIPAMP
(S)-(-)-7'-〔4(S)-(苄基)恶唑-2-基]-7-二(3,5-二-叔丁基苯基)膦基-2,2',3,3'-四氢-1,1-螺二氢茚
(S)-盐酸沙丁胺醇
(S)-3-(叔丁基)-4-(2,6-二甲氧基苯基)-2,3-二氢苯并[d][1,3]氧磷杂环戊二烯
(S)-2,2'-双[双(3,5-三氟甲基苯基)膦基]-4,4',6,6'-四甲氧基联苯
(S)-1-[3,5-双(三氟甲基)苯基]-3-[1-(二甲基氨基)-3-甲基丁烷-2-基]硫脲
(R)富马酸托特罗定
(R)-(-)-盐酸尼古地平
(R)-(-)-4,12-双(二苯基膦基)[2.2]对环芳烷(1,5环辛二烯)铑(I)四氟硼酸盐
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[((6-甲基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[(4-叔丁基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[(3-甲基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-4,7-双(3,5-二-叔丁基苯基)膦基-7“-[(吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2”,3,3'-四氢1,1'-螺二茚满
(R)-3-(叔丁基)-4-(2,6-二苯氧基苯基)-2,3-二氢苯并[d][1,3]氧杂磷杂环戊烯
(R)-2-[((二苯基膦基)甲基]吡咯烷
(R)-1-[3,5-双(三氟甲基)苯基]-3-[1-(二甲基氨基)-3-甲基丁烷-2-基]硫脲
(N-(4-甲氧基苯基)-N-甲基-3-(1-哌啶基)丙-2-烯酰胺)
(5-溴-2-羟基苯基)-4-氯苯甲酮
(5-溴-2-氯苯基)(4-羟基苯基)甲酮
(5-氧代-3-苯基-2,5-二氢-1,2,3,4-oxatriazol-3-鎓)
(4S,5R)-4-甲基-5-苯基-1,2,3-氧代噻唑烷-2,2-二氧化物-3-羧酸叔丁酯
(4S,4''S)-2,2''-亚环戊基双[4,5-二氢-4-(苯甲基)恶唑]
(4-溴苯基)-[2-氟-4-[6-[甲基(丙-2-烯基)氨基]己氧基]苯基]甲酮
(4-丁氧基苯甲基)三苯基溴化磷
(3aR,8aR)-(-)-4,4,8,8-四(3,5-二甲基苯基)四氢-2,2-二甲基-6-苯基-1,3-二氧戊环[4,5-e]二恶唑磷
(3aR,6aS)-5-氧代六氢环戊基[c]吡咯-2(1H)-羧酸酯
(2Z)-3-[[(4-氯苯基)氨基]-2-氰基丙烯酸乙酯
(2S,3S,5S)-5-(叔丁氧基甲酰氨基)-2-(N-5-噻唑基-甲氧羰基)氨基-1,6-二苯基-3-羟基己烷
(2S,2''S,3S,3''S)-3,3''-二叔丁基-4,4''-双(2,6-二甲氧基苯基)-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-2,2''-联苯并[d][1,3]氧杂磷杂戊环
(2S)-(-)-2-{[[[[3,5-双(氟代甲基)苯基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基}-N-(二苯基甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-[[[[[((1S,2S)-2-氨基环己基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基]-N-(二苯甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-[[[[[[((1R,2R)-2-氨基环己基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基]-N-(二苯甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2-硝基苯基)磷酸三酰胺
(2,6-二氯苯基)乙酰氯
(2,3-二甲氧基-5-甲基苯基)硼酸
(1S,2S,3S,5S)-5-叠氮基-3-(苯基甲氧基)-2-[(苯基甲氧基)甲基]环戊醇
(1S,2S,3R,5R)-2-(苄氧基)甲基-6-氧杂双环[3.1.0]己-3-醇
(1-(4-氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(3-溴苯基)环丁基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2-氯苯基)环丁基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2-氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2,6-二氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(-)-去甲基西布曲明
龙蒿油
龙胆酸钠
龙胆酸叔丁酯
龙胆酸
龙胆紫-d6
龙胆紫