胆酸 | 81-25-4
中文名称
胆酸
中文别名
胆汁酸;3Alpha.7Alpha.12Alpha-三羟胆烷酸;3alpha,7alpha,12alpha-三羟基-5beta-胆烷酸;胆甾烷酸;胆酸,由牛或羊胆汁中提取;3α,7α,12α-三羟基-5β-胆烷酸
英文名称
cholate
英文别名
cholic acid;3α,7α,12α-trihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-oic acid;(4R)-4-[(3R,5S,7R,8R,9S,10S,12S,13R,14S,17R)-3,7,12-trihydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]pentanoic acid
CAS
81-25-4
化学式
C24H40O5
mdl
MFCD02940838
分子量
408.579
InChiKey
BHQCQFFYRZLCQQ-OELDTZBJSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:200-201 °C (lit.)
-
比旋光度:36 º (c=0.6, 95% EtOH)
-
沸点:449.08°C (rough estimate)
-
密度:1.0310 (rough estimate)
-
闪点:9℃
-
溶解度:溶于甲醇,溶解度为0.1g/mL,澄清
-
LogP:2.03-2.615 at 20℃
-
物理描述:Solid; [HSDB] White powder; [MSDSonline]
-
颜色/状态:Plates from dilute acetic acid
-
味道:Bitter with sweetish aftertaste
-
蒸汽压力:9.66X10-15 mm Hg at 25 °C (est)
-
水溶性:-3.37
-
亨利常数:Henry's Law constant = 5.16X10-13 atm-cu m/mol at 25 °C (est)
-
稳定性/保质期:
Stable under recommended storage conditions.
-
旋光度:Specific optical rotation: +37 deg at 20 °C/D (c = 0.6 in alcohol)
-
分解:When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
-
解离常数:4.98 (at 20 °C)
-
碰撞截面:197.3 Ų [M+Na]+ [CCS Type: DT, Method: single field calibrated with Agilent tune mix (Agilent)]
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):3.6
-
重原子数:29
-
可旋转键数:4
-
环数:4.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.96
-
拓扑面积:98
-
氢给体数:4
-
氢受体数:5
ADMET
代谢
胆固醇侧链羟基化在胆酸合成中的作用机制和顺序在隔离灌注的兔肝中进行了研究。比较了26-羟基化和25-羟基化在兔胆酸生物合成中的重要性。当肝脏被灌注5beta-[G-(3)H]胆甾烷-3alpha, 7alpha-二醇、5beta-[G-(3)H]胆甾烷-3alpha, 7alpha, 12alpha-三醇和5beta-[G-(3)H]胆甾烷-3alpha, 7alpha, 26-三醇时,观察到[G-(3)H]胆酸的形成。胆汁中没有检测到[G-(3)H]鹅脱氧胆酸。这些发现表明,鹅脱氧胆酸的潜在前体在12alpha位置的羟基化是在胆固醇侧链羟基化之前或之后进行的。此外,当这些化合物在肝脏中灌注时,胆汁中没有发现其他中间体(四羟基或五羟基胆醇)。当兔肝被灌注5beta-[24-(14)C]胆甾烷-3alpha, 7alpha, 25-三醇时,在胆汁中检测到了胆酸前体。5beta-[24-(14)C]胆甾烷-3alpha, 7alpha, 25-三醇在肝脏的12alpha位置被羟基化,产生相应的5beta-胆甾烷-3alpha, 7alpha, 12alpha, 25-四醇。四醇进一步代谢为一组五醇(5beta-胆甾烷-3alpha, 7alpha, 12alpha, 22, 25-五醇;5beta-胆甾烷-3alpha, 7alpha, 12alpha, 23, 25-五醇;5beta-胆甾烷-3alpha, 7alpha, 12alpha, 24, 25-五醇和5beta-胆甾烷-3alpha, 7alpha, 12alpha, 25, 26-五醇)。从5beta-胆甾烷-3alpha, 7alpha, 25-三醇灌注得到的主要胆酸是胆酸。实验表明,在兔肝中,12alpha-羟基化可以在胆固醇侧链在C-25(5beta-胆甾烷-3alpha, 7alpha, 25-三醇)或C-26(5beta-胆甾烷-3alpha, 7alpha-26-三醇)羟基化之后发生。显然,兔可以通过经典的26-羟基化途径以及通过25-羟基化中间体形成胆酸。
The mechanism and sequence of side chain hydroxylation of cholesterol in bile acid synthesis was studied in the isolated perfused rabbit liver. A comparison was made between the importance of 26- and 25-hydroxylation in cholic acid biosynthesis in the rabbit. The formation of [G-(3)H]cholic acid was observed when the liver was perfused with 5beta-[G-(3)H]cholestane-3alpha, 7alpha-diol, 5beta-[G-(3)H]cholestane-3alpha, 7alpha-12alpha-triol, and 5beta-[G-(3)H]cholestane-3alpha, 7alpha, 26-triol. No [G-(3)H]chenodeoxycholic acid was detected in the bile. These findings indicate that potential precursors of chenodeoxycholic acid were hydroxylated at position 12alpha either subsequent to or before hydroxylation of the cholesterol side chain. In addition, no other intermediates (tetrahydroxy or pentahydroxy bile alcohols) were found in the bile when these compounds were perfused in the liver. Bile acid precursors were detected in bile when the rabbit liver was perfused with 5beta-[24-(14)C]cholestane-3alpha, 7alpha, 25-triol. The 5beta-[24-(14)C]cholestane-3alpha, 7alpha, 25-triol was hydroxylated in the liver at the 12alpha position to yield the corresponding 5beta-cholestane-3alpha, 7alpha, 12alpha, 25-tetrol. The tetrol was further metabolized to a series of pentols (5beta-cholestane-3alpha, 7alpha, 12alpha, 22, 25-pentol; 5beta-cholestane-3alpha, 7alpha, 12alpha, 23, 25-pentol; 5beta-cholestane-3alpha, 7alpha, 12alpha, 24, 25-pentol; and 5beta-cholestane-3alpha, 7alpha, 12alpha, 25, 26-pentol). The major bile acid obtained from the perfusion of the 5beta-cholestane-3alpha, 7alpha, 25-triol was cholic acid. The experiments indicated that in the rabbit liver 12alpha-hydroxylation can occur after hydroxylation of the cholesterol side chain at either C-25 (5 beta-cholestane-3alpha, 7alpha, 25-triol) or C-26 (5beta-cholestane-3alpha, 7alpha-26-triol). Apparently, the rabbit can form cholic acid via the classical 26-hydroxylation pathway as well as via 25-hydroxylated intermediates.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
在经典的胆酸生物合成中,胆固醇的一系列环修饰发生在侧链裂解之前,并产生5beta-胆烷-3alpha, 7alpha, 12alpha-三醇。然后,三醇的侧链反应通过线粒体的27-羟基化途径或微囊体的25-羟基化途径进行。我们已经开发出特异和精确的测定方法来测量这两个途径中关键酶的活性,即5beta-胆烷-3alpha, 7alpha, 12alpha-三醇25-和27-羟化酶以及5beta-胆烷-3alpha, 7alpha, 12alpha, 25-四醇23R-, 24R-, 24S-和27-羟化酶。通过一次性硅胶柱的纯化,将线粒体或微囊体孵化混合物的提取物转化为三甲基硅醚,并通过高分辨率模式的气相色谱-质谱法进行定量分析。与在丙酮中添加底物相比,使用2-羟基丙基-beta-环糊精的人类肝脏中,线粒体三醇27-羟化酶活性增加了132%,但微囊体25-羟基化途径(三醇25-羟化酶和5beta-胆烷-3alpha, 7alpha, 12alpha, 25-四醇23R-, 24R-, 24S-和27-羟化酶)的酶活性降低了13%-60%。与人类肝脏相比,小鼠和兔子的两个途径中的酶活性通常是2到4倍。在所有物种中,微囊体三醇25-羟化酶活性是线粒体三醇27-羟化酶活性的4到11倍,但在我们的实验条件下,四醇24S-羟化酶的活性与三醇27-羟化酶的活性相似。在兔子肝脏中,当胆酸合成受到干扰后,研究了两个途径的调节。胆固醇饲养上调了参与25-(64%-142%)和27-(77%)羟基化途径的酶活性,而胆汁引流仅上调了25-羟基化途径(178%-371%)中的酶。使用这些新的测定方法,我们证明了胆酸生物合成中的25-和27-羟基化途径在小鼠和兔子肝脏中比人类肝脏更活跃,并且在兔子肝脏中是分别调节的。
In classic cholic acid biosynthesis, a series of ring modifications of cholesterol precede side chain cleavage and yield 5beta-cholestane-3alpha, 7alpha, 12alpha-triol. Side chain reactions of the triol then proceed either by the mitochondrial 27-hydroxylation pathway or by the microsomal 25-hydroxylation pathway. We have developed specific and precise assay methods to measure the activities of key enzymes in both pathways, 5beta-cholestane-3alpha, 7alpha, 12alpha-triol 25- and 27-hydroxylases and 5beta-cholestane-3alpha, 7alpha, 12alpha, 25-tetrol 23R-, 24R-, 24S- and 27-hydroxylases. The extracts from either the mitochondrial or microsomal incubation mixtures were purified by means of a disposable silica cartridge column, derivatized into trimethylsilyl ethers, and quantified by gas chromatography;-mass spectrometry with selected-ion monitoring in a high resolution mode. Compared with the addition of substrates in acetone, those in 2-hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin increased mitochondrial triol 27-hydroxylase activity 132% but decreased activities of the enzymes in microsomal 25-hydroxylation pathway (triol 25-hydroxylase and 5beta-cholestane-3alpha, 7alpha, 12alpha, 25-tetrol 23R-, 24R-, 24S- and 27-hydroxylases) 13;-60% in human liver. The enzyme activities in both pathways were generally 2- to 4-times higher in mouse and rabbit livers compared with human liver. In all species, microsomal triol 25-hydroxylase activities were 4- to 11-times larger than mitochondrial triol 27-hydroxylase activities but the activities of tetrol 24S-hydroxylase were similar to triol 27-hydroxylase activities in our assay conditions. The regulation of both pathways in rabbit liver was studied after bile acid synthesis was perturbed. Cholesterol feeding up-regulated enzyme activities involved in both 25- (64;-142%) and 27- (77%) hydroxylation pathways, while bile drainage up-regulated only the enzymes in the 25-hydroxylation pathway (178;-371%). Using these new assays, we demonstrated that the 25- and 27-hydroxylation pathways for cholic acid biosynthesis are more active in mouse and rabbit than human livers and are separately regulated in rabbit liver.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
脱氧胆酸是胆酸的主要代谢产物。患有3alpha-羟基类固醇脱氢酶(3alpha-HSD)缺乏症和delta4-3-氧代胆固醇缺乏症的病人以及胆酸代谢正常的受试者,在接受胆酸治疗后,血清和胆汁中主要含有胆酸和脱氧胆酸,而鹅脱氧胆酸及其代谢物似乎有所减少。因此,在胆酸治疗下,患者会暴露于比正常更高的脱氧胆酸浓度,尽管这些浓度的确切量化尚未被描述。在单次和重复剂量研究中,脱氧胆酸在大约一半的剂量下就显示出致死效应、胃肠道和肝脏毒性,而胆酸需要更高的剂量才能产生相同的效果。因此,认为脱氧胆酸比胆酸更有毒性,实际上可能是胆酸毒性的原因之一。脱氧胆酸的细菌致突变性数据存在争议,但在体外微核试验中脱氧胆酸显示出基因毒性。此外,通过彗星试验研究了胆酸(主要集中在鹅脱氧胆酸和脱氧胆酸)对人类结肠细胞和结肠肿瘤细胞HT 29的基因毒性潜力。在两种细胞类型中,观察到两种胆酸引起的明显的剂量依赖性基因毒性效应,其中脱氧胆酸更具基因毒性。细胞的存活率似乎大于75%。使用经过Ⅲ型核酸酶修饰的彗星试验表明,DNA损伤可能是由活性氧种类的产生介导的,但通过加入抗氧化剂得到了一定程度的保护。短期致癌性研究建议,脱氧胆酸像胆酸一样具有促进致癌性的特性。在大鼠肝脏中,脱氧胆酸(75-150 mg/kg)显示出促进作用,与对照组相比,接受致癌物二乙基亚硝胺(DEN)单独处理的相应对照组,alpha-谷氨酰转肽酶阳性(alpha-GT+)肝焦点显著增加。脱氧胆酸(20 mg/kg)在大鼠结肠中增强了氧化偶氮甲烷(AOM)诱导的异常隐窝焦点的发育和生长。在平行研究中,在没有AOM的情况下,脱氧胆酸并没有显著诱导异常隐窝焦点。然而,一项研究得出结论,脱氧胆酸可能不仅作为促进剂,还可能是多阶段致癌过程启动剂的结论。
Deoxycholic acid is the main metabolite of cholic acid. Patients with 3alpha-HSD deficiency and delta4-3-oxoR deficiency and subjects with a normal bile acid metabolism have shown that upon treatment with cholic acid, serum and bile predominantly contain cholic acid and deoxycholic acid, while chenodeoxycholic acid and its metabolites appear to be reduced. Under cholic acid treatment, patients are therefore exposed to higher than normal deoxycholic acid concentrations, although the exact quantifications of these concentrations have not been described. In single- and repeat-dose studies, deoxycholic acid showed lethal effects, gastrointestinal and hepatic toxicities at approximately half the doses needed for cholic acid to produce the same effects. It is therefore considered that deoxycholic acid is more toxic than cholic acid and may in fact be the causative agent of some of cholic acid's toxicity. Mutagenicity data from bacterial test for deoxycholic acid is ambiguous but deoxycholic acid was genotoxic in an in vitro micronucleus assay. Additionally, ... the genotoxic potential of BA (focusing on chenodeoxycholic acid and deoxycholic acid) on human colonocytes and colon tumor cells HT 29 by a comet assay /was investigated/. In both cell types a clear dose-dependent genotoxic effect induced by the two bile acids was observed, with deoxycholic acid being more genotoxic. Viability of cells appeared to be greater than 75%. Use of a nuclease III modified comet assay suggested that the DNA damage could be mediated by reactive oxygen species production but was somewhat protected by inclusion of anti-oxidants. Short term carcinogenicity studies suggest that deoxycholic acid like cholic acid has carcinogenicity promoting properties. In rat liver, deoxycholic acid (75-150 mg/kg) exerted promoting activity as evidenced by significantly increased values of alpha-glutamyl transpeptidase-positive (alpha-GT+) liver foci compared with the corresponding controls given the carcinogen, diethylnitrosamine (DEN) alone. Deoxycholic acid (20 mg/kg) enhanced the development and growth of azoxymethane (AOM)-induced aberrant crypt foci in rat colons. In a parallel study, deoxycholic acid in the absence of AOM did not significantly induce aberrant crypt foci. However, /a study/ concluded that deoxycholic acid may act not only as promoters but also initiators of the multistage process of carcinogenesis.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
Cholic acid has known human metabolites that include Cholic acid glucuronide.
来源:NORMAN Suspect List Exchange
毒理性
识别和使用:胆酸用于生物化学研究,作为药物中间体,以及作为食品中的乳化剂(最高0.1%)。它也是一种药物,用于治疗由于单个酶缺陷引起的胆酸合成障碍,以及作为辅助治疗过氧化物酶体障碍,包括在表现出肝脏疾病、脂肪泻或因脂肪溶性维生素吸收减少引起的并发症的泽尔韦格谱系障碍患者。人类暴露和毒性:胆酸是一种主要胆酸。主要胆酸在肝脏中生物合成,是正常胆汁的关键成分。当作为治疗胆酸合成障碍患者的药物配方和使用时,主要的毒性效应是对肝功能的影响。给患者输注的胆酸剂量旨在恢复相当于人体内生理存在的浓度。因此,患者对胆酸和脱氧胆酸的任何感知到的基因毒性风险将与正常健康成人内源性地产生这些胆酸的风险相当。总的来说,胆酸在体外进行的基因毒性测试中显示了非显著的诱变活性。动物研究:胆酸已知通过肝脏的的法尼醇X受体(FXR-SHP)和肠道(FXR-Fgf15)来调节胆酸合成和运输。缺乏维持肝胆酸水平的法尼醇X受体(FXR)的小鼠对胆酸诱导的肝毒性非常敏感。在喂食0.25%胆酸饮食五天后,血清天门冬氨酸转氨酶(AST)活性升高了15.7倍,而在喂食0.25和1%胆酸饮食的野生型小鼠中,血清AST仅略有增加(分别为1.7倍和2.5倍)。在大鼠化学诱导结肠癌模型中,研究了主要胆酸作为可能的结肠肿瘤促进剂或抑制剂。胆酸喂食增加了带有肿瘤的动物数量、每只动物的肿瘤数量以及带有肿瘤的动物的平均肿瘤数量。肿瘤增强归因于胆酸的细菌代谢物脱氧胆酸。给雄性大鼠连续三天喂食胆酸(饮食的1.0%)导致结肠隐窝柱中的DNA合成上皮细胞数量增加,与对照组或0.2%胆酸喂食的大鼠相比。通过使用Salmonella typhimurium TA100和TA98作为测试菌株的波动试验检测了胆酸的诱变性。胆酸和脱氧胆酸在这种测试中具有诱变性。胆酸的诱变性大约是中等强诱变剂甲基甲磺酸的四分之一。怀孕的仓鼠摄入0.5%胆酸,会导致成年动物不同程度的导管/小导管增殖和肝胆炎症损伤,幼年动物损伤程度较轻;并且幼仔的数量也会减少。在怀孕期间,仓鼠摄入这些胆酸会对母体和新生儿的肝胆系统造成不同程度的毒性。在大鼠发育研究中,胆酸处理组的大鼠胎儿大脑出现了明显的病理变化,神经元退化和线粒体肿胀主要出现在低胆酸组,而神经元坏死和线粒体减少主要出现在高胆酸组。
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: Cholic acid is used in biochemical research, as a pharmaceutical intermediate, and as an emulsifying agent in foods (up to 0.1%). It is also a medication used for the treatment of bile acid synthesis disorders due to single enzyme defects and for the adjunctive treatment of peroxisomal disorders including Zellweger spectrum disorders in patients who exhibit manifestations of liver disease, steatorrhea or complications from decreased fat soluble vitamin absorption. HUMAN EXPOSURE AND TOXICITY: Cholic acid is a primary bile acid. Primary bile acids are biosynthesized in the liver and are key constituents of normal bile. When formulated and used as a treatment for patients with bile acid synthesis disorders the major toxic effect is on liver function. The dose of cholic acid to be administered to the patients is intended to restore a concentration that is equivalent to that physiologically present in humans. Therefore any perceived genotoxic risk from cholic acid and deoxycholic acid to the patients would be equivalent to that of a normal healthy adult that produces these bile acids intrinsically. Overall, cholic acid showed nonsignificant mutagenic activity in a battery of genotoxicity tests performed in vitro. ANIMAL STUDIES: Bile acids are known to regulate bile acid synthesis and transport by the farnesoid X receptor in the liver (FXR-SHP) and intestine (FXR-Fgf15). Mice lacking the farnesoid X receptor (FXR) involved in the maintenance of hepatic bile acid levels are highly sensitive to cholic acid-induced liver toxicity. Serum aspartate aminotransferase (AST) activity was elevated 15.7-fold after feeding a 0.25% cholic acid diet for five days, whereas only slight increases in serum AST (1.7- and 2.5-fold) were observed in wild-type mice fed 0.25 and 1% cholic acid diet, respectively. Primary bile acids were studied as possible colon tumor promoters or inhibitors in a rat model of chemically induced colon cancer. Cholic acid feeding increased the number of animals with tumors, the number of tumors per animal, and the number of tumors per tumor-bearing animal. Tumor enhancement was attributed to deoxycholic acid, the bacterial metabolite of cholic acid. Administration of cholic acid (1.0% of the diet) to male rats for 3 days resulted in increased numbers of DNA synthesizing epithelial cells per colonic crypt column as compared to those found in either control or 0.2% cholic acid-fed rats. The mutagenicity of bile acids was detected by a fluctuation test using Salmonella typhimurium TA100 and TA98 as tester strains. Cholic acid and deoxycholic acid were mutagenic in this test. The mutagenicity of the bile acids on a molar basis was roughly one-fourth that of methyl methanesulfonate, a moderately potent mutagen. 0.5% cholic acid ingested by pregnant hamsters, caused ductal/ductular proliferation and hepatobiliary inflammatory damage in a different degree of intensity in adult animals and mild intensity in the young; and also the number of the young was reduced in the litter. The ingestion of these bile acids by hamsters, during gestational period caused different degrees of toxicity on maternal and neonatal hepatobiliary systems. In rat developmental studies there was apparent pathological change of fetal rats brain in cholic acid-treated groups, the neuronal degeneration and the mitochondria swelling was mainly found in low cholic acid group, the neuronal necrosis and the mitochondria decrease was mainly found in high cholic acid group.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
在小规模开放标签试验中,发现胆酸能改善脂肪溶性维生素的吸收,并减轻胆酸合成缺陷的许多临床特征,包括血清转氨酶水平的改善、胆红素和黄疸的降低以及总体健康和生长的改善。在某些情况下,较高剂量的胆酸与血清转氨酶水平的升高有关。然而,这些异常是轻微的、暂时的,并且随着每日剂量的降低迅速逆转。在标准剂量下给予胆酸治疗时,尚未有临床明显的肝损伤伴黄疸的报道。
In small, open label trials, cholic acid was found to improve fat soluble vitamin absorption and to ameliorate many of the clinical features of the bile acid synthetic defects including improvement in serum aminotransferase levels, decrease in bilirubin and jaundice and improvement in general health and growth. In some instances, higher doses of cholic acid were associated with elevations in serum aminotransferase levels. These abnormalities, however, were mild, transient and rapidly reversed with lowering the daily dose. There have been no reports of clinically apparent liver injury with jaundice attributed to cholic acid therapy given in standard doses.
来源:LiverTox
毒理性
对人类不具有致癌性(未被国际癌症研究机构IARC列名)。
No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC).
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
Chronically high levels of cholic acid are associated with Familial Hypercholanemia.
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
Aluminum-based antacids have been shown to adsorb bile acids in vitro and can reduce the bioavailability of Cholbam. Take Cholbam at least 1 hour before or 4 to 6 hours (or at as great an interval as possible) after an aluminum-based antacid.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
服用后,胆酸首先会被小肠吸收,然后通过血液运输到肝脏进行进一步处理。
Following ingestion, absorption of cholic acid will first be by the small intestine, and is then transported to the liver by the blood for further processing.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
口服胆酸与内源性胆酸遵循相同的代谢途径。胆酸通过被动扩散沿着胃肠道的全长被吸收。一旦被吸收,胆酸就进入人体的胆汁酸池,并主要以结合形式进行肠肝循环。在肝脏中,胆酸通过胆酸-CoA合成酶和胆酸-CoA:氨基酸N-乙酰转移酶与甘氨酸或牛磺酸结合。结合胆酸主要通过胆盐外排泵(BSEP)积极地分泌到胆汁中,然后释放到小肠,与其他胆汁成分一起。结合胆酸主要在回肠通过顶膜钠依赖胆酸转运体再次吸收,通过包括钠牛磺胆酸共转运多肽和有机阴离子转运蛋白的转运体返回肝脏,并进入另一个肠肝循环周期。在回肠未被吸收的结合胆酸会进入结肠,在那里通过细菌介导的去结合和7-脱羟基作用形成胆酸和去氧胆酸,这些胆酸可以在结肠再次吸收或随粪便排出。胆酸的损失通过从胆固醇新合成胆酸来补偿,以维持健康受试者的胆汁酸池。
Orally administered cholic acid is subject to the same metabolic pathway as endogenous cholic acid. Cholic acid is absorbed by passive diffusion along the length of the gastrointestinal tract. Once absorbed, cholic acid enters into the body's bile acid pool and undergoes enterohepatic circulation mainly in conjugated forms. In the liver, cholic acid is conjugated with glycine or taurine by bile acid-CoA synthetase and bile acid-CoA: amino acid N-acetyltransferase. Conjugated cholic acid is actively secreted into bile mainly by the Bile Salt Efflux Pump (BSEP), and then released into the small intestine, along with other components of bile. Conjugated cholic acid is mostly re-absorbed in the ileum mainly by the apical-sodium-dependent-bile acid transporter, passed back to the liver by transporters including sodium-taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide and organic anion transport protein and enters another cycle of enterohepatic circulation. Any conjugated cholic acid not absorbed in the ileum passes into the colon where deconjugation and 7-dehydroxylation are mediated by bacteria to form cholic acid and deoxycholic acid which may be re-absorbed in the colon or excreted in the feces. The loss of cholic acid is compensated by de-novo synthesis of cholic acids from cholesterol to maintain the bile acid pool in healthy subjects.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
Excretion studies in rat showed that cholic acid (CA) is almost exclusively excreted in the feces in the form of metabolite. Only minor amounts of CA were found in the unconjugated form in rat feces. Urinary excretion of bile acids is minimal and in mice fed a 1% CA diet, the excretion of bile acids was 2000-fold higher in feces than in urine
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
胆酸在大鼠的小肠中主要在远端(回肠)而不是近端段被吸收。
Cholic acid was shown to be mainly absorbed in the distal (ileal) rather than proximal segments of the small intestine in the guinea pig.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
安全信息
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险品标志:Xi
-
安全说明:S24/25
-
危险类别码:R36/37/38
-
WGK Germany:2
-
海关编码:2942000000
-
危险品运输编号:UN1230 - class 3 - PG 2 - Methanol, solution
-
RTECS号:FZ9350000
-
危险标志:GHS07
-
危险性描述:H315,H319
-
危险性防范说明:P305 + P351 + P338
SDS
制备方法与用途
简介
胆酸是一种宿主和微生物群相关的代谢物。它为无色片状物或白色结晶粉末,能够调节宿主免疫力与微生物的毒力。在宿主体内合成后,胆酸会分泌进入肠道。而微生物进一步将其代谢成结构多样的初级和次级胆酸。这些胆酸在宿主免疫调节、抗菌等方面发挥作用。
鉴别试验- 溶解性:极难溶于水;溶于乙醇。
- 熔点:197~202℃。
- 玫瑰色反应:取试样,加50%醋酸液0.02%,再加入1%糠醛溶液、水及浓硫酸混合后,在5分钟内应呈现玫瑰色并转变为紫色。
- 棕色反应:取约10mg试样,滴加苯甲醛和3:1的硫酸在50℃下加热5分钟后呈棕色。
精确称取140℃真空干燥4小时后的胆酸约400mg,放入250ml烧瓶中。加入水20ml及乙醇40ml,在蒸汽浴上温和加热至溶解后冷却。加酚酞试液(TS-167)5滴,用0.1mol/L氢氧化钠液滴定至粉红色,并保持15秒进行空白试验并作必要校正。每mL 0.1mol/L氢氧化钠相当于胆酸(C₂₄H₄₀O₅)40.86mg。
毒性ADI值为0~1.25mg/kg(FAO/WHO,2001)。
化学性质胆酸存在于牛、羊、猪的胆汁中。无色片状物或白色结晶粉末,有苦味并尝后带甜味。熔点198℃,比旋度(c=0.6,乙醇)为+37°。1g胆酸可溶于约300ml乙醇或丙酮、7ml冰醋酸,少量溶解于水。一水合物为白色片状结晶。1927年,H.Wieland(德国)研究了胆酸的组成并获得了诺贝尔化学奖。
用途 制备方法乙醇精制法
乙酸乙酯分离法
具体步骤如下:
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 (3alpha,5beta,7alpha,12beta)-3,7,12-三羟基胆烷-24-酸 3αβ,7α,12β-trihydroxy-5β-cholanoic acid 71883-64-2 C24H40O5 408.579 去氧胆酸 Deoxycholic acid 83-44-3 C24H40O4 392.579 (3a,5b,7a,12a)-3,7,12-三羟基-胆甾烷-26-酸 3α,7α,12α-trihydroxy-5β-cholestan-26-oic acid 547-98-8 C27H46O5 450.659 胆酸甲酯 methyl cholate 1448-36-8 C25H42O5 422.605 —— 3α,7α,12α-trihydroxycholan-24-ol 3758-71-2 C24H42O4 394.595 5beta-胆烷酸-3alpha,7alpha,12alpha-三醇乙酯 ethyl iso-allocholate 47676-48-2 C26H44O5 436.632 石胆酸 Lithocholic acid 434-13-9 C24H40O3 376.58 —— (24S,25R)-3α,7α,12α,24-tetrahydroxy-5β-cholestan-26-oic acid 85552-43-8 C27H46O6 466.659 —— (24S,25S)-3α,7α,12α,24-tetrahydroxy-5β-cholestan-26-oic acid 85552-44-9 C27H46O6 466.659 —— (24R,25S)-3α,7α,12α,24-tetrahydroxy-5β-cholestan-26-oic acid 85552-42-7 C27H46O6 466.659 —— (24R,25R)-3α,7α,12α,24-tetrahydroxy-5β-cholestan-26-oic acid 85552-41-6 C27H46O6 466.659 —— tert-butyl cholate 122752-67-4 C28H48O5 464.686 7-酮基-3alpha,12alpha-二羟基胆烷酸 7-ketodeoxycholic acid 911-40-0 C24H38O5 406.563 —— 7,12-dihydroxy-3-(sulfooxy)(3α,5β,7α,12α)-cholan-24-oic acid —— C24H40O8S 488.643 甘氨胆酸 glycocholic acid 475-31-0 C26H43NO6 465.631 —— 7α-hydroxy-3,12-dioxo-5β-cholan-24-oic acid ethyl ester —— C26H40O5 432.601 - 1
- 2
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 4-[(5S,7S,8S,10S,13R,17R)-3,7,12-三羟基-10,13-二甲基-2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-十四氢-1H-环戊二烯并[a]菲-17-基]戊酸 ursocholic acid 2955-27-3 C24H40O5 408.579 7alpha,12alpha-二羟基-5beta-胆烷-24-酸 7α,12α-dihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-oic acid 566-17-6 C24H40O4 392.579 —— 6α-ethyl-cholic acid —— C26H44O5 436.632 去氧胆酸 Deoxycholic acid 83-44-3 C24H40O4 392.579 —— cholic acid 7170-94-7 C25H42O5 422.605 —— 27-nor-3α,7α,12α-trihydroxy-5β-cholestan-26-oic acid 6246-77-1 C26H44O5 436.632 鹅去氧胆酸 chenodeoxycholic acid 474-25-9 C24H40O4 392.579 熊去氧胆酸 ursodeoxycholic acid 128-13-2 C24H40O4 392.579 —— (25R)-3α,7α,12α-trihydroxy-5β-cholestan-26-oic acid 23740-14-9 C27H46O5 450.659 —— (25R)-3α,7α,12α-trihydroxy-5β-cholestan-26-oic acid 23047-29-2 C27H46O5 450.659 胆酸甲酯 methyl cholate 1448-36-8 C25H42O5 422.605 熊胆酸甲酯 methyl (4R)-4-[(3R,5S,7S,8R,9S,10S,12S,13R,14S,17R)-3,7,12-trihydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]pentanoate 28050-56-8 C25H42O5 422.605 —— methyl 7α,12a-dihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-oate 3701-54-0 C25H42O4 406.606 —— 3β,7α,12α-trihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-oic acid methyl ester 28050-54-6 C25H42O5 422.605 (3a,5b,6a,12a)-3,6,12-三羟基-胆烷-24-酸 3α,6α,12α-trihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-oic acid 21066-18-2 C24H40O5 408.579 —— 3α,7α,12α,16α-tetrahydroxy-5β-cholan-24-oic acid —— C24H40O6 424.578 —— 3α,12α,16α-trihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-oic acid 640-90-4 C24H40O5 408.579 —— 3α,7α,12α-trihydroxycholan-24-ol 3758-71-2 C24H42O4 394.595 粪甾烷酸 5beta-cholestan-3alpha,7alpha,12alpha-triol 547-96-6 C27H48O3 420.676 —— (3R,5S,7R,8R,9S,10S,12S,13R,14S,17R)-17-((R)-sec-butyl)-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,7,12-triol —— C23H40O3 364.569 —— 3α,7α,12α-trihydroxy-5β-cholane 4086-94-6 C24H42O3 378.596 5beta-胆烷酸-3alpha,7alpha,12alpha-三醇乙酯 ethyl iso-allocholate 47676-48-2 C26H44O5 436.632 3-氧代脱氧胆酸 7α,12α-dihydroxy-3-oxocholanoic acid 2304-89-4 C24H38O5 406.563 鹅脱氧胆酸甲酯 chenodeoxycholic acid methyl ester 3057-04-3 C25H42O4 406.606 甲基3,7-二羟基胆烷-24-酸酯 3α,7β-dihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-oic acid methyl ester 10538-55-3 C25H42O4 406.606 —— 3α,6α,7α,12α-tetrahydroxy-5β-cholan-24-oic acid 80875-92-9 C24H40O6 424.578 (3alpha,5beta,6beta,7alpha,12alpha)-3,6,7,12-四羟基胆烷-24-酸 3α,6β,7α,12α-tetrahydroxy-5β-cholan-24-oic acid 80875-93-0 C24H40O6 424.578 (3R,5S,7R,8R,9S,10S,12S,13R,14S)-17-[(2R)-6-羟基-6-甲基庚烷-2-基]-10,13-二甲基-2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-十四氢-1H-环戊二烯并[a]菲-3,7,12-三醇 5β-Cholestane-3α,7α,12α,25-tetrol 18866-87-0 C27H48O4 436.676 —— 5β-cholestane-3α,7α,12α,26,27-pentol —— C27H48O5 452.675 —— 3α,7α,12α-trihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-amide 6786-09-0 C24H41NO4 407.594 —— (R)-4-[(3R,5S,7R,8R,9S,10S,12S,13R,14S,17R)-3,7,12-trimethoxy-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]pentanoic acid 117832-92-5 C27H46O5 450.659 7alpha,12alpha-二羟基-5beta-胆甾烷-3-酮 7α,12α-dihydroxy-5β-cholestan-3-one 547-97-7 C27H46O3 418.66 石胆酸 Lithocholic acid 434-13-9 C24H40O3 376.58 —— propargyl 3α,7α,12α-trihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-oate 868595-12-4 C27H42O5 446.627 —— methyl 3,7,12-trimethoxycholanoate 75469-14-6 C28H48O5 464.686 (2R,3R,6R)-2,3-二羟基-6-[(3R,5R,8R,9S,10S,13R,14S,17R)-3-羟基-10,13-二甲基十六碳氢-1H-环戊二烯并[a]菲-17-基]庚酸 3α,7α,12α,24ξ-tetrahydroxy-5β-cholestan-26-oic acid 1061-64-9 C27H46O6 466.659 —— tert-butyl cholate 122752-67-4 C28H48O5 464.686 7alpha,12alpha-二羟基-3-氧代-5beta-胆烷-24-酸甲酯 3-oxo cholic acid methyl ester 14772-99-7 C25H40O5 420.59 鲨胆甾醇 scymnol 6785-34-8 C27H48O6 468.675 7-酮基-3alpha,12alpha-二羟基胆烷酸 7-ketodeoxycholic acid 911-40-0 C24H38O5 406.563 —— cholic acid triformate 2097-89-4 C27H40O8 492.61 (3alpha,5beta,7alpha,12alpha)-7,12-双(甲酰氧基)-3-羟基胆烷-24-酸 7,12 diformate of cholic acid 64986-86-3 C26H40O7 464.599 —— N methyl(3α,5β,7α,12α)3,7,12-trihydroxy-cholan-24-amide 86678-84-4 C25H43NO4 421.621 —— methyl 3α,7α,12α-triformyloxy-5β-cholanoate 33744-75-1 C28H42O8 506.637 —— cholylhydrazide 80948-49-8 C24H42N2O4 422.608 —— (3R,5S,7R,8R,9S,10S,12S,13R,14S,17R)-17-((R)-But-3-en-2-yl)-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,7,12-triol 59648-66-7 C23H38O3 362.553 (3alpha,5beta,12alpha)-3,12-二羟基-7-酮基胆烷-24-酸甲酯 methyl 3α,12α-dihydroxy-7-oxo-5β-cholate 10538-65-5 C25H40O5 420.59 —— <23R>-3α,7α,12α,23-tetrahydroxy-5β-cholan-24-oic acid ethyl ester 84958-40-7 C26H44O6 452.632 —— (R)-4-((3R,5S,7R,8R,9S,10S,12S,13R,14S,17R)-3,7,12-Trimethoxy-10,13-dimethyl-hexadecahydro-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl)-pentan-1-ol 272115-35-2 C27H48O4 436.676 —— N-propylcholamide —— C27H47NO4 449.674 (3a,5b,7a)-3,7-二羟基-12-氧代-胆烷-24-酸 3α,7α-dihydroxy-12-oxo-5β-cholan-24-oic acid 2458-08-4 C24H38O5 406.563 12-氧代-乌苏基脱氧胆酸 12-ketoursodeoxycholic acid 81873-91-8 C24H38O5 406.563 —— 12-Oxocholic acid —— C24H38O5 406.6 —— cholic acid 3,7-diacetate 7432-64-6 C28H44O7 492.653 —— N-2'-aminoethyl 3α,7α,12α-trihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-amide 78793-09-6 C26H46N2O4 450.662 —— (4R,4R)-N,N-(pentane-1,5-diyl)bis(4-((3R,5S,7R,8R,9S,10S,12S,13R,14S,17R)-3,7,12-trihydroxy-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl)pentanamide) —— C53H90N2O8 883.306 甲基(4R)-4-[(3R,5S,7R,8R,9S,10S,12S,13R,14S,17R)-3,7-二乙酰氧基-12-羟基-10,13-二甲基-2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-十四氢-1H-环戊二烯并[a]菲-17-基]戊酸酯 methyl 3α,7α-diacetoxy-12α-hydroxy cholanate 3749-87-9 C29H46O7 506.68 (3alpha,5beta,7alpha,12alpha)-7-乙酰氧基-3,12-二羟基胆烷-24-酸甲酯 methyl 7α-acetoxy-3α,12α-dihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-oate 7432-44-2 C27H44O6 464.643 —— N-(3'-aminopropyl)cholamide —— C27H48N2O4 464.689 —— N-(2'-cyanoethyl)-3α,7α,12α-trihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-amide —— C27H44N2O4 460.657 —— 7α-hydroxy-3,12-dioxo-5β-cholan-24-oic acid 2304-91-8 C24H36O5 404.547 —— N-(propargyl)-3α,7α,12α-trihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-amide 1021182-35-3 C27H43NO4 445.643 —— cholic acid 3,7,12-triacetate 52840-09-2 C30H46O8 534.69 —— 3α-hydroxy-7α,12α-diacetoxy-5β-cholan-24-oic acid 61543-86-0 C28H44O7 492.653 —— 3α,7α,12α-triformyloxy-5β-cholan-24-ol 96736-29-7 C27H42O7 478.626 —— 7,12-dihydroxy-3-(sulfooxy)(3α,5β,7α,12α)-cholan-24-oic acid —— C24H40O8S 488.643 —— methyl 3,7,12-triacetoxycholan-24-oate 6818-44-6 C31H48O8 548.717 5β-胆烷酸 cholanic acid 546-18-9 C24H40O2 360.58 —— triformylcholic acid chloride 74670-08-9 C27H39ClO7 511.055 —— 3α-ethoxycarbonyloxy-7α,12α-dihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-oic acid methyl ester 21059-36-9 C28H46O7 494.669 —— methyl 3-oxo-7α,12α-bis(formyloxy)-5β-cholan-24-oate 97412-84-5 C27H40O7 476.61 —— N1-(3α,7α,12α-trihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-carbonyl)-1,12-diamino-4,9-diazadodecane —— C34H64N4O4 592.907 —— 4-(7,12-dihydroxy-3-methanesulfonyloxy-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl)pentanoic acid —— C25H42O7S 486.67 —— 3-mesylcholic acid 135053-65-5 C25H42O7S 486.67 3-(胆酰胺基丙基)-1,1-二甲胺 N-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]cholanamide 76555-98-1 C29H52N2O4 492.743 —— methyl 3α,7α-dihydroxy-12-oxo-5β-cholanoate 10538-64-4 C25H40O5 420.59 —— 7α,12α-diformyloxy-5β-cholestan-3-one 1448262-81-4 C29H46O5 474.681 3Α-羟基-7-氧代-5Β-胆烷酸 7-Ketolithocholic acid 4651-67-6 C24H38O4 390.563 甘氨胆酸 glycocholic acid 475-31-0 C26H43NO6 465.631 —— (1S,4R,5R,15S,17S,18S,21R,23S,25R,26R,27R)-5,18,27-trimethyl-9,14-dioxapentacyclo[13.11.1.04,27.017,26.018,23]heptacosane-21,25-diol 1365549-65-0 C28H48O4 448.687 —— 3α,7α,12α-tris(chloroacetyloxy)-5β-cholanic acid —— C30H43Cl3O8 638.026 —— 3α.12α-diformyloxy-7-oxo-5β-cholanoic acid-(24) 109845-11-6 C26H38O7 462.584 —— methyl (7α,12α)-7,12-di(methoxymethyloxy)-3-oxo-5β-cholan-24-oate 831171-65-4 C29H48O7 508.696 —— 3α,7α,12α-triallyloxy-24-hydroxyl-5β-cholane 321126-93-6 C33H54O4 514.789 —— (3R,5S,7R,8R,9S,10S,12S,13R,14S,17R)-3,7-dimethoxy-10,13-dimethyl-12-prop-2-enoxy-17-[(2R)-5-prop-2-enoxypentan-2-yl]-2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene 1365549-56-9 C32H54O4 502.778 —— N-(cyclopentyl)-3α,7α,12α-trihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-amide —— C29H49NO4 475.712 —— 3α,7α-Dihydroxy-chol-11-ensaeure —— C24H38O4 390.563 —— [(4R)-4-[(3R,5S,7R,8R,9S,10S,12S,13R,14S,17R)-3,7-dimethoxy-10,13-dimethyl-12-prop-2-enoxy-2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]pentyl] hex-5-enoate 1365549-88-7 C35H58O5 558.843 —— (R)-1-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)-4-((3R,5S,7R,8R,9S,10S,12S,13R,14S,17R)-3,7,12-trihydroxy-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl)pentan-1-one —— C28H47NO4 461.685 (5beta,7alpha,12alpha)-7,12-双(乙酰氧基)-3-酮基胆烷-24-酸 3-oxo-7α,12α-diacetoxy-5β-cholan-24-oic acid 300386-87-2 C28H42O7 490.637 —— octyl (4R)-4-[(3R,5S,7R,8R,9S,10S,12S,13R,14S,17R)-3,7,12-tris[(2-aminoacetyl)oxy]-10,13-dimethyl-2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]pentanoate 302784-38-9 C38H65N3O8 691.949 —— methyl 3-keto-7,12-diacetylcholate 4947-65-3 C29H44O7 504.664 3α-羟基-7-氧代-胆烷酸-24-甲酯 7-ketolithocholic methyl ester 10538-59-7 C25H40O4 404.59 —— [(4R)-4-[(3R,5S,7R,8R,9S,10S,12S,13R,14S,17R)-3,7-dimethoxy-10,13-dimethyl-12-prop-2-enoxy-2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]pentyl] pent-4-enoate 1365549-86-5 C34H56O5 544.816 —— [(4R)-4-[(3R,5S,7R,8R,9S,10S,12S,13R,14S,17R)-3,7-dimethoxy-10,13-dimethyl-12-prop-2-enoxy-2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]pentyl] prop-2-enoate 1365549-73-0 C32H52O5 516.762 —— propargyl 3α-chloroacetoxy-7α,12α-diformyloxy-5β-cholan-24-oate 1353720-59-8 C31H43ClO8 579.131 —— methyl 3α,7α-dimethoxy-12-oxo-5β-cholan-24-oate 1351984-86-5 C27H44O5 448.643 胆酸杂质 7,12-dioxolitocholic acid 517-33-9 C24H36O5 404.547 —— [(4R)-4-[(3R,5S,7R,8R,9S,10S,12S,13R,14S,17R)-3,7-dimethoxy-10,13-dimethyl-12-prop-2-enoxy-2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]pentyl] but-3-enoate 1365549-84-3 C33H54O5 530.789 (5beta)-3-氧代-胆烷-24-酸 dehydrolithocholic acid 1553-56-6 C24H38O3 374.564 - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:通过 C3,C7-选择性缩酮保护简明高效合成 3,7-Dioxo-5β-胆酸摘要:熊去氧胆酸 (UDCA, 1) 最初于 1927 年由 Shoda 从黑熊的胆汁中分离出来(图 1)。它是唯一获得 FDA 批准的治疗原发性硬化性胆管炎的药物。通常,该药物是通过胆酸 (CA, 2) 的有机半合成生产的,胆酸是一种丰富且廉价的天然胆汁酸。在半合成的最后一步,1 的 3 和 7-羟基部分是通过立体选择性还原 3,7dioxo-5b-胆酸 3 形成的。酸 3 是合成 UDCA 的关键前体,是一种有价值的具有有用的合成、医药和制药应用的氧代胆酸衍生物。DOI:10.1080/00304948.2017.1291005
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:胆酸中间体A4及其制备方法摘要:本发明提供了一种胆酸中间体A4及其制备方法。所述胆酸中间体A4的制备方法包括:以甲苯为溶剂,以乙二醇为缩酮反应试剂,以对甲苯磺酸为催化剂,将式A3所示化合物与甲苯、乙二醇和对甲苯磺酸混合后,使体系升温至回流状态进行反应,直至反应完全,得到反应产物,所述反应产物经后处理得到式A4所示化合物。本发明提供一种反应条件温和的化学合成方法生产胆酸中间体A4,该胆酸中间体A4最终可以用于高效制备胆酸,以解决通过动物内脏提取胆酸带来的病毒传染的风险。公开号:CN116023424A
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:O'Connor, Charmian J.; Wallace, Robert G., Australian Journal of Chemistry, 1984, vol. 37, # 9, p. 1881 - 1893摘要:DOI:
文献信息
-
Small molecules for treatment of hypercholesterolemia and related diseases申请人:Sircar C. Jagadish公开号:US20050277690A1公开(公告)日:2005-12-15The present invention provides compositions adapted to enhance reverse cholesterol transport in mammals. The compositions are suitable for oral delivery and useful in the treatment and/or prevention of hypercholesterolemia, atherosclerosis and associated cardiovascular diseases.
-
[EN] CATHEPSIN INHIBITORS<br/>[FR] INHIBITEURS DE LA CATHEPSINE申请人:ACADEMISCH ZIEKENHUIS LEIDEN公开号:WO2019112426A1公开(公告)日:2019-06-13This invention relates to compounds that are useful as inhibitors, in particular as inhibitors of Cathepsin K (CatK), and to a method of inhibiting cathepsin activity, comprising administering a compound or formulation comprising a compound according to the invention.
-
A Bifunctional Copper Catalyst Enables Ester Reduction with H<sub>2</sub>: Expanding the Reactivity Space of Nucleophilic Copper Hydrides作者:Birte M. Zimmermann、Trung Tran Ngoc、Dimitrios-Ioannis Tzaras、Trinadh Kaicharla、Johannes F. TeichertDOI:10.1021/jacs.1c09626日期:2021.10.13activation of esters through hydrogen bonding and formation of nucleophilic copper(I) hydrides from H2, resulting in a catalytic hydride transfer to esters. The reduction step is further facilitated by a proton shuttle mediated by the guanidinium subunit. This bifunctional approach to ester reductions for the first time shifts the reactivity of generally considered “soft” copper(I) hydrides to previously
-
Pharmaceutical compositions of drug-oligomer conjugates and methods of treating diseases therewith申请人:——公开号:US20030069170A1公开(公告)日:2003-04-10Pharmaceutical compositions that include a drug-oligomer conjugate, a fatty acid component, and a bile salt component are described. The drug is covalently coupled to an oligomeric moiety. The fatty acid component and the bile salt component are present in a weight-to-weight ratio of between 1:5 and 5:1. Methods of treating diseases in a subject in need of such treatment using such pharmaceutical compositions are also provided, as are methods of providing such pharmaceutical compositions.
-
Esterification of Aryl/Alkyl Acids Catalysed by N-bromosuccinimide under Mild Reaction Conditions作者:Klara Čebular、Bojan Božić、Stojan StavberDOI:10.3390/molecules23092235日期:——(NBS) has been promoted as the most efficient and selective catalyst among the NXSs in the reaction of direct esterification of aryl and alkyl carboxylic acids. Comprehensive esterification of substituted benzoic acids, mono-, di- and tri-carboxy alkyl derivatives has been performed under neat reaction conditions. The method is metal-free, air- and moisture-tolerant, allowing for a simple synthetic and
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
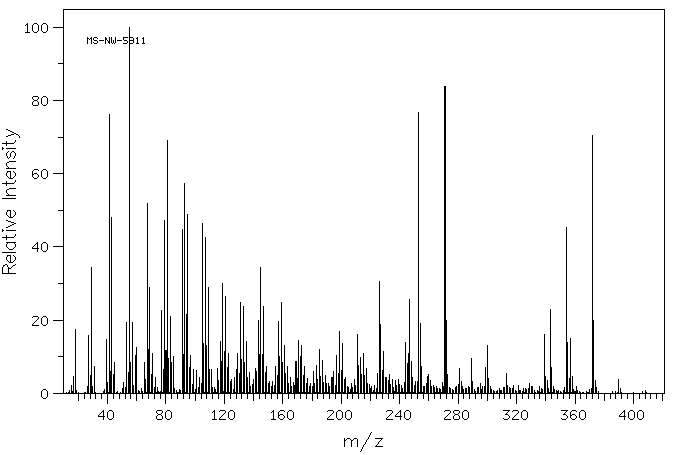
质谱MS
-
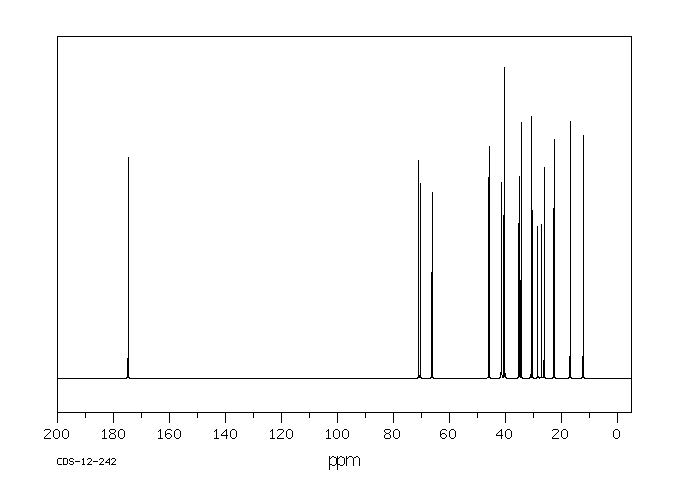
碳谱13CNMR
-
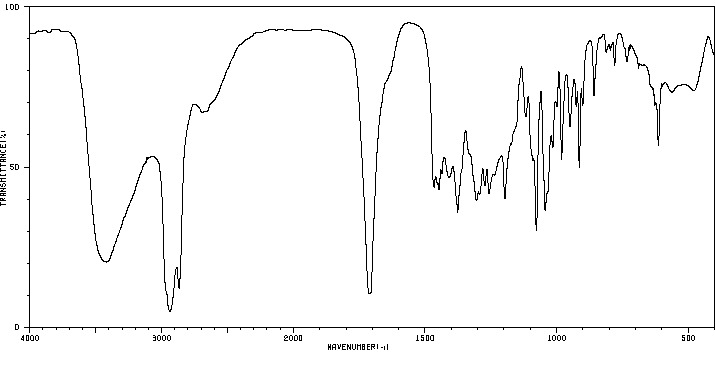
红外IR
-
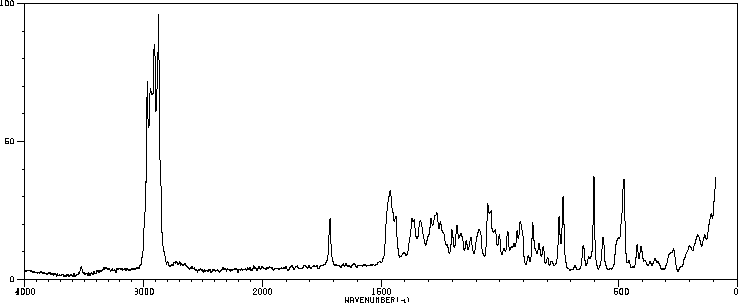
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(5β)-17,20:20,21-双[亚甲基双(氧基)]孕烷-3-酮
(5α)-2′H-雄甾-2-烯并[3,2-c]吡唑-17-酮
(3β,20S)-4,4,20-三甲基-21-[[[三(异丙基)甲硅烷基]氧基]-孕烷-5-烯-3-醇-d6
(25S)-δ7-大发酸
(20R)-孕烯-4-烯-3,17,20-三醇
(11β,17β)-11-[4-({5-[(4,4,5,5,5-五氟戊基)磺酰基]戊基}氧基)苯基]雌二醇-1,3,5(10)-三烯-3,17-二醇
齐墩果酸衍生物1
黄麻属甙
黄芪皂苷III
黄芪皂苷 II
黄芪甲苷 IV
黄芪甲苷
黄肉楠碱
黄果茄甾醇
黄杨醇碱E
黄姜A
黄夹苷B
黄夹苷
黄夹次甙乙
黄夹次甙乙
黄夹次甙丙
黄体酮环20-(乙烯缩醛)
黄体酮杂质EPL
黄体酮杂质1
黄体酮杂质
黄体酮杂质
黄体酮EP杂质M
黄体酮EP杂质G(RRT≈2.53)
黄体酮EP杂质F
黄体酮6-半琥珀酸酯
黄体酮 17alpha-氢过氧化物
黄体酮 11-半琥珀酸酯
黄体酮
麦角甾醇葡萄糖苷
麦角甾醇氢琥珀酸盐
麦角甾烷-6-酮,2,3-环氧-22,23-二羟基-,(2b,3b,5a,22R,23R,24S)-(9CI)
麦角甾烷-3,6,8,15,16-五唑,28-[[2-O-(2,4-二-O-甲基-b-D-吡喃木糖基)-a-L-呋喃阿拉伯糖基]氧代]-,(3b,5a,6a,15b,16b,24x)-(9CI)
麦角甾烷-26-酸,5,6:24,25-二环氧-14,17,22-三羟基-1-羰基-,d-内酯,(5b,6b,14b,17a,22R,24S,25S)-(9CI)
麦角甾-8-烯-3-醇
麦角甾-8,24(28)-二烯-26-酸,7-羟基-4-甲基-3,11-二羰基-,(4a,5a,7b,25S)-
麦角甾-7,22-二烯-3-酮
麦角甾-7,22-二烯-17-醇-3-酮
麦角甾-5,24-二烯-26-酸,3-(b-D-吡喃葡萄糖氧基)-1,22,27-三羟基-,d-内酯,(1a,3b,22R)-
麦角甾-5,22,25-三烯-3-醇
麦角甾-4,6,8(14),22-四烯-3-酮
麦角甾-1,4-二烯-3-酮,7,24-二(乙酰氧基)-17,22-环氧-16,25-二羟基-,(7a,16b,22R)-(9CI)
麦角固醇
麦冬皂苷D
麦冬皂苷D
麦冬皂苷 B