4-甲氧基苯酚 | 150-76-5
中文名称
4-甲氧基苯酚
中文别名
对苯二酚甲基醚;4-甲氧基酚;对甲氧基苯酚;氢醌-甲基醚;氢醌单甲醚;对苯二酚单甲醚;MEHQ;对羟基茴香醚;对羟基苯甲醚;对羟基苯甲醚(MEHQ)
英文名称
4-methoxy-phenol
英文别名
para-methoxyphenol;anisole;p-methoxyphenol;p-hydroxyanisole;MeHQ;mequinol;hydroquinone monomethyl ether;p-methoxylphenol;PMPOH;MOP;4-methoxyphenol
CAS
150-76-5
化学式
C7H8O2
mdl
MFCD00002332
分子量
124.139
InChiKey
NWVVVBRKAWDGAB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:56 °C
-
沸点:243 °C(lit.)
-
密度:1,55 g/cm3
-
蒸气密度:4.3 (vs air)
-
闪点:>230 °F
-
溶解度:易溶于丙酮、乙酸乙酯、乙醇、乙醚、苯和四氯化碳。
-
暴露限值:ACGIH: TWA 5 mg/m3NIOSH: TWA 5 mg/m3
-
LogP:1.3 at 20℃
-
物理描述:Hydroquinone monomethyl ether appears as pink crystals or white waxy solid. (NTP, 1992)
-
颜色/状态:Plates
-
气味:Odor of caramel and phenol
-
蒸汽密度:4.3 (Air = 1)
-
蒸汽压力:6.75X10-3 mm Hg at 20 °C
-
自燃温度:790 °F (421 °C)
-
分解:When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and fumes.
-
燃烧热:Standard Net Heat of Combustion = -3.4X10+9 J/kmol at 25 °C (est)
-
电离电位:7.50 eV
-
解离常数:pKa = 10.05 at 23 °C
-
保留指数:1183;1210;1197;1198;1180;1185;1186;1186;1187;1210;1210
-
稳定性/保质期:
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):1.3
-
重原子数:9
-
可旋转键数:1
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.142
-
拓扑面积:29.5
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:2
ADMET
代谢
来自接受靛红治疗的黑色素瘤患者的尿液样本被分析,并鉴定出了多种靛红代谢物,包括3,4-二羟基苯甲醚,两种邻甲基衍生物3-羟基-4-甲氧基苯甲醚和4-羟基-3-甲氧基苯甲醚,甚至还有至少部分源于靛红的对苯二酚。所有这些鉴定的代谢物主要以硫酸盐和葡萄糖苷酸的形式排出 - 只有很小一部分物质以未结合的形式存在于尿液中。最终,3,4-二羟基苯甲醚被认为是靛红最重要的代谢物。
Urine samples from melanoma patients treated with mequinol were analyzed and various mequinol metabolites were identified, including 3,4-dihydroxyanisole, the two o-methyl derivatives 3-hydroxy-4-methoxyanisole and 4-hydroxy-3-methoxyanisole, and even hydroquinone which may have originated at least partly from mequinol. All these identified metabolites were excreted predominantly as sulphates and glucuronides - only a small portion of the substances were present in urine in an unconjugated form. Ultimately, the 3,4-dihydroxyanisole is considered the most important metabolite of mequinol.
来源:DrugBank
代谢
一种针对恶性黑色素瘤的酪氨酸酶定向治疗策略使用脱色酚类前药,如4-羟基茴香醚(4-HA),通过黑色素瘤酪氨酸酶的氧化作用形成细胞毒性的o-醌。然而,在最近的一项临床试验中,报道了4-HA治疗的副作用,包括肾脏和肝脏毒性。在下文中,给小鼠腹腔注射4-HA(200 mg/kg)导致血浆转氨酶毒性增加7倍,这是肝脏毒性的迹象。此外,4-HA对分离的肝细胞诱导的细胞毒性之前发生了谷胱甘肽(GSH)的耗竭,而细胞色素p450抑制剂可以防止这种耗竭,并且部分防止了细胞毒性。通过NADPH/微粒体和GSH形成的4-HA代谢物被鉴定为一种羟基醌单-谷胱甘肽结合物。GSH耗竭的肝细胞对4-HA或其活性代谢物羟基醌(HQ)诱导的细胞毒性更为敏感。双香豆素(一种NAD(P)H/醌氧化还原酶抑制剂)也增强了4-HA或HQ诱导的毒性,而山梨醇(一种生成NADH的营养素)则预防了这种细胞毒性。乙二胺(一个o-醌陷阱)并没有防止4-HA诱导的细胞毒性,这表明细胞毒性不是由4-HA环羟基化产生的o-醌引起的。去铁胺和抗氧化剂pyrogallol/4-羟基-2,2,6,6-四甲基哌啶-1-氧基(TEMPOL)并没有防止4-HA诱导的细胞毒性,因此排除了氧化应激作为4-HA的细胞毒性机制。当4-HA与大鼠微粒体/NADPH一起孵育时,形成的甲醛量可以忽略不计。这些结果表明,4-HA的细胞毒性机制涉及4-HA环氧或p-醌对细胞蛋白的烷基化,而不是涉及氧化应激。
A tyrosinase-directed therapeutic approach for treating malignant melanoma uses depigmenting phenolic prodrugs such as 4-hydroxyanisole (4-HA) for oxidation by melanoma tyrosinase to form cytotoxic o-quinones. However, in a recent clinical trial, both renal and hepatic toxicity were reported as side effects of 4-HA therapy. In the following, 4-HA (200 mg/kg i.p.) administered to mice caused a 7-fold increase in plasma transaminase toxicity, an indication of liver toxicity. Furthermore, 4-HA induced-cytotoxicity toward isolated hepatocytes was preceded by glutathione (GSH) depletion, which was prevented by cytochrome p450 inhibitors that also partly prevented cytotoxicity. The 4-HA metabolite formed by NADPH/microsomes and GSH was identified as a hydroquinone mono-glutathione conjugate. GSH-depleted hepatocytes were much more prone to cytotoxicity induced by 4-HA or its reactive metabolite hydroquinone (HQ). Dicumarol (an NAD(P)H/quinone oxidoreductase inhibitor) also potentiated 4-HA- or HQ-induced toxicity whereas sorbitol, an NADH-generating nutrient, prevented the cytotoxicity. Ethylenediamine (an o-quinone trap) did not prevent 4-HA-induced cytotoxicity, which suggests that the cytotoxicity was not caused by o-quinone as a result of 4-HA ring hydroxylation. Deferoxamine and the antioxidant pyrogallol/4-hydroxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidene-1-oxyl (TEMPOL) did not prevent 4-HA-induced cytotoxicity, therefore excluding oxidative stress as a cytotoxic mechanism for 4-HA. A negligible amount of formaldehyde was formed when 4-HA was incubated with rat microsomal/NADPH. These results suggest that the 4-HA cytotoxic mechanism involves alkylation of cellular proteins by 4-HA epoxide or p-quinone rather than involving oxidative stress.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
许多知名的脱色剂,如氢醌和对羟基茴香醚,实际上是对黑素细胞有毒的化学物质,它们在黑素细胞中被氧化,产生高度有毒的化合物,如醌类。这些细胞毒化合物负责破坏色素细胞,导致皮肤脱色。然而,细胞能够通过细胞内谷胱甘肽(GSH)来保护自己免受细胞毒剂的侵害。这种保护是在解毒酶谷胱甘肽S-转移酶(GST)的酶促作用下发生的,该酶负责将有毒物质与GSH结合。氢醌的脱色效果被证明可以通过丁硫氨酸亚砜胺(BSO)和胱胺增强,因为这两种物质通过降低细胞内GSH的水平。此外,BSO和胱胺也被证明可以抑制GST的活性。全反式维甲酸(维甲酸,TRA)与氢醌或对羟基茴香醚的组合也已知能产生协同的皮肤脱色作用。TRA是一种有效的哺乳动物GST抑制剂,已知可以通过抑制这种酶的活性使细胞更容易受到化学物质的细胞毒作用。这种剂也被证明可以降低某些细胞内GSH的水平。我们提出,TRA的作用机制是通过抑制GST并损害对黑素细胞毒剂依赖的谷胱甘肽介导的细胞保护,从而协同增强化学物质的黑素细胞毒效果。
Many of the well-known depigmenting agents such as hydroquinone and 4-hydroxyanisole are, in fact, melanocytotoxic chemicals which are oxidized in melanocytes to produce highly toxic compounds such as quinones. These cytotoxic compounds are responsible for the destruction of pigment cells, which results in skin depigmentation. However, cells are capable of protecting themselves against cytotoxic agents by intracellular glutathione (GSH). This protection takes place under the enzymatic action of the detoxification enzyme glutathione S-transferase (GST), which is responsible for the conjugation of toxic species to GSH. The depigmenting effect of hydroquinone is shown to be potentiated by buthionine sulfoximine (BSO) and cystamine as the result of the reduction of intracellular levels of GSH by these two agents. Additionally, BSO and cystamine are shown to inhibit the activity of GST. The combination of all-trans-retinoic acid (tretinoin, TRA) with hydroquinone or 4-hydroxyanisole is also known to produce synergetic skin depigmentation. TRA serves as a potent inhibitor of mammalian GSTs and is known to make cells more susceptible to the cytotoxic effect of chemicals by inhibiting the activity of this enzyme. This agent is also shown to reduce the level of intracellular GSH in certain cells. We have proposed that the mechanism of action of TRA to synergistically enhance the melanocytotoxic effect of chemicals involves the inhibition of GST and the impairment of glutathione-dependent cytoprotection against melanocytotoxic agents.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
Yields 1,4-dimethoxybenzene in guinea pig, rat, rabbit, mouse. Yields 4-methoxycatechol, p-methoxyphenyl-beta-d-glucuronide, & p-methoxyphenyl sulfate in rabbit. /From Table/
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
4-Methoxyphenol has known human metabolites that include (2S,3S,4S,5R)-3,4,5-Trihydroxy-6-(4-methoxyphenoxy)oxane-2-carboxylic acid.
来源:NORMAN Suspect List Exchange
毒理性
识别和使用:4-甲氧基苯酚(4-MP)是一种无色至白色、蜡状固体或白色至棕色、片状、结晶物质,具有焦糖和苯酚的气味。它被用作丙烯酸单体和丙烯腈的抑制剂,氯代烃和乙基纤维素的稳定剂,紫外线抑制剂,以及制造抗氧化剂、药品、塑化剂和染料的化学中间体。它还用作治疗色素异常的药物,尤其是与Tretinoin(Solage)联合使用的过度色素沉着。人类暴露和毒性:在16名患者中的11名(69%;95%置信区间[CI],41%-89%)使用4-MP乳膏实现了完全脱色。脱色开始于4到12个月之间。4例(25%)报告使用该乳膏时有轻微烧灼感或瘙痒。在响应4-MP乳膏的11名患者中,有4名在2到36个月的无治疗期后色素沉着复发(复发率为36%;95% CI,11%-69%)。过度应用4-MP可能导致明显的红斑、脱皮、不适或色素减退。口服该药物可能导致与过度口服维生素A(维生素A过多症)相同的不良反应。在一家氯乙烯工厂,8名处理对甲氧基苯酚的工艺工人中有2人出现前臂皮肤白斑(职业性白斑),其中1人还出现额头皮肤白斑。对8年前暴露于4-MP后的2例白斑病(白癜风)的随访报告和169名暴露于4-MP或对叔戊基酚或两者兼有的男性的调查结果显示,有1名男性出现显著程度的复色,另1名男性出现有限程度的复色。使用Wood's光技术(一种被正常色素沉着皮肤吸收并由非色素沉着皮肤反射的紫外线)对同一工厂中调查的169名男性进行的筛查显示,在测试的148名男性或暴露于对叔戊基酚的129名男性中,没有因暴露于4-MP而引起的白斑病例。关于可能的遗传毒性,细胞遗传学分析的结果显示,4-MP的盐(对甲氧基苯酚磷酸盐)在处理细胞的第一次传递后诱导了数值和结构染色体畸变的减少。根据细胞遗传学分析的结果,遗传不稳定性的减少似乎在第一次到第六次细胞培养中处理对甲氧基苯酚磷酸盐联合苯并(a)芘时保持恒定。动物研究:兔子的研究表明,如果4-MP的暴露时间不仅限于1天,它可能造成相当大的坏死。长时间的接触可能导致严重烧伤。还有迹象表明,当物质处于溶液中时,尤其是通过磨伤的皮肤,会被吸收到有毒的量。兔子经腹腔急性中毒包括低剂量时的瘫痪和缺氧以及高剂量时的中枢神经系统抑制。当将4-MP局部应用于豚鼠(治疗5至10天内)和小型猪时,它会导致皮肤脱色。在兔子的皮肤畸胎学研究中,胎儿的畸形数据没有统计学意义上的差异;然而,在中剂量组中观察到一窝明显的脑积水,头部可见隆起(每千克12和0.06毫克或每平方米132和0.66毫克的4-MP和Tretinoin)。当4-MP局部应用于小鼠(93周内每周两次,每次0.02毫升,在肩胛骨之间)或兔子的内耳时,与对照相比,存活率或肿瘤发生率没有显著下降。当4-MP以2%的剂量加入F344大鼠(30只雄性和30只雌性)的饲料中,连续104周时,发现肿瘤。4-MP案例的组织病理学发现包括非典型增生(雄性67%,雌性37%)、乳头状瘤(50%,23%)和鳞状细胞癌(77%,20%)在 forestomach. 4-MC诱导 forestomach 乳头状瘤(70%,93%)和鳞状细胞癌(53%,37%),还腺胃粘膜下增生(90%,93%)、腺瘤(100%,100%)和腺癌(57%,47%),伴溃疡或侵蚀。在Salmonella typhimurium TA98、TA100、TA1535和TA1537的测试中,或在大鼠经皮肤暴露6个月的测试中,没有观察到遗传毒性效应。
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: 4-Methoxyphenol (4-MP) is available as a colorless to white, waxy solid or white to tan, flaky, crystalline substance with the odor of caramel and phenol. It is used as an inhibitor for acrylic monomers and acrylonitirles, as a stabilizer for chlorinated hydrocarbons and ethyl cellulose, as an ultraviolet inhibitor, as a chemical intermediate in the manufacture of antioxidants, pharmaceuticals, plasticizers, and dyestuffs. It is also used as a medication for dyschromias, especially hyperpigmentation often in combination with Tretinoin (Solage). HUMAN EXPOSURE AND TOXICITY: In 11 of the 16 patients (69%; 95% confidence interval [CI], 41%-89%) total depigmentation was achieved using the 4-MP cream. Onset of depigmentation was between 4 and 12 months. Mild burning or itching was reported with the cream in 4 cases (25%). Of the 11 patients who responded to the 4-MP cream, 4 had recurrence of pigmentation (relapse rate of 36%; 95% CI, 11%-69%) after a treatment-free period of 2 to 36 months. Excessive application of 4-MP, can result in marked redness, peeling, discomfort, or hypopigmentation. Oral ingestion of the drug may lead to the same adverse effects as those associated with excessive oral intake of vitamin A (hypervitaminosis A). In a vinylidene chloride plant 2 out of 8 process workers handling hydroquinone monomethyl ether developed depigmentation (occupational leukoderma) of skin of forearms and in 1 of them depigmentation of skin of forehead. Report of the follow-up of 2 cases of leukodermia (vitiligo) following exposure to 4-MP described 8 years previously and survey of 169 men exposed to 4-MP or paratertiary-amyl-phenol or both revealed that repigmentation of a significant degree was found in one man and of a limited degree in the other. Screening by means of the Wood's light technique (an ultra-violet light which is absorbed by normally pigmented skin and reflected by non-pigmented skin) of the 169 men surveyed in the same plant revealed no cases of leukoderma attributed to exposure to 4-MP in 148 men tested or in the 129 men exposed to paratertiary-amyl-phenol. In regards to possible genotoxicity, results from cytogenetic analysis show that the salt of 4-MP (p-methoxyphenol phosphate) induced the decrease of numerical and structural chromosome aberration after the first passage of the treated cells. In terms of the results obtained by cytogenetic analysis the reduction of genetic instability seems to remain constant from the first to the sixth passage in the cell cultures treated with p-methoxyphenol phosphate associated to benzo(a)pyrene. ANIMAL STUDIES: Rabbit studies with 4-MP have shown that it can cause considerable necrosis if exposure is not limited to 1 day. Prolonged contact can cause a severe burn. There is also indication that the material is absorbed in toxic amounts when in solution, especially through abraded skin. Acute parenteral poisoning in rabbits included paralysis and anoxia at lower doses and CNS depression at high doses. 4-MP caused depigmentation of the skin when applied topically to guinea pigs (within 5 to 10 days of treatment) and miniature pigs. In a dermal teratology study in rabbits, there were no statistically significant differences in fetal malformation data; however marked hydrocephaly with visible doming of the head was observed in one mid-dose litter (12 and 0.06 mg/kg or 132 and 0.66 mg/sq m of 4-MP and tretinoin, respectively. 4-MP does not appear to be carcinogenic when applied topically. In studies with 5% or 10% 4-MP (0.02 mL) twice a week between the shoulder blades of mice (for 93 weeks) or interior ears of rabbits, there was no significant decrease in survival rates, or tumor incidence compared to controls. Tumors were evident when 4-MP was administered in the diet of F344 rats (30 male and 30 females) administered diets of 2% 4-MP for 104 weeks. Histopathological findings in the 4-MP case included atypical hyperplasias (male, 67%, female, 37%), papillomas (50%, 23%) and squamous-cell carcinomas (77%, 20%) in the forestomach. 4-MC induced forestomach papillomas (70%, 93%) and squamous-cell carcinomas (53%, 37%), also glandular stomach submucosal hyperplasias (90%, 93%), adenomas (100%, 100%) and adenocarcinomas (57%, 47%), with ulceration or erosion. No genotoxic effects were observed when 4-MP was tested in Salmonella typhimurium TA98, TA100, TA1535, and TA1537 or in rats exposed dermally for 6 months.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
该物质可以通过摄入被身体吸收。
The substance can be absorbed into the body by ingestion.
来源:ILO-WHO International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs)
毒理性
吸入,皮肤吸收,吞食,皮肤和/或眼睛接触
inhalation, skin absorption, ingestion, skin and/or eye contact
来源:The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH)
毒理性
眼睛、皮肤、鼻子、喉咙、上呼吸道的刺激;眼睛、皮肤烧伤;中枢神经系统抑制
irritation eyes, skin, nose, throat, upper respiratory system; eye, skin burns; central nervous system depression
来源:The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH)
毒理性
红斑。灼热感。疼痛。
Redness. Burning sensation. Pain.
来源:ILO-WHO International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs)
吸收、分配和排泄
在八名健康受试者中评估了在使用视黄醇和甲氧基酚组合产品进行为期两周的每日两次局部治疗后的甲氧基酚的系统暴露情况。将大约相当于37.3微克/平方厘米的甲氧基酚量的产品剂量应用于受试者的背部。甲氧基酚的平均Cmax为9.92纳克/毫升(范围在4.22至23.62纳克/毫升之间),Tmax为2小时(范围在1至2小时之间)。甲氧基酚在这种组合配方中的安全性得到了受试者中该制剂低系统暴露的支持。
The systemic exposure to mequinol was assessed in eight healthy subjects following two weeks of twice-daily topical treatment of a tretinoin and mequinol combination product. About dose of the product corresponding to about 37.3 ug/cm^2 of mequinol was applied to the subjects' backs. The mean Cmax for mequinol was 9.92 ng/mL (range between 4.22 and 23.62 ng/mL) and the Tmax was 2 hours (range between 1 to 2 hours). The safety of mequinol in this combination formulation is supported by the low systemic exposures of the agent in the subjects.
来源:DrugBank
吸收、分配和排泄
Mequinol主要以其代谢物形式通过肾脏排出。
Mequinol is predominantly renally eliminated as its metabolites.
来源:DrugBank
吸收、分配和排泄
The volume of distribution is one that suggests mequinol is distributed throughout the total body water, and intracellular concentrations are not expected to vary greatly from gross measurements.
来源:DrugBank
吸收、分配和排泄
关于米奎酸的清除数据并不容易获得。含有米奎酸的产品通常指示为局部使用。
Readily accessible data regarding the clearance of mequinol is not available. The use of mequinol containing products is typically indicated for topical use.
来源:DrugBank
吸收、分配和排泄
Solage是一种组合产品,由2%的梅奎醇(4-羟基苯甲醚)和0.01%的全反式维甲酸(维甲酸)溶于乙醇溶液中组成……本研究旨在评估[(3)H]维甲酸的经皮吸收程度,并估计当这种组合产品外用于健康受试者背部时,系统接触梅奎醇的暴露量。八名受试者在外用400平方厘米背部面积上,每天两次外用非放射性标记的2%梅奎醇/0.01%维甲酸溶液,持续14天。然后,受试者接受一次外用2%梅奎醇/0.01%[(3)H]维甲酸溶液。12小时后,移除放射性标记的剂量,并继续每天两次使用非放射性标记的2%梅奎醇/0.01%维甲酸溶液,持续7天。通过GC/MS程序分析血浆、尿液和粪便样本中的总放射性,并分析血浆中的梅奎醇和维甲酸。根据尿和粪便中放射性活性的累积回收率,[(3)H]维甲酸的平均经皮吸收率约为4.5%(中位数为2.18%)。血浆中的维甲酸浓度没有超过内源性水平。这与血浆中放射性的浓度一致,平均Cmax为91 pg-eq/mL(中位数为26 ng/mL)。梅奎醇的平均Cmax和AUC(0-12小时)值分别为10 ng/mL和33 ng·h/mL。根据本研究的结果,由于维甲酸的经皮吸收极小,且在每天两次使用这种组合制剂后内源性维甲酸水平没有增加,因此这种制剂中外用维甲酸的系统毒性不太可能发生。本研究中受试者的低系统暴露量与小鼠(16.6倍)和大鼠(34.6倍)皮肤毒性研究中最高剂量的系统暴露量相比,支持了梅奎醇在这种组合制剂中的安全性。
Solage is a combination product composed of 2% mequinol (4-hydroxyanisole) and 0.01% tretinoin (all-trans-retinoic acid) in an ethanolic solution ... The purpose of this study was to evaluate the extent of percutaneous absorption of [(3)H]tretinoin and to estimate the systemic exposure to mequinol from this combination product when topically applied to the backs of healthy subjects. Eight subjects received bid /twice per day/ topical applications of nonradiolabelled 2% mequinol/0.01% tretinoin solution on a 400 sq cm area of the back for 14 days. The subjects then received a single topical application of 2% mequinol/0.01% ((3)H)tretinoin solution. After 12 hr, the radiolabelled dose was removed and bid /twice per day/ treatment with nonradiolabelled 2% mequinol/0.01% tretinoin solution was continued for 7 days. Plasma, urine and faecal samples were analysed for total radioactivity and plasma was analysed for both mequinol and tretinoin by GC/MS procedure. Mean percutaneous absorption of [(3)H]tretinoin based on the cumulative recoveries of radioactivity in the urine and faeces was about 4.5% (median 2.18%). Tretinoin concentrations in plasma did not increase above endogenous levels. This was consistent with the concentrations of radioactivity in plasma, which showed an average Cmax of 91 pg-eq/mL (median 26 ng/mL). Average Cmax and AUC(0-12 hr) values for mequinol were 10 ng/mL and 33 ng h/mL, respectively. Based on the results of this study, systemic toxicity from topical application of tretinoin in this formulation is unlikely, because percutaneous absorption of tretinoin is minimal and because endogenous levels of tretinoin are not increased following bid /twice per day/ dosing with this combination formulation. The safety of mequinol in this combination formulation is supported by the low systemic exposures of the subjects in this study compared with the systemic exposures at the highest doses in the dermal toxicity studies in mice (16.6-fold) and rats (34.6-fold).
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
安全信息
-
职业暴露等级:B
-
职业暴露限值:TWA: 5 mg/m3
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险品标志:Xn
-
安全说明:S24/25,S26,S37/39,S46
-
危险类别码:R22,R36,R43
-
WGK Germany:1
-
海关编码:2909500000
-
危险品运输编号:NONH for all modes of transport
-
RTECS号:SL7700000
-
包装等级:Z01
-
危险性防范说明:P501,P261,P273,P272,P270,P264,P280,P302+P352,P337+P313,P305+P351+P338,P362+P364,P333+P313,P301+P312+P330
-
危险性描述:H302,H315,H319,H317,H402
-
储存条件:请将密封产品存放在干燥阴凉的地方。
SDS
| 第一部分:化学品名称 |
| 化学品中文名称: | 对甲氧基苯酚;氢醌-甲基醚 |
| 化学品英文名称: | p-Methoxyphenol;4-Methoxyphenol |
| 中文俗名或商品名: | |
| Synonyms: | |
| CAS No.: | 150-76-5 |
| 分子式: | C 7 H 8 O 2 |
| 分子量: | 124.13 |
| 第二部分:成分/组成信息 |
| 纯化学品 混合物 | ||||||
| 化学品名称:对甲氧基苯酚;氢醌-甲基醚 | ||||||
|
| 第三部分:危险性概述 |
| 危险性类别: | |
| 侵入途径: | 吸入 食入 经皮吸收 |
| 健康危害: | 本品对眼睛、皮肤、粘膜和上呼吸道有刺激作用。长时间的接触对眼有损害,有强烈的刺激作用或可引起灼伤。 |
| 环境危害: | |
| 燃爆危险: | 本品可燃,具强刺激性。 |
| 第四部分:急救措施 |
| 皮肤接触: | 脱去污染的衣着,用流动清水冲洗。若有灼伤,就医治疗。 |
| 眼睛接触: | 立即翻开上下眼睑,用流动清水冲洗15分钟。就医。 |
| 吸入: | 脱离现场至空气新鲜处。呼吸困难时给输氧。呼吸停止时,立即进行人工呼吸。就医。 |
| 食入: | 误服者给饮牛奶或蛋清。就医。 |
| 第五部分:消防措施 |
| 危险特性: | 遇高热、明火或与氧化剂接触,有引起燃烧的危险。 |
| 有害燃烧产物: | 一氧化碳、二氧化碳。 |
| 灭火方法及灭火剂: | 泡沫、二氧化碳、干粉、砂土。 |
| 消防员的个体防护: | 消防人员须戴好防毒面具,在安全距离以外,在上风向灭火 |
| 禁止使用的灭火剂: | |
| 闪点(℃): | >110 |
| 自燃温度(℃): | 引燃温度(℃):420 |
| 爆炸下限[%(V/V)]: | 无资料 |
| 爆炸上限[%(V/V)]: | 无资料 |
| 最小点火能(mJ): | |
| 爆燃点: | |
| 爆速: | |
| 最大燃爆压力(MPa): | |
| 建规火险分级: |
| 第六部分:泄漏应急处理 |
| 应急处理: | 隔离泄漏污染区,周围设警告标志,切断火源。应急处理人员戴好防毒面具,穿化学防护服。用砂土、干燥石灰或苏打灰混合,然后在专用废弃场所深层掩埋。如大量泄漏,收集回收或无害处理后废弃。 |
| 第七部分:操作处置与储存 |
| 操作注意事项: | 密闭操作,局部排风。操作人员必须经过专门培训,严格遵守操作规程。建议操作人员佩戴防尘面具(全面罩),穿连衣式胶布防毒衣,戴橡胶手套。远离火种、热源,工作场所严禁吸烟。使用防爆型的通风系统和设备。避免与氧化剂、碱类接触。搬运时要轻装轻卸,防止包装及容器损坏。配备相应品种和数量的消防器材及泄漏应急处理设备。倒空的容器可能残留有害物。 |
| 储存注意事项: | 储存于阴凉、通风的库房。远离火种、热源。应与氧化剂、碱类等分开存放,切忌混储。配备相应品种和数量的消防器材。储区应备有合适的材料收容泄漏物。 |
| 第八部分:接触控制/个体防护 |
| 最高容许浓度: | 中 国 MAC:未制订标准前苏联MAC:未制订标准美国TLVTN: ACGIH 5mg/m3 |
| 监测方法: | 4-氨基安替比林分光光度法;溶剂解吸-气相色谱法 |
| 工程控制: | 密闭操作,局部排风。 |
| 呼吸系统防护: | 空气中浓度超标时,佩带防毒面具。 |
| 眼睛防护: | 戴化学安全防护眼镜。 |
| 身体防护: | 穿防腐工作服。 |
| 手防护: | 戴橡皮手套。 |
| 其他防护: | 工作现场禁止吸烟、进食和饮水。工作后,淋浴更衣。单独存放被毒物污染的衣服,洗后再用。保持良好的卫生习 |
| 第九部分:理化特性 |
| 外观与性状: | 淡色固体,有焦饴糖和酚的气味。 |
| pH: | |
| 熔点(℃): | 52.5 |
| 沸点(℃): | 246 |
| 相对密度(水=1): | 1.55(20℃) |
| 相对蒸气密度(空气=1): | 4.3 |
| 饱和蒸气压(kPa): | <0.0013(20℃) |
| 燃烧热(kJ/mol): | |
| 临界温度(℃): | |
| 临界压力(MPa): | |
| 辛醇/水分配系数的对数值: | |
| 闪点(℃): | >110 |
| 引燃温度(℃): | 引燃温度(℃):420 |
| 爆炸上限%(V/V): | 无资料 |
| 爆炸下限%(V/V): | 无资料 |
| 分子式: | C 7 H 8 O 2 |
| 分子量: | 124.13 |
| 蒸发速率: | |
| 粘性: | |
| 溶解性: | 微溶于水。 |
| 主要用途: | 用作纺织润滑油的稳定剂和化工中间体。 |
| 第十部分:稳定性和反应活性 |
| 稳定性: | 在常温常压下 稳定 |
| 禁配物: | 碱类、酰基氯、酸酐、氧化剂。 |
| 避免接触的条件: | |
| 聚合危害: | 不能出现 |
| 分解产物: | 一氧化碳、二氧化碳。 |
| 第十一部分:毒理学资料 |
| 急性毒性: | LD50:1600mg/kg(大鼠经口) LC50: |
| 急性中毒: | |
| 慢性中毒: | |
| 亚急性和慢性毒性: | |
| 刺激性: | |
| 致敏性: | |
| 致突变性: | |
| 致畸性: | |
| 致癌性: |
| 第十二部分:生态学资料 |
| 生态毒理毒性: | |
| 生物降解性: | |
| 非生物降解性: | |
| 生物富集或生物积累性: |
| 第十三部分:废弃处置 |
| 废弃物性质: | |
| 废弃处置方法: | 处置前应参阅国家和地方有关法规。建议用焚烧法处置。 |
| 废弃注意事项: |
| 第十四部分:运输信息 |
| |
| 危险货物编号: | |
| UN编号: | |
| 包装标志: | |
| 包装类别: | |
| 包装方法: | |
| 运输注意事项: | 起运时包装要完整,装载应稳妥。运输过程中要确保容器不泄漏、不倒塌、不坠落、不损坏。严禁与氧化剂、碱类、食用化学品等混装混运。运输途中应防曝晒、雨淋,防高温。运输车船必须彻底清洗、消毒,否则不得装运其它物品。 |
| RETCS号: | |
| IMDG规则页码: |
| 第十五部分:法规信息 |
| 国内化学品安全管理法规: | 化学危险物品安全管理条例 (1987年2月17日国务院发布),化学危险物品安全管理条例实施细则 (化劳发[1992] 677号),工作场所安全使用化学品规定 ([1996]劳部发423号)等法规,针对化学危险品的安全使用、生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应规定。 |
| 国际化学品安全管理法规: |
| 第十六部分:其他信息 |
| 参考文献: | 1.周国泰,化学危险品安全技术全书,化学工业出版社,1997 2.国家环保局有毒化学品管理办公室、北京化工研究院合编,化学品毒性法规环境数据手册,中国环境科学出版社.1992 3.Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety,CHEMINFO Database.1998 4.Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety, RTECS Database, 1989 |
| 填表时间: | 年月日 |
| 填表部门: | |
| 数据审核单位: | |
| 修改说明: | |
| 其他信息: | 3 |
| MSDS修改日期: | 年月日 |
制备方法与用途
对羟基苯甲醚
简介
对羟基苯甲醚是一种白色片状或蜡状结晶体,主要用于乙烯基型塑料单体的阻聚剂、紫外线抑制剂、染料中间体以及合成食用油脂和化妆品抗氧化剂BHA等。它最大的优点是添加MEHQ后的单体和其他单体共聚时不必除去,可直接三元共聚,并且还可用作防老剂和抗氧剂。
用途对羟基苯甲醚是不饱和聚酯树脂、甲基丙烯酸甲酯、丙烯腈、醋酸乙烯等的高效阻聚剂;同时也是聚氯乙烯、聚甲基丙烯酸等高聚物的稳定剂。此外,它还可作为抗氧剂和医药中间体,并制成软膏用于漂白、脱色以及红外线吸收剂。
合成对苯二酚单甲醚的合成方法主要有三种:苯甲醚法、对苯二酚法及苯甲醛法。目前应用最广泛的是对苯二酚法,即以对苯二酚为原料,采用硫酸二甲酯、甲醇或碳酸二甲酯等作为甲基化剂进行合成,催化剂通常为硫酸、杂多酸、固体酸或强酸树脂。
化学性质白色片状或蜡状结晶体。熔点52.5℃(55-57℃),沸点243℃,相对密度1.55(20/20℃)。易溶于乙醇、醚、丙酮、苯和乙酸乙酯,微溶于水。
用途主要用于乙烯基型塑料单体的阻聚剂、紫外线抑制剂、染料中间体及合成食用油脂和化妆品抗氧化剂BHA。此外还广泛用于医药、香料、农药等精细化工产品的重要中间体,并作为高分子的阻聚剂、防老剂、增塑剂等多种用途。
生产方法以对苯二酚为原料,使用硫酸二甲酯作甲基化剂合成4-甲氧基酚。另一种较新的方法是在存在对苯醌的情况下,由对苯二酚与甲醇反应制得相同产物。具体步骤包括:将甲醇和浓硫酸混合均匀后加入对苯二酚,加热回流并滴加对苯醌的甲醇溶液3小时。冷却后用40%氢氧化钠溶液中和滤除沉淀,并回收甲醇、萃取蒸馏最终得到成品,收率为76%。
类别有毒物质
- 毒性分级:中毒
- 急性毒性:口服 - 大鼠 LD50: 1600 毫克/公斤;腹腔 - 小鼠 LD50: 250 毫克/公斤
- 刺激数据:皮肤 - 兔子 6000 毫克/12天 轻度
- 可燃性危险特性:可燃,火场释放辛辣刺激烟雾
- 储运特性:库房低温、通风、干燥;防火;与强氧化剂分开存放
TWA 5 毫克/立方米;STEL 10 毫克/立方米
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 对苯二甲醚 1,4-dimethoxybezene 150-78-7 C8H10O2 138.166 苯甲醚 methoxybenzene 100-66-3 C7H8O 108.14 —— 4-methoxyphenyl formate 4525-64-8 C8H8O3 152.15 4-乙氧基苯酚 4-Ethoxyphenol 622-62-8 C8H10O2 138.166 —— 1-(ethynyloxy)-4-methoxybenzene 75290-86-7 C9H8O2 148.161 1-甲氧基-4-(甲氧基甲氧基)苯 4-methoxyphenyl methoxymethyl ether 25458-46-2 C9H12O3 168.192 2-(4-甲氧基苯氧基)-1-乙醇 2-(4-methoxyphenoxy)ethanol 5394-57-0 C9H12O3 168.192 —— p-Isopropoxyphenyl methyl ether 20744-02-9 C10H14O2 166.22 1-甲氧基-4-(2-丙炔-1-基氧基)苯 1-methoxy-4-(2-propynyloxy)benzene 17061-86-8 C10H10O2 162.188 4-烯丙氧基苯甲醚 allyl (4-methoxyphenyl) ether 13391-35-0 C10H12O2 164.204 3-甲氧基苯酚 3-Methoxyphenol 150-19-6 C7H8O2 124.139 4-叔-丁氧基苯甲醚 p-tert-butoxyanisole 15360-00-6 C11H16O2 180.247 —— 1-methoxy-4-((D3)-methoxy)benzene 54536-21-9 C8H10O2 141.142 对苯二酚 hydroquinone 123-31-9 C6H6O2 110.112 木榴油 2-methoxy-phenol 90-05-1 C7H8O2 124.139 3-氯丙基4-甲氧基苯基醚 1-(3-chloropropoxy)-4-methoxybenzene 20744-03-0 C10H13ClO2 200.665 —— 4-(4-methoxybenzyloxy)butan-1-ol 123731-28-2 C11H16O3 196.246 1-甲氧基-4-苯氧基苯 1-methoxy-4-phenoxy-benzene 1655-69-2 C13H12O2 200.237 双(4-甲氧基二苯基)醚 bis(4-methoxyphenyl) ether 1655-74-9 C14H14O3 230.263 4-甲氧基苯乙酸 4-methoxyphenyl acetate 1200-06-2 C9H10O3 166.177 4-碘苯甲醚 para-iodoanisole 696-62-8 C7H7IO 234.036 氯甲酸4-甲氧基苯酯 4-methoxyphenylchloroformate 7693-41-6 C8H7ClO3 186.595 —— (4-D)-Anisol 20938-43-6 C7H8O 109.132 对氟苯甲醚 1-fluoro-4-methoxybenzene 459-60-9 C7H7FO 126.13 (4-甲氧基苯基)硅烷 (4-methoxy-phenyl)-silane 696-64-0 C7H10OSi 138.241 对甲苯甲醚 4-Methylanisole 104-93-8 C8H10O 122.167 —— 1-methoxy-4-(3-methylbut-2-enyloxy)benzene 34125-69-4 C12H16O2 192.258 对甲氧基苯氧乙酸 2-(4-methoxyphenoxy)acetic acid 1877-75-4 C9H10O4 182.176 4-氯苯甲醚 4-chloromethoxybenzene 623-12-1 C7H7ClO 142.585 4-溴苯甲醚 1-bromo-4-methoxy-benzene 104-92-7 C7H7BrO 187.036 甲氧苯胺 4-methoxy-aniline 104-94-9 C7H9NO 123.155 —— [2-(4-methoxyphenoxy)ethyl]trimethylsilane 939018-15-2 C12H20O2Si 224.375 苯甲醚-甲基-d3 trideuteriomethoxy-benzene 4019-63-0 C7H8O 111.116 - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 对苯二甲醚 1,4-dimethoxybezene 150-78-7 C8H10O2 138.166 苯甲醚 methoxybenzene 100-66-3 C7H8O 108.14 —— 4-methoxyphenyl formate 4525-64-8 C8H8O3 152.15 —— bromomethyl 4-methoxyphenyl ether 121824-55-3 C8H9BrO2 217.062 (4-甲氧基苯基)氰酸酯 4-methoxyphenyl cyanate 2983-74-6 C8H7NO2 149.149 4-甲氧基苯乙醚 1-ethoxy-4-methoxybenzene 5076-72-2 C9H12O2 152.193 —— 1-methoxy-4-(vinyloxy)benzene 4024-19-5 C9H10O2 150.177 —— 1-(ethynyloxy)-4-methoxybenzene 75290-86-7 C9H8O2 148.161 1-(氯甲氧基)-4-甲氧基苯 p-methoxyphenoxymethyl chloride 35657-08-0 C8H9ClO2 172.611 —— 4-methoxyphenoxyamine 147169-98-0 C7H9NO2 139.154 1-甲氧基-4-(甲氧基甲氧基)苯 4-methoxyphenyl methoxymethyl ether 25458-46-2 C9H12O3 168.192 4,4'-[亚甲基二(氧基)]二苯甲醚 bis(4-methoxyphenoxy)methane 56207-34-2 C15H16O4 260.29 2-(4-甲氧基苯氧基)-1-乙醇 2-(4-methoxyphenoxy)ethanol 5394-57-0 C9H12O3 168.192 1-甲氧基-4-丙氧基苯 1-methoxy-4-propoxybenzene 20743-94-6 C10H14O2 166.22 —— 1-methoxy-4-(propa-1,2-dien-1-yloxy)benzene 66397-26-0 C10H10O2 162.188 —— p-Isopropoxyphenyl methyl ether 20744-02-9 C10H14O2 166.22 1-(2-氯乙氧基)-4-甲氧基苯 p-Methoxy-phenyl-(β-chlor-ethyl)-ether 3383-74-2 C9H11ClO2 186.638 —— 1-(difluoromethoxy)-4-methoxybenzene 659-33-6 C8H8F2O2 174.147 1-甲氧基-4-(2-丙炔-1-基氧基)苯 1-methoxy-4-(2-propynyloxy)benzene 17061-86-8 C10H10O2 162.188 (4-甲氧基苯氧基)乙醛 (4-methoxyphenoxy)acetaldehyde 68426-09-5 C9H10O3 166.177 4-甲氧基苯氧基乙腈 2-(4-methoxyphenoxy)acetonitrile 22446-12-4 C9H9NO2 163.176 1-(2-溴乙氧基)-4-甲氧基苯 1-(2-bromoethoxy)-4-methoxybenzene 22921-76-2 C9H11BrO2 231.089 4-烯丙氧基苯甲醚 allyl (4-methoxyphenyl) ether 13391-35-0 C10H12O2 164.204 2-(4-甲氧基苯氧基)乙胺 2-(4-methoxyphenoxy)ethylamine 50800-92-5 C9H13NO2 167.208 顺式-4-甲氧基苯基1-丙烯基醚 (Z)-1-methoxy-4-(prop-1-en-1-yloxy)benzene 51896-37-8 C10H12O2 164.204 —— 4-methoxyphenyl-1-propenyl ether 51896-38-9 C10H12O2 164.204 —— 1-methoxy-4-(prop-1-yn-1-yloxy)benzene 102508-25-8 C10H10O2 162.188 3-甲氧基苯酚 3-Methoxyphenol 150-19-6 C7H8O2 124.139 3-(4-甲氧基苯氧基)丙醇 3-(4-methoxyphenoxy)propan-1-ol 118943-21-8 C10H14O3 182.219 1-甲氧基-4-[2-(4-甲氧基苯氧基)乙氧基]苯 1,2-bis-(4-methoxy-phenoxy)-ethane 61165-99-9 C16H18O4 274.317 —— 1-methoxy-4-(2-phenoxy-ethoxy)-benzene 98183-24-5 C15H16O3 244.29 4-甲氧基苯-1,2-二醇 4-methoxycatechol 3934-97-2 C7H8O3 140.139 4-丁氧基苯甲醚 1-butoxy-4-methoxybenzene 20743-95-7 C11H16O2 180.247 —— 1,3-bis(4-methoxyphenoxy)propane 3875-75-0 C17H20O4 288.343 4-叔-丁氧基苯甲醚 p-tert-butoxyanisole 15360-00-6 C11H16O2 180.247 1-甲氧基-4-[(4-甲氧基苯氧基)甲氧基甲氧基]苯 bis(4-methoxyphenoxy) 63195-89-1 C16H18O5 290.316 4-(三氟甲氧基)苯甲醚 1-methoxy-4-(trifluoromethoxy)benzene 710-18-9 C8H7F3O2 192.138 —— 1-methoxy-4-((D3)-methoxy)benzene 54536-21-9 C8H10O2 141.142 对苯二酚 hydroquinone 123-31-9 C6H6O2 110.112 —— 1-(2'-methoxyethoxy)-4-methoxybenzene —— C10H14O3 182.219 —— 1-but-2-ynyloxy-4-methoxy-benzene 41580-74-9 C11H12O2 176.215 3-(4-甲氧基苯氧基)-1-丙胺 3-(4-methoxyphenoxy)propan-1-amine 100841-00-7 C10H15NO2 181.235 —— (E)-1-(but-2-enyloxy)-4-methoxybenzene 474352-92-6 C11H14O2 178.231 1-(3-溴丙氧基)-4-甲氧基苯 1-(3-bromopropoxy)-4-methoxybenzene 6267-37-4 C10H13BrO2 245.116 —— 4-(4-methoxyphenoxy)but-1-yn 120211-74-7 C11H12O2 176.215 —— 3-(4-methoxyphenoxy)propionaldehyde 479192-15-9 C10H12O3 180.203 3-(4-甲氧基苯氧基)-1-碘丙烷 1-(3-iodopropoxy)-4-methoxybenzene 118943-23-0 C10H13IO2 292.117 —— 3-(4-methoxyphenoxy)propane-1-thiol 864389-74-2 C10H14O2S 198.286 3-(4-甲氧基苯氧基)丙腈 3-(4-methoxyphenoxy)propanenitrile 63815-39-4 C10H11NO2 177.203 —— 4-(3-Phenoxypropoxy)phenol 30311-36-5 C10H14O3 182.219 3-氯丙基4-甲氧基苯基醚 1-(3-chloropropoxy)-4-methoxybenzene 20744-03-0 C10H13ClO2 200.665 —— 1-(but-3-en-1-yloxy)-4-methoxybenzene 2653-90-9 C11H14O2 178.231 —— chestersiene 84765-78-6 C11H12O2 176.215 —— 1-methoxy-4-((2-methylprop-1-en-1-yl)oxy)benzene 5820-36-0 C11H14O2 178.231 1-甲氧基-4-苯氧基苯 1-methoxy-4-phenoxy-benzene 1655-69-2 C13H12O2 200.237 双(4-甲氧基二苯基)醚 bis(4-methoxyphenyl) ether 1655-74-9 C14H14O3 230.263 —— 3-(4-methoxyphenoxy)prop-2-yn-1-ol 1188296-85-6 C10H10O3 178.188 —— 4-(4-methoxyphenoxy)phenol 10181-93-8 C13H12O3 216.236 1-甲氧基-4-(戊氧基)苯 1-methoxy-4-(pentyloxy)benzene 20743-96-8 C12H18O2 194.274 —— 1,4-bis(4-methoxyphenoxy)butane 111647-69-9 C18H22O4 302.37 1,4-双(4-甲氧基苯氧基)苯 1,4-bis(p-methoxyphenoxyl)benzene 78563-40-3 C20H18O4 322.361 4-(4-甲氧基苯氧基)丁-2-炔-1-醇 4-(4-methoxyphenoxy)but-2-yn-1-ol 105630-27-1 C11H12O3 192.214 —— 4,4'-bis(4-dimethoxyphenoxyl)phenyl ether 5024-85-1 C26H22O5 414.458 —— p-methoxyphenyl neopentyl ether 14225-17-3 C12H18O2 194.274 —— (Z)-3-chloro-1-(4-methoxy)phenyloxyprop-2-ene 5335-21-7 C10H11ClO2 198.649 对二乙酰氧基苯 benzene-1,4-diyl diacetate 1205-91-0 C10H10O4 194.187 4-甲氧基苯乙酸 4-methoxyphenyl acetate 1200-06-2 C9H10O3 166.177 —— 4-(4'-methoxyphenyloxy)-(2E)-buten-1-ol 225936-85-6 C11H14O3 194.23 1-甲氧基-4-(3-甲基丁氧基)苯 1-isopentyloxy-4-methoxy-benzene 20744-00-7 C12H18O2 194.274 —— 4-methoxyphenyl carbamate 63082-07-5 C8H9NO3 167.164 —— 1,4-Bis-(p-Methoxy-phenoxy)-but-2-in 4200-28-6 C18H18O4 298.339 4-碘苯甲醚 para-iodoanisole 696-62-8 C7H7IO 234.036 邻苯二甲醚 1,2-dimethoxybenzene 91-16-7 C8H10O2 138.166 氯甲酸4-甲氧基苯酯 4-methoxyphenylchloroformate 7693-41-6 C8H7ClO3 186.595 1-(4-溴丁氧基)-4-甲氧基苯 1-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-4-bromobutane 2033-83-2 C11H15BrO2 259.143 对甲氧基苯基硫代氯甲酸酯 4-methoxyphenyl chlorothionoformate 940-58-9 C8H7ClO2S 202.661 1-甲氧基-4-(2,2,2-三氟乙氧基)苯 1-methoxy-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)benzene 62158-88-7 C9H9F3O2 206.164 —— 1,5-bis-(4-methoxy-phenoxy)-pentane 134925-35-2 C19H24O4 316.397 —— 4-(4-methoxyphenoxy)butanenitrile 20744-06-3 C11H13NO2 191.23 烯丙基苯基醚 allyl phenyl ether 1746-13-0 C9H10O 134.178 对氟苯甲醚 1-fluoro-4-methoxybenzene 459-60-9 C7H7FO 126.13 —— 4-[18F]fluoroanisole —— C7H7FO 125.132 对甲苯甲醚 4-Methylanisole 104-93-8 C8H10O 122.167 —— 3-(4-Methoxyphenoxy)-2-methylpropan-1-ol 1226162-37-3 C11H16O3 196.246 [3-(4-甲氧基-苯氧基)-丙基]-甲胺 (3-(4-methoxyphenoxy)propyl)methylamine 303104-76-9 C11H17NO2 195.261 4-甲氧基苯硫酚 4-Methoxybenzenethiol 696-63-9 C7H8OS 140.206 —— 1-(4-chlorobutoxy)-4-methoxybenzene 20744-08-5 C11H15ClO2 214.692 —— 1-(hexyloxy)-4-methoxybenzene 20743-91-3 C13H20O2 208.301 —— 5-(4-methoxyphenoxy)pent-1-yn 139063-66-4 C12H14O2 190.242 —— 1-methoxy-4-(pent-4-en-1-yloxy)benzene 1330533-75-9 C12H16O2 192.258 —— 4-(2-(dimethylamino)ethoxy)phenol 100238-29-7 C10H15NO2 181.235 —— 1-methoxy-4-(3-methylbut-2-enyloxy)benzene 34125-69-4 C12H16O2 192.258 1-(4-甲氧基苯氧基)-2-丙醇 1-(4-methoxyphenoxy)propan-2-ol 42900-54-9 C10H14O3 182.219 2-(4-甲氧基-苯氧基)-1-甲基-乙基胺 1-methyl-2-p-methoxyphenoxyethylamine 66145-39-9 C10H15NO2 181.235 —— 6-(4-methoxyphenoxy)hexan-1-ol 122004-89-1 C13H20O3 224.3 —— 1-[6-(4-methoxyphenoxy)hexyloxy]-4-methoxybenzene —— C20H26O4 330.424 2-(4-甲氧基苯氧基)-N,N-二甲基-乙胺 2-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-N,N-dimethylethanamine 51344-12-8 C11H17NO2 195.261 对甲氧基苯氧乙酸 2-(4-methoxyphenoxy)acetic acid 1877-75-4 C9H10O4 182.176 1-(4-甲氧基苯氧基)-2-丙酮 p-acetonyloxyanisole 6698-71-1 C10H12O3 180.203 - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Novel Bioactivation Pathway of Benzbromarone Mediated by Cytochrome P450摘要:苯溴马隆(BBR)是一种具有肝毒性的药物,但其毒性的详细机制仍不清楚。我们通过与化学合成的标准化合物对比,在鼠和人肝微粒体系统中鉴定出两种新的BBR代谢产物:2,6-二溴氢醌(DBH)和单脱溴儿茶酚(2-乙基-3-(3-溴-4,5-二羟基苯甲酰)苯并呋喃;CAT)。我们还阐明了DBH是由细胞色素P450 2C9形成的,而CAT主要由CYP1A1、2D6、2E1和3A4形成。此外,在HepG2细胞中,CAT、DBH以及DBH的氧化形式都比BBR具有更高的细胞毒性。综上所述,我们的数据表明,新型活性代谢物DBH可能与BBR诱导的肝毒性有关。DOI:10.1124/dmd.115.065037
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:Selective indirect oxidation of phenol to hydroquinone and catechol摘要:DOI:10.1021/jo00210a029
-
作为试剂:描述:四氯丙烯 在 chromium(III) oxide 、 FeCl3/C 氢氟酸 、 4-甲氧基苯酚 作用下, 180.0~350.0 ℃ 、239.23 kPa 条件下, 生成 三氟氯丙烯 、 2-氯-1,1,1,2-四氟丙烷 、 1,2-dichloro-3,3,3-trifluoropropene参考文献:名称:METHOD FOR PRODUCING 2-CHLORO-3,3,3-TRIFLUOROPROPENE (HCFC-1233xf)摘要:本发明涉及一种改进的方法,通过在蒸汽相反应器中,在蒸汽相氟化催化剂和稳定剂的存在下,将1,1,2,3-四氯丙烯、1,1,1,2,3-五氯丙烷和/或2,3,3,3-四氯丙烯与氟化氢反应,制造2-氯-3,3,3-三氟丙烯(HCFC-1233xf)。HCFC-1233xf是生产2,3,3,3-四氟丙烯(HFO-1234yf)的中间体,后者是一种具有低全球变暖潜力的制冷剂。公开号:US20090030244A1
文献信息
-
Expanding the Scope of Hypervalent Iodine Reagents for Perfluoroalkylation: From Trifluoromethyl to Functionalized Perfluoroethyl作者:Václav Matoušek、Jiří Václavík、Peter Hájek、Julie Charpentier、Zsófia E. Blastik、Ewa Pietrasiak、Alena Budinská、Antonio Togni、Petr BeierDOI:10.1002/chem.201503531日期:2016.1.4A series of new hypervalent iodine reagents based on the 1,3‐dihydro‐3,3‐dimethyl‐1,2‐benziodoxole and 1,2‐benziodoxol‐3‐(1H)‐one scaffolds, which contain a functionalized tetrafluoroethyl group, have been prepared, characterized, and used in synthetic applications. Their corresponding electrophilic fluoroalkylation reactions with various sulfur, oxygen, phosphorus, and carbon‐centered nucleophiles
-
[EN] HYPERVALENT IODINE CF2CF2X REAGENTS AND THEIR USE<br/>[FR] RÉACTIFS CF2CF2X À BASE D'IODE HYPERVALENT ET LEUR UTILISATION申请人:ETH ZUERICH公开号:WO2016019475A1公开(公告)日:2016-02-11A hypervalent iodine of formula (I) or formula (II) wherein R is a nucleophile and a method for their production is described. Such compounds can be used for fluoroethylation of compounds carrying a reactive group. A preferred compound carrying a reactive group is cystein in any environment such as peptide targets.
-
Nitrosonium ion catalysis: aerobic, metal-free cross-dehydrogenative carbon–heteroatom bond formation作者:Luis Bering、Laura D’Ottavio、Giedre Sirvinskaite、Andrey P. AntonchickDOI:10.1039/c8cc08328b日期:——coupling of heteroarenes with thiophenols and phenothiazines has been developed under mild and environmentally benign reaction conditions. For the first time, NOx+ was applied for catalytic C–S and C–N bond formation. A comprehensive scope for the C–H/S–H and C–H/N–H cross-dehydrogenative coupling was demonstrated with >60 examples. The sustainable cross-coupling conditions utilize ambient oxygen as the
-
Synthesis and characterizations of novel thiazolyl-thiadiazole derivatives as telomerase activators作者:Kayagil, Ismail、Mutlu, Ayşe Gül、Bayhan, Ülkü、Yilmaz, Inanç、Demirayak, ŞerefDOI:10.3906/kim-1711-92日期:——Pyridine-3/4-thiocarboxamide derivatives were used as starting materials for the synthesis of the target compounds. The pyridine-3/4-thiocarboxamide derivatives were reacted with ethyl 2-chloroacetoacetate in ethanol to give the thiazole derivatives (1, 2). The two ethyl thiazole-carboxylate derivatives (1, 2) thus obtained were treated with sodium hydroxide solution and ethanol and converted to carboxylic acids (3, 4). The carboxylic acid derivatives (3, 4) were reacted with thiosemicarbazide in phosphoroxy trichloride and aminothiadiazole rings (5, 6) were formed. Thus, two thiazolyl-thiadiazole amine derivatives (5, 6) were obtained. These two derivatives (5, 6) were converted into two chloroacetamidothiadiazole derivatives (7, 8) by reaction with chloroacetylchloride over the amino group in the presence of triethylamine in acetone. After all these steps, the starting materials (7, 8) needed to reach the target compounds were obtained. With the two derivatives (7, 8) obtained in this last step, phenol and thiophenol derivatives were reacted in acetone in the presence of potassium carbonate. The target compounds, thiazolyl-thiadiazole derivatives (TDA$_\mathbf1-16}})$, are completely unique and their structure has been elucidated by elemental analysis, IR, NMR, and MS spectral data. After all these synthesis steps, telomerase activity studies were performed on the target compounds obtained. For this purpose, a PCR ELISA-based TRAP method was used on the heart of zebrafish. According to the enzyme assay results, derivative TDA$_\mathbf8}}$ has shown an increase of telomerase enzyme activity.吡啶-3/4-硫代羰胺衍生物被用作合成目标化合物的起始材料。吡啶-3/4-硫代羰胺衍生物与乙基2-氯乙酰乙酸酯在乙醇中反应,得到噻唑衍生物(1,2)。获得的两种乙基噻唑羧酸酯衍生物(1,2)经氢氧化钠溶液和乙醇处理,转化为羧酸(3,4)。羧酸衍生物(3,4)与硫半卡巴脲在磷酰氯中反应,形成氨基噻二唑环(5,6)。因此,得到了两种噻唑基噻二唑胺衍生物(5,6)。这两种衍生物(5,6)通过在醋酮中以三乙胺为存在下的氨基上与氯乙酰氯反应,转化为两种氯乙酰胺基噻二唑衍生物(7,8)。经过所有这些步骤后,得到了达到目标化合物所需的起始材料(7,8)。用最后一步获得的两种衍生物(7,8),在碳酸钾存在下在醋酮中与酚和苯硫酚反应。目标化合物,噻唑基噻二唑衍生物(TDA$_1-16}$),是完全独特的,其结构通过元素分析、红外、核磁共振和质谱数据阐明。经过所有这些合成步骤后,对获得的目标化合物进行了端粒酶活性研究。为此,在斑马鱼心脏上使用了基于PCR ELISA的TRAP方法。根据酶活性测定结果,衍生物TDA$_8}$显示了端粒酶酶活性的增加。
-
4-芳香胺-香豆素衍生物及其制备方法和医药 用途
表征谱图
-
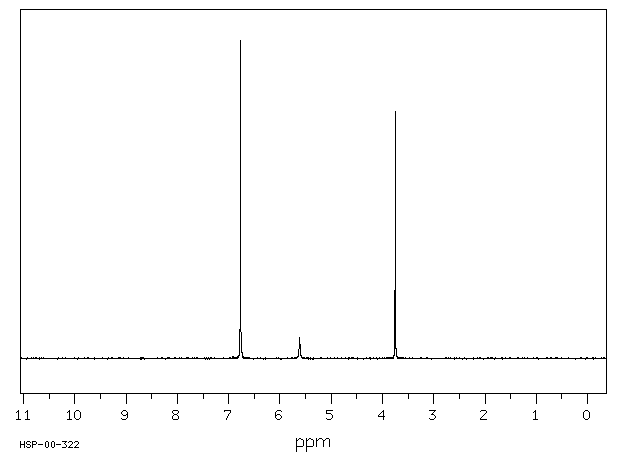
氢谱1HNMR
-
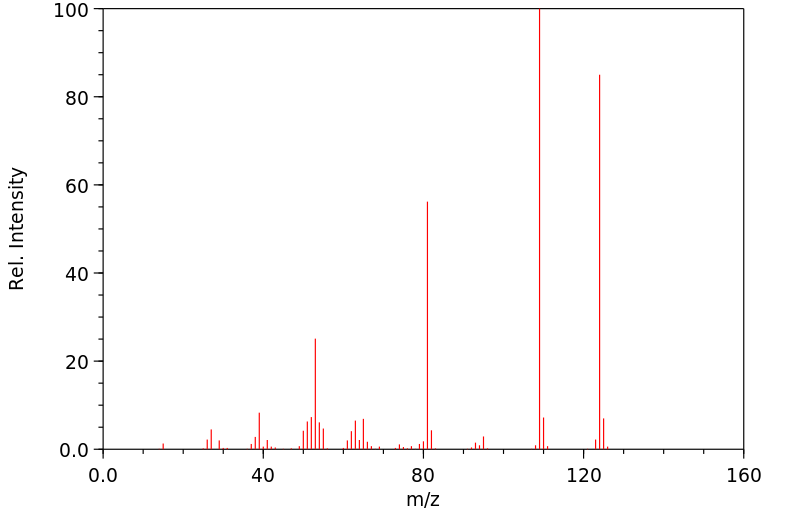
质谱MS
-
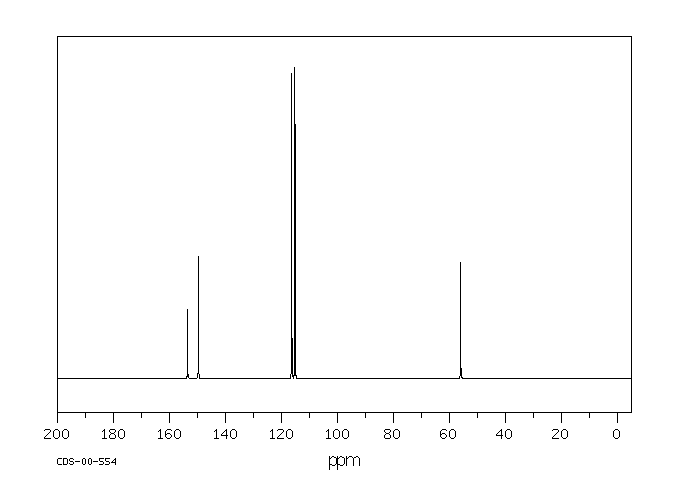
碳谱13CNMR
-
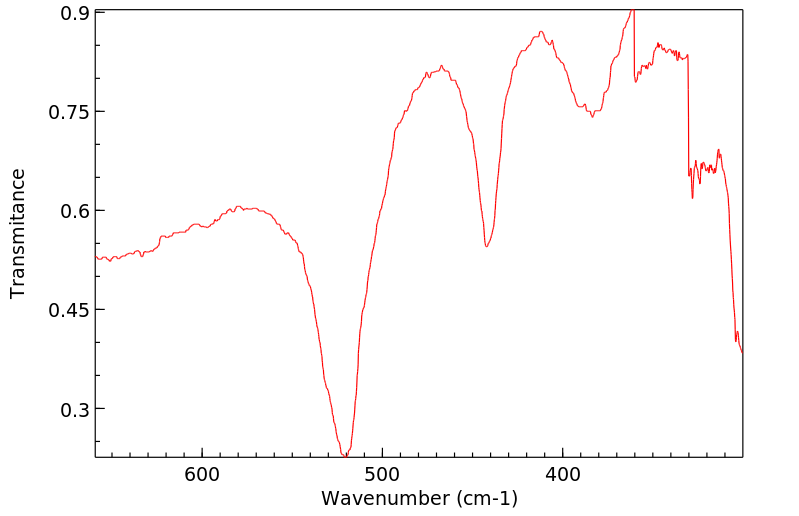
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(2-氯-6-羟基苯基)硼酸
黄柄曲菌素
高香草酸-d3
高香草酸-13C6
高香草酸
高香兰酸乙酯
高辣椒素II
高二氢辣椒素I
香草醛醛肟
香草醛苯腙
香草醛-甲氧基-13C
香草醛-(N-对甲苯基肟)
香草醛
香草酸肼
香草壬酰胺
香草基扁桃酸乙酯
香草吗啉
香草二乙胺
香兰素胺硬脂酸盐
香兰素胺硬脂酸盐
香兰素胺盐酸盐
香兰素丙二醇缩醛
香兰素13C6
香兰素-D3
香兰基乙基醚
香兰基丁醚
顺式-5-正十五碳-8'-烯基间苯二酚
顺式-1-(2-羟基-5-甲基苯基)-2-丁烯-1-酮
顺式-1-(2-羟基-4-甲氧基苯基)-2-丁烯-1-酮
顺-3-氯二氢-5-苯基呋喃-2(3H)-酮
雌二醇杂质1
降二氢辣椒碱
阿诺洛尔
阿瓦醇
阿普斯特杂质
间苯二酚双(二苯基磷酸酯)
间苯二酚-烯丙醇聚合物
间苯二酚-D6
间苯二酚
间苯三酚甲醛
间苯三酚二水合物
间苯三酚
间羟基苯乙基溴
间硝基苯酚
间甲酚紫钠盐
间甲酚与对甲酚和苯酚甲醛树脂的聚合物
间甲酚-D7
间甲酚-D3
间甲酚
间溴苯酚