松油醇 | 98-55-5
物质功能分类
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:18°C
-
沸点:213-218 °C (lit.)
-
密度:0.934 g/mL at 20 °C (lit.)
-
闪点:95°C
-
溶解度:乙醇:可溶1.25ml/10ml,澄清至微浑浊,无色至浅黄色(50%乙醇)
-
介电常数:2.8(20℃)
-
LogP:3.330 (est)
-
物理描述:Liquid
-
颜色/状态:Colorless solid
-
气味:Floral, lilac
-
味道:Lime (distilled)
-
蒸汽压力:0.0423 mm Hg at 24 °C
-
亨利常数:2.23e-06 atm-m3/mole
-
稳定性/保质期:
Chemical stability: Stable under recommended storage conditions.
-
旋光度:Specific optical rotation: 106.4 deg at 20 °C/D
-
分解:When heated to decomp it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
-
气味阈值:Aroma threshold values: Detection: 280-350 ppb
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.4831 at 20 C/D
-
保留指数:1209;1198
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):1.8
-
重原子数:11
-
可旋转键数:1
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.8
-
拓扑面积:20.2
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:1
ADMET
安全信息
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险品标志:Xi
-
安全说明:S37
-
危险类别码:R38
-
WGK Germany:1
-
海关编码:29061400
-
危险品运输编号:NONH for all modes of transport
-
RTECS号:WZ6700000
-
危险标志:GHS07
-
危险性描述:H315,H319
-
危险性防范说明:P305 + P351 + P338
SDS
制备方法与用途
电子级松油醇专为印刷电路板清洗应用而设计,用于清除印刷电路板表面的助焊剂。
香料松油醇具有类似松木和丁香的香气。它是一种粘性液体,但在一定条件下易结晶。沸点在218~219℃之间,在85℃/400Pa时沸腾,在35℃时(α-松油醇)会结晶。主要用于调配紫丁香、铃兰、金合欢和橙花等香型的香皂、化妆品香精,纯α-松油醇还可以用于制造柠檬、橙子和桃子等食用香精。以松油醇为原料制备的各种酯类化合物也是优质的香料。
理化性质松油醇有α、β、γ三种异构体,在市场上多呈液态,主要用途是作为香料或药用。它的急性毒性数据如下:口服LD50值为4.3g/kg(大鼠),皮下注射LD50大于3g/kg(兔子)。
香料规格与药用规格香料级松油醇具有良好的香气适应性和稳定性,广泛应用于各种用途的香精配方中。在调合香皂和化妆品香料以及制造类似紫丁香香气的高级香精时也有广泛应用,并可用于制药、电机和油墨等工业。
合成方法与化学性质合成方法包括使用松节油与硫酸反应生成水合萜二醇晶体,再进行脱水步骤。其无色液体或低熔点透明结晶体,具有丁香味,1份松油醇可溶于2份(体积)70%的乙醇溶液中,微溶于水和甘油。
用途松油醇广泛用于医药、农药、塑料、肥皂和油墨工业中。同时它也是玻璃器皿上色彩的溶剂,并大量作为矿物浮选起泡剂,如铜矿、铅锌矿等有色金属矿和粉煤的浮选,也用作印染助剂、颜料湿润剂、油漆抗结皮剂、绵羊皮脱脂剂及环氧树脂流平剂。
合成松油的主要成分合成松油含有较高的萜品油烯,不含有茴香脑和甲基佳味酚,并存在痕量樟脑。水蒸气蒸馏所得松油含龙脑和茴香脑较多。
根据RIFM提供的资料,松油醇的急性毒性数据:口服LD50为4.3g/kg(大鼠),皮试LD50大于3g/kg(兔子)。
用途总结松油醇分为香料规格和药用规格两种。香料级松油醇具有较好的香气适应性和稳定性,广泛用于各种用途的香精配方中,并作为增加新鲜气息剂;在百合、紫丁香、铃兰、金合欢等香精中是重要香料,在玉兰、栀子、水仙和松针型香精中也是重要成分。含醇量40%~80%的馏份则称合成松油,主要用于有色金属的浮选起泡剂。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 2-(4-甲基-3-环己烯-1-基)丙烷-1,2-二醇 uroterpenol 6252-35-3 C10H18O2 170.252 —— 4-(2-(allyloxy)propan-2-yl)-1-methylcyclohex-1-ene —— C13H22O 194.317 —— 4-(1-methyl-1-methoxymethoxyethyl)-1-methylcyclohexene 124727-36-2 C12H22O2 198.305 反式-索布瑞醇 (-)-trans-sobrerol 71697-84-2 C10H18O2 170.252 —— trimethyl((2-(4-methylcyclohex-3-en-1-yl)propan-2-yl)oxy)silane 90934-33-1 C13H26OSi 226.434 乙酸松油酯 terpinyl acetate 80-26-2 C12H20O2 196.29 —— 9-acetoxy-8-hydroxy-p-menth-1-ene 10090-80-9 C12H20O3 212.289 —— methyl α-terpinyl carbonate 34985-04-1 C12H20O3 212.289 2,2,6-三甲基-1-氧杂螺[2.5]辛-5-烯 terpinolene oxide 4584-23-0 C10H16O 152.236 (R)-2-((2-((R)-4-甲基环己-3-烯-1-基)丙-2-基)氧基)四氢-2H-吡喃 4-(1-methyl-1-tetrahydropyranyloxyethyl)-1-methylcyclohexene 124727-35-1 C15H26O2 238.37 —— 2-(4-methylcyclohex-3-en-1-yl)propan-2-yl 2,2,2-trifluoroacetate 28664-18-8 C12H17F3O2 250.261 —— tert-Butyl-dimethyl-[1-methyl-1-(4-methyl-cyclohex-3-enyl)-ethoxy]-silane 809240-22-0 C16H32OSi 268.515 - 1
- 2
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 2-(4-甲基-3-环己烯-1-基)丙烷-1,2-二醇 uroterpenol 6252-35-3 C10H18O2 170.252 4-(2-羟基-2-丙基)环己烯-1-甲醇 7-hydroxyterpineol 5502-74-9 C10H18O2 170.252 4-(1-甲氧基-1-甲基乙基)-1-甲基-环己烯 4-(2-methoxypropan-2-yl)-1-methylcyclohex-1-ene 14576-08-0 C11H20O 168.279 甲酸松油酯 2-(4-methylcyclohex-3-enyl)propan-2-yl formate 2153-26-6 C11H18O2 182.263 —— 4-(2-(allyloxy)propan-2-yl)-1-methylcyclohex-1-ene —— C13H22O 194.317 —— 4-(1-methyl-1-methoxymethoxyethyl)-1-methylcyclohexene 124727-36-2 C12H22O2 198.305 反式-索布瑞醇 (-)-trans-sobrerol 71697-84-2 C10H18O2 170.252 1-对孟烯-6,8-二醇 sobrerol 498-71-5 C10H18O2 170.252 —— trimethyl((2-(4-methylcyclohex-3-en-1-yl)propan-2-yl)oxy)silane 90934-33-1 C13H26OSi 226.434 4-萜烯醇 TERPINEN-4-OL 562-74-3 C10H18O 154.252 5-(1-羟基-1-甲基乙基)-2-甲基-2-环己烯 5-(1-Hydroxy-1-methyl-ethyl)-2-methyl-cyclohex-2-enone 7712-46-1 C10H16O2 168.236 乙酸松油酯 terpinyl acetate 80-26-2 C12H20O2 196.29 —— (4R)-(+)-α-terpinyl acetate 7785-54-8 C12H20O2 196.29 丙酸松油酯 α,α-4-trimethyl-3-cyclohexene-1-methanol 80-27-3 C13H22O2 210.316 6-(2-羟基-2-丙基)-3-甲基-2-环己烯-1-酮 p-menth-1-en-3-on-8-ol 87791-00-2 C10H16O2 168.236 丁酸1-甲基-1-(4-甲基-3-环己烯-1-基)乙酯 2-(4-methylcyclohex-3-enyl)propan-2-yl butyrate 2153-28-8 C14H24O2 224.343 2-甲基-丙酸-1-甲基-1-(4-甲基-3-环己烯-1-基)乙酯 isobutyric acid 1-methyl-1-(4-methylcyclohex-3-enyl)ethyl ester 7774-65-4 C14H24O2 224.343 —— methyl α-terpinyl carbonate 34985-04-1 C12H20O3 212.289 —— terpineol acrylate —— C13H20O2 208.301 —— 2-(4-methylcyclohex-3-enyl)propan-2-yl 2-bromoacetate —— C12H19BrO2 275.186 —— heptanoic acid p-menth-1-en-8-yl ester —— C17H30O2 266.424 —— 2-(4-methylcyclohex-3-enyl)propan-2-yl pivalate —— C15H26O2 238.37 1-甲基-1-(4-甲基-3-环己烯-1-基)乙基辛酸酯 1-Methyl-1-(4-methyl-3-cyclohexen-1-yl)ethyl octanoate 71648-35-6 C18H32O2 280.451 —— p-menth-1-ene 27966-26-3 C10H18 138.253 (R)-2-((2-((R)-4-甲基环己-3-烯-1-基)丙-2-基)氧基)四氢-2H-吡喃 4-(1-methyl-1-tetrahydropyranyloxyethyl)-1-methylcyclohexene 124727-35-1 C15H26O2 238.37 —— 2-(4-methylcyclohex-3-en-1-yl)propan-2-yl 2,2,2-trifluoroacetate 28664-18-8 C12H17F3O2 250.261 —— tert-Butyl-dimethyl-[1-methyl-1-(4-methyl-cyclohex-3-enyl)-ethoxy]-silane 809240-22-0 C16H32OSi 268.515 - 1
- 2
- 3
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Wallach, Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie, 1896, vol. 291, p. 342摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:描述:桉叶油醇 在 chromium chloride 、 tetrakis(tetrabutylammonium)decatungstate(VI) 、 caesium carbonate 、 苯甲醛 作用下, 以 乙酸乙酯 、 乙腈 为溶剂, 反应 48.0h, 以24%的产率得到松油醇参考文献:名称:醛与非活性碳氢化合物之间通过还原性自由基-极性交换途径的偶联反应。摘要:在本文中,我们描述了由未活化的CH键生成有机铬型碳负离子及其对醛的亲核加成反应。催化碳负离子的产生通过温和条件下未活化的CH键的正式去质子化而发生,不需要预官能化或阴离子稳定基团。铬酸盐通过还原自由基-极性交叉反应捕获由去阳离子钨酸盐光催化剂介导的氢提取产生的碳自由基中间体,从而生成有机铬碳负离子。DOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.0c00096
-
作为试剂:描述:参考文献:名称:A Study of the Photochemical Reactions of 2-Cyclohexenones with Substituted Olefins摘要:DOI:10.1021/ja01078a034
文献信息
-
A Method for the Net Contra-thermodynamic Isomerization of Cyclic Trisubstituted Alkenes作者:Raphaël F. Guignard、Laurent Petit、Samir Z. ZardDOI:10.1021/ol4018744日期:2013.8.16A simple sequence for the net contra-thermodynamic isomerization of cyclic trisubstituted alkenes is reported consisting of a radical addition of p-chlorothiophenol, followed by oxidation to the sulfoxide and thermal syn-elimination to give the least substituted isomeric cycloalkene.为环状三取代烯烃的净禁忌热力学异构化的简单序列报道由自由基加成的p -chlorothiophenol,随后氧化成亚砜和热合成β-消除,得到至少取代的同分异构的环烯烃。
-
[EN] PHENOTHIAZINE DERIVATIVES AND USES THEREOF<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS DE PHÉNOTHIAZINE ET LEURS UTILISATIONS申请人:CAMP4 THERAPEUTICS CORP公开号:WO2019195789A1公开(公告)日:2019-10-10The present invention provides phenothiazine compounds, processes for their preparation, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds, and the use of the compounds or the compositions in the treatment of various diseases or conditions, for example ribosomal disorders and ribosomopathies, e.g. Diamond Blackfan anemia (DBA).
-
A New Dioxazolone for the Synthesis of 1,2‐Aminoalcohols via Iridium(III)‐Catalyzed C(sp <sup>3</sup> )−H Amidation作者:Kevin Antien、Andrea Geraci、Michael Parmentier、Olivier BaudoinDOI:10.1002/anie.202110019日期:2021.10.113. leads to amide products which can be hydrolyzed under mild conditions. The amidation reaction is mild, general and compatible with both primary C−H bonds of tertiary and secondary alcohols, as well as secondary C−H bonds of cyclic secondary alcohols. This method provides an easy access to free 1,2-aminoalcohols after efficient and mild cleavage of the oxime directing group and activated amide.
-
Preparation of Mono-/Difluorinated Hydrocarbon Compounds申请人:Saint-Jalmes Laurent公开号:US20090234151A1公开(公告)日:2009-09-17Mono- or difluorinated hydrocarbon compounds are prepared from an alcohol or a carbonylated compound by reacting one of these with a fluorinating reagent, optionally in the presence of a base, the fluorinating agent comprising a pyridinium reactant having the following formula (F), wherein R 0 is an alkyl or cycloalkyl radical:
-
Fe‐Catalyzed Anaerobic Mukaiyama‐Type Hydration of Alkenes using Nitroarenes作者:Anup Bhunia、Klaus Bergander、Constantin Gabriel Daniliuc、Armido StuderDOI:10.1002/anie.202015740日期:2021.4.6Hydration of alkenes using first row transition metals (Fe, Co, Mn) under oxygen atmosphere (Mukaiyama‐type hydration) is highly practical for alkene functionalization in complex synthesis. Different hydration protocols have been developed, however, control of the stereoselectivity remains a challenge. Herein, highly diastereoselective Fe‐catalyzed anaerobic Markovnikov‐selective hydration of alkenes
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
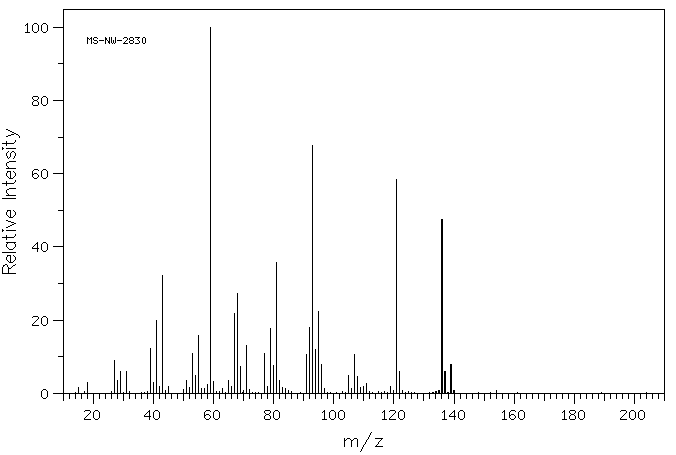
质谱MS
-
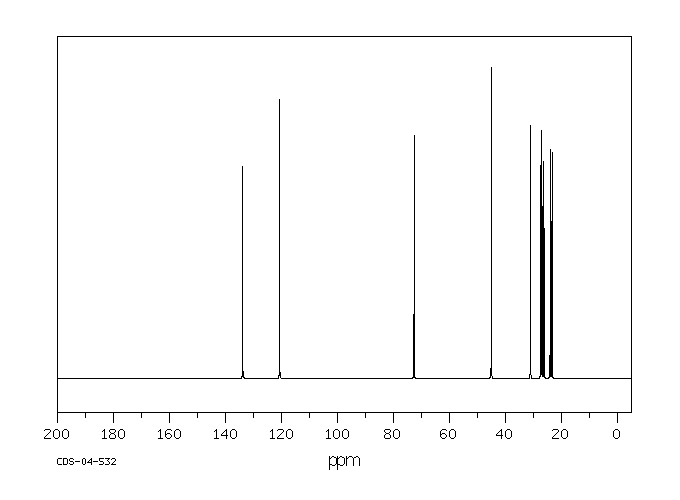
碳谱13CNMR
-
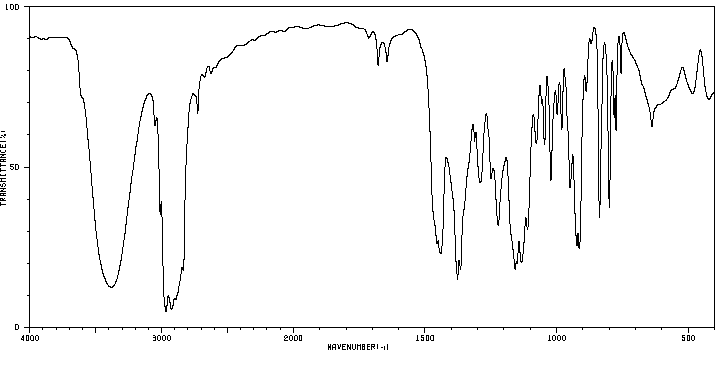
红外IR
-
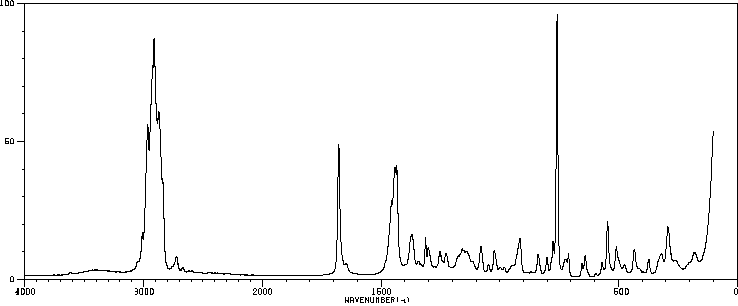
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息