环丙沙星 | 85721-33-1
中文名称
环丙沙星
中文别名
1-环丙烷基-6-氟-1,4-二氢-4-氧代-7-(1-哌嗪基)-3-喹啉羧酸;环丙沙星,环丙氟哌酸;1-环丙基-6-氟-1,4-二氢-4-氧代-7(1-哌嗪基)-3-喹啉羧酸;香草酰二乙胺;西普乐
英文名称
ciproflaxin
英文别名
ciprofloxacin;cip;ciprofloxacine;CPFx;ciprofoxacin;1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(piperazin-1-yl)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid;1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-piperazin-1-ylquinoline-3-carboxylic acid;ciprobay;cipro;1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-piperazin-4-ium-1-ylquinoline-3-carboxylate
CAS
85721-33-1
化学式
C17H18FN3O3
mdl
MFCD00185755
分子量
331.347
InChiKey
MYSWGUAQZAJSOK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:255-257°C
-
沸点:581.8±50.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:1.461±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted)
-
溶解度:溶于 0.1N HCl,浓度为 25mg/ml。难溶于DMSO
-
物理描述:Solid
-
颜色/状态:Faint to light yellow crystalline powder
-
蒸汽压力:2.85X10-13 mm Hg at 25 °C (est)
-
稳定性/保质期:
Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride ophthalmic solution should be stored in tight, light-resistant containers at 2-25 °C. When stored as directed, the commercially available ophthalmic solution has an expiration date of 24 months following the date of manufacture. Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride ophthalmic ointment should be stored at 2-25 °C. Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride and hydrocortisone otic suspension should be stored in light-resistant containers below 25 °C; freezing should be avoided. Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride and dexamethasone otic suspension should be stored at 15-30 °C and protected from light; freezing should be avoided.
-
分解:When heated to decomposition material emits toxic fumes of /nitrogen oxides and hydrogen fluoride/.
-
解离常数:pKa = 6.09 (carboxylic acid group); pKa = 8.74 (nitrogen on piperazinyl ring)
-
碰撞截面:185.3 Ų [M+H]+ [CCS Type: TW, Method: calibrated with polyalanine and drug standards]
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-1.1
-
重原子数:24
-
可旋转键数:3
-
环数:4.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.411
-
拓扑面积:72.9
-
氢给体数:2
-
氢受体数:7
ADMET
代谢
环丙沙星主要通过CYP1A2代谢。主要代谢物氧环丙沙星和硫环丙沙星各占总剂量的3-8%。环丙沙星还转化为次要代谢物去乙烯环丙沙星和甲酰环丙沙星。这四种代谢物占总口服剂量的15%。关于形成这些代谢物的酶和反应类型的数据目前尚不足。
Ciprofloxacin is primarily metabolized by CYP1A2. The primary metabolites oxociprofloxacin and sulociprofloxacin make up 3-8% of the total dose each. Ciprofloxacin is also converted to the minor metabolites desethylene ciprofloxacin and formylciprofloxacin. These 4 metabolites account for 15% of a total oral dose. There is a lack of available data on the enzymes and types of reactions involved in forming these metabolites.
来源:DrugBank
代谢
药物在肝脏中部分代谢,通过改变哌嗪基团至少形成4种代谢物。这些代谢物已被鉴定为脱乙酰西诺沙星(M1)、硫酸西诺沙星(M2)、氧西诺沙星(M3)和N-甲酰西诺沙星(M4),它们的微生物活性低于母药,但可能相似或高于其他一些喹诺酮类药物(例如,M3和M4对某些微生物的活性与诺氟沙星相当)。
The drug is partially metabolized in the liver by modification of the piperazinyl group to at least 4 metabolites. These metabolites, which have been identified as desethyleneciprofloxacin (M1), sulfociprofloxacin (M2), oxociprofloxacin (M3), and N-formylciprofloxacin (M4), have microbiologic activity that is less than that of the parent drug but may be similar to or greater than that of some other quinolones (e.g., M3 and M4 are comparable to norfloxacin for certain organisms).
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
肝脏。已在人尿中鉴定出四种代谢物,这些代谢物共同约占口服剂量的15%。这些代谢物具有抗菌活性,但活性低于未改变的环丙沙星。
消除途径:口服给药剂量的约40至50%以未改变药物的形态从尿液中排出。
半衰期:4小时
Hepatic. Four metabolites have been identified in human urine which together account for approximately 15% of an oral dose. The metabolites have antimicrobial activity, but are less active than unchanged ciprofloxacin.
Route of Elimination: Approximately 40 to 50% of an orally administered dose is excreted in the urine as unchanged drug.
Half Life: 4 hours
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
The bactericidal action of ciprofloxacin results from inhibition of the enzymes topoisomerase II (DNA gyrase) and topoisomerase IV, which are required for bacterial DNA replication, transcription, repair, strand supercoiling repair, and recombination.
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
环丙沙星与其他氟喹诺酮类药物一样,在治疗期间与低比率(1%至3%)的血清酶升高相关。这些异常通常是轻微的、无症状的且短暂的,即使在继续治疗的情况下也会解决。更重要的是,环丙沙星与罕见但偶尔严重甚至致命的急性肝损伤病例有关。发病时间通常很短(2天到2周),表现为突然的恶心、疲劳和腹痛,随后出现深色尿和黄疸。血清酶升高的模式可以是肝细胞性或胆汁淤积性;发病时间较短的病例通常更倾向于肝细胞性,表现为ALT水平显著升高,偶尔伴有凝血酶原时间的迅速恶化和肝衰竭的早期迹象。疾病的发生也可能在停药后几天出现。胆汁淤积性酶模式病例可能病程延长,但通常是自限性的。尽管如此,慢性胆汁淤积和消失胆管综合征已有报道与环丙沙星和其他氟喹诺酮类药物有关。最后,酶模式最初可能是肝细胞性的,然后在病程中从肝细胞性演变为混合性或胆汁淤积性模式。许多(但不是所有)病例出现了伴有发热、皮疹和嗜酸性粒细胞的过敏表现。自身抗体通常不存在。
Ciprofloxacin like other fluoroquinolones is associated with a low rate (1% to 3%) of serum enzyme elevations during therapy. These abnormalities are generally mild, asymptomatic and transient, resolving even with continuation of therapy. More importantly, ciprofloxacin has been linked to rare, but occasionally severe and even fatal cases of acute liver injury. The time to onset is typically short (2 days to 2 weeks) and the presentation is often abrupt with nausea, fatigue and abdominal pain, followed by dark urine and jaundice. The pattern of serum enzyme elevations can be either hepatocellular or cholestatic; cases with the shorter times to onset usually being more hepatocellular with markedly elevated ALT levels, and occasionally with rapid worsening of prothrombin time and early signs of hepatic failure. The onset of illness also may occur a few days after the medication is stopped. Cases with a cholestatic pattern of enzymes may run a prolonged course, but are usually self-limiting. Nevertheless, chronic cholestasis and vanishing bile duct syndrome have been reported with ciprofloxacin and other fluoroquinolones. Finally, the enzyme pattern can be initially hepatocellular and then evolve during the course of illness from a hepatocellular into a mixed or cholestatic pattern. Many (but not all) cases have had allergic manifestations with fever, rash and eosinophilia. Autoantibodies are usually not present.
来源:LiverTox
毒理性
DILI 注解:最令人关注的药物性肝损伤
DILI Annotation:Most-DILI-Concern
来源:Drug Induced Liver Injury Rank (DILIrank) Dataset
毒理性
严重等级:7
Severity Grade:7
来源:Drug Induced Liver Injury Rank (DILIrank) Dataset
吸收、分配和排泄
250毫克的环丙沙星口服剂量在0.81小时内达到平均最高浓度0.94毫克/升,平均药时曲线下面积为1.013升/小时*千克。美国食品药品监督管理局报告环丙沙星的口服生物利用度为70-80%,而其他研究报道称大约为60%。早期对环丙沙星的一项评估报告其口服生物利用度为64-85%,但建议所有实际应用中使用70%。
A 250mg oral dose of ciprofloxacin reaches an average maximum concentration of 0.94mg/L in 0.81 hours with an average area under the curve of 1.013L/h\*kg. The FDA reports an oral bioavailability of 70-80% while other studies report it to be approximately 60%. An early review of ciprofloxacin reported an oral bioavailability of 64-85% but recommends 70% for all practical uses.
来源:DrugBank
吸收、分配和排泄
口服剂量的27%未发生代谢并以原形从尿液中排出,而静脉剂量的46%未发生代谢并以原形从尿液中排出。收集放射性标记的环丙沙星后,尿液中的回收率为45%,粪便中的回收率为62%。
27% of an oral dose was recovered unmetabolized in urine compared to 46% of an intravenous dose. Collection of radiolabelled ciprofloxacin resulted in 45% recovery in urine and 62% recovery in feces.
来源:DrugBank
吸收、分配和排泄
环丙沙星遵循一个三室分布模型,其中中央室容积为0.161L/kg,总体分布容积为2.00-3.04L/kg。
Cirpofloxacin follws a 3 compartment distribution model with a central compartment volume of 0.161L/kg and a total volume of distribution of 2.00-3.04L/kg.
来源:DrugBank
吸收、分配和排泄
250毫克口服给药后的平均肾清除率为5.08毫升/分钟*千克。在100毫克静脉给药后,平均总清除率为9.62毫升/分钟*千克,平均肾清除率为4.42毫升/分钟*千克,平均非肾清除率为5.21毫升/分钟*千克。
The average renal clearance after a 250mg oral dose is 5.08mL/min\*kg. Following a 100mg intravenous dose, the average total clearance is 9.62mL/min\*kg, average renal clearance is 4.42mL/min\*kg, and average non renal clearance is 5.21mL/min\*kg.
来源:DrugBank
吸收、分配和排泄
基于群体药代动力学,儿童服用环丙沙星口服混悬液的生物利用度大约为60%。在4个月至7岁的儿童单次口服10 mg/kg的环丙沙星口服混悬液后,平均血药峰浓度为2.4 ug/mL。未发现明显的年龄依赖性,多次给药后血药峰浓度也没有增加。
Based on population pharmacokinetics, bioavailability of ciprofloxacin oral suspension in children is approximately 60%. Following a single oral dose of 10 mg/kg of ciprofloxacin given as the oral suspension to children 4 months to 7 years of age, the mean peak plasma concentration was 2.4 ug/mL. There was no apparent age dependence and no increase in peak plasma concentrations following multiple doses.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
安全信息
-
危险品标志:Xi
-
安全说明:S26,S36
-
危险类别码:R36/37/38
-
WGK Germany:2
-
海关编码:3004909090
-
危险品运输编号:NONH for all modes of transport
-
RTECS号:VB1993800
-
储存条件:请将药品存放在避光、密封且干燥的地方保存。
SDS
1.1 产品标识符
: Ciprofloxacin
化学品俗名或商品名
1.2 鉴别的其他方法
Ciprobay
1.3 有关的确定了的物质或混合物的用途和建议不适合的用途
仅供科研用途,不作为药物、家庭备用药或其它用途。
模块 2. 危险性概述
2.1 GHS分类
急性毒性, 经口 (类别5)
2.2 GHS 标记要素,包括预防性的陈述
危害类型象形图 无
信号词 警告
危险申明
H303 吞咽可能有害。
警告申明
措施
P312 如感觉不适,呼救解毒中心或医生。
当心 - 物质尚未完全测试。
2.3 其它危害物 - 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
3.1 物 质
: Ciprobay
别名
: C17H18FN3O3
分子式
: 331.34 g/mol
分子量
成分 浓度
Ciprofloxacin
-
化学文摘编号(CAS No.) 85721-33-1
模块 4. 急救措施
4.1 必要的急救措施描述
一般的建议
请教医生。 出示此安全技术说明书给到现场的医生看。
如果吸入
如果吸入,请将患者移到新鲜空气处。 如果停止了呼吸,给于人工呼吸。 请教医生。
在皮肤接触的情况下
用肥皂和大量的水冲洗。 请教医生。
在眼睛接触的情况下
用水冲洗眼睛作为预防措施。
如果误服
切勿给失去知觉者从嘴里喂食任何东西。 用水漱口。 请教医生。
4.2 最重要的症状和影响,急性的和滞后的
4.3 及时的医疗处理和所需的特殊处理的说明和指示
无数据资料
模块 5. 消防措施
5.1 灭火介质
灭火方法及灭火剂
用水雾,耐醇泡沫,干粉或二氧化碳灭火。
5.2 源于此物质或混合物的特别的危害
碳氧化物, 氮氧化物, 氟化氢
5.3 救火人员的预防
如必要的话,戴自给式呼吸器去救火。
5.4 进一步的信息
无数据资料
模块 6. 泄露应急处理
6.1 人员的预防,防护设备和紧急处理程序
使用个人防护设备。 防止粉尘的生成。 防止吸入蒸汽、气雾或气体。 避免吸入粉尘。
6.2 环境预防措施
不要让产物进入下水道。
6.3 抑制和清除溢出物的方法和材料
收集、处理泄漏物,不要产生灰尘。 扫掉和铲掉。 存放在合适的封闭的处理容器内。
6.4 参考其他部分
丢弃处理请参阅第13节。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
7.1 安全操作的注意事项
防止粉尘和气溶胶生成。
在有粉尘生成的地方,提供合适的排风设备。
7.2 安全储存的条件,包括任何不兼容性
贮存在阴凉处。 容器保持紧闭,储存在干燥通风处。
7.3 特定用途
无数据资料
模块 8. 接触控制/个体防护
8.1 控制参数
最高容许浓度
没有已知的国家规定的暴露极限。
8.2 暴露控制
适当的技术控制
根据工业卫生和安全使用规则来操作。 休息以前和工作结束时洗手。
人身保护设备
眼/面保护
请使用经官方标准如NIOSH (美国) 或 EN 166(欧盟) 检测与批准的设备防护眼部。
皮肤保护
戴手套取 手套在使用前必须受检查。
请使用合适的方法脱除手套(不要接触手套外部表面),避免任何皮肤部位接触此产品.
使用后请将被污染过的手套根据相关法律法规和有效的实验室规章程序谨慎处理. 请清洗并吹干双手
所选择的保护手套必须符合EU的89/686/EEC规定和从它衍生出来的EN 376标准。
身体保护
根据危险物质的类型,浓度和量,以及特定的工作场所来选择人体保护措施。,
防护设备的类型必须根据特定工作场所中的危险物的浓度和含量来选择。
呼吸系统防护
不需要保护呼吸。如需防护粉尘损害,请使用N95型(US)或P1型(EN 143)防尘面具。
呼吸器使用经过测试并通过政府标准如NIOSH(US)或CEN(EU)的呼吸器和零件。
模块 9. 理化特性
9.1 基本的理化特性的信息
a) 外观与性状
形状: 粉末
颜色: 淡黄
b) 气味
无数据资料
c) 气味临界值
无数据资料
d) pH值
3.0 - 4.5
e) 熔点/凝固点
无数据资料
f) 起始沸点和沸程
无数据资料
g) 闪点
无数据资料
h) 蒸发速率
无数据资料
i) 可燃性(固体,气体)
无数据资料
j) 高的/低的燃烧性或爆炸性限度 无数据资料
k) 蒸气压
无数据资料
l) 相对蒸气密度
无数据资料
m) 相对密度
无数据资料
n) 水溶性
无数据资料
o) 辛醇/水分配系数的对数值
无数据资料
p) 自燃温度
无数据资料
q) 分解温度
无数据资料
r) 粘度
无数据资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应活性
10.1 反应性
无数据资料
10.2 化学稳定性
无数据资料
10.3 危险反应的可能性
无数据资料
10.4 避免接触的条件
无数据资料
10.5 不兼容的材料
强氧化剂
10.6 危险的分解产物
其它分解产物 - 无数据资料
模块 11. 毒理学资料
11.1 毒理学影响的信息
急性毒性
半致死剂量(LD50) 经口 - 大鼠 - > 2,000 mg/kg
半致死剂量(LD50) 静脉内的 - 大鼠 - 207 mg/kg
备注: 行为的:睡眠时间改变(包括正位反射的改变)。 行为的:嗜睡(全面活力抑制)。
皮肤腐蚀/刺激
无数据资料
严重眼损伤 / 眼刺激
无数据资料
呼吸道或皮肤过敏
无数据资料
生殖细胞诱变
离体的基因毒性 - 人 - 淋巴细胞
DNA损伤
离体的基因毒性 - 人 - 淋巴细胞
非常规DNA合成
离体的基因毒性 - 仓鼠 - 肺
微核测试
离体的基因毒性 - 仓鼠 - 肺
细胞发生分析
对体内基因的毒性 - 老鼠 - 腹膜内的
细胞发生分析
对体内基因的毒性 - 老鼠 - 腹膜内的
姐妹染色单体互换
致癌性
IARC:
此产品中没有大于或等于 0。1%含量的组分被 IARC鉴别为可能的或肯定的人类致癌物。
生殖毒性
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触)
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(反复接触)
无数据资料
吸入危险
无数据资料
潜在的健康影响
吸入 吸入可能有害。 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
摄入 如服入是有害的。
皮肤 如果通过皮肤吸收可能是有害的。 可能引起皮肤刺激。
眼睛 可能引起眼睛刺激。
附加说明
化学物质毒性作用登记: VB1993800
模块 12. 生态学资料
12.1 毒性
无数据资料
12.2 持久存留性和降解性
无数据资料
12.3 生物积累的潜在可能性
无数据资料
12.4 土壤中的迁移
无数据资料
12.5 PBT 和 vPvB的结果评价
无数据资料
12.6 其它不利的影响
无数据资料
模块 13. 废弃处置
13.1 废物处理方法
产品
将剩余的和未回收的溶液交给处理公司。
与易燃溶剂相溶或者相混合,在备有燃烧后处理和洗刷作用的化学焚化炉中燃烧
污染了的包装物
作为未用过的产品弃置。
模块 14. 运输信息
14.1 UN编号
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.2 联合国(UN)规定的名称
欧洲陆运危规: 无危险货物
国际海运危规: 无危险货物
国际空运危规: 无危险货物
14.3 运输危险类别
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.4 包裹组
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.5 环境危险
欧洲陆运危规: 否 国际海运危规 海运污染物: 否 国际空运危规: 否
14.6 对使用者的特别预防
无数据资料
模块 15 - 法规信息
N/A
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
: Ciprofloxacin
化学品俗名或商品名
1.2 鉴别的其他方法
Ciprobay
1.3 有关的确定了的物质或混合物的用途和建议不适合的用途
仅供科研用途,不作为药物、家庭备用药或其它用途。
模块 2. 危险性概述
2.1 GHS分类
急性毒性, 经口 (类别5)
2.2 GHS 标记要素,包括预防性的陈述
危害类型象形图 无
信号词 警告
危险申明
H303 吞咽可能有害。
警告申明
措施
P312 如感觉不适,呼救解毒中心或医生。
当心 - 物质尚未完全测试。
2.3 其它危害物 - 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
3.1 物 质
: Ciprobay
别名
: C17H18FN3O3
分子式
: 331.34 g/mol
分子量
成分 浓度
Ciprofloxacin
-
化学文摘编号(CAS No.) 85721-33-1
模块 4. 急救措施
4.1 必要的急救措施描述
一般的建议
请教医生。 出示此安全技术说明书给到现场的医生看。
如果吸入
如果吸入,请将患者移到新鲜空气处。 如果停止了呼吸,给于人工呼吸。 请教医生。
在皮肤接触的情况下
用肥皂和大量的水冲洗。 请教医生。
在眼睛接触的情况下
用水冲洗眼睛作为预防措施。
如果误服
切勿给失去知觉者从嘴里喂食任何东西。 用水漱口。 请教医生。
4.2 最重要的症状和影响,急性的和滞后的
4.3 及时的医疗处理和所需的特殊处理的说明和指示
无数据资料
模块 5. 消防措施
5.1 灭火介质
灭火方法及灭火剂
用水雾,耐醇泡沫,干粉或二氧化碳灭火。
5.2 源于此物质或混合物的特别的危害
碳氧化物, 氮氧化物, 氟化氢
5.3 救火人员的预防
如必要的话,戴自给式呼吸器去救火。
5.4 进一步的信息
无数据资料
模块 6. 泄露应急处理
6.1 人员的预防,防护设备和紧急处理程序
使用个人防护设备。 防止粉尘的生成。 防止吸入蒸汽、气雾或气体。 避免吸入粉尘。
6.2 环境预防措施
不要让产物进入下水道。
6.3 抑制和清除溢出物的方法和材料
收集、处理泄漏物,不要产生灰尘。 扫掉和铲掉。 存放在合适的封闭的处理容器内。
6.4 参考其他部分
丢弃处理请参阅第13节。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
7.1 安全操作的注意事项
防止粉尘和气溶胶生成。
在有粉尘生成的地方,提供合适的排风设备。
7.2 安全储存的条件,包括任何不兼容性
贮存在阴凉处。 容器保持紧闭,储存在干燥通风处。
7.3 特定用途
无数据资料
模块 8. 接触控制/个体防护
8.1 控制参数
最高容许浓度
没有已知的国家规定的暴露极限。
8.2 暴露控制
适当的技术控制
根据工业卫生和安全使用规则来操作。 休息以前和工作结束时洗手。
人身保护设备
眼/面保护
请使用经官方标准如NIOSH (美国) 或 EN 166(欧盟) 检测与批准的设备防护眼部。
皮肤保护
戴手套取 手套在使用前必须受检查。
请使用合适的方法脱除手套(不要接触手套外部表面),避免任何皮肤部位接触此产品.
使用后请将被污染过的手套根据相关法律法规和有效的实验室规章程序谨慎处理. 请清洗并吹干双手
所选择的保护手套必须符合EU的89/686/EEC规定和从它衍生出来的EN 376标准。
身体保护
根据危险物质的类型,浓度和量,以及特定的工作场所来选择人体保护措施。,
防护设备的类型必须根据特定工作场所中的危险物的浓度和含量来选择。
呼吸系统防护
不需要保护呼吸。如需防护粉尘损害,请使用N95型(US)或P1型(EN 143)防尘面具。
呼吸器使用经过测试并通过政府标准如NIOSH(US)或CEN(EU)的呼吸器和零件。
模块 9. 理化特性
9.1 基本的理化特性的信息
a) 外观与性状
形状: 粉末
颜色: 淡黄
b) 气味
无数据资料
c) 气味临界值
无数据资料
d) pH值
3.0 - 4.5
e) 熔点/凝固点
无数据资料
f) 起始沸点和沸程
无数据资料
g) 闪点
无数据资料
h) 蒸发速率
无数据资料
i) 可燃性(固体,气体)
无数据资料
j) 高的/低的燃烧性或爆炸性限度 无数据资料
k) 蒸气压
无数据资料
l) 相对蒸气密度
无数据资料
m) 相对密度
无数据资料
n) 水溶性
无数据资料
o) 辛醇/水分配系数的对数值
无数据资料
p) 自燃温度
无数据资料
q) 分解温度
无数据资料
r) 粘度
无数据资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应活性
10.1 反应性
无数据资料
10.2 化学稳定性
无数据资料
10.3 危险反应的可能性
无数据资料
10.4 避免接触的条件
无数据资料
10.5 不兼容的材料
强氧化剂
10.6 危险的分解产物
其它分解产物 - 无数据资料
模块 11. 毒理学资料
11.1 毒理学影响的信息
急性毒性
半致死剂量(LD50) 经口 - 大鼠 - > 2,000 mg/kg
半致死剂量(LD50) 静脉内的 - 大鼠 - 207 mg/kg
备注: 行为的:睡眠时间改变(包括正位反射的改变)。 行为的:嗜睡(全面活力抑制)。
皮肤腐蚀/刺激
无数据资料
严重眼损伤 / 眼刺激
无数据资料
呼吸道或皮肤过敏
无数据资料
生殖细胞诱变
离体的基因毒性 - 人 - 淋巴细胞
DNA损伤
离体的基因毒性 - 人 - 淋巴细胞
非常规DNA合成
离体的基因毒性 - 仓鼠 - 肺
微核测试
离体的基因毒性 - 仓鼠 - 肺
细胞发生分析
对体内基因的毒性 - 老鼠 - 腹膜内的
细胞发生分析
对体内基因的毒性 - 老鼠 - 腹膜内的
姐妹染色单体互换
致癌性
IARC:
此产品中没有大于或等于 0。1%含量的组分被 IARC鉴别为可能的或肯定的人类致癌物。
生殖毒性
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触)
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(反复接触)
无数据资料
吸入危险
无数据资料
潜在的健康影响
吸入 吸入可能有害。 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
摄入 如服入是有害的。
皮肤 如果通过皮肤吸收可能是有害的。 可能引起皮肤刺激。
眼睛 可能引起眼睛刺激。
附加说明
化学物质毒性作用登记: VB1993800
模块 12. 生态学资料
12.1 毒性
无数据资料
12.2 持久存留性和降解性
无数据资料
12.3 生物积累的潜在可能性
无数据资料
12.4 土壤中的迁移
无数据资料
12.5 PBT 和 vPvB的结果评价
无数据资料
12.6 其它不利的影响
无数据资料
模块 13. 废弃处置
13.1 废物处理方法
产品
将剩余的和未回收的溶液交给处理公司。
与易燃溶剂相溶或者相混合,在备有燃烧后处理和洗刷作用的化学焚化炉中燃烧
污染了的包装物
作为未用过的产品弃置。
模块 14. 运输信息
14.1 UN编号
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.2 联合国(UN)规定的名称
欧洲陆运危规: 无危险货物
国际海运危规: 无危险货物
国际空运危规: 无危险货物
14.3 运输危险类别
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.4 包裹组
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.5 环境危险
欧洲陆运危规: 否 国际海运危规 海运污染物: 否 国际空运危规: 否
14.6 对使用者的特别预防
无数据资料
模块 15 - 法规信息
N/A
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
制备方法与用途
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 恩诺沙星 enrofloxacin 93106-60-6 C19H22FN3O3 359.4 —— N-nitroso-ciprofloxacin 864443-44-7 C17H17FN4O4 360.345 环丙沙星甲酯 ciprofloxacin methyl ester 107884-23-1 C18H20FN3O3 345.374 1-环丙基-6-氟-4-氧代-7-(哌嗪-1-基)-1,4-二氢喹啉-3-羧酸乙酯 ethyl 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(piperazin-1-yl)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylate 105404-65-7 C19H22FN3O3 359.4 环丙沙星杂质7 7-[4-(ethoxycarbonyl)piperazin-1-yl]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 93594-29-7 C20H22FN3O5 403.41 —— 7-(4-(tert-butoxycarbonyl)piperazin-1-yl)-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 93594-48-0 C22H26FN3O5 431.464 —— 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(4-((2-(4-fluorobenzoyl)hydrazono)methyl)piperazin-1-yl)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 1340587-05-4 C25H23F2N5O4 495.486 1-环丙基-6,7-二氟-1,4-二氢-4-氧喹啉-3-羧酸 1-cyclopropyl-6,7-difluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 93107-30-3 C13H9F2NO3 265.216 —— 4-[10-(17'-Tetrabenzo[acgi]fluorenyl)decyloxy]benzyl 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-3-quinolinecarboxylate —— C63H60FN3O4 942.186 7-氯-6-氟-1-环丙基-1,4-二氢-4-氧-3-喹啉羧酸 7-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-3-quinoline carboxylic acid 86393-33-1 C13H9ClFNO3 281.671 1-环丙基-6,7-二氟-4-氧代-1,4-二氢喹啉-3-羧酸乙酯 ethyl 1-cyclopropyl-6,7-difluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylate 98349-25-8 C15H13F2NO3 293.27 —— 7-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester 104599-90-8 C14H11ClFNO3 295.698 —— 7-[4-[3-[5-[5-[[4-[5-[[4-[5-[Acetyl(hydroxy)amino]pentylamino]-4-oxobutanoyl]-hydroxyamino]pentylamino]-4-oxobutanoyl]-hydroxyamino]pentylcarbamoylamino]-2,4-dimethyl-3,6-dioxocyclohexa-1,4-dien-1-yl]-3-methylbutanoyl]piperazin-1-yl]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid —— C56H79FN10O15 1151.3 7-氯-1-环丙基-6-氟-4-氧代-1,4-二氢-喹啉-3-羧酸乙基酯 ethyl 7-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylate 86483-54-7 C15H13ClFNO3 309.725 —— 7-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylate boron diacetate 119489-54-2 C17H14BClFNO7 409.563 —— gemifloxacin 175463-14-6 C18H20FN5O4 389.386 7-氯-6-氟-4-氧代-1,4-二氢喹啉-3-羧酸乙酯 ethyl 7-chloro-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline 3-carboxylate 75073-15-3 C12H9ClFNO3 269.66 - 1
- 2
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— N'4-[11C]methyl-ciprofloxacin —— C18H20FN3O3 344.363 —— N-methylciprofloxacin 86483-46-7 C18H20FN3O3 345.374 —— 7-(4-allylpiperazin-1-yl)-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid —— C20H22FN3O3 371.411 (环丙沙星M4) 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-7-(4-formylpiperazin-1-yl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 93594-39-9 C18H18FN3O4 359.357 —— 1-Cyclopropyl-6-fluor-1,4-dihydro-7-<4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazinyl>-4-oxo-3-chinolincarbonsaeure 86483-47-8 C19H22FN3O4 375.4 —— alanyl ciprofloxacin —— C20H25FN4O3 388.442 —— N'-butylciprofloxacin —— C21H26FN3O3 387.454 —— N-nitroso-ciprofloxacin 864443-44-7 C17H17FN4O4 360.345 N-乙酰基环丙沙星 N-acetylciprofloxacin 93594-20-8 C19H20FN3O4 373.384 环丙沙星甲酯 ciprofloxacin methyl ester 107884-23-1 C18H20FN3O3 345.374 —— 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-<4-(3-oxobutyl)piperazin-1-yl>quinoline-3-carboxylic acid 93106-51-5 C21H24FN3O4 401.438 —— N'-hexylciprofloxacin —— C23H30FN3O3 415.508 —— 7-(4-(3-azidopropyl)piperazin-1-yl)-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 1144106-71-7 C20H23FN6O3 414.439 —— 1-cyclopropyl-7-(4-cyclopropylmethyl-1-piperazinyl)-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid —— C21H24FN3O3 385.438 —— 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(4-(2-oxopropyl)piperazin-1-yl)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid —— C20H22FN3O4 387.411 —— 7-[4-(aminoacetyl)-piperazin-1-yl]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid —— C19H21FN4O4 388.399 —— 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(4-propylsulfanylpiperazin-1-yl)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid —— C20H24FN3O3S 405.493 —— 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(4-trifluoromethylthiomethyl-1-piperazinyl)-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid —— C19H19F4N3O3S 445.438 —— N-acryloyl ciprofloxacin —— C20H20FN3O4 385.395 —— 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-7-(4-(2-hydrazinyl-2-oxoethyl)piperazin-1-yl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid —— C19H22FN5O4 403.413 —— 7-[4-(2-chloroacetyl) piperazin-1-yl]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid —— C19H19ClFN3O4 407.829 —— 7-(4-(2-hydroxyacetyl)piperazin-1-yl)-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid —— C19H20FN3O5 389.383 —— 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(4-propionylpiperazin-1-yl)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 93594-21-9 C20H22FN3O4 387.411 —— 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-7-(4-(2-methoxy-2-oxoethyl)piperazin-1-yl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid —— C20H22FN3O5 403.41 7-(2-氨基乙基氨基)-1-环丙基-6-氟-4-氧代喹啉-3-羧酸 Desethyleneciprofloxacin 103222-12-4 C15H16FN3O3 305.309 —— 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-((4-(2-oxo-2-(phenyl)amino)ethyl)piperazin-1-yl)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 1276690-30-2 C25H25FN4O4 464.496 —— 7-[4-(2E)-but-2-enoyl-piperazin-1-yl]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid —— C21H22FN3O4 399.422 —— N-benzylciprofloxacin 93107-14-3 C24H24FN3O3 421.471 —— 1-cyclopropyl-7-(4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethyl)piperazin-1-yl)-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid —— C21H24FN3O5 417.437 —— 7-(4-butyrylpiperazin-1-yl)-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 93594-22-0 C21H24FN3O4 401.438 —— 7-[4-(2-methoxycarbonylethyl)-1-piperazinyl]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid 93398-81-3 C21H24FN3O5 417.437 1-环丙基-6-氟-4-氧代-7-(哌嗪-1-基)-1,4-二氢喹啉-3-羧酸乙酯 ethyl 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(piperazin-1-yl)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylate 105404-65-7 C19H22FN3O3 359.4 —— 7-[4-(2,2-diethoxyethyl)-1-piperazinyl]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid —— C23H30FN3O5 447.507 —— 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-7-(4-(oxiran-2-ylmethyl)piperazin-1-yl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid —— C20H22FN3O4 387.411 —— 1-cyclopropyl-7-[4-(2-{4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl}acetyl)piperazin-1-yl]-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid —— C25H32FN5O4 485.559 —— 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(4-(pent-4-enoyl)piperazin-1-yl)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid —— C22H24FN3O4 413.449 —— 7-[4-(2E,4E)-hexa-2,4-dienoyl-piperazin-1-yl]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid —— C23H24FN3O4 425.46 —— 7-(4-pentanoylpiperazin-1-yl)-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 1051329-81-7 C22H26FN3O4 415.465 —— 7-(4-(((4-carboxyphenyl)amino)methyl)piperazin-1-yl)-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid —— C25H25FN4O5 480.496 —— 7-[4-(2-{4-acetylpiperazin-1-yl}acetyl)piperazin-1-yl]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid —— C25H30FN5O5 499.542 —— 7-[4-(pivaloyl)piperazin-1-yl]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 1044145-95-0 C22H26FN3O4 415.465 —— 7-[4-(3-methyl-butyryl)-piperazin-1-yl]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid —— C22H26FN3O4 415.465 —— 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-7-(4-(2-(methyl(phenyl)amino)-2-oxoethyl) piperazin-1-yl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 1276690-29-9 C26H27FN4O4 478.523 —— 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(4-phosphono-piperazin-1-yl)-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid —— C17H19FN3O6P 411.327 环丙沙星杂质7 7-[4-(ethoxycarbonyl)piperazin-1-yl]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 93594-29-7 C20H22FN3O5 403.41 —— benzyl 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(piperazin-1-yl)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylate 1281884-94-3 C24H24FN3O3 421.471 —— 7-(4-(3-azido-2-hydroxypropyl)piperazin-1-yl)-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 1144106-75-1 C20H23FN6O4 430.439 —— isopropyl 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(piperazin-1-yl)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylate 1427036-10-9 C20H24FN3O3 373.427 —— 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-7-(4-hexanoylpiperazin-1-yl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 151602-46-9 C23H28FN3O4 429.491 —— propyl 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(piperazin-1-yl)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylate 1239881-81-2 C20H24FN3O3 373.427 —— 7,7'-((1,3-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(piperazine-4,1-diyl))bis(1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid) —— C42H42F2N6O6 764.829 —— 7-(4-heptanoylpiperazin-1-yl)-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 1186385-02-3 C24H30FN3O4 443.518 —— 7-(4-decanoylpiperazin-1-yl)-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 1044145-99-4 C27H36FN3O4 485.599 —— 7-[4-[14-[4-(3-Carboxy-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxoquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-yl]-14-oxotetradecanoyl]piperazin-1-yl]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 1350462-69-9 C48H58F2N6O8 885.021 —— 7-[4-[15-[4-(3-Carboxy-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxoquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-yl]-15-oxopentadecanoyl]piperazin-1-yl]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 1350462-70-2 C49H60F2N6O8 899.048 —— 7-[4-[16-[4-(3-Carboxy-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxoquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-yl]-16-oxohexadecanoyl]piperazin-1-yl]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 1350462-71-3 C50H62F2N6O8 913.074 —— 7-[4-[10-[4-(3-Carboxy-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxoquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-yl]-10-oxodecanoyl]piperazin-1-yl]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 1350462-67-7 C44H50F2N6O8 828.913 —— 7-[4-[18-[4-(3-Carboxy-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxoquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-yl]-18-oxooctadecanoyl]piperazin-1-yl]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 1350462-72-4 C52H66F2N6O8 941.128 —— 7-(4-hexadecanoyl-piperazin-1-yl)-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid 1186385-05-6 C33H48FN3O4 569.76 —— 7-[4-[12-[4-(3-Carboxy-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxoquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-yl]-12-oxododecanoyl]piperazin-1-yl]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 1350462-68-8 C46H54F2N6O8 856.967 —— 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-7-(4-nonanoylpiperazin-1-yl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 1044145-97-2 C26H34FN3O4 471.572 —— 7-(4-octanoylpiperazin-1-yl)-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 1044145-96-1 C25H32FN3O4 457.545 —— 7-(4-dodecanoylpiperazin-1-yl)-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 1186385-03-4 C29H40FN3O4 513.653 —— 7-(4-tetradecanoylpiperazin-1-yl)-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 1186385-04-5 C31H44FN3O4 541.706 —— 1-Cyclopropyl-7-[4-(2-ethylbutanoyl)piperazin-1-yl]-6-fluoro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 1404192-19-3 C23H28FN3O4 429.491 —— butyl 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(piperazin-1-yl)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylate 1208308-62-6 C21H26FN3O3 387.454 1-环丙基-6-氟-4-氧代-7-哌嗪-1-基喹啉-3-甲醛 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-7-piperazin-1-yl-quinolin-4(1H)-one-3-carbaldehyde 110719-57-8 C17H18FN3O2 315.347 —— 7-(4-(2-((4-chlorophenyl)amino)-2-oxoethyl)piperazin-1-yl)-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid —— C25H24ClFN4O4 498.941 —— 1-Cyclopropyl-7-[4-(2,2-dimethylbutanoyl)piperazin-1-yl]-6-fluoro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 1365998-76-0 C23H28FN3O4 429.491 —— 7-(4-(tert-butoxycarbonyl)piperazin-1-yl)-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 93594-48-0 C22H26FN3O5 431.464 —— 1-Cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-7-[4-(2-methylpentanoyl)piperazin-1-yl]-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 1404192-20-6 C23H28FN3O4 429.491 —— 7-[4-(3-carboxypropionyl)-1-piperazinyl]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1H-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid 93594-40-2 C21H22FN3O6 431.421 —— 1-Cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-7-[4-(3-nitropropanoyl)piperazin-1-yl]-4-oxo-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid 1333341-18-6 C20H21FN4O6 432.408 —— 7-[4-(9E)-octadec-9-enoyl-piperazin-1-yl]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid —— C35H50FN3O4 595.798 —— 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(4-(phenylcarbamoyl)piperazin-1-yl)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid —— C24H23FN4O4 450.469 —— 7-(4-(4-carboxybutanoyl)piperazin-1-yl)-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid —— C22H24FN3O6 445.447 —— 1-Cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-[4-(2-oxo-2-phenyl-ethyl)-piperazin-1-yl]-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid —— C25H24FN3O4 449.482 —— hexyl 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(piperazin-1-yl)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylate 1427036-14-3 C23H30FN3O3 415.508 —— 7-[4-(butoxycarbonyl)piperazin-1-yl]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 93594-30-0 C22H26FN3O5 431.464 —— 1-Cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-[4-(2-propylpentanoyl)piperazin-1-yl]quinoline-3-carboxylic acid 1404192-18-2 C25H32FN3O4 457.545 —— 7-(4-(2-benzyloxyacetyl)piperazin-1-yl)-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 1186385-07-8 C26H26FN3O5 479.508 —— 1-cyclopropyl-7-(4-(4,6-diamino-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)piperazin-1-yl)-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 1158040-66-4 C20H21FN8O3 440.437 —— 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-[4-(2-phenylacetyl)piperazin-1-yl]quinoline-3-carboxylic acid 1186385-06-7 C25H24FN3O4 449.482 —— 7-[4-(2E)-3,7-dimethylocta-2,6-dienoyl-piperazin-1-yl]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid —— C27H32FN3O4 481.567 —— 1-Cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-[4-(3,5,5-trimethylhexanoyl)piperazin-1-yl]quinoline-3-carboxylic acid 1404192-21-7 C26H34FN3O4 471.572 —— 1-Cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-[4-(2-oxo-2-p-tolyl-ethyl)-piperazin-1-yl]-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid —— C26H26FN3O4 463.509 —— 1-Cyclopropyl-7-[4-(2-ethylhexanoyl)piperazin-1-yl]-6-fluoro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 1404192-17-1 C25H32FN3O4 457.545 —— 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-7-(4-((3-fluorophenyl)carbamothioyl)piperazin-1-yl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid —— C24H22F2N4O3S 484.526 —— 7-[4-(4-fluorophenacyl)-1-piperazinyl]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid —— C25H23F2N3O4 467.472 —— 7-{4-[(3-methoxycarbonylpropyl)-carbamoyl]-piperazin-1-yl}-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid —— C23H27FN4O6 474.489 —— 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-piperazin-1-yl-quinoline-3-naphthyl ester 1146142-90-6 C27H24FN3O3 457.504 —— 2-propenyl 1-cyclopropyl-1,4-dihydro-6-fluoro-7-[4-(3-hydroxypropyl)piperazinyl]-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylate 247075-64-5 C23H28FN3O4 429.491 —— 7-[4-((octyloxy)carbonyl)piperazin-1-yl]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 1186384-95-1 C26H34FN3O5 487.571 —— 7-[4-((decyloxy)carbonyl)piperazin-1-yl]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 1186384-98-4 C28H38FN3O5 515.625 —— 7-[4-((dodecyloxy)carbonyl)piperazin-1-yl]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 1186385-00-1 C30H42FN3O5 543.679 —— 7-[4-((nonyloxy)carbonyl)piperazin-1-yl]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 1186384-96-2 C27H36FN3O5 501.598 —— N-benzoylciprofloxacin —— C24H22FN3O4 435.455 —— 7-(4-(2-(benzyloxycarbonylamino)acetyl)piperazin-1-yl)-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 1593704-97-2 C27H27FN4O6 522.533 —— 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(4-((2-(4-fluorobenzoyl)hydrazono)methyl)piperazin-1-yl)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 1340587-05-4 C25H23F2N5O4 495.486 —— 7-(4-(2,2-bisphosphonoethyl)piperazin-1-yl)-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid —— C19H24FN3O9P2 519.36 - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:6-氟-3-苯基-7-哌嗪基喹诺酮衍生物作为潜在的拓扑异构酶I抑制剂的合成及生物学评估摘要:基于1-乙基-3-(6-硝基苯并恶唑-2-基)-6,8-二氟-描述了7-(3-甲基哌嗪-1-基)-4(1H)-喹诺酮。这些化合物为拓扑异构酶I(Top I)抑制剂的发现提供了新的支架,基于靶标的测定表明它们可以明显抑制100μM的TopI。在体外,这些新化合物的抗增殖活性对A549,Hela细胞,BGC-823,和HepG2细胞系进行评估。化合物18a - g显示出对那些癌细胞系生长的有效抑制活性。最阳性的化合物18f和18g在Top I抑制试验和MTT试验中证明与喜树碱一样有效。化合物18f和18g在24小时内导致细胞S期的百分比明显增加。的体内数据显示,18F和18克抑制肿瘤生长分别为29.25%的抑制率,并在20mg / kg的42.75%。数据表明了进一步发展的治疗潜力。DOI:10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.06.054
-
作为产物:描述:7-(4-(tert-butoxycarbonyl)piperazin-1-yl)-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 在 三氟乙酸 作用下, 以 二氯甲烷 为溶剂, 反应 2.0h, 以98.7%的产率得到环丙沙星参考文献:名称:[EN] ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE BREAKERS
[FR] AGENTS DE RUPTURE DE RÉSISTANCE AUX ANTIBIOTIQUES摘要:该发明涉及公式(A1)的抗生素化合物及其药学上可接受的盐、溶剂化合物、互变异构体和它们的组合,其中X和L是可选的连接物,RA或R1中的一个包括Ar1,其中Ar1是一种抗生素耐药性破坏基团,包括可选择取代的C6-10芳基,C7-13芳基烷基,C5-10杂芳基,C6-13杂芳基烷基,C5-10杂环烷基,C6-13杂环烷基,C3-10碳环烷基,C4-13碳环烷基,-C(=NR')-NR'R''或–CH2- CH=CH2基团;在将该化合物用于细菌感染后,该基团减少或预防外流。该发明还公开了包括公式(A1)化合物的药物组合物以及将这些化合物用作药物的用途,特别是用于治疗细菌感染,如耐药性细菌感染。公开号:WO2018220365A1 -
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:Cryogel bandage containing therapeutic agent摘要:公开了一种含有治疗剂的控释绷带,该绷带采用聚乙烯醇冻凝胶制成。该绷带可以包括颗粒吸附剂,如离子交换树脂和疏水颗粒,以进一步确保治疗剂的控制和恒定释放。该绷带还可以包括可塑剂,以在绷带干燥时提供柔软性。公开号:US05260066A1
文献信息
-
Compositions for Treatment of Cystic Fibrosis and Other Chronic Diseases申请人:Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated公开号:US20150231142A1公开(公告)日:2015-08-20The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising an inhibitor of epithelial sodium channel activity in combination with at least one ABC Transporter modulator compound of Formula A, Formula B, Formula C, or Formula D. The invention also relates to pharmaceutical formulations thereof, and to methods of using such compositions in the treatment of CFTR mediated diseases, particularly cystic fibrosis using the pharmaceutical combination compositions.
-
[EN] ANTIBACTERIAL 8-PHENYLAMINO-3-(PYRAZOL-4-YL)IMIDAZO[1,2-A]PYRAZINE DERIVATIVES<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS ANTIBACTÉRIENS DE 8-PHÉNYLAMINO-3-(PYRAZOL-4-YL)IMIDAZO[1,2-A]PYRAZINE申请人:HOFFMANN LA ROCHE公开号:WO2021219578A1公开(公告)日:2021-11-04The invention provides novel imidazopyrazine derivatives having the general formula (I), wherein X and R3 to R9 are as described herein or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, wherein X and R3 to R9 are as defined herein. Further provided are pharmaceutical compositions including the compounds, processes of manufacturing the compounds and methods of using the compounds as medicaments, in particular methods of using the compounds as antibiotics for the treatment or prevention of bacterial infections and resulting diseases.
-
[EN] HIGHLY 6-SUBSTITUTED -2,4-DIAMINOPYRIMIDINES AS INHIBITORS OF ANTHRAX<br/>[FR] 2,4-DIAMINOPYRIMIDINES HAUTEMENT SUBSTITUÉES EN POSITION 6 EN TANT QU'INHIBITEURS DE L'ANTHRAX申请人:UNIV OKLAHOMA STATE公开号:WO2013138787A1公开(公告)日:2013-09-192,4-diaminopyrimidine compounds of generic Formula 1, where R and R' may be the same or different and are independently selected from: C1-C6 alkyl or alkenyl groups with 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6 carbon atoms, which may be: branched or unbranched; saturated or unsaturated; and may or may not be substituted, are used to treat anthrax.
-
Integrase inhibitors申请人:Cai R. Zhenhong公开号:US20080058315A1公开(公告)日:2008-03-06Tricyclic compounds, protected intermediates thereof, and methods for inhibition of HIV-integrase are disclosed.三环化合物,其受保护的中间体,以及用于抑制HIV整合酶的方法被披露。
-
[EN] OXAZOLIDINONE COMPOUNDS AND METHODS OF USE THEREOF AS ANTIBACTERIAL AGENTS<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS OXAZOLIDINONE ET PROCÉDÉS D'UTILISATION DE CES DERNIERS EN TANT QU'AGENTS ANTIBACTÉRIENS申请人:MERCK SHARP & DOHME公开号:WO2017066964A1公开(公告)日:2017-04-27The present invention relates to oxazolidinone compounds of Formula (I): and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, wherein A, E, and R1 are as defined herein. The present invention also relates to compositions which comprise at least one oxazolidinone compound of the invention. The invention also provides methods for inhibiting growth of mycobacterial cells as well as a method of treating mycobacterial infections by Mycobacterium tuberculosiscomprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of an oxazolidinone of the invention and/or apharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a composition comprising such compound and/or salt.
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
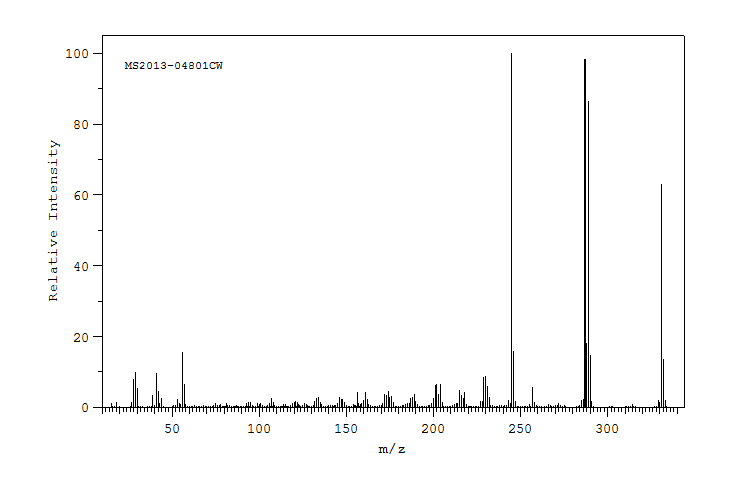
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
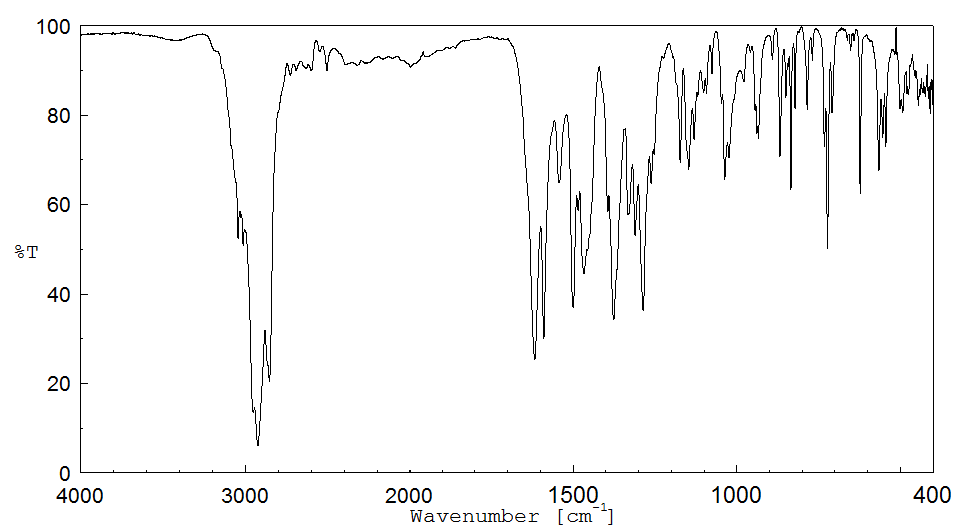
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(S)-4-(叔丁基)-2-(喹啉-2-基)-4,5-二氢噁唑
(SP-4-1)-二氯双(喹啉)-钯
(E)-2-氰基-3-[5-(2,5-二氯苯基)呋喃-2-基]-N-喹啉-8-基丙-2-烯酰胺
(8α,9S)-(+)-9-氨基-七氢呋喃-6''-醇,值90%
(6,7-二甲氧基-4-(3,4,5-三甲氧基苯基)喹啉)
(1-羟基-5-硝基-8-氧代-8,8-dihydroquinolinium)
黄尿酸 8-甲基醚
麻保沙星EP杂质D
麻保沙星EP杂质B
麻保沙星EP杂质A
麦角腈甲磺酸盐
麦角腈
麦角灵
麦皮星酮
麦特氧特
高铁试剂
高氯酸3-苯基[1,3]噻唑并[3,2-f]5-氮杂菲-4-正离子
马波沙星EP杂质F
马波沙星
马来酸茚达特罗杂质
马来酸茚达特罗
马来酸维吖啶
马来酸来那替尼
马来酸四甲基铵
香草木宁碱
颜料红R-122
颜料红210
颜料红
顺式-苯并(f)喹啉-7,8-二醇-9,10-环氧化物
顺式-(alphaR)-N-(4-氯苯基)-4-(6-氟-4-喹啉基)-alpha-甲基环己烷乙酰胺
非那沙星
非那沙星
青花椒碱
青色素863
雷西莫特
隐花青
阿莫地喹-d10
阿莫地喹
阿莫吡喹N-氧化物
阿美帕利
阿米诺喹
阿立哌唑溴代杂质
阿立哌唑杂质B
阿立哌唑杂质38
阿立哌唑杂质1750
阿立哌唑杂质13
阿立哌唑杂质
阿立哌唑杂质
阿尔马尔
阿加曲班杂质43