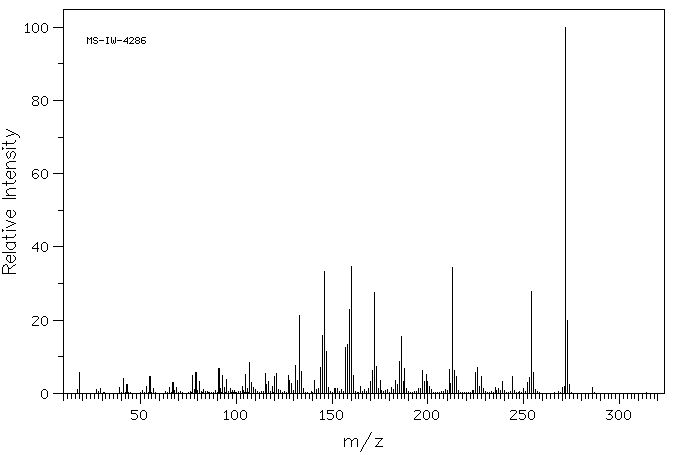
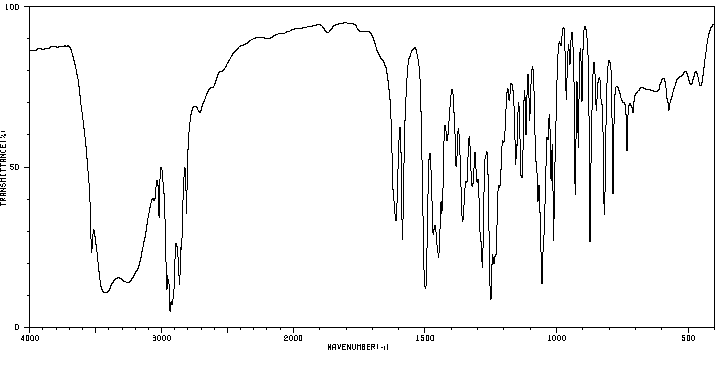
代谢
外源性给予的雌激素以与内源性雌激素相同的方式被代谢。代谢转化主要发生在肝脏和肠道。雌二醇被代谢为雌酮,两者都转化为雌三醇,后者随后随尿液排出。硫酸和葡萄糖苷酸结合的雌激素也在肝脏中进行。代谢结合物的胆汁分泌进入肠道,在肠道中发生雌激素的水解,随后再次被吸收。CYP3A4肝细胞色素酶在雌二醇的代谢中起主要作用。CYP1A2也发挥作用。
Exogenously administered estrogens are metabolized in the same fashion as endogenous estrogens. Metabolic transformation occurs primarily in the liver and intestine. Estradiol is metabolized to estrone, and both are converted to estriol, which is later excreted in the urine. Sulfate and glucuronide conjugation estrogens also take place in the liver. Biliary secretion of metabolic conjugates are released into the intestine, and estrogen hydrolysis in the gut occurs, followed by reabsorption. The CYP3A4 hepatic cytochrome enzyme is heavily involved in the metabolism of estradiol. CYP1A2 also plays a role.
来源:DrugBank