维生素 D3 | 67-97-0
物质功能分类
分子结构分类
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:83-86 °C(lit.)
-
比旋光度:105 º (c=0.8, EtOH 25 ºC)
-
沸点:451.27°C (rough estimate)
-
密度:0.9717 (rough estimate)
-
闪点:14 °C
-
溶解度:几乎不溶于水,易溶于乙醇(96%),溶于三甲基戊烷和脂肪油。它对空气、热和光敏感。不含抗氧化剂的溶剂溶液不稳定,应立即使用。根据温度和时间,在溶液中可发生前胆钙化醇的可逆异构化。该活性归因于这两种化合物。
-
LogP:9.085 (est)
-
物理描述:Vitamin d3 appears as fine colorless crystals. Water insoluble. (NTP, 1992)
-
颜色/状态:Fine needles from dilute acetone
-
气味:ODORLESS
-
蒸汽压力:2.4X10-9 mm Hg at 25 °C (est)
-
稳定性/保质期:
In dry propylene glycol, therapeutic concentrations are stored in amber screw cap bottles at 38 °C no change after 36 mo
-
旋光度:Specific optical rotation (1.6% in acetone): +84.8 deg at 20 °C/D; (1.6% in chloroform): +51.9 deg at 20 °C/D
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):7.9
-
重原子数:28
-
可旋转键数:6
-
环数:3.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.78
-
拓扑面积:20.2
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:1
ADMET
安全信息
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险品标志:Xn,T+,T
-
安全说明:S28,S28A,S36/37,S45
-
危险类别码:R26,R48/25,R24/25
-
WGK Germany:2
-
海关编码:2936240000
-
危险品运输编号:UN 2811 6.1/PG 2
-
危险类别:6.1
-
RTECS号:VS2900000
-
包装等级:II
-
危险标志:GHS06,GHS08
-
危险性描述:H301 + H311,H330,H372
-
危险性防范说明:P260,P280,P284,P301 + P310,P310
SDS
制备方法与用途
维生素D3,又称胆钙化醇,是维生素D的一种,被证明是维生素D在体内的真正活性形式。目前已知的维生素D至少有10种,但最重要的是维生素D2(麦角骨化醇)和维生素D3(胆钙化醇)。胆钙化醇是最重要的一种形式,主要调节体内的钙磷代谢。它可通过7-脱氢胆固醇在紫外光照射下转化而来。
化学性质白色柱状结晶或结晶性粉末,无臭无味。熔点84~88℃,比旋光度αD20=+105°~+112°。极易溶于氯仿,易溶于乙醇、乙醚、环己烷和丙酮,微溶于植物油,不溶于水。耐热性好,但对光不稳定,在空气中易氧化。
生产方法维生素D3自然存在于肝、奶和蛋黄中,工业上的生产方法是先从植物油或酵母中提取人体不能吸收的7-脱氢胆固醇,再将其溶液于氯仿或环己烷后,在石英玻璃烧瓶中用紫外线照射转化成维生素D3。也可将7-脱氢胆固醇溶于乙醇,用紫外光照射开环,反应液浓缩、冷冻、过滤,滤液通氮减压浓缩至干,得粗维生素D3液,再经精制而得。
用途 防治疾病维生素D3能保持钙和磷的代谢正常,促进机体对钙和磷的吸收。缺乏时,儿童易得佝偻病,成人则得骨软化病。
- 用途:用于治疗佝偻病及骨质软化病。
作为营养增补剂,可用于液体奶、人造奶油、乳制品和婴幼儿食品中。
- 用途:日本以生产和使用D2为多,在各种需求量中,医药占30%,饲料添加剂占65%,食品添加剂占5%。
维生素D3通过受体起作用,该受体是具配体依赖性转录因子大家庭的一员,调控正常细胞和癌细胞的增殖和分化。对乳腺癌、结肠癌和前列腺癌具有抗增殖、抗转移效果。
- 用途:主要用于食品,保健品及其他相关产品。
化学性质极易溶于氯仿,易溶于乙醇、乙醚、环己烷和丙酮,微溶于植物油,不溶于水。耐热性好,但对光不稳定,在空气中易氧化。猪对维生素D2和D3的利用率是同等的,但禽类对维生素D2的利用率仅为D3的1/40-1/30。用量为1000-1500IU/kg。
日本使用上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— trans-vitamin D3 57651-83-9 C27H44O 384.646 3Β,5E,7E-9,10-断胆甾-5,7,10[1P]-三烯-3-醇 5,6-trans-vitamin D3 22350-41-0 C27H44O 384.646 骨化三醇 calcitriol 32222-06-3 C27H44O3 416.645 7-去氢胆固醇 7-dehydrocholesterol 434-16-2 C27H44O 384.646 3Β,6Z-9,10-断胆甾基-5(10),6,8-三烯甘油酯-3 previtamin D3 1173-13-3 C27H44O 384.646 豆甾醇 β-sitosterol 83-46-5 C29H50O 414.715 胆固醇 cholesterol 57-88-5 C27H46O 386.662 豆甾醇 Stigmasterol 83-48-7 C29H48O 412.7 —— [(3aS4E)-1t-((R)-1,5-dimethyl-hexyl)-7a-methyl-(3ar,7at)-octahydro-inden-4-yliden]-acetaldehyde 84928-46-1 C20H34O 290.489 胆固醇醋酸酯 Cholesteryl acetate 604-35-3 C29H48O2 428.699 羊毛甾醇 tirucallol 79-63-0 C30H50O 426.726 —— cholesta-5,22-dien-3β-ol acetate —— C29H46O2 426.683 醋酸豆甾醇 stigmasterol acetate 4651-48-3 C31H50O2 454.737 7-脱氢苯甲酸胆固醇 3β-benzoyloxycholesta-5,7-diene 1182-06-5 C34H48O2 488.754 - 1
- 2
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 3Β,5E,7E-9,10-断胆甾-5,7,10[1P]-三烯-3-醇 5,6-trans-vitamin D3 22350-41-0 C27H44O 384.646 —— trans-vitamin D3 57651-83-9 C27H44O 384.646 —— cholecalciferol 22350-41-0 C27H44O 384.646 维生素D2 Calciferol 50-14-6 C28H44O 396.657 骨化二醇 calcidiol 19356-17-3 C27H44O2 400.645 —— vitamin D3 53954-32-8 C27H44O 384.646 阿法骨化醇 1α-hydroxyvitamin D3 41294-56-8 C27H44O2 400.645 —— (5Z,7E,10Z)-19-fluoro-9,10-seco-5,7,10(19)-cholestatriene-3β-ol —— C27H43FO 402.636 —— (5Z,7E,10E)-19-fluoro-9,10-seco-5,7,10(19)-cholestatriene-3β-ol 182231-94-3 C27H43FO 402.636 —— (5E,7E,10Z)-19-fluoro-9,10-seco-5,7,10(19)-cholestatriene-3β-ol 182232-42-4 C27H43FO 402.636 —— (5E,7E,10E)-19-fluoro-9,10-seco-5,7,10(19)-cholestatriene-3β-ol 182232-49-1 C27H43FO 402.636 1beta-羟基维他命D3 1α-hydroxyvitamin D3 63181-13-5 C27H44O2 400.645 异维生素D3 all-trans-9,10-seco-1(10),5,7-cholestatrien-3β-ol 42607-12-5 C27H44O 384.646 骨化三醇 calcitriol 32222-06-3 C27H44O3 416.645 1,25-二羟维生素D calcitriol 32511-63-0 C27H44O3 416.645 —— 20S-Hydroxyvitamin D3 651734-12-2 C27H44O2 400.645 —— 20,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 1372617-13-4 C27H44O3 416.645 —— 23-oxa-25-hydroxyvitamin D3 84927-61-7 C26H42O3 402.618 双氢速甾醇 3 (3S,5E,7E,10S)-9,10-seco-cholesta-5,7-dien-3-ol 22481-38-5 C27H46O 386.662 —— 20S,23S-dihydroxyvitamin D3 1033416-82-8 C27H44O3 416.645 (24R)-1(alpha),24,25-三羟基维他命 D3* 1α,24(R),25-trihydroxyvitamin D3 56142-94-0 C27H44O4 432.644 —— (5Z,7E)-3β-acetoxy-9,10-secocholesta-5,7,10(19)-triene 2871-23-0 C29H46O2 426.683 (3beta, 5Z,7E)-9,10-开链胆甾-5,7,10(19)-三烯-3-基丁酸酯 vitamin D3 butyrate 31316-20-8 C31H50O2 454.737 —— 1α,20,25-trihydroxyvitamin D3 158946-37-3 C27H44O4 432.644 —— 1α,20-dihydroxyvitamin D3 158946-41-9 C27H44O3 416.645 —— vitamin D3 palmitate 13403-10-6 C43H74O2 623.059 —— (3S,9R,10R,13R,14S,17R)-10,13-dimethyl-17-[(2R)-6-methylheptan-2-yl]-2,3,4,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-decahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-ol —— C27H44O 384.6 7-去氢胆固醇 7-dehydrocholesterol 434-16-2 C27H44O 384.646 光甾醇 lumisterol 474-69-1 C28H44O 396.657 —— previtamin D3 —— C27H44O 384.646 3Β,6Z-9,10-断胆甾基-5(10),6,8-三烯甘油酯-3 previtamin D3 1173-13-3 C27H44O 384.646 速甾醇 tachysterol 115-61-7 C28H44O 396.657 —— (1R,3aS,7aR,E)-7a-methyl-4-((Z)-2-(6-methylenecyclohex-2-en-1-ylidene)ethylidene)-1-((R)-6-methylheptan-2-yl)octahydro-1H-indene —— C27H42 366.63 —— tachysterol 63882-05-3 C27H46O 386.662 异速甾醇3 all-trans-9,10-seco-5(10),6,8(14)-cholestatrien-3β-ol 22350-43-2 C27H44O 384.646 —— 3-Desoxy-3-epiamino-Vitamin D3 —— C27H45N 383.661 —— (5Z,7E)-9,10-seco-cholesta-5,7,10(19)-trien-3-one 125521-02-0 C27H42O 382.63 —— (5E)-10-Oxo-19-norcholecalciferol 62743-71-9 C26H42O2 386.618 —— (1R,2R,3R,Z)-5-(2-((1R,7aR,E)-1-((R)-6-hydroxy-6-methylheptan-2-yl)-7a-methyloctahydro-4H-inden-4-ylidene)ethylidene)-2-(3-hydroxypropoxy)-4-methylenecyclohexane-1,3-diol —— C30H50O5 490.724 艾地骨化醇 Eldecalcitol 104121-92-8 C30H50O5 490.724 —— (7E)-(3S,6S)-6,19-cyclo-9,10-seco-5(10),7-cholestadien-3-ol 40803-65-4 C27H44O 384.646 胆固醇 cholesterol 57-88-5 C27H46O 386.662 —— (E)-3-[(1R,3aR,7aR)-1-((R)-1,5-dimethylhexyl)-7a-methyl-2,3,3a,6,7,7a-hexahydro-1H-inden-4-yl]-prop-2-en-1-ol 1314446-07-5 C21H36O 304.516 —— (1R,3aR,7aR)-1-((R)-1,5-dimethylhexyl)-4-vinyl-7a-methyl-2,3,3a,6,7,7a-hexahydro-1H-indene 188577-74-4 C20H34 274.49 —— [(3aS4E)-1t-((R)-1,5-dimethyl-hexyl)-7a-methyl-(3ar,7at)-octahydro-inden-4-yliden]-acetaldehyde 84928-46-1 C20H34O 290.489 —— vitamin D3 p-nitrobenzoate 6183-79-5 C34H47NO4 533.751 —— (1R,3aR,7aR)-1-((R)-1,5-Dimethyl-hexyl)-4-{1-hydroxy-2-[(S)-5-hydroxy-2-methylene-cyclohex-(Z)-ylidene]-ethyl}-7a-methyl-octahydro-inden-4-ol 174176-73-9 C27H46O3 418.66 —— [(6R)-6-[(1R,3aR,4E,7aR)-4-[(2Z)-2-[(3S,5R)-3,5-bis[[tert-butyl(dimethyl)silyl]oxy]-2-methylidenecyclohexylidene]ethylidene]-1,2,3,3a,5,6,7,7a-octahydroinden-1-yl]-2-methylheptan-2-yl]oxy-triethylsilane 178765-12-3 C44H84O3Si3 745.406 - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:维生素 D3 在 hydrogen (18)O-peroxide 作用下, 以 aq. phosphate buffer 为溶剂, 反应 1.0h, 生成参考文献:名称:灰霉菌过氧化物酶生产25-羟基维生素D的区域选择性羟化反应摘要:维生素D 3(胆钙化固醇)和维生素D 2(麦角钙化固醇)的单羟基化代谢物(通常称为25-羟基钙化固醇)比维生素D (钙化固醇)更适合于多种疾病和其他应用。这项工作描述了从容易获得的胆钙化醇和麦角钙化醇开始制备25-羟基钙化醇的新型生物技术方法。该方法通过使用灰霉菌真菌的过氧化物酶(来自测序基因组的基因模型CC1G_08427T0 )在温和且环境友好的条件下使这些化合物(在C-25位置)的区域选择性(100%)羟基化,从而催化单氧合反应。 H 2 O 2作为唯一的共底物(过氧化酶)。胆钙化固醇和麦角钙化固醇的羟基化是真正的过氧化,如通过将H 2 18 O 2中的18 O掺入产品中所证明的。过氧合酶具有与其重组性质相关的其他优势,可在工业宿主中进行酶工程和低成本过表达。因此,过氧合酶是生产维生素D活性代谢产物的有前途的生物催化剂。DOI:10.1002/cctc.201402795
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:一种维生素D3类似物的合成方法摘要:本发明公开了一种维生素D 3 类似物的合成方法,本发明公开了由反式起始物(Ⅱ)制备顺式中间体(Ⅰ)的光化学反应方法。该方法制备的中间体可以作为合成活性维生素D类似物(如阿法骨化醇、骨化三醇)的中间体,使得此类活性物质合成条件温和,减少副反应生成,并提高收率。公开号:CN110143979A
-
作为试剂:描述:(R)-(+)-杀鼠灵 在 NADPH-generating system 、 recombinant human cytochrome P450 or CYP enzymes 、 维生素 D3 作用下, 以 phosphate buffer 为溶剂, 生成 (R)-7-羟基华法林参考文献:名称:花生四烯酸,前列腺素,视黄醇,视黄酸和胆钙化固醇对人细胞色素P450酶催化的异种生物氧化的影响。摘要:1.研究了花生四烯酸,前列腺素,视黄醇,视黄酸和胆钙化固醇对12种重组人细胞色素P450(P450或CYP)酶和人肝微粒体催化的异种生物氧化的影响。2.花生四烯酸(50 microM)显着抑制CYP1A1和1A2依赖性7-乙氧基香豆素O-去乙基化,CYP2C8依赖性紫杉醇6α-羟基化和CYP2C19依赖性R-华法林7-羟基化。在重组酶系统中,该化学物质还略微抑制了CYP1B1、2B6、2C9、2D6、2E1和3A4催化的异种生物氧化。3.视黄醇,视黄酸和胆钙化醇是重组CYP1A1、2C8和2C19催化的异种生物氧化的强抑制剂。[4]。花生四烯酸对CYP1A1-,1A2-,2C8-和2C19依赖性异生素氧化的抑制作用的狄克逊图,视黄醇对CYP1A1、2B6和2C19的依赖性,以及胆钙化醇对CYP1A1和2C19的依赖性,表明这些化学物质主要通过竞争机制抑制P450的活性。5.在人肝微粒体中,DOI:10.1080/004982599238632
文献信息
-
[EN] CATHEPSIN CYSTEINE PROTEASE INHIBITORS<br/>[FR] INHIBITEURS DE PROTÉASES À CYSTÉINE DE TYPE CATHEPSINES申请人:MERCK SHARP & DOHME公开号:WO2015054038A1公开(公告)日:2015-04-16This invention relates to a novel class of compounds which are cysteine protease inhibitors, including but not limited to, inhibitors of cathepsins K, L, S and B. These compounds are useful for treating diseases in which inhibition of bone resorption is indicated, such as osteoporosis.
-
[EN] NOVEL COMPOUNDS AND PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOSITIONS THEREOF FOR THE TREATMENT OF INFLAMMATORY DISORDERS<br/>[FR] NOUVEAUX COMPOSÉS ET COMPOSITIONS PHARMACEUTIQUES LES COMPRENANT POUR LE TRAITEMENT DE TROUBLES INFLAMMATOIRES申请人:GALAPAGOS NV公开号:WO2017012647A1公开(公告)日:2017-01-26The present invention discloses compounds according to Formula (I), wherein R1, R3, R4, R5, L1, and Cy are as defined herein. The present invention also provides compounds, methods for the production of said compounds of the invention, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the same and their use in allergic or inflammatory conditions, autoimmune diseases, proliferative diseases, transplantation rejection, diseases involving impairment of cartilage turnover, congenital cartilage malformations, and/or diseases associated with hypersecretion of IL6 and/or interferons. The present invention also methods for the prevention and/or treatment of the aforementioned diseases by administering a compound of the invention.本发明公开了根据式(I)的化合物,其中R1、R3、R4、R5、L1和Cy如本文所定义。本发明还提供了该发明的化合物、制备该化合物的方法、包括相同化合物的药物组合物以及它们在过敏或炎症症状、自身免疫疾病、增殖性疾病、移植排斥、涉及软骨周转障碍的疾病、先天软骨畸形和/或与IL6和/或干扰素过度分泌相关的疾病中的使用。本发明还提供了通过给予该发明的化合物来预防和/或治疗上述疾病的方法。
-
[EN] MICROBIOCIDAL OXADIAZOLE DERIVATIVES<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS D'OXADIAZOLE MICROBIOCIDES申请人:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG公开号:WO2017157962A1公开(公告)日:2017-09-21Compounds of the formula (I) wherein the substituents are as defined in claim 1, useful as a pesticides, especially fungicides.式(I)的化合物,其中取代基如权利要求1所定义,作为杀虫剂特别是杀菌剂有用。
-
[EN] INSECTICIDAL TRIAZINONE DERIVATIVES<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS DE TRIAZINONE INSECTICIDES申请人:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG公开号:WO2013079350A1公开(公告)日:2013-06-06Compounds of the formula (I) or (I'), wherein the substituents are as defined in claim 1, are useful as pesticides.式(I)或(I')的化合物,其中取代基如权利要求1所定义的那样,可用作杀虫剂。
-
[EN] METALLOENZYME INHIBITOR COMPOUNDS<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS INHIBITEURS DE MÉTALLOENZYMES
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
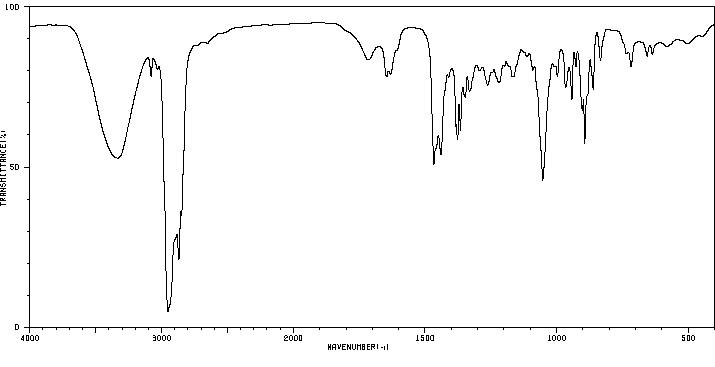
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息