二聚环戊二烯 | 77-73-6
中文名称
二聚环戊二烯
中文别名
双环戊二烯;环戊二烯二聚体;4,7-亚甲基-4,7,8,9-四氢茚;二环戊二烯
英文名称
bi(cyclopentadiene)
英文别名
Dicyclopentadiene;DCPD;tricyclo[5.2.1.0^{2,6}]deca-3,8-diene;cyclopentadiene dimer;tricyclo[5.2.1.02,6]deca-3,8-diene
CAS
77-73-6
化学式
C10H12
mdl
MFCD00078246
分子量
132.205
InChiKey
HECLRDQVFMWTQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:33 °C(lit.)
-
沸点:170 °C(lit.)
-
密度:0.986 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
-
闪点:114 °F
-
溶解度:可溶于氯仿(少许)、甲醇(少许)
-
介电常数:2.4900000000000002
-
暴露限值:ACGIH: TWA 0.5 ppm; STEL 1 ppmNIOSH: TWA 5 ppm(30 mg/m3)
-
LogP:3.300 (est)
-
物理描述:Dicyclopentadiene appears as a liquid with an acrid odor. Flash point 90°F. The vapors are irritating to the eyes and respiratory system. Subject to polymerization if subjected to heat for prolonged periods or if contaminated. If the polymerization takes place inside a container, the container may violently rupture. Insoluble in water. Density 8.2 lb / gal. Used in paints, varnishes, as an intermediate in insecticides, as a flame retardant in plastics.
-
颜色/状态:Colorless crystalline solid [Note: A liquid above 90 degrees F]
-
气味:Disagreeable camphor-like odor
-
蒸汽密度:4.55 (NTP, 1992) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:2.30 mm Hg at 25 °C /Extrapolated from a measured range of 33 °C and higher/
-
亨利常数:Henry's Law constant = 0.02 atm-cum/mol at 25 °C (est)
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
自燃温度:937 °F (503 °C)
-
分解:... /Dicyclopentadiene/ decomposes on heating above 170 °C.
-
粘度:0.736 cP (est) at 70 °F
-
腐蚀性:Non-corrosive
-
燃烧热:-18,800 BTU/lb = -10,400 cal/g = -437X10+5 J/kg
-
汽化热:38.5 kJ/mol
-
聚合:If the polymerization takes place inside a container, the container may violently rupture.
-
气味阈值:Odor Threshold Low: 0.003 [mmHg]; Odor Threshold High: 0.01 [mmHg]; Detection odor threshold from AIHA (mean = 0.011 ppm)
-
折光率:Index of refraction = 1.5073 at 31 °C
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):2.5
-
重原子数:10
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:3.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.6
-
拓扑面积:0
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:0
ADMET
代谢
When given by oral admin to lactating cows, metabolites were present in urine mainly in form of glucuronide conjugates. It is suggested that epoxidation of double bonds occurred, followed by hydrolysis of epoxides to diols & conjugation with glucuronic acid.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
... 二环戊二烯的尿代谢物没有特定地被识别,但是通过薄层色谱分析表明,小鼠和大鼠的尿液中各含有七个组分。在狗的尿液中发现了六个组分。这些组分的Rf值相似;因此,这三种生物体中都有共同的代谢物。在所有三种生物体中,只有1-3%的放射性归因于未代谢的(14)碳-二环戊二烯。当所有物种的尿液经过葡萄糖苷酶(β-葡萄糖苷酶和磺酸酶)的酶促水解并提取后,在提取物中回收,表明尿液中存在结合物。
... Urinary metabolites of dicyclopentadiene were not identified specifically, but analysis by thin layer chromatography indicated that the urine of mice and rats each had seven components. Six components were found in the urine of dogs. The Rf values of these components were similar; therefore, common metabolites were indicated in all three species. Only 1-3% of the radioactivity was attributed to nonmetabolized (14)carbon-dicyclopentadiene in all three species. When the urine from all species was subjected to enzymatic hydrolysis by glusulase (beta glucuronidase and sulfatase) and extracted, was recovered in the extract, indicating the presence of urine conjugates.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
识别和使用:环戊二烯(DCPD)是一种无色结晶固体(在90华氏度以上为液体)。DCPD用于制造环戊二烯作为杀虫剂中间体;在生产铁茂化合物;在油漆、清漆和树脂制造中;在生产弹性体、树脂系统和聚合物中。它还用作动物如野兔、兔子和鹿的驱避剂,在冬季或夏季。以浸渍条的形式应用于落叶树和针叶树上,或者通过喷洒在观赏植物和灌木周围。人类暴露和毒性:吸入后暴露迹象——咳嗽、喉咙痛和头痛;皮肤暴露——发红和疼痛;眼睛暴露——发红和疼痛;摄入——腹痛和恶心。研究了三名志愿者对DCPD的人类感官反应。据报道,气味阈值低至0.003 ppm。在两名受试者接触1和5.5 ppm 30分钟后,一名受试者在1 ppm下7分钟后出现轻度眼睛和喉咙刺激,另一名受试者在24分钟后报告嗅觉疲劳。在5.5 ppm下10分钟后报告眼睛刺激,但两名测试受试者均未报告嗅觉疲劳。工人的意外暴露,在前2个月内出现头痛,但在接下来的3个月内没有出现头痛,这表明一定程度的适应。动物研究:在兔子上对皮肤和眼睛有轻微刺激作用。四只大鼠中有三只在250 ppm下每天暴露6小时,连续10天存活,所有大鼠在100 ppm下连续15次暴露存活。在大鼠连续10天每天暴露于DCPD的情况下,大鼠在332 ppm水平死亡,但在146和72 ppm水平下没有死亡。所有死亡的大鼠都有抽搐和肺出血,肠内有血;雌性大鼠出现胸腺出血。小鼠在相同的暴露计划下,在146和72 ppm下死亡。在大鼠每天暴露7小时,连续89天暴露于74和35 ppm DCPD的情况下,观察到肾脏损伤。观察到一些肺部病变,如慢性肺炎和支气管扩张,但在检查的其他器官中没有看到剂量相关效应。在相同的暴露计划(89天暴露)下,在32、23和9 ppm DCPD下暴露的狗在所用的生化测试中只显示出最小的变化,在检查的28个器官中没有剂量相关变化。在雄性大鼠暴露于5和50 ppm DCPD时,在近曲小管上皮细胞中观察到透明滴状物,在第13周时,所有暴露于50 ppm DCPD的雄性大鼠都出现了管状蛋白尿。将小鼠通过吸入方式暴露于DCPD,每天7小时,每周5天,连续10天,剂量为47、72和146 ppm。所有小鼠在暴露的第一天表现出抽搐性死亡。在72 ppm下,五分之六的雄性和雌性小鼠在10天的暴露期间死亡,与在大鼠中观察到的抽搐或大体病变无关。在47 ppm下没有死亡发生,也没有观察到其他处理效应。在另一项研究中,四组各含45只雄性和45只雌性B6C3F1小鼠,通过吸入暴露于目标浓度为0、1.0、5.0或50 ppm的DCPD蒸气,每天6小时,每周5天,连续13周(64次暴露)。在最高暴露组中,有10只雄性和9只雌性小鼠在研究期间死亡,而其他任何一组中死亡的小鼠不超过2只。20只雌性怀孕大鼠在妊娠第6至15天口服给予DCPD,剂量为0、80、250、750 mg/kg/天。在第19天,母鼠被处死并检查;检查每个子宫的着床点、子宫角的位置、活胎和死胎的数量以及重吸收情况。对胎儿进行软组织变化和骨骼畸形的检查。母鼠没有观察到与化合物相关的肉眼病理效应或生殖性能的变化。胎儿没有内脏或骨骼畸形或性别比例的变化。在Salmonella测试中,DCPD在0、3、10、33、100和333 ug/板的剂量下对Salmonella typhimurium菌株(TA98、TA100、TA1535和TA1537)进行代谢激活或不激活,不具有诱变性。DCPD未诱导CHL/IU细胞的结构染色体畸变或多倍体;在体外微核试验中证实了阴性发现。
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: Dicyclopentadiene (DCPD) is a colorless crystalline solid (a liquid above 90 degrees F). DCPD is used in the manufacture of cyclopentadiene as a pesticide intermediate; in the production of ferrocene compounds; in paints, varnishes, and resin manufacture; in production of elastomers, resin systems, and polymers. It is also used as a repellent for animals such as hares, rabbits, and deer, in winter or in summer. Applied in the form of impregnated strip on deciduous and coniferous trees, or by spraying around ornamental plants and shrubs. HUMAN EXPOSURE AND TOXICITY: Signs of exposure after inhalation--cough, sore throat, and headache; skin exposure--redness and pain; eyes exposure--redness and pain; Ingestion--abdominal pain, and nausea. Human sensory responses to DCPD were studied in three human volunteers. The odor threshold was reported to be as low as 0.003 ppm. In two of the subjects exposed to 1 and 5.5 ppm for 30 minutes, one subject experienced mild eye and throat irritation after 7 minutes at 1 ppm, and the other subject reported olfactory fatigue after 24 minutes. Eye irritation was reported after 10 minutes, but no olfactory fatigue was reported by either test subject at 5.5 ppm. Accidental exposures of workers, in which headaches were experienced during first 2 months but were not experienced during next 3 months, indicate a certain degree of inurement. ANIMAL STUDIES: In rabbits it was slightly irritating to skin and eyes. Three of four rats survived ten 6-hour daily exposures at 250 ppm, and all survived 15 such exposures at 100 ppm. On daily, repeated exposures to DCPD for 10 days, rats succumbed at the 332 ppm level, but not at the 146 and 72 ppm levels. All dying rats succumbed with convulsions and hemorrhage of the lungs with blood in the intestines; with the females, hemorrhage of the thymus. Mice exposed under the same schedule died at both 146 and 72 ppm. After exposures of 7 hours/day for 89 exposure days, kidney damage was seen in rats exposed at 74 and 35 ppm DCPD. Some lung involvement was seen as chronic pneumonia and bronchiectasis, but no dose related effect was seen in other organs examined. Dogs exposed under the same schedule (89 exposure days) at 32, 23, and 9 ppm DCPD showed only minimal changes in the biochemical tests used, and no changes that were dose-related in 28 organs examined. Hyaline droplets in the proximal convoluted tubular epithelial cells of the kidney were seen in male rats exposed to 5 and 50ppm DCPD and tubular proteinosis was seen by week 13 in all male rats exposed to 50ppm DCPD. Mice were exposed to DCPD by inhalation for 7 hours per day, 5 days per week for 10 days at 47, 72, and 146 ppm. All mice exhibited convulsive deaths on the first day of exposure. Death at 72 ppm occurred in five of six mice of each sex during the 10 days of exposure and was not associated with the convulsions or gross lesions observed in rats. No deaths occurred at 47 ppm and no other effects of treatment were observed. In other study four groups, each consisting of 45 male and 45 female B6C3F1 mice, were exposed to DCPD vapor by inhalation 6 hr/day, 5 days/week, for 13 weeks (64 exposures) at targeted concentrations of 0, 1.0, 5.0, or 50 ppm. Ten male and nine female mice in the highest exposure group died during the study, while no more than two mice died in any other group. 20 female pregnant rats were admin DCPD orally at 0, 80, 250, 750 mg/kg/day for days 6 to 15 gestation. On day 19, the dams were sacrificed and examined; each uterus was examined for implantation sites, placement in uterine horns, number of live and dead fetuses and resorptions. Fetuses were examined for soft tissue changes and skeletal abnormalities. No compound-related gross pathological effects or changes in reproductive performance were seen in the dams. There were no visceral or skeletal malformations or changes in sex ratio in the fetuses. DCPD was not mutagenic in the Salmonella assay at doses of 0, 3, 10, 33, 100, and 333 ug/plate in Salmonella typhimurium strains (TA98, TA100, TA1535, and TA1537) with or without metabolic activation. DCPD did not induce structural chromosomal aberration or polyploidy in CHL/IU cells; negative finding were confirmed in the in vitro micronucleus test.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
该物质可以通过吸入和摄入被身体吸收。
The substance can be absorbed into the body by inhalation and by ingestion.
来源:ILO-WHO International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs)
毒理性
吸入,吞食,皮肤和/或眼睛接触
inhalation, ingestion, skin and/or eye contact
来源:The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH)
毒理性
眼睛、皮肤、鼻子、喉咙刺激;不协调,头痛;打喷嚏,咳嗽;皮肤水泡;在动物中:肾脏、肺损伤
irritation eyes, skin, nose, throat; incoordination, headache; sneezing, cough; skin blisters; In Animals: kidney, lung damage
来源:The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH)
毒理性
咳嗽。喉咙痛。头痛。
Cough. Sore throat. Headache.
来源:ILO-WHO International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs)
吸收、分配和排泄
In general, although some dicyclopentadiene can be exhaled unchanged, most of that absorbed is hydroxylated in the liver, undergoes glucuronide conjugation, and is excreted in the urine.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
/MILK/ 当通过口服给药给哺乳期奶牛时,尿液和粪便中含有86%的给药剂量,只有极少量的药物分泌到牛奶中。有些可能以气态形式被排除。该化合物从胃肠道被广泛吸收。
/MILK/ When given by oral administration to lactating cows urine and feces contained 86% of administered dose with only trace amounts being secreted in milk. Some may have been eliminated in gaseous form. Compound was extensively absorbed from GI tract.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
二环戊二烯被预测为无论通过任何给药途径都会被迅速吸收和分布。它从胃肠道被广泛吸收。
Dicyclopentadiene is predicted to be rapidly absorbed and distributed following any route of administration. It is extensively absorbed from the GI tract.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
该物质可以通过吸入和摄入被身体吸收。
The substance can be absorbed into the body by inhalation and by ingestion.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
四甲撑亚磷酰衍生物的诺波烷(TPNB)和二环戊二烯(TPDCPD)被显示能够轻易与(99m)Tc形成稳定的螯合物,这些螯合物在骨骼中有高且选择性的摄取。在 rats 和 rabbits 中,(99m)Tc-TPNB的骨骼摄取和血液清除特性与(99m)Tc-MDP相似。这表明,需要进一步研究以评估(99m)Tc-TPNB 或其他基于大有机多元螯合磷酸盐配体作为潜在的骨显像剂。
Tetramethylenephosphonate derivatives of norborane (TPNB) and dicyclopentadiene (TPDCPD) were shown to readily form stable chelates with (99m)Tc that had high and selective bone uptake. The skeletal uptake and blood clearance properties of (99m)Tc-TPNB were similar to (99m)Tc-MDP in both rats and rabbits. This suggests additional studies to further evaluate (99m)Tc-TPNB or perhaps other large-organic based multidentate phosphonate ligands as potential bone imaging agents is warranted.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
安全信息
-
职业暴露等级:A
-
职业暴露限值:TWA: 5 ppm (30 mg/m3)
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:3
-
危险品标志:F
-
安全说明:S36/37,S61
-
危险类别码:R20/22,R51/53,R36/37/38,R11
-
WGK Germany:2,3
-
海关编码:29021990
-
危险品运输编号:UN 2048
-
RTECS号:PC1050000
-
包装等级:III
-
危险标志:GHS02,GHS06,GHS09
-
危险性描述:H226,H302,H315,H319,H330,H335,H411
-
危险性防范说明:P260,P273,P284,P305 + P351 + P338,P310
-
储存条件:常温下应密封保存在阴凉、通风的库房内,远离火种和热源。本品采用小口铁桶包装,需贮存于阴凉通风处,并按有毒易燃危险品的规定进行贮存和运输。
SDS
| 第一部分:化学品名称 |
| 化学品中文名称: | 二聚环戊二烯;双茂 |
| 化学品英文名称: | Dicyclopentadiene;4,7-Methylene-4,7,8,9-tetrahydroindene |
| 中文俗名或商品名: | |
| Synonyms: | |
| CAS No.: | 77-73-6 |
| 分子式: | C 10 H 12 |
| 分子量: | 132.2 |
| 第二部分:成分/组成信息 |
| 纯化学品 混合物 | |||
| 化学品名称:二聚环戊二烯;双茂 | |||
|
| 第三部分:危险性概述 |
| 危险性类别: | 第3.3类 高闪点易燃液体 |
| 侵入途径: | 吸入 食入 经皮吸收 |
| 健康危害: | 接触高浓度本品蒸气有刺激和麻醉作用,引起眼、鼻、喉和肺刺激,头痛、头晕及其他中枢神经系统症状。有可能引起肝、肾损害。长期反复皮肤接触可致皮肤损害。 |
| 环境危害: | |
| 燃爆危险: | 本品易燃,有毒,具刺激性。 |
| 第四部分:急救措施 |
| 皮肤接触: | 脱去污染的衣着,用肥皂水和流动清水彻底冲洗。 |
| 眼睛接触: | 立即翻开上下眼睑,用流动清水冲洗。就医。 |
| 吸入: | 迅速脱离现场至空气新鲜处。保持呼吸道通畅。呼吸困难时给输氧。呼吸停止时,立即进行人工呼吸。就医。 |
| 食入: | 误服者漱口,饮足量温水,催吐,就医。 |
| 第五部分:消防措施 |
| 危险特性: | 其蒸气与空气可形成爆炸性混合物,遇明火、高热能引起燃烧爆炸。与氧化剂可发生反应。容易自聚,聚合反应随着温度的上升而急骤加剧。 |
| 有害燃烧产物: | 一氧化碳、二氧化碳。 |
| 灭火方法及灭火剂: | 消防人员须佩戴防毒面具、穿全身消防服,在上风向灭火。灭火剂:雾状水、泡沫、干粉、二氧化碳、砂土。 |
| 消防员的个体防护: | |
| 禁止使用的灭火剂: | |
| 闪点(℃): | 26 |
| 自燃温度(℃): | 503 |
| 爆炸下限[%(V/V)]: | 1.0 |
| 爆炸上限[%(V/V)]: | 10 |
| 最小点火能(mJ): | |
| 爆燃点: | |
| 爆速: | |
| 最大燃爆压力(MPa): | |
| 建规火险分级: |
| 第六部分:泄漏应急处理 |
| 应急处理: | 隔离泄漏污染区,限制出入。切断火源。建议应急处理人员戴防尘面具(全面罩),穿防毒服。用洁净的铲子收集于干燥、洁净、有盖的容器中。若大量泄漏,收集回收或运至废物处理场所处置。 |
| 第七部分:操作处置与储存 |
| 操作注意事项: | 密闭操作,全面通风。操作人员必须经过专门培训,严格遵守操作规程。建议操作人员佩戴自吸过滤式防尘口罩,戴化学安全防护眼镜,穿防毒物渗透工作服,戴橡胶手套。远离火种、热源,工作场所严禁吸烟。使用防爆型的通风系统和设备。避免产生粉尘。避免与氧化剂、酸类、碱类接触。搬运时要轻装轻卸,防止包装及容器损坏。配备相应品种和数量的消防器材及泄漏应急处理设备。倒空的容器可能残留有害物。 |
| 储存注意事项: | 储存于阴凉、通风的库房。远离火种、热源。应与氧化剂、酸类、碱类、食用化学品分开存放,切忌混储。不宜大量储存或久存。采用防爆型照明、通风设施。禁止使用易产生火花的机械设备和工具。储区应备有合适的材料收容泄漏物。 |
| 第八部分:接触控制/个体防护 |
| 最高容许浓度: | 中 国 MAC:未制订标准前苏联MAC:1mg/m3 美国TLV—TWA:ACGIH 5p |
| 监测方法: | |
| 工程控制: | 生产过程密闭,全面通风。 |
| 呼吸系统防护: | 可能接触毒物时,应戴口罩。 |
| 眼睛防护: | 一般不需特殊防护。 |
| 身体防护: | 穿防静电工作服。 |
| 手防护: | 必要时戴防护手套。 |
| 其他防护: | 工作现场严禁吸烟。工作后,淋浴更衣。保持良好的卫生习惯。 |
| 第九部分:理化特性 |
| 外观与性状: | 无色晶体。 |
| pH: | |
| 熔点(℃): | 32.5 |
| 沸点(℃): | 172 |
| 相对密度(水=1): | 0.98(35℃) |
| 相对蒸气密度(空气=1): | 4.55 |
| 饱和蒸气压(kPa): | 1.33(47.6℃) |
| 燃烧热(kJ/mol): | |
| 临界温度(℃): | |
| 临界压力(MPa): | |
| 辛醇/水分配系数的对数值: | |
| 闪点(℃): | 26 |
| 引燃温度(℃): | 503 |
| 爆炸上限%(V/V): | 10 |
| 爆炸下限%(V/V): | 1.0 |
| 分子式: | C 10 H 12 |
| 分子量: | 132.2 |
| 蒸发速率: | |
| 粘性: | |
| 溶解性: | 不溶于水,溶于乙醇、乙醚。 |
| 主要用途: | 用于制乙丙橡胶的第三单体乙叉降冰片烯、多聚环戊二烯农药、聚酯、树脂、塑料的阻燃剂、药物、香料等。 |
| 第十部分:稳定性和反应活性 |
| 稳定性: | 在常温常压下 稳定 |
| 禁配物: | 强氧化剂、强酸、强碱。 |
| 避免接触的条件: | |
| 聚合危害: | 能发生 |
| 分解产物: | 一氧化碳、二氧化碳。 |
| 第十一部分:毒理学资料 |
| 急性毒性: | LD50:820mg/kg(大鼠经口);0.72ml/kg[兔经皮] LC50: |
| 急性中毒: | |
| 慢性中毒: | |
| 亚急性和慢性毒性: | |
| 刺激性: | |
| 致敏性: | |
| 致突变性: | |
| 致畸性: | |
| 致癌性: |
| 第十二部分:生态学资料 |
| 生态毒理毒性: | |
| 生物降解性: | |
| 非生物降解性: | |
| 生物富集或生物积累性: |
| 第十三部分:废弃处置 |
| 废弃物性质: | |
| 废弃处置方法: | 处置前应参阅国家和地方有关法规。建议用焚烧法处置。 |
| 废弃注意事项: |
| 第十四部分:运输信息 |
| |
| 危险货物编号: | 33517 |
| UN编号: | 2048 |
| 包装标志: | |
| 包装类别: | Ⅲ |
| 包装方法: | 小开口钢桶;安瓿瓶外普通木箱;螺纹口玻璃瓶、铁盖压口玻璃瓶、塑料瓶或金属桶(罐)外普通木箱;螺纹口玻璃瓶、塑料瓶、复合塑料瓶或铝瓶外普通木箱。 |
| 运输注意事项: | 运输时运输车辆应配备相应品种和数量的消防器材及泄漏应急处理设备。夏季最好早晚运输。运输时所用的槽(罐)车应有接地链,槽内可设孔隔板以减少震荡产生静电。严禁与氧化剂、酸类、碱类、食用化学品等混装混运。运输途中应防曝晒、雨淋,防高温。中途停留时应远离火种、热源、高温区。装运该物品的车辆排气管必须配备阻火装置,禁止使用易产生火花的机械设备和工具装卸。铁路运输时要禁止溜放。严禁用木船、水泥船散装运输。 |
| RETCS号: | |
| IMDG规则页码: |
| 第十五部分:法规信息 |
| 国内化学品安全管理法规: | 化学危险物品安全管理条例 (1987年2月17日国务院发布),化学危险物品安全管理条例实施细则 (化劳发[1992] 677号),工作场所安全使用化学品规定 ([1996]劳部发423号)等法规,针对化学危险品的安全使用、生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应规定;常用危险化学品的分类及标志 (GB 13690-92)将该物质划为第3.3 类高闪点易燃液体。 |
| 国际化学品安全管理法规: |
| 第十六部分:其他信息 |
| 参考文献: | 1.周国泰,化学危险品安全技术全书,化学工业出版社,1997 2.国家环保局有毒化学品管理办公室、北京化工研究院合编,化学品毒性法规环境数据手册,中国环境科学出版社.1992 3.Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety,CHEMINFO Database.1998 4.Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety, RTECS Database, 1989 |
| 填表时间: | 年月日 |
| 填表部门: | |
| 数据审核单位: | |
| 修改说明: | |
| 其他信息: | 3 |
| MSDS修改日期: | 年月日 |
制备方法与用途
双环戊二烯 (Dicyclopentadiene, DCPC)
双环戊二烯(Dicyclopentadiene,简称DCPC)是环戊二烯的二聚物。生产过程通常包括以下步骤:首先加热环戊二烯使其共聚成双环戊二烯,并从沸点小于45℃的轻组分中通过蒸馏分离出双环戊二烯;接着利用溶剂萃取出其他需要的双烯、单烯及饱和烃成分。高纯度的双环戊二烯在室温下为无色结晶体,而含有杂质时则呈现浅黄色油状液体,并带有刺激性的樟脑味。这种化合物不溶于水,但可溶于醇和醚等有机溶剂。
应用由于DCPD可以在特定温度下转化为CPD(环戊二烯),极大地拓宽了其应用范围。它不仅在医药、农药、香料等领域有着广泛用途,还可以作为生产不饱和树脂、金属茂、金刚烷、戊二醛、双环戊二烯氯化物等原料,并用于合成橡胶、高能燃料等多个领域。
用途- 双环戊二烯可用作聚戊烯橡胶的原料。
- 生产环戊二醇-1,2和环戊烯氧化物(如双环戊二烯二羧酸)。
- 制造有机磷系杀菌剂稳定剂、氯代烃杀虫剂、医药原料等。
- 在加热条件下解聚生成环戊二烯。
- 与丙烯、苯乙烯、丙烯腈、异戊二烯等进行Diels-Alders反应,生成合成树脂的单体。
- 作为乙基纤维素涂料和油墨的成分。
- 加氢后用作高能燃料。
双环戊二烯可从煤焦油轻苯馏分或C5烃裂解工业中的原料中提取。通过加热聚合、蒸馏分离而得成品,或者以环戊二烯为原料直接进行二聚反应制备。
物理化学性质与安全信息- 类别:易燃液体
- 毒性分级:高毒
-
急性毒性:
- 大鼠口服LD50: 353毫克/公斤;
- 小鼠口服LD50: 190毫克/公斤。
-
刺激数据:
- 皮肤接触兔子,10毫克/24小时重度刺激;
- 眼睛接触兔子,500毫克/24小时轻度刺激。
- 爆炸物危险特性:与空气混合可燃
- 可燃性危险特性:遇明火、高温或氧化剂易燃;燃烧产生刺激烟雾。
-
储运特性:
- 库房需保持通风干燥;
- 需分开存放于氧化剂附近,不宜长期储存以免聚合。
- 灭火剂:干粉、干砂、二氧化碳、泡沫、1211灭火剂。
-
职业卫生标准:
- TWA: 30毫克/立方米
- STEL: 54毫克/立方米
请注意安全规范,在处理双环戊二烯时需采取相应防护措施。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— dicyclopentadiene —— C10H12 132.205 —— tetracyclododecene 90242-59-4 C12H16 160.259 5-降冰片烯-2-甲醛 5-Norbornene-2-carboxaldehyde 5453-80-5 C8H10O 122.167 2-氰基-5-降冰片烯 bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-ene-2-carbonitrile 95-11-4 C8H9N 119.166 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— dicyclopentadiene 247936-95-4 C10H12 132.205 —— exo-DCPD —— C10H12 132.205 —— dicyclopentadiene —— C10H12 132.205 —— 1,3-divinyl-1,2,3,3a,4,6a-hexahydropentalene 142936-10-5 C12H16 160.259 —— 1,4,4a,5,8,8a-hexahydro-1,4,5,8-exo-endo-dimethanonaphthalene —— C12H14 158.243 —— Tricyclo<5.2.2.02,6>undeca-3,8-dien 19574-35-7 C11H14 146.232 5-乙烯基双环[2.2.1]庚-2-烯 5-vinyl-2-norbornene 3048-64-4 C9H12 120.194 —— endo-5-vinylbicyclo<2.2.1>hept-2-ene 25093-48-5 C9H12 120.194 —— 5-ethenyl-2-norbornene 3048-64-4 C9H12 120.194 —— pentacyclo[6.5.1.13.6.0 2, 7.0 9,13]pentadecane-4,10-diene 36806-65-2 C15H18 198.308 —— 5-(cyclohex-3-en-1-yl)bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-2-ene 4711-96-0 C13H18 174.286 —— tricyclo[5.2.1.02,6 ]dec-8-ene 19398-83-5 C10H14 134.221 —— (3aR*,4S*,7R*,7aS*)-2,3,3a,4,7,7a-hexahydro-4,7-methano-1H-indene 2826-19-9 C10H14 134.221 3a,4,4a,5,8,8a,9,9a-八氢-4,9:5,8-二甲桥-1H-苯并[f]茚 endo,exo,endo-pentacyclo<6.5.1.02,7.13,6.09,13>pentadeca-4,10-diene 7158-25-0 C15H18 198.308 四环戊二烯 Δ1,7-dodecahydro-4,11;5,10;6,9-trimethano-cyclopenta[b]anthracene 23197-86-6 C20H24 264.411 —— 2,3-(Δ1-Cyclopenteno-3,4)-1,4-endomethylen-1,2,3,4,5,5a,8,8a-octahydronaphthalin 37746-35-3 C14H18 186.297 —— decyl norbornene —— C17H30 234.425 —— 5-propyl-bicyclo[2.2.1]-hept-2-ene 22094-80-0 C10H16 136.237 —— Bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-2-ene, 5-octyl- 22094-84-4 C15H26 206.37 5-乙基双环(2.2.1)-2-庚烯 5-ethylbicyclo[2.2.1]hept-2-ene 15403-89-1 C9H14 122.21 —— (+/-)-endo-2-n-hexyl-5-norbornene 85288-84-2 C13H22 178.318 —— (1α,4α,4aβ,5α,8α,8aβ)-1,2,3,4,4a,5,8,8a-octahydro-1,4:5,8-dimethanonaphthalene 90243-18-8 C12H16 160.259 —— tetracyclododecene 90242-59-4 C12H16 160.259 —— 2-methyl-1,2,3,4,4a,5,8,8a-octahydro-1,4:5,8-dimethylnaphthalene 21681-47-0 C13H18 174.286 —— endo,exo,endo,endo-hexacyclo<6.6.1.02,7.13,6.09,14.110,13>heptadeca-4,11-diene 50415-43-5 C17H20 224.346 5,6-二氢二环戊二烯 3a,4,5,6,7,7a-hexahydro-1H-4,7-methanoindene 4488-57-7 C10H14 134.221 —— 3a,4,5,6,7,7a-hexahydro-4,7-methano-1H-indene 2825-86-7 C10H14 134.221 5-甲基二环[2.2.1]庚-2-烯 5-methyl-2-norbornene 822-96-8 C8H12 108.183 —— 5-methylbicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-ene 822-96-8 C8H12 108.183 3a,4,7,7a-四羟基茚 bicyclo[4.3.0]nona-3,7-diene 3048-65-5 C9H12 120.194 1,2,3,4,4a,5,8,8a-八氢-1,4:5,8-二甲桥萘-2-甲醇 2-Hydroxymethyl-1,2,3,4,4a,5,8,8a-octahydro-1,4,5,8-dimethano-naphthalin 7329-04-6 C13H18O 190.285 —— octahydrodimethanonaphtalenedimethanol 7329-09-1 C14H20O2 220.312 —— 8-formyltricyclo[5,2,1,0(2),(6)]dec-3-ene 81739-42-6 C11H14O 162.232 —— 9-formyltricyclo[5,2,1,0(2),(6)]dec-3-ene 81739-43-7 C11H14O 162.232 3-甲基双环[2.2.1]庚-5-烯-2-甲醛 2-formyl-3-methyl-5-norbornene 6465-95-8 C9H12O 136.194 —— 3-methylnorborn-5-ene-2-methanol 20529-84-4 C9H14O 138.21 5-降冰片烯-2,3-二甲醇 5,6-bis(hydroxymethyl)bicyclo<2.2.1>hept-2-ene 85-39-2 C9H14O2 154.209 —— (1R,2S,3R,4S)-bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-ene-2,3-dimethanol 941567-71-1 C9H14O2 154.209 —— 2-methyl-1,2,3,4,4a,5,8,8a-octahydro-1,4:5,8-dimethanonaphthalene-2-carbonitrile —— C14H17N 199.296 5-降冰片烯-2-甲胺 5-norbornene-2-methylamine 95-10-3 C8H13N 123.198 5-溴甲基双环[2.2.1]庚-2-烯 5-(bromomethyl)bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-2-ene 16002-25-8 C8H11Br 187.079 —— 5endo-Brommethyl-2-norbornen 16002-25-8 C8H11Br 187.079 —— (1R,2S,4R)-((bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-en-2-yl)methyl)amine 945829-45-8 C8H13N 123.198 5-降冰片烯-2-甲醛 5-Norbornene-2-carboxaldehyde 5453-80-5 C8H10O 122.167 5-降冰片烯-2-甲醇 5-hydroxymethyl-2-norbornene 95-12-5 C8H12O 124.183 —— 5-norbornene-2-methanol 13360-81-1 C8H12O 124.183 —— 5-norbornene-2-methanol 15507-06-9 C8H12O 124.183 1-羟基双环戊二烯 3-hydroxytricyclo<5.2.1.02,6>deca-4,8-diene 6814-80-8 C10H12O 148.205 2-氰基-5-降冰片烯 bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-ene-2-carbonitrile 95-11-4 C8H9N 119.166 —— 5-norbornene-2-carbonitrile 2890-96-2 C8H9N 119.166 —— 5-norbornene-2-carbonitrile 2888-90-6 C8H9N 119.166 —— endo-tricyclo[5.2.1.0(2,6)]deca-4,8-dien-3-one —— C10H10O 146.189 —— tricyclo[5.2.1.02,6]deca-4,8-dien-3-one 15584-54-0 C10H10O 146.189 —— 3-bromotricyclo<5.2.1.02,6>deca-4,8-diene 16327-41-6 C10H11Br 211.101 —— 5,6-bis(chloromethyl)bicyclo<2.2.1>hept-2-ene 5992-56-3 C9H12Cl2 191.1 —— endo-5-(chloromethyl)norbornene 95-09-0 C8H11Cl 142.628 三环癸-3-烯-8-醇 tricyclo<5,2,1,0 2,6>-3-decene-8-ol 3385-61-3 C10H14O 150.221 —— tricyclo<5.2.1.02,6>dec-4-en-9-one 14888-58-5 C10H12O 148.205 3,3A,4,6,7,7alpha-六氢-4,7-甲桥-5H-茚-5-酮 Keto-dihydro-dicyclo-pentadien 14888-58-5 C10H12O 148.205 内型-5-乙酰基-2-降冰片烯 2-acetyl-5-norbornene 824-60-2 C9H12O 136.194 1-[(1S,2R,4S)-双环[2.2.1]庚-5-烯-2-基]乙酮 exo-5-acetyl-2-norbornene 159651-24-8 C9H12O 136.194 —— (+)-1-((1R,2R,3S,4S)-3-methylbicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-en-2-yl)propan-1-one 70681-55-9 C11H16O 164.247 —— [3-Methyl-3-(4-methyl-pent-3-enyl)-bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-en-2-yl]-methanol 61432-79-9 C15H24O 220.355 降冰片烯 norborn-2-ene 498-66-8 C7H10 94.1564 4,4a,6,7,8,8alpha-六氢-1,4-甲桥萘-5(1H)-酮 tricyclo[6.2.1.02,7 ]undec-9-en-3-one 51519-65-4 C11H14O 162.232 羟基双环戊烯 tricyclo<5,2,1,0 2,6>-3-decene-9-ol 133-21-1 C10H14O 150.221 - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:的(1制备- [R,4小号)-4-羟基环戊-2-烯-1-基乙酸酯的Novozym经由-435 ®的催化desymmetrization顺-3,5-二乙酰氧基-1-环戊烯摘要:环戊二烯的光氧化反应是在甲醇中使用LED灯的白光,玫瑰红作为光引发剂和压缩空气在0°C进行的。在[硫脲]≫ [环戊二烯]的条件下,硫脲的消耗遵循拟一级反应动力学,半衰期为75±10分钟;更正 效率 r = 0.989。缓慢加入单体并保持反应物料中过量的硫脲浓度可提高产率。不分离地将顺式-3,5-二羟基-1-环戊烯乙酰化,得到高纯度(> 99%)的顺式-3,5-二乙酰氧基-1-环戊烯,总分离产率为30%。双乙酸盐的不对称化为(1 R,4 S基)-4-羟基环戊-2-烯-1-基乙酸酯已经经由进行酶促酯交换反应用甲醇在甲基叔丁基醚(MTBE)在5℃下使用的Novozym-435 ®。得到对映体纯的单乙酸酯(ee> 99%),分离产率为95%。回收的酶可重复使用10次以上,而不会损失收率和选择性。整个方案不需要通过色谱法纯化最终产物。DOI:10.1016/j.tet.2018.09.052
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:Cyclopentadiene fuels摘要:一种制备环戊二烯燃料的方法,包括从生物基源产生环戊-2-烯-1-酮或环戊-2-烯-1-酮混合物。将环戊-2-烯-1-酮或环戊-2-烯-1-酮混合物加氢,从而形成环戊-2-烯-1-醇或环戊-2-烯-1-醇混合物。将环戊-2-烯-1-醇或环戊-2-烯-1-醇混合物与脱水剂脱水,从而形成环戊二烯或环戊二烯混合物。将环戊二烯或环戊二烯混合物转化为二环戊二烯或二氢二环戊二烯。将二环戊二烯或二氢二环戊二烯加氢,从而形成四氢二环戊二烯。四氢二环戊二烯进行异构化,从而形成外消旋四氢二环戊二烯。公开号:US11078139B1
-
作为试剂:描述:4-环戊烯-1,3-二酮 在 lithium aluminium tetrahydride 、 二聚环戊二烯 作用下, 以 甲醇 、 乙醚 、 苯 为溶剂, 生成 Bicyclo<4.3.0>nona-1(6),3-dien-7-one参考文献:名称:Perhydroindanone Derivatives. I. Applicability of the Diels-Alder Reaction摘要:DOI:10.1021/jo01036a005
文献信息
-
Chiral Anion Phase-Transfer Catalysis Applied to the Direct Enantioselective Fluorinative Dearomatization of Phenols作者:Robert J. Phipps、F. Dean TosteDOI:10.1021/ja311798q日期:2013.1.30ambient reaction conditions with high enantioselectivity. The close relationship of the products with well-studied o-quinols provides numerous avenues for synthetic elaboration and exciting opportunities for bioisosteric replacement of hydroxyl with fluorine in natural products.
-
Pyrazinyl-substituted naphthalene derivatives申请人:——公开号:US20010004669A1公开(公告)日:2001-06-21Compounds of the formula 1 where R 1 is of the formulae 2 R 2 is —R 4 , —O—R 4 , —O—S (O) 2 —R 4 , —NR 4 R 5 , R 4 —(CH 2 ) b —NH(C═X)—(CH 2 )—, R 4 —(CH 2 ) b —O(C═O)NH—(CH 2 ) c —(C═O)NH—, R 4 (C═O)NH—(C═O)NH—, —(CH 2 ) b —NH(C═X)—(CH 2 ) c —R 4 , R 4 —(CH 2 ) b —O(C═)—(CH 2 ) c —, —(CH 2 ) b —O(C═O)—(CH 2 ) c —R 4 , —NH(C═X)NH—R 4 , R 4 —O(C═O)O—, —O(C═)NH—R 4 , R 4 —O(C═O)NH—, —(CH 2 ) b —(C═0)—(CH 2 ) c —R 4 , —NH—S(O) 2 —R 4 , —C(OH)R 4 R 5 , —CH(OH)—R 4 , —(C═O)—NR 4 R 5 , —CN, —NO 2 , substituted C 1 to C 6 alkyl, substituted or unsubstituted C 1 to C 6 alkenyl, or substituted or unsubstituted C 1 to C 6 alkynyl, said substituted moieties substituted with a moiety of the formulae —R 4 , —R 4 R 5 , —O—R 4 , or —S(O) d —R 4 . These compounds are useful psychotherapeutics and are potent serotonin (5-HT 1 ) agonists and antagonists and may be used in the treatment of depression, anxiety, eating disorders, obesity, drug abuse, cluster headache, migraine, pain and chronic paroxysmal hemicrania and headache associated with vascular disorders, and other disorders arising from deficient serotonergic neurotranmission. The compounds can also be used as centrally acting antihypertensives and vasodilators.公式1的化合物,其中R1是公式2,R2是—R4,—O—R4,—O—S(O)2—R4,—NR4R5,R4—(CH2)b—NH(C═X)—( )c—,R4—( )b—O(C═O)NH—( )c—(C═O)NH—,R4(C═O)NH—(C═O)NH—,—( )b—NH(C═X)—( )c—R4,R4—( )b—O(C═)—( )c—,—( )b—O(C═O)—( )c—R4,—NH(C═X)NH—R4,R4—O(C═O)O—,—O(C═)NH—R4,R4—O(C═O)NH—,—( )b—(C═O)—( )c—R4,—NH—S(O)2—R4,—C(OH)R4R5,—CH(OH)—R4,—(C═O)—NR4R5,—CN,—NO2,取代的C1至C6烷基,取代或未取代的C1至C6烯基,或取代或未取代的C1至C6炔基,所述取代基团被公式—R4,—R4R5,—O—R4或—S(O)d—R4的基团取代。这些化合物是有用的精神治疗剂,并且是强效的血清素(5-HT1)激动剂和拮抗剂,可用于治疗抑郁症、焦虑症、饮食失调、肥胖、药物滥用、丛集性头痛、偏头痛、疼痛和慢性阵发性偏头痛以及与血管疾病相关的头痛,以及其他由血清素神经传递不足引起的疾病。这些化合物还可用作中枢作用抗高血压药和血管扩张剂。
-
Compositions containing sertraline and a 5-HT.sub.1D receptor agonist or申请人:Pfizer Inc.公开号:US05597826A1公开(公告)日:1997-01-28The present invention relates to novel compositions containing the serotonin selective re-uptake inhibitor (SSRI), preferably (1S-cis)-4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-N-methyl-1-naphthalenam ine, and an agonist or antagonist of the serotonin 1 (5-HT.sub.1) receptor and to the use of such compositions for treating or preventing a condition selected from mood disorders, including depression, seasonal affective disorders and dysthmia, anxiety disorders including generalized anxiety disorder and panic disorder; agoraphobia, avoidant personality disorder; social phobia; obsessive compulsive disorder; post-traumatic stress disorder; memory disorders including dementia, amnestic disorders and age-associated memory impairment; disorders of eating behavior, including anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa; obesity; cluster headache; migraine; pain; Alzheimer's disease; chronic paroxysmal hemicrania; headache associated with vascular disorders; Parkinson's disease, including dementia in Parkinson's disease, neuroleptic-induced parkinsonism and tardive dyskinesias; endocrine disorders such as hyperprolactinaemia; vasospasm (particularly in the cerebral vasculature); hypertension; disorders in the gastrointestinal tract where changes in motility and secretion are involved; sexual dysfunction, including premature ejaculation; and chemical dependencies.本发明涉及包含选择性5-羟色胺再摄取抑制剂(SSRI),优选(1S-顺)-4-(3,4-二氯苯基)-1,2,3,4-四氢-N-甲基-1-萘胺,以及5-羟色胺1(5-HT1)受体的激动剂或拮抗剂的新组合物,以及使用这样的组合物治疗或预防情绪障碍,包括抑郁症、季节性情感障碍和情绪恶劣,焦虑障碍,包括广泛性焦虑障碍和恐慌障碍;恐旷症,回避性人格障碍;社交恐惧症;强迫症;创伤后应激障碍;记忆障碍,包括痴呆、遗忘障碍和与年龄相关的记忆减退;饮食行为障碍,包括厌食症和贪食症;肥胖;丛集性头痛;偏头痛;疼痛;阿尔茨海默病;慢性阵发性偏头痛;与血管疾病相关的头痛;帕金森病,包括帕金森病性痴呆、神经阻滞剂诱发的帕金森综合症和迟发性运动障碍;内分泌障碍,如高催乳素血症;血管痉挛(特别是在脑血管中);高血压;涉及运动和分泌变化的胃肠道疾病;性功能障碍,包括早泄;以及化学依赖性。
-
Addition of C–H Bonds of Pyridine Derivatives to Alkenes Catalyzed by Zirconium Complexes Bearing Amine-Bridged Bis(phenolato) Ligands作者:Qiu Sun、Ping Chen、Yaorong Wang、Yunjie Luo、Dan Yuan、Yingming YaoDOI:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.8b01959日期:2018.9.17Cationic zirconium complexes in situ generated from zirconium dibenzyl complexes bearing amine-bridged bis(phenolato) ligands have been developed to catalyze addition of C(sp2)–H and C(sp3)–H bonds of pyridine derivatives to alkenes. A series of zirconium complexes bearing different ligands have been synthesized, and their activities in catalyzing addition of C(sp3)–H bonds of pyridine derivatives to alkenes
-
一种制备二氯二茂钛的方法申请人:西安凯立新材料股份有限公司公开号:CN111217859A公开(公告)日:2020-06-02本发明公开了一种制备二氯二茂钛的方法,包括双环戊二烯裂解精馏制备环戊二烯,将制备得到的环戊二烯与包含四氯化钛、四氢呋喃和二乙胺的混合溶液进行回流反应,以及将回流反应后体系经后处理,得到二氯二茂钛;后处理包括以下步骤:步骤一、冰浴冷却回流反应后体系,过滤,将截留物依次用四氢呋喃和石油醚洗涤,得到洗涤后截留物;步骤二、将洗涤后截留物加入到盐酸溶液中搅拌,过滤,得到过滤后截留物;步骤三、将过滤后截留物依次用冰水和乙醇洗涤,干燥,得到二氯二茂钛。本发明采用裂解‑回流反应‑后处理的方法制备二氯二茂钛,能够避免原料环戊二烯二聚变性,影响合成反应的进行,采用本发明的方法制备得到的二氯二茂钛纯度在98%以上。
表征谱图
-
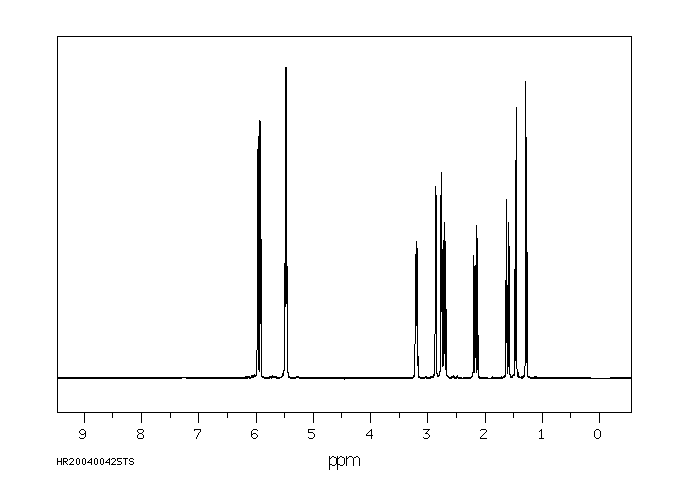
氢谱1HNMR
-
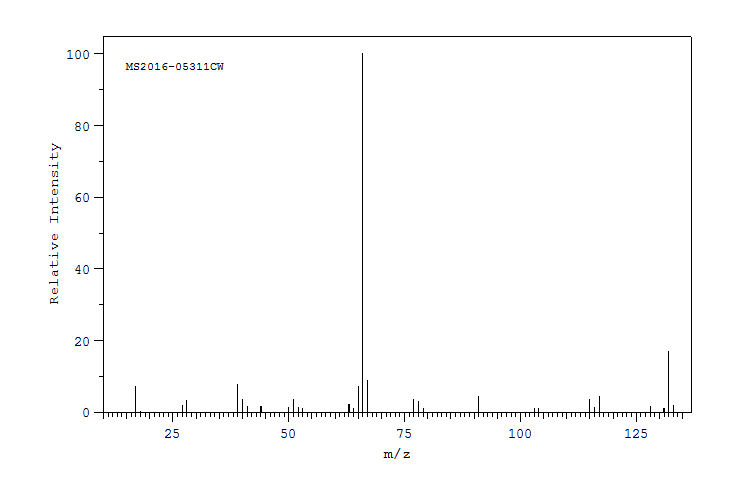
质谱MS
-
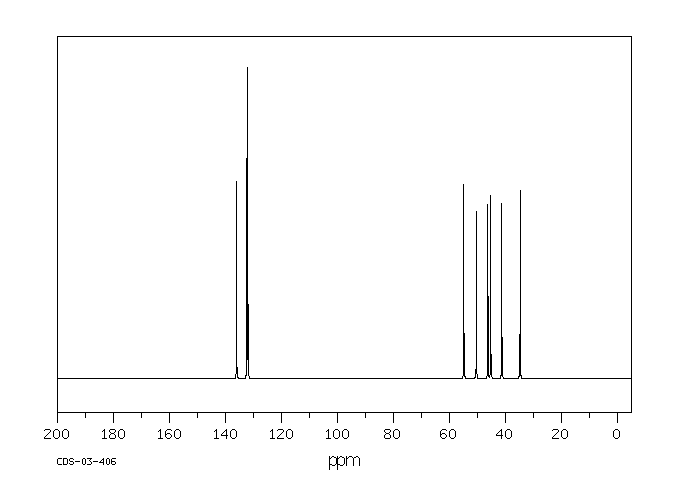
碳谱13CNMR
-
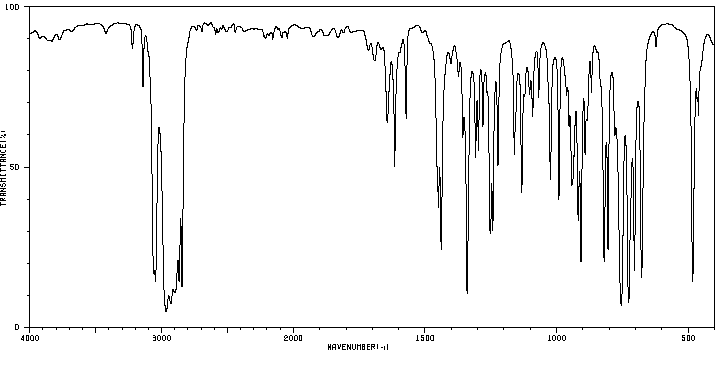
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
降冰片烯
金刚烷-D16
金刚烷
螺戊烷
螺二環己烷
螺[5.6]十二烷
螺[5.5]十一碳-4-烯
螺[5.2]辛-2-烯
螺[4.5]癸烷
螺[4.4]壬-8-烯
螺[3.4]辛烷
螺[3.4]辛-7-烯
螺[3.3]庚-2,5-二烯
螺[2.5]辛烷
螺[2.5]辛-7-烯
螺[2.5]辛-5,7-二烯
螺[2.4]庚-4,6-二烯
螺[2.4]庚-1-烯
螺[2.3]己-1-烯
螺[2.2]戊-1-烯
螺<二环<2.2.2>辛-5-烯-2,1'-环丙烷>
螺<4.4>壬-1,3,7-三烯
螺<4.4>壬-1,3,6,8-四烯
螺(4.4)壬烷
螺(4.4)壬-1,3-二烯
螺(3.4)辛-5,7-二烯
trans-perhydroazulene
萘烷
萘,1,2,3,4,4a,8a-六氢-,顺-
美罗培南中间体F9
篮烷
立方烷
氨基甲硫酸,二甲基-,O,O-(3,3-二甲基1,1-联苯基-2,2-二基)酯
棱晶烷
杜瓦苯
新戊基-1金刚烷
抗氧化剂TH-CPL
庚搭烯
四螺[2.0.2:0.2:0.2:0]十二烷
四螺[2.0.0.0.2.1.1.1]十一烷,顺-
四环己基铅
四环[5.3.0.0<2,6>.0<3,10>]癸-4,8-二烯
四环[5.3.0.0(2,6).0(3,10)]癸烷
四环[4.4.0.02,10.03,7]癸-4,8-二烯
四环[4.2.2.26,5.01,6]十二烷
四环[4.2.0.02,5.03,8]辛烷
四环[3.3.0.02,4.03,6]辛-7-烯
四环<5.3.1.02,6.04,9>十一烷
四环(8.2.2.22,5.26,9)十八碳-1,5,9-三烯
四环(4.1.0.0(2,4).0(3,5))庚烷