阿司匹林 | 50-78-2
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:134-136 °C (lit.)
-
沸点:272.96°C (rough estimate)
-
密度:1.35
-
闪点:250 °C
-
溶解度:在水中的溶解度10 mg/mLat 37 °C
-
暴露限值:ACGIH: TWA 5 mg/m3NIOSH: TWA 5 mg/m3
-
LogP:1.190
-
物理描述:Acetylsalicylic acid appears as odorless white crystals or crystalline powder with a slightly bitter taste. (NTP, 1992)
-
颜色/状态:Monoclinic tablets or needle-like crystals
-
气味:Odorless, but in moist air it is gradually hydrolyzed and acquires odor of acetic acid
-
蒸汽压力:2.52X10-5 mm Hg at 25 °C (calc)
-
稳定性/保质期:
- 口服有毒,大量使用时应穿戴适当的防护服。
-
分解:140 °C
-
解离常数:pKa = 3.49 at 25 °C
-
碰撞截面:146.8 Ų [M+Na]+ [CCS Type: DT, Method: stepped-field]
-
保留指数:1270;1315;1309;1309
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):1.2
-
重原子数:13
-
可旋转键数:3
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.11
-
拓扑面积:63.6
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:4
ADMET
安全信息
-
职业暴露等级:B
-
职业暴露限值:TWA: 5 mg/m3
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:6.1
-
危险品标志:Xn
-
安全说明:S26,S36/37/39
-
危险类别码:R22,R36/37/38
-
WGK Germany:1
-
海关编码:3004909090
-
危险品运输编号:UN 1851
-
RTECS号:VO0700000
-
包装等级:III
-
危险标志:GHS07
-
危险性描述:H302,H315,H319,H335
-
危险性防范说明:P261,P305 + P351 + P338
-
储存条件:1. 生产设备应密闭,确保车间内保持良好的通风状态。 2. 应避光、密闭存放在干燥处。
SDS
模块 1. 化学品
1.1 产品标识符
: 乙酰水杨酸
产品名称
: VetEC
1.2 鉴别的其他方法
无数据资料
1.3 有关的确定了的物质或混合物的用途和建议不适合的用途
仅用于研发。不作为药品、家庭或其它用途。
模块 2. 危险性概述
2.1 GHS-分类
急性毒性, 经口 (类别 3)
皮肤刺激 (类别 2)
眼睛刺激 (类别 2A)
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触) (类别 3)
2.2 GHS 标记要素,包括预防性的陈述
象形图
警示词 危险
危险申明
H301 吞咽会中毒
H315 造成皮肤刺激。
H319 造成严重眼刺激。
H335 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
警告申明
预防措施
P261 避免吸入粉尘/烟/气体/烟雾/蒸气/喷雾.
P264 操作后彻底清洁皮肤。
P270 使用本产品时不要进食、饮水或吸烟。
P271 只能在室外或通风良好之处使用。
P280 穿戴防护手套/ 眼保护罩/ 面部保护罩。
事故响应
P301 + P310 如果吞下去了: 立即呼救解毒中心或医生。
P302 + P352 如果皮肤接触:用大量肥皂和水清洗。
P304 + P340 如吸入: 将患者移到新鲜空气处休息,并保持呼吸舒畅的姿势。
P305 + P351 + P338 如与眼睛接触,用水缓慢温和地冲洗几分钟。如戴隐形眼镜并可方便地取
出,取出隐形眼镜,然后继续冲洗.
P312 如感觉不适,呼救中毒控制中心或医生.
P321 具体处置(见本标签上提供的急救指导)。
P330 漱口。
P332 + P313 如觉皮肤刺激:求医/就诊。
P337 + P313 如仍觉眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
P362 脱掉沾污的衣服,清洗后方可再用。
安全储存
P403 + P233 存放于通风良的地方。 保持容器密闭。
P405 存放处须加锁。
废弃处置
P501 将内容物/ 容器处理到得到批准的废物处理厂。
2.3 其它危害物 - 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
3.1 物 质
: C9H8O4
分子式
: 180.16 g/mol
分子量
组分 浓度或浓度范围
O-Acetylsalicylic acid
<=100%
化学文摘登记号(CAS 50-78-2
No.) 200-064-1
EC-编号
模块 4. 急救措施
4.1 必要的急救措施描述
一般的建议
请教医生。 向到现场的医生出示此安全技术说明书。
吸入
如果吸入,请将患者移到新鲜空气处。 如呼吸停止,进行人工呼吸。 请教医生。
皮肤接触
用肥皂和大量的水冲洗。 请教医生。
眼睛接触
用大量水彻底冲洗至少15分钟并请教医生。
食入
切勿给失去知觉者通过口喂任何东西。 用水漱口。 请教医生。
4.2 主要症状和影响,急性和迟发效应
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
4.3 及时的医疗处理和所需的特殊处理的说明和指示
无数据资料
模块 5. 消防措施
5.1 灭火介质
灭火方法及灭火剂
用水雾,抗乙醇泡沫,干粉或二氧化碳灭火。
5.2 源于此物质或混合物的特别的危害
碳氧化物
5.3 给消防员的建议
如必要的话,戴自给式呼吸器去救火。
5.4 进一步信息
无数据资料
模块 6. 泄露应急处理
6.1 作业人员防护措施、防护装备和应急处置程序
使用个人防护用品。 避免粉尘生成。 避免吸入蒸气、烟雾或气体。 保证充分的通风。
人员疏散到安全区域。 避免吸入粉尘。
6.2 环境保护措施
不要让产品进入下水道。
6.3 泄漏化学品的收容、清除方法及所使用的处置材料
收集和处置时不要产生粉尘。 扫掉和铲掉。 放入合适的封闭的容器中待处理。
6.4 参考其他部分
丢弃处理请参阅第13节。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
7.1 安全操作的注意事项
避免接触皮肤和眼睛。 避免形成粉尘和气溶胶。
在有粉尘生成的地方,提供合适的排风设备。
7.2 安全储存的条件,包括任何不兼容性
贮存在阴凉处。 使容器保持密闭,储存在干燥通风处。
7.3 特定用途
无数据资料
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
8.1 容许浓度
最高容许浓度
组分 化学文摘登 值 容许浓度 基准
记号(CAS
No.)
O-Acetylsalicylic PC- 5 mg/m3 工作场所有害因素职业接触限值 -
acid TWA 化学有害因素
8.2 暴露控制
适当的技术控制
根据良好的工业卫生和安全规范进行操作。 休息前和工作结束时洗手。
个体防护设备
眼/面保护
带有防护边罩的安全眼镜符合 EN166要求请使用经官方标准如NIOSH (美国) 或 EN 166(欧盟)
检测与批准的设备防护眼部。
皮肤保护
戴手套取 手套在使用前必须受检查。
请使用合适的方法脱除手套(不要接触手套外部表面),避免任何皮肤部位接触此产品.
使用后请将被污染过的手套根据相关法律法规和有效的实验室规章程序谨慎处理. 请清洗并吹干双手
所选择的保护手套必须符合EU的89/686/EEC规定和从它衍生出来的EN 376标准。
完全接触
物料: 丁腈橡胶
最小的层厚度 0.11 mm
溶剂渗透时间: 480 min
测试过的物质Dermatril® (KCL 740 / Z677272, 规格 M)
飞溅保护
物料: 丁腈橡胶
最小的层厚度 0.11 mm
溶剂渗透时间: 480 min
测试过的物质Dermatril® (KCL 740 / Z677272, 规格 M)
, 测试方法 EN374
如果以溶剂形式应用或与其它物质混合应用,或在不同于EN
374规定的条件下应用,请与EC批准的手套的供应商联系。
这个推荐只是建议性的,并且务必让熟悉我们客户计划使用的特定情况的工业卫生学专家评估确认才可.
这不应该解释为在提供对任何特定使用情况方法的批准.
身体保护
全套防化学试剂工作服, 防护设备的类型必须根据特定工作场所中的危险物的浓度和数量来选择。
呼吸系统防护
如须暴露于有害环境中,请使用P95型(美国)或P1型(欧盟 英国
143)防微粒呼吸器。如需更高级别防护,请使用OV/AG/P99型(美国)或ABEK-P2型 (欧盟 英国 143)
防毒罐。
呼吸器使用经过测试并通过政府标准如NIOSH(US)或CEN(EU)的呼吸器和零件。
模块 9. 理化特性
9.1 基本的理化特性的信息
a) 外观与性状
形状: 粉末
颜色: 白色
b) 气味
无数据资料
c) 气味阈值
无数据资料
d) pH值
3.5 在 2.5 g/l 在 20 °C
e) 熔点/凝固点
熔点/凝固点: 138 - 140 °C
f) 沸点、初沸点和沸程
无数据资料
g) 闪点
250 °C - 闭杯
h) 蒸发速率
无数据资料
i) 易燃性(固体,气体)
无数据资料
j) 高的/低的燃烧性或爆炸性限度 无数据资料
k) 蒸气压
无数据资料
l) 蒸汽密度
无数据资料
m) 密度/相对密度
无数据资料
n) 水溶性
无数据资料
o) n-辛醇/水分配系数
辛醇--水的分配系数的对数值: 1.19
p) 自燃温度
无数据资料
q) 分解温度
无数据资料
r) 粘度
无数据资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应活性
10.1 反应性
无数据资料
10.2 稳定性
无数据资料
10.3 危险反应
无数据资料
10.4 应避免的条件
加热。 暴露在光照下。
10.5 不相容的物质
强氧化剂, 强酸, 强碱
10.6 危险的分解产物
模块 11. 毒理学资料
11.1 毒理学影响的信息
急性毒性
半数致死剂量 (LD50) 经口 - 大鼠 - 1,500 mg/kg
半数致死剂量 (LD50) 腹膜内的 - 大鼠 - 340 mg/kg
半数致死剂量 (LD50) 腹膜内的 - 小鼠 - 167 mg/kg
皮肤刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
眼睛刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
呼吸道或皮肤过敏
无数据资料
生殖细胞致突变性
无数据资料
致癌性
IARC:
此产品中没有大于或等于 0。1%含量的组分被 IARC鉴别为可能的或肯定的人类致癌物。
生殖毒性
无数据资料
从实验动物的结果看,过度接触能导致生殖紊乱
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触)
吸入 - 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
特异性靶器官系统毒性(反复接触)
无数据资料
吸入危险
无数据资料
潜在的健康影响
吸入 吸入可能有害。 引起呼吸道刺激。
摄入 误吞对人体有害。
皮肤 通过皮肤吸收可能有害。 造成皮肤刺激。
眼睛 造成严重眼刺激。
接触后的征兆和症状
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
附加说明
化学物质毒性作用登记: 无数据资料
模块 12. 生态学资料
12.1 生态毒性
对鱼类的毒性 半数致死浓度(LC50) - 高体雅罗鱼 (金雅罗鱼) - > 1,000 mg/l - 48 h
对水蚤和其他水生无脊 半数效应浓度(EC50) - 水蚤 - > 100 mg/l - 48 h
椎动物的毒性
细菌毒性 半数致死浓度(LC50) - 细菌 - > 10,000 mg/l - 48 h
12.2 持久性和降解性
生物降解能力
备注: 预计可生物降解
12.3 潜在的生物累积性
无数据资料
12.4 土壤中的迁移性
无数据资料
12.5 PBT 和 vPvB的结果评价
无数据资料
12.6 其它不良影响
无数据资料
模块 13. 废弃处置
13.1 废物处理方法
产品
将剩余的和不可回收的溶液交给有许可证的公司处理。
与易燃溶剂相溶或者相混合,在备有燃烧后处理和洗刷作用的化学焚化炉中燃烧
受污染的容器和包装
按未用产品处置。
模块 14. 运输信息
14.1 联合国危险货物编号
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.2 联合国运输名称
欧洲陆运危规: 非危险货物
国际海运危规: 非危险货物
国际空运危规: 非危险货物
14.3 运输危险类别
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.4 包裹组
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.5 环境危险
欧洲陆运危规: 否 国际海运危规 国际空运危规: 否
海洋污染物(是/否): 否
14.6 对使用者的特别提醒
无数据资料
模块 15 - 法规信息
N/A
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
制备方法与用途
阿司匹林又名乙酰水杨酸,是一种非甾体类抗炎药,最初用于消炎镇痛。后来的研究发现其具有防止血小板凝集、预防血栓的作用。随着对阿司匹林的深入研究,人们发现了更多新用途,例如它能降低心肌梗死和脑卒中的死亡率,并有助于减少结直肠癌的风险。
药理作用乙酰水杨酸(阿司匹林)是传统的解热镇痛药,同时具有抗血小板聚集的作用。在体内,阿司匹林抑制周围动脉中阻塞性血栓的形成,通过抑制血小板释放反应以及内源性ADP、5-HT等物质的释放,从而减少血小板第二相聚集而不影响第一相聚集。
其作用机制在于使血小板环氧酶乙酰化,从而抑制环内过氧化物和TXA2的生成。同时还能使血小板膜蛋白乙酰化,并抑制血小板膜酶,有助于进一步抑制血小板功能。因环氧化酶受抑制,阿司匹林还会影响血管壁合成PGI2;大剂量时则可能影响TXA2及PGI2的生成。
阿司匹林适用于缺血性心脏病、冠状动脉成形术(PTCA)后、冠状动脉搭桥术后预防短暂性脑缺血发作、心肌梗死,减少心律失常的发生率。
适应症乙酰水杨酸对血小板聚集有抑制作用,可阻止血栓形成。临床上用于预防暂时性脑缺血发作、心肌梗死、急性风湿热及类风湿关节炎等。此外,它也是治疗感冒发热、头痛、神经痛、关节痛、肌肉痛、急性风湿性关节炎、牙痛等的常用解热镇痛药。
用途阿司匹林是最早、最广泛和最常见的解热镇痛抗风湿药物,具有多方面的药理作用。常用于治疗感冒发热、头痛、神经痛、关节痛及风湿性疾病。作为《国家基本药物目录》中的品种之一,它也是其他药物的中间体。
生产方法阿司匹林可通过乙酰化水杨酸制得。在反应罐中加入适量乙酐(加料量为水杨酸总量的0.7889倍),再加入三分之二量的水杨酸并搅拌升温,于81-82℃反应40-60分钟,降温至81-82℃保温反应2小时。检查游离水杨酸合格后,降温至13℃析出结晶,甩滤、洗涤、干燥得乙酰水杨酸。
另一种方法是将水杨酸与乙酐投入三口瓶中搅拌,反应温度不超过60℃约1小时后倒入冰水中,有结晶析出,过滤、干燥即得产品。
安全性阿司匹林为有毒物品,具有高毒性。急性口服毒性实验显示LD50值分别为大鼠200毫克/公斤和小鼠250毫克/公斤。该物质可燃并受热分解产生刺激气体;应储存在库房中保持通风、干燥,并与氧化剂及食品添加剂分开存放。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 乙酰水杨酸甲酯 methyl acetylsalicylate 580-02-9 C10H10O4 194.187 甲基硫基甲基2-乙酰基氧基苯甲酸酯 methylthiomethyl 2-acetoxybenzoate 76432-30-9 C11H12O4S 240.28 2-乙酰基氧基苯甲酸苯基酯 phenyl 2-acetoxybenzoate 134-55-4 C15H12O4 256.258 2-(乙酰氧基)苯甲酸酐 aspirin anhydride 1466-82-6 C18H14O7 342.305 阿司匹林杂质8 (2-acetoxy-benzoic acid )-acetic acid-anhydride 18698-59-4 C11H10O5 222.197 —— 2-acetoxybenzaldehyde 5663-67-2 C9H8O3 164.161 —— aspirin acetoxymethyl ester 118247-06-6 C12H12O6 252.224 甲基亚磺酰甲基2-乙酰基氧基苯甲酸酯 methylsulfinylmethyl 2-acetoxybenzoate 76432-33-2 C11H12O5S 256.279 —— 4-(2-acetoxybenzoyloxy)benzaldehyde 203065-56-9 C16H12O5 284.268 —— (2-Formylphenyl) 2-acetyloxybenzoate 203065-54-7 C16H12O5 284.268 甲基磺酰基甲基2-乙酰基氧基苯甲酸酯 methylsulfonylmethyl 2-acetoxybenzoate 76432-35-4 C11H12O6S 272.279 乙酰水杨酰水杨酸 acetylsalicylsalicylic acid 530-75-6 C16H12O6 300.268 3-甲酰基苯基 2-乙酰氧基苯甲酸 2-(acetyloxy)benzoic acid 3-(formyl)phenyl ester 203065-55-8 C16H12O5 284.268 —— 2-[2-(ethanoyloxy)benzoyloxy]-N,N-dimethylethanamide 118247-04-4 C13H15NO5 265.266 —— 2-[2-(acetoxy)benzoyloxy]-N,N-diethylacetamide 116482-56-5 C15H19NO5 293.32 —— 2-[2-Nitrooxyethyl(propyl)amino]ethyl 2-acetyloxybenzoate 941702-72-3 C16H22N2O7 354.36 —— [2-[2-Hydroxyethyl(methyl)amino]-2-oxoethyl] 2-acetyloxybenzoate 118247-05-5 C14H17NO6 295.292 —— 2-(2-Acetoxybenzoyloxy)acetophenone 53278-17-4 C17H14O5 298.295 —— 2-Acetoxy-benzoic acid dipropylcarbamoylmethyl ester 116482-75-8 C17H23NO5 321.373 —— 2-(Diisopropylamino)-2-oxoethyl 2-acetoxybenzoate 116482-76-9 C17H23NO5 321.373 —— 2-(4-Morpholinyl)-2-oxoethyl 2-acetoxybenzoate 116482-80-5 C15H17NO6 307.303 —— 2-[(2-Amino-2-oxoethyl)(methyl)amino]-2-oxoethyl 2-acetoxybenzoate 116482-78-1 C14H16N2O6 308.291 邻乙酰水杨酰氯 O-acetylsalicyloyl chloride 5538-51-2 C9H7ClO3 198.606 —— (2,5-Dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl)methyl 2-(acetyloxy)benzoate 32620-72-7 C14H13NO6 291.26 乙酸-2-甲基苯基酯 2-methylphenyl acetate 533-18-6 C9H10O2 150.177 水杨酸 salicylic acid 69-72-7 C7H6O3 138.123 水杨酸甲酯 methyl salicylate 119-36-8 C8H8O3 152.15 - 1
- 2
- 3
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 乙酰水杨酸甲酯 methyl acetylsalicylate 580-02-9 C10H10O4 194.187 乙酰水杨酸乙酯 ethyl acetylsalicylate 529-68-0 C11H12O4 208.214 2-辛酰氧基苯甲酸 O-octanoylsalicylic acid 70424-62-3 C15H20O4 264.321 —— vinyl 2-acetoxybenzoate 39033-93-7 C11H10O4 206.198 —— allyl 2-acetyloxybenzoate 77101-49-6 C12H12O4 220.225 —— O-ethanoylsalicyloyloxyethanaldehyde 547753-21-9 C11H10O5 222.197 2-溴乙基-2-乙酰氧基苯甲酸酯 2-bromoethyl 2-acetoxybenzoate 79874-87-6 C11H11BrO4 287.11 —— β-Oxyaethyl-acetylsalicylat 42353-74-2 C11H12O5 224.213 —— (prop-2-ynyl)-2-acetoxybenzoate —— C12H10O4 218.209 2-乙酰氧基苯甲酸苄酯 2-acetoxybenzoic acid benzyl ester 52602-17-2 C16H14O4 270.285 甲基硫基甲基2-乙酰基氧基苯甲酸酯 methylthiomethyl 2-acetoxybenzoate 76432-30-9 C11H12O4S 240.28 —— o-hydroxybenzyl O-acetylsalicylate —— C16H14O5 286.284 2-乙酰基氧基苯甲酸苯基酯 phenyl 2-acetoxybenzoate 134-55-4 C15H12O4 256.258 —— 1,3-Propandiolbis(acetylsalicylat) 19283-97-7 C21H20O8 400.385 3-溴丙基-2-乙酰氧基苯甲酸酯 3-bromopropyl 2-acetoxybenzoate 204632-98-4 C12H13BrO4 301.137 —— Trimethylsilyl-2-acetoxybenzoat 25436-28-6 C12H16O4Si 252.342 —— diethyleneglycol bis-acetylsalicylate 19284-01-6 C22H22O9 430.411 2-(乙酰氧基)苯甲酸酐 aspirin anhydride 1466-82-6 C18H14O7 342.305 —— 1,4-buthanediol bis-acetylsalicylate —— C22H22O8 414.412 —— 2-[2-[2-(2-Hydroxyethoxy)ethoxy]ethoxy]ethyl 2-acetyloxybenzoate —— C17H24O8 356.373 阿司匹林杂质8 (2-acetoxy-benzoic acid )-acetic acid-anhydride 18698-59-4 C11H10O5 222.197 —— 2-acetoxybenzoic acid carboxymethyl ester 677716-61-9 C11H10O6 238.197 —— 2-acetoxybenzaldehyde 5663-67-2 C9H8O3 164.161 —— 1,6-hexanediol bis-acetylsalicylate —— C24H26O8 442.466 甲基亚磺酰甲基2-乙酰基氧基苯甲酸酯 methylsulfinylmethyl 2-acetoxybenzoate 76432-33-2 C11H12O5S 256.279 —— 2-acetyloxybenzoic acid 4-hydroxymethylphenyl ester 175077-14-2 C16H14O5 286.284 —— 4-(2-acetoxybenzoyloxy)benzaldehyde 203065-56-9 C16H12O5 284.268 —— Acetylsalicyloylglykolamid 50785-22-3 C11H11NO5 237.212 —— 3-(hydroxymethyl)benzyl 2-acetoxybenzoate 1345092-35-4 C17H16O5 300.311 —— 6-bromohexyl 2-(acetyloxy)benzoate —— C15H19BrO4 343.217 —— (2-Formylphenyl) 2-acetyloxybenzoate 203065-54-7 C16H12O5 284.268 —— 2-acetyloxybenzoic acid 2-hydroxymethylphenyl ester 850341-99-0 C16H14O5 286.284 —— 2-(3-phenylaminopropionyloxy)benzoic acid 1620837-97-9 C16H15NO4 285.299 降钙素(humanreduced),8-L-缬氨酸-(9CI) 2-Acetoxy-benzoic acid 3-methoxy-phenyl ester 94159-26-9 C16H14O5 286.284 甲基磺酰基甲基2-乙酰基氧基苯甲酸酯 methylsulfonylmethyl 2-acetoxybenzoate 76432-35-4 C11H12O6S 272.279 乙酰水杨酰水杨酸 acetylsalicylsalicylic acid 530-75-6 C16H12O6 300.268 2-[[2-(乙酰氧基)苯甲酰基]氧基]苯甲酸2-[(2-羧基苯氧基)羰基]苯基酯 2-{2-[2-(2-acetoxy-benzoyloxy)-benzoyloxy]-benzoyloxy}-benzoic acid 85539-30-6 C30H20O10 540.483 2-(乙酰氧基)苯甲酸4-(氯甲基)苯基酯 2-(acetyloxy)benzoic acid 4-(chloromethyl) phenyl ester 410071-22-6 C16H13ClO4 304.73 —— Methylsulfanylcarbonyloxymethyl 2-acetyloxybenzoate 1225454-47-6 C12H12O6S 284.29 2-(乙酰氧基)苯甲酸3-(羟基甲基)苯基酯 NCX 4017 287118-98-3 C16H14O5 286.284 —— acetylsalicylic acid 4-(nitroxy)butyl ester 171781-26-3 C13H15NO7 297.265 3-甲酰基苯基 2-乙酰氧基苯甲酸 2-(acetyloxy)benzoic acid 3-(formyl)phenyl ester 203065-55-8 C16H12O5 284.268 —— NCX 4018 —— C13H15NO8 313.264 —— 2-acetoxybenzoic acid benzyloxycarbonylmethyl ester 941702-75-6 C18H16O6 328.321 —— benzyl 4-{[2-(acetyloxy)phenyl]carbonyloxy}butanoate 1314539-40-6 C20H20O6 356.375 —— 2-((2-(nitrooxy)ethyl)disulfanyl)ethyl 2-acetoxybenzoate —— C13H15NO7S2 361.397 —— 2-[2-(ethanoyloxy)benzoyloxy]-N-ethylethanamide 118247-01-1 C13H15NO5 265.266 —— (ethylthiocarbonyl)oxymethyl 2-(acetyloxy)benzoate 1314004-84-6 C13H14O6S 298.317 —— N-Methyl-N-{2-[(2'-acetoxybenzoyl)oxy]ethyl}acetamide 118247-08-8 C14H17NO5 279.293 —— Acetylsalicyloylethylcarbonat 36335-42-9 C12H12O6 252.224 2-[4-[2-(2-乙酰氧基苯甲酰基)氧乙基]哌嗪-1-基]乙基2-乙酰基氧基苯甲酸酯 1,4-BIS-[2-(ACETYLSALICYLOYLOXY)ETHYL] PIPERAZINE 79874-85-4 C26H30N2O8 498.533 —— Pivaloyloxymethyl-O-acetylsalicylat 66195-30-0 C15H18O6 294.304 —— 2-[2-(ethanoyloxy)benzoyloxy]-N,N-dimethylethanamide 118247-04-4 C13H15NO5 265.266 —— 4-carbamoylphenyl 2-acetoxybenzoate 1000700-38-8 C16H13NO5 299.283 —— O2-(acetylsalicyloyloxymethyl)-1-(N-isopropylamino)-diazen-1-ium-1,2-diolate 1334486-41-7 C13H17N3O6 311.294 呱西替柳 Guaiaspir 55482-89-8 C16H14O5 286.284 2-(乙酰基氧基)-4-[(硝基氧基)甲基]苯甲酸苯酯 [2-(acetyloxy)benzoicacid 4-(nitrooxy methyl)phenyl ester] 287118-97-2 C16H13NO7 331.282 —— 1-Phenylethyl 2-acetyloxybenzoate 88354-03-4 C17H16O4 284.312 —— 2-acetoxybenzoic acid 4-bromobutoxycarbonylmethyl ester 1240261-39-5 C15H17BrO6 373.2 —— tert-butyldimethylsilyl 2-acetoxybenzoate 129512-44-3 C15H22O4Si 294.423 —— ({4-[3-(nitrooxy)propoxy]benzoyl}oxy)methyl 2-(acetyloxy)benzoate 1144618-37-0 C20H19NO10 433.372 —— 2-[2-(acetoxy)benzoyloxy]-N,N-diethylacetamide 116482-56-5 C15H19NO5 293.32 —— [2-[(2-Amino-2-oxoethyl)amino]-2-oxoethyl] 2-acetyloxybenzoate 118247-02-2 C13H14N2O6 294.264 —— [2-[2-Hydroxyethyl(methyl)amino]-2-oxoethyl] 2-acetyloxybenzoate 118247-05-5 C14H17NO6 295.292 贝诺酯 Fenasprate 5003-48-5 C17H15NO5 313.31 —— ((3-nitrooxypropyloxy)carbonyl)oxymethyl 2-(acetyloxy)-benzoate 1314004-76-6 C14H15NO10 357.274 —— Acetylsalicylsaeure-4-nitrophenylester 77008-82-3 C15H11NO6 301.255 —— 2-(2-Acetoxybenzoyloxy)acetophenone 53278-17-4 C17H14O5 298.295 —— 2-acetoxy-benzoic acid 4-nitrooxy-butoxy carbonyl methyl ester 1240261-40-8 C15H17NO9 355.301 —— [2-(acetyloxy)benzoic acid 2-(nitrooxy methyl)phenyl ester] —— C16H13NO7 331.282 2-(乙酰氧基)-苯甲酸 3-[(硝基氧基)甲基]苯基酯 2-(acetyloxy)benzoic acid 3-[(nitrooxy)methyl]phenyl ester 175033-36-0 C16H13NO7 331.282 —— [2-[(2-Ethoxy-2-oxoethyl)amino]-2-oxoethyl] 2-acetyloxybenzoate 118247-03-3 C15H17NO7 323.302 —— 2-Acetoxy-benzoic acid dipropylcarbamoylmethyl ester 116482-75-8 C17H23NO5 321.373 —— 2-(Diisopropylamino)-2-oxoethyl 2-acetoxybenzoate 116482-76-9 C17H23NO5 321.373 —— 2-(4-Morpholinyl)-2-oxoethyl 2-acetoxybenzoate 116482-80-5 C15H17NO6 307.303 2-(氨基羰基)苯基乙酸酯 O-acetylsalicylamide 5663-71-8 C9H9NO3 179.175 —— 2-Acetoxybenzoyl bromide 88803-91-2 C9H7BrO3 243.057 —— 2-(2-((2-(nitrooxy)ethyl)disulfanyl)ethoxy)-2-oxoethyl 2-acetoxybenzoate 1192130-19-0 C15H17NO9S2 419.433 双水杨酸酯 2-hydroxy-benzoic acid, 2-carboxyphenyl ester 552-94-3 C14H10O5 258.23 —— pyridin-2-yl 2-acetoxybenzoate —— C14H11NO4 257.246 三-水杨酸 trisalicylide 85531-17-5 C21H14O7 378.338 四水杨酸 tetra-salicylic acid 85531-18-6 C28H18O9 498.446 雙柳酸內酯 disalicylide 486-58-8 C14H8O4 240.215 —— 1,9,17-trioxa-[2.2.2]orthocyclophane-2,10,18-trione 5981-18-0 C21H12O6 360.323 —— 2-[(2-Amino-2-oxoethyl)(methyl)amino]-2-oxoethyl 2-acetoxybenzoate 116482-78-1 C14H16N2O6 308.291 邻乙酰水杨酰氯 O-acetylsalicyloyl chloride 5538-51-2 C9H7ClO3 198.606 —— 1-(nitrooxy)propyl 2-acetoxybenzoate 1620191-06-1 C12H13NO7 283.238 —— (2,5-Dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl)methyl 2-(acetyloxy)benzoate 32620-72-7 C14H13NO6 291.26 —— [2-[(2-Ethoxy-2-oxoethyl)-methylamino]-2-oxoethyl] 2-acetyloxybenzoate 116482-77-0 C16H19NO7 337.329 —— 5-chloropyridin-3-yl 2-acetoxybenzoate 1026417-26-4 C14H10ClNO4 291.691 —— [2-[4-[2,2-Bis(hydroxymethyl)butanoyloxy]butoxy]-2-oxoethyl] 2-acetyloxybenzoate 1609647-77-9 C21H28O10 440.447 —— (4-(3-nitrooxypropyl)phenoxycarbonyl)oxymethyl 2-(acetyloxy)benzoate 1314004-78-8 C20H19NO10 433.372 —— o-acetoxybenzoyl hydrazine 147091-07-4 C9H10N2O3 194.19 —— 2-[(2'-Acetoxybenzoyl)oxy]-2'-methyl-N,N-diethylacetamide 118247-09-9 C16H21NO5 307.346 水杨酸 salicylic acid 69-72-7 C7H6O3 138.123 —— 1-(nitrooxy)butyl 2-acetoxybenzoate 1620191-07-2 C13H15NO7 297.265 —— [6-(Chloromethyl)pyridin-2-yl]methyl 2-acetyloxybenzoate 290335-38-5 C16H14ClNO4 319.744 —— Benzamide, 2-(acetyloxy)-N-hydroxy- 16063-88-0 C9H9NO4 195.175 —— acetylsalicylic acid N-oxysuccinimide ester 84388-73-8 C13H11NO6 277.233 —— (R)-4-(nitrooxy)butyl 2-((5-(1,2-dithiolan-3-yl)pentanoyl)oxy)benzoate 1357392-70-1 C19H25NO7S2 443.542 - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:氧杂环的研究:第1部分:某些芳基重氮酮的酸催化和光化学反应摘要:三氟乙酸催化的2-甲氧基苯基重氮甲基甲酮(4a),2-乙酰氧基苯基重氮甲基甲酮(4b)和3-(2-茴香基)-∞-重氮-2-丙酮(11)导致香豆烷酮(6)和3-苯并二氢吡喃酮的形成(12),而4-(2-茴香基)-∞-重氮-2-丁酮(16)提供了苯并[b] -1-氧杂-3-酮(17)和5-甲氧基-2-四氢萘酮(18)产量适中。所述重氮酮(4a,11和16)的光化学分解产生产物,这取决于底物中存在的侧链的长度。DOI:10.1016/0040-4020(89)80142-5
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:Attanasi, Orazio; Filippone, Paolino; Serra-Zanetti, Franco, Synthetic Communications, 1982, vol. 12, # 14, p. 1155 - 1162摘要:DOI:
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:铜催化的甲基萘和电子不足的烯烃的脱氢形式[4 + 2]和[3 + 2]环加成反应摘要:甲基萘中包含的较高π扩展萘可以通过SOMO-LUMO相互作用捕获烷基,从而促进了甲基萘和缺电子烯烃之间铜催化的正式[4 + 2]和[3 + 2]环加成反应的发展。在铜催化下,一系列具有不同取代基的缺电子烯烃和甲基萘已成功地与过氧化二叔丁基(TBP)结合用作氧化剂和自由基引发剂,从而提供了多种环加合物。DOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.7b03194
文献信息
-
[EN] ACC INHIBITORS AND USES THEREOF<br/>[FR] INHIBITEURS DE L'ACC ET UTILISATIONS ASSOCIÉES
-
[EN] AZA PYRIDONE ANALOGS USEFUL AS MELANIN CONCENTRATING HORMONE RECEPTOR-1 ANTAGONISTS<br/>[FR] ANALOGUES D'AZAPYRIDONE UTILES COMME ANTAGONISTES DU RÉCEPTEUR 1 DE L'HORMONE CONCENTRANT LA MÉLANINE申请人:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO公开号:WO2010104818A1公开(公告)日:2010-09-16MCHR1 antagonists are provided having the following Formula (I): A1 and A2 are independently C or N; E is C or N; Q1, Q2, and Q3 are independently C or N provided that at least one of Q1, Q2, and Q3 is N but not more than one of Q1, Q2, and Q3 is N; D1 is a bond, -CR8R9 X-, -XCR8R9-, -CHR8CHR9-, -CR10=CR10'-, -C≡C-, or 1,2-cyclopropyl; X is O, S or NR11; R1, R2, and R3 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, lower cycloalkyl, -CF3, -OCF3, -OR12 and -SR12; G is O, S or -NR15; D2 is lower alkyl, lower cycloalkyl, lower alkylcycloalkyl, lower cycloalkylalkyl, lower cycloalkoxyalkyl or lower alkylcycloalkoxy or when G is NR15, G and D2 together may optionally form an azetidine, pyrrolidine or piperidine ring; Z1 and Z2 are independently hydrogen, lower alkyl, lower cycloalkyl, lower alkoxy, lower cycloalkoxy, halo, -CF3, -OCONR14R14', -CN, -CONR14R14', -SOR12, -SO2R12, -NR14COR14', -NR14CO2R14', -CO2R12, NR14SO2R12 or COR12; R5, R6, and R7 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen lower alkyl, lower cycloalkyl, -CF3, -SR12, lower alkoxy, lower cycloalkoxy, -CN, -CONR14R14', SOR12, SO2R12, NR14COR14', NR14CO2R12, CO2R12, NR14SO2R12 and -COR12; R8, R9, R10, R10', R11 are independently hydrogen or lower alkyl; R12 is lower alkyl or lower cycloalkyl; R14 and R14' are independently H, lower alkyl, lower cycloalkyl or R14 and R14' together with the N to which they are attached form a ring having 4 to 7 atoms; and R15 is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen and lower alkyl. Such compounds are useful for the treatment of MCHR1 mediated diseases, such as obesity, diabetes, IBD, depression, and anxiety.MCHR1拮抗剂具有以下化学式(I):A1和A2独立地为C或N;E为C或N;Q1、Q2和Q3独立地为C或N,但至少其中一个为N,但不超过一个为N;D1为键,-CR8R9 X-,-XCR8R9-,-CHR8CHR9-,-CR10=CR10'-,-C≡C-,或1,2-环丙基;X为O、S或NR11;R1、R2和R3独立地从氢、卤素、低烷基、低环烷基、-CF3、-O 、-OR12和-SR12组成的群体中选择;G为O、S或-NR15;D2为低烷基、低环烷基、低烷基环烷基、低环烷基烷基、低环烷氧基烷基或低烷基环烷氧基,或当G为NR15时,G和D2一起可以选择形成氮杂环丙烷、吡咯烷或哌啶环;Z1和Z2独立地为氢、低烷基、低环烷基、低烷氧基、低环烷氧基、卤素、- 、-OCONR14R14'、-CN、-CONR14R14'、-SOR12、-SO2R12、-NR14COR14'、-NR14CO2R14'、-CO2R12、NR14SO2R12或COR12;R5、R6和R7独立地从氢、低烷基、低环烷基、- 、-SR12、低烷氧基、低环烷氧基、-CN、-CONR14R14'、SOR12、SO2R12、NR14COR14'、NR14CO2R12、CO2R12、NR14SO2R12和-COR12组成的群体中选择;R8、R9、R10、R10'、R11独立地为氢或低烷基;R12为低烷基或低环烷基;R14和R14'独立地为H、低烷基、低环烷基或R14和R14'与其连接的N一起形成具有4至7个原子的环;R15独立地从氢和低烷基组成的群体中选择。这些化合物对于治疗MCHR1介导的疾病,如肥胖症、糖尿病、炎症性肠病、抑郁症和焦虑症非常有用。
-
[EN] SULFINYLPYRIDINES AND THEIR USE IN THE TREATMENT OF CANCER<br/>[FR] SULFINYLPYRIDINES ET LEUR UTILISATION DANS LE TRAITEMENT DU CANCER申请人:OBLIQUE THERAPEUTICS AB公开号:WO2018146468A1公开(公告)日:2018-08-16There is provided compounds of formula I (I) or pharmaceutically-acceptable salts thereof, wherein L, R1, R2, R3, R4 and n have meanings provided in the description, which compounds are useful in the treatment of cancers.提供了式I(I)的化合物或其药用盐,其中L、R1、R2、R3、R4和n的含义如描述中所提供,这些化合物在治疗癌症方面是有用的。
-
Novel processes for the preparation of adenosine compounds and intermediates thereto申请人:——公开号:US20030069423A1公开(公告)日:2003-04-10Novel processes for the preparation of adenosine compounds and intermediates thereto. The adenosine compounds prepared by the present processes may be useful as cardiovascular agents, more particularly as antihypertensive and anti-ischemic agents, as cardioprotective agents which ameliorate ischemic injury or myocardial infarct size consequent to myocardial ischemia, and as an antilipolytic agents which reduce plasma lipid levels, serum triglyceride levels, and plasma cholesterol levels. The present processes may offer improved yields, purity, ease of preparation and/or isolation of intermediates and final product, and more industrially useful reaction conditions and workability.
-
[EN] QUINUCLIDINE COMPOUNDS AS ALPHA-7 NICOTINIC ACETYLCHOLINE RECEPTOR LIGANDS<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS QUINUCLIDINE EN TANT QUE LIGANDS DU RÉCEPTEUR NICOTINIQUE ALPHA-7 DE L'ACÉTYLCHOLINE申请人:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO公开号:WO2016073407A1公开(公告)日:2016-05-12There are disclosed a series of quinuclidines having the Formula (I). which bind to the nicotinic α7 receptor and may be useful for the treatment of disorders of the central nervous system.
表征谱图
-
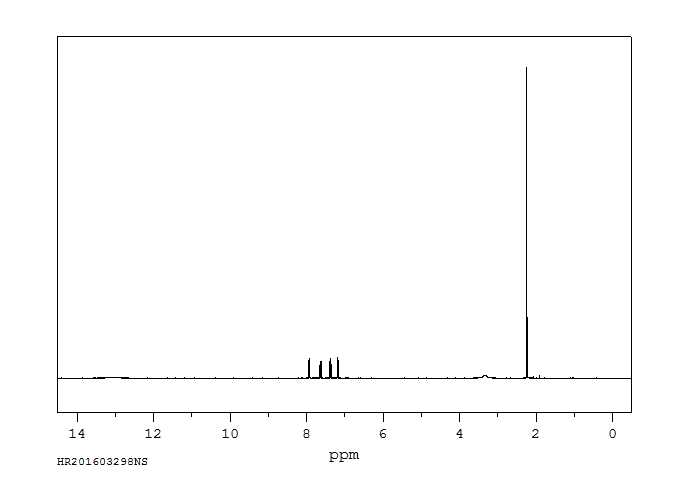
氢谱1HNMR
-
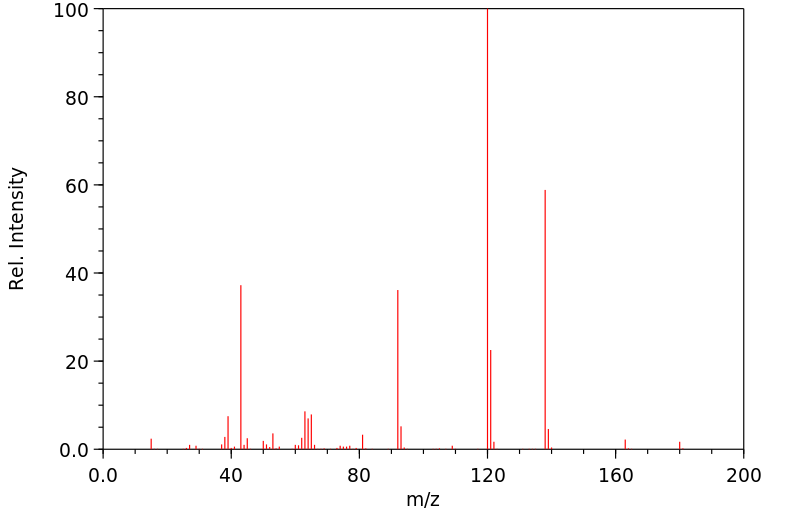
质谱MS
-
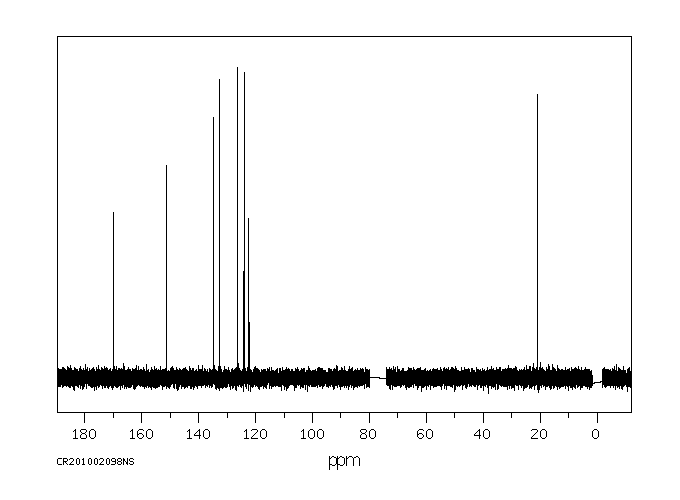
碳谱13CNMR
-
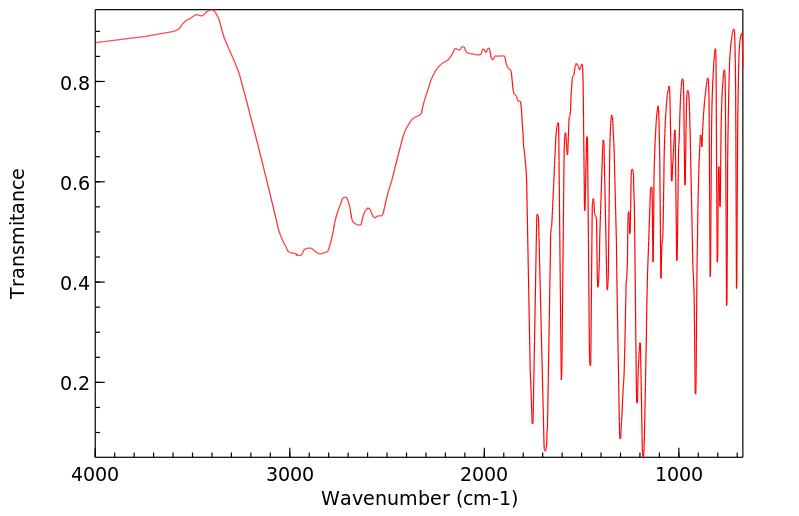
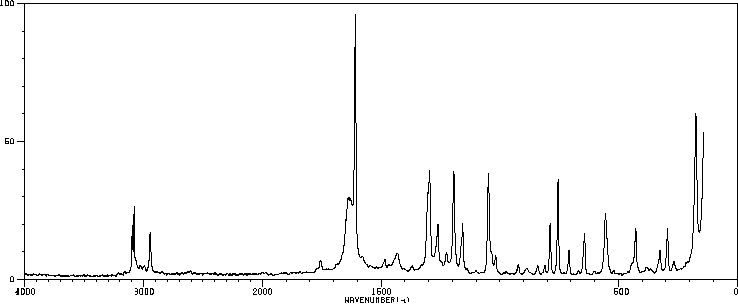
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息