alpha,alpha-二甲基苯乙酸 | 826-55-1
物质功能分类
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:80-82°C
-
沸点:146.5°C
-
密度:1.089±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted)
-
闪点:146.5°C
-
溶解度:可溶于氯仿(少许)、甲醇(少许)
-
LogP:2.3 at 20℃
-
稳定性/保质期:
在常温常压下稳定,避免与强氧化剂和酸直接接触。
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):1.6
-
重原子数:12
-
可旋转键数:2
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.3
-
拓扑面积:37.3
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:2
安全信息
-
安全说明:S26,S36/37/39
-
海关编码:2942000000
-
危险类别码:R36/37/38
-
WGK Germany:3
-
危险性防范说明:P261,P305+P351+P338
-
危险性描述:H315,H319,H335
-
储存条件:请将容器密封保存,并存放在阴凉、干燥处。
SDS
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: 2-Phenylisobutyric Acid
修改号码: 5
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害 未分类
健康危害
皮肤腐蚀/刺激 第2级
严重损伤/刺激眼睛 2A类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志
信号词 警告
危险描述 造成皮肤刺激
造成严重眼刺激
防范说明
[预防] 处理后要彻底清洗双手。
穿戴防护手套/护目镜/防护面具。
[急救措施] 眼睛接触:用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续冲洗。
眼睛接触:求医/就诊
皮肤接触:用大量肥皂和水轻轻洗。
若皮肤刺激:求医/就诊。
脱掉被污染的衣物,清洗后方可重新使用。
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 2-苯基异丁酸
百分比: >98.0%(T)
CAS编码: 826-55-1
俗名: 2-Methyl-2-Phenylpropionic Acid
2-苯基异丁酸 修改号码:5
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
分子式: C10H12O2
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用大量肥皂和水轻轻洗。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,雾状水,二氧化碳
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 清扫收集粉尘,封入密闭容器。注意切勿分散。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的
法律法规处置。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止粉尘扩散。处理后彻底清洗双手
和脸。
注意事项: 如果粉尘或浮质产生,使用局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗处。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防尘面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
外形(20°C): 固体
外观: 晶体-粉末
颜色: 白色-微浅黄色
2-苯基异丁酸 修改号码:5
模块 9. 理化特性
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点: 无资料
沸点/沸程 无资料
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 无资料
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂] 无资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在可燃溶剂中溶解混合,在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中
焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
2-苯基异丁酸 修改号码:5
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 2-苯基丙酸 hydratropic acid 492-37-5 C9H10O2 150.177 2,2-二甲基苯乙酸甲酯 methyl 2-methyl-2-phenylpropionate 57625-74-8 C11H14O2 178.231 2-甲基-2-苯基丙酸乙酯 ethyl 2-methyl-2-phenylpropionate 2901-13-5 C12H16O2 192.258 Alpha-甲基苯乙酸甲酯 2-phenylpropionic acid methyl ester 31508-44-8 C10H12O2 164.204 2-甲基-2-苯基丙醛 2,2-(dimethyl)-2-phenylacetaldehyde 3805-10-5 C10H12O 148.205 —— 2-Ethoxyethyl 2-methyl-2-phenylpropanoate —— C14H20O3 236.311 2-苯基丙醛 2-Phenylpropanal 93-53-8 C9H10O 134.178 苯乙酸 phenylacetic acid 103-82-2 C8H8O2 136.15 3-甲基-3-苯基丁烷-2-酮 2-methyl-2-phenylbutan-3-one 770-85-4 C11H14O 162.232 2-甲基-2-苯基丙酰胺 2-methyl-2-phenyl-propanamide 826-54-0 C10H13NO 163.219 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— 2-(4-ethylphenyl)-2-methylpropionic acid —— C12H16O2 192.258 2-(4-溴苯基)-2-甲基丙酸 2-(4-bromophenyl)-2-methylpropanoic acid 32454-35-6 C10H11BrO2 243.1 2,2-二甲基苯乙酸甲酯 methyl 2-methyl-2-phenylpropionate 57625-74-8 C11H14O2 178.231 2-(4-乙酰苯基)-2,2-二甲基-乙酸 2-(4-acetyl-phenyl)-2-methyl-propionic acid 857768-18-4 C12H14O3 206.241 2-甲基-2-苯基丙酸乙酯 ethyl 2-methyl-2-phenylpropionate 2901-13-5 C12H16O2 192.258 比拉斯汀中间体 2-(4-hydroxyethylphenyl)-2-methylpropionic acid ethyl ester 1181267-31-1 C14H20O3 236.311 —— 2-(4-formylphenyl)-2-methylpropionic acid methyl ester 84542-11-0 C12H14O3 206.241 2-甲基-2-苯基丙烷-1-醇 2-methyl-2-phenyl-propan-1-ol 2173-69-5 C10H14O 150.221 —— 2-Ethoxyethyl 2-methyl-2-phenylpropanoate —— C14H20O3 236.311 2-甲基-2-苯基丙醛 2,2-(dimethyl)-2-phenylacetaldehyde 3805-10-5 C10H12O 148.205 2-甲基-2-苯基丙酸叔丁酯 tert-butyl 2-methyl-2-phenylpropanoate 2901-24-8 C14H20O2 220.312 —— pent-4-enyl-2-methyl-2-phenylpropanoate 1160843-11-7 C15H20O2 232.323 2-甲基-2-(4-硝基苯基)-丙酸 2-methyl-2-(4-nitro-phenyl)-propionic acid 42206-47-3 C10H11NO4 209.202 —— 2-(2-Hydroxyphenyl)isobutyric Acid 86549-98-6 C10H12O3 180.203 艾乐替尼中间体 2-(4-ethyl-3-iodophenyl)-2-methylpropionic acid 1256584-73-2 C12H15IO2 318.154 2-[4-(4-氯-丁基)-苯基]-2-甲基-丙酸 2-[4-(4-chloro-butyryl)-phenyl]-2-methyl-propionic acid 169280-21-1 C14H17ClO3 268.74 2-(4-溴苯基)-2-甲基丙烷-1-醇 2-(4-bromophenyl)-2-methylpropan-1-ol 32454-37-8 C10H13BrO 229.117 非索非那定杂质1 Methyl 2-[4-(1-hydroxy-4-chlorobutyl)phenyl]isobutyrate 252022-32-5 C15H21ClO3 284.783 4-[4-氯-1-丁酰基]-A,A-二甲基苯乙酸甲酯 2-[4-(4-Chloro-butyryl)-phenyl]-2-methyl-propionic acid, methyl ester 154477-54-0 C15H19ClO3 282.767 3-甲基-3-苯基丁烷-2-酮 2-methyl-2-phenylbutan-3-one 770-85-4 C11H14O 162.232 (2-甲基-2-苯基-丙基)乙酸酯 (2-acetoxy-1,1-dimethylethyl)benzene 18755-52-7 C12H16O2 192.258 4-(环丙基羰基)-alpha,alpha-二甲基苯乙酸甲酯 2-(4-cyclopropanecarbonyl-phenyl)-2-methyl-propionic acid, methyl ester 880088-78-8 C15H18O3 246.306 —— 2-methyl-2-phenylpropanoyl chloride 36293-05-7 C10H11ClO 182.65 2-甲基-2-苯基丙酰胺 2-methyl-2-phenyl-propanamide 826-54-0 C10H13NO 163.219 4-(4-氯-1-氧代丁基)-alpha,alpha-二甲基苯乙酸乙酯 4-(4-chloro-1-oxobutyl)-α,α-dimethylbenzeneacetic acid ethyl ester 76811-97-7 C16H21ClO3 296.794 4-(1-羟基-2-甲基丙-2-基)苯甲酸 4-(1-hydroxy-2-methylpropan-2-yl)benzoic acid 75492-21-6 C11H14O3 194.23 - 1
- 2
- 3
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:alpha,alpha-二甲基苯乙酸 在 4-二甲氨基吡啶 、 tris(bipyridine)ruthenium(II) dichloride hexahydrate 、 二氢吡啶 、 溶剂黄146 、 N,N'-二环己基碳二亚胺 、 锌 作用下, 以 四氢呋喃 、 二氯甲烷 、 N,N-二甲基甲酰胺 为溶剂, 反应 36.0h, 生成 2-苯基-2-丙醇参考文献:名称:N-(酰氧基)邻苯二甲酰亚胺对Ru-光催化还原脂肪族羧酸的脱羧氧化作用摘要:报道了在钌光氧化还原催化下,脂肪族羧酸衍生物与(2,2,6,6-四甲基哌啶-1-基)氧基(TEMPO)的脱羧氨氧基化反应。关键的转变需要使用Hantzsch酯作为还原剂进行高效的光氧化还原催化循环。随后的烷氧基胺可以很容易地在一个罐中转化为相应的醇,代表了在光氧化还原条件下接触脂肪族醇的另一种方法。DOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.8b01885
-
作为产物:描述:叠氮磷酸二苯酯 在 氢氧化钾 、 4 A molecular sieve 、 三氟化硼乙醚 、 lithium diisopropyl amide 作用下, 以 乙二醇 为溶剂, 反应 68.08h, 生成 alpha,alpha-二甲基苯乙酸参考文献:名称:Kawai, Nobutaka; Shioiri, Takayuki, Chemical and pharmaceutical bulletin, 1983, vol. 31, # 8, p. 2564 - 2573摘要:DOI:
-
作为试剂:描述:苯基乙烯基砜 、 2-(cyclohex-2-en-1-yloxy)-1,10-phenanthroline 在 alpha,alpha-二甲基苯乙酸 、 palladium diacetate 、 silver trifluoroacetate 、 对苯醌 作用下, 以 乙腈 为溶剂, 50.0 ℃ 、101.33 kPa 条件下, 反应 22.0h, 以68%的产率得到(E)-2-((2-(2-(phenylsulfonyl)vinyl)cyclohex-2-en-1-yl)oxy)-1,10-phenanthroline参考文献:名称:钯催化的区域选择性C–H烯基化和烯丙醇的炔基化反应,并带有二齿邻菲咯啉助剂摘要:已开发了钯催化的烯丙基醇与电子缺陷型烯烃的区域选择性C–H烯基化反应。成功的关键是引入双配位菲咯啉指导基团,该基团可以使在烯基C–H键近端的竞争性和区域选择性C–H激活超过竞争性的烯丙基C–O键激活。相同的Pd /菲咯啉系统对于烯丙基醇与炔基溴的C–H炔基化反应有效。DOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.0c03444
文献信息
-
Compositions for Treatment of Cystic Fibrosis and Other Chronic Diseases申请人:Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated公开号:US20150231142A1公开(公告)日:2015-08-20The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising an inhibitor of epithelial sodium channel activity in combination with at least one ABC Transporter modulator compound of Formula A, Formula B, Formula C, or Formula D. The invention also relates to pharmaceutical formulations thereof, and to methods of using such compositions in the treatment of CFTR mediated diseases, particularly cystic fibrosis using the pharmaceutical combination compositions.
-
[EN] 4(PHENYL-PIPERAZINYL-METHYL) BENZAMIDE DERIVATIVES AND THEIR USE FOR THE TREATMENT OF PAIN OR GASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS<br/>[FR] DERIVES DE 4(PHENYL-PIPERAZINYL-METHYL) BENZAMIDE ET LEUR UTILISATION POUR LE TRAITEMENT DE DOULEUR OU DE TROUBLES GASTRO-INTESTINAUX申请人:ASTRAZENECA AB公开号:WO2004041801A1公开(公告)日:2004-05-21Compounds of general formula:[Chemical formula should be inserted here. Please see paper copy] wherein R1, R2, and R3 are as defined in the specification, as well as salts, enantiomers thereof and pharmaceutical compositions including the compounds are prepared. They are useful in therapy, in particular in the management of pain.通式化合物:[化学式应在此处插入。请参阅纸质副本]其中R1、R2和R3如规范中定义,以及其盐、对映体和包括该化合物的药物组合物已经制备。它们在治疗中很有用,特别是在疼痛管理中。
-
Intermediates useful for the preparation of antihistaminic piperidine derivatives申请人:Merrell Pharmaceuticals, Inc.公开号:US06348597B2公开(公告)日:2002-02-19The present invention is related to a novel intermediates and processes which are useful in the preparation of certain antihistaminic piperidine derivatives of the formula wherein W represents —C(═O)— or —CH(OH)—; R1 represents hydrogen or hydroxy; R2 represents hydrogen; R1 and R2 taken together form a second bond between the carbon atoms bearing R1 and R2; n is an integer of from 1 to 5; m is an integer 0 or 1; R3 is —COOH or —COOalkyl wherein the alkyl moiety has from 1 to 6 carbon atoms and is straight or branched each of A is hydrogen or hydroxy; and pharmaceutically acceptable salts and individual optical isomers thereof, with the proviso that where R1 and R2 are taken together to form a second bond between the carbon atoms bearing R1 and R2 or where R1 represented hydroxy, m is an integer 0.
-
Controlling parameters for radical cation fragmentation reactions: Origin of the intrinsic barrier作者:Deepak Shukla、Guanghua Liu、Joseph P Dinnocenzo、Samir FaridDOI:10.1139/v03-078日期:2003.6.1
CC bond cleavages of radical cations of 2-substituted benzothiazoline derivatives were investigated to determine the parameters controlling the fragmentation rate constants. In spite of the low oxidation potentials of the compounds, fragmentation rate constants greater than 1 × 106 s1 could be achieved through weakening of the fragmenting bond by substituents that stabilize the radical fragment and exert steric crowding. A quantitative assessment of the relative roles of radical stabilization vs. steric effects to weaken the fragmenting CC bond was achieved through DFT calculations. The calculated activation enthalpies matched reasonably well with the experimentally determined values. A thermokinetic analysis revealed that the fragmentations of benzothiazoline radical cations have relatively large intrinsic kinetic barriers, ascribed to the delocalized nature of the product radical and cation fragments. Interestingly, the same factors that lead to the large intrinsic barriers led, simultaneously, to large thermodynamic driving forces for the fragmentations, which should lead to lower activation barriers. These effects oppose each other kinetically and provide important insight into the design of fast radical ion fragmentation reactions.Key words: benzothiazoline, radical cation, fragmentation, steric effects, DFT.
2-取代苯并噻唑啉衍生物的自由基阳离子的C-C键裂解进行了研究,以确定控制裂解速率常数的参数。尽管化合物的氧化电位较低,但通过通过取代基使裂解键变弱,从而稳定自由基片段并施加立体阻碍,可以实现大于1×10^6 s^-1的裂解速率常数。通过密度泛函理论(DFT)计算,对自由基稳定与立体效应相对作用于使裂解的C-C键变弱的定量评估取得了成功。计算得到的活化焓与实验测定值相当吻合。热动力学分析显示,苯并噻唑啉自由基阳离子的裂解具有相对较大的固有动力学壁垒,归因于产物自由基和阳离子片段的离域性质。有趣的是,导致大固有壁垒的因素同时导致了裂解的大热力学驱动力,这应该导致较低的活化壁垒。这些效应在动力学上相互对立,并为设计快速自由基离子裂解反应提供了重要见解。关键词:苯并噻唑啉,自由基阳离子,裂解,立体效应,DFT。 -
COMPOSITIONS FOR TREATMENT OF CYSTIC FIBROSIS AND OTHER CHRONIC DISEASES申请人:Van Goor Fredrick F.公开号:US20110098311A1公开(公告)日:2011-04-28The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising an inhibitor of epithelial sodium channel activity in combination with at least one ABC Transporter modulator compound of Formula A, Formula B, Formula C, or Formula D. The invention also relates to pharmaceutical formulations thereof, and to methods of using such compositions in the treatment of CFTR mediated diseases, particularly cystic fibrosis using the pharmaceutical combination compositions.
表征谱图
-
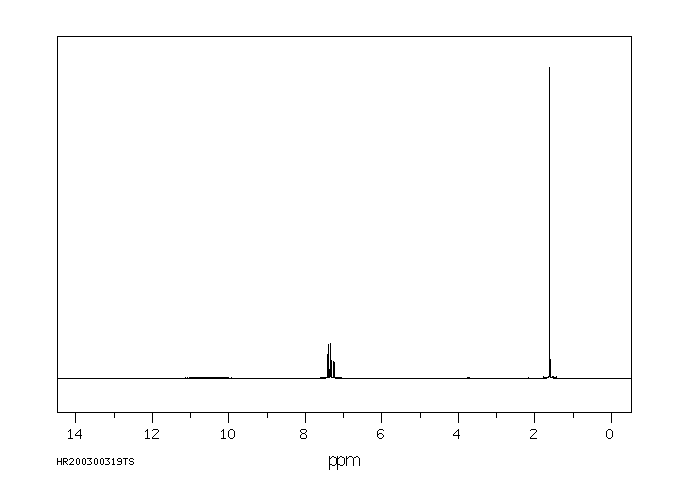
氢谱1HNMR
-
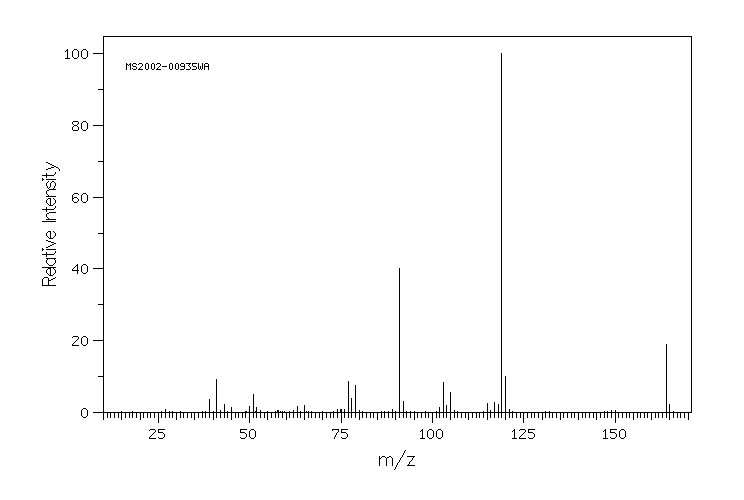
质谱MS
-
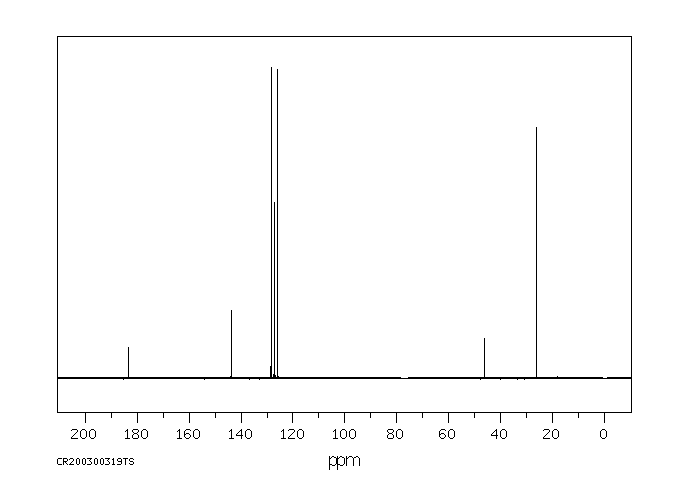
碳谱13CNMR
-
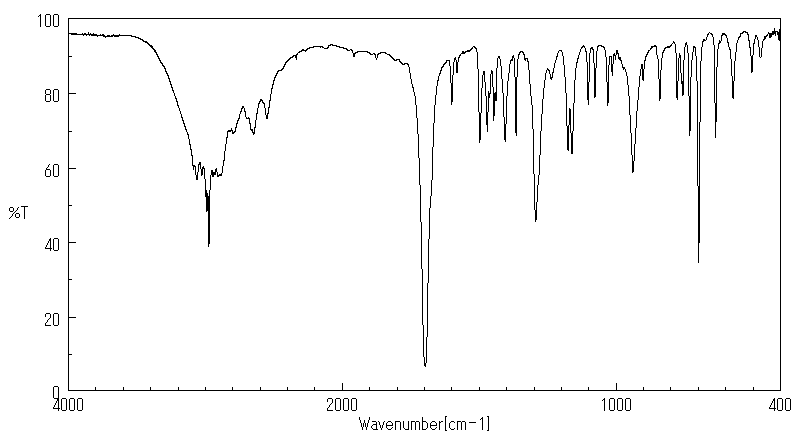
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息