代谢
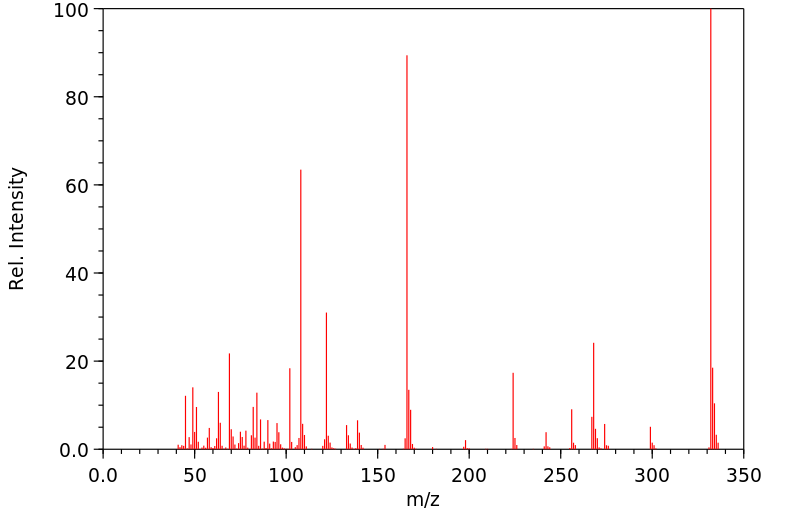
在这项研究中,我们使用含有放射性同位素碳-14(14C)和硫-35(35S)的L-半胱氨酸和2-硫代苯并噻唑(TBT)代谢物,在一系列大鼠实验中研究了2-硫代苯并噻唑代谢物中巯基团中硫原子的代谢命运。实验中,给雄性Wistar大鼠口服了14C标记的N-氧化二乙基-2-苯并噻唑(ODEBT)、35S标记的ODEBT、35S标记的2-巯基苯并噻唑(MBT)和35S标记的2,2'-二苯并噻唑-二硫醚(BTDS)。在72小时内定期收集尿液和粪便,并确定尿中和粪便中的代谢物。在口服ODEBT的大鼠中确定了2-苯并噻唑-巯基尿酸(BTMA)的尿中水平。在口服ODEBT的大鼠中确定了14C或35S标记的L-半胱氨酸的掺入情况。在离体的大鼠肝脏中确定了胆汁代谢物中MBT与谷胱甘肽的结合物。BTDS和MBT的35S保留率超过90%。在BTMA中,只有0.5%的35S被保留。使用35S标记化合物得到的结合型与非结合型放射活性的比率,与使用14C标记化合物得到的比率相比有所降低。同时给予半胱氨酸增加了肝脏中谷胱甘肽水平和巯基尿酸的排泄,而加入谷胱甘肽合成酶抑制剂L-甲硫氨酸-SR-亚砜胺降低了这些水平。这些数据表明,BTMA中的硫原子大部分被来自半胱氨酸池的内源性硫所替代。
The metabolic fate of the sulfur atom in the sulfhydryl group of 2-thiobenzothiazole (TBT) metabolites was examined in a series of experiments in rats using (14)C and (35)S labeled L-cysteine and TBT metabolites. Male Wistar rats were orally administered (14)C labeled N-oxydiethylene-2-benzothiazole ODEBT, (35)S labeled ODEBT, (35)S labeled 2-mercaptobenzothiazole (MBT) and (35)S labeled 2,2'-dibenzothiazyl-disulfide (BTDS). Urine and feces were collected periodically for 72 hours and the urinary and fecal metabolites were determined. The urinary level of 2-benzothiazyl-mercapturic acid (BTMA) was determined in rats administered OCEBT orally. The incorporation of (14)C or (35)S labeled L-cysteine was determined in rats administered ODEBT orally. Glutathione conjugates of MBT from biliary metabolites were determined in rat liver in vitro. The (35)S retention ratios in BTDS and MBT was over 90%. In BTMA only 0.5% of the (35)S was retained. The ratios of conjugated to nonconjugated radioactivity obtained using (35)S labeled compounds were reduced when compared to those found for (14)C labeled compounds. Coadministration of cysteine increased the hepatic glutathione level and mercapturate excretion while inclusion of the glutathione synthetase inhibitor L-methionine-SR-sulfoximine decreased levels. The /data indicate/ that the sulfur atom in BTMA is mostly replaced by the endogenous sulfur from the cysteine pool.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)