1,2-二氯乙烷 | 107-06-2
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:-35 °C (lit.)
-
沸点:83 °C (lit.)
-
密度:1.256 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
-
蒸气密度:3.4 (20 °C, vs air)
-
闪点:60 °F
-
溶解度:7.9g/l
-
介电常数:10.7(20℃)
-
暴露限值:TLV-TWA 10 ppm (~40 mg/m3) (ACGIH), 1 ppm (NIOSH), 50 ppm (MSHA and OSHA); ceiling 2 ppm/15 min (NIOSH); carcinogenicity: Animal Sufficient Evidence, Human Limited Evidence (IARC).
-
LogP:1.45 at 20℃
-
物理描述:Ethylene dichloride appears as a clear colorless liquid with a chloroform-like odor. Flash point 56°F. Denser than water and insoluble in water. Vapors are heavier than air. Density 10.4 lb / gal.
-
颜色/状态:Heavy liquid
-
气味:Pleasant, chloroform-like
-
味道:Sweet taste
-
蒸汽密度:3.4 (NTP, 1992) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:78.9 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
水溶性:-1.06
-
亨利常数:Henry's Law constant = 1.18X10-3 atm-cu m/mole at 25 °C
-
大气OH速率常数:2.48e-13 cm3/molecule*sec
-
稳定性/保质期:
Stable under recommended storage conditions.
-
自燃温度:775 °F (413 °C)
-
分解:Decomposes to vinyl chloride and HCl anove 600 °C.
-
粘度:0.84 cP at 20 °C
-
腐蚀性:Corrodes iron and other metals at elevated temperatures when in contact with water.
-
燃烧热:12.57 kJ/g
-
汽化热:138 Btu/lb = 76.4 cal/g = 3.2X10+5 J/kg
-
表面张力:32.2 dynes/cm = 0.0322 N/m at 20 °C
-
电离电位:11.05 eV
-
气味阈值:Odor Threshold Low: 6.0 [mmHg]; Odor Threshold High: 111.0 [mmHg]; Detection odor threshold from AIHA (mean = 26 ppm)
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.4422 at 25 °C/D
-
保留指数:620 ;628.6 ;660 ;644.8 ;645.4 ;647.7 ;648.2 ;650.1 ;654 ;656.2 ;629 ;632 ;630 ;632 ;633 ;638 ;641 ;645 ;640 ;621 ;606 ;607 ;610 ;632 ;623.7 ;632 ;632 ;632 ;627 ;628.9 ;626.6 ;633 ;630 ;632 ;632 ;630 ;631 ;631.4 ;632 ;631 ;623
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):1.5
-
重原子数:4
-
可旋转键数:1
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:1.0
-
拓扑面积:0
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:0
ADMET
安全信息
-
职业暴露等级:B
-
职业暴露限值:TWA: 1 ppm (4 mg/m3), STEL: 2 ppm (8 mg/m3) (Chloroethanes)
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:3
-
立即威胁生命和健康浓度:50 ppm
-
危险品标志:F,T
-
安全说明:S16,S24,S45,S53,S7
-
危险类别码:R22,R45,R36/37/38,R11
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:2903150000
-
危险品运输编号:UN 1184 3/PG 2
-
危险类别:3
-
RTECS号:KI0525000
-
包装等级:II
-
危险标志:GHS02,GHS06,GHS08
-
危险性描述:H225,H302,H315,H319,H331,H335,H350
-
危险性防范说明:P201,P210,P280,P308 + P313,P370 + P378,P403 + P235
-
储存条件:储存于阴凉、通风良好的库房中,并远离火种与热源。库温不宜超过37℃,确保容器密封。避免与氧化剂、酸类、碱类及食用化学品混存,以防发生危险。使用防爆型照明和通风设施,并禁止使用易产生火花的机械设备和工具。储存区应配备泄漏应急处理设备和合适的收容材料。
SDS
| 国标编号: | 32035 |
| CAS: | 107-06-2 |
| 中文名称: | 1,2-二氯乙烷 |
| 英文名称: | 1,2-dichloroethane |
| 别 名: | 乙撑二氯;亚乙基二氯;1,2-二氯化乙烯;二氯乙烷(对称) |
| 分子式: | C 2 H 4 Cl 2 ;Cl(CH 2 ) 2 Cl |
| 分子量: | 98.97 |
| 熔 点: | -35.7℃ |
| 密 度: | 相对密度(水=1)1.26; |
| 蒸汽压: | 13℃ |
| 溶解性: | 微溶于水,可混溶于醇、醚、氯仿 |
| 稳定性: | 稳定 |
| 外观与性状: | 无色或浅黄色透明液体,有类似氯仿的气味 |
| 危险标记: | 7(中闪点易燃液体) |
| 用 途: | 用作蜡、脂肪、橡胶等的溶剂及谷物杀虫剂 |
2.对环境的影响:
一、健康危害
侵入途径:吸入、食入、经皮吸收。 健康危害:对眼睛及呼吸道有刺激作用;吸入可引起肺水肿;抑制中枢神经系统、刺激胃肠道和引起肝、肾和肾上腺损害。皮肤与液体反复接触能引起皮肤干燥、脱屑和裂隙性皮炎。液体和蒸气还能刺激眼,引起严重操作,角膜混浊。吸入高浓度的蒸气能刺激粘膜,抑制中枢神经系统,引起眩晕、恶心、呕吐、精神错乱,有的可致肺水肿。还能刺激胃肠道,引起肝和肾的脂肪性病变,严重的直至死亡。 急性中毒:其表现有二种类型,一为头痛、恶心、兴奋、激动,严重者很快发生中枢神经系统抑制而死亡;另一类型以胃肠道症状为主,呕吐、腹痛、腹泻,严重者可发生肝坏死和肾病变。急性暴露能导致呼吸和循环衰竭而死亡。其尸体剖检呈现出大多数内脏损伤和广泛性出血。
二、毒理学资料及环境行为
毒性:属高毒类,蒸气有剧毒。 急性毒性:LD50670mg/kg(大鼠经口);2800mg/kg(兔经皮);LC504050mg/m3,7小时(大鼠吸入) 刺激性:家兔经眼:63mg,重度刺激。家兔经皮开放性刺激试验:625mg,轻度刺激。 亚急性和慢性毒性:猴吸入0.22g/m3,7小时/天,5天/周,125次,无症状;4.11g/m3,7小时/天,5天/周,25~50次,死亡率较高;大鼠吸入4.11g/m3×7小时/日×5日/周×3~14次,致死;豚鼠吸入4.113×7小时/日×2次,致死。 致突变性:DNA抑制:人淋巴细胞5ml/L。哺乳动物体细胞突变:人淋巴细胞100mg/L。 生殖毒性:大鼠吸入最低中毒浓度(TCL0):300ppm(7小时,孕6-15天),引起植入死亡率增加。 致癌性:IARC致癌性评论:动物阳性,人类可疑。小/大鼠吸入250ppm×7小时/日×18月,终身未见肿瘤发病率增高;大鼠经口25ppm×5天/周×78周,致癌阳性。
污染来源:1,2-二氯乙烷用于制造乙二醇、乙二胺、聚氯乙烯、尼龙、粘胶人造纤维、苯乙烯-丁二烯橡胶和各种塑料、香料、肥皂、粘合剂、润肤剂、药物及假漆;用作树脂、沥青、橡胶、醋酸纤维素、纤维素酯、油漆、油脂、蜡及聚合物(如聚苯乙烯的溶剂),豆油和咖啡因的提取剂;浸渍剂、湿润剂、渗透剂、熏蒸剂;还用于照像术、静电印刷、水软化中。裂解法制造氯乙烯单体时可产生二氯乙烷;二氯乙烷也是某些有机化学合成中的副产品。在以上生产和使用1,2-二氯乙烷的企业在生产和贮运过程中由于意外事故均可对环境造成污染,对人体造成危害。
代谢和降解:氯乙醇是1,2-氯乙烷在温血动物体内的主要代谢物之一。进入体内的1,2-二氯乙 烷首先贮存于脂肪组织中,以后(2天内)从脂肪组织转移进入血液,由于酶的脱氢作用,代谢转化变成氯乙醇,氯乙醇系一种高毒化学物质。它进一步代谢可变成一氯乙酸,氯乙醛是介于氯乙烷与一氯乙酸之间的又一个中间代谢产物。在1,2-二氯乙烷代谢产物中,氯乙醇和一氯乙酸的毒性比二氯乙烷本身更大。CH2Cl- - -CH2OH- -CHO- -COOH 在环境中,二氯乙烷代谢生成氯乙酸的速度,随湿度与温度的增加而加快,在90℃的湿空气中,二氯乙烷有0.66%分解生成氯乙酸,当温度升高到110℃和140℃时,氯乙酸含量分别为4%和7%-12%。1,2-二氯乙烷在常温和干燥的环境中较难被降解。光与大气中氧对纯品二氯乙烷很少发生影响,而含有杂质的工业品二氯乙烷受到光与所的联合作用可产生光气和某些聚合化学物。 残留、蓄积与扩散:二氯乙烷能迅速透进无损伤皮肤吸收并在血液中达很高水平。不论染毒剂量和途径怎样,二氯乙烷在人体和动物体各个器官内的含量关系基本上是个常数,例如假定在血液中的含量为1,那么在其它各器官中相应比率为:肝脏0.8;肾脏0.44;心脏0.7;延脑0.57;小脑、脑皮质和皮质下的中枢为0.15-0.2,显然这与该组织中的脂肪含量有关,因为二氯乙烷在脂肪中的溶解度是很大的。氯乙烷可以通过以代谢物的形式从人体和动物各个系统排出,二氯乙烷可以经肾脏从尿中排出,出可以通过呼气排出。 危险特性:易燃,其蒸气与空气可形成爆炸性混合物。遇明火、高热能引起燃烧爆炸。受高热分解产生有毒的腐蚀性烟气。与氧化剂接触发生反应,遇明火、高热易引起燃烧,并放出有毒气体。其蒸气比空气重,能在较低处扩散到相当远的地方,遇明火会引着回燃。 燃烧(分解)产物:一氧化碳、二氧化碳、氯化氢、光气。
3.现场应急监测方法:
直接进水样气相色谱法快速检测管法;便携式气相色谱法《突发性环境污染事故应急监测与处理处置技术》万本太主编
4.实验室监测方法:
| 监测方法 | 来源 | 类别 |
| 溶剂解吸气相色谱法 | WS/T138-1999 | 作业场所空气 |
| 无泵型采样气相色谱法 | WS/T154-1999 | 作业场所空气 |
| 气相色谱法; 吡啶-碱比色法 | 《空气中有害物质的测定方法》(第二版),杭士平编 | 空气 |
| 气相色谱法 | 《固体废弃物试验与分析评价手册》中国环境监测总站等译 | 固体废弃物 |
| 硫氰酸汞比色法 | 《化工企业空气中有害物质测定方法》,化学工业出版社 | 化工企业空气 |
| 吹扫捕集-气相色谱法 | 中国环境监测总站 | 水质 |
| 色谱/质谱法 | 美国EPA524.2方法 | 水质 |
5.环境标准:
| 中国(TJ36-79) | 车间空气中有害物质的最高容许浓度 | 25mg/m 3 |
| 中国(待颁布) | 饮用水源中有害物质的最高容许浓度 | 0.03mg/L |
| 中国(GHZB1-1999) | 地表水环境质量标准(I、II、III类水域) | 0.005mg/L |
| 日本(1993) | 环境标准 | 地面水:0.004mg/L 废水:0.004mg/L 土壤浸出液:0.004mg/L |
6.应急处理处置方法:
一、泄漏应急处理
迅速撤离泄漏污染区人员至安全区,并进行隔离,严格限制出入。切断火源。1,2-二氯乙烷与四氯化碳的物理特征相似,故在土壤和水体受到其污染后可用相同的处置技术。 ⑴1,2-二氯乙烷,发生于地面上的污染事故紧急处理方法: ①迅速用土、沙子或其它可以取到的材料筑成坝以阻止液体的流动,特别要防止其流入附近的水体中,用土壤将其覆盖并将其吸收。也可以在其流动的下方向挖一坑,将其收集在坑内以防四处扩散,然后将液体收集到合适的容器中。 ②在处理过程中不要用铁器(如铁勺、铁容器、铁铲等),应改用其它工具,因为铁有助于1,2-二氯乙烷分解生成毒性更大的光气。有条件的话,操作人员在处理过程中应戴上防毒面具,或其它防护设备。 ③将受污染的土壤清除剥离后集中进行处理,有以下几种方法可视情况选用: a.加热土壤并加水,使1,2-二氯乙烷生成甲酸、一氧化碳和盐酸; b.将浓碱液加入到土壤中使其与1,2-二氯乙烷反应生成一氧化碳; c.将稀的氢氧化钠或氢氧化钾加入土壤中,使其与1,2-二氯乙烷反应生成甲酸钠或甲酸钾; 以上操作应避免在光照条件下进行。 d.对土壤进行焚烧处理,要保证完全燃烧,以防止光气产生。 ⑵由于1,2-二氯乙烷在环境中很稳定,可利用其易挥发的特点进行自然或人工强制性挥发至大气中。当有大量气态1,2-二氯乙烷挥发弥散时,应疏散污染源下风向的人群,以防中毒。 ⑶水体中受到污染时的处理处置技术:当1,2-二氯乙烷液体进入水体后,应设法阻断受污染水域与其它水域的通道,其方法为筑坝使其停止流动;开沟使其流向另一水体(如排污渠)等等。由于四氯甲烷属挥发性卤代烃类,对受其污染的水体最为简便易行处理方法是使用曝气(包括深进曝气)法,使其迅速从水体中逸散到大气中。另外,处理土壤的几种方法也可酌情使用。 废弃物处置方法:用焚烧法。废料同其他燃料混合后焚烧。燃烧要充分,防止生成光气。焚烧炉排气中的卤化氢通过酸洗涤器除去。
二、防护措施
呼吸系统防护:空气中浓度超标时,应该佩戴过滤式防毒面具(半面罩)。紧急事态抢救可撤离时,佩戴隔离式呼吸器。 眼睛防护:戴化学安全防护眼镜。 身体防护:穿防静电工作服。 手防护:戴橡胶手套。 其它:工作现场禁止吸烟、进食和饮水。工作毕,淋浴更衣。注意个人清洁卫生。
三、急救措施
皮肤接触:脱去被污染的衣着,用肥皂水和清水彻底冲洗皮肤。 眼睛接触:提起眼睑,用流动清水或生理盐水冲洗。就医。 吸入:迅速脱离现场至空气新鲜处。保持呼吸道通畅。如呼吸困难,给输氧。如呼吸停止,立即进行人工呼吸。就医。 食入:洗胃。就医。
灭火方法:喷水冷却容器,可能的话将容器从火场移至空旷处。处在火场中的容器若已变色或从安全泄压装置中产生声音,必须马上撤离。灭火剂:泡沫、干粉、二氧化碳、砂土。用水灭火无效。
制备方法与用途
- 毒性:LD₅₀为770 mg/kg(大鼠,经口)。ADI尚未规定(FAO/WHO,2001)。
-
食品添加剂最大允许使用量和残留标准:
- 添加剂中文名称:1,2-二氯乙烷
- 允许使用该种添加剂的食品中文名称:食品
- 添加剂功能:食品工业用加工助剂
- 最大允许使用量(g/kg):/
- 最大允许残留量(g/kg):食品工业用加工助剂一般应在制成最后成品之前除去,有规定食品中残留量的除外。成品中最高允许残留量为30 mg/kg。
- 主要用于制造氯乙烯、乙二酸和乙二胺,还可作溶剂、谷物熏蒸剂、洗涤剂、萃取剂、金属脱油剂等。
- 用作溶剂
- 用作有机溶剂和油脂的萃取剂,也用于有机合成。
- 1,2-二氯乙烷是杀菌剂稻瘟灵和植物生长调节剂矮壮素的中间体。
- 抽提溶剂。主要用于由香辛料抽提油树脂,成品中最高允许残留量为30 mg/kg。
- GB 2760-96列为食品加工助剂。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 氯乙烷 chloroethane 75-00-3 C2H5Cl 64.5147 1,1,2-三氯乙烷 1,1,2-trichloroethane 79-00-5 C2H3Cl3 133.405 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 氯乙烷 chloroethane 75-00-3 C2H5Cl 64.5147 1,1,2-三氯乙烷 1,1,2-trichloroethane 79-00-5 C2H3Cl3 133.405
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:Production of halo-nitro-alkanes摘要:公开号:US02345701A1
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:保留在壳中:乙炔盐酸中高性能石墨烯限制的钌纳米粒子。摘要:钌基催化剂在通过乙炔氢氯化生产聚氯乙烯中的潜在应用受到阻碍,因为它们的活性和稳定性均比金基体系低,尽管价格低4倍。结合深入的表征和动力学分析,我们揭示了掺杂在氮掺杂碳(NC)上的最佳纳米尺寸为1.5 nm的钌纳米粒子的优越活性,并确定了它们的失活模式:1)纳米粒子再分散为非活性单原子和2)焦炭在金属部位形成。调节NC载体的密度可以在1073 K下将钌纳米颗粒催化包封到单层石墨烯壳中,从而防止不希望的金属再分散。最后,DOI:10.1002/anie.201906916
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:钌和碘阴离子共催化级联二卤化和内部炔系环己二烯与 1,2-二卤乙烷的环化摘要:我们建立了一种高效的钌(II)和碘阴离子共催化二卤化和内炔束缚环己二烯酮的级联环化,其在温和条件下以高产率立体选择性地提供了大量具有生物活性氢苯并呋喃骨架的二卤化产物。在该转化中,反应途径由亲电子碘试剂的浓度决定,这也为控制反应选择性提供了策略。此外,该方法的特点是通过碘阴离子催化剂使用1,2-二卤乙烷作为卤素源。DOI:10.1021/acs.joc.4c00951
文献信息
-
[EN] BCR-ABL TYROSINE-KINASE LIGANDS CAPABLE OF DIMERIZING IN AN AQUEOUS SOLUTION, AND METHODS OF USING SAME<br/>[FR] LIGANDS DE TYROSINE-KINASE BCR-ABL CAPABLES DE SE DIMÉRISER DANS UNE SOLUTION AQUEUSE, ET PROCÉDÉS D'UTILISATION DE CEUX-CI申请人:COFERON INC公开号:WO2015106292A1公开(公告)日:2015-07-16Described herein are monomers capable of forming a biologically useful multimer when in contact with one, two, three or more other monomers in an aqueous media. In one aspect, such monomers may be capable of binding to another monomer in an aqueous media (e.g. invivo) to form a multimer (e.g. a dimer). Contemplated monomers may include a ligand moiety, a linker element, and a connector element that joins the ligand moiety and the linker element. In an aqueous media, such contemplated monomers may join together via each linker element and may thus be capable of modulating one or more biomolecules substantially simultaneously, e.g., modulate two or more binding sites on a Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase.
-
DIHYDROPYRIDAZINE-3,5-DIONE DERIVATIVE AND PHARMACEUTICALS CONTAINING THE SAME申请人:CHUGAI SEIYAKU KABUSHIKI KAISHA公开号:US20160002251A1公开(公告)日:2016-01-07The present invention provides a dihydropyridazine-3,5-dione derivative or a salt thereof, or a solvate of the compound or the salt, a pharmaceutical drug, a pharmaceutical composition, a sodium-dependent phosphate transporter inhibitor, and a preventive and/or therapeutic agent for hyperphosphatemia, secondary hyperparathyroidism, chronic renal failure, chronic kidney disease, and arteriosclerosis associated with vascular calcification comprising the compound as an active ingredient, and a method for prevention and/or treatment.
-
NMDA (n-methyl-d-aspartate) antagonists申请人:Hoechst Marion Roussell, Inc.公开号:US05922752A1公开(公告)日:1999-07-13The present invention is new excitatory amino acid antagonists (herein referred to as compounds of formula (1)): below: ##STR1## These new antagonists are useful as NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate) antagonists.
-
Novel phenylacetic acid derivatives申请人:Schering Aktiengesellschaft公开号:US04407823A1公开(公告)日:1983-10-04Phenylacetic acid derivatives of the formula ##STR1## wherein n is an integer of 2 to 5; ##STR2## R.sub.1 is hydrogen, halogen, trifluoromethyl, nitro or amino; R.sub.2 and R.sub.3 each independently is hydrogen or lower alkyl; or together form an ethylene group; X.sub.1 represents two hydrogen atoms or an oxo group; and Y.sub.1 is cyano, hydroxyamidocarbonyl, carbamoyl, 5-tetrazolyl or carboxyl; and for derivatives wherein Y is carboxyl, salts thereof with physiologically compatible bases, esters thereof from physiologically acceptable alcohols and amides thereof from physiologically acceptable amines have valuable pharmacological activity, e.g., as antiinflammatory agents.
-
[EN] SELF-IMMOLATIVE LINKERS CONTAINING MANDELIC ACID DERIVATIVES, DRUG-LIGAND CONJUGATES FOR TARGETED THERAPIES AND USES THEREOF<br/>[FR] LIEURS AUTO-IMMOLABLES CONTENANT DES DÉRIVÉS D'ACIDE MANDÉLIQUE, CONJUGUÉS MÉDICAMENT-LIGAND POUR THÉRAPIES CIBLÉES, ET LEURS UTILISATIONS申请人:ASANA BIOSCIENCES LLC公开号:WO2015038426A1公开(公告)日:2015-03-19The invention provides a therapeutic drug and targeting conjugate, pharmaceutical compositions containing these conjugates in pharmaceutical composition, and uses of these conjugates in anti-neoplastic and other therapeutic regimens. Also provided are novel intermediates thereof. The conjugates provide a therapeutic drug fragment or prodrug fragment bound to a targeting moiety via a linker which comprises a substrate cleavable by a protease such as Cathepsin B. The targeting moiety is a ligand which targets a cell surface molecule, such as a cell surface receptor on an anti-neoplastic cell. The ligand may function solely as a targeting moiety or may itself have a therapeutic effect. Following administration of the therapeutic drug and targeting conjugate of formula I and exposure of the conjugate to the protease specific for the substrate, the linker is cleaved and the targeting moiety is separated from the conjugate, which causes the drug fragment or prodrug fragment to convert to the drug or prodrug. The recited conjugates are useful in anti-neoplastic therapies. Also provided are methods of making the therapeutic drug and targeting conjugates and intermediates thereof, and kits comprising the therapeutic drug and targeting conjugates.该发明提供了一种治疗药物和靶向共轭物,包含这些共轭物的药物组合物,以及这些共轭物在抗肿瘤和其他治疗方案中的用途。还提供了其新颖的中间体。这些共轭物通过一个由蛋白酶如半胱氨酸蛋白酶B可切割的底物组成的连接物将治疗药物片段或前药片段与靶向基团结合。靶向基团是一个以细胞表面分子为靶点的配体,例如抗肿瘤细胞上的细胞表面受体。该配体可能仅作为靶向基团,也可能本身具有治疗效果。在给药公式I的治疗药物和靶向共轭物并使共轭物暴露于特异于底物的蛋白酶的情况下,连接物被切割,靶向基团与共轭物分离,导致药物片段或前药片段转化为药物或前药。所述的共轭物在抗肿瘤疗法中很有用。还提供了制备治疗药物和靶向共轭物及其中间体的方法,以及包含治疗药物和靶向共轭物的试剂盒。
表征谱图
-
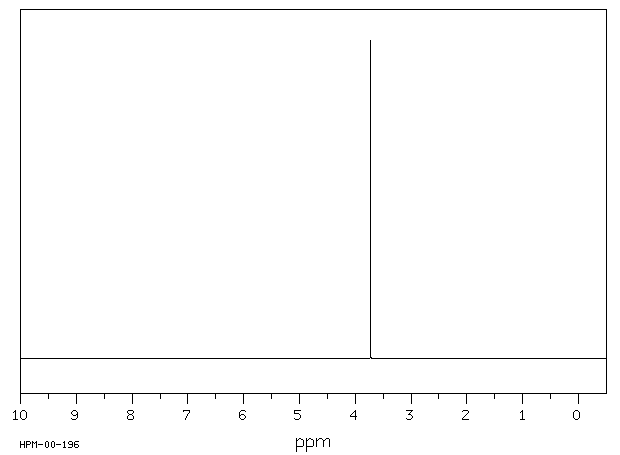
氢谱1HNMR
-
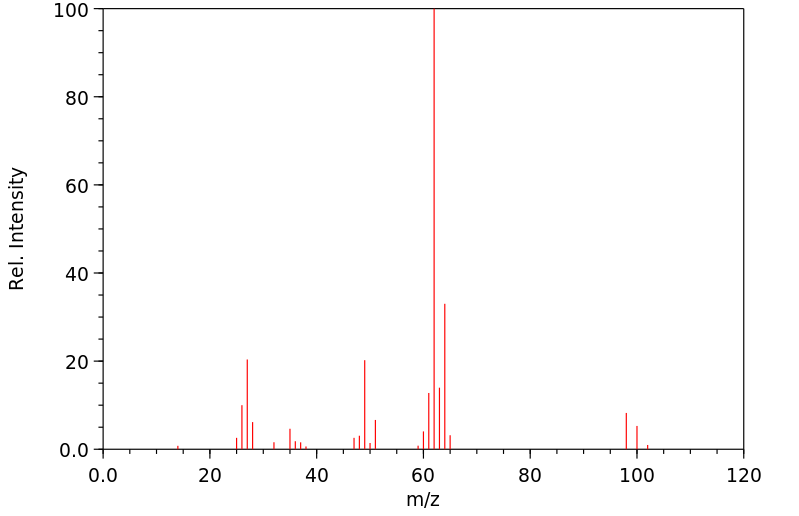
质谱MS
-
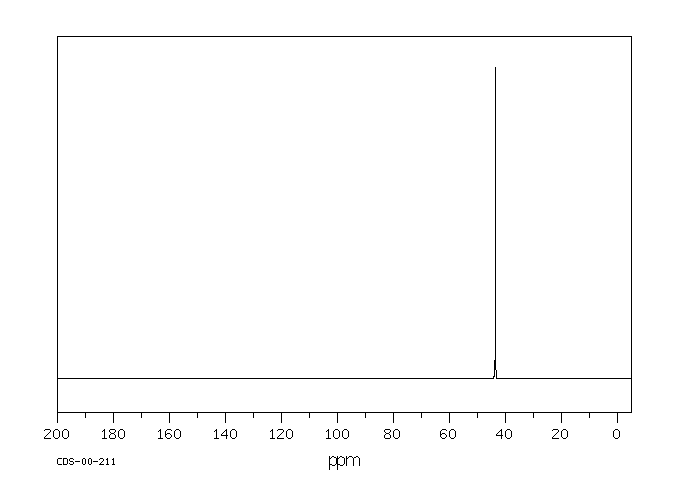
碳谱13CNMR
-
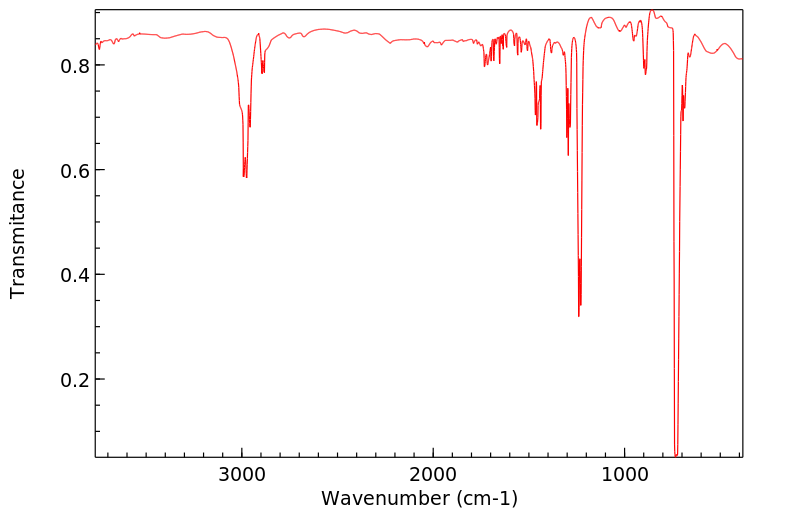
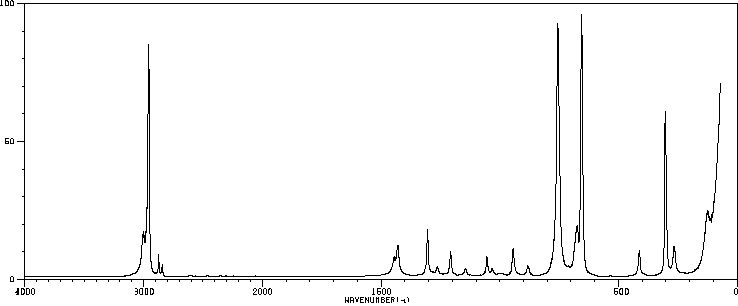
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息