代谢
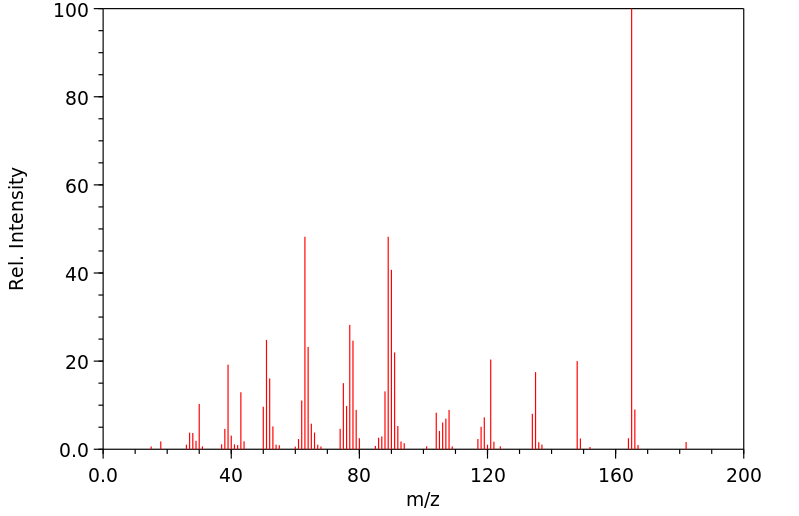
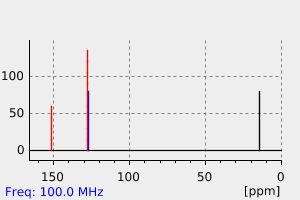
接触二硝基甲苯的工人水解尿液中含有2,4-和2,6-DNT、2,4-和2,6-二硝基苯甲酸、2,4-和2,6-二硝基苄醇、2-氨基-4-硝基苯甲酸以及2-(N-乙酰基)氨基-4-硝基苯甲酸。...个别受试者尿液中2,4-和2,6-DNT代谢物的百分比从79%到93%不等。
Hydrolyzed urine from workers exposed to dinitrotoluene contained 2,4- and 2,6-DNT, 2,4- and 2,6-dinitrobenzoic acid, 2,4- and 2,6-dinitrobenzyl alcohol, 2-amino-4-nitrobenzoic acid, and 2-(N-acetyl)amino-4-nitrobenzoic acid. ... The percentages of 2,4- and 2,6-DNT metabolites in the urine of individual subjects ranged from 79% to 93%.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)