2-甲基-2-丁醇 | 75-85-4
物质功能分类
中文名称
2-甲基-2-丁醇
中文别名
叔戊醇;二甲基乙基甲醇;TAA;二甲基二丁醇
英文名称
tert-Amyl alcohol
英文别名
tert-pentyl alcohol;2-methyl-2-butanol;2-methylbutan-2-ol;t-amyl alcohol;tert-pentanol
CAS
75-85-4
化学式
C5H12O
mdl
MFCD00004478
分子量
88.1497
InChiKey
MSXVEPNJUHWQHW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:-12 °C
-
沸点:102 °C(lit.)
-
密度:0.805 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
-
蒸气密度:3 (vs air)
-
闪点:20 °C
-
溶解度:与醇、醚、苯、可溶于氯仿、甘油、油类和丙酮混溶。
-
介电常数:11.7(20℃)
-
LogP:0.890
-
物理描述:Tert-amyl alcohol appears as a clear, colorless liquid with an odor of camphor. Slightly soluble in water.
-
颜色/状态:Colorless liquid
-
气味:Characteristic odor
-
味道:Burning taste
-
蒸汽压力:16.7 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
亨利常数:1.38e-05 atm-m3/mole
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
自燃温度:819 °C
-
粘度:3.79 centipoise at 25 °C
-
燃烧热:789.45 kcal/mol at 25 °C
-
汽化热:40.11 kJ/mol at boiling point
-
表面张力:22.77 dyne/cm at 20 °C; 21.89 dyne/cm at 30 °C
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.4052 at 20 °C/4 °C
-
保留指数:614;625;628;644;652;628;642;644;652;662;628;642;644;652;662;625;628;622;628;626;628;628;628;631;622.9;619;626;658;628;629;628;636;626;636
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):0.9
-
重原子数:6
-
可旋转键数:1
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:1.0
-
拓扑面积:20.2
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:1
ADMET
代谢
...对叔戊基甲基醚(TAME)在大鼠和一名志愿者体内的生物转化进行了研究,在吸入(12)C-或(13)C标记的TAME后。此外,还研究了叔戊醇[(13)C]在大鼠灌胃后的生物转化。...大鼠(两雄两雌)分别暴露于2000 ppm [(12)C]-或[(13)C]TAME 6小时,并收集48小时的尿液。以(13)C NMR信号的相对强度为依据,将自由态和葡萄糖苷化的2-甲基-2,3-丁二醇以及叔戊醇的葡萄糖苷酸定为主要尿液代谢物。根据(13)C NMR,还表明存在几种次要代谢物,它们被鉴定为叔戊醇、2-羟基-2-甲基丁酸和3-羟基-3-甲基丁酸。一名志愿者通过吸入2升气袋中的27,000 ppm [(13)C]TAME 初始浓度4分钟,并分析了尿液中TAME的代谢物通过(13)C NMR。在大鼠中鉴定的所有TAME代谢物也存在于人类尿液中。为了研究叔戊醇的生物转化,雄性大鼠(n = 3)通过灌胃250 mg/kg [(13)C]-叔戊醇溶解在玉米油中处理,并收集48小时的尿液。尿液样本的(13)C NMR显示了与[(13)C]TAME处理的大鼠尿液中相同的代谢物存在。我们的结果表明,TAME在大鼠和人类体内广泛代谢为叔戊醇,叔戊醇可能进一步氧化为二醇和羧酸。这些反应可能是由细胞色素P450依赖性氧化介导的。
... the biotransformation of tert-Amyl methyl ether (TAME) /was studied/ in rats and one human volunteer after inhalation of (12)C- or (13)C-labeled TAME. In addition, the biotransformation of [(13)C]-tert-amyl alcohol was studied in rats after gavage. ... Rats (two males and two females) were individually exposed to 2000 ppm [(12)C]- or [(13)C]TAME for 6 hr, and urine was collected for 48 hr. Free and glucuronidated 2-methyl-2,3-butanediol and a glucuronide of tert-amyl alcohol were identified ... as major urinary metabolites on the basis of the relative intensities of the (13)C NMR signals. The presence of several minor metabolites was also indicated by (13)C NMR; they were identified as tert-amyl alcohol, 2-hydroxy-2-methylbutyric acid, and 3-hydroxy-3-methylbutyric acid. One human volunteer was exposed to an initial concentration of 27,000 ppm [(13)C]TAME by inhalation for 4 min from a 2 L gas sampling bag, and metabolites of TAME excreted in urine were analyzed by (13)C NMR. All TAME metabolites identified in rats were also present in the human urine samples. To study tert-amyl alcohol biotransformation, male rats (n = 3) were treated with 250 mg/kg [(13)C]-tert-amyl alcohol dissolved in corn oil by gavage, and urine was collected for 48 hr. (13)C NMR of the urine samples showed the presence of metabolites identical to those in the urine of [(13)C]TAME-treated rats. Our results suggest that TAME is extensively metabolized by rats and humans to tert-amyl alcohol which may be further oxidized to diols and carboxylic acids. These reactions are likely mediated by cytochrome P450-dependent oxidations.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
该研究的目的是使用基于生理学的药代动力学(PBPK)模型来描述叔戊基甲基醚(TAME)及其主要代谢物叔戊醇(TAA)在雄性Fischer-344大鼠体内的处置情况。TAME和TAA的模型室是流量受限的。TAME的生理模型有6个室:肺、肝、快速灌注组织、慢速灌注组织、脂肪和肾脏。TAA模型有3个室:肺、肝和总体水。这两个模型通过TAME在肝脏中代谢为TAA而相互连接。模型模拟与从雄性Fischer-344大鼠在6小时吸入2500、500或100 ppm TAME暴露期间和之后采集的TAME和TAA血液浓度数据进行了比较。当包括两个可饱和的TAME氧化途径时,PBPK模型预测了TAME的药代动力学。包括TAA氧化和葡萄糖醛酸苷结合途径的TAA模型,在暴露后较晚时间点的实验数据收集时预测偏低。为了解释这一时期的生物过程,提出了三种假设:TAA的非特异性结合、TAA的扩散限制传输和TAA葡萄糖醛酸苷的肠肝循环。这些假设通过三种不同的模型结构进行了测试。视觉检查和最大似然技术的统计分析表明,包含TAA非特异性结合的模型与数据的拟合效果最好。
... The objective of this study was to use a physiologically-based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) model to describe the disposition of tert-amyl methyl ether (TAME) and its major metabolite, tert-amyl alcohol (TAA), in male Fischer-344 rats. The model compartments for TAME and TAA were flow-limited. The TAME physiological model had 6 compartments: lung, liver, rapidly perfused tissues, slowly perfused tissues, fat, and kidney. The TAA model had 3 compartments: lung, liver, and total-body water. The 2 models were linked through metabolism of TAME to TAA in the liver. Model simulations were compared with data on blood concentrations of TAME and TAA taken from male Fischer-344 rats during and after a 6-hour inhalation exposure to 2500, 500, or 100 ppm TAME. The PBPK model predicted TAME pharmacokinetics when 2 saturable pathways for TAME oxidation were included. The TAA model, which included pathways for oxidation and glucuronide conjugation of TAA, underpredicted the experimental data collected at later times postexposure. To account for biological processes occurring during this time, three hypotheses were developed: nonspecific binding of TAA, diffusion-limited transport of TAA, and enterohepatic circulation of TAA glucuronide. These hypotheses were tested using three different model structures. Visual inspection and statistical evaluation involving maximum likelihood techniques indicated that the model incorporating nonspecific binding of TAA provided the best fit to the data. ...
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
... tert-戊基甲基醚(TAME)的生物转化在吸入4和40 ppm的... TAME ... 4小时后在人类和大鼠中进行了研究,并在人类摄入5和15 mg水中的... TAME后对其生物转化进行了研究。.../摄入后/ 戊醇(TAA),自由的和葡萄糖苷化的2-甲基-2,3-丁二醇(TAA的葡萄糖苷酸),2-羟基-2-甲基丁酸和3-羟基-3-甲基丁酸被确定为TAME的代谢物。吸入后... TAME /被/大鼠和人类迅速吸收;在暴露结束后,通过呼气和生物转化为尿液代谢物从血液中清除醚的过程在大鼠和人类中的半衰期小于7小时。... TAME的生物转化在大鼠和人类中在性质上是相似的,但代谢途径不同。在人类中,2-甲基-2,3-丁二醇,2-羟基-2-甲基丁酸和3-羟基-3甲基丁酸作为主要的尿液产物被回收。然而,在大鼠中,2-甲基-2,3-丁二醇及其葡萄糖苷酸是尿液中回收的主要TAME代谢物。摄入后... TAME /被/... 从胃肠道迅速吸收。肝脏首过代谢... 没有观察到,并且很大一部分给药剂量被转移到血液中并通过呼气清除。摄入和吸入暴露后... TAME的代谢途径和排泄动力学是相同的。...
The biotransformation of ... tert-amyl methyl ether (TAME) was studied in humans and in rats after inhalation of 4 and 40 ppm of ... TAME ... for 4 hours, and the biotransformation of ... TAME was studied after ingestion exposure in humans to 5 and 15 mg in water. .../Following ingestion/ tert-Amyl alcohol (TAA), free and glucuronidated 2-methyl-2,3-butanediol (a glucuronide of TAA), 2-hydroxy-2-methyl butyrate, and 3-hydroxy-3-methyl butyrate were found to be metabolites of TAME. After inhalation ... TAME /was/ rapidly taken up by both rats and humans; after termination of exposure, clearance from blood of the ethers by exhalation and biotransformation to urinary metabolites occurred with half-times of less than 7 hours in rats and humans. ... Biotransformation of TAME was qualitatively similar in rats and humans, but the metabolic pathways were different. In humans, 2-methyl-2,3-butanediol, 2-hydroxy-2-methyl butyrate, and 3-hydroxy-3methyl butyrate were recovered as major urinary products. In rats, however, 2-methyl-2,3-butanediol and its glucuronide were major TAME metabolites recovered in urine. After ingestion ... TAME /was/ ... rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Hepatic first-pass metabolism ... was not observed, and a significant part of the administered dose was transferred into blood and cleared by exhalation. Metabolic pathways for ... TAME and kinetics of excretion were identical after ingestion and inhalation exposures. ...
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
... ICR品系雄性小鼠暴露于大约5%的异戊烷中一小时,同时维持环境空气中的氧气浓度在大约20%。然后收集它们的血液和肝脏组织,并通过气相色谱和气相色谱-质谱(GC和GC-MS)进行分析。由此获得的代谢物包括3-甲基-2-丁醇、2-甲基-2-丁醇和3-甲基-2-丁酮。在存在NADPH生成系统的条件下,肝脏微粒体被用来与饱和...异戊烷水溶液在37摄氏度下反应一小时。结果,产生了与暴露实验中获得的相同代谢物。因此,建议...异戊烷主要通过肝脏微粒体代谢。ICR品系雄性小鼠连续四天喂食80 mg/kg体重的苯巴比妥,并暴露于...异戊烷中一小时。这导致在异戊烷吸入实验中2-甲基-2-丁醇的量增加。...
... Male mice of ICR strain were exposed to about 5% /isopentane/ for one hour while the oxygen in the environmental air was maintained at about 20%. Then their blood and liver tissue were collected and analyzed by means of GC and GC-MS. The metabolites thus obtained were ... 3-methyl-2-butanol, 2-methyl-2-butanol and 3-methyl-2-butanone were detected as the resultant metabolites. In the presence of the NADPH-generating system liver microsomes were made to react to the substrate of saturated ... isopentane aqueous solution at 37 degrees C for one hour. As a result, the same metabolites were produced as obtained in the exposure experiment. It was therefore suggested that ... isopentane /was/ metabolized chiefly by liver microsomes. Male mice of ICR strain were fed with 80 mg/kg b.w. of phenobarbital for consecutive four days and exposed to ... isopentane for one hour. This resulted in an increase in the amount of ... 2-methyl-2-butanol in the isopentane inhalation experiment. ...
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
Tert-amyl alcohol is a known human metabolite of tert-amyl methyl ether.
来源:NORMAN Suspect List Exchange
毒理性
神经毒素 - 急性溶剂综合征
Neurotoxin - Acute solvent syndrome
来源:Haz-Map, Information on Hazardous Chemicals and Occupational Diseases
毒理性
LCLo(大鼠)= 5,700 ppm/6小时
LCLo (rat) = 5,700 ppm/6h
来源:Haz-Map, Information on Hazardous Chemicals and Occupational Diseases
毒理性
2-甲基-2-丁醇(4.1 mmol/kg)在大鼠(雄性,Sprague-Dawley,体重160至300克)腹膜内给药戊醇后8分钟引起了行为性中毒。中毒程度按照0到4的等级评分,其中3分代表“几乎不恢复或没有恢复翻转反射,重度镇静,无自发运动活动,肌肉软弱无力,骨盆和腹部不抬起”,2分代表“重度镇静,明显的运动协调障碍和迟缓动作,四肢远离身体伸展”。仅给予2-甲基-2-丁醇后,中毒评分大约为2.9。预先给予咪唑苯二氮䓬Ro15-4513(在给予酒精前5分钟)部分逆转了2-甲基-2-丁醇的中毒作用,评分降低到大约1.8。Ro15-4513在乙醇处理后比戊醇处理后更能有效减少中毒程度。
2-Methyl-2-butanol (4.1 mmol/kg) induced a behavioral intoxication in rats (male, Sprague-Dawley, 160 to 300 g) at 8 min after the intraperitoneal administration of the pentanol. The intoxication was scored on a scale of 0 to 4, where 3 = 'very little or no recovery of righting reflex, heavy sedation, no spontaneous locomotor activity, flaccid muscles, absence of pelvic and abdominal elevation' and 2 = 'heavy sedation, pronounced motor coordination and sluggish movement, limbs extended away from the body'. After 2-methyl-2-butanol alone the intoxication was scored as approximately 2.9. The prior administration of the imidazobenzodiazepine Ro15-4513 (5 min before the alcohol) partially reversed the intoxication by 2-methyl-2-butanol and the score decreased to approximately 1.8. The Ro15-4513 was more effective at reducing the intoxication after treatment with ethanol than after treatment with the pentanol.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
立即急救:确保已经进行了充分去污。如果患者停止呼吸,开始人工呼吸,最好使用需求阀复苏器、气囊面罩装置或口袋面罩,按训练进行操作。根据需要执行心肺复苏。立即用缓慢流动的水冲洗受污染的眼睛。不要催吐。如果发生呕吐,让患者前倾或置于左侧(如果可能的话,头部向下)以保持呼吸道畅通,防止吸入。保持患者安静,维持正常体温。寻求医疗帮助。/高醇(大于3个碳)及相关化合物/
Immediate first aid: Ensure that adequate decontamination has been carried out. If patient is not breathing, start artificial respiration, preferably with a demand-valve resuscitator, bag-valve-mask device, or pocket mask, as trained. Perform CPR as necessary. Immediately flush contaminated eyes with gently flowing water. Do not induce vomiting. If vomiting occurs, lean patient forward or place on left side (head-down position, if possible) to maintain an open airway and prevent aspiration. Keep patient quiet and maintain normal body temperature. Obtain medical attention. /Higher alcohols (>3 carbons) and related compounds/
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
基本治疗:建立专利气道(如需要,使用口咽或鼻咽气道)。如有必要,进行吸痰。密切观察呼吸不足的迹象,如有必要,协助通气。通过非循环呼吸面罩以10至15升/分钟的速度给予氧气。监测休克并视需要进行治疗……监测肺水肿并视情况进行治疗……预期癫痫发作并视情况进行治疗……对于眼睛污染,立即用水冲洗眼睛。在运输过程中,用0.9%的生理盐水(NS)连续冲洗每只眼睛……不要使用催吐剂。对于摄入,如果患者能够吞咽、有强烈的干呕反射且不流口水,则用水冲洗口腔,并给予5毫升/千克,最多200毫升的水进行稀释。给予活性炭……/更高醇(>3个碳)及相关化合物/
Basic Treatment: Establish a patent airway (oropharyngeal or nasopharyngeal airway, if needed). Suction if necessary. Watch for signs of respiratory insufficiency and assist ventilations if necessary. Administer oxygen by nonrebreather mask at 10 to 15 L/min. Monitor for shock and treat if necessary ... . Monitor for pulmonary edema and treat if necessary ... . Anticipate seizures and treat if necessary ... . For eye contamination, flush eyes immediately with water. Irrigate each eye continuously with 0.9% saline (NS) during transport ... . Do not use emetics. For ingestion, rinse mouth and administer 5 ml/kg up to 200 ml of water for dilution if the patient can swallow, has a strong gag reflex, and does not drool. Administer activated charcoal ... . /Higher alcohols (>3 carbons) and related compounds/
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
Dog weighing 11 kg, when injected sc with dose of 0.1 mL of 2-methyl-2-butanol...exhaled 65% of it within 5.75 hr. Another dog given slightly larger dose of same alc iv exhaled 52% within 6 hr. Cats also exhaled large quantity unchanged.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
当兔子被注射了两种剂量的药物时...它们在第一个实例中在4小时内以未改变的形式呼出了21%的酒精,在第二个实例中,在3小时内呼出了22%。...给予相同同分异构体的老鼠在50小时内通过呼出的空气排出了26.4%未改变的物质,并通过尿液排出了8.9%。
When rabbits were injected with 2 levels of dosage ... they exhaled, in first instance 21% of alc in unchanged form within 4 hr, & in second, 22% within 3 hr. ... rat given 1 g/kg of same isomer eliminated 26.4% unchanged in expired air and 8.9% in the urine within 50 hr.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
The rate of elimination of amyl alcohols from the blood of rats decreases in the order of primary, secondary, and tertiary. tert-Amyl alcohol did not disappear from the blood of rats until 50 hr following an ip dose of 1 g/kg.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
少量的一级和二级醇以及相当可观的叔醇同分异构体在呼出的空气和尿液中以未改变的形式排出。/戊醇/
Small amts of the primary and secondary alcohols, and appreciable amts of the tertiary isomer, are excreted unchanged in the respired air and urine. /Amyl alcohols/
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
在大鼠体内注射1.0千克剂量的叔戊醇1小时后,作者们在血液中发现了浓度为12.5毫克百分比的叔戊醇。他们还发现在大鼠因呼吸衰竭死亡时,颈静脉血液中的浓度为191毫克百分比。在大鼠吸入150、500或1500 ppm的叔戊醇6小时后大约0.6小时,血浆中的浓度分别为9.6、59.9和337微克/毫升。
... /The authors/ Found a conc of 12.5 mg percent of tert-amyl alcohol in the blood of rats 1 hr following an ip dose of 1.0 kg. They also found a conc of 191 mg percent in the jugular blood of rats at the time of death from respiratory failure. Conc in the plasma of rats about 0.6 hr after they had inhaled 150, 500, or 1500 ppm of tert-amyl alcohol for 6 hr were 9.6, 59.9, and 337 ug/mL, respectively.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
安全信息
-
职业暴露等级:A
-
职业暴露限值:TWA: 100.0 ppm; 360.0 mg/m3, STEL: 125.0 ppm; 450.0 mg/m3
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:3
-
危险品标志:F
-
安全说明:S46
-
危险类别码:R37/38,R11,R20
-
WGK Germany:1
-
海关编码:2905199090
-
危险品运输编号:UN 1105 3/PG 2
-
危险类别:3
-
RTECS号:SC0175000
-
包装等级:II
-
储存条件:本品应密封于阴凉避光通风处保存。165kg铁桶包装。请将其置于通风、干燥环境中,并注意防火、防爆和密封贮存。务必防止猛烈撞击,避免日晒或雨淋。
制备方法与用途
叔戊醇
简介 叔戊醇,系统名为2-甲基-2-丁醇,是一种无色透明的液体。它微溶于水,并能与水形成共沸混合物,共沸点为87.4℃。叔戊醇能够与乙醇、乙醚、苯、氯仿及甘油等物质混溶。作为化工原料,叔戊醇广泛应用于合成香料、医药和彩色胶片等行业。
七十年代中叶,日本通过以叔戊醇为原料合成中间体频那酮取得了成功,推动了一系列高附加值产品的开发,使叔戊醇的深度加工达到了新的高度。
化学性质无色易燃液体,燃烧时散发类似樟脑的独特气味。它能溶解于8倍量的水中,并可与乙醇、乙醚、苯、氯仿和甘油及各类油类混溶。水溶液呈中性。
用途用作合成香料和农药原料的同时,也是优质的溶剂。 主要用于生产新型农药如粉锈宁、频那酮、三唑酮、三唑醇以及种子保护剂;并用于合成茚烷麝香及作为彩色胶片的成色剂。此外,甲基丁炔醇——叔戊醇的中间产物,亦是有效的医药中间体和萜烯类香料中间体,并应用于酸蚀抑止剂、粘度稳定剂、减粘剂以及镀镍、镀铜上光剂与氯化烃稳定剂等。
生产方法 (1)以丙酮与乙炔为原料,经炔化加氢而得。将乙炔溶解在液氨中,并与丙酮和催化剂混合后送入炔化反应器。反应液经过闪蒸分离未反应的乙炔及氨,随后加热除去未反应的丙酮,得到甲基丁炔醇进入加氢反应器,在此生成叔戊醇并经脱水精制而成产品。
(2)由异戊烯加水而成。 (3)通过将戊烷进行氯化和水解后分馏而得。原料戊烷先经过无水氯化氢处理去水,然后蒸发并与氯气混合进入反应器,在250-300℃温度下发生反应生成物,经四个精馏塔分离得到氯戊烷。在水解器中使用油酸钠作为催化剂和氢氧化钠溶液将氯戊烷水解为粗戊醇,通过与水分离、蒸馏可获得含有伯醇(59%)、仲醇(36%)及叔醇(5%)的混合物。采用丙酮与乙炔为原料的方法可产出纯度高达99%的产品。原料消耗定额:每吨产品需要1040公斤丙酮、1500公斤电石、650立方米氢气(99.5%)、液氨135公斤以及碳酸钾340公斤。
类别易燃液体
毒性分级中毒
急性毒性- 大鼠口服LD50:1000毫克/公斤;
- 小鼠口服LDLo:2500毫克/公斤
与空气混合可爆炸。
可燃性危险特性遇明火、高温或氧化剂较易燃烧,燃烧时会产生刺激性的烟雾。
储运特性应储存在通风良好、低温干燥的库房中,并与其他氧化剂分开存放。
灭火剂 职业标准时间加权平均容许浓度(TWA)为360毫克/立方米。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 甲基叔戊醚 tert-Amyl methyl ether 994-05-8 C6H14O 102.177 叔丁醇 tert-butyl alcohol 75-65-0 C4H10O 74.1228 异戊醇 i-Amyl alcohol 123-51-3 C5H12O 88.1497 2-羟基-2-甲基丁腈 2-hydroxy-2-methyl-butyronitrile 4111-08-4 C5H9NO 99.1326 1,3-环氧-3-甲基丁烷 2,2-dimethyl-oxetane 6245-99-4 C5H10O 86.1338 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 仲丁醇 iso-butanol 78-92-2 C4H10O 74.1228 甲基叔戊醚 tert-Amyl methyl ether 994-05-8 C6H14O 102.177 特戊基过氧化氢 tert-amyl hydroperoxide 3425-61-4 C5H12O2 104.149 —— tert-Pentylhypochlorit 24251-12-5 C5H11ClO 122.595 —— O-tert-pentylhydroxylamin 38091-80-4 C5H13NO 103.164
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:Wibaut et al., Recueil des Travaux Chimiques des Pays-Bas, 1939, vol. 58, p. 347摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:Enthalpies of hydration of alkenes. 4. Formation of acyclic tert-alcohols摘要:The enthalpies of hydration of a series of acyclic alkenes that lead to tert-alcohols were determined. Several pairs of alkenes that give the same alcohol were studied and gave the differences in enthalpy of formation of the alkenes. A consistent difference in DELTA-H(f) of 1.84 kcal/mol was found between di- and trisubstituted alkenes. It was related to the difference in DELTA-H(f) for pairs of exocyclic and endocyclic alkenes. The enthalpies of formation of the alcohols were obtained and were related to data for primary and secondary alcohols.DOI:10.1021/jo00017a022
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:A New Indirect Application of Aggregative Activation: Synthesis of Esters by Cobalt-Catalyzed Carbonylation of Aryl, Heterocyclic, and Vinyl Halides under Atmospheric Pressure摘要:Sun lamp illuminated alkoxycarbonylation of aryl, heteroaryl, and vinyl halides was performed under atmospheric pressure of CO in the presence of a cobalt catalyst in situ generated from Co(OAc)(2). Illumination through a Pyrex flask was sufficient to catalyze the reaction. This process avoids the use of Co-2(CO)(8) and excess CH3I, which were required in the earlier procedure. A S-RN(1) mechanism is proposed.DOI:10.1021/jo00131a005
文献信息
-
Synthesis of 1,2-amino alcohols via catalytic C–H amidation of sp<sup>3</sup> methyl C–H bonds作者:Taek Kang、Heejeong Kim、Jeung Gon Kim、Sukbok ChangDOI:10.1039/c4cc05655h日期:——Herein a new synthetic route to 1,2-amino alcohols is presented by using C-H amidation of sp(3) methyl C-H bonds as a key step. Readily available alcohols were employed as starting materials after converting them to removable ketoxime chelating groups. Iridium catalysts were found to be effective for the C-H amidation, and LAH reduction was then used to furnish beta-amino alcohol products.
-
Practical in situ-generation of phosphinite ligands for palladium-catalyzed carbonylation of (hetero)aryl bromides forming esters作者:Lin Wang、Helfried Neumann、Anke Spannenberg、Matthias BellerDOI:10.1039/c7cc02828h日期:——An effective method for alkoxycarbonylation of (hetero)aryl bromides is developed in the presence of in situ-generated phosphinite ligands tBu2POR (R = nBu, nPr, Et or Me). For this purpose commercially available tBu2PCl was used as the pre-ligand in the presence of different alcohols. For the first time cross coupling reactions with two alcohols – one generating the ligand, the other used as substrate
-
A mild and efficient rhenium-catalyzed transfer hydrogenation of terminal olefins using alcoholysis of amine–borane adducts as a reducing system作者:Hailin Dong、Heinz BerkeDOI:10.1016/j.jorganchem.2011.01.027日期:2011.5mantane) catalyzes the alcoholysis of ammonia–borane and amine–boranes and the catalytic transfer hydrogenations of various terminal olefins. Excellent yields were achieved at 70 °C in isopropanol using tBuOK as a co-catalyst affording TOF values up to 396 h−1.
-
Controllable Intramolecular Unactivated C(sp3)-H Amination and Oxygenation of Carbamates作者:Qihang Guo、Xiang Ren、Zhan LuDOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.8b03299日期:2019.2.15catalyst-controlled intramolecular unactivated C(sp3)-H amination and oxygenation of carbamates merging visible-light photocatalysis and earth-abundant transition metal catalysis have been reported. Useful amino alcohol and diol derivatives could be selectively obtained from readily available tertiary alcohol derivatives. The possible mechanisms have been proposed via a 1,5-HAT process followed by Lewis acid-controlled
-
NITROGEN-CONTAINING HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUND OR SALT THEREOF申请人:FUJIFILM Corporation公开号:US20150322063A1公开(公告)日:2015-11-12A compound represented by Formula [1] (in the formula, Z 1 represents N, CH, or the like; X 1 represents NH or the like; R 1 represents a heteroaryl group or the like; each of R 2 , R 3 , and R 4 represents a hydrogen atom, a halogen atom, an alkoxy group, or the like; and R 5 represents a heteroaryl group or the like) or salt thereof.由式[1]表示的化合物(在该式中,Z表示N、CH或类似物;X表示NH或类似物;R表示杂环烷基或类似物;R2、R3和R4中的每一个表示氢原子、卤原子、烷氧基或类似物;R5表示杂环烷基或类似物)或其盐。
表征谱图
-
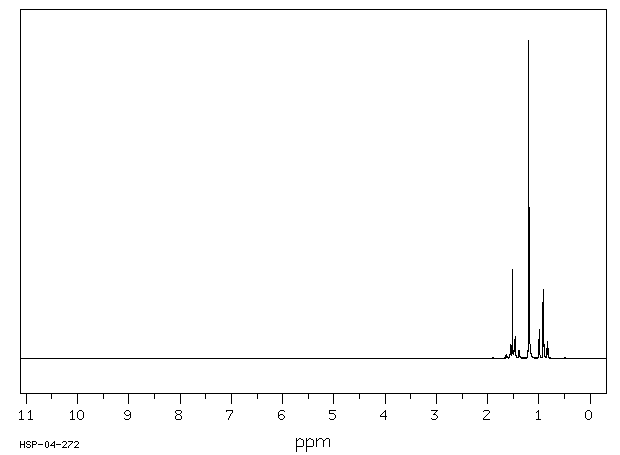
氢谱1HNMR
-
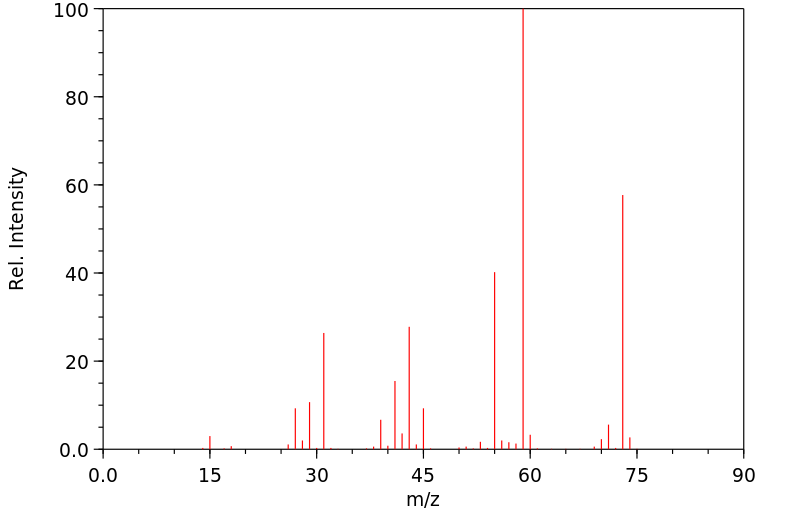
质谱MS
-
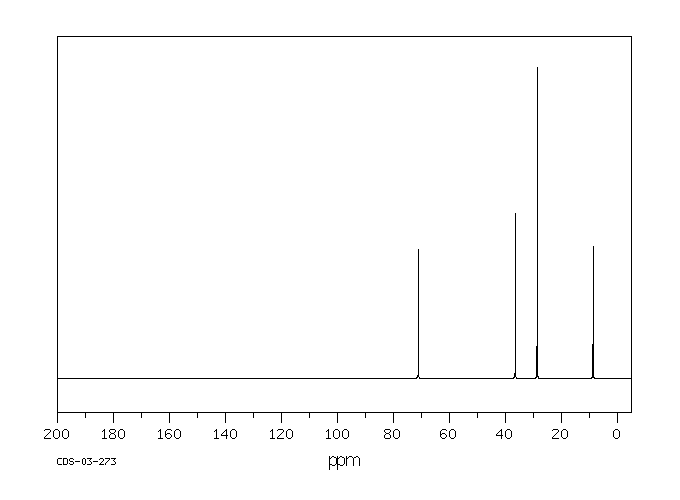
碳谱13CNMR
-
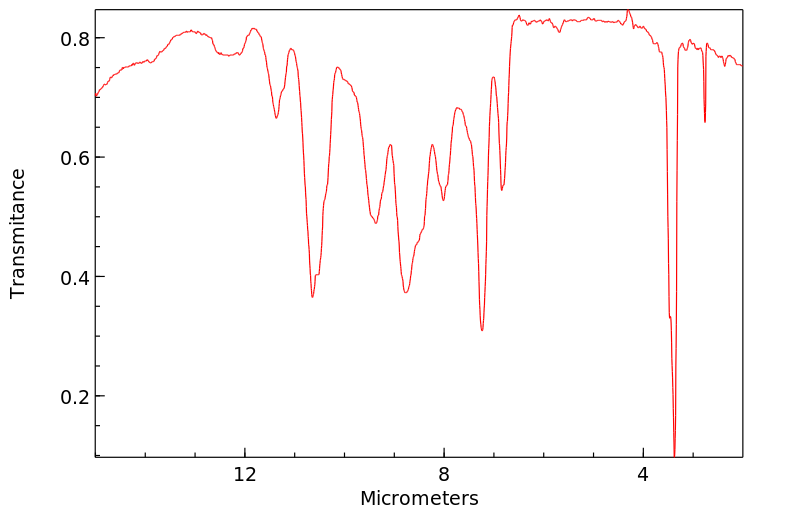
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(反式)-4-壬烯醛
(s)-2,3-二羟基丙酸甲酯
([1-(甲氧基甲基)-1H-1,2,4-三唑-5-基](苯基)甲酮)
(Z)-4-辛烯醛
(S)-氨基甲酸酯β-D-O-葡糖醛酸
(S)-3-(((2,2-二氟-1-羟基-7-(甲基磺酰基)-2,3-二氢-1H-茚满-4-基)氧基)-5-氟苄腈
(R)-氨基甲酸酯β-D-O-葡糖醛酸
(5,5-二甲基-2-(哌啶-2-基)环己烷-1,3-二酮)
(2,5-二氟苯基)-4-哌啶基-甲酮
龙胆苦苷
龙胆二糖甲乙酮氰醇(P)
龙胆二糖丙酮氰醇(P)
龙胆三糖
龙涎酮
齐罗硅酮
齐留通beta-D-葡糖苷酸
鼠李糖
黑芥子苷单钾盐
黑海棉酸钠盐
黑木金合欢素
黑曲霉三糖
黑介子苷
黄尿酸8-O-葡糖苷
麻西那霉素II
麦迪霉素
麦芽糖脎
麦芽糖基海藻糖
麦芽糖1-磷酸酯
麦芽糖
麦芽四糖醇
麦芽四糖
麦芽十糖
麦芽六糖
麦芽五糖水合物
麦芽五糖
麦芽五糖
麦芽五糖
麦芽三糖醇
麦芽三糖
麦芽三糖
麦芽三塘水合
麦芽七糖水合物
麦芽七糖
麦法朵
麦可酚酸-酰基-Β-D-葡糖苷酸
麦利查咪
麝香酮
鹤草酚
鸢尾酚酮 3-C-beta-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷
鸡矢藤苷