一氧化碳 | 630-08-0
物质功能分类
分子结构分类
中文名称
一氧化碳
中文别名
纯一氧化碳
英文名称
carbon monoxide
英文别名
carbon monooxide;carbon oxide
CAS
630-08-0
化学式
CO
mdl
——
分子量
28.0104
InChiKey
UGFAIRIUMAVXCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:−205 °C(lit.)
-
沸点:−191.5 °C(lit.)
-
密度:d4-195 (liq) 0.814; d (gas) 0.968 (air = 1.000); d40 at 760 mm: 1.250 g/liter
-
蒸气密度:0.97 (vs air)
-
溶解度:在 20 °C 和 101 kPa 的压力下,2.266 体积的一氧化碳溶解在 100 体积的水中。
-
暴露限值:TLV-TWA 50 ppm (~55 mg/m3) (ACGIH, MSHA, and OSHA); STEL 400 ppm (ACGIH); IDLH 1500 ppm (NIOSH).
-
物理描述:Carbon monoxide is a colorless, odorless gas. Prolonged exposure to carbon monoxide rich atmospheres may be fatal. It is easily ignited. It is just lighter than air and a flame can flash back to the source of leak very easily. Under prolonged exposure to fire or intense heat the containers may violently rupture and rocket.
-
颜色/状态:Colorless gas [Note: Shipped as a nonliquefied or liquefied compressed gas].
-
气味:Odorless
-
味道:Tasteless
-
闪点:Flammable gas
-
蒸汽密度:0.968 (Air = 1)
-
蒸汽压力:1.55X10+8 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
亨利常数:Henry's Law constant = 1.04 atm-cu m/mol at 25 °C (reported as 57978.5 atm/mol fraction)
-
自燃温度:1292 °F (700 °C)
-
粘度:Viscosity gas at 273 K = 16.62 uN s/sq m
-
燃烧热:-4.343 BTU/lb = -2,412 cal/g = -101X10+5 joules/kg
-
汽化热:Latent: 92.8 BTU/lb = 51.6 cal/g = 2.16X10+5 joules/kg
-
表面张力:9.8 mN/m (of the liquid at 80 K)
-
电离电位:14.01 eV
-
折光率:Refractive index of gas = 1.0003364 at 273 K and 546.1 nm
-
稳定性/保质期:
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):0.7
-
重原子数:2
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:1
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:1
ADMET
代谢
Metabolism of the dihalomethanes leads to dehalogenation, and the end product is carbon monoxide ... The carbon monoxide appears to arise from a formyl halide intermediate resulting from the loss of one halide atom from the halocarbon. This intermediate as an alternative to losing carbon monoxide can covalently bind to cellular protein or lipid.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
除了外源性来源之外,人类还会接触到少量内源产生的碳 monoxide。在血红素自然降解为胆色素的过程中,与微粒体还原型烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸磷酸(NADPH)细胞色素 P-450 还原酶协同作用,两种同工酶血红素加氧酶,HO-1 和 HO-2,催化血红素四吡咯环的 alpha-亚甲基桥的氧化断裂,导致胆绿素和碳 monoxide 的形成。血红素分解的主要部位,因此也是内源性碳 monoxide 产生的主要器官,是肝脏。脾脏和红细胞生成系统是其他重要的碳 monoxide 分解生成器......其他含铁蛋白,如肌红蛋白、细胞色素、过氧化物酶和过氧化氢酶,大约贡献了总碳 monoxide 生成量的 20-25%。由血红素分解产生的碳 monoxide 大约是 0.4 毫升/小时,而非血红素来源的大约是 0.1 毫升/小时。
In addition to exogenous sources, humans are also exposed to small amounts of carbon monoxide produced endogenously. In the process of natural degradation of hemoglobin to bile pigments, in concert with the microsomal reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) cytochrome P-450 reductase, two heme oxygenase isoenzymes, HO-1 and HO-2, catalyse the oxidative breakdown of the alpha-methene bridge of the tetrapyrrole ring of heme, leading to the formation of biliverdin and carbon monoxide. The major site of heme breakdown, and therefore the major organ for production of endogenous carbon monoxide, is the liver. The spleen and the erythropoietic system are other important catabolic generators of carbon monoxide ... Other hemoproteins, such as myoglobin, cytochromes, peroxidases and catalase, contribute approximately 20-25% to the total amount of carbon monoxide generated. Approximately 0.4 mL carbon monoxide/hr is formed by hemoglobin catabolism, and about 0.1 mL/hr originates from non-hemoglobin sources.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
任何导致红细胞破坏增加和其他血红蛋白加速分解的干扰,都会导致一氧化碳产生增加。血肿、红细胞血管内溶血、输血和无效的红细胞生成都会提高血液中一氧化碳的浓度。在贫血(溶血性、铁粒幼细胞性、镰状细胞性)、地中海贫血、伴有溶血的吉尔伯特综合征以及其他血液病等病理条件下,红细胞的降解也会加速一氧化碳的产生。
Any disturbance leading to increased destruction of red blood cells and accelerated breakdown of other haemoproteins would lead to increased production of carbon monoxide. Hematomas, intravascular hemolysis of red blood cells, blood transfusion and ineffective erythropoiesis will all elevate the carbon monoxide concentration in the blood. Degradation of red blood cells under pathological conditions such as anemias (hemolytic, sideroblastic, sickle cell), thalassaemia, Gilbert's syndrome with hemolysis and other hematological diseases will also accelerate carbon monoxide production.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
决定碳氧血红蛋白最终水平的主要因素包括:吸入的一氧化碳量;静息和运动时的每分钟肺泡通气量;内源性一氧化碳产生量;血容量;大气压力;以及肺的相对扩散能力。从肺泡扩散的速度以及一氧化碳与血液中血红蛋白结合的步骤限制了血液吸收的速率。
The primary factors that determine the final level of carboxyhemoglobin are: the amount of inspired carbon monoxide; minute alveolar ventilation at rest and during exercise; endogenous carbon monoxide production; blood volume; barometric pressure; and the relative diffusion capability of the lungs. The rate of diffusion from the alveoli and the binding of carbon monoxide with the blood hemoglobin are the steps limiting the rate of uptake into the blood.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
一氧化碳是含碳燃料不完全燃烧的产物,也由自然过程或人体内卤代甲烷的生物转化产生。在外部接触更多一氧化碳的情况下,可能会开始出现微妙的影响,而接触更高水平的一氧化碳可能导致死亡。一氧化碳的健康影响主要是由于形成碳氧血红蛋白(COHb)的结果,这会降低血液的携氧能力……在典型的日常活动中,人们在各种微环境中遇到一氧化碳——在乘坐机动车辆、在工作、访问与燃烧源相关的城市地区、或使用家用气体、木炭或木材烹饪或取暖时——以及烟草烟雾中……人类暴露的研究表明,机动车尾气是定期遇到的一氧化碳水平升高的最重要来源……工作场所是一氧化碳暴露的另一个重要场所……某些工业过程可能会使工人直接或作为副产品暴露于一氧化碳……一氧化碳通过肺部吸收,碳氧血红蛋白的浓度将主要取决于吸入一氧化碳和氧气的浓度……还将取决于暴露的持续时间、肺通气量和最初存在的碳氧血红蛋白的浓度……除了与血红蛋白反应外,一氧化碳还与肌红蛋白、细胞色素以及诸如细胞色素c氧化酶和细胞色素P-450等金属酶结合……一氧化碳与血红蛋白结合,产生碳氧血红蛋白并降低血液的携氧能力,似乎是低水平一氧化碳暴露诱导有毒效果的主要机制。确切的一氧化碳有毒效果诱导机制尚未完全了解,但可能包括在多种不同器官系统的许多组织中诱导缺氧状态……因此,一氧化碳暴露的一个独特特点是,血液中的碳氧血红蛋白水平代表了个体接收剂量的一个有用的生物学标志……碳氧血红蛋白的形成是一个可逆过程;然而,由于一氧化碳与血红蛋白的紧密结合,消除半衰期相当长,范围从2到6.5小时……血液中的碳氧血红蛋白水平可以通过血液分析直接确定,也可以通过测量呼出气体中的一氧化碳间接确定……在最大运动条件下,氧气摄取量和随之而来的工作能力下降已经被清楚地证明……然而,在更典型的一氧化碳暴露水平上,更值得关注的是可能发生在较小但可观的普通人群中的一定的心血管效果(即,运动中加重心绞痛症状)这一群体,慢性心绞痛患者,目前被视为对一氧化碳暴露效果最敏感的风险群体……对于患有缺血性心脏病的患者,低水平一氧化碳暴露的负面健康后果在心脏疾病风险人群中很难预测……在一氧化碳浓度高时,血红蛋白和白细胞的过度增加可能会对心脏施加额外的负担并损害组织的血液流动……一氧化碳对肺组织的任何直接影响都不太可能,除非是与一氧化碳中毒相关的高浓度……职业性或意外接触燃烧和热解产物,特别是在室内,如果碳氧血红蛋白水平高,可能会导致急性肺功能下降。然而,将一氧化碳的潜在效果与烟雾和尾气中的其他呼吸刺激物产生的效果区分开来是困难的……特别值得注意的是那些正在服用主要或次要具有抑制作用的药物,这些药物可能会加剧一氧化碳相关神经行为下降的个体。其他可能增加一氧化碳诱导神经行为效果风险的群体是老年人和病人……在正常情况下,大脑可以增加血液流量或组织氧提取来补偿一氧化碳暴露引起的缺氧……
It is a product of the incomplete combustion of carbon-containing fuels and is also produced by natural processes or by biotransformation of halomethanes within the human body. With external exposures to additional carbon monoxide, subtle effects can begin to occur, and exposure to higher levels can result in death. The health effects of carbon monoxide are largely the result of the formation of carboxyhemoglobin (COHb), which impairs the oxygen carrying capacity of the blood ... During typical daily activities, people encounter carbon monoxide in a variety of microenvironments - while travelling in motor vehicles, working at their jobs, visiting urban locations associated with combustion sources, or cooking or heating with domestic gas, charcoal or wood fires - as well as in tobacco smoke. ... Studies of human exposure have shown that motor vehicle exhaust is the most important source for regularly encountered elevated carbon monoxide levels ... The workplace is another important setting for carbon monoxide exposures ... Certain industrial processes can expose workers to carbon monoxide produced directly or as a byproduct ... Carbon monoxide is absorbed through the lungs, and the concentration of carboxyhemoglobin will depend ... mainly on the concentrations of inspired carbon monoxide and oxygen ... and will also depend on the duration of exposure, pulmonary ventilation, and the concentration of carboxyhemoglobin originally present ... In addition to its reaction with hemoglobin, carbon monoxide combines with myoglobin, cytochromes, and metalloenzymes such as cytochromoe c oxidase and cytochrome P-450 ... The binding of carbon monoxide to hemoglobin, producing carboxyhemoglobin and decreasing the oxygen carrying capacity of blood, appears to be the principal mechanism of action underlying the induction of toxic effects of low-level carbon monoxide exposures. The precise mechanisms by which toxic effects are induced ... are not understood fully but likely include the induction of a hypoxic state in many tissues of diverse organ systems ... A unique feature of carbon monoxide exposure, therefore, is that the blood carboxyhemoglobin level represents a useful biological marker of the dose that the individual has received ... The formation of carboxyhemoglobin is a reversible process; however, because of the tight binding of carbon monoxide to hemoglobin, the elimination half-time is quite long, ranging from 2 to 6.5 hr ... The level of carboxyhemoglobin in the blood may be determined directly by blood analysis or indirectly by measuring carbon monoxide in exhaled breath ... Decreased oxygen uptake and the resultant decreased work capacity under maximal exercise conditions have clearly been shown to occur ... However, of greater concern at more typical ambient carbon monoxide exposure levels are certain cardiovascular effects (i.e., aggravation of angina symptoms during exercise) likely to occur in a smaller, but sizeable, segment of the general population. This group, chronic angina patients, is currently viewed as the most sensitive risk group for carbon monoxide exposure effects ... The adverse health consequences of low level carbon monoxide exposure to patients with ischemic heart disease are very difficult to predict in the at-risk population of individuals with heart disease ... At high carbon monoxide concentrations, excessive increases in hemoglobin and hematocrit may impose an additional workload on the heart and compromise blood flow to the tissues ... It is unlikely that carbon monoxide has any direct effects on lung tissue except for extremely high concentrations associated with carbon monoxide poisoning ... Occupational or accidental exposure to the products of combustion and pyrolysis, particularly indoors, may lead to acute decrements in lung function if the carboxyhemoglobin levels are high. It is difficult, however, to separate the potential effects of carbon monoxide from those due to other respiratory irritants in the smoke and exhaust ... Of special note are those individuals who are taking drugs with primary or secondary depressant effects that would be expected to exacerbate carbon monoxide-related neurobehavorial decrements. Other groups at possible increased risk for carbon monoxide-induced neurobehavorial effects are the aged and ill ... Under normal circumstances, the brain can increase blood flow or tissue oxygen extraction to compensate for the hypoxia caused by exposure to carbon monoxide ...
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
多项实验室动物研究表明,母体接触一氧化碳会导致出生体重降低、心肌肥大、行为发育迟缓和认知功能受损。实验室动物研究还表明,外源性化合物的酶代谢可能受到一氧化碳暴露的影响。一氧化碳暴露导致的内生素代谢降低,可能对接受药物治疗的人尤为重要。高度活跃的氧代谢组织,如心脏、大脑、肝脏、肾脏和肌肉,可能对一氧化碳中毒特别敏感。有报道称一氧化碳对肝脏、肾脏、骨骼以及肺和脾的免疫能力有影响。人们普遍认为,急性一氧化碳中毒时发生的严重组织损伤是由以下一种或多种原因引起的:(1)由于碳氧血红蛋白的形成导致的缺血,(2)抑制氧从氧合血红蛋白释放,(3)抑制细胞色素功能(例如,细胞色素氧化酶)和(4)代谢性酸中毒。尽管某些数据也表明围产期影响(例如,出生体重降低、出生后发育迟缓、婴儿猝死综合症)与一氧化碳暴露有关,但缺乏足够的证据来定性地确认人类中的这种关联或建立任何相关的暴露-效应关系。关于药物使用或滥用可能增强一氧化碳毒性的直接信息很少。最有力的证据来自实验室动物和人类与酒精的研究,至少得到了相加效应。这种重要性由于酒精使用和一氧化碳暴露的高发率而增强。除了对吸烟者和非吸烟者都是一氧化碳的来源外,烟草烟雾也是其他化学物质的来源,这些化学物质可能与环境中的一氧化碳相互作用。基于已知的描述效果,可重复运动诱发缺血的患者似乎是在一般人群中确定的敏感群体,他们处于增加的风险中,可能会在环境或接近环境一氧化碳浓度下经历关注健康影响(即,由于加剧心血管症状而减少运动时间)。因此,健康人群中运动时间的减少主要对竞技运动员构成关注,而不是对进行日常活动的普通人。然而,从临床和理论工作以及实验室动物的实验研究中,可以假设,人群中可能还有其他群体由于接触一氧化碳而处于可能的风险中。可识别的可能风险群体可以根据性别差异、年龄、遗传变异、先存疾病或使用药物、娱乐药物或环境变化进行分类。不幸的是,目前很少有经验证据可以用来指定与这些可能风险群体接触环境或接近环境一氧化碳暴露相关的健康影响。
... Studies in several laboratory animal species provide strong evidence that maternal carbon monoxide exposures ... produce reductions of birth weight, cardiomegaly, delays in behavorial development and disruptions in cognitive function ... Laboratory animal studies suggest that enzyme metabolism of xenobiotic compounds may be affected by carbon monoxide exposure ... The decreases in xenobiotic metabolism shown with carbon monoxide exposure might be important to individuals receiving treatment with drugs ... Tissues of highly active oxygen metabolism, such as heart, brain, liver, kidney, and muscle, may be particularly sensitive to carbon monoxide poisoning. There are reports ... of effects on liver, kidney, bone and the immune capacity of the lung and spleen. It is generally agreed that the severe tissue damage occurring during acute carbon monoxide poisoning is due to one of more of the following: (1) ischemia resulting from the formation of carboxyhemoglogin, (2) inhibition of oxygen release from oxyhemoglobin, (3) inhibition of oxygen release from oxyhemoglobin, (3) inhibition of cellular cytochrome function (e.g., cytochrome oxidases) and (4) metabolic acidosis ... Whereas certain data also suggest that perinatal effects (e.g., reduced birth weight, slowed post-natal developments, sudden infant death syndrome) are associated with carbon monoxide exposure, insufficient evidence exists by which to either qualitatively confirm such an association in humans or establish any pertinent exposure-effect relationships ... There remains little direct information on the possible enhancement of carbon monoxide toxicity by concomitant drug use or abuse ... The greatest evidence for a potentially important interaction of carbon monoxide comes from studies with alcohol in both laboratory animals and humans, where at least additive effects have been obtained. The significance of this is augmented by the high probable incidence of combined alcohol use and carbon monoxide exposure ... Besides being a source of carbon monoxide for smokers as well as non-smokers, tobacco smoke is also a source of other chemicals with which environmental carbon monoxide could interact ... On the basis of known effects described, patients with reproducible exercise-induced ischemia appear to be the best established as a sensitive group within the general population that is at increased risk for experiencing health effects of concern (i.e., decreased exercise duration due to exacerbation of cardiovascular symptoms) at ambient or near-ambient carbon monoxide concentrations ... Decrements in exercise duration in the healthy population would therefore be of concern mainly to competing athletes, rather than to ordinary people carrying out the common activities of daily life. It can be hypothesized, however, from both clinical and theoretical work and from experimental research on laboratory animals, that certain other groups in the population may be at probable risk from exposure to carbon monoxide. Identifiable probable risk groups can be categorized by gender differences; by age ...; by genetic variations ...; by pre-existing diseases ...; or by the use of medications, recreational drugs or alterations in environment ... Unfortunately, little empirical evidence is currently available by which to specify health effects associated with ambient or near-ambient carbon monoxide exposure to these probable risk groups ...
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
一氧化碳是每年全球报告的意外中毒和死亡案例中的很大一部分原因。在户外,一氧化碳的浓度在街道交叉口、拥挤的交通、内燃机排放的尾气和工业源附近以及通风不良的区域(如停车库和隧道)最高。在室内,一氧化碳的浓度在有故障或通风不良的燃烧设备、下行气流或逆行气流的工作场所或家庭中最高。急性一氧化碳中毒的症状和体征与到医院时测量的碳氧血红蛋白水平的相关性较差。一氧化碳中毒的神经症状可能发生,如头痛、头晕、虚弱、恶心、混乱、定向障碍和视觉干扰。在持续暴露下,可观察到劳力性呼吸困难、脉搏和呼吸频率的增加以及晕厥。当碳氧血红蛋白水平高于50%时,可能会发生抽搐和心肺骤停。一氧化碳中毒并发症发生频繁(立即死亡、心肌损伤、低血压、心律失常、肺水肿)。一氧化碳中毒最阴险的影响可能是神经精神损害的延迟发展以及神经行为后果,特别是在儿童中。孕期一氧化碳中毒对母亲来说风险很高,因为它增加了短期并发症的几率,对胎儿来说,因为它会导致胎儿死亡、发育障碍和脑缺氧性损伤。此外,胎儿中毒的严重程度无法通过母体率来评估。一氧化碳中毒发生频繁,后果严重,包括立即死亡,涉及并发症和晚期后遗症,并且常常被忽视。
... Carbon monoxide is responsible for a large percentage of the accidental poisonings and deaths reported throughout the world each year ... Outdoors, concentrations of carbon monoxide are highest near street intersections, in congested traffic, near exhaust gases from internal combustion engines and from industrial sources, and in poorly ventilated areas such as parking garages and tunnels. Indoors, carbon monoxide concentrations are highest in workplaces or in homes that have faulty or poorly vented combustion appliances or downdrafts or backdrafts. The symptoms and signs of acute carbon monoxide poisoning correlate poorly with the level of carboxyhemoglobin measured at the time of arrival at the hospital ... Neurological symptoms of carbon monoxide poisoning can ocur, such as headache, dizziness, weakness, nausea, confusion, disorientation and visual disturbances. Exertional dyspnea, increases in pulse and respiratory rates and syncope are observed with continuous exposure ... When carboxyhemoglobin levels are higher than 50%, convulsions and cardiopulmonary arrest may occur. Complications occur frequently in carbon monoxide poisoning (immediate death, myocardial impairment, hypotension, arrhythmias, pulmonary edema). Perhaps the most insidious effect of carbon monoxide poisoning is the delayed development of neuropyschiatric impairment ... and the neurobehavioral consequences, especially in children. Carbon monoxide poisoning during pregnancy results in high risk for the mother, by increasing the short-term complications rate and for the fetus by causing fetal death, developmental disorders, and cerebral anoxic lesions. Furthermore, the severity of fetal intoxication cannot be assessed by the maternal rate. Carbon monoxide poisoning occurs frequently, has severe consequences, including immediate death, involves complications and late sequelae and is often overlooked ...
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
一氧化碳比氧气更具亲和力,能与血红蛋白结合形成碳氧血红蛋白,从而引起缺氧。一氧化碳还能与肌红蛋白结合,影响其利用氧气的能力。它也能与细胞色素c氧化酶结合,尽管其亲和力低于氧气。这干扰了细胞的需氧代谢和高效率的ATP合成。因此,细胞会转向厌氧代谢,导致缺氧、乳酸酸中毒和最终的细胞死亡。一氧化碳还会引起内皮细胞和血小板的氧化氮释放,以及氧气自由基的形成。这导致脂质过氧化,从而在脑内引起水肿和坏死。
Carbon monoxide possesses a higher affinity than oxygen for hemoglobin, leading to the formation of carboxyhemoglobin, this provoking anoxemia. Carbon monoxide also binds to myoglobin, impairing its ability to utilize oxygen. It can also bind to cytochrome c oxidase, though with a lesser affinity than oxygen. This interferes with aerobic metabolism and efficient ATP synthesis. As a result, cells switch to anaerobic metabolism, causing anoxia, lactic acidosis, and eventual cell death. Carbon monoxide also causes endothelial cell and platelet release of nitric oxide, and the formation of oxygen free radicals. This results in lipid peroxidation, leading to edema and necrosis within the brain. (L961)
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
对人类无致癌性(未列入国际癌症研究机构IARC清单)。
No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC).
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
吸收、分配和排泄
尽管一氧化碳(CO)不是呼吸气体之一,但由于一氧化碳与氧气(O2)在物理化学性质上的相似性,使得可以将关于氧气传输动力学的研究成果扩展到一氧化碳上。一氧化碳血红蛋白(COHb)的生成和消除速率、血液中的浓度及其分解代谢受到众多物理因素和生理机制的控制。
从处理过的食品中吸收的一氧化碳并不显著。从包装过程或消费一氧化碳处理过的肉类中产生的一氧化碳中毒风险是可以忽略的。
Although CO is not one of the respiratory gases, the similarity of physico-chemical properties of CO and oxygen (O2) permits an extension of the findings of studies on the kinetics of transport of O2 to those of CO. The rate of formation and elimination of COHb, its concentration in blood, and its catabolism is controlled by numerous physical factors and physiological mechanisms. The absorption of carbon monoxide from the consumption treated food products is not significant. Risk of CO toxicity from the packaging process or from consumption of CO-treated meats is negligible.
来源:DrugBank
吸收、分配和排泄
Carbon monoxide is eliminated through the lungs when air free of carbon monoxide is inhaled.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
一氧化碳容易穿过胎盘。
... /Carbon monoxide/ readily crosses placenta.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
Carbon monoxide is not a cumulative poison in the usual sense. Carboxyhemoglobin is fully dissociable, and once exposure has been terminated, the pigment will revert to oxyhemoglobin. Liberated carbon monoxide is eliminated via the lungs.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
据说一氧化碳不会被吸收,但是它被表皮吸收后发生氧化的情况尚未被排除。
The absorption of carbon monoxide is said not to occur, but its absorption followed by oxidation within the epidermis has not been excluded.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
安全信息
-
职业暴露等级:A
-
职业暴露限值:TWA: 35 ppm (40 mg/m3), Ceiling: 200 ppm (229 mg/m3)
-
危险等级:2.3
-
立即威胁生命和健康浓度:1,200 ppm
-
危险品标志:F+,T
-
安全说明:S45,S53
-
危险类别码:R61
-
WGK Germany:1
-
危险品运输编号:UN 1016 2.3
-
RTECS号:FG3500000
-
包装等级:O52
-
危险类别:2.3
-
危险标志:GHS02,GHS06,GHS08
-
危险性描述:H220,H280,H331,H360D,H372
-
危险性防范说明:P201,P210,P261,P311,P410 + P403
-
储存条件:储存注意事项:应存于阴凉、通风的易燃气体专用库房中,远离火种和热源,库温不宜超过30℃。需与氧化剂、碱类及食用化学品分开存放,切忌混储。使用防爆型照明和通风设施,并禁止使用可能产生火花的机械设备和工具。储存区应配备泄漏应急处理设备。
制备方法与用途
水中溶解度(g/100ml) 每100毫升水中的溶解克数:2.6×10⁻³/20℃
化学性质
无色、无臭、无味的可燃有毒气体。熔点 -199°C(-213°F),沸点 191.5°C(-190°F)。在25℃时,其在水中的溶解度为0.0026g/100g水。不易液化和固化,在燃烧时生成二氧化碳,火焰呈蓝色。
用途
一氧化碳是合成气和各类煤气的主要组分,也是有机化工的重要原料,是C1化学的基础。它可用于制造一系列产品如甲醇、乙酸及光气等,并在冶金工业中作为还原剂。目前工业化生产的C1化学技术包括:(1)乙酸合成。(2)乙酐合成。(3)草酸合成。(4)费托合成。(5)莫比尔法。
生产方法
在许多工业过程中都会产生一氧化碳,例如合成氨原料气、黄磷生产尾气以及钢铁工业的高炉气和转炉气。从一氧化碳资源来说,钢厂气体数量庞大。对纯度要求高但需求量不是特别大的场合,通常会建立专门的一氧化碳生产装置或利用处理成本较低的副产煤气。常用的方法有以下几种:
类别 有害气体
毒性分级 高毒
急性毒性
吸入 - 大鼠 LC50:1807 ppm/4小时;吸入 - 小鼠 LC50: 2444 ppm/4小时
爆炸物危险特性 与空气混合可爆
可燃性危险特性 明火、受热易燃;燃烧产生窒息性二氧化碳气体。
储运特性
库房需通风、低温干燥,轻装轻卸。一氧化碳钢瓶应与其他氧气或空气钢瓶分开存放。
职业标准
TWA 40 毫克/立方米;STEL 60 毫克/立方米
上下游信息
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:在Pd催化CO氧化偶联制草酸二甲酯的微纤维结构Al纤维上低温合成α-氧化铝纳米片摘要:我们报道的α-Al的低温合成2 ö 3纳米片上微纤维结构的Al-纤维在800 º C.勃姆石最初形成在Al-纤维(AlOOH的)纳米片通过原位生增长。然后,AlOOH的/铝纤维,转化所述α-Al 2 ö 3 / Al的纤维在800复合 °下用单一的加热步骤。低温相变暂定归因于AlOOH / Al纤维中的Al金属。然后钯分散在上的α-Al 2 ö 3 /铝纤维的复合,并且将所得的Pd /α-Al系2 ö 3/ Al-纤维催化剂在强烈放热的CO氧化偶联至草酸二甲酯(DMO)反应中进行了研究。获得并维持用于使用CH的原料气的至少150 H的58%的高CO转化率和95%的DMO的选择性3 ONO / CO / N 2(1 / 1.4 / 7.6,摩尔)在150 º下用气体每小时空速为20,000 mL g ―1 h ―1。计算流体动力学的计算结果和实验结果表明的Pd /α-Al系2 ö 3 /DOI:10.1016/j.cattod.2019.03.005
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:OCS的非绝热弯曲解离:弯曲激发对跃迁概率的影响摘要:将OCS从弯曲激发(0 1 0)状态开始的紫外光解离动力学与从地面振动状态(0 0 0)开始的紫外光解离动力学进行了比较。CO的旋转分配(X 1 Σ +)由(2 + 1)共振增强多光子电离,其中来自两个不同的初始状态解离是从CO片段的平移能量鉴别测定。定量分析显示,从(0 1 0)开始的解离非绝热转变概率为0.21,与从(0 0 0)开始的0.34值相似,但略小于该值。DOI:10.1016/s0009-2614(02)00788-1
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:PRMT5抑制剂摘要:本发明提供了一类式(I)所示的PRMT5抑制剂,或其药学上可接受的盐、同位素变体、互变异构体、立体异构体、前药、多晶型、水合物或溶剂合物。本发明还提供了所述化合物的制备方法、包含所述化合物的药物组合物,以及所述化合物在预防和治疗癌症中的作用。#imgabs0#公开号:CN118221579A
文献信息
-
Pd-catalyzed carbonylative access to aroyl phosphonates from (hetero)aryl bromides
-
Compositions for Treatment of Cystic Fibrosis and Other Chronic Diseases申请人:Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated公开号:US20150231142A1公开(公告)日:2015-08-20The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising an inhibitor of epithelial sodium channel activity in combination with at least one ABC Transporter modulator compound of Formula A, Formula B, Formula C, or Formula D. The invention also relates to pharmaceutical formulations thereof, and to methods of using such compositions in the treatment of CFTR mediated diseases, particularly cystic fibrosis using the pharmaceutical combination compositions.
-
Highly Regio- and Enantioselective Alkoxycarbonylative Amination of Terminal Allenes Catalyzed by a Spiroketal-Based Diphosphine/Pd(II) Complex作者:Jiawang Liu、Zhaobin Han、Xiaoming Wang、Zheng Wang、Kuiling DingDOI:10.1021/jacs.5b07764日期:2015.12.16An enantioselective alkoxycarbonylation-amination cascade process of terminal allenes with CO, methanol, and arylamines has been developed. It proceeds under mild conditions (room temperature, ambient pressure CO) via oxidative Pd(II) catalysis using an aromatic spiroketal-based diphosphine (SKP) as a chiral ligand and a Cu(II) salt as an oxidant and affords a wide range of α-methylene-β-arylamino
-
Antithrombotic agents申请人:Eli Lilly And Company公开号:US06350774B1公开(公告)日:2002-02-26This application relates to novel compounds of formula (I) (and their pharmaceutically acceptable salts), as defined herein, processes and intermediates for their preparation, pharmaceutical formulations comprising the novel compounds of formula (I), and the use of the compounds of formula (I) as thrombin inhibitors.这项申请涉及到式(I)的新化合物(及其药用可接受的盐),如本文所定义,用于它们的制备的工艺和中间体,包括式(I)的新化合物的药物配方,以及将式(I)的化合物用作凝血酶抑制剂。
-
[EN] BICYCLYL-SUBSTITUTED ISOTHIAZOLINE COMPOUNDS<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS ISOTHIAZOLINE SUBSTITUÉS PAR UN BICYCLYLE申请人:BASF SE公开号:WO2014206910A1公开(公告)日:2014-12-31The present invention relates to bicyclyl-substituted isothiazoline compounds of formula (I) wherein the variables are as defined in the claims and description. The compounds are useful for combating or controlling invertebrate pests, in particular arthropod pests and nematodes. The invention also relates to a method for controlling invertebrate pests by using these compounds and to plant propagation material and to an agricultural and a veterinary composition comprising said compounds.本发明涉及公式(I)中变量如索权和说明中所定义的自行车基取代异噻唑啉化合物。这些化合物对抗或控制无脊椎动物害虫,特别是节肢动物害虫和线虫方面具有用途。该发明还涉及一种通过使用这些化合物来控制无脊椎动物害虫的方法,以及包含所述化合物的植物繁殖材料、农业和兽医组合物。
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
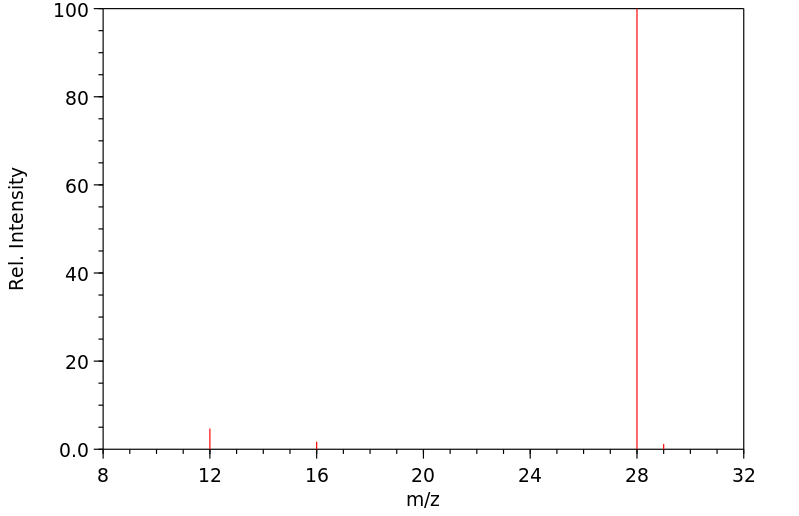
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
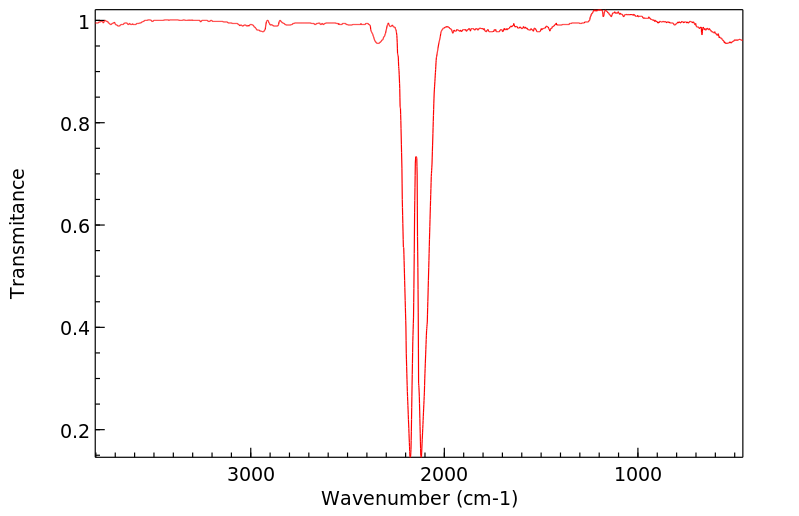
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息