乙二醇单丁醚 | 111-76-2
物质功能分类
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:-70 °C
-
沸点:171 °C
-
密度:0.902 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
-
蒸气密度:4.1 (vs air)
-
闪点:140 °F
-
溶解度:900g/l完全混溶
-
最大波长(λmax):λ: 230 nm Amax: 1.0λ: 250 nm Amax: 0.10λ: 275 nm Amax: 0.05λ: 300-400 nm Amax: 0.01
-
介电常数:5.2999999999999998
-
暴露限值:TLV-TWA skin 25 ppm (121 mg/m3) (ACGIH), 50 ppm (242 mg/m3) (OSHA); STEL 75 ppm (363 mg/m3) (ACGIH);IDLH 700 ppm (NIOSH). .
-
LogP:0.81 at 20℃
-
物理描述:Ethylene glycol monobutyl ether appears as a colorless liquid with a mild, pleasant odor. Less dense than water. Flash point 160°F. Irritates skin and eyes and may be toxic by ingestion. Used as a solvent and to make paints and varnish.
-
颜色/状态:Colorless liquid
-
气味:Mild, ether-like odor
-
蒸汽密度:4.07 (NTP, 1992) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:0.88 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
亨利常数:1.60e-06 atm-m3/mole
-
大气OH速率常数:1.86e-11 cm3/molecule*sec
-
自燃温度:238 °C (460 °F)
-
分解:When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
-
粘度:3.15 centistokes at 25 °C
-
燃烧热:-12,915 btu/lb = -7,180 cal/g = -848,000 cal/mol
-
汽化热:56.59 kJ/mol at 25 °C
-
表面张力:27.36 mN/m at 10 deg; 26.14 mN/m at 25 °C; 24.10 mN/m at 50 deg; 22.06 mN/m at 75 °C; 22.02 mN/m at 100 °C
-
电离电位:10.00 eV
-
气味阈值:Odor perception threshold is 9.3 mg/L.
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.4198 at 20 °C/D
-
相对蒸发率:0.08 (Butyl acetate = 1.0)
-
保留指数:891;898.6;900;884.4;887;887;891;898;893;888;900;890.7;889.1;885;890;889;894.7;888;888;901
-
稳定性/保质期:
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):0.8
-
重原子数:8
-
可旋转键数:5
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:1.0
-
拓扑面积:29.5
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:2
ADMET
安全信息
-
职业暴露等级:A
-
职业暴露限值:TWA: 5 ppm (24 mg/m3) [skin]
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:6.1
-
立即威胁生命和健康浓度:700 ppm
-
危险品标志:Xn
-
安全说明:S36/37,S46
-
危险类别码:R20/21/22,R36/38
-
WGK Germany:1
-
海关编码:2909440000
-
危险品运输编号:1986
-
危险类别:6.1
-
RTECS号:KJ8575000
-
包装等级:III
-
危险标志:GHS07
-
危险性描述:H302 + H312 + H332,H315,H319
-
危险性防范说明:P261,P301 + P312 + P330,P302 + P352 + P312,P304 + P340 + P312,P305 + P351 + P338,P337 + P313
-
储存条件:1. 储存在阴凉、通风的库房中,远离火源和热源。包装需密封,避免与空气接触。 2. 应与氧化剂、酸类等分开存放,严禁混储。不宜大量储存或长时间保存。 3. 配备相应的消防器材,并在储区准备好泄漏应急处理设备及合适的收容材料。
SDS
| 第一部分:化学品名称 |
| 化学品中文名称: | 乙二醇丁醚 |
| 化学品英文名称: | Ethylene glycol monobutyl ether |
| 中文俗名或商品名: | |
| Synonyms: | |
| CAS No.: | 111-76-2 |
| 分子式: | C 6 H 14 O 2 |
| 分子量: | 118.17 |
| 第二部分:成分/组成信息 |
| 纯化学品 混合物 | |||
| 化学品名称:乙二醇丁醚 | |||
|
| 第三部分:危险性概述 |
| 危险性类别: | 第6.1类 毒害品 |
| 侵入途径: | 吸入 食入 经皮吸收 |
| 健康危害: | 吸入本品蒸气后,导致呼吸道刺激及肝肾损害。蒸气对眼有刺激性。皮肤接触可致皮炎。 |
| 环境危害: | |
| 燃爆危险: | 本品可燃,有毒,具刺激性。 |
| 第四部分:急救措施 |
| 皮肤接触: | 脱去污染的衣着,用大量流动清水彻底冲洗。 |
| 眼睛接触: | 立即提起眼睑,用流动清水冲洗。 |
| 吸入: | 脱离现场至空气新鲜处。必要时进行人工呼吸。就医。 |
| 食入: | 误服者给饮大量温水,催吐,就医。 |
| 第五部分:消防措施 |
| 危险特性: | 遇高热、明火或与氧化剂接触,有引起燃烧的危险。接触空气或在光照条件下可生成具有潜在爆炸危险性的过氧化物。若遇高热,容器内压增大,有开裂和爆炸的危险。 |
| 有害燃烧产物: | 一氧化碳、二氧化碳。 |
| 灭火方法及灭火剂: | 干粉、泡沫、二氧化碳、砂土。 |
| 消防员的个体防护: | |
| 禁止使用的灭火剂: | |
| 闪点(℃): | 71(O.C) |
| 自燃温度(℃): | 244 |
| 爆炸下限[%(V/V)]: | 1.1(170℃) |
| 爆炸上限[%(V/V)]: | 10.6(180℃) |
| 最小点火能(mJ): | |
| 爆燃点: | |
| 爆速: | |
| 最大燃爆压力(MPa): | |
| 建规火险分级: |
| 第六部分:泄漏应急处理 |
| 应急处理: | 疏散泄漏污染区人员至安全区,禁止无关人员进入污染区,切断火源。建议应急处理人员戴好防毒面具,穿化学防护服。在确保安全情况下堵漏。喷水雾会减少蒸发,但不能降低泄漏物在受限制空间内的易燃性。用沙土或其它不燃性吸附剂混合吸收,收集运至废物处理场所处置。也可以用大量水冲洗,经稀释的洗水放入废水系统。如大量泄漏,利用围堤收容,然后收集、转移、回收或无害处理后废弃。 |
| 第七部分:操作处置与储存 |
| 操作注意事项: | 密闭操作,提供充分的局部排风。操作人员必须经过专门培训,严格遵守操作规程。建议操作人员佩戴自吸过滤式防毒面具(半面罩),戴化学安全防护眼镜,穿防毒物渗透工作服,戴橡胶手套。远离火种、热源,工作场所严禁吸烟。使用防爆型的通风系统和设备。防止蒸气泄漏到工作场所空气中。避免与氧化剂、酸类接触。搬运时要轻装轻卸,防止包装及容器损坏。配备相应品种和数量的消防器材及泄漏应急处理设备。倒空的容器可能残留有害物。 |
| 储存注意事项: | 储存于阴凉、通风的库房。远离火种、热源。包装要求密封,不可与空气接触。应与氧化剂、酸类等分开存放,切忌混储。不宜大量储存或久存。配备相应品种和数量的消防器材。储区应备有泄漏应急处理设备和合适的收容材料。 |
| 第八部分:接触控制/个体防护 |
| 最高容许浓度: | 中国MAC:未制定标准 苏联MAC:未制定标准 美国TWA:ACGIH 25ppm,106mg/m3 TLVWN: 未制定标准 |
| 监测方法: | |
| 工程控制: | 严加密闭,提供充分的局部排风。 |
| 呼吸系统防护: | 可能接触其蒸气时,应该佩带防毒面具。紧急事态抢救或逃生时,佩带自给式呼吸器。 |
| 眼睛防护: | 高浓度蒸气接触可戴化学安全防护眼镜。 |
| 身体防护: | 穿相应的防护服。 |
| 手防护: | 戴防化学品手套。 |
| 其他防护: | 工作现场禁止吸烟、进食和饮水。工作后,彻底清洗。单独存放被毒物污染的衣服,洗后再用。保持良好的卫生习 |
| 第九部分:理化特性 |
| 外观与性状: | 无色液体,略有气味。 |
| pH: | |
| 熔点(℃): | -74.8 |
| 沸点(℃): | 170.2 |
| 相对密度(水=1): | 0.90 |
| 相对蒸气密度(空气=1): | 4.07 |
| 饱和蒸气压(kPa): | 40.00/140℃ |
| 燃烧热(kJ/mol): | 无资料 |
| 临界温度(℃): | 无资料 |
| 临界压力(MPa): | 无资料 |
| 辛醇/水分配系数的对数值: | |
| 闪点(℃): | 71(O.C) |
| 引燃温度(℃): | 244 |
| 爆炸上限%(V/V): | 10.6(180℃) |
| 爆炸下限%(V/V): | 1.1(170℃) |
| 分子式: | C 6 H 14 O 2 |
| 分子量: | 118.17 |
| 蒸发速率: | |
| 粘性: | |
| 溶解性: | 溶于水、乙醇、乙醚等多数有机溶剂。 |
| 主要用途: | 用作溶剂和测定铁、钼的试剂。 |
| 第十部分:稳定性和反应活性 |
| 稳定性: | 在常温常压下 稳定 |
| 禁配物: | 强氧化剂、强酸、酰基氯、酸酐、卤素。 |
| 避免接触的条件: | 接触空气。 |
| 聚合危害: | 不能出现 |
| 分解产物: | 一氧化碳、二氧化碳。 |
| 第十一部分:毒理学资料 |
| 急性毒性: | 属低毒类 LD50:2500 mg/kg(大鼠经口);1200 mg/kg(小鼠经口) LC50:无资料 |
| 急性中毒: | |
| 慢性中毒: | |
| 亚急性和慢性毒性: | |
| 刺激性: | |
| 致敏性: | |
| 致突变性: | |
| 致畸性: | |
| 致癌性: |
| 第十二部分:生态学资料 |
| 生态毒理毒性: | |
| 生物降解性: | |
| 非生物降解性: | |
| 生物富集或生物积累性: |
| 第十三部分:废弃处置 |
| 废弃物性质: | |
| 废弃处置方法: | 处置前应参阅国家和地方有关法规。建议用焚烧法处置。 |
| 废弃注意事项: |
| 第十四部分:运输信息 |
| |
| 危险货物编号: | 61592 |
| UN编号: | 2369 |
| 包装标志: | |
| 包装类别: | Ⅲ |
| 包装方法: | 小开口钢桶;薄钢板桶或镀锡薄钢板桶(罐)外花格箱;螺纹口玻璃瓶、铁盖压口玻璃瓶、塑料瓶或金属桶(罐)外普通木箱。 |
| 运输注意事项: | 运输前应先检查包装容器是否完整、密封,运输过程中要确保容器不泄漏、不倒塌、不坠落、不损坏。严禁与酸类、氧化剂、食品及食品添加剂混运。运输时运输车辆应配备相应品种和数量的消防器材及泄漏应急处理设备。运输途中应防曝晒、雨淋,防高温。公路运输时要按规定路线行驶,勿在居民区和人口稠密区停留。 |
| RETCS号: | |
| IMDG规则页码: |
| 第十五部分:法规信息 |
| 国内化学品安全管理法规: | 化学危险物品安全管理条例 (1987年2月17日国务院发布),化学危险物品安全管理条例实施细则 (化劳发[1992] 677号),工作场所安全使用化学品规定 ([1996]劳部发423号)等法规,针对化学危险品的安全使用、生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应规定;常用危险化学品的分类及标志 (GB 13690-92)将该物质划为第6.1 类毒害品。 |
| 国际化学品安全管理法规: |
| 第十六部分:其他信息 |
| 参考文献: | 1.周国泰,化学危险品安全技术全书,化学工业出版社,1997 2.国家环保局有毒化学品管理办公室、北京化工研究院合编,化学品毒性法规环境数据手册,中国环境科学出版社.1992 3.Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety,CHEMINFO Database.1998 4.Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety, RTECS Database, 1989 |
| 填表时间: | 年月日 |
| 填表部门: | |
| 数据审核单位: | |
| 修改说明: | |
| 其他信息: | 1 |
| MSDS修改日期: | 年月日 |
制备方法与用途
乙二醇丁醚是环氧乙烷(EO)的重要衍生物之一,是一种绿色环保溶剂。它为无色液体,分子量118.17,沸点171.1℃,闪点60.5℃,不易挥发且相对密度0.9019。虽然有毒性,但它能与水、亚麻仁油的烃类溶剂混溶,并对天然橡胶和合成橡胶具有极强的溶解能力。此外,它也用作松香、虫胶、贝壳松脂及氧茚树脂、乙基纤维和硝酸纤维的溶剂。
物理性质乙二醇丁醚为无色易燃液体,有中等程度的醚味,并能溶于20倍量的水。它还溶于大多数有机溶剂及矿物油,适用于油漆、油墨的溶剂、金属清洗剂组分及染料分散剂的原料。
应用作为环氧化合物的重要工业衍生物之一,乙二醇丁醚是极为重要的精细化学品。由于分子中含有两个强溶解功能的基团——醚键和羟基,前者具有亲油性,后者则具亲水性,使其具备了极强的溶解能力,被称为“万能溶剂”。它广泛应用于涂料、油墨、清洗剂及药物萃取等领域。
生产方法乙二醇丁醚由环氧乙烷正丁醇加成而得。首先将正丁醇加入三氟化硼-乙醚络合物中,在25~30℃条件下通入环氧乙烷,自动升温至80℃左右完成反应。反应产物经回收丁醇后中和、蒸馏得粗品,再进行分馏以得到成品。
化学性质无色易燃液体,具有中等程度的醚味,并能溶于20倍量的水及大多数有机溶剂和矿物油。它被广泛用作油漆、油墨溶剂、金属清洗剂组分及染料分散剂原料。
用途主要用作硝酸纤维素、喷漆、快干漆、清漆、搪瓷和脱漆剂的溶剂,还能作为纤维润湿剂、农药分散剂、树脂增塑剂、有机合成中间体以及测定铁和钼的试剂。此外,它还用于分离硝酸盐中的钙和锶,并用作涂料、印刷油墨、图章用印台油墨、油类及树脂等溶剂金属洗涤剂、脱漆剂、脱润滑油剂、汽车引擎洗涤剂、干洗溶剂、环氧树脂溶剂、药物萃取剂,以及乳胶漆的稳定剂和飞机涂料蒸发抑制剂。
生产方法工业生产可采用在高温高压(反应温度180-250℃,压力为2.1-4.6MPa)下非催化反应的方法,反应6小时。也可采用碱催化剂,在近于常压及较低的温度下进行。
安全信息乙二醇丁醚属于易燃液体(类别),毒性分级为中毒级别。急性口服毒性:大鼠LD50: 470毫克/公斤;小鼠LD50: 1230毫克/公斤。刺激数据:皮肤-兔子500毫克轻度,眼睛-兔子100毫克重度。与空气混合可爆,遇明火、高温或强氧化剂可燃,并释放出刺激烟雾。
储存和运输时需注意库房通风良好,避免靠近明火和高温环境,远离氧化剂存放。灭火可用泡沫、二氧化碳、干粉或砂土。职业暴露限值(TLV-TWA)为25ppm(120毫克/立方米),短期接触极限(STEL)为200毫克/立方米。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 2-丙基-1,3-二氧戊环 2-propyl-1,3-dioxolane 3390-13-4 C6H12O2 116.16 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 丁基2-甲氧基乙基醚 1-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-butane 13343-98-1 C7H16O2 132.203 乙二醇二丁醚 1,2-dibutoxyethane 112-48-1 C10H22O2 174.283 1-丁氧基-2-乙氧基乙烷 1-(2-Ethoxyethoxy)butan 4413-13-2 C8H18O2 146.23 二乙二醇二丁醚 diethylene glycol dibutyl ether 112-73-2 C12H26O3 218.337 二乙二醇丁醚 Diethylene glycol monobutyl ether 112-34-5 C8H18O3 162.229 三乙二醇单丁醚 butyltriethyleneglycol 143-22-6 C10H22O4 206.282 乙烯二醇丁基乙烯基醚 ethylene glycol n-butyl vinyl diether 4223-11-4 C8H16O2 144.214 —— Butoxyethylformat 20442-04-0 C7H14O3 146.186 3-(2-丁氧基乙氧基)丙腈 3-(2-n-Butoxyethoxy)-propionitril 68140-96-5 C9H17NO2 171.239 1-[2-(烯丙氧基)乙氧基]丁烷 1-Allyloxy-2-butoxy-ethan 18854-51-8 C9H18O2 158.241 2-丁氧基乙酸 2-butoxyacetic acid 2516-93-0 C6H12O3 132.159 5,8,10,13-四氧杂十七烷 Di-(2-butoxyethoxy)-methan 17392-22-2 C13H28O4 248.363 1-(2-丁氧基乙氧基)庚烷 1-butoxy-2-heptyloxy-ethane 100799-15-3 C13H28O2 216.364 —— nitrous acid-(2-butoxy-ethyl ester) 41051-48-3 C6H13NO3 147.174 1-(2-丁氧基乙氧基)十一烷 1-butoxy-2-undecyloxy-ethane 108063-05-4 C17H36O2 272.472 1-(2-丁氧基乙氧基)十二烷 1-butoxy-2-dodecyloxy-ethane 101882-93-3 C18H38O2 286.499 1-(2-丁氧基乙氧基)辛烷 1-butoxy-2-octyloxy-ethane 100888-17-3 C14H30O2 230.391 1-(2-丁氧基乙氧基)癸烷 1-butoxy-2-decyloxy-ethane 101433-23-2 C16H34O2 258.445 1-(2-丁氧基乙氧基)壬烷 1-butoxy-2-nonyloxy-ethane 101082-17-1 C15H32O2 244.418 —— 3-butoxypropanal 13159-39-2 C7H14O2 130.187 N-丁氧基乙醛 2-butoxyacetaldehyde 29043-89-8 C6H12O2 116.16 (2-丁氧基乙基)胺盐酸盐 2-butoxyethylamine 6338-52-9 C6H15NO 117.191 2-丁氧基氯乙烷 1-(2-chloroethoxy)butane 10503-96-5 C6H13ClO 136.622 2-丁氧基乙基溴 1-(2-bromoethoxy)butane 6550-99-8 C6H13BrO 181.073 —— 3-(2-n-butoxyethoxy)-1,2-propanediole 20248-81-1 C9H20O4 192.255 乙二醇丁醚醋酸酯 2-butoxyethyl acetate 112-07-2 C8H16O3 160.213 2-羟基乙基丁酸酯 2-hydroxyethyl butanoate 4219-46-9 C6H12O3 132.159 3-(2-丁氧基乙氧基)丙酸 3-(2-n-Butoxyethoxy)-propionsaeure 7420-07-7 C9H18O4 190.24 —— 3-(2-n-butoxyethoxy)propylene 1,2-oxide 13483-47-1 C9H18O3 174.24 —— 1,3-Bis(2-butoxyethoxy)propan-2-ol —— C15H32O5 292.416 - 1
- 2
- 3
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Preparation of serotonine and derivatives摘要:一种从咖啡蜡中分离血清素的方法,其中将咖啡蜡溶液在惰性气氛中经受碱性水解,使用强碱和水,在此之后回收含有血清素的反应介质,其特征在于用于咖啡蜡的溶剂是具有通式II的化合物:R--(OC.sub.2 H.sub.4).sub.x --OC.sub.n H.sub.2n OH II,其中R是氢或含有1至4个碳原子的烷基基团,x为0或1,n为2至4之间的整数,但当n为3或4时,x不能为1。通过对血清素进行乙酰化制备N-乙酰血清素,然后选择性水解O-乙酰基团。通过在N-乙酰血清素的5-位置进行甲基化获得褪黑激素。通过在含有水不溶性醇的热碱性溶液中脱乙酰化褪黑激素,并用盐酸使醇相酸化得到梅夏明。公开号:US04506080A1
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:OPEN-FLASK HYDROBORATION AND THE USE THEREOF摘要:本公开涉及一种使用氨硼烷(AB)对烯烃或炔烃进行氢硼化的方法。具体而言,本发明涉及在空气或湿气存在下对烯烃或炔烃进行氢硼化,并通过氧化所形成的有机硼烷与过氧化氢进行简便制备醇的过程。本公开范围包括所制备的产物,包括氨基二烷基硼烷、氨三烷基硼烷配合物以及各种所制备的醇。公开号:US20180050972A1
-
作为试剂:描述:2-(4-氨基苯)-1,1,1,3,3,3-六氟-2-丙醇 、 二(2-氯乙基)胺盐酸盐 在 乙二醇单丁醚 、 potassium carbonate 作用下, 反应 24.0h, 以43%的产率得到1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoro-2-(4-(piperazin-1-yl)phenyl)-propan-2-ol参考文献:名称:JP2015/48326摘要:公开号:
文献信息
-
[EN] SUBSTITUTED QUINAZOLINES AS FUNGICIDES<br/>[FR] QUINAZOLINES SUBSTITUÉES, UTILISÉES EN TANT QUE FONGICIDES申请人:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG公开号:WO2010136475A1公开(公告)日:2010-12-02The present invention relates to a compound of formula (I) wherein wherein the substituents have the definitions as defined in claim 1or a salt or a N-oxide thereof, their use and methods for the control and/or prevention of microbial infection, particularly fungal infection, in plants and to processes for the preparation of these compounds.本发明涉及一种具有如下式(I)的化合物,其中取代基具有权利要求1中定义的定义,或其盐或N-氧化物,它们的用途以及用于控制和/或预防植物中微生物感染,特别是真菌感染的方法,以及制备这些化合物的方法。
-
[EN] MICROBIOCIDAL OXADIAZOLE DERIVATIVES<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS D'OXADIAZOLE MICROBIOCIDES申请人:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG公开号:WO2017157962A1公开(公告)日:2017-09-21Compounds of the formula (I) wherein the substituents are as defined in claim 1, useful as a pesticides, especially fungicides.式(I)的化合物,其中取代基如权利要求1所定义,作为杀虫剂特别是杀菌剂有用。
-
DIHYDROPYRIDAZINE-3,5-DIONE DERIVATIVE AND PHARMACEUTICALS CONTAINING THE SAME申请人:CHUGAI SEIYAKU KABUSHIKI KAISHA公开号:US20160002251A1公开(公告)日:2016-01-07The present invention provides a dihydropyridazine-3,5-dione derivative or a salt thereof, or a solvate of the compound or the salt, a pharmaceutical drug, a pharmaceutical composition, a sodium-dependent phosphate transporter inhibitor, and a preventive and/or therapeutic agent for hyperphosphatemia, secondary hyperparathyroidism, chronic renal failure, chronic kidney disease, and arteriosclerosis associated with vascular calcification comprising the compound as an active ingredient, and a method for prevention and/or treatment.
-
SYNTHESIS OF MORPHOLINO OLIGOMERS USING DOUBLY PROTECTED GUANINE MORPHOLINO SUBUNITS申请人:REEVES MATTHEW DALE公开号:US20090131624A1公开(公告)日:2009-05-21Morpholino compounds are provided having the structure: where R 1 is selected from the group consisting of lower alkyl, di(lower alkyl)amino, and phenyl; R 2 is selected from the group consisting of lower alkyl, monocyclic arylmethyl, and monocyclic (aryloxy)methyl; R 3 is selected from the group consisting of triarylmethyl and hydrogen; and Y is selected from the group consisting of: a protected or unprotected hydroxyl or amino group; a chlorophosphoramidate group; and a phosphorodiamidate linkage to the ring nitrogen of a further morpholino compound or a morpholino oligomer. Such compounds include doubly protected morpholino guanine (MoG) monomers. Also described is their use in synthesis of morpholino oligomers.
-
TAU-PROTEIN TARGETING PROTACS AND ASSOCIATED METHODS OF USE申请人:Arvinas, Inc.公开号:US20180125821A1公开(公告)日:2018-05-10The present disclosure relates to bifunctional compounds, which find utility as modulators of tau protein. In particular, the present disclosure is directed to bifunctional compounds, which contain on one end a VHL or cereblon ligand which binds to the E3 ubiquitin ligase and on the other end a moiety which binds tau protein, such that tau protein is placed in proximity to the ubiquitin ligase to effect degradation (and inhibition) of tau. The present disclosure exhibits a broad range of pharmacological activities associated with degradation/inhibition of tau protein. Diseases or disorders that result from aggregation or accumulation of tau protein are treated or prevented with compounds and compositions of the present disclosure.本公开涉及双功能化合物,其作为tau蛋白的调节剂具有实用性。具体而言,本公开涉及含有一端结合到E3泛素连接酶的VHL或cereblon配体,另一端结合到tau蛋白的双功能化合物,使得tau蛋白与泛素连接酶靠近,以实现tau蛋白的降解(和抑制)。本公开展示了与tau蛋白降解/抑制相关的广泛药理活性。本公开的化合物和组合物用于治疗或预防由tau蛋白聚集或积累导致的疾病或紊乱。
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
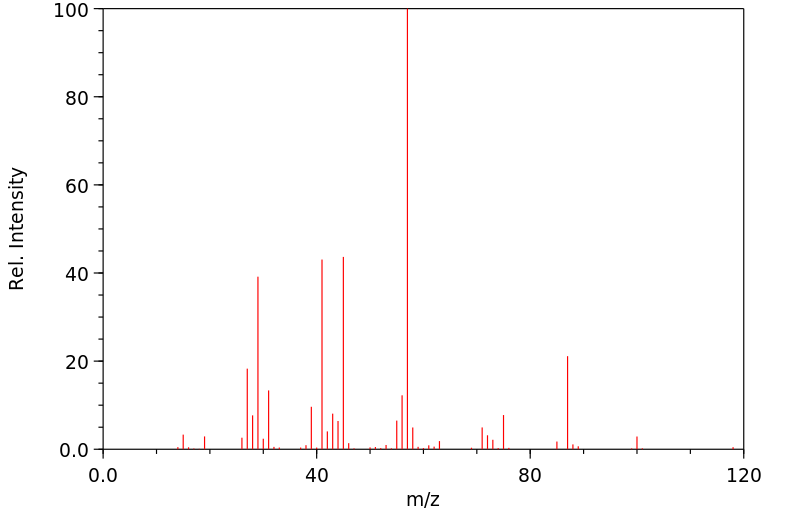
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
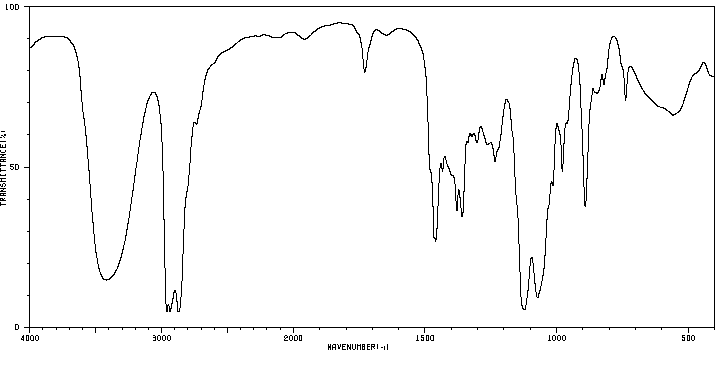
红外IR
-
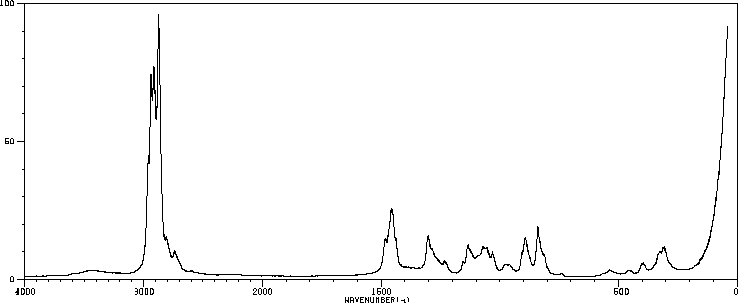
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息