乙氧基喹啉 | 91-53-2
中文名称
乙氧基喹啉
中文别名
乙氧喹啉;防老剂AW;抗氧宝;抗氧喹;虎皮灵;防老化剂AN;6-乙氧基-2,2,4-三甲基-1,2-二氢喹啉;6-乙氧基-2,2,4-三甲基-1,2-二氢化喹啉;乙氧喹;6-乙氧基-1,2-二氢-2,2,4-三甲基喹啉;1,2-二氢-6-乙氧基-2,2,4-三甲基喹啉;橡胶防老剂AW;山道喹
英文名称
Ethoxyquin
英文别名
6-ethoxy-2,2,4-trimethyl-1,2-dihydroquinoline;6-Ethoxy-2,2,4-trimethyl-1,2-dihydro-chinolin;6-ethoxy-1,2-dihydro-2,2,4-trimethyl quinoline;2,2,4-Trimethyl-6-ethoxy-1,2-dihydro-chinolin;6-Ethoxy-2,2,4-trimethyl-1,2-dihydrochinolin; Ethoxyquin;6-ethoxy-2,2,4-trimethyl-1H-quinoline
CAS
91-53-2
化学式
C14H19NO
mdl
MFCD00441325
分子量
217.311
InChiKey
DECIPOUIJURFOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:<0°C
-
沸点:123-125°C
-
密度:1.03 g/mL at 20 °C (lit.)
-
闪点:137 °C
-
溶解度:乙醇:50 mL/L,澄清,棕色
-
LogP:3.39
-
物理描述:Ethoxyquin is a clear light yellow to dark brown viscous liquid. Discolors and stains badly. Mercaptan-like odor. (NTP, 1992)
-
颜色/状态:YELLOW LIQUID
-
蒸汽密度:7.48 (NTP, 1992) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:1.82e-05 mm Hg at 32 °F ; 0.000256 mm Hg at 77° F (NTP, 1992)
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
分解:... WHEN HEATED TO DECOMP, EMITS TOXIC FUMES ... .
-
折光率:INDEX OF REFRACTION: 1.569-1.672 AT 25 °C/D
-
碰撞截面:152.6 Ų [M+H]+ [CCS Type: TW, Method: calibrated with polyalanine and drug standards]
-
保留指数:1717.6;1714.6
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):3.1
-
重原子数:16
-
可旋转键数:2
-
环数:2.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.43
-
拓扑面积:21.3
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:2
ADMET
代谢
主要代谢反应是乙氧基喹的脱乙基化,产生了6-羟基-2,2,4-三甲基-1,2-二氢喹啉和2,2,4-三甲基-6-喹啉。其他反应包括羟基化,形成了四种不同的羟基化代谢物和一个二羟基化代谢物。
MAJOR METABOLIC REACTION WAS DEETHYLATION OF ETHOXYQUIN WHICH PRODUCED 6-HYDROXY-2,2,4-TRIMETHYL-1,2-DIHYDROQUINOLINE & 2,2,4-TRIMETHYL-6-QUINOLINE. OTHER REACTIONS WERE HYDROXYLATION TO FOUR DIFFERENT HYDROXYLATED METABOLITES & ONE DIHYDROXYLATED METABOLITE.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
在给胆管插管的 rats 进行胃内给药 (14)C-ethoxyquin 后,12小时和24小时分别有28%和36%的放射性剂量在胆汁中恢复。除了未改变的 ethoxyquin 外,胆汁中的放射性物质还包括8-hydroxyethoxyquin、羟基化的8-hydroxyethoxyquin、6-ethoxy-2,2,4-trimethylquinolone、羟基化的6-ethoxy-2,2,4-trimethyl-8-quinolone、6-ethoxy-2,4-dimethylquinoline 和 2,2,4-trimethyl-6-quinolone。
An avg of 28 & 36% of dose of radioactivity was recovered in bile in 12 & 24 hr respectively following intragastric admin of (14)C-ethoxyquin to bile duct cannulated rats. Biliary radioactive substances included, in addn to unchanged ethoxyquin...8-hydroxyethoxyquin; hydroxylated 8-hydroxyethoxyquin; 6-ethoxy-2,2,4-trimethylquinolone; hydroxylated 6-ethoxy-2,2,4-trimethyl-8-quinolone; 6-ethoxy-2,4-dimethylquinoline; and 2,2,4-trimethyl-6-quinolone.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
对人类无致癌性(未列入国际癌症研究机构IARC清单)。
No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC).
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
职业性肝毒素 - 第二性肝毒素:在职业环境中的毒性效应潜力是基于人类摄入或动物实验的中毒病例。
Occupational hepatotoxin - Secondary hepatotoxins: the potential for toxic effect in the occupational setting is based on cases of poisoning by human ingestion or animal experimentation.
来源:Haz-Map, Information on Hazardous Chemicals and Occupational Diseases
毒理性
ELEVATION OF EPOXIDE HYDRATASE ACTIVITY IS OBTAINED BY IP OR ORAL TREATMENT OF MICE WITH ETHOXYQUIN. THIS ELEVATION IS PREVENTED BY CONCOMITANT TREATMENT WITH CYCLOHEXIMIDE.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
单次口服给予大鼠乙氧基喹(200毫克/千克)抑制了肝脏微粒体对噻菌灵、苯胺和联苯的羟基化作用,在给药后1小时体外分别减少了65%,40%和40%。口服乙氧基喹(400毫克/千克)延迟了噻菌灵的吸收并降低了其血浆浓度。
SINGLE ORAL DOSE OF ETHOXYQUIN (200 MG/KG) TO RATS INHIBITED HEPATIC MICROSOMAL HYDROXYLATION OF THIABENDAZOLE, ANILINE & BIPHENYL BY 65, 40 & 40% IN VITRO AT 1 HR AFTER DOSAGE. ORAL ETHOXYQUIN (400 MG/KG) DELAYED ABSORPTION OF & DECR PLASMA CONCN OF THIABENDAZOLE.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
研究了乙氧基喹在雄性Fischer大鼠饮食中的摄入对黄曲霉毒素B1代谢、DNA加合物形成与清除以及肝脏肿瘤发生的影响。大鼠被喂食含有0.4%乙氧基喹的半纯化饮食1周,然后在接下来的2周内每周5次通过胃管给予每公斤体重250微克的黄曲霉毒素B1,最后在停止给药后1周恢复到对照饮食。在4个月时,通过染色肝脏切片进行γ-谷氨酰转肽酶来识别和量化肝细胞变化的焦点区域。乙氧基喹的处理将γ-谷氨酰转肽酶阳性焦点的肝脏面积和体积减少了95%以上。使用相同的多剂量协议,确定了黄曲霉毒素B1对DNA的共价修饰模式。乙氧基喹显著减少了黄曲霉毒素B1与肝DNA的结合:初始时减少了18倍,在给药期末减少了3倍。尽管在给药后3个月和4个月时可以检测到结合,但乙氧基喹没有观察到效果,这表明这些持续的加合物与黄曲霉毒素B1致癌性没有直接相关性。通过高效液相色谱分析核酸碱基,发现治疗组之间加合物种类没有质的差异。乙氧基喹对黄曲霉毒素B1与DNA结合和肿瘤发生的抑制作用似乎与诱导解毒酶有关。喂食0.4%乙氧基喹7天的大鼠,肝细胞质谷胱甘肽S-转移酶(GST)的特异性活性增加了5倍。诱导了多种分子形式的谷胱甘肽S-转移酶,并且编码谷胱甘肽S-转移酶亚单位合成的信使RNA水平也相应升高。因此,在口服给予每公斤体重250微克黄曲霉毒素B1后的前2小时内,乙氧基喹饮食动物的胆汁中黄曲霉毒素B1-谷胱甘肽结合物的排泄增加了4.5倍。因此,乙氧基喹诱导的、对黄曲霉毒素B1解毒重要的酶,如谷胱甘肽S-转移酶,可以导致致癌物消除的增强,以及黄曲霉毒素B1-DNA加合物形成的减少和随后癌前病变的表达,最终减少肿瘤的发生。
The effects of dietary administration of ethoxyquin on aflatoxin B1 metabolism, DNA adduct formation and removal and hepatic tumorigenesis were examined in male Fischer rats. Rats were fed a semipurified diet containing 0.4% ethoxyquin for 1 wk, gavaged with 250 ug of aflatoxin B1 per kg 5 times a wk during the next 2 wk, and finally restored to the control diet 1 wk after cessation of dosing. At 4 mo, focal areas of hepatocellular alteration were identified and quantitated by staining sections of liver for gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. Treatment with ethoxyquin reduced by greater than 95% both area and volume of liver occupied by gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase-positive foci. Utilizing the same multiple dosing protocol, patterns of covalent modifications of DNA by aflatoxin B1 were determined. Ethoxyquin produced a dramatic reduction in the binding of aflatoxin B1 to hepatic DNA: 18-fold initially and 3-fold at the end of the dosing period. Although binding was detectable at 3 and 4 mo postdosing, no effect of ethoxyquin was observed, suggesting that these persistent adducts are not of primary relevance to aflatoxin B1 carcinogenesis. Analysis of nucleic acid bases by high-performance liquid chromatography revealed no qualitative differences in adduct species between treatment groups. The inhibitory effect of ethoxyquin on aflatoxin B1 binding to DNA and tumorigenesis appears related to induction of detoxication enzymes. Rats fed 0.4% ethoxyquin for 7 days showed a 5-fold increase in hepatic cytosolic glutathione S-transferase (GST)-specific activities. Multiple molecular forms of glutathione S-transferase were induced, and concomitant elevations in messenger RNA levels coding for the synthesis of glutathione S-transferase subunits were observed. Correspondingly, billary elimination of aflatoxin B1-glutathione conjugate was increased 4.5-fold in animals on the ethoxyquin diet during the first 2 hr following oral administration of 250 micrograms of aflatoxin B1 per kg. Thus, induction by ethoxyquin of enzymes important to aflatoxin B1 detoxication, such as glutathione S-transferase can lead to enhanced carcinogen elimination, as well as reductions of aflatoxin B1-DNA adduct formation and subsequent expression of preneoplastic lesions, and, ultimately, neoplasia.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
FEEDING TRIAL IN COWS WAS CONDUCTED TO DETERMINE WHETHER ETHOXYQUIN OR ITS RESIDUES ARE TRANSFERRED FROM FEED TO MILK WHEN ADDED TO COW FEED AT 0.015% OF DRY MATTER INTAKE. LESS THAN 7 UG ETHOXYQUIN/L WAS DETECTED IN MILK BY FLUORIMETRY & BY THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
(14)C-ETHOXYQUIN在给大鼠给药0.5小时后分布到大多数组织和血液中。在整个实验过程中,肝、肾、胃肠和脂肪组织的放射性最高。中枢神经系统没有活性。在大鼠给药后0.5小时和6天,分别有2.2%和0.2%的剂量在肝脏中找到。肝的放射性活性峰值在8小时测量;6天后,7.5%的此水平仍存在于肝脏中。在大鼠给药后6天,ETHOXYQUIN及其代谢物残留在肾皮质、肠、肺、各种脂肪组织和血液中。
(14)C-ETHOXYQUIN WAS DISTRIBUTED THROUGHOUT MOST TISSUES & BLOOD AT 0.5 HR AFTER ADMIN TO RATS. HIGHEST RADIOACTIVITY THROUGHOUT EXPERIMENT WAS OBSERVED IN LIVER, KIDNEY, GI TRACT & ADIPOSE TISSUE. THERE WAS NO ACTIVITY IN CNS. OF DOSE INGESTED BY RAT 2.2 & 0.2% WERE FOUND IN LIVER AT 0.5 HR & 6 DAYS RESPECTIVELY FOLLOWING DOSE. HEPATIC PEAK IN RADIOACTIVITY WAS MEASURED AT 8 HR; & AFTER 6 DAYS 7.5% OF THIS LEVEL WAS STILL PRESENT IN LIVER. 6 DAYS AFTER ADMIN TO RATS RESIDUES OF ETHOXYQUIN & METABOLITES WERE PRESENT IN KIDNEY CORTEX, INTESTINES, LUNG, VARIOUS ADIPOSE TISSUES & BLOOD.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
这种化合物容易被吸收、代谢,并随尿液和粪便排出。
The compound is readily absorbed, metabolized, and excreted in urine and feces.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
小鼠组织中的乙氧基喹残留量是通过高效液相色谱-荧光检测法测定的。给小鼠喂食含有0、0.125和0.5%乙氧基喹盐酸的粉末饲料,并在2、4、6、10和14周后(每组4只小鼠)测定肝脏、肾脏、肺和脑组织中的乙氧基喹残留量。组织样本在乙腈-水(7:3 v/v)的10倍体积(w/v)中匀浆,离心后,将上清液储存在冰箱中2-3小时,或者直到两层分离;然后分析清晰的上层。组织中乙氧基喹的平均残留量在0.84-4.58微克乙氧基喹/克肝脏和0.11-0.92微克乙氧基喹/克大脑之间。接受乙氧基喹的小鼠的肝脏相对重量(5.21-7.07%体重)和肝脏谷胱甘肽水平(5.99-7.83 uM GSH/克组织)显著高于对照组(4.67-5.05%体重和4.30-5.78 uM GSH/克组织)。在饮食中添加乙氧基喹14周后,高剂量乙氧基喹喂养组的小鼠肝脏线粒体谷胱甘肽平均水平大约是对照组和低剂量乙氧基喹喂养组(分别为0.83和0.74 nM GSH/毫克蛋白)的两倍(1.68 nM GSH/毫克蛋白)。
Ethoxyquin residue levels in the mouse tissue were determined by the HPLC-fluorometric detection method. Mice were given powdered feed containing 0, 0.125, and 0.5% ethoxyquin hydrochloric acid and the ethoxyquin residue levels in liver kidney, lung, and brain tissues were determined after 2, 4, 6, 10, and 14 wk (4 mice/group). The tissue samples were homogenized in 10 volumes (w/v) of acetonitrile-water (7:3 v/v) centrifuged and the supernatants were stored in a freezer for 2-3 hr or until the two layers separated; then the clear upper layers were analyzed. The mean ethoxyquin residue levels in the tissue ranged 0.84-4.58 ug ethoxyquin/g liver and 0.11-0.92 ug ethoxyquin/g brain. The relative weight of the liver (5.21-7.07% body weight) and the hepatic glutathione level (5.99-7.83 uM GSH/g tissue) of mice that received ethoxyquin were significantly higher than those of the controls (4.67-5.05% body weight and 4.30-5.78 uM GSH/g tissue, respectively). The mean hepatic mitochondrial glutathione levels of the higher ethoxyquin feeding group following dietary administration of ethoxyquin for 14 wk, was approximately twofold (1.68 nM GSH/mg protein) of both the control and the lower ethoxyquin feeding groups (0.83 and 0.74 nM GSH/mg protein, respectively.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
安全信息
-
危险等级:9
-
危险品标志:Xn
-
安全说明:S24
-
危险类别码:R22
-
WGK Germany:1
-
海关编码:2933499090
-
危险品运输编号:200kgs
-
RTECS号:VB8225000
-
储存条件:应密封于阴凉、通风处保存,防火、防潮、防晒。
SDS
1.1 产品标识符
: Ethoxyquin
化学品俗名或商品名
1.2 鉴别的其他方法
6-Ethoxy-1,2-dihydro-2,2,4-trimethylquinoline
1,2-Dihydro-6-ethoxy-2,2,4-trimethylquinoline
1.3 有关的确定了的物质或混合物的用途和建议不适合的用途
仅供科研用途,不作为药物、家庭备用药或其它用途。
模块 2. 危险性概述
2.1 GHS分类
急性毒性, 经口 (类别4)
皮肤敏化作用 (类别1)
急性的水体毒性 (类别2)
2.2 GHS 标记要素,包括预防性的陈述
危害类型象形图
信号词 警告
危险申明
H302 吞咽有害。
H317 可能导致皮肤过敏反应。
H401 对水生生物有毒。
警告申明
预防
P261 避免吸入粉尘/ 烟/ 气体/ 烟雾/ 蒸汽/ 喷雾。
P264 操作后彻底清洁皮肤。
P270 使用本产品时不要进食、饮水或吸烟。
P272 污染了的工作服不得带出工作场所。
P273 避免释放到环境中。
P280 戴防护手套。
措施
P301 + P312 如果吞下去了: 如感觉不适,呼救解毒中心或看医生。
P302 + P352 如果在皮肤上: 用大量肥皂和水淋洗。
P321 具体治疗(见本标签上提供的急救指导)。
P330 漱口。
P333 + P313 如发生皮肤刺激或皮疹:求医/ 就诊。
P363 沾染的衣服清洗后方可重新使用。
处理
P501 将内容物/ 容器处理到得到批准的废物处理厂。
2.3 其它危害物 - 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
3.1 物 质
: 6-Ethoxy-1,2-dihydro-2,2,4-trimethylquinoline
别名
1,2-Dihydro-6-ethoxy-2,2,4-trimethylquinoline
: C14H19NO
分子式
: 217.31 g/mol
分子量
成分 浓度
Ethoxyquin
-
化学文摘编号(CAS No.) 91-53-2
EC-编号 202-075-7
索引编号 613-014-00-2
模块 4. 急救措施
4.1 必要的急救措施描述
一般的建议
请教医生。 出示此安全技术说明书给到现场的医生看。
如果吸入
如果吸入,请将患者移到新鲜空气处。 如果停止了呼吸,给于人工呼吸。 请教医生。
在皮肤接触的情况下
用肥皂和大量的水冲洗。 请教医生。
在眼睛接触的情况下
用水冲洗眼睛作为预防措施。
如果误服
切勿给失去知觉者从嘴里喂食任何东西。 用水漱口。 请教医生。
4.2 最重要的症状和影响,急性的和滞后的
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
4.3 及时的医疗处理和所需的特殊处理的说明和指示
无数据资料
模块 5. 消防措施
5.1 灭火介质
灭火方法及灭火剂
用水雾,耐醇泡沫,干粉或二氧化碳灭火。
5.2 源于此物质或混合物的特别的危害
碳氧化物, 氮氧化物
5.3 救火人员的预防
如必要的话,戴自给式呼吸器去救火。
5.4 进一步的信息
无数据资料
模块 6. 泄露应急处理
6.1 人员的预防,防护设备和紧急处理程序
使用个人防护设备。 防止吸入蒸汽、气雾或气体。 保证充分的通风。
6.2 环境预防措施
在确保安全的条件下,采取措施防止进一步的泄漏或溢出。 不要让产物进入下水道。
防止排放到周围环境中。
6.3 抑制和清除溢出物的方法和材料
用惰性吸附材料吸收并当作危险废品处理。 存放在合适的封闭的处理容器内。
6.4 参考其他部分
丢弃处理请参阅第13节。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
7.1 安全操作的注意事项
避免接触皮肤和眼睛。 防止吸入蒸汽和烟雾。
7.2 安全储存的条件,包括任何不兼容性
贮存在阴凉处。 容器保持紧闭,储存在干燥通风处。
7.3 特定用途
无数据资料
模块 8. 接触控制/个体防护
8.1 控制参数
最高容许浓度
没有已知的国家规定的暴露极限。
8.2 暴露控制
适当的技术控制
根据工业卫生和安全使用规则来操作。 休息以前和工作结束时洗手。
人身保护设备
眼/面保护
面罩與安全眼鏡请使用经官方标准如NIOSH (美国) 或 EN 166(欧盟) 检测与批准的设备防护眼部。
皮肤保护
戴手套取 手套在使用前必须受检查。
请使用合适的方法脱除手套(不要接触手套外部表面),避免任何皮肤部位接触此产品.
使用后请将被污染过的手套根据相关法律法规和有效的实验室规章程序谨慎处理. 请清洗并吹干双手
所选择的保护手套必须符合EU的89/686/EEC规定和从它衍生出来的EN 376标准。
身体保护
全套防化学试剂工作服, 防护设备的类型必须根据特定工作场所中的危险物的浓度和含量来选择。
呼吸系统防护
如危险性评测显示需要使用空气净化的防毒面具,请使用全面罩式多功能防毒面具(US)或ABEK型
(EN
14387)防毒面具筒作为工程控制的候补。如果防毒面具是保护的唯一方式,则使用全面罩式送风防
毒面具。 呼吸器使用经过测试并通过政府标准如NIOSH(US)或CEN(EU)的呼吸器和零件。
模块 9. 理化特性
9.1 基本的理化特性的信息
a) 外观与性状
形状: 透明, 液体
颜色: 深棕
b) 气味
无数据资料
c) 气味临界值
无数据资料
d) pH值
无数据资料
e) 熔点/凝固点
无数据资料
f) 起始沸点和沸程
无数据资料
g) 闪点
无数据资料
h) 蒸发速率
无数据资料
i) 可燃性(固体,气体)
无数据资料
j) 高的/低的燃烧性或爆炸性限度 无数据资料
k) 蒸气压
无数据资料
l) 相对蒸气密度
无数据资料
m) 相对密度
1.03 g/cm3 在 20 °C
n) 水溶性
无数据资料
o) 辛醇/水分配系数的对数值
无数据资料
p) 自燃温度
无数据资料
q) 分解温度
无数据资料
r) 粘度
无数据资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应活性
10.1 反应性
无数据资料
10.2 化学稳定性
无数据资料
10.3 危险反应的可能性
无数据资料
10.4 避免接触的条件
无数据资料
10.5 不兼容的材料
无数据资料
10.6 危险的分解产物
其它分解产物 - 无数据资料
模块 11. 毒理学资料
11.1 毒理学影响的信息
急性毒性
半致死剂量(LD50) 经口 - 大鼠 - 800 mg/kg
皮肤腐蚀/刺激
无数据资料
严重眼损伤 / 眼刺激
无数据资料
呼吸道或皮肤过敏
会引起过敏性皮肤反应。
生殖细胞诱变
离体的基因毒性 - 组氨酸逆转(Ames)
对体内基因的毒性 - 大鼠 - 经口
非常规DNA合成
致癌性
IARC:
此产品中没有大于或等于 0。1%含量的组分被 IARC鉴别为可能的或肯定的人类致癌物。
生殖毒性
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触)
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(反复接触)
无数据资料
吸入危险
无数据资料
潜在的健康影响
吸入 吸入可能有害。 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
摄入 误吞对人体有害。
皮肤 如果通过皮肤吸收可能是有害的。 可能引起皮肤刺激。
眼睛 可能引起眼睛刺激。
接触后的征兆和症状
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
附加说明
化学物质毒性作用登记: VB8225000
模块 12. 生态学资料
12.1 毒性
对水蚤和其他水生无脊 半致死有效浓度(EC50) - Daphnia magna (大型蚤) - 2.0 mg/l - 48 h
椎动物的毒性。
12.2 持久存留性和降解性
无数据资料
12.3 生物积累的潜在可能性
无数据资料
12.4 土壤中的迁移
无数据资料
12.5 PBT 和 vPvB的结果评价
无数据资料
12.6 其它不利的影响
对水生生物有毒。
无数据资料
模块 13. 废弃处置
13.1 废物处理方法
产品
将剩余的和未回收的溶液交给处理公司。
污染了的包装物
作为未用过的产品弃置。
模块 14. 运输信息
14.1 UN编号
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.2 联合国(UN)规定的名称
欧洲陆运危规: 无危险货物
国际海运危规: 无危险货物
国际空运危规: 无危险货物
14.3 运输危险类别
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.4 包裹组
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.5 环境危险
欧洲陆运危规: 否 国际海运危规 海运污染物: 否 国际空运危规: 否
14.6 对使用者的特别预防
无数据资料
公司对任何操作或者接触上述产品而引起的损害不负有任何责任,。更多使用条款,参见发票或包
装条的反面。
模块 15 - 法规信息
N/A
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
: Ethoxyquin
化学品俗名或商品名
1.2 鉴别的其他方法
6-Ethoxy-1,2-dihydro-2,2,4-trimethylquinoline
1,2-Dihydro-6-ethoxy-2,2,4-trimethylquinoline
1.3 有关的确定了的物质或混合物的用途和建议不适合的用途
仅供科研用途,不作为药物、家庭备用药或其它用途。
模块 2. 危险性概述
2.1 GHS分类
急性毒性, 经口 (类别4)
皮肤敏化作用 (类别1)
急性的水体毒性 (类别2)
2.2 GHS 标记要素,包括预防性的陈述
危害类型象形图
信号词 警告
危险申明
H302 吞咽有害。
H317 可能导致皮肤过敏反应。
H401 对水生生物有毒。
警告申明
预防
P261 避免吸入粉尘/ 烟/ 气体/ 烟雾/ 蒸汽/ 喷雾。
P264 操作后彻底清洁皮肤。
P270 使用本产品时不要进食、饮水或吸烟。
P272 污染了的工作服不得带出工作场所。
P273 避免释放到环境中。
P280 戴防护手套。
措施
P301 + P312 如果吞下去了: 如感觉不适,呼救解毒中心或看医生。
P302 + P352 如果在皮肤上: 用大量肥皂和水淋洗。
P321 具体治疗(见本标签上提供的急救指导)。
P330 漱口。
P333 + P313 如发生皮肤刺激或皮疹:求医/ 就诊。
P363 沾染的衣服清洗后方可重新使用。
处理
P501 将内容物/ 容器处理到得到批准的废物处理厂。
2.3 其它危害物 - 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
3.1 物 质
: 6-Ethoxy-1,2-dihydro-2,2,4-trimethylquinoline
别名
1,2-Dihydro-6-ethoxy-2,2,4-trimethylquinoline
: C14H19NO
分子式
: 217.31 g/mol
分子量
成分 浓度
Ethoxyquin
-
化学文摘编号(CAS No.) 91-53-2
EC-编号 202-075-7
索引编号 613-014-00-2
模块 4. 急救措施
4.1 必要的急救措施描述
一般的建议
请教医生。 出示此安全技术说明书给到现场的医生看。
如果吸入
如果吸入,请将患者移到新鲜空气处。 如果停止了呼吸,给于人工呼吸。 请教医生。
在皮肤接触的情况下
用肥皂和大量的水冲洗。 请教医生。
在眼睛接触的情况下
用水冲洗眼睛作为预防措施。
如果误服
切勿给失去知觉者从嘴里喂食任何东西。 用水漱口。 请教医生。
4.2 最重要的症状和影响,急性的和滞后的
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
4.3 及时的医疗处理和所需的特殊处理的说明和指示
无数据资料
模块 5. 消防措施
5.1 灭火介质
灭火方法及灭火剂
用水雾,耐醇泡沫,干粉或二氧化碳灭火。
5.2 源于此物质或混合物的特别的危害
碳氧化物, 氮氧化物
5.3 救火人员的预防
如必要的话,戴自给式呼吸器去救火。
5.4 进一步的信息
无数据资料
模块 6. 泄露应急处理
6.1 人员的预防,防护设备和紧急处理程序
使用个人防护设备。 防止吸入蒸汽、气雾或气体。 保证充分的通风。
6.2 环境预防措施
在确保安全的条件下,采取措施防止进一步的泄漏或溢出。 不要让产物进入下水道。
防止排放到周围环境中。
6.3 抑制和清除溢出物的方法和材料
用惰性吸附材料吸收并当作危险废品处理。 存放在合适的封闭的处理容器内。
6.4 参考其他部分
丢弃处理请参阅第13节。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
7.1 安全操作的注意事项
避免接触皮肤和眼睛。 防止吸入蒸汽和烟雾。
7.2 安全储存的条件,包括任何不兼容性
贮存在阴凉处。 容器保持紧闭,储存在干燥通风处。
7.3 特定用途
无数据资料
模块 8. 接触控制/个体防护
8.1 控制参数
最高容许浓度
没有已知的国家规定的暴露极限。
8.2 暴露控制
适当的技术控制
根据工业卫生和安全使用规则来操作。 休息以前和工作结束时洗手。
人身保护设备
眼/面保护
面罩與安全眼鏡请使用经官方标准如NIOSH (美国) 或 EN 166(欧盟) 检测与批准的设备防护眼部。
皮肤保护
戴手套取 手套在使用前必须受检查。
请使用合适的方法脱除手套(不要接触手套外部表面),避免任何皮肤部位接触此产品.
使用后请将被污染过的手套根据相关法律法规和有效的实验室规章程序谨慎处理. 请清洗并吹干双手
所选择的保护手套必须符合EU的89/686/EEC规定和从它衍生出来的EN 376标准。
身体保护
全套防化学试剂工作服, 防护设备的类型必须根据特定工作场所中的危险物的浓度和含量来选择。
呼吸系统防护
如危险性评测显示需要使用空气净化的防毒面具,请使用全面罩式多功能防毒面具(US)或ABEK型
(EN
14387)防毒面具筒作为工程控制的候补。如果防毒面具是保护的唯一方式,则使用全面罩式送风防
毒面具。 呼吸器使用经过测试并通过政府标准如NIOSH(US)或CEN(EU)的呼吸器和零件。
模块 9. 理化特性
9.1 基本的理化特性的信息
a) 外观与性状
形状: 透明, 液体
颜色: 深棕
b) 气味
无数据资料
c) 气味临界值
无数据资料
d) pH值
无数据资料
e) 熔点/凝固点
无数据资料
f) 起始沸点和沸程
无数据资料
g) 闪点
无数据资料
h) 蒸发速率
无数据资料
i) 可燃性(固体,气体)
无数据资料
j) 高的/低的燃烧性或爆炸性限度 无数据资料
k) 蒸气压
无数据资料
l) 相对蒸气密度
无数据资料
m) 相对密度
1.03 g/cm3 在 20 °C
n) 水溶性
无数据资料
o) 辛醇/水分配系数的对数值
无数据资料
p) 自燃温度
无数据资料
q) 分解温度
无数据资料
r) 粘度
无数据资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应活性
10.1 反应性
无数据资料
10.2 化学稳定性
无数据资料
10.3 危险反应的可能性
无数据资料
10.4 避免接触的条件
无数据资料
10.5 不兼容的材料
无数据资料
10.6 危险的分解产物
其它分解产物 - 无数据资料
模块 11. 毒理学资料
11.1 毒理学影响的信息
急性毒性
半致死剂量(LD50) 经口 - 大鼠 - 800 mg/kg
皮肤腐蚀/刺激
无数据资料
严重眼损伤 / 眼刺激
无数据资料
呼吸道或皮肤过敏
会引起过敏性皮肤反应。
生殖细胞诱变
离体的基因毒性 - 组氨酸逆转(Ames)
对体内基因的毒性 - 大鼠 - 经口
非常规DNA合成
致癌性
IARC:
此产品中没有大于或等于 0。1%含量的组分被 IARC鉴别为可能的或肯定的人类致癌物。
生殖毒性
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触)
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(反复接触)
无数据资料
吸入危险
无数据资料
潜在的健康影响
吸入 吸入可能有害。 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
摄入 误吞对人体有害。
皮肤 如果通过皮肤吸收可能是有害的。 可能引起皮肤刺激。
眼睛 可能引起眼睛刺激。
接触后的征兆和症状
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
附加说明
化学物质毒性作用登记: VB8225000
模块 12. 生态学资料
12.1 毒性
对水蚤和其他水生无脊 半致死有效浓度(EC50) - Daphnia magna (大型蚤) - 2.0 mg/l - 48 h
椎动物的毒性。
12.2 持久存留性和降解性
无数据资料
12.3 生物积累的潜在可能性
无数据资料
12.4 土壤中的迁移
无数据资料
12.5 PBT 和 vPvB的结果评价
无数据资料
12.6 其它不利的影响
对水生生物有毒。
无数据资料
模块 13. 废弃处置
13.1 废物处理方法
产品
将剩余的和未回收的溶液交给处理公司。
污染了的包装物
作为未用过的产品弃置。
模块 14. 运输信息
14.1 UN编号
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.2 联合国(UN)规定的名称
欧洲陆运危规: 无危险货物
国际海运危规: 无危险货物
国际空运危规: 无危险货物
14.3 运输危险类别
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.4 包裹组
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.5 环境危险
欧洲陆运危规: 否 国际海运危规 海运污染物: 否 国际空运危规: 否
14.6 对使用者的特别预防
无数据资料
公司对任何操作或者接触上述产品而引起的损害不负有任何责任,。更多使用条款,参见发票或包
装条的反面。
模块 15 - 法规信息
N/A
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
制备方法与用途
理化性质
乙氧基喹啉(简称EQ或EMQ,又名乙氧喹)商品名为山道喹、珊多喹、虎皮灵、衣索金。是一种黄色至黄褐色的黏滞性液体,并带有特殊气味。不溶于水,但易溶于苯、汽油、醚、醇、四氯化碳和丙酮等有机溶剂中。在自然光下易氧化,遇空气和氧气后色泽会变深呈暗褐色且粘度增加。应避光密闭保存,溶液颜色变化不会影响其使用效果。本品系合成的抗氧化剂,含量为97.5%,主要用作食品和饲料的抗氧剂。
鉴别试验将1mg试样溶于乙腈10ml中,在短波紫外线下观察时应呈强荧光。
含量分析精确称取约200mg样品,置于-150ml烧杯中,加入50ml冰醋酸,立即用0.1mol/L高氯酸的冰醋酸溶液滴定。以电势法确定终点,并进行空白试验并作必要校正。每mL 0.1mol/L高氯酸相当于乙氧基喹(C14H19NO)21.73mg。
毒性GRAS(FDA,§172.140,2000)。LD50为800mg/kg(大鼠经口)。
使用限量- GB 2760-96:苹果保鲜,以GMP为限,残留量≤lmg/kg。
- FDA,§172.140(2000):辣椒制品的护色≤100mg/kg。
2022年10月31日,欧盟委员会将合成抗氧化剂乙氧基喹啉列入禁用名单,除了欧盟进口鱼粉不得含有该物质外,任何投喂过含该物质饲料的农产品也被禁止。2022年8月5日,欧盟委员会通过第2022/1375号法规拒绝在所有动物养殖和食品类别中重新授权乙氧基喹啉的使用。
化学性质纯品为浅褐色粘稠液体。溶于苯、汽油、乙醚、乙醇、四氯化碳、丙酮、二氯乙烷,不溶于水。
生产方法一般由对氨基苯乙醚与丙酮在催化剂作用下缩合而得。将对氨基苯乙醚、催化剂(对甲苯磺酸或碘),在155~165℃和搅拌下通入丙酮蒸气进行缩合,反应生成的水和未反应的丙酮经冷凝后入丙酮回收器以回收丙酮。反应结束后,蒸馏得到成品。每吨产品消耗对氨基苯乙醚1000kg、丙酮800kg、苯磺酸100kg。
物理化学性质上下游信息
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 2,2,4-三甲基-1,2-二氢-喹啉-6-醇 2,2,4-trimethyl-6-hydroxy-1,2-dihydroquinoline 72107-05-2 C12H15NO 189.257 —— 6-ethoxy-1,2,2,4-tetramethyl-1,2-dihydroquinoline 71043-65-7 C15H21NO 231.338 —— 8-cyclopentenyl-6-ethoxy-1,2-dihydro-2,2,4-trimethylquinoline 1359974-05-2 C19H25NO 283.414 —— 8-cyclohexenyl-6-ethoxy-1,2-dihydro-2,2,4-trimethylquinoline 1359974-04-1 C20H27NO 297.44 —— 6-Ethoxy-2,2,4-trimethyl-1-phenyl-1,2-dihydroquinoline 105825-14-7 C20H23NO 293.4 —— 1,2-dihydro-2,2,4-trimethyl-6-quinolinyl retinoate 79787-62-5 C32H41NO2 471.683 —— 1-benzyl-6-ethoxy-1,2-dihydro-2,2,4-trimethylquinoline 126769-68-4 C21H25NO 307.436 —— 1-chlorocarbonyl-6-ethoxy-1,2-dihydro-2,2,4-trimethylquinoline 68056-76-8 C15H18ClNO2 279.766 —— 1-benzyl-1,2-dihydro-2,2,4-trimethylquinolin-6-yl acetate 1203564-82-2 C21H23NO2 321.419 —— 1-(4-isopropylbenzyl)-1,2-dihydro-2,2,4-trimethylquinolin-6-yl acetate 1265153-65-8 C24H29NO2 363.5 —— 1-benzyl-1,2-dihydro-2,2,4-trimethylquinolin-6-ol 1203564-68-4 C19H21NO 279.382 —— 1-(3,4-difluorobenzyl)-6-ethoxy-1,2-dihydro-2,2,4-trimethylquinoline 1265153-62-5 C21H23F2NO 343.417 —— 6-ethoxy-2,2,4-trimethyl-1-phenylcarbamoyl-1,2-dihydro-quinoline 102375-14-4 C21H24N2O2 336.434 —— 1-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1,2-dihydro-2,2,4-trimethylquinolin-6-yl acetate 1265153-64-7 C22H25NO3 351.445 —— 1-(3,4-difluorobenzyl)-1,2-dihydro-2,2,4-trimethylquinolin-6-yl acetate 1265153-63-6 C21H21F2NO2 357.4 —— 1-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1,2-dihydro-2,2,4-trimethylquinolin-6-ol 1265153-75-0 C20H23NO2 309.408 —— 6-ethoxy-1-(3,4-dichloro-phenylcarbamoyl)-2,2,4-trimethyl-1,2-dihydro-quinoline 113491-87-5 C21H22Cl2N2O2 405.324 —— 1-(3,4-difluorobenzyl)-1,2-dihydro-2,2,4-trimethylquinolin-6-ol 1265153-74-9 C19H19F2NO 315.363 —— (all-E)-1-[3,7-dimethyl-1-oxo-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenyl]-6-ethoxy-1,2-dihydro-2,2,4-trimethylquinoline 79787-61-4 C34H45NO2 499.737 乙氧基喹啉二聚体 6-ethoxy-1-(6-ethoxy-1,2-dihydro-2,2,4-trimethylquinolin-8-yl)-1,2-dihydro-2,2,4-trimethylquinoline 74681-77-9 C28H36N2O2 432.606 6-乙氧基-1,2,3,4-四氢-2,2,4-三甲基喹啉 6-ethoxy-2,2,4-trimethyl-1,3-dihydroquinoline 16489-90-0 C14H21NO 219.327 - 1
- 2
- 3
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:SUBSTITUTED 1,2-DIHYDROQUINOLINES WITH LOW CONTAMINANT LEVELS AND PROCESSES FOR PREPARING摘要:制备含有取代1,2-二氢喹啉且具有低或不可检测水平的取代苯胺的组合物的过程,其中该过程包括从含有取代1,2-二氢喹啉和取代苯胺的进料流中去除取代苯胺。公开号:US20170298006A1
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:Multifaceted approach toward mapping out the anticancer properties of small molecules via in vitro evaluation on melanoma and nonmelanoma skin cancer cells, and in silico target fishing摘要:摘要 黑色素瘤和非黑色素瘤皮肤癌是发病率最高、致死率最高的皮肤癌之一。为了鉴定具有潜在抗癌特性的新先导化合物并进行进一步优化,我们采用体外试验结合体内靶标捕获和对接的方法,从我们实验室以前制备的小型化合物库中鉴定并进一步绘制出分子的抗增殖作用和潜在作用模式图。通过对 A375、SK-MEL-28、A431 和 SCC-12 皮肤癌细胞系进行体外筛选,35 个化合物显示出微摩水平的抗增殖活性,其中大多数化合物主要对 A431 和 SCC-12 鳞癌细胞系有效。活性最强的化合物 11(A431:IC50 = 5.0 μM;SCC-12:IC50 = 2.9 μM;SKMEL-28:IC50 = 4.9 μM;A375:IC50 = 6.7 μM)和 13(A431:IC50 = 5.0 μM,SCC-12:IC50 = 3.3 μM,SKMEL-28:IC50 = 13.8 μM,A375:两种药物都能显著诱导 SCC-12 和 SK-MEL-28 细胞凋亡,且呈剂量依赖性,表现为抑制 Bcl-2,上调 Bax、裂解的 caspase-3、caspase-9 和 PARP 蛋白表达水平。这两种制剂都能明显降低划痕伤口愈合、集落形成以及包括 RSK/Akt/ERK1/2 和 S6K1 在内的失调癌症分子靶点的表达水平。利用 SwissTargetPrediction 网络工具进行的硅学靶点预测和对接研究表明,CDK8、CLK4、核受体 ROR、酪氨酸蛋白激酶 Fyn/LCK、ROCK1/2 和 PARP(所有这些靶点在皮肤癌中都失调)可能是这两种活性最强的化合物的潜在靶点。通过西部印迹分析对这些靶点的进一步验证表明,ROCK/Fyn 及其相关的刺猬(Hh)通路受到这两种先导化合物的下调或调节。总之,这些结果为进一步验证观察到的活性以及通过制备和生物评估类似物来发展更全面的结构-活性关系提供了一个强有力的框架。DOI:10.1111/cbdd.14418
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:1-Acylethoxyquin compounds and compositions for treating vitamin摘要:本发明涉及6-乙氧基-1,2-二氢-2,2,4-三甲基喹啉(称为“乙氧喹啉”)的衍生物,其制备方法及其作为药物组合物的活性成分的效用。所述化合物在生物条件下具有抗氧化特性,可用于保护缺乏维生素E的动物,并作为促进生长的剂。公开号:US04305932A1
文献信息
-
[EN] MICROBIOCIDAL OXADIAZOLE DERIVATIVES<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS D'OXADIAZOLE MICROBIOCIDES申请人:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG公开号:WO2017157962A1公开(公告)日:2017-09-21Compounds of the formula (I) wherein the substituents are as defined in claim 1, useful as a pesticides, especially fungicides.式(I)的化合物,其中取代基如权利要求1所定义,作为杀虫剂特别是杀菌剂有用。
-
Thieno-pyrimidine compounds having fungicidal activity
-
Molecules having pesticidal utility, and intermediates, compositions, and processes, related thereto申请人:Dow AgroSciences LLC公开号:US20180279612A1公开(公告)日:2018-10-04This disclosure relates to the field of molecules having pesticidal utility against pests in Phyla Arthropoda, Mollusca, and Nematoda, processes to produce such molecules, intermediates used in such processes, pesticidal compositions containing such molecules, and processes of using such pesticidal compositions against such pests. These pesticidal compositions may be used, for example, as acaricides, insecticides, miticides, molluscicides, and nematicides. This document discloses molecules having the following formula (“Formula One”).
-
CONDENSED HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS AND PESTICIDES申请人:Nissan Chemical Industries, Ltd.公开号:US20180022760A1公开(公告)日:2018-01-25To provide novel pesticides, especially insecticides or acaricides. A condensed heterocyclic compound represented by the formula (1) or its salt or an N-oxide thereof: wherein D substituted with —S(O) n R 1 is a ring represented by any one of D1, D2 and D3, Q is a ring represented by any one of Q1, Q2, Q3 and Q4, R 1 is C 1 -C 6 alkyl, C 1 -C 6 haloalkyl, (C 1 -C 6 ) alkyl optionally substituted with R 1a , C 2 -C 6 alkenyl, C 2 -C 6 haloalkenyl, C 2 -C 6 alkynyl, C 2 -C 6 haloalkynyl, C 3 -C 6 cycloalkyl, C 3 -C 6 halocycloalkyl, C 3 -C 6 cycloalkyl (C 1 -C 6 ) alkyl, C 3 -C 6 halocycloalkyl (C 1 -C 6 ) alkyl or hydroxy (C 1 -C 6 ) alkyl, R 1a is C 1 -C 8 alkoxycarbonyl, and n is an integer of 0, 1 or 2.
-
[EN] MOLECULES HAVING PESTICIDAL UTILITY, AND INTERMEDIATES, COMPOSITIONS, AND PROCESSES, RELATED THERETO<br/>[FR] MOLÉCULES PRÉSENTANT UNE UTILITÉ EN TANT QUE PESTICIDE, ET LEURS INTERMÉDIAIRES, COMPOSITIONS ET PROCÉDÉS申请人:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC公开号:WO2017040194A1公开(公告)日:2017-03-09This disclosure relates to the field of molecules having pesticidal utility against pests in Phyla Arthropoda, Mollusca, and Nematoda, processes to produce such molecules, intermediates used in such processes, pesticidal compositions containing such molecules, and processes of using such pesticidal compositions aga inst such pests. These pesticidal compositions may be used, for example, as acaricides, insecticides, miticides, molluscicides, and nematicides. This document discloses molecules having the following formula ("Formula One").
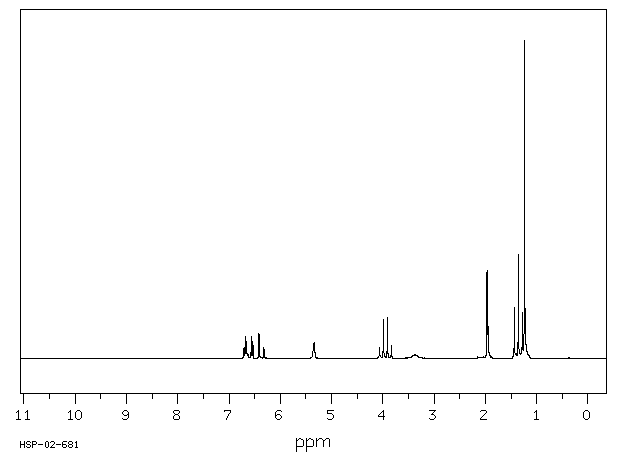
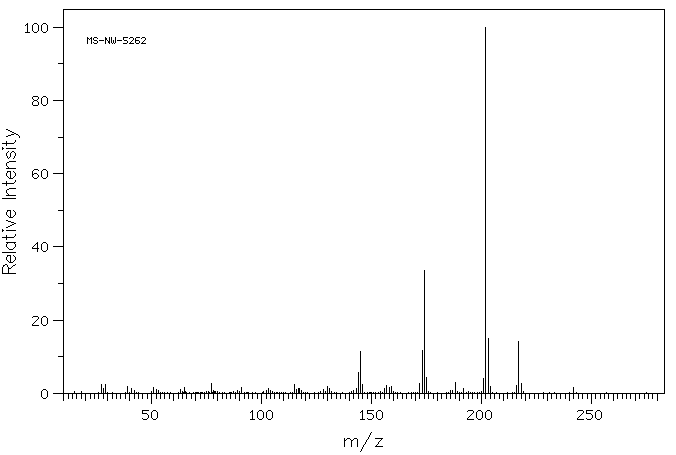
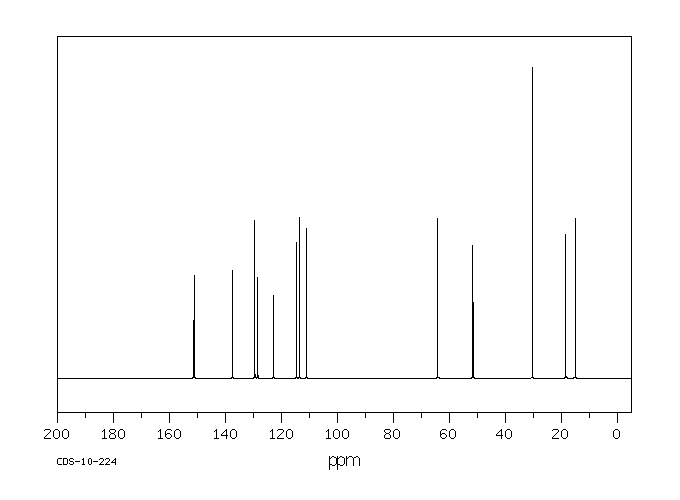
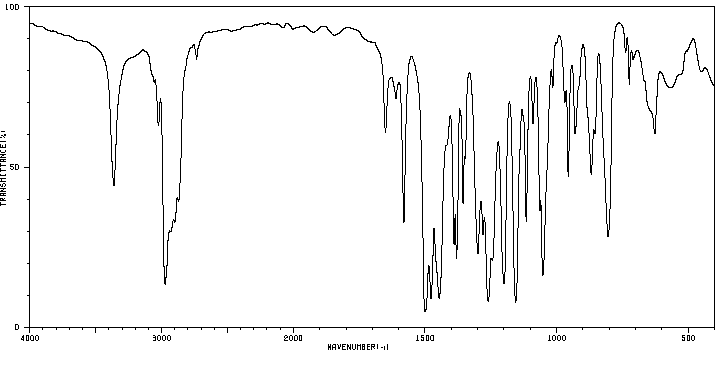
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(S)-4-(叔丁基)-2-(喹啉-2-基)-4,5-二氢噁唑
(SP-4-1)-二氯双(喹啉)-钯
(E)-2-氰基-3-[5-(2,5-二氯苯基)呋喃-2-基]-N-喹啉-8-基丙-2-烯酰胺
(8α,9S)-(+)-9-氨基-七氢呋喃-6''-醇,值90%
(6,7-二甲氧基-4-(3,4,5-三甲氧基苯基)喹啉)
(1-羟基-5-硝基-8-氧代-8,8-dihydroquinolinium)
黄尿酸 8-甲基醚
麻保沙星EP杂质D
麻保沙星EP杂质B
麻保沙星EP杂质A
麦角腈甲磺酸盐
麦角腈
麦角灵
麦皮星酮
麦特氧特
高铁试剂
高氯酸3-苯基[1,3]噻唑并[3,2-f]5-氮杂菲-4-正离子
马波沙星EP杂质F
马波沙星
马来酸茚达特罗杂质
马来酸茚达特罗
马来酸维吖啶
马来酸来那替尼
马来酸四甲基铵
香草木宁碱
颜料红R-122
颜料红210
颜料红
顺式-苯并(f)喹啉-7,8-二醇-9,10-环氧化物
顺式-(alphaR)-N-(4-氯苯基)-4-(6-氟-4-喹啉基)-alpha-甲基环己烷乙酰胺
非那沙星
非那沙星
青花椒碱
青色素863
雷西莫特
隐花青
阿莫地喹-d10
阿莫地喹
阿莫吡喹N-氧化物
阿美帕利
阿米诺喹
阿立哌唑溴代杂质
阿立哌唑杂质B
阿立哌唑杂质38
阿立哌唑杂质1750
阿立哌唑杂质13
阿立哌唑杂质
阿立哌唑杂质
阿尔马尔
阿加曲班杂质43