毒理性
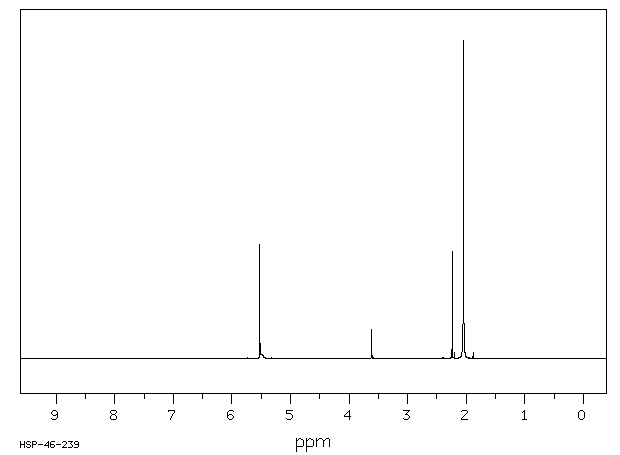
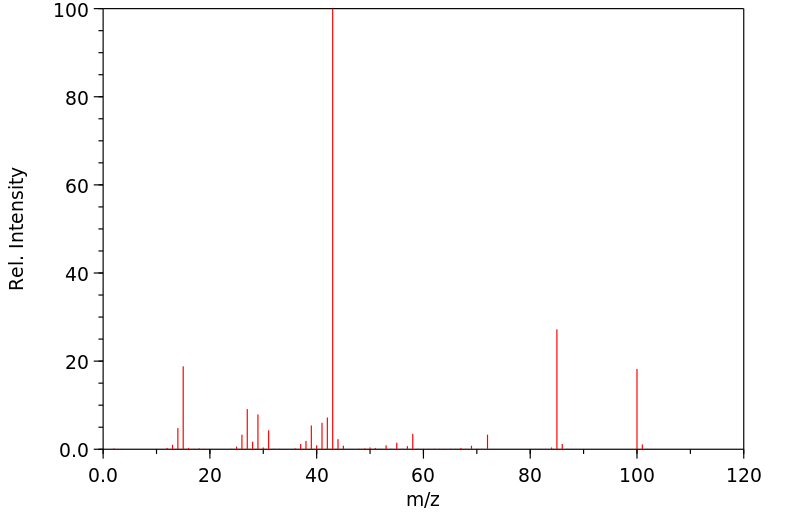
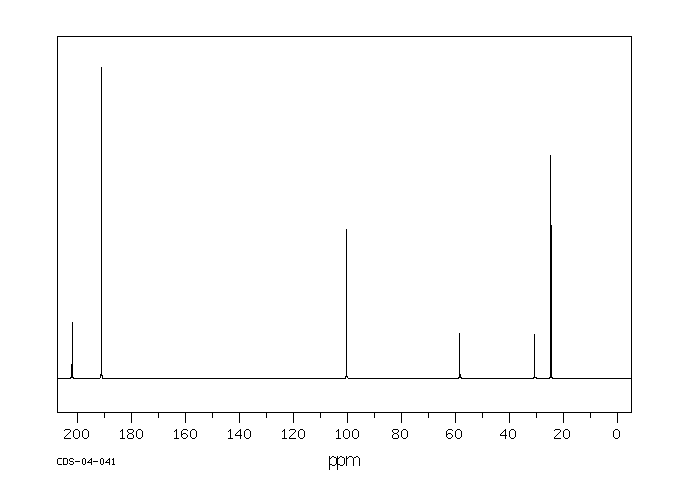
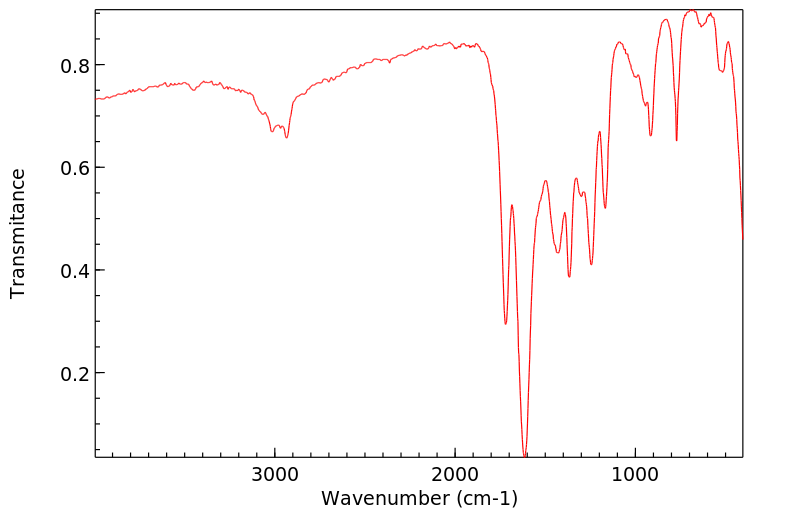
识别和使用:乙酰丙酮是一种无色或微黄色液体。它形成的有机金属络合物用作汽油添加剂、润滑剂添加剂、清漆和印刷油墨的干燥剂。人体研究:据报道,乙酰丙酮(2至14 ppm)会在几个人中产生恶心和头痛。有一个案例涉及一个对Cu(II)-乙酰丙酮发生接触性皮炎的人,并且对乙酰丙酮也有交叉反应。在人体贴片试验中检查了乙酰丙酮的皮肤致敏性。在测试的12个人中,三个人没有反应,七个人结果不确定,两个人在暴露24小时后出现阳性反应。在48小时和72小时后,没有明显的皮肤反应。人体贴片试验的结果被解释为刺激性而非致敏性效应。动物研究:乙酰丙酮对兔子的皮肤没有刺激性。在兔子眼刺激试验中,接触乙酰丙酮会导致轻微的暂时性刺激,没有角膜损伤。大鼠口服给药后,毒性迹象表现为迟钝、震颤、驼背、流泪、步态不稳、昏迷外观和虚脱。在另一项口服研究中,通过灌胃给大鼠的剂量为0、100、500和1000 mg/kg bw,给药1到15天,每次1到11次。在最高剂量组中,所有动物在给药后1小时内死亡。在500 mg/kg bw组中,3/5的动物死亡,2/5的动物在四次给药后因状况不佳而被处死。在这个剂量组中可以观察到各种与物质相关的系统性影响,如膀胱扩张、肺充血、角膜混浊、胸腺坏死、肝细胞肿胀和充血、肾病、肠系膜淋巴结淋巴腺炎和心脏炎症。在大鼠吸入(4小时;628、919、1231和1508 ppm)后,两个最高剂量组的动物出现了死亡。毒性迹象包括反射减少、呼吸困难和震颤,以及眼周、口周和鼻周的湿润和结痂。乙酰丙酮在大鼠中具有神经毒性。在大鼠发育试验中,在398 ppm和202 ppm时,每胎的胎儿体重减轻。在398 ppm时,部分胎儿肺不张增加,17种骨骼变异(79种观察到的变异中)的发生率增加,表明在398 ppm时存在一致的胎儿毒性模式。乙酰丙酮在沙门氏菌(TA-104)上表现出强烈的致突变效应。在中国仓鼠卵巢细胞中,乙酰丙酮在存在和不存在代谢激活系统的情况下,显著增加了每个细胞的姐妹染色单体交换数量。
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: Acetyl acetone is a colorless or slightly yellow liquid. It forms organometallic complexes which are used as gasoline additives, lubricant additives, driers for varnishes and printer's inks. HUMAN STUDIES: Acetly acetone (2 to 14 ppm) was reported to produce nausea and headaches in several persons. A case was reported involving an individual who had developed contact dermatitis to Cu(II)-acetyl acetonate and who also showed a cross reaction to acetyl acetone. The skin sensitizing properties of acetyl acetate were examined in a human patch test. Of the 12 persons tested three showed no reaction, seven doubtful, and two had a positive reaction after an exposure period of 24 hr. No skin reactions were evident after 48 and 72 hr, respectively. The results observed in the human patch test were interpreted as an irritating rather than a sensitizing effect. ANIMAL STUDIES: Acetyl acetone was not irritating to the skin of rabbits. In a rabbits eye irritation test, exposure to acetyl acetone resulted in minor transient irritation with no corneal involvement. After oral administration to rats, signs of toxicity were characterized by sluggishness, tremors, kyphosis, lacrimation, unsteady gait, comatose appearance and prostration. In another oral study, doses given by gavage to rats were 0, 100, 500 and 1,000 mg/kg bw given for 1 to 15 days in 1 to 11 applications. In the highest dose group all animals died within 1 hour after dosing. In the 500 mg/kg bw group 3/5 animals died and 2/5 were sacrificed due to poor condition after four applications. Various substance related systemic effects were observable in this dose group such as distended bladder, congested lungs, clouding of cornea, thymic necrosis, hepatocyte swelling and congestion, nephrosis, lymphadenitis of mesenteric lymph nodes and inflammation of the heart. After inhalation in rats (4 hr; 628, 919, 1231 and 1508 ppm) mortalities were observed in animals of the two highest dose groups. Signs of toxicity included reduced reflexes, respiratory difficulties, tremor as well as periocular, perioral and perinasal wetness and encrustation. Acetyl acetate was neurotoxic in rats. In rat developmental test reduced fetal body weight per litter was seen at 398 ppm and 202 ppm. Partial fetal atelectasis was increased at 398 ppm, and the increased incidence of 17 skeletal variants (out of 79 observed) indicated a consistent pattern of fetotoxicity at 398 ppm. Acetylacetone demonstrated a strong mutagenic effect on Salmonella typhimurium (TA-104). In Chinese hamster ovary cells acetyl acetate produced a statistically significant increase in the number of sister chromatid exchanges per cell in the presence and absence of a metabolic activation system.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)