(±)-α-硫辛酸 | 1077-28-7
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:60-62 °C
-
沸点:160-165 °C(lit.)
-
密度:1.2888 (rough estimate)
-
闪点:160-165°C
-
溶解度:乙醇:50 mg/mL
-
LogP:2.530 (est)
-
颜色/状态:Forms yellowish flakes
-
蒸汽压力:9.49X10-1 mm Hg at 25 °C (est)
-
分解:When heated to decomposition, material mits toxic fumes of /sulfur oxides/.
-
解离常数:pKa = 5.10
-
碰撞截面:133.8 Ų [M+H-H2O]+ [CCS Type: DT, Method: single field calibrated with Agilent tune mix (Agilent)]
-
稳定性/保质期:
常温常压下稳定,避免与氧化物接触。
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):1.7
-
重原子数:12
-
可旋转键数:5
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.875
-
拓扑面积:87.9
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:4
ADMET
安全信息
-
危险品标志:Xn
-
安全说明:S24/25,S26,S36,S37/39
-
危险类别码:R22
-
WGK Germany:2,3
-
海关编码:2934999090
-
危险品运输编号:NONH for all modes of transport
-
危险标志:GHS07
-
危险性描述:H302
-
包装等级:III
-
危险类别:9
-
危险性防范说明:P273,P280,P305+P351+P338,P501
-
储存条件:密封冷藏
SDS
模块 1. 化学品
1.1 产品标识符
: (±)-α-硫辛酸
产品名称
1.2 鉴别的其他方法
Lip(S2)
(±)-1,2-Dithiolane-3-pentanoic acid
6,8-Dithiooctanoic acid
DL-α-Lipoic acid
DL-6,8-Thioctic acid
1.3 有关的确定了的物质或混合物的用途和建议不适合的用途
仅供科研用途,不作为药物、家庭备用药或其它用途。
模块 2. 危险性概述
2.1 GHS分类
急性毒性, 经口 (类别4)
2.2 GHS 标记要素,包括预防性的陈述
象形图
警示词 警告
危险申明
H302 吞咽有害。
警告申明
预防
P264 操作后彻底清洁皮肤。
P270 使用本产品时不要进食、饮水或吸烟。
措施
P301 + P312 如果吞下去了: 如感觉不适,呼救解毒中心或看医生。
P330 漱口。
处理
P501 将内容物/ 容器处理到得到批准的废物处理厂。
2.3 其它危害物 - 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
3.1 物 质
: Lip(S2)
别名
(±)-1,2-Dithiolane-3-pentanoic acid
6,8-Dithiooctanoic acid
DL-α-Lipoic acid
DL-6,8-Thioctic acid
: C8H14O2S2
分子式
: 206.33 g/mol
分子量
组分 浓度或浓度范围
5-(Dithiolan-3-yl)valeric acid
-
CAS 号 1077-28-7
EC-编号 214-071-2
模块 4. 急救措施
4.1 必要的急救措施描述
一般的建议
请教医生。 出示此安全技术说明书给到现场的医生看。
吸入
如果吸入,请将患者移到新鲜空气处。 如果停止了呼吸,给于人工呼吸。 请教医生。
皮肤接触
用肥皂和大量的水冲洗。 请教医生。
眼睛接触
用水冲洗眼睛作为预防措施。
食入
切勿给失去知觉者从嘴里喂食任何东西。 用水漱口。 请教医生。
4.2 主要症状和影响,急性和迟发效应
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
4.3 及时的医疗处理和所需的特殊处理的说明和指示
无数据资料
模块 5. 消防措施
5.1 灭火介质
灭火方法及灭火剂
用水雾,耐醇泡沫,干粉或二氧化碳灭火。
5.2 源于此物质或混合物的特别的危害
碳氧化物, 硫氧化物
5.3 给消防员的建议
如必要的话,戴自给式呼吸器去救火。
5.4 进一步信息
无数据资料
模块 6. 泄露应急处理
6.1 人员的预防,防护设备和紧急处理程序
使用个人防护设备。 防止粉尘的生成。 防止吸入蒸汽、气雾或气体。 保证充分的通风。 避免吸入粉尘。
6.2 环境保护措施
不要让产物进入下水道。
6.3 抑制和清除溢出物的方法和材料
收集、处理泄漏物,不要产生灰尘。 扫掉和铲掉。 存放进适当的闭口容器中待处理。
6.4 参考其他部分
丢弃处理请参阅第13节。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
7.1 安全操作的注意事项
避免接触皮肤和眼睛。 防止粉尘和气溶胶生成。
在有粉尘生成的地方,提供合适的排风设备。
7.2 安全储存的条件,包括任何不兼容性
贮存在阴凉处。 容器保持紧闭,储存在干燥通风处。
7.3 特定用途
无数据资料
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
8.1 容许浓度
最高容许浓度
没有已知的国家规定的暴露极限。
8.2 暴露控制
适当的技术控制
按照良好工业和安全规范操作。 休息前和工作结束时洗手。
个体防护设备
眼/面保护
带有防护边罩的安全眼镜符合 EN166要求请使用经官方标准如NIOSH (美国) 或 EN 166(欧盟)
检测与批准的设备防护眼部。
皮肤保护
戴手套取 手套在使用前必须受检查。
请使用合适的方法脱除手套(不要接触手套外部表面),避免任何皮肤部位接触此产品.
使用后请将被污染过的手套根据相关法律法规和有效的实验室规章程序谨慎处理. 请清洗并吹干双手
所选择的保护手套必须符合EU的89/686/EEC规定和从它衍生出来的EN 376标准。
身体保护
全套防化学试剂工作服, 防护设备的类型必须根据特定工作场所中的危险物的浓度和含量来选择。
呼吸系统防护
如须暴露于有害环境中,请使用P95型(美国)或P1型(欧盟 英国
143)防微粒呼吸器。如需更高级别防护,请使用OV/AG/P99型(美国)或ABEK-P2型 (欧盟 英国 143)
防毒罐。
呼吸器使用经过测试并通过政府标准如NIOSH(US)或CEN(EU)的呼吸器和零件。
模块 9. 理化特性
9.1 基本的理化特性的信息
a) 外观与性状
形状: 粉末
颜色: 淡黄
b) 气味
无数据资料
c) 气味阈值
无数据资料
d) pH值
无数据资料
e) 熔点/凝固点
熔点/凝固点: 60 °C
f) 起始沸点和沸程
160 - 165 °C
g) 闪点
无数据资料
h) 蒸发速率
无数据资料
i) 易燃性(固体,气体)
无数据资料
j) 高的/低的燃烧性或爆炸性限度 无数据资料
k) 蒸汽压
无数据资料
l) 蒸汽密度
无数据资料
m) 相对密度
无数据资料
n) 水溶性
无数据资料
o) n-辛醇/水分配系数
无数据资料
p) 自燃温度
无数据资料
q) 分解温度
无数据资料
r) 粘度
无数据资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应活性
10.1 反应性
无数据资料
10.2 稳定性
无数据资料
10.3 危险反应的可能性
无数据资料
10.4 应避免的条件
无数据资料
10.5 不兼容的材料
强氧化剂
10.6 危险的分解产物
其它分解产物 - 无数据资料
模块 11. 毒理学资料
11.1 毒理学影响的信息
急性毒性
无数据资料
半数致死剂量 (LD50) 腹膜内的 - 老鼠 - 235 mg/kg
皮肤刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
眼睛刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
呼吸道或皮肤过敏
无数据资料
生殖细胞突变性
无数据资料
致癌性
IARC:
此产品中没有大于或等于 0。1%含量的组分被 IARC鉴别为可能的或肯定的人类致癌物。
生殖毒性
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触)
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(反复接触)
无数据资料
吸入危险
无数据资料
潜在的健康影响
吸入 吸入可能有害。 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
摄入 误吞对人体有害。
皮肤 如果通过皮肤吸收可能是有害的。 可能引起皮肤刺激。
眼睛 可能引起眼睛刺激。
接触后的征兆和症状
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
附加说明
化学物质毒性作用登记: JP1192000
模块 12. 生态学资料
12.1 生态毒性
无数据资料
12.2 持久存留性和降解性
无数据资料
12.3 潜在的生物蓄积性
无数据资料
12.4 土壤中的迁移性
无数据资料
12.5 PBT 和 vPvB的结果评价
无数据资料
12.6 其它不利的影响
无数据资料
模块 13. 废弃处置
13.1 废物处理方法
产品
将剩余的和未回收的溶液交给处理公司。
与易燃溶剂相溶或者相混合,在备有燃烧后处理和洗刷作用的化学焚化炉中燃烧
受污染的容器和包装
作为未用过的产品弃置。
模块 14. 运输信息
14.1 联合国危险货物编号
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.2 联合国(UN)规定的名称
欧洲陆运危规: 非危险货物
国际海运危规: 非危险货物
国际空运危规: 非危险货物
14.3 运输危险类别
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.4 包裹组
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.5 环境危险
欧洲陆运危规: 否 国际海运危规 海运污染物: 否 国际空运危规: 否
14.6 对使用者的特别提醒
无数据资料
模块 15 - 法规信息
N/A
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
制备方法与用途
DL-硫辛酸是一种独特的抗自由基物质,通常被称为广泛抗氧化剂。它是一种体内产生的维生素样物质。与其他体内产生的有特殊作用的抗氧化剂不同,DL-硫辛酸既不是严格的脂溶性,也不是水溶性。这使得它可以促进体内其他抗氧化剂的活性,并在抗氧化剂不足时作为广泛存在的替代品。例如,在体内储存的维生素C、维生素E含量很低时,DL-硫辛酸可以进行暂时补充。因为DL-硫辛酸可以通过血脑屏障,它可以帮助逆转脑卒中引起的不良反应。
此外,DL-硫辛酸也帮助维持血糖的正常水平,预防糖尿病严重并发症。随着年龄的增长,人体将不能制造充足的DL-硫辛酸来维持健康。因此,如果已经年过四旬,补充DL-硫辛酸是非常必要的。市售DL-硫辛酸多为片剂或含有DL-硫辛酸的抗氧化剂配方产品,建议每天服用1~2片50mg的DL-硫辛酸。
理化性质α-硫辛酸是一种淡黄色粉末状结晶,几乎无味,化学结构是6,8二取代的硫辛酸,在6,8碳之间以二硫键相连形成内二硫化合物。当被还原时,二硫键断裂形成二氢DL-硫辛酸。α-硫辛酸不溶于水而溶于脂溶剂,有人将其列为脂溶性维生素;在甲醇、乙醇、氯仿、乙醚中易溶。
用途α-硫辛酸是一种高效抗氧化剂,在许多疾病的预防和治疗方面具有重要作用。尤其在医药领域里,它被广泛应用于预防和辅助治疗糖尿病及其相关并发症。它可以增强糖代谢、减弱氧化应激、缓解糖尿病性神经病症状、预防糖尿病性白内障、预防糖尿病心血管损伤。
生化功能DL-硫辛酸通过氧化型与还原型之间的相互转变可以递氢,为抗氧化剂。人体能合成所需的DL-硫辛酸,目前尚未发现有DL-硫辛酸缺乏症。作为一种维生素类药物,它能刺激脂肪代谢,并用于治疗急性及慢性肝炎、肝硬化、肝性昏迷、脂肪肝以及糖尿病等病的治疗和疗效保健。
此外,外源性硫辛酸作为如丙酮酸脱氢酶(pyruvate dehydrogenase) 和甘氨酸脱羧酶(glycine decarboxylase) 的辅酶被细胞内多种酶还原。这种还原形式影响了细胞清除自由基的进程,增加谷胱甘肽(glutathione)合成,并调控转录因子活性。
体内研究C57BL/6J小鼠分为四组,给予高脂饮食24周以诱导非酒精性脂肪肝病 (NAFLD),随后每日给予DL-硫辛酸治疗。结果表明,100 mg/kg或200 mg/kg DL-硫辛酸显著减少腹腔脂肪质量(P<0.05),同时抑制食欲并导致体重急剧下降。
体内研究C57BL/6J小鼠被分为四组,给予高脂饮食24周以诱导非酒精性脂肪肝病 (NAFLD),随后每日给予DL-硫辛酸治疗。结果表明,100 mg/kg或200 mg/kg DL-硫辛酸显著减少肝脏内脂肪积累(P<0.05),并抑制食欲导致体重急剧下降。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 R-(+)-硫辛酸 (R)-1,2-dithiolane-3-pentanoic acid 1200-22-2 C8H14O2S2 206.33 —— (R)-(+)-methyl lipoate 99427-00-6 C9H16O2S2 220.357 —— 1,2-dithiolane-3-pentanoic acid methyl ester 46236-19-5 C9H16O2S2 220.357 硫辛酸乙酯 ethyl lipoate 46353-61-1 C10H18O2S2 234.384 —— (R)-(+)-Ethyl Lipoate 104726-74-1 C10H18O2S2 234.384 (+/-)-二氢硫辛酸 dihydrolipoic acid 462-20-4 C8H16O2S2 208.346 —— (+/-)-8-hydroxy-6-mercapto-octanoic acid 101567-87-7 C8H16O3S 192.279 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 R-(+)-硫辛酸 (R)-1,2-dithiolane-3-pentanoic acid 1200-22-2 C8H14O2S2 206.33 左旋硫辛酸 (S)-lipoic acid 1077-27-6 C8H14O2S2 206.33 —— 1,2-dithiolane-3-pentanoic acid methyl ester 46236-19-5 C9H16O2S2 220.357 —— 5-(1,2-dithiolan-3-yl)pentan-1-ol 539-55-9 C8H16OS2 192.346 硫辛酸乙酯 ethyl lipoate 46353-61-1 C10H18O2S2 234.384 —— lipoic acid butyl ester 130995-97-0 C12H22O2S2 262.437 —— lipoic acid octadecyl ester 112667-35-3 C26H50O2S2 458.814 —— ALA2(1,12-dodecanediol) —— C28H50O4S4 578.967 —— 5-(Dithiolan-3-yl)pentyl 5-(dithiolan-3-yl)pentanoate 113534-82-0 C16H28O2S4 380.661 —— 5-[1,2]dithiolan-3-ylpentanoic acid 10-(5-[1,2]dithiolan-3-ylpentanoyloxy)decyl ester —— C26H46O4S4 550.913 —— 5-[1,2]dithiolan-3-ylpentanoic acid 8-(5-[1,2]dithiolan-3-ylpentanoyloxy)octyl ester —— C24H42O4S4 522.859 —— ethylene glycol, thioctic acid —— C10H18O3S2 250.383 —— 5-[1,2]dithiolan-3-ylpentanoic acid 6-(5-[1,2]dithiolan-3-ylpentanoyloxy)hexyl ester —— C22H38O4S4 494.805 —— 2-propynyl 5-(1,2-dithiolan-3-yl)pentanoate 1310919-98-2 C11H16O2S2 244.379 —— α-lipoic acid anhydride 91319-83-4 C16H26O3S4 394.645 —— 5-[1,2]dithiolan-3-ylpentanoic acid 3-(5-[1,2]dithiolan-3-ylpentanoyloxy)propyl ester —— C19H32O4S4 452.725 —— but-3-yn-1-yl 5-(1,2-dithiolan-3-yl)pentanoate —— C12H18O2S2 258.406 —— (ALA)2/ethylene glycol 914923-41-4 C18H30O4S4 438.698 —— 5-[1,2]-dithiolan-3-yl-pentoic acid 2-{2-[2-(2-hydroxy-ethoxy)-ethoxy]-ethoxy}-ethyl ester —— C16H30O6S2 382.543 —— (ALA)2/tetraethylene glycol —— C24H42O7S4 570.857 —— 2-{2-[2-(2-methoxyethoxy)-ethoxy]-ethoxy}-ethyl-5-[1,2]dithiolan-3-ylpentanoate 1015088-11-5 C17H32O6S2 396.569 —— 2-(2-(2-methoxyethoxy)ethoxy)ethyl 5-(1,2-dithiolan-3-yl) pentanoate 1138326-51-8 C15H28O5S2 352.516 (R,S)-硫辛酰氯 lipoyl chloride 13880-12-1 C8H13ClOS2 224.776 (+/-)-alpha-硫辛酰胺 lipoamide 940-69-2 C8H15NOS2 205.345 —— 1-oxide-β-lipoic acid —— C8H14O3S2 222.329 —— 2-(dimethylamino)ethyl 5-[(3R)-1,2-dithiolan-3-yl]pentanoate 245112-99-6 C12H23NO2S2 277.452 硫辛酸杂质D 2-oxide-β-lipoic acid 108015-78-7 C8H14O3S2 222.329 (+/-)-二氢硫辛酸 dihydrolipoic acid 462-20-4 C8H16O2S2 208.346 R-(+)-二氢硫辛酸 (R)-dihydrolipoic acid 119365-69-4 C8H16O2S2 208.346 —— (trimethylsilyl)methyl 5-(1,2-dithiolan-3-yl)pentanoate 1026779-40-7 C12H24O2S2Si 292.539 —— mono-ALA-TEG-SA 1227675-90-2 C20H34O9S2 482.617 —— 5-(1,2-Dithiolan-3-yl)pentanohydroxamic acid —— C8H15NO2S2 221.345 —— lipoic acid hydrazide 145459-24-1 C8H16N2OS2 220.36 —— ethyl 5-(1-oxo-1,2-dithiolan-3-yl)pentanoate 214554-87-7 C10H18O3S2 250.383 —— HEMA-LA 126449-41-0 C14H22O4S2 318.458 —— N-(6-hydroxyhexyl)-5-(1,2-dithiolan-3-yl)pentanamide 1257340-36-5 C14H27NO2S2 305.506 二氢硫辛酸甲酯 6,8-dimercaptooctanoic acid methyl ester 50628-93-8 C9H18O2S2 222.373 —— N-(6-hydroxypentyl)-5-(1,2-dithiolan-3-yl)pentanamide 1257340-38-7 C13H25NO2S2 291.479 —— ethyl 5-(2-oxo-1,2-dithiolan-3-yl)pentanoate 214556-10-2 C10H18O3S2 250.383 —— N-propyl-5-(1,2-dithiolan-3-yl)pentanamide —— C11H21NOS2 247.426 —— Methyl-5-[5-(1,2-dithiolan-3-yl)pentanoylamino]pentanoate —— C14H25NO3S2 319.489 —— N-butyl-5-(1,2-dithiolan-3-yl)pentanamide 1225192-68-6 C12H23NOS2 261.453 —— 5-(1,2-dithiolan-3-yl)-N-(2-hydroxyethyl)pentanamide —— C10H19NO2S2 249.398 —— 4-[3-(1,2-dithiolane)]butyl isocyanate 76197-63-2 C8H13NOS2 203.329 —— N-octadecyl-5-(1,2-dithiolan-3-yl)pentanamide —— C26H51NOS2 457.829 —— 5-(dithiolan-3-yl)-N-[5-(dithiolan-3-yl)pentyl]pentanamide 1027016-09-6 C16H29NOS4 379.676 —— 5-(1,2-dithiolan-3-yl)-N-hexylpentanamide 920510-68-5 C14H27NOS2 289.506 —— 5-(1,2-dithiolan-3-yl)-N-tetradecylpentanamide 920510-71-0 C22H43NOS2 401.722 —— N6-α-Lipoyl-L-lysin 1676-89-7 C14H26N2O3S2 334.504 —— N-2-propen-1-yl-5-(1,2-dithiolan-3-yl)pentanamide —— C11H19NOS2 245.41 硫辛酸杂质9 N-(2-aminoethyl)-5-(1,2-dithiolan-3-yl)pentanamide 728854-75-9 C10H20N2OS2 248.414 —— Ethyl 6,8-dimercaptooctanoat 91009-31-3 C10H20O2S2 236.4 —— 5-(1,2-dithiolan-3-yl)-N-(prop-2-yn-1-yl)pentanamide 1304779-08-5 C11H17NOS2 243.394 硫辛酸杂质28 BMOA 91009-30-2 C10H20O2S2 236.4 —— 5-([1,2]dithiolan-3-yl)pentanoic acid N-{3-[5-([1,2]dithiolan-3-yl)pentanoylamino]propyl}amide 691410-93-2 C19H34N2O2S4 450.755 —— (ALA3)/glycerol 1151767-41-7 C27H44O6S6 657.039 —— 2,3-di-O-phytanyl-sn-glycerol-1-tetraethylene glycol D,L-α-lipoic acid ester —— C59H116O8S2 1017.7 辛酸,6,8-二[(苯基甲基)二硫代]- 6,8-Bis(benzyldisulfanyl)octanoic acid 108110-79-8 C22H28O2S4 452.727 —— 5-(1,2-Dithiolan-3-yl)-N-(2-hydroxy-1-methylethyl)pentanamide —— C11H21NO2S2 263.425 —— 2-(5-(1,2-dithiolane-3-yl)pentanamido)acetic acid 14631-30-2 C10H17NO3S2 263.382 —— N-{2-[(2-hydroxyethyl)amino]ethyl}-5-(1,2-dithiolan-3-yl)pentanamide 1309825-96-4 C12H24N2O2S2 292.467 - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Lipoic acid derivatives摘要:含有硫辛酸衍生物的制剂和药物制剂在治疗和预防疾病方面非常有用,这些疾病的特征是疾病细胞对硫辛酸衍生物敏感。公开号:US08785475B2
-
作为产物:描述:trans-2-(L-Arabino-1',2',3',4'-tetrahydroxybutyl)-1,3-dithianyl-4-valeric acid 在 盐酸 、 air 、 硫化氢 、 三氯化铁 、 potassium carbonate 、 mercury dichloride 作用下, 反应 1.42h, 生成 (±)-α-硫辛酸参考文献:名称:将外消旋硫辛酸拆分成对映体的新方法摘要:硫辛酸 (I) 是 1 ,2 - 二硫代 1 -3 - 戊酸(硫辛酸,原 A)并进入影响丙酮酸脱羧的酶。通过合成获得的外消旋硫辛酸的活性是天然 (+) 形式的一半。1,2-二硫杂环戊烷环决定了该化合物的反应活性,并容易在还原时分解,得到二氢硫辛酸。DOI:10.1007/bf01156381
文献信息
-
Additives and products including oligoesters申请人:——公开号:US20030199593A1公开(公告)日:2003-10-23The present invention relates to oligoesters and their use or the creation of additives. Oligoester containing additives and/or oligoesters themselves may be used for formulating pharmaceutical preparations, cosmetics or personal care products such as shampoos and conditioners. These oligoesters are particularly useful for the creation of multi-purpose additives that can impart conditioning, long substantivity and/or UV protection. Individual oligoesters and oligoester mixtures are described.本发明涉及寡酯及其用途或添加剂的制备。含有寡酯的添加剂和/或寡酯本身可用于配制药物制剂、化妆品或个人护理产品,如洗发水和护发素。这些寡酯对于制备能够赋予调理、长效性和/或紫外线保护的多功能添加剂特别有用。描述了单独的寡酯和寡酯混合物。
-
[EN] HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS FOR THE TREATMENT OF STRESS-RELATED CONDITIONS<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS HÉTÉROCYCLIQUES POUR LE TRAITEMENT D'ÉTATS LIÉS AU STRESS申请人:OTSUKA PHARMA CO LTD公开号:WO2010137738A1公开(公告)日:2010-12-02The present invention provides a novel heterocyclic compound. A heterocyclic compound represented by general formula (1) wherein, R1 and R2, each independently represent hydrogen; a phenyl lower alkyl group that may have a substituent(s) selected from the group consisting of a lower alkyl group and the like on a benzene ring and/or a lower alkyl group; or a cyclo C3-C8 alkyl lower alkyl group; or the like; R3 represents a lower alkynyl group or the like; R4 represents a phenyl group that may have a substituent(s) selected from the group consisting of a 1,3,4-oxadiazolyl group that may have e.g., halogen or a heterocyclic group selected from pyridyl group and the like; the heterocyclic group may have at least one substituent(s) selected from a lower alkoxy group and the like or a salt thereof.
-
[EN] COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS FOR THE TREATMENT OF ATHEROTHROMBOSIS<br/>[FR] COMPOSITIONS ET PROCÉDÉS POUR LE TRAITEMENT DE L'ATHÉROTROMBOSE申请人:KANDULA MAHESH公开号:WO2013024376A1公开(公告)日:2013-02-21The disclosures herein provide compounds of formula I or its pharmaceutical acceptable salts, as well as polymorphs, enantiomers, stereoisomers, solvates, and hydrates thereof. These salts may be formulated as pharmaceutical compositions. The pharmaceutical compositions may be formulated for peroral administration- transdermal administration, transmucosal, syrups, topical, extended release, sustained release, or injection. Such compositions may foe used to treatment of vascular disorders or conditions such as thrombotic cerebrovascular or cardiovascular disease or its associated complications.本公开提供公式I的化合物或其药用可接受的盐,以及其多晶型、对映体、立体异构体、溶剂合物和水合物。这些盐可以制成药物组合物。药物组合物可以用于口服、经皮、经粘膜、糖浆、局部、延长释放、持续释放或注射的给药。这种组合物可用于治疗血管疾病或病况,如血栓性脑血管或心血管疾病或其相关并发症。
-
ANTI-EGFR ANTIBODY DRUG CONJUGATES
-
[EN] FUSED RING COMPOUNDS AND USE THEREOF<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS CYCLIQUES CONDENSÉS ET UTILISATION DE CEUX-CI申请人:TAKEDA PHARMACEUTICAL公开号:WO2009125873A1公开(公告)日:2009-10-15The present invention aims to provide a glucokinase activator useful as a pharmaceutical agent such as an agent for the prophylaxis or treatment of diabetes, obesity and the like. The present invention provides a glucokinase activator containing a compound represented by the formula (I): wherein each symbol is defined in the specification, or a salt thereof or a prodrug thereof.
表征谱图
-
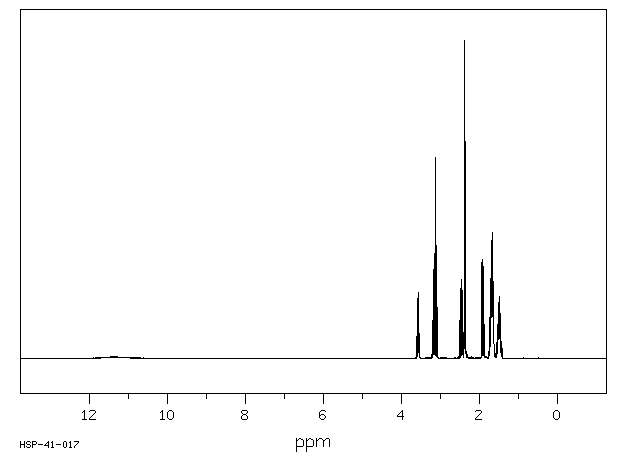
氢谱1HNMR
-
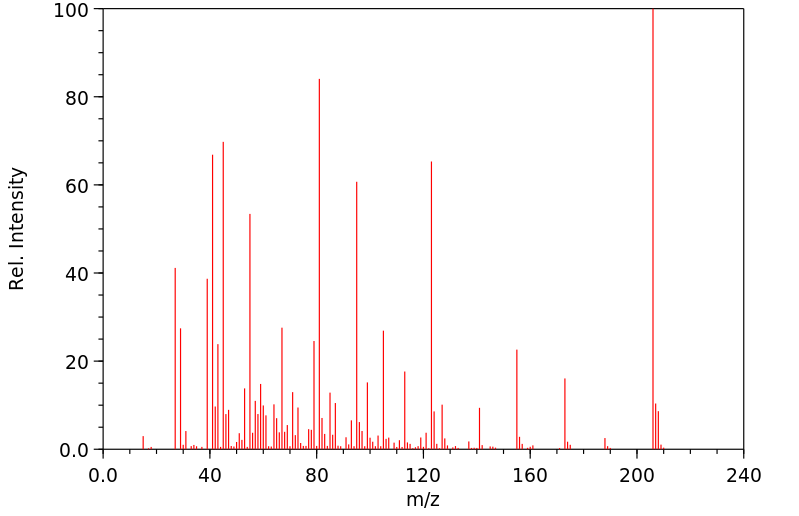
质谱MS
-
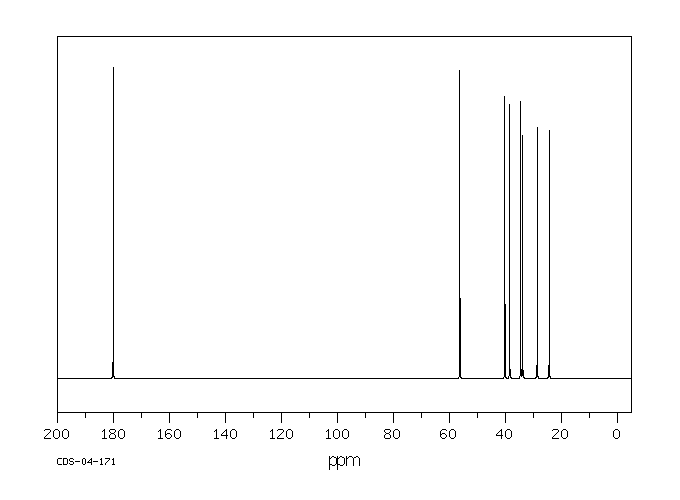
碳谱13CNMR
-
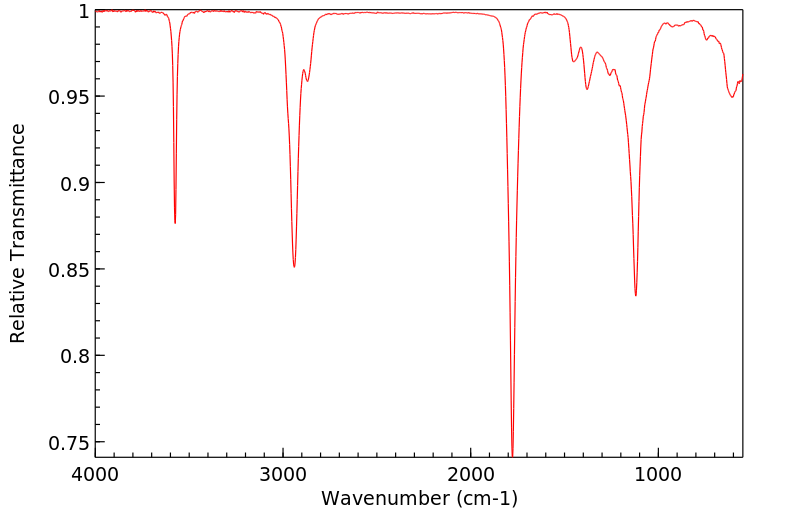
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息