异烟肼 | 54-85-3
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:171-173 °C (lit.)
-
沸点:251.97°C (rough estimate)
-
密度:1.2620 (rough estimate)
-
闪点:>250°C
-
溶解度:125克/升
-
物理描述:Isoniazid appears as odorless colorless or white crystals or white crystalline powder. Taste is slightly sweet at first and then bitter. pH (1% aqueous solution) 5.5-6.5. pH (5% aqueous solution) 6-8. (NTP, 1992)
-
颜色/状态:COLORLESS OR WHITE CRYSTALS, OR A WHITE, CRYSTALLINE POWDER
-
蒸汽压力:4.6X10-5 mm Hg at 25 °C /Estimated/
-
水溶性:0.01
-
稳定性/保质期:
STABLE AT ROOM TEMP FOR MORE THAN 14 DAYS IN AQ SOLN AND MORE THAN 6 WK WHEN STORED AT ABOUT 4 °C.
-
分解:When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of /nitrogen oxides/.
-
解离常数:pK1= 1.75; pK2= 3.57; pK3= 10.75
-
碰撞截面:125.6 Ų [M+H]+ [CCS Type: TW, Method: calibrated with polyalanine and drug standards]
-
保留指数:1582
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-0.7
-
重原子数:10
-
可旋转键数:1
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:68
-
氢给体数:2
-
氢受体数:3
ADMET
安全信息
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险品标志:Xn
-
安全说明:S26,S36/37/39,S37
-
危险类别码:R22,R40,R36/37/38,R38
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:29333999
-
危险品运输编号:2811
-
RTECS号:NS1751850
-
包装等级:III
-
危险标志:GHS07
-
危险性描述:H302,H315
-
危险性防范说明:P280,P305+P351+P338
-
储存条件:本品应密封避光保存。
SDS
: 异烟肼
产品名称
1.2 鉴别的其他方法
Isonicotinic acid hydrazide
INH
Isonicotinic hydrazide
1.3 有关的确定了的物质或混合物的用途和建议不适合的用途
仅供科研用途,不作为药物、家庭备用药或其它用途。
模块 2. 危险性概述
2.1 GHS分类
急性毒性, 经口 (类别4)
皮肤刺激 (类别2)
2.2 GHS 标记要素,包括预防性的陈述
象形图
警示词 警告
危险申明
H302 吞咽有害。
H315 造成皮肤刺激。
警告申明
预防
P264 操作后彻底清洁皮肤。
P270 使用本产品时不要进食、饮水或吸烟。
P280 戴防护手套。
措施
P301 + P312 如果吞下去了: 如感觉不适,呼救解毒中心或看医生。
P302 + P352 如与皮肤接触,用大量肥皂和水冲洗受感染部位.
P321 具体治疗(见本标签上提供的急救指导)。
P330 漱口。
P332 + P313 如发生皮肤刺激:求医/ 就诊。
P362 脱掉沾染的衣服,清洗后方可重新使用。
处理
P501 将内容物/ 容器处理到得到批准的废物处理厂。
2.3 其它危害物 - 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
3.1 物 质
: Isonicotinic acid hydrazide
别名
INH
Isonicotinic hydrazide
: C6H7N3O
分子式
: 137.14 g/mol
分子量
组分 浓度或浓度范围
Isoniazid
-
CAS 号 54-85-3
EC-编号 200-214-6
模块 4. 急救措施
4.1 必要的急救措施描述
一般的建议
请教医生。 出示此安全技术说明书给到现场的医生看。
吸入
如果吸入,请将患者移到新鲜空气处。 如果停止了呼吸,给于人工呼吸。 请教医生。
皮肤接触
用肥皂和大量的水冲洗。 请教医生。
眼睛接触
用水冲洗眼睛作为预防措施。
食入
切勿给失去知觉者从嘴里喂食任何东西。 用水漱口。 请教医生。
4.2 主要症状和影响,急性和迟发效应
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
4.3 及时的医疗处理和所需的特殊处理的说明和指示
无数据资料
模块 5. 消防措施
5.1 灭火介质
灭火方法及灭火剂
用水雾,耐醇泡沫,干粉或二氧化碳灭火。
5.2 源于此物质或混合物的特别的危害
碳氧化物, 氮氧化物
5.3 给消防员的建议
如必要的话,戴自给式呼吸器去救火。
5.4 进一步信息
无数据资料
模块 6. 泄露应急处理
6.1 人员的预防,防护设备和紧急处理程序
使用个人防护设备。 防止粉尘的生成。 防止吸入蒸汽、气雾或气体。 保证充分的通风。 避免吸入粉尘。
6.2 环境保护措施
不要让产物进入下水道。
6.3 抑制和清除溢出物的方法和材料
收集、处理泄漏物,不要产生灰尘。 扫掉和铲掉。 存放进适当的闭口容器中待处理。
6.4 参考其他部分
丢弃处理请参阅第13节。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
7.1 安全操作的注意事项
避免接触皮肤和眼睛。 防止粉尘和气溶胶生成。
在有粉尘生成的地方,提供合适的排风设备。一般性的防火保护措施。
7.2 安全储存的条件,包括任何不兼容性
贮存在阴凉处。 容器保持紧闭,储存在干燥通风处。
7.3 特定用途
无数据资料
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
8.1 容许浓度
最高容许浓度
没有已知的国家规定的暴露极限。
8.2 暴露控制
适当的技术控制
按照良好工业和安全规范操作。 休息前和工作结束时洗手。
个体防护设备
眼/面保护
带有防护边罩的安全眼镜符合 EN166要求请使用经官方标准如NIOSH (美国) 或 EN 166(欧盟)
检测与批准的设备防护眼部。
皮肤保护
戴手套取 手套在使用前必须受检查。
请使用合适的方法脱除手套(不要接触手套外部表面),避免任何皮肤部位接触此产品.
使用后请将被污染过的手套根据相关法律法规和有效的实验室规章程序谨慎处理. 请清洗并吹干双手
所选择的保护手套必须符合EU的89/686/EEC规定和从它衍生出来的EN 376标准。
身体保护
全套防化学试剂工作服, 防护设备的类型必须根据特定工作场所中的危险物的浓度和含量来选择。
呼吸系统防护
如须暴露于有害环境中,请使用P95型(美国)或P1型(欧盟 英国
143)防微粒呼吸器。如需更高级别防护,请使用OV/AG/P99型(美国)或ABEK-P2型 (欧盟 英国 143)
防毒罐。
呼吸器使用经过测试并通过政府标准如NIOSH(US)或CEN(EU)的呼吸器和零件。
模块 9. 理化特性
9.1 基本的理化特性的信息
a) 外观与性状
形状: 粉末
颜色: 白色
b) 气味
无数据资料
c) 气味阈值
无数据资料
d) pH值
5.5 - 6.5 在 10 g/l 在 25 °C
e) 熔点/凝固点
熔点/凝固点: 171 - 173 °C - lit.
f) 起始沸点和沸程
无数据资料
g) 闪点
无数据资料
h) 蒸发速率
无数据资料
i) 易燃性(固体,气体)
无数据资料
j) 高的/低的燃烧性或爆炸性限度 无数据资料
k) 蒸汽压
无数据资料
l) 蒸汽密度
无数据资料
m) 相对密度
无数据资料
n) 水溶性
可溶的
o) n-辛醇/水分配系数
辛醇--水的分配系数的对数值: -0.7
p) 自燃温度
无数据资料
q) 分解温度
无数据资料
r) 粘度
无数据资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应活性
10.1 反应性
无数据资料
10.2 稳定性
无数据资料
10.3 危险反应的可能性
无数据资料
10.4 应避免的条件
无数据资料
10.5 不兼容的材料
氧化剂强氧化剂
10.6 危险的分解产物
其它分解产物 - 无数据资料
模块 11. 毒理学资料
11.1 毒理学影响的信息
急性毒性
半数致死剂量 (LD50) 经口 - 大鼠 - 1,250 mg/kg
皮肤刺激或腐蚀
皮肤 - 兔子 - 皮肤刺激 - 24 h
眼睛刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
呼吸道或皮肤过敏
无数据资料
生殖细胞突变性
无数据资料
致癌性
该产品不是或不包含被IARC, ACGIH, EPA, 和 NTP 列为致癌物的组分
IARC:
3 - 第3组:未被分类为对人类致癌 (Isoniazid)
生殖毒性
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触)
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(反复接触)
无数据资料
吸入危险
无数据资料
潜在的健康影响
吸入 吸入可能有害。 引起呼吸道刺激。
摄入 误吞对人体有害。
皮肤 如果通过皮肤吸收可能是有害的。 造成皮肤刺激。
接触后的征兆和症状
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
附加说明
化学物质毒性作用登记: NS1751850
模块 12. 生态学资料
12.1 生态毒性
无数据资料
12.2 持久存留性和降解性
无数据资料
12.3 潜在的生物蓄积性
无数据资料
12.4 土壤中的迁移性
无数据资料
12.5 PBT 和 vPvB的结果评价
无数据资料
12.6 其它不利的影响
无数据资料
模块 13. 废弃处置
13.1 废物处理方法
产品
将剩余的和未回收的溶液交给处理公司。 联系专业的拥有废弃物处理执照的机构来处理此物质。
与易燃溶剂相溶或者相混合,在备有燃烧后处理和洗刷作用的化学焚化炉中燃烧
受污染的容器和包装
作为未用过的产品弃置。
模块 14. 运输信息
14.1 联合国危险货物编号
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.2 联合国(UN)规定的名称
欧洲陆运危规: 非危险货物
国际海运危规: 非危险货物
国际空运危规: 非危险货物
14.3 运输危险类别
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.4 包裹组
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.5 环境危险
欧洲陆运危规: 否 国际海运危规 海运污染物: 否 国际空运危规: 否
14.6 对使用者的特别提醒
无数据资料
模块 15 - 法规信息
N/A
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
制备方法与用途
异烟肼是一种无色结晶或白色结晶性粉末,微苦且性质稳定,易溶于水。其肼基具有强还原性,在碱性条件下可与水中溶解氧反应生成过氧化氢,但速率较慢。金纳米颗粒可以催化这一过程,并与鲁米诺构成发光体系。此外,异烟肼的肼基上的氨基(-NH2)能参与一些化学反应,例如与活泼羰基化合物形成席夫碱,以及与羧酸衍生物或磺酰氯反应生成酰化异烟肼或磺酰异烟肼。
药理作用异烟肼对结核杆菌具有强大的抑菌和杀菌作用,并可穿透进入细胞内的细菌;其毒性较低且容易被吸收。适用于各种类型的结核病治疗,但单独使用时易产生抗药性,通常与对氨基水杨酸盐或链霉素联合应用。
药代动力学口服后异烟肼在肠道迅速吸收,在服药1~2小时血液浓度达到峰值。该药物穿透力强,可渗入体内各部位,并能透过血脑屏障进入脑脊液中。胸水和脑脊液中的药物浓度与血浆相近,还可渗透到干酪化或纤维化的结核病灶中。体内的代谢过程尚不完全清楚,肝脏中的乙酰化作用是主要的生物转化途径;不同个体对异烟肼的代谢速度存在差异,受基因影响。我国慢代谢型约占25.6%,快代谢型约占49.3%。口服后24小时内,尿中排泄量约为50~75%。
应用异烟肼主要用于治疗结核病、耐药金葡菌感染以及沙眼和麻风病等疾病。它对结核杆菌高度敏感,同时也作用于革兰阴性杆菌,且对革兰阳性球菌有很强的抗菌活性。
制备方法异烟肼可通过将异烟酸溶解在水合肼中,加入上批粗制母液后减压蒸馏至129-130℃,反应3小时。随后稀释反应液、加活性炭脱色、过滤,并冷却结晶于10℃左右的环境中进行过滤和洗涤,最终通过重结晶、活性炭脱色及干燥得到成品。收率约为90%。
用途异烟肼主要用作抗结核药物,适用于各种类型的肺结核和结核性脑膜炎等疾病,并常与其他抗结核病药联合使用。此外,在生化研究中,它还用于高效液相色谱荧光检定∆4(4上标)-3甾酮类化合物,并应用于制药工业中作为高效、低毒且经济的首选药物。异烟肼衍生物如甲烷磺酸和双异烟肼也是抗结核药物的重要组成部分。
这些用途不仅限于临床治疗,还包括电镀添加剂与制药中间体等领域的应用。同时,异烟肼对结核杆菌具有高度选择性,其作用机制是通过抑制分枝菌酸的生物合成,并作为一种强烈的DPH代谢抑制剂,能够可逆地抑制cyp2c19和cyp3a4并失活cyp1a2和cyp2a6。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 4-吡啶甲酰胺 isonicotinamide 1453-82-3 C6H6N2O 122.126 N-甲氧基异烟酰胺 N-methoxypyridine-4-carboxamide 83421-33-4 C7H8N2O2 152.153 4-吡啶甲醛 pyridine-4-carbaldehyde 872-85-5 C6H5NO 107.112 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— 1-Isonicotinoyl-2-methyl-hydrazin 2365-19-7 C7H9N3O 151.168 N-(亚甲基氨基)-4-吡啶甲酰胺 N'-(methylidene)isonicotinic acid hydrazide 4813-02-9 C7H7N3O 149.152 —— 1-isonicotinoyl-2-formylhydrazine 89792-19-8 C7H7N3O2 165.151 —— isonicotinic acid-(N',N'-dimethyl-hydrazide) 63884-58-2 C8H11N3O 165.195 4-吡啶甲酰胺 isonicotinamide 1453-82-3 C6H6N2O 122.126 —— Acetaldehyde isonicotinoyl hydrazone —— C8H9N3O 163.18 4-吡啶羧酸,乙亚基酰肼 N'-(ethylidene)isonicotinic acid hydrazide 4813-03-0 C8H9N3O 163.179 —— 1-methyl-1-isonicotinoylhydrazine 89853-54-3 C7H9N3O 151.168 1,2-二异烟酰基肼 N,N'-bis(isonicotinoyl)hydrazine 4329-75-3 C12H10N4O2 242.237 异丙烟肼 iproniazid 54-92-2 C9H13N3O 179.222 —— N'-(2-Hydroxyethyl)isonicotinsaeurehydrazid 1078-39-3 C8H11N3O2 181.194 甲烟肼 metazid 1707-15-9 C13H14N6O2 286.293 N-(二氨基亚甲基氨基)吡啶-4-甲酰胺 isonicotinic acid 2-amidinohydrazide 4427-16-1 C7H9N5O 179.181 —— N'-[(1E)-propylidene]pyridine-4-carbohydrazide 14339-46-9 C9H11N3O 177.206 2-丙酮异烟酰腙 isonicotinic acid isopropylidenehydrazide 4813-04-1 C9H11N3O 177.206 —— N'-(propylidene)isonicotinic acid hydrazide 14339-46-9 C9H11N3O 177.206 —— glycolaldehyde isonicotinylhydrazone 78009-74-2 C8H9N3O2 179.178 —— isonicotinic acid-(N'-isobutyl-hydrazide) 26723-19-3 C10H15N3O 193.249 —— glyoxal-bis-isonicotinoylhydrazone 3734-37-0 C14H12N6O2 296.288 4-吡啶羧酸2-乙酰基酰肼 N-acetyl-N'-isonicotinoylhydrazine 1078-38-2 C8H9N3O2 179.178 —— 1-isonicotinoyl semicarbazide 2845-81-0 C7H8N4O2 180.166 丁烯烟肼 crotoniazide 7007-96-7 C10H11N3O 189.217 —— isonicotinic acid N2-(2-trans-butenylidene)hydrazide 14506-81-1 C10H11N3O 189.217 —— ethyl isonicotinoylhydrazonoformate 5459-11-0 C9H11N3O2 193.205 —— isonicotinic acid but-2-enylidenehydrazide 7007-96-7 C10H11N3O 189.217 1-异烟酰(硫代氨基甲酰肼) 2-(pyridin-4-ylcarbonyl)hydrazinecarbothioamide 14397-24-1 C7H8N4OS 196.233 —— isonicotinic acid isobutylidenehydrazide 14918-57-1 C10H13N3O 191.233 —— N-(2-methylpropylideneamino)pyridine-4-carboxamide 14918-57-1 C10H13N3O 191.233 —— N'-isonictinoyl-N,N-dimethylhydrazonoformamide 16825-24-4 C9H12N4O 192.22 —— N′-(E)-butylideneisonicotinohydrazide 14339-48-1 C10H13N3O 191.233 —— N-(dimethylaminomethylideneamino)pyridine-4-carboxamide 16825-24-4 C9H12N4O 192.22 —— N-(butylideneamino)pyridine-4-carboxamide 14339-48-1 C10H13N3O 191.233 —— isonicotinoyldithiocarbazic acid 119247-82-4 C7H7N3OS2 213.284 —— isonicotinic acid-(N'-sec-butyl-hydrazide) 3038-64-0 C10H15N3O 193.249 N-(羟甲基)异烟酰胺 isonicotinic acid-(N',N'-diethyl-hydrazide) 91977-38-7 C10H15N3O 193.249 —— isonicotinic acid isopentylidenehydrazide —— C11H15N3O 205.26 —— isonicotinic acid N2-(2-trans-pentenylidene)hydrazide 433719-12-1 C11H13N3O 203.244 —— Butanon- 61524-27-4 C10H13N3O 191.233 —— isonicotinic acid-[N'-(1-ethyl-propyl)-hydrazide] —— C11H17N3O 207.275 —— N′-(E)-hexylideneisonicotinohydrazide —— C12H17N3O 219.286 —— Isonicotinsaeure- 7034-12-0 C9H13N3O3 211.221 —— N-Isonicotinoyl-N'-propionyl-hydrazin 4462-35-5 C9H11N3O2 193.205 —— Heptanal- 79844-01-2 C13H19N3O 233.313 —— isonicotinic acid-(1-ethyl-propylidenehydrazide) 91337-62-1 C11H15N3O 205.26 —— N'-[(1E)-octylidene]pyridine-4-carbohydrazide —— C14H21N3O 247.34 —— N'-[(1E)-decylidene]pyridine-4-carbohydrazide 88564-51-6 C16H25N3O 275.394 —— N'-[(1E)-undecylidene]pyridine-4-carbohydrazide —— C17H27N3O 289.421 —— Isonicotinic acid N'-(2-chloro-acetyl)-hydrazide 113603-98-8 C8H8ClN3O2 213.623 —— isonicotinic acid N2-tetradecanylidenehydrazide 433719-19-8 C20H33N3O 331.502 —— isonicotinic acid N2-tridecanylidenehydrazide 433719-16-5 C19H31N3O 317.475 —— 2-isonicotinoyl-N-methylhydrazine-1-carboxamide 117258-28-3 C8H10N4O2 194.193 —— isonicotinic acid-[N'-(1-cyano-1-methyl-ethyl)-hydrazide] 99069-49-5 C10H12N4O 204.231 N’-(吡啶-4-基亚甲基)异烟酰肼 (E)-N'-(pyridin-4-ylmethylene)isonicotinohydrazide 13025-99-5 C12H10N4O 226.238 —— 4-pyridinecarbaldehyde isonicotinoyl hydrazone —— C12H10N4O 226.238 N1-甲基-2-(4-吡啶羰基)肼-1-硫代甲酰胺 1-isonicotinoyl-4-methyl(thiosemicarbazide) 4406-96-6 C8H10N4OS 210.26 —— N-benzoyl-N'-isonicotinoylhydrazine 27293-29-4 C13H11N3O2 241.249 —— N'-(pyridine-4-carbonyl) hydrazine carbodithioic acid methyl ester 66528-28-7 C8H9N3OS2 227.311 —— isonicotinic acid-(2-ethyl-butylidenehydrazide) —— C12H17N3O 219.286 —— N-[[2-(pyridine-4-carbonyl)hydrazinyl]methylideneamino]pyridine-4-carboxamide —— C13H12N6O2 284.277 —— N-Butyl-N'-isonicotinoyl-hydrazin 4462-39-9 C10H13N3O2 207.232 —— isonicotinic acid-(3-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-propylidenehydrazide) 136-61-8 C11H15N3O2 221.259 甲磺烟肼 (N'-isonicotinoyl-hydrazino)-methanesulfonic acid 13447-95-5 C7H9N3O4S 231.232 —— isonicotinic acid-[N'-(1,3-dimethyl-butyl)-hydrazide] 15856-16-3 C12H19N3O 221.302 —— isonicotinoyl azide 4013-73-4 C6H4N4O 148.124 —— methylglyoxal bis(isonicotinoylhydrazone) 145325-70-8 C15H14N6O2 310.315 N'-亚苄基-4-吡啶甲酰肼 benzylideneisonicotinohydrazide 533-02-8 C13H11N3O 225.25 —— (E)-N'-benzylideneisonicotinohydrazide 533-02-8 C13H11N3O 225.25 —— isonicotinic acid-[N'-(4-hydroxy-1-methyl-butyl)-hydrazide] —— C11H17N3O2 223.275 —— N'-isonicotinoyl-hydrazinecarboxylic acid ethyl ester 4811-93-2 C9H11N3O3 209.205 —— N-ethyl-2-isonicotinoylhydrazine-1-carboxamide 6266-82-6 C9H12N4O2 208.22 —— 4-Methyl-pentan-2-on- 91646-42-3 C12H17N3O 219.286 —— N'-cyclopentylideneisonicotinohydrazide 4427-18-3 C11H13N3O 203.244 —— N-ethyl-2-isonicotinoylhydrazinecarbothioamide 26036-34-0 C9H12N4OS 224.286 —— N'-(pyridine-4-carbonyl)-hydrazinecarbodithioic acid ethyl ester 66528-29-8 C9H11N3OS2 241.338 —— 4-methylbenzoic acid (pyridine-4-carbonyl)hydrazide 325472-26-2 C14H13N3O2 255.276 —— N-Cyclohexyl-N'-isonicotinoyl-hydrazin 15407-87-1 C12H17N3O 219.286 —— isonicotinic acid phenethylidenehydrazide —— C14H13N3O 239.277 —— (E)-N’-(4-methylbenzylidene)isonicotinohydrazide 40205-21-8 C14H13N3O 239.277 —— N'-(4-methylbenzylidene)isonicotinohydrazide 40205-21-8 C14H13N3O 239.277 —— (4-Methyl-benzaldehyd)-isonicotinoylhydrazon 40205-21-8 C14H13N3O 239.277 —— terephthalaldehyde di-isonicotinoylhydrazone 3525-80-2 C20H16N6O2 372.386 —— 2,3-butanedione monoisonicotinoylhydrazone 104026-72-4 C10H11N3O2 205.216 —— benzene-1,4-dicarboxaldehyde bis(pyridin-4-ylcarbonylhydrazone) —— C20H16N6O2 372.386 —— isonicotinic acid-(1-methyl-heptylidenehydrazide) 94025-26-0 C14H21N3O 247.34 —— N'-isonicotinoyl-N-hexanoic acid hydrazide 91646-61-6 C12H17N3O2 235.286 —— (E)-2-(2-isonicotinoylhydrazineylidene)propanoic acid 1081-50-1 C9H9N3O3 207.189 —— 2-isonicotinoylhydrazono-propionic acid 1081-50-1 C9H9N3O3 207.189 N-[[(3Z)-3-(吡啶-4-羰基异二氮烯)丁烷-2-亚基]氨基]吡啶-4-甲酰胺 2,3-butanedione bisisonicotinoylhydrazone 80623-34-3 C16H16N6O2 324.342 —— 2,3-butanedione bis(isonicotinylhydrazone) 80623-34-3 C16H16N6O2 324.342 —— 2-isonicotinoyl-N-propylhydrazine-1-carboxamide —— C10H14N4O2 222.247 —— N-isonicotinoyl-N'-trichloroacetyl-hydrazine 100191-65-9 C8H6Cl3N3O2 282.514 —— isonicotinic acid-[N'-(1-isobutyl-3-methyl-butyl)-hydrazide] —— C15H25N3O 263.383 N'-环己基亚基异烟酰肼 cyclohexanone isonicotinoylhydrazone 15407-81-5 C12H15N3O 217.271 —— N'-(1,3-dithiolan-2-ylidene)isonicotinehydrazide —— C9H9N3OS2 239.322 —— N,N'-diisonicotinoylhexandioic acid dihydrazide 39642-76-7 C18H20N6O4 384.395 —— N'-[(1E,2E)-3,7-dimethylocta-2,6-dien-1-ylidene]pyridine-4-carbohydrazide —— C16H21N3O 271.362 —— isonicotinic acid N2-(3,7-dimethyl-2,6-octadienylidene)hydrazide 13059-78-4 C16H21N3O 271.362 —— N'-(cyclohexylmethylene)isonicotinohydrazide 344248-01-7 C13H17N3O 231.297 —— 1-isonicotinoyl-4-propyl thiosemicarbazide 94646-91-0 C10H14N4OS 238.313 - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Discovery of a Novel Series of Indolyl Hydrazide Derivatives as Diacylglycerol Acyltransferase‐1 Inhibitors摘要:研究人员合成了一系列新型酰肼衍生物,作为潜在的二酰基甘油酰基转移酶(DGAT)抑制剂。其中,化合物 8u 和 8v 具有选择性和强效的 DGAT-1 抑制活性。此外,化合物 8u 还能剂量依赖性地抑制 HepG2 细胞株中甘油三酯的合成。此外,用化合物 8u 进行口服脂质耐受性试验显示,与用车辆处理的对照组动物相比,血浆甘油三酯水平显著下降,这表明急性脂质挑战后甘油三酯的吸收延迟。DOI:10.1002/bkcs.10123
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:一种异烟肼的制备方法摘要:本发明公开了一种异烟肼的制备方法,该制备方法以异烟酸、氯化亚砜以及醇为原料,采用一步法合成异烟酸酯盐酸盐,再由异烟酸酯盐酸盐直接与水合肼进行缩合反应,制得异烟肼成品,或者将异烟酸酯盐酸盐进行碱游离后,再与水合肼进行缩合反应,制得异烟肼成品;该制备方法具有反应条件温和,操作简单,成品纯度高,制备速度快,能耗低等优点,适合工业化生产等优点。公开号:CN111732537A
-
作为试剂:描述:β-烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸 在 异烟肼 、 bovine CD38/NAD+ glycohydrolase 作用下, 以 aq. phosphate buffer 为溶剂, 以44.7%的产率得到参考文献:名称:Probing the catalytic mechanism of bovine CD38/NAD+glycohydrolase by site directed mutagenesis of key active site residues摘要:Bovine CD38/NAD(+) glycohydrolase catalyzes the hydrolysis of NAD(+) to nicotinamide and ADP-ribose and the formation of cyclic ADP-ribose via a stepwise reaction mechanism. Our recent crystallographic study of its Michaelis complex and covalently-trapped intermediates provided insights into the modalities of substrate binding and the molecular mechanism of bCD38. The aim of the present work was to determine the precise role of key conserved active site residues (Trp118, Glu138, Asp147, Trp181 and Glu218) by focusing mainly on the cleavage of the nicotinamide-ribosyl bond. We analyzed the kinetic parameters of mutants of these residues which reside within the bCD38 subdomain in the vicinity of the scissile bond of bound NAD(+). To address the reaction mechanism we also performed chemical rescue experiments with neutral (methanol) and ionic (azide, formate) nucleophiles. The crucial role of Glu218, which orients the substrate for cleavage by interacting with the N-ribosyl 2'-OH group of NAD(+), was highlighted. This contribution to catalysis accounts for almost half of the reaction energy barrier. Other contributions can be ascribed notably to Glu138 and Asp147 via ground-state destabilization and desolvation in the vicinity of the scissile bond. Key interactions with Trp118 and Trp181 were also proven to stabilize the ribooxocarbenium ion-like transition state. Altogether we propose that, as an alternative to a covalent acylal reaction intermediate with Glu218, catalysis by bCD38 proceeds through the formation of a discrete and transient ribooxocarbenium intermediate which is stabilized within the active site mostly by electrostatic interactions. (C) 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.DOI:10.1016/j.bbapap.2014.03.014
文献信息
-
[EN] PYRAZOLE DERIVATIVES USEFUL AS INHIBITORS OF FAAH<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS DE PYRAZOLE UTILES COMME INHIBITEURS DE FAAH申请人:MERCK & CO INC公开号:WO2009151991A1公开(公告)日:2009-12-17The present invention is directed to certain imidazole derivatives which are useful as inhibitors of Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase (FAAH). The invention is also concerned with pharmaceutical formulations comprising these compounds as active ingredients and the use of the compounds and their formulations in the treatment of certain disorders, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, skeletomuscular pain, and fibromyalgia, as well as acute pain, migraine, sleep disorder, Alzheimer disease, and Parkinson's disease
-
SUBSTITUTED ARYL AND HETEROARYL CARBOXYLIC ACID HYDRAZIDES OR SALTS THEREOF AND USE THEREOF TO INCREASE STRESS TOLERANCE IN PLANTS申请人:BAYER CROPSCIENCE AKTIENGESELLSCHAFT公开号:US20180206495A1公开(公告)日:2018-07-26Substituted aryl- and heteroarylcarbonyl hydrazides The invention relates to substituted aryl- and heteroarylcarbonyl hydrazides of the general formula (I) or salts thereof where the radicals of the formula (I) are each as defined in the description for enhancing stress tolerance in plants to abiotic stress, and for enhancing plant growth and/or for increasing plant yield.
-
[EN] THIOPHENE DERIVATIVES FOR THE TREATMENT OF DISORDERS CAUSED BY IGE<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS DE THIOPHÈNE POUR LE TRAITEMENT DE TROUBLES PROVOQUÉS PAR IGE申请人:UCB BIOPHARMA SRL公开号:WO2019243550A1公开(公告)日:2019-12-26Thiophene derivatives of formula (I) and a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof are provided. These compounds have utility for the treatment or prevention of disorders caused by IgE, such as allergy, type 1 hypersensitivity or familiar sinus inflammation.
-
Cobalamin conjugates for anti-tumor therapy申请人:Weinshenker M. Ned公开号:US20050054607A1公开(公告)日:2005-03-10The present invention provides a cobalamin-drug conjugate suitable for the treatment of tumor related diseases. Cobalamin is indirectly covalently bound to an anti-tumor drug via a cleavable linker and one or more optional spacers. Cobalamin is covalently bound to a first spacer or the cleavable linker via the 5′-OH of the cobalamin ribose ring. The drug is bound to a second spacer of the cleavable linker via an existing or added functional group on the drug. After administration, the conjugate forms a complex with transcobalamin (any of its isoforms). The complex then binds to a receptor on a cell membrane and is taken up into the cell. Once in the cell, an intracellular enzyme cleaves the conjugate thereby releasing the drug. Depending upon the structure of the conjugate, a particular class or type of intracellular enzyme affects the cleavage. Due to the high demand for cobalamin in growing cells, tumor cells typically take up a higher percentage of the conjugate than do normal non-growing cells. The conjugate of the invention advantageously provides a reduced systemic toxicity and enhanced efficacy as compared to a corresponding free drug.本发明提供了一种适用于治疗肿瘤相关疾病的钴胺素-药物结合物。钴胺素通过可切割的连接剂间接共价结合到抗肿瘤药物上,还可以通过一个或多个可选的间隔物。钴胺素通过其核糖环的5'-OH与第一间隔物或可切割连接剂共价结合。药物通过其现有或添加的功能基团与可切割连接剂的第二间隔物结合。在给药后,结合物与转钴胺素(其任何同工异构体)形成复合物。然后,该复合物结合到细胞膜上的受体并被细胞摄取。一旦进入细胞,细胞内酶将切割结合物,从而释放药物。根据结合物的结构,特定类别或类型的细胞内酶影响切割。由于生长细胞对钴胺素的需求量较高,肿瘤细胞通常摄取结合物的比例高于正常非生长细胞。本发明的结合物与相应的游离药物相比,具有较低的全身毒性和增强的疗效。
-
[EN] POLYCONJUGATES FOR DELIVERY OF RNAI TRIGGERS TO TUMOR CELLS IN VIVO<br/>[FR] POLYCONJUGUÉS POUR L'ADMINISTRATION DE DÉCLENCHEURS D'ARNI À DES CELLULES TUMORALES IN VIVO申请人:ARROWHEAD RES CORP公开号:WO2015021092A1公开(公告)日:2015-02-12The present invention is directed compositions for delivery of RNA interference (RNAi) triggers to integrin positive tumor cells in vivo. The compositions comprise RGD ligand- targeted amphipathic membrane active polyamines reversibly modified with enzyme cleavable dipeptide-amidobenzyl-carbonate masking agents. Modification masks membrane activity of the polymer while reversibility provides physiological responsiveness. The reversibly modified polyamines (dynamic polyconjugate or conjugate) are further covalently linked to an RNAi trigger.
表征谱图
-
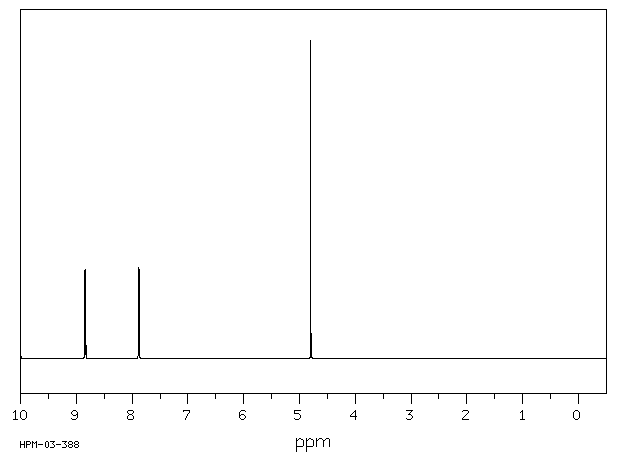
氢谱1HNMR
-
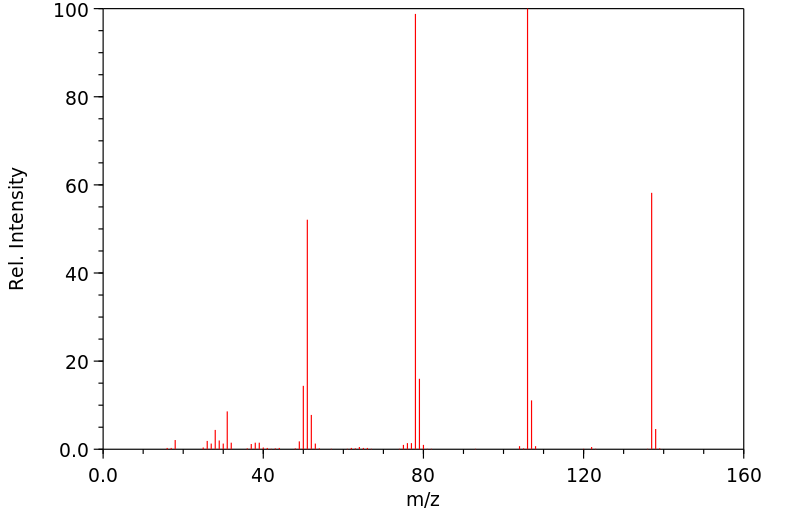
质谱MS
-
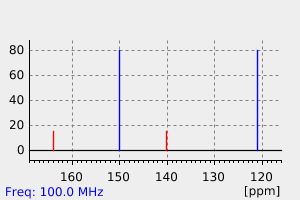
碳谱13CNMR
-
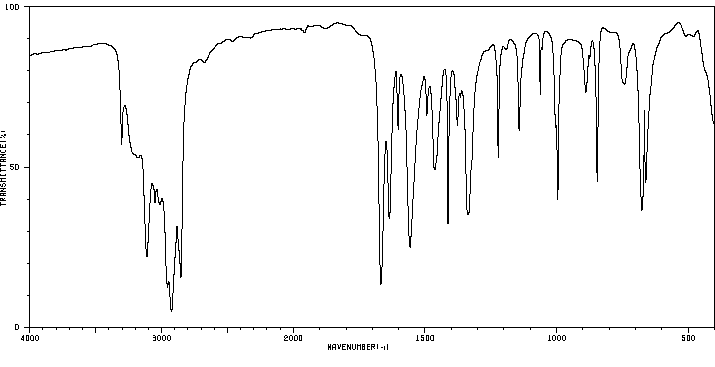
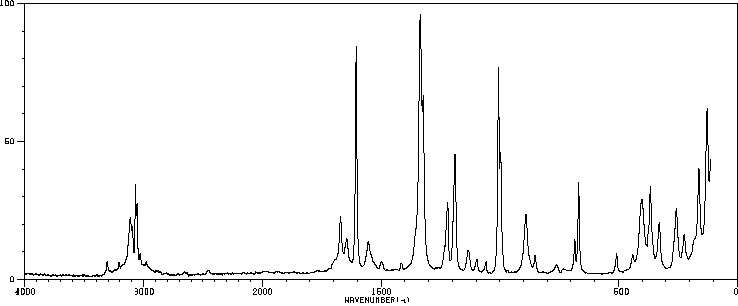
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息