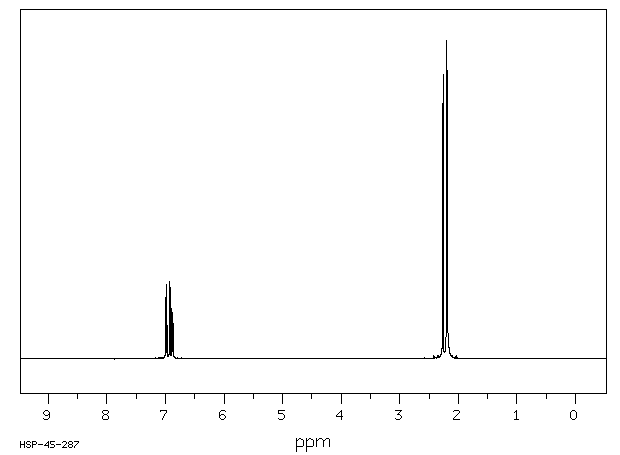
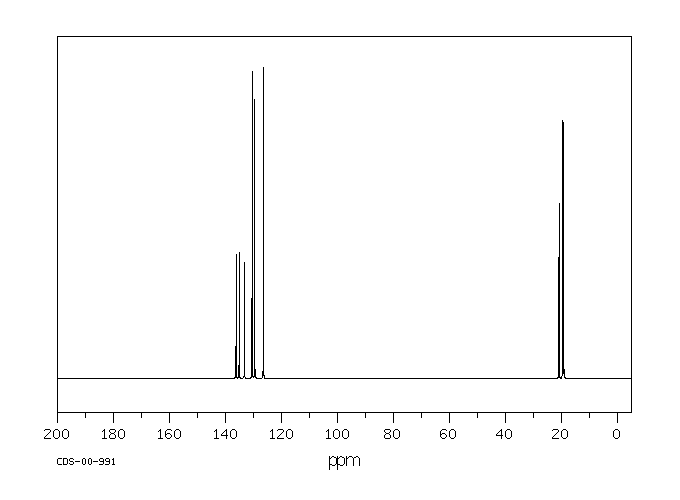
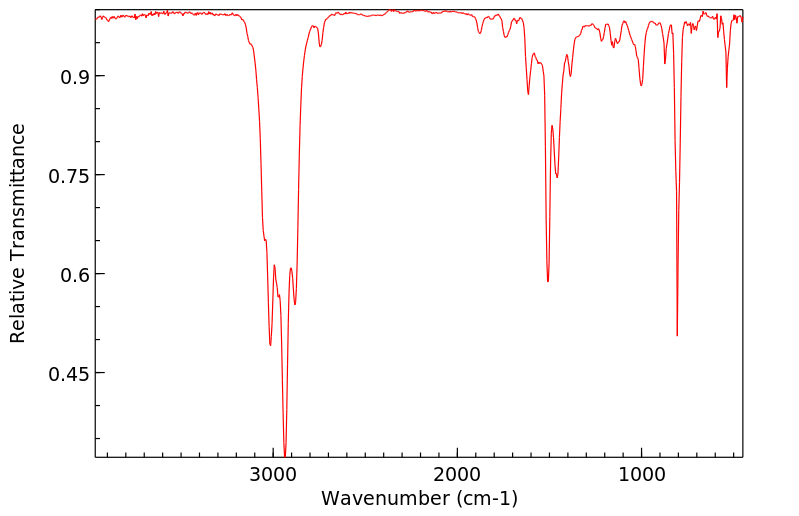
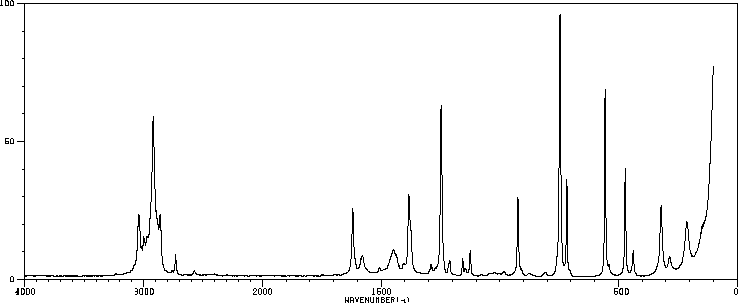
代谢
1,2,4-TMB在人类和动物体内的代谢主要是通过侧链氧化形成醇和羧酸,或者通过羟基化形成酚,然后这些代谢物会与葡萄糖醛酸、甘氨酸或硫酸结合,在排泄到尿液中之前进行共轭反应……在实验动物和人类中,已经确定1,2,4-TMB的代谢主要转化为异构体的二甲苯甲酸……在大鼠中,1,2,4-TMB的代谢导致产生异构体的二甲苯甲酸,其中3,4-二甲苯甲酸在尿液中最为显著……3,4-二甲苯甘酸在人类中被报道为一种次要代谢物……这种代谢物也在兔子上观察到,此外还有2,4-二甲苯甲酸……。
Metabolism of 1,2,4-TMB in humans and animals occurs by side-chain oxidation to form alcohols and carboxylic acids or hydroxylation to phenols, which are then conjugated with glucuronic acid, glycine, or sulphates prior to urinary excretion ... . Both in laboratory animals and in humans, it was identified that 1,2,4-TMB metabolism is mainly directed towards isomeric dimethylbenzoic acids ... . In rats, 1,2,4-TMB metabolism leads to the production of isomeric dimethylbenzoic acids, of which 3,4-dimethylbenzoic acid was identified as the most prominent in the urine . ... 3,4-Dimethylhippuric acid has been reported to be a minor metabolite in humans ... . This metabolite has also been observed in rabbits, in addition to 2,4-dimethylbenzoic acid... .
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)