牛磺酸 | 107-35-7
中文名称
牛磺酸
中文别名
牛胆碱;牛胆酸;2-氨基乙烷磺酸;氨基乙磺酸;2-氨基乙磺酸;牛胆素;硫磺酸;α-氨基乙磺酸
英文名称
Tau
英文别名
taurine;2-aminoethanesulfonic acid;2-aminoethane-1-sulfonic acid;2-Ammonioethanesulfonate;2-azaniumylethanesulfonate
CAS
107-35-7
化学式
C2H7NO3S
mdl
——
分子量
125.148
InChiKey
XOAAWQZATWQOTB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:>300 °C (lit.)
-
密度:1.00 g/mL at 20 °C
-
溶解度:在水中的溶解度0.5 Mat 20 °C,澄清,无色
-
最大波长(λmax):λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.006λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.005
-
LogP:-3.36--1.2 at 20℃
-
物理描述:Large white crystals or white powder.
-
颜色/状态:Colorless crystals
-
气味:Odorless
-
味道:Slightly acidic taste
-
沸点:It decomposes before reaching boiling point (325ºC)
-
蒸汽压力:1.7X10-7 mm Hg at 25 °C (est)
-
稳定性/保质期:
避免与强氧化剂接触。
-
分解:When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of SOx and NOx
-
碰撞截面:135.4 Ų [M+H-H2O]+ [CCS Type: DT, Method: single field calibrated with Agilent tune mix (Agilent)]
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-4.1
-
重原子数:7
-
可旋转键数:2
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:1.0
-
拓扑面积:88.8
-
氢给体数:2
-
氢受体数:4
ADMET
代谢
牛磺酸可以通过多种生物体代谢,形成从牛磺酸原始形态衍生出的不同类型的代谢物。在人体中,牛磺酸的代谢途径分为通过酶γ-谷氨酰转移酶6的作用形成5-谷氨酰牛磺酸,或者通过胆酸-CoA:氨基酸N-酰基转移酶的作用形成牛磺胆酸。
Taurine can be metabolized by diverse organisms to form different types of metabolites derived from the original form of taurine. In the human, the pathways that form the metabolism of taurine are divided in the formation of 5-glutamyl-taurine by the action of the enzyme gamma-glutamyltransferase 6 or the formation of taurocholate by the action of the bile acid-CoA:amino acid N-acyltransferase.
来源:DrugBank
代谢
人体中有两种牛磺酸的来源:饮食和内源性。在哺乳动物中,牛磺酸在很多组织中合成;主要部位是肝脏、大脑和胰腺,主要在α细胞中。牛磺酸是通过半胱氨酸和甲硫氨酸经过几个步骤合成的,其中一个步骤需要吡哆醛-5-磷酸(维生素B6)作为半胱氨酸亚磺酸脱羧酶的辅酶。在非哺乳动物中,牛磺酸的生物合成研究得很少。不同物种之间的合成程度差异很大。一只成年大鼠食用标准实验室食物可以产生其体内约80%的牛磺酸,其余从饮食中获取。然而,如果需要,大鼠可以通过生物合成获得所有的牛磺酸,因为长期食用不含牛磺酸的食物的大鼠在组织牛磺酸浓度上没有表现出任何下降。猫的半胱氨酸亚磺酸脱羧酶活性较低,这是牛磺酸生物合成的限速酶,因此猫依赖于饮食来源来维持体内这种氨基酸的池。因此,牛磺酸对猫来说是必需的营养素。
There are two sources of taurine in the body: dietary and endogenous. In mammals, taurine is synthesised in many tissues; the main sites are liver, brain and pancreas, predominantly in alpha-islets. Taurine is synthesised from cysteine and methionine in a few steps, one of which requires pyridoxal-5-phosphate (vitamin B6) as coenzyme of cysteine sulphinate decarboxylase. In species other than mammals, the biosynthesis of taurine has been poorly studied. The extent of synthesis varies widely between species. An adult rat consuming standard laboratory food produces about 80 % of its total body taurine and obtains the remainder from the diet. However, if required, rats can obtain all body taurine from biosynthesis, since rats fed taurine-free diets for extended periods do not exhibit any decrease in tissue taurine concentrations. Cats have low levels of activity of cysteine sulphinate decarboxylase, the rate-limiting enzyme for taurine biosynthesis, and are, therefore, dependent on a dietary source to maintain their body pool of this amino acid. Thus, taurine is an essential nutrient in cats.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
Taurocholate, the bile salt conjugate of taurine and cholic acid, is the principal conjugate formed via the action of the enzyme choloyl-CoA N-acyltransferase.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
在除哺乳动物外的所有脊椎动物中,牛磺酸是唯一与胆盐结合的氨基酸。在哺乳动物中,肉食动物也倾向于仅将牛磺酸结合,而其他物种倾向于将牛磺酸和甘氨酸都结合。牛磺酸在视网膜、肝脏、胰腺、中枢神经系统和白细胞中含量很高。牛磺酸的最大储存池位于骨骼肌和心肌中,它在其中调节细胞内Ca2+浓度...
In all vertebrates except mammals, taurine is the sole amino acid conjugated to form bile salts. Among the mammals, carnivores also tend to be conjugators of taurine only, whereas other species tend to conjugate both taurine and glycine. High concentrations of taurine are present in retina, liver, pancreas, central nervous system and white blood cells. The largest pools of taurine are found in skeletal and cardiac muscles, where it regulates intracellular Ca2+ concentration...
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
它阻止了大鼠中乙醇引起的高血压的发展。
It prevented the development of ethanol-induced hypertension in rats.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
In animal studies, taurine was found to ameliorate the pulmonary side effects (pulmonary fibrosis) of bleomycin.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
...Three fatalities occurred after "energy" drinks had been consumed in combination with alcohol, whereby the forensic examinations including autopsy yielded negative results concerning medicaments and drugs, values between 0.59 and 0.87 parts per thousand of ethanol in blood samples, but no clear causes of death.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
在参加一场3000米比赛的同时,一位31岁的定期训练的男性饮用了一瓶750毫升的“能量”饮料。比赛后一周,他出现了全身状况不佳、横纹肌溶解和急性肾衰竭伴肾小管坏死的症状。
...Severe adverse effects arose after consumption of an "energy" drink in combination with physical efforts: A 31-year old regularly trained man consumed 750 mL of an "energy" drink while taking part in a 3,000 m competition. He developed a poor general condition with a rhabdomyolysis and acute kidney failure with tubular necrosis diagnosed one week after the competition.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
/SRP:/ 立即急救:确保已经进行了充分的中毒物清除。如果患者停止呼吸,开始人工呼吸,最好使用需求阀复苏器、袋阀面罩装置或口袋面罩,按训练操作。如有必要,执行心肺复苏。立即用缓慢流动的水冲洗受污染的眼睛。不要催吐。如果发生呕吐,让患者前倾或置于左侧(如果可能的话,头部向下)以保持呼吸道畅通,防止吸入。保持患者安静,维持正常体温。寻求医疗帮助。 /毒物A和B/
/SRP:/ Immediate first aid: Ensure that adequate decontamination has been carried out. If patient is not breathing, start artificial respiration, preferably with a demand valve resuscitator, bag-valve-mask device, or pocket mask, as trained. Perform CPR if necessary. Immediately flush contaminated eyes with gently flowing water. Do not induce vomiting. If vomiting occurs, lean patient forward or place on the left side (head-down position, if possible) to maintain an open airway and prevent aspiration. Keep patient quiet and maintain normal body temperature. Obtain medical attention. /Poisons A and B/
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
对牛磺酸的口服给药进行了研究,报告了AUC、Cmax和tmax的剂量依赖性值,其中1-30 mg/kg剂量的范围分别为89-3452 mcg min/L、2-15.7 mcg min/ml和15分钟。在健康个体中的进一步研究给出的AUC、Cmax和tmax范围分别为116-284.5 mg h/L、59-112.6 mg/L和1-2.5小时。
Oral administration of taurine was studied and it reported dose-dependent values of AUC, Cmax and tmax wherein a dose of 1-30 mg/kg ranged from 89-3452 mcg min/L, 2-15.7 mcg min/ml and 15 min respectively. Further studies in healthy individuals gave an AUC, Cmax and tmax in the range of 116-284.5 mg h/L, 59-112.6 mg/L and 1-2.5 h.
来源:DrugBank
吸收、分配和排泄
Taurine flows and gets distributed in veins and arteries and reports have observed the presence of a significant released of taurine in portally drained viscera, thus suggesting that the main elimination route of taurine is by the gut. This elimination route may be explained by the enterohepatic cycle of taurine.
来源:DrugBank
吸收、分配和排泄
在双室模型下研究了牛磺酸的分布,每个室在小鼠中给出的分布容积范围是:室1为299-353毫升/千克,室2为4608-8374毫升/千克。在健康个体中的进一步研究给出的分布容积范围从19.8到40.7升。
The distribution of taurine was studied under the two-compartment model and each one of the compartments gave a range for the volume of distribution of 299-353 ml/kg in compartment 1 and 4608-8374 ml/kg in compartment 2 in mice. Further studies in healthy indivudals gave a volume of distribution that ranged from 19.8 to 40.7 L.
来源:DrugBank
吸收、分配和排泄
口服牛磺酸的清除率据报道是剂量依赖性的,其中1 mg/kg剂量的清除率为11.7 ml/min/kg,10 mg/kg剂量产生的清除率为18.7 ml/min/kg,30 mg/kg剂量的清除率为9.4 ml/min/kg。在健康个体中的进一步研究产生的清除率范围从14到34.4 L/h。
The clearance rate of orally administered taurine was reported to be dose-dependent wherein a dose of 1 mg/kg it presents a clearance rate of 11.7 ml min/kg, 10 mg/kg generates a clearance rate of 18.7 ml min/kg and a dose of 30 mg/kg reports a clearance rate of 9.4 ml min/kg. Further studies in healthy individuals generate a clearance rate that ranged from 14 to 34.4 L/h.
来源:DrugBank
安全信息
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险品标志:Xi
-
安全说明:S24/25,S26,S36
-
危险类别码:R36/37/38
-
WGK Germany:2
-
海关编码:2921199090
-
危险品运输编号:NONH for all modes of transport
-
RTECS号:WX0175000
-
危险性防范说明:P261,P305+P351+P338
-
危险性描述:H315,H319,H335
-
储存条件:1. 存于阴凉、通风的库房,远离火种和热源,确保容器密封,并与氧化剂分开存放,切忌混储。使用防爆型照明和通风设施,禁止使用易产生火花的机械设备和工具。储存区应配备泄漏应急处理设备和合适的收容材料。 2. 本品采用25kg纸板圆桶、纸箱或纸袋包装,并内衬两层聚乙烯袋,需遮光、密闭,在干燥处于室温下保存。
SDS
模块 1. 化学品
1.1 产品标识符
: 牛磺酸
产品名称
1.2 鉴别的其他方法
2-Aminoethanesulfonic acid
1.3 有关的确定了的物质或混合物的用途和建议不适合的用途
仅用于研发。不作为药品、家庭或其它用途。
模块 2. 危险性概述
2.1 GHS-分类
皮肤刺激 (类别 2)
眼睛刺激 (类别 2A)
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触) (类别 3)
2.2 GHS 标记要素,包括预防性的陈述
象形图
警示词 警告
危险申明
H315 造成皮肤刺激。
H319 造成严重眼刺激。
H335 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
警告申明
预防措施
P261 避免吸入粉尘/烟/气体/烟雾/蒸气/喷雾.
P264 操作后彻底清洁皮肤。
P271 只能在室外或通风良好之处使用。
P280 穿戴防护手套/ 眼保护罩/ 面部保护罩。
事故响应
P302 + P352 如果皮肤接触:用大量肥皂和水清洗。
P304 + P340 如吸入: 将患者移到新鲜空气处休息,并保持呼吸舒畅的姿势。
P305 + P351 + P338 如与眼睛接触,用水缓慢温和地冲洗几分钟。如戴隐形眼镜并可方便地取
出,取出隐形眼镜,然后继续冲洗.
P312 如感觉不适,呼救中毒控制中心或医生.
P321 具体处置(见本标签上提供的急救指导)。
P332 + P313 如觉皮肤刺激:求医/就诊。
P337 + P313 如仍觉眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
P362 脱掉沾污的衣服,清洗后方可再用。
安全储存
P403 + P233 存放于通风良的地方。 保持容器密闭。
P405 存放处须加锁。
废弃处置
P501 将内容物/ 容器处理到得到批准的废物处理厂。
2.3 其它危害物 - 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
3.1 物 质
: 2-Aminoethanesulfonic acid
别名
: C2H7NO3S
分子式
: 125.15 g/mol
分子量
组分 浓度或浓度范围
Taurine
<=100%
化学文摘登记号(CAS 107-35-7
No.) 203-483-8
EC-编号
模块 4. 急救措施
4.1 必要的急救措施描述
一般的建议
请教医生。 向到现场的医生出示此安全技术说明书。
吸入
如果吸入,请将患者移到新鲜空气处。 如呼吸停止,进行人工呼吸。 请教医生。
皮肤接触
用肥皂和大量的水冲洗。 请教医生。
眼睛接触
用大量水彻底冲洗至少15分钟并请教医生。
食入
切勿给失去知觉者通过口喂任何东西。 用水漱口。 请教医生。
4.2 主要症状和影响,急性和迟发效应
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
4.3 及时的医疗处理和所需的特殊处理的说明和指示
无数据资料
模块 5. 消防措施
5.1 灭火介质
灭火方法及灭火剂
用水雾,抗乙醇泡沫,干粉或二氧化碳灭火。
5.2 源于此物质或混合物的特别的危害
碳氧化物, 氮氧化物, 硫氧化物
5.3 给消防员的建议
如必要的话,戴自给式呼吸器去救火。
5.4 进一步信息
无数据资料
模块 6. 泄露应急处理
6.1 作业人员防护措施、防护装备和应急处置程序
使用个人防护用品。 避免粉尘生成。 避免吸入蒸气、烟雾或气体。 保证充分的通风。
人员疏散到安全区域。 避免吸入粉尘。
6.2 环境保护措施
不要让产品进入下水道。
6.3 泄漏化学品的收容、清除方法及所使用的处置材料
收集和处置时不要产生粉尘。 扫掉和铲掉。 放入合适的封闭的容器中待处理。
6.4 参考其他部分
丢弃处理请参阅第13节。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
7.1 安全操作的注意事项
避免接触皮肤和眼睛。 避免形成粉尘和气溶胶。
在有粉尘生成的地方,提供合适的排风设备。一般性的防火保护措施。
7.2 安全储存的条件,包括任何不兼容性
贮存在阴凉处。 使容器保持密闭,储存在干燥通风处。
7.3 特定用途
无数据资料
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
8.1 容许浓度
最高容许浓度
没有已知的国家规定的暴露极限。
8.2 暴露控制
适当的技术控制
根据良好的工业卫生和安全规范进行操作。 休息前和工作结束时洗手。
个体防护设备
眼/面保护
带有防护边罩的安全眼镜符合 EN166要求请使用经官方标准如NIOSH (美国) 或 EN 166(欧盟)
检测与批准的设备防护眼部。
皮肤保护
戴手套取 手套在使用前必须受检查。
请使用合适的方法脱除手套(不要接触手套外部表面),避免任何皮肤部位接触此产品.
使用后请将被污染过的手套根据相关法律法规和有效的实验室规章程序谨慎处理. 请清洗并吹干双手
所选择的保护手套必须符合EU的89/686/EEC规定和从它衍生出来的EN 376标准。
完全接触
物料: 丁腈橡胶
最小的层厚度 0.11 mm
溶剂渗透时间: 480 min
测试过的物质Dermatril® (KCL 740 / Z677272, 规格 M)
飞溅保护
物料: 丁腈橡胶
最小的层厚度 0.11 mm
溶剂渗透时间: 480 min
测试过的物质Dermatril® (KCL 740 / Z677272, 规格 M)
, 测试方法 EN374
如果以溶剂形式应用或与其它物质混合应用,或在不同于EN
374规定的条件下应用,请与EC批准的手套的供应商联系。
这个推荐只是建议性的,并且务必让熟悉我们客户计划使用的特定情况的工业卫生学专家评估确认才可.
这不应该解释为在提供对任何特定使用情况方法的批准.
身体保护
防渗透的衣服, 防护设备的类型必须根据特定工作场所中的危险物的浓度和数量来选择。
呼吸系统防护
如须暴露于有害环境中,请使用P95型(美国)或P1型(欧盟 英国
143)防微粒呼吸器。如需更高级别防护,请使用OV/AG/P99型(美国)或ABEK-P2型 (欧盟 英国 143)
防毒罐。
呼吸器使用经过测试并通过政府标准如NIOSH(US)或CEN(EU)的呼吸器和零件。
模块 9. 理化特性
9.1 基本的理化特性的信息
a) 外观与性状
形状: 固体
b) 气味
无数据资料
c) 气味阈值
无数据资料
d) pH值
4.5 - 6 在 62.6 g/l 在 25 °C
e) 熔点/凝固点
熔点/凝固点: > 300 °C
f) 沸点、初沸点和沸程
无数据资料
g) 闪点
无数据资料
h) 蒸发速率
无数据资料
i) 易燃性(固体,气体)
无数据资料
j) 高的/低的燃烧性或爆炸性限度 无数据资料
k) 蒸气压
无数据资料
l) 蒸汽密度
无数据资料
m) 密度/相对密度
无数据资料
n) 水溶性
62.6 g/l 在 20 °C - 完全溶解
o) n-辛醇/水分配系数
无数据资料
p) 自燃温度
无数据资料
q) 分解温度
无数据资料
r) 粘度
无数据资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应活性
10.1 反应性
无数据资料
10.2 稳定性
无数据资料
10.3 危险反应
无数据资料
10.4 应避免的条件
无数据资料
10.5 不相容的物质
强氧化剂
10.6 危险的分解产物
其它分解产物 - 无数据资料
模块 11. 毒理学资料
11.1 毒理学影响的信息
急性毒性
半数致死剂量 (LD50) 经口 - 大鼠 - > 5,000 mg/kg
皮肤刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
眼睛刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
呼吸道或皮肤过敏
无数据资料
生殖细胞致突变性
无数据资料
致癌性
IARC:
此产品中没有大于或等于 0。1%含量的组分被 IARC鉴别为可能的或肯定的人类致癌物。
生殖毒性
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触)
吸入 - 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(反复接触)
无数据资料
吸入危险
无数据资料
潜在的健康影响
吸入 吸入可能有害。 引起呼吸道刺激。
摄入 如服入是有害的。
皮肤 通过皮肤吸收可能有害。 造成皮肤刺激。
眼睛 造成严重眼刺激。
接触后的征兆和症状
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
附加说明
化学物质毒性作用登记: WX0175000
模块 12. 生态学资料
12.1 生态毒性
无数据资料
12.2 持久性和降解性
无数据资料
12.3 潜在的生物累积性
无数据资料
12.4 土壤中的迁移性
无数据资料
12.5 PBT 和 vPvB的结果评价
无数据资料
12.6 其它不良影响
无数据资料
模块 13. 废弃处置
13.1 废物处理方法
产品
将剩余的和不可回收的溶液交给有许可证的公司处理。
联系专业的拥有废弃物处理执照的机构来处理此物质。
与易燃溶剂相溶或者相混合,在备有燃烧后处理和洗刷作用的化学焚化炉中燃烧
受污染的容器和包装
按未用产品处置。
模块 14. 运输信息
14.1 联合国危险货物编号
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.2 联合国运输名称
欧洲陆运危规: 非危险货物
国际海运危规: 非危险货物
国际空运危规: 非危险货物
14.3 运输危险类别
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.4 包裹组
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.5 环境危险
欧洲陆运危规: 否 国际海运危规 国际空运危规: 否
海洋污染物(是/否): 否
14.6 对使用者的特别提醒
无数据资料
模块 15 - 法规信息
N/A
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
制备方法与用途
1. 牛磺酸的制备
方法一:硫酸酯化法
步骤:
- 在500 mL烧瓶中加入36.6 g乙醇胺(0.6 mol)和100 mL甲苯。
- 水浴冷却下滴加98%的硫酸(61.4 g,0.626 mol),约需50分钟滴完。
- 再加入1.4 g十六烷基三乙基氯化铵(CTC)(0.0039 mol),加热回流1.5~2小时。
- 分离出理论量的水后,冷却、过滤、洗涤并干燥得83 g 2-氨基乙基硫酸氢酯(mp 273~279℃)。
合成反应: [ \text{NH}_2\text{CH}_2\text{CH}_2\text{OH} + \text{H}_2\text{SO}_4 \rightarrow \text{NH}_2\text{CH}_2\text{CH}_2\text{OSO}_3\text{H} + \text{H}_2\text{O} ]
- 在500 mL烧瓶中加入75.6 g亚硫酸钠(0.6 mol)和250 mL水。
- 在氮气保护下,均匀缓慢地加入28.2 g 2-氨基乙基硫酸氢酯(0.2 mol),反应10~12小时生成牛磺酸。
- 减压蒸去水分后加浓盐酸(100 mL)搅拌1小时,使产物溶解完全。
- 滤出无机盐晶体,并用20 mL浓盐酸洗涤两次。
- 滤液减压浓缩至原体积的一半,加入95%乙醇50 mL,冷却结晶得牛磺酸。
合成反应: [ \text{NH}_2\text{CH}_2\text{CH}_2\text{OSO}_3\text{H} + \text{Na}_2\text{SO}_3 \rightarrow \text{NH}_2\text{CH}_2\text{CH}_2\text{SO}_3\text{H} + 2 \text{NaCl} ]
收率与纯度:
- 牛磺酸提取收率为91.5%,纯度为99.6%。
- 总收率为83.6%。
步骤:
合成反应: [ \text{NH}_2\text{CH}_2\text{CH}_2\text{OSO}_3\text{H} + \text{Na}_2\text{SO}_3 \rightarrow \text{NH}_2\text{CH}_2\text{CH}_2\text{SO}_3\text{H} + 2 \text{NaCl} ]
收率与纯度:
- 提取收率为91.5%,纯度为99.6%。总收率83.6%。
- 初始步骤: [ \text{NH}_2\text{CH}_2\text{CH}_2\text{OH} + \text{H}_2\text{SO}_4 \rightarrow \text{NH}_2\text{CH}_2\text{CH}_2\text{OSO}_3\text{H} + \text{H}_2\text{O} ]
- 中间产物: [ \text{NH}_2\text{CH}_2\text{CH}_2\text{OSO}_3\text{H} + \text{Na}_2\text{SO}_3 \rightarrow \text{NH}_2\text{CH}_2\text{CH}_2\text{SO}_3\text{H} + 2 \text{NaCl} ]
此方法未直接涉及牛磺酸的合成,而是用于制备其中间体2-氯乙醇胺。该过程不在此详细讨论。
这些步骤和反应展示了如何从原料开始通过一系列化学反应最终获得高纯度的牛磺酸产品。希望这有助于您了解相关过程的具体细节。如果需要进一步信息或特定部分的详细解释,请随时告知。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 亚牛磺酸 hypotaurine 300-84-5 C2H7NO2S 109.149 2-羟乙基磺酸 2-hydroxyethanesulfonic acid 107-36-8 C2H6O4S 126.133 脒基牛磺酸 taurocyamine 543-18-0 C3H9N3O3S 167.189 —— cyanomethane-sulfonic acid 753386-85-5 C2H3NO3S 121.117 2-氯乙烷磺酸钠 2-chloroethanesulphonic acid 18024-00-5 C2H5ClO3S 144.579 2-硝基-乙磺酸 2-nitro-ethanesulfonic acid 503863-49-8 C2H5NO5S 155.131 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— 8α-hydroxytaurine —— C2H7NO4S 141.148 N-氯牛磺酸 N-chlorotaurine 51036-13-6 C2H6ClNO3S 159.594 —— 2-hydrazino-ethanesulfonic acid 25355-29-7 C2H8N2O3S 140.163 N-溴牛磺酸 taurine bromamine 52316-57-1 C2H6BrNO3S 204.045 —— N,N-dimethyltaurine 637-95-6 C4H11NO3S 153.202 —— isocyanatotaurine —— C3H5NO4S 151.143 2-(二氯氨基)乙磺酸 taurine dichloramine 83152-69-6 C2H5Cl2NO3S 194.039 —— N,N-bis(2-sulfonic acid ethyl)amine —— C4H11NO6S2 233.266 —— N,N-dibromotaurine 162069-44-5 C2H5Br2NO3S 282.941 2-羟乙基磺酸 2-hydroxyethanesulfonic acid 107-36-8 C2H6O4S 126.133 脒基牛磺酸 taurocyamine 543-18-0 C3H9N3O3S 167.189 —— 2-aminoethanesulfonic acid ethyl ester —— C4H11NO3S 153.202 - 1
- 2
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:One-electron oxidation and reduction of glycosaminoglycan chloramides: A kinetic study摘要:Hypochlorous acid and its acid-base counterpart, hypochlorite ions, produced under inflammatory conditions, may produce chloramides of glycosaminoglycans, these being significant components of the extracellular matrix (ECM). This may occur through the binding of myeloperoxidase directly to the glycosaminoglycans. The N-Cl group in the chloramides is a potential selective target for both reducing and oxidizing radicals, leading possibly to more efficient and damaging fragmentation of these biopolymers relative to the parent glycosaminoglycans. In this study, the fast reaction techniques of pulse radiolysis and nanosecond laser flash photolysis have been used to generate both oxidizing and reducing radicals to react with the chloramides of hyaluronan (HAG) and heparin (HepCl). The strong reducing formate radicals and hydrated electrons were found to react rapidly with both HACl and HepCl with rate constants of 1-1.7 x 10(8) and 0.7-12 x 10(8) M-1 s(-1) for formate radicals and 2.2 x 10(9) and 7.2 x 10(8) M-1 s(-1) for hydrated electrons, respectively. The spectral characteristics of the products of these reactions were identical and were consistent with initial attack at the N-Cl groups, followed by elimination of chloride ions to produce nitrogen-centered radicals, which rearrange subsequently and rapidly to produce C-2 radicals on the glucosamine moiety, supporting an earlier EPR study by M.D. Rees et al. (J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125: 13719-13733; 2003). The oxidizing hydroxyl radicals also reacted rapidly with HACl and HepCl with rate constants of 2.2 x 10(8) and 1.6 x 10(8) M-1 s(-1), with no evidence from these data for any degree of selective attack on the N-Cl group relative to the N-H groups and other sites of attack. The carbonate anion radicals were much slower with HACl and HepCl than hydroxyl radicals (1.0 x 10(5) and 8.0 x 10(4) M-1 s(-1), respectively) but significantly faster than with the parent molecules (3.5 x 10(4) and 5.0 x 10(4) M-1 s(-1), respectively). These findings suggest that these potential in vivo radicals may react in a site-specific manner with the N-Cl group in the glycosaminoglycan chloramides of the ECM, possibly to produce more efficient fragmentation. This is the first study therefore to conclusively demonstrate that reducing radicals react rapidly with glycosaminoglycan chloramides in a site-specific attack at the N-Cl group, probably to produce a 100% efficient biopolymer fragmentation process. Although less reactive, carbonate radicals, which may be produced in vivo via reactions of peroxynitrite with serum levels of carbon dioxide, also appear to react in a highly site-specific manner at the N-Cl group. It is not yet known if such site-specific attacks by this important in vivo species lead to a more efficient fragmentation of the biopolymers than would be expected for attack by the stronger oxidizing species, the hydroxyl radical. It is clear, however, that the N-Cl group formed under inflammatory conditions in the extracellular matrix does present a more likely target for both reactive oxygen species and reducing species than the N-H groups in the parent glycosaminoglycans. (C) 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.DOI:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.05.012
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:一种牛磺酸合成方法摘要:本发明提供一种牛磺酸合成方法,解决传统牛磺酸合成工艺中存在的加成反应中副产积累、氨解反应中高温高压和酸化中的强酸强碱等危险且苛刻的工艺难题。包括如下步骤:1)将硫磺溶液和乙烯接触进行环化反应,得到环硫乙烷;优选的,所述硫磺溶液为硫磺溶于二硫化碳的溶液;2)所述环硫乙烷与氨气或液氨接触进行加成反应,得到氨基硫醇;3)所述氨基硫醇在催化剂存在下进行氧化反应得到牛磺酸粗品。公开号:CN111362845A
-
作为试剂:描述:对苯二甲醛 、 5,5-二甲基-1,3-环己二酮 在 牛磺酸 作用下, 以 水 为溶剂, 反应 0.42h, 以85%的产率得到2,2'-(1,4-phenylene-bis((2-hydroxy-4,4-dimethyl-6-oxocyclohexyl)methylene))-bis(3-hydroxy-5,5-dimethylcyclohex-2-enone)参考文献:名称:引入牛磺酸(2-氨基乙烷磺酸)作为绿色生物有机催化剂,以促进绿色条件下的有机反应†摘要:牛磺酸(2-氨基乙烷磺酸)是存在于人体和许多其他生物中的半必需氨基酸,被用作绿色生物有机催化剂,以促进醛与丙二腈之间的Knoevenagel反应。同样,四酮也可以通过Knoevenagel反应生成,然后进行迈克尔加成反应。2-氨基-3-氰基-4 H-吡喃衍生物可通过以下方法简单地制备牛磺酸作为催化剂的三组分反应。所有这些反应均在绿色溶剂水中进行。使用牛磺酸作为催化剂的优点是环境友好,成本低廉,可商购,易于从反应混合物中分离并且具有高可重复使用性。使用这种催化剂可在不使用任何有机溶剂的情况下获得可接受的反应时间,高产率和高纯度的所得产物。DOI:10.1039/c6ra15432h
文献信息
-
[EN] BICYCLIC ARYL SPHINGOSINE 1-PHOSPHATE ANALOGS<br/>[FR] ANALOGUES D’ARYLSPHINGOSINE-1-PHOSPHATE BICYCLIQUES申请人:BIOGEN IDEC INC公开号:WO2011017561A1公开(公告)日:2011-02-10Compounds that have agonist activity at one or more of the SlP receptors are provided. The compounds are sphingosine analogs that, after phosphorylation, can behave as agonists at SlP receptors.
-
[EN] TRIAZINES SUITABLE FOR USE IN FABRIC TREATMENT COMPOSITIONS<br/>[FR] TRIAZINES POUVANT ETRE UTILISEES DANS DES COMPOSITIONS DE TRAITEMENT DE TISSUS申请人:UNILEVER PLC公开号:WO2005123699A1公开(公告)日:2005-12-29A water-soluble, triazine-based, non-dye, cellulose cross-linking agent that has a highly flexible linking group between at least two, mono-reactive cross-linking moieties and further hydrophilic or non-hydrophilic substituents, being preferrably represented by the general formula (I): (R1)(X1)T-L1-B-T(X2)(R2) wherein: R1 et R2 are cellulose-unreactive substituent groups on the s-triazine (T) and may be the same or different, X1 and X2 are leaving groups on the s-triazine which are lost on reaction with cellulose and may be the same or different, L1 et L2 are linking groups, an may be the same or different or absent, B is the bridging group comprising or consisting of at least one aliphatic polyoalkylene chain.
-
棉酚衍生物和它们的制备 ,在农药上的应用及 抗癌活性
-
[EN] TRIAZOLE AND IMIDAZOLE DERIVATIVES FOR USE AS TGR5 AGONISTS IN THE TREATMENT OF DIABETES AND OBESITY<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS DE TRIAZOLE ET D'IMIDAZOLE DESTINÉS À ÊTRE UTILISÉS EN TANT QU'AGONISTES DE TGR5 DANS LE TRAITEMENT DU DIABÈTE ET DE L'OBÉSITÉ申请人:EXELIXIS INC公开号:WO2010093845A1公开(公告)日:2010-08-19The present invention comprises TGR5 agonists of structural formula I, wherein X, R1, R2, and R5 are defined herein, as well as N-oxides of them and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof. The invention further comprises composition comprising the compounds, N-oxides, and/or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof. The invention also comprises use of the compounds and compositions for treating diseases in which TGR5 is a mediator or is implicated. The invention also comprises use of the compounds in and for the manufacture of medicaments, particularly for treating diseases in which TGR5 is a mediator or is implicated.本发明包括结构式I的TGR5激动剂,其中X、R1、R2和R5在此处定义,以及它们的N-氧化物和其药学上可接受的盐。该发明还包括包含这些化合物、N-氧化物和/或其药学上可接受的盐的组合物。该发明还包括利用这些化合物和组合物治疗TGR5是介质或涉及的疾病。该发明还包括利用这些化合物制造药物,特别是用于治疗TGR5是介质或涉及的疾病。
-
Potential antiatherosclerotic agents. 3. Substituted benzoic and nonbenzoic acid analogs of cetaben作者:J. Donald Albright、Vern G. DeVries、Mila T. Du、Elwood E. Largis、Thomas G. Miner、Marvin F. Reich、Robert G. ShepherdDOI:10.1021/jm00364a010日期:1983.10acid group of cetaben is replaced by carboxylate ester, carboxamide, or a variety of other substituent groups is described. Also reported are the syntheses of analogues in which the phenyl ring of cetaben is either modified by the presence of additional substituents or replaced entirely by another moiety. Structure-activity relationships of these compounds both as hypolipidemic agents and as inhibitors
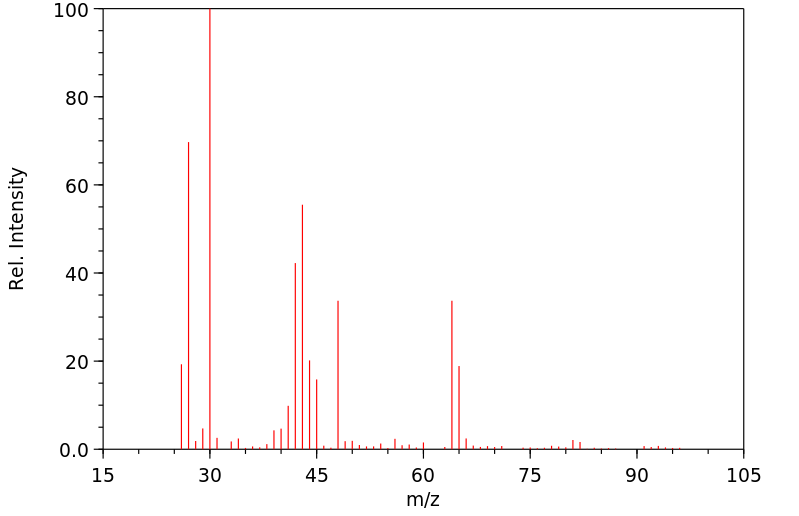
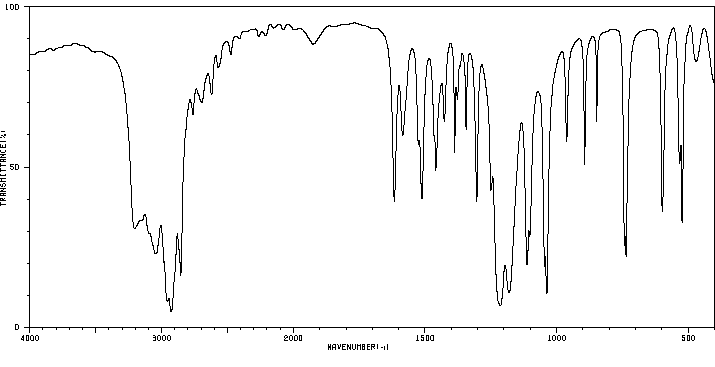
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
高烯丙基(甲磺酰基)胺
高炔丙基(甲磺酰基)胺
顺式-9-十八碳烯基甲烷磺酸酯
顺式-4-乙基环己基甲烷磺酸酯
顺-1,2-双(甲磺酰基氧基甲基)环己烷
阿坎酸杂质
阿坎酸
锌甲烷磺酸盐
铵磺酸甜菜碱-3
铵磺酸甜菜碱-2
铵磺酸甜菜碱-1
铬雾抑制剂
铁三(三氟甲基磺酰基)亚胺
钾3-(三羟基硅烷基)-1-丙烷磺酸酯
钾1,1,2,2,3,3,4,4-八氟丁烷-1-磺酸盐
钡二乙烷磺酸酯
钠3-氨基丙烷磺酸酯
钠3-氨基-3-氧代-丙烷-1-磺酸酯
钠3-(三羟基硅烷基)-1-丙烷磺酸酯
钠2-[2-[2-[2-[2-[2-[2-[2-[2-[2-(2-十八碳-9-烯氧基乙氧基)乙氧基]乙氧基]乙氧基]乙氧基]乙氧基]乙氧基]乙氧基]乙氧基]乙氧基]-2-氧代-乙烷磺酸酯
钠1-羟基-1-庚烷磺酸酯
钠(1E)-1-十二碳烯-1-磺酸酯
酪朊酸钠
辛烷-1-磺酸甲酯
辛烷-1-磺酸乙酯
辛基-1-磺酸戊酯
辛-2-烯-1-磺酸
辅酶 M
西尼必利杂质7
萘-1,8-二甲醇
英丙舒凡对甲苯磺酸盐
英丙舒凡
苯基硒基三氟甲烷磺酸酯
芥酸酰胺丙基羟基磺基甜菜碱
艾日布林中间体
脒基牛磺酸
胺磺酸甜菜碱-4
联硫亚盐氯乙醛钠水合物
羧基-五聚乙二醇-磺酸
羟甲基磺酸钠
羟基甲烷磺酸铵盐
羟基甲烷磺酸钾
羟基甲氧基甲醇甲磺酸酯
羟乙磺酸钾
羟乙基磺酸铵盐
羟乙基磺酸钠
羟丙基硫代硫酸钠
美司那
磺酸钠
磺酸己烷