联苯 | 92-52-4
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:68-70 °C (lit.)
-
沸点:255 °C (lit.)
-
密度:0.992
-
蒸气密度:5.31 (vs air)
-
闪点:113 °C
-
溶解度:溶于乙醇和乙醚
-
介电常数:20.0(Ambient)
-
暴露限值:NIOSH REL: TWA 0.2 ppm, IDLH 100 mg/m3; OSHA PEL: TWA 0.2 ppm; ACGIH TLV: TWA 0.2 ppm.
-
LogP:4.008 at 25℃
-
物理描述:Biphenyl appears as a clear colorless liquid with a pleasant odor. Flash point 180°F. Insoluble in water. Vapors are heavier than air. Used to manufacture other chemicals and as a fungicide.
-
颜色/状态:White scales
-
气味:Pleasant, peculiar odor
-
蒸汽密度:5.31 (USCG, 1999) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:8.93X10-3 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
亨利常数:3.08e-04 atm-m3/mole
-
大气OH速率常数:7.20e-12 cm3/molecule*sec
-
稳定性/保质期:
请注意:此物品易燃,请远离火源。
-
自燃温度:540 °C
-
分解:This substance decomposes on heating producing toxic gases, acrid smokes and fumes.
-
粘度:0.98 cSt at 100 °C
-
燃烧热:624.3 kJ/mol
-
汽化热:397.0 J/g at 100 °C
-
电离电位:7.95 eV
-
气味阈值:low 0.0062 mg/cu m, high 0.3 mg/cu m
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.475 @ 20 °C/D; 1.588 @ 75 °C/D
-
保留指数:1338.4;1392.2;1375;1375.78;1377.2;1377.91;1390.72;1392;1392.64;1396.81;1374;1378;1349;1350;1369;1369;1370;1378;1353;1345;1346;1349;1340;1340;1351;1351;1351;1352;1352;1352;1352;1352;1352;1352;1354;1387;1359;1350;1366.3;1377.9;1389;1396;1373;1405;1398.7;1354;1354;1380;1399;1369;1349;1369.7;1388;1354;1360;1360;1366;1375;1356;1374.2;1356;1370.9;1342;1358;1366;1345;1368;1352.4;1369;1408;1342;1343;1348;1349;1350;1389;1389;1368;1396;235;233.78;236.2
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):4
-
重原子数:12
-
可旋转键数:1
-
环数:2.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:0
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:0
ADMET
安全信息
-
职业暴露等级:C
-
职业暴露限值:TWA: 1 mg/m3 (0.2 ppm)
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:9
-
立即威胁生命和健康浓度:100 mg/m3
-
危险品标志:Xi
-
安全说明:S23,S60,S61
-
危险类别码:R36/37/38,R50/53
-
WGK Germany:2
-
海关编码:2902909010
-
危险品运输编号:UN 3077
-
RTECS号:DU8050000
-
包装等级:III
-
储存条件:1. 本品应密封保存在阴凉处。 2. 本品具有可燃性,遇高温、明火或氧化剂时存在燃烧危险,因此应储存在阴凉通风的仓库内,并远离火源和热源。此外,还需与氧化剂及强酸类物质分开存放,轻拿轻放,确保包装完好。
SDS
| 第一部分:化学品名称 |
| 化学品中文名称: | 联苯;苯基苯 |
| 化学品英文名称: | Diphenyl;Biphenyl |
| 中文俗名或商品名: | |
| Synonyms: | |
| CAS No.: | 92-52-4 |
| 分子式: | C 12 H 10 |
| 分子量: | 154.21 |
| 第二部分:成分/组成信息 |
| 纯化学品 混合物 | |||
| 化学品名称:联苯;苯基苯 | |||
|
| 第三部分:危险性概述 |
| 危险性类别: | |
| 侵入途径: | 吸入 食入 经皮吸收 |
| 健康危害: | 对皮肤、粘膜有轻度刺激性,高浓度吸入,主要损害神经系统和肝脏,可致过敏性或接触性皮炎。急性中毒主要表现为神经系统和消化系统症状,如头晕、头痛、眩晕、嗜睡、恶心、呕吐等,有时可出现肝功能障碍。高浓度接触,对呼吸道和眼睛有明显刺激,长期接触可引起头痛、乏力、失眠等以及呼吸道刺激症状。 |
| 环境危害: | 对环境有危害,对大气可造成污染。 |
| 燃爆危险: | 本品易燃。 |
| 第四部分:急救措施 |
| 皮肤接触: | 脱去污染的衣着,用肥皂水及清水彻底冲洗。 |
| 眼睛接触: | 立即翻开上千眼睑,用流动清水冲洗15分钟。就医。 |
| 吸入: | 脱离现场至空气新鲜处。就医。 |
| 食入: | 误服者给饮足量温水,催吐,就医。 |
| 第五部分:消防措施 |
| 危险特性: | 遇高热、明火或与氧化剂接触,有引起燃烧的危险。 |
| 有害燃烧产物: | 一氧化碳、二氧化碳、成分未知的黑色烟雾。 |
| 灭火方法及灭火剂: | 尽可能将容器从火场移至空旷处。灭火剂:泡沫、二氧化碳、1211灭火剂、干粉、砂土。用水可引起沸溅。 |
| 消防员的个体防护: | |
| 禁止使用的灭火剂: | |
| 闪点(℃): | 113 |
| 自燃温度(℃): | 引燃温度(℃):540 |
| 爆炸下限[%(V/V)]: | 0.6(111℃) |
| 爆炸上限[%(V/V)]: | 5.8(155℃) |
| 最小点火能(mJ): | |
| 爆燃点: | |
| 爆速: | |
| 最大燃爆压力(MPa): | |
| 建规火险分级: |
| 第六部分:泄漏应急处理 |
| 应急处理: | 隔离泄漏污染区,周围设警告标志,切断火源。应急处理人员戴好防毒面具,穿化学防护服。收集于密闭容器中作好标记,等待处理。如大量泄漏,收集回收或无害处理后废弃。 |
| 第七部分:操作处置与储存 |
| 操作注意事项: | 密闭操作,提供良好的自然通风条件。操作人员必须经过专门培训,严格遵守操作规程。建议操作人员佩戴自吸过滤式防尘口罩,戴化学安全防护眼镜,穿防毒物渗透工作服,戴防化学品手套。远离火种、热源,工作场所严禁吸烟。使用防爆型的通风系统和设备。避免产生粉尘。避免与氧化剂接触。搬运时要轻装轻卸,防止包装及容器损坏。配备相应品种和数量的消防器材及泄漏应急处理设备。倒空的容器可能残留有害物。 |
| 储存注意事项: | 储存于阴凉、通风的库房。远离火种、热源。应与氧化剂分开存放,切忌混储。采用防爆型照明、通风设施。禁止使用易产生火花的机械设备和工具。储区应备有合适的材料收容泄漏物。 |
| 第八部分:接触控制/个体防护 |
| 最高容许浓度: | 中 国 MAC:未制订标准前苏联MAC:未制订标准美国TLV—TWA:1.5mg/m3 |
| 监测方法: | |
| 工程控制: | 提供良好的自然通风条件。 |
| 呼吸系统防护: | 空气中浓度较高时,佩带防毒面具。 |
| 眼睛防护: | 必要时戴安全防护眼镜。 |
| 身体防护: | 穿工作服。 |
| 手防护: | 必要时戴防护手套。 |
| 其他防护: | 工作现场严禁吸烟。工作后,淋浴更衣。 |
| 第九部分:理化特性 |
| 外观与性状: | 无色或淡黄色、片状晶体,略带甜嗅味。 |
| pH: | |
| 熔点(℃): | 69.71 |
| 沸点(℃): | 254.25 |
| 相对密度(水=1): | 1.04 |
| 相对蒸气密度(空气=1): | 5.80 |
| 饱和蒸气压(kPa): | 0.66(101.8℃) |
| 燃烧热(kJ/mol): | |
| 临界温度(℃): | |
| 临界压力(MPa): | |
| 辛醇/水分配系数的对数值: | |
| 闪点(℃): | 113 |
| 引燃温度(℃): | 引燃温度(℃):540 |
| 爆炸上限%(V/V): | 5.8(155℃) |
| 爆炸下限%(V/V): | 0.6(111℃) |
| 分子式: | C 12 H 10 |
| 分子量: | 154.21 |
| 蒸发速率: | |
| 粘性: | |
| 溶解性: | 不溶于水,溶于乙醇、乙醚等。 |
| 主要用途: | 用作热交换剂,并用于有机合成。 |
| 第十部分:稳定性和反应活性 |
| 稳定性: | 在常温常压下 稳定 |
| 禁配物: | 强氧化剂。 |
| 避免接触的条件: | |
| 聚合危害: | 不能出现 |
| 分解产物: | 一氧化碳、二氧化碳、成分未知的黑色烟雾。 |
| 第十一部分:毒理学资料 |
| 急性毒性: | 属低毒类 LD50:大鼠经口;3.28g/kg LC50: |
| 急性中毒: | |
| 慢性中毒: | |
| 亚急性和慢性毒性: | |
| 刺激性: | |
| 致敏性: | |
| 致突变性: | |
| 致畸性: | |
| 致癌性: |
| 第十二部分:生态学资料 |
| 生态毒理毒性: | |
| 生物降解性: | |
| 非生物降解性: | |
| 生物富集或生物积累性: |
| 第十三部分:废弃处置 |
| 废弃物性质: | |
| 废弃处置方法: | 用焚烧法处置。 |
| 废弃注意事项: |
| 第十四部分:运输信息 |
| |
| 危险货物编号: | |
| UN编号: | |
| 包装标志: | |
| 包装类别: | |
| 包装方法: | |
| 运输注意事项: | 储存于阴凉、通风仓间内。远离火种、热源。防止阳光直射。保持容器密封。应与氧化剂分开存放。搬运时要轻装轻卸,防止包装及容器损坏。起运时包装要完整,装载应稳妥。运输过程中要确保容器不泄漏、不倒塌、不坠落、不损坏。严禁与氧化剂等混装混运。运输途中应防曝晒、雨淋,防高温。运输时运输车辆应配备相应品种和数量的消防器材及泄漏应急处理设备。装运本品的车辆排气管须有阻火装置。中途停留时应远离火种、热源。铁路运输时要禁止溜放。 |
| RETCS号: | |
| IMDG规则页码: |
| 第十五部分:法规信息 |
| 国内化学品安全管理法规: | 化学危险物品安全管理条例 (1987年2月17日国务院发布),化学危险物品安全管理条例实施细则 (化劳发[1992] 677号),工作场所安全使用化学品规定 ([1996]劳部发423号)等法规,针对化学危险品的安全使用、生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应规定。 |
| 国际化学品安全管理法规: |
| 第十六部分:其他信息 |
| 参考文献: | 1.周国泰,化学危险品安全技术全书,化学工业出版社,1997 2.国家环保局有毒化学品管理办公室、北京化工研究院合编,化学品毒性法规环境数据手册,中国环境科学出版社.1992 3.Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety,CHEMINFO Database.1998 4.Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety, RTECS Database, 1989 |
| 填表时间: | 年月日 |
| 填表部门: | |
| 数据审核单位: | |
| 修改说明: | |
| 其他信息: | 4 |
| MSDS修改日期: | 年月日 |
制备方法与用途
联苯又称为苯基苯、二苯,是由两个苯环相连形成的化合物。纯品为白色或无色至淡黄色片状晶体,工业品则呈微黄色,并具有特殊香味。熔点69.2℃,沸点255.2℃。不溶于水,但可溶于有机溶剂中。联苯常用于有机合成前体,是有机高温载热体的主要组分之一。其衍生物包括联苯胺、联苯醚、八溴联苯醚和多氯联苯等。天然联苯存在于煤焦油、原油及天然气中,在煤焦油中的质量分数为0.20%-0.40%。目前,联苯的制备方法主要包括煤焦油提取法和化学合成法。
联苯中间的化学键可以自由旋转;但若四个邻位有体积较大的基团时,则会因旋转受阻而产生阻转异构体。此类型的化合物(如BINAP)可作为手性配体。取代联苯可通过Suzuki反应和Ullmann反应等偶联反应制取。
含量分析精确称取试样约100mg,用甲醇溶解后定容至1000ml,从中取出10ml,再加甲醇稀释至200ml作为试样液。以甲醇为对照液,在248nm波长处测定吸光度A。联苯含量计算公式如下:含量(%) = A/1118 × 20 × 10000 / 试样量(mg)× 100%
毒性ADI值为0~0.05mg/kg(某些条件下为0.05~0.25mg/kg;FAO/WHO,2001)。小鼠经口LD50值为3.28~5.04g/kg。
使用限量FAO/WHO、美国和加拿大规定联苯残留量≤110mg/kg;日本、法国、德国及荷兰则规定不超过70mg/kg。
化学性质联苯为白色或略带黄色鳞片状结晶,具有独特的香味。不溶于水、酸及碱,但可溶于醇、醚、苯等有机溶剂中。
用途联苯是工程塑料聚砜的原料,并可用于制备三氯联苯和五氯联苯;用作热载体、防腐剂等。此外,联苯也是杀鼠剂鼠得克和溴鼠灵的中间体,同时还是性能较好的有机载体制品。
联苯具有高热稳定性及低挥发性,遇明火或高温时易燃,并能产生刺激烟雾。吸入少量可导致恶心、呕吐、胃不适以及麻痹感。储运时应注意包装完整且轻装轻放,存放于通风库房中,远离明火和高温环境。
急性毒性口服- 大鼠 LD50: 2140 毫克/ 公斤;口服- 小鼠 LD50: 1900 毫克/ 公斤
刺激数据眼- 兔子 100 毫克 轻度刺激;皮肤-兔 500 毫克/24小时 重度刺激
爆炸物危险特性与空气混合可爆;遇氧化剂反应剧烈。
可燃性危险特性遇明火或高温时易燃,燃烧排放刺激烟雾。吸入少量会导致恶心、呕吐和胃不适感及麻痹。
储运特性包装完整且轻装轻放;存放于通风库房中,并远离明火和高温环境,与氧化剂分开存放。
灭火剂 职业标准TWA 0.2 PPM (1 毫克/ 立方米);STEL 0.6 PPM (3 毫克/ 立方米)。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 对三联苯 [1,1';4',1'']terphenyl 92-94-4 C18H14 230.309 对羟基联苯 4-Phenylphenol 92-69-3 C12H10O 170.211 4,4-二碘联苯 4,4'-diiodobiphenyl 3001-15-8 C12H8I2 406.005 4-碘联苯 4-iodo-biphenyl 1591-31-7 C12H9I 280.108 4,4'-二羟基联苯 4,4'-Dihydroxybiphenyl 92-88-6 C12H10O2 186.21 4-溴代联苯 4-bromo-1,1'-biphenyl 92-66-0 C12H9Br 233.107 4,4'-二溴联苯 4,4'-Dibromobiphenyl 92-86-4 C12H8Br2 312.004 4-氨基联苯 4-Aminobiphenyl 92-67-1 C12H11N 169.226 联苯胺 p,p'-diaminobiphenyl 92-87-5 C12H12N2 184.241 4,4'-二氯联苯 4,4'-dichlorobiphenyl 2050-68-2 C12H8Cl2 223.102 4-氯联苯 4'-biphenyl chloride 2051-62-9 C12H9Cl 188.656 4-苯基苯-1-硫醇 4-biphenylthiol 19813-90-2 C12H10S 186.277 4-氟联苯 4-fluoro-biphenyl 324-74-3 C12H9F 172.202 4,4'-二氟联苯 4,4'-difluorobiphenyl 398-23-2 C12H8F2 190.192 1,3,5-三苯基苯 1,3,5-triphenylbenzene 612-71-5 C24H18 306.407 1-碘-4-(4-苯基苯基)苯 4''-iodo[1,1';4',1'']terphenyl 1762-85-2 C18H13I 356.206 3-碘联苯 3-iodo-1,1'-biphenyl 20442-79-9 C12H9I 280.108 - 1
- 2
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 对三联苯 [1,1';4',1'']terphenyl 92-94-4 C18H14 230.309 四联苯 p-quaterphenyl 135-70-6 C24H18 306.407 对六联苯 para-hexaphenyl 4499-83-6 C36H26 458.602 对羟基联苯 4-Phenylphenol 92-69-3 C12H10O 170.211 4,4'-二甲基联苯 (4,4'-dimethyl-1,1'-biphenyl) 613-33-2 C14H14 182.265 4-甲基联苯 4-Methylbiphenyl 644-08-6 C13H12 168.238 4-碘联苯 4-iodo-biphenyl 1591-31-7 C12H9I 280.108 4,4'-二羟基联苯 4,4'-Dihydroxybiphenyl 92-88-6 C12H10O2 186.21 4,4-二碘联苯 4,4'-diiodobiphenyl 3001-15-8 C12H8I2 406.005 联苯胺 p,p'-diaminobiphenyl 92-87-5 C12H12N2 184.241 4,4'-二溴联苯 4,4'-Dibromobiphenyl 92-86-4 C12H8Br2 312.004 4-溴代联苯 4-bromo-1,1'-biphenyl 92-66-0 C12H9Br 233.107 4-氨基联苯 4-Aminobiphenyl 92-67-1 C12H11N 169.226 4,4'-二氯联苯 4,4'-dichlorobiphenyl 2050-68-2 C12H8Cl2 223.102 4-氯联苯 4'-biphenyl chloride 2051-62-9 C12H9Cl 188.656 联苯-D1 1,1'-biphenyl-4-d 4819-98-1 C12H10 155.203 间三联苯 1,3-diphenylbenzene 92-06-8 C18H14 230.309 —— 4-[18F]fluorobiphenyl —— C12H9F 171.203 4-氟联苯 4-fluoro-biphenyl 324-74-3 C12H9F 172.202 —— 3-phenyl-p-quaterphenyl 13478-57-4 C30H22 382.505 1-甲基-4-(4-苯基苯基)苯 4-methyl-p-terphenyl 28952-41-2 C19H16 244.336 1-氯-4-(4-苯基苯基)苯 4-chloro-1,1’:4’,1”-terphenyl 1762-83-0 C18H13Cl 264.754 4-氨基对三联苯 4-aminoterphenyl 7293-45-0 C18H15N 245.324 4-溴对三联苯 4-bromo-p-terphenyl 1762-84-1 C18H13Br 309.205 4,4''-二溴三联苯 4,4''-dibromo-p-terphenyl 17788-94-2 C18H12Br2 388.101 —— 4-Fluor-p-terphenyl 3799-84-6 C18H13F 248.3 间羟基联苯 3-phenylphenol 580-51-8 C12H10O 170.211 - 1
- 2
- 3
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:N-氯糖精在乙酸水溶液中氧化4-含氧酸的动力学摘要:已在乙酸水溶液中研究了 N-氯糖精 (NCSA) 对取代和未取代 4-含氧酸 (S) 的氧化动力学。该反应遵循 4-含氧酸、NCSA 和 H+ 中的每一个的一级动力学。底物电子性质变化的影响表明,在过渡态中会产生正电荷。基于动力学结果和产物分析,已经提出了NCSA与4-含氧酸反应的合适机制。DOI:10.1007/s10953-006-9116-z
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:Reactions of organometallic compounds, catalyzed by transition metal complexes. 7. Oxidative demercuration of arylmercury in the presence of complexes of palladium and rhodium摘要:DOI:10.1007/bf00948854
-
作为试剂:描述:丙烯酸乙酯 、 2,2-dimethyl-3-vinyloxy-propan-1-ol 在 联苯 、 9-cyano-10-methoxycarbonylanthracene 作用下, 以 乙腈 为溶剂, 以38 %的产率得到参考文献:名称:双分子光氧化还原体系中乙烯基醚系链亲核试剂与缺电子烯烃的双双官能化摘要:通过在双分子光氧化还原系统中可见光照射,实现了乙烯基醚连接的羟基或氨基甲酰基与缺电子烯烃(例如丙烯腈或丙烯酸酯)的双双官能化。使用无水乙腈溶液作为溶剂促进了富电子烯烃的自由基阳离子与富电子烯烃的二聚以及分子内亲核加成以产生富电子自由基,该富电子自由基被添加到缺电子烯烃中以提供双双官能化产物。光反应中使用了多种电子分化的富烯烃和缺烯烃;在温和条件下成功地简单构建了包含简单烯烃缩醛的复杂碳框架。 图文摘要DOI:10.1007/s43630-024-00588-5
文献信息
-
Nickel(II) N‐Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes: Versatile Catalysts for C–C, C–S and C–N Coupling Reactions作者:Lourdes Benítez Junquera、Francys E. Fernández、M. Carmen Puerta、Pedro ValergaDOI:10.1002/ejic.201700057日期:2017.5.18A variety of Ni(II) complexes with a wide range of electronic and steric properties, bearing picolyl-imidazolidene ligands (a-g) and Cp (2a-f) or Cp* (3a,c,g) groups, have been synthesised and characterised using NMR and single crystal X-ray crystallography. The complexes have been used as precatalysts for a wide range of catalytic transformations most likely involving a Ni0/NiII catalytic cycle. In
-
Nickel-catalyzed reductive defunctionalization of esters in the absence of an external reductant: activation of C–O bonds作者:Yasuaki Iyori、Kenjiro Takahashi、Ken Yamazaki、Yusuke Ano、Naoto ChataniDOI:10.1039/c9cc07710c日期:——
The nickel-catalyzed reductive cleavage of esters in the absence of an external reductant, which involves the cleavage of an inert acyl C–O bond in
O -alkyl esters is reported.镍催化剂在无外部还原剂的情况下,报告了酯的还原裂解,其中涉及对惰性酰基C-O键进行裂解,这种裂解发生在O-烷基酯中。 -
Regiospecific Cleavage of S–N Bonds in Sulfonyl Azides: Sulfonyl Donors作者:Zhiguo Zhang、Songnan Wang、Yong Zhang、Guisheng ZhangDOI:10.1021/acs.joc.8b03046日期:2019.4.5Sulfonyl azides have been widely used as sulfonamido, diazo, and azido donors, as well as all-nitrogen 1,3-dipoles donors in synthetic chemistry. Here, the sulfonyl azides were used as efficient sulfonyl donors, which is very unusual. Trifluoromethanesulfonic acid-induced formation of the sulfonyl cation reactive species from sulfonyl azides was developed and used for the first time to couple various
-
Regioselective Arylation Reactions of Biphenyl-2-ols, Naphthols, and Benzylic Compounds with Aryl Halides under Palladium Catalysis作者:Tetsuya Satoh、Jun-ichi Inoh、Yoshiki Kawamura、Yuichiro Kawamura、Masahiro Miura、Masakatsu NomuraDOI:10.1246/bcsj.71.2239日期:1998.9Biphenyl-2-ols undergo regioselective mono- and diarylation upon a treatment with aryl iodides in the presence of a palladium catalyst in DMF using Cs2CO3 as a base to produce 1,1′ : 2′,1″-terphenyl-2-ol and 2′,6′-diphenylbiphenyl-2-ol and their derivatives. The reaction of 1-naphthol selectively occurs at its 8-position to give 8-aryl-1-naphthols. In the reaction of 2-naphthol with aryl bromides, diarylated
-
Mild electrophilic trifluoromethylation of secondary and primary aryl- and alkylphosphines using hypervalent iodine(iii)–CF3 reagents作者:Patrick Eisenberger、Iris Kieltsch、Nicolas Armanino、Antonio TogniDOI:10.1039/b801424h日期:——A direct, mild and efficient trifluoromethylation of primary and secondary phosphines is achieved with easily accessible, cheap hypervalent iodine compounds acting as electrophilic CF(3)-transfer reagents.
表征谱图
-
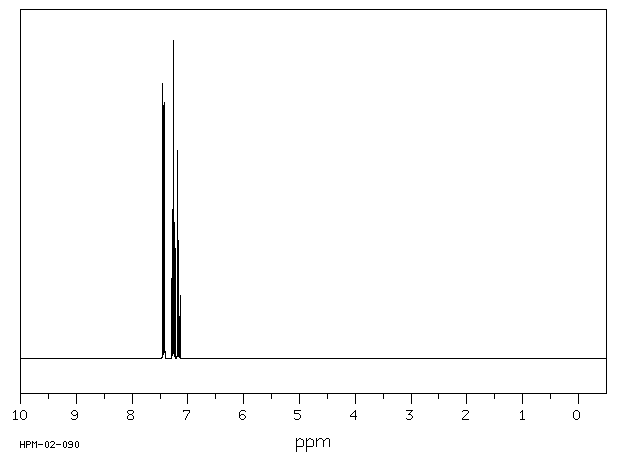
氢谱1HNMR
-
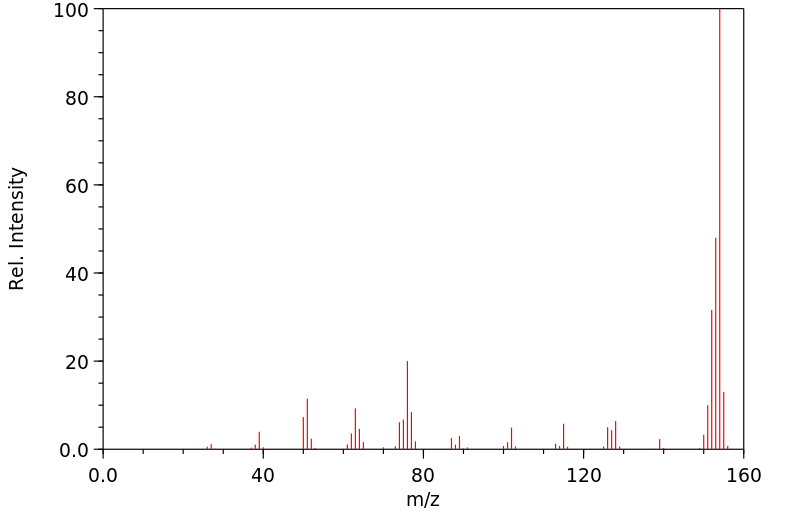
质谱MS
-
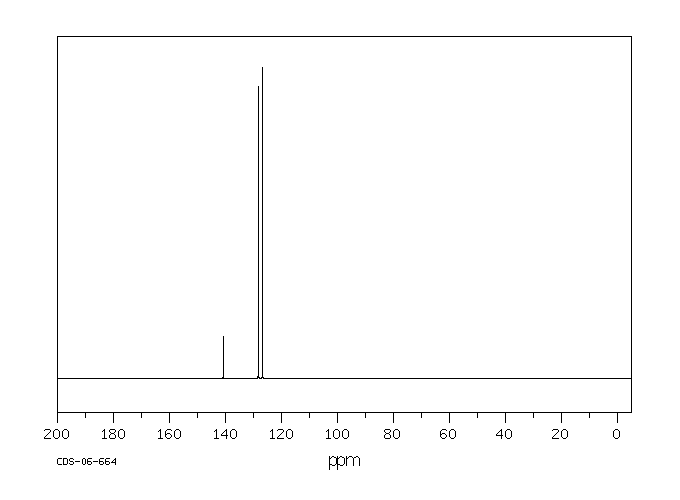
碳谱13CNMR
-
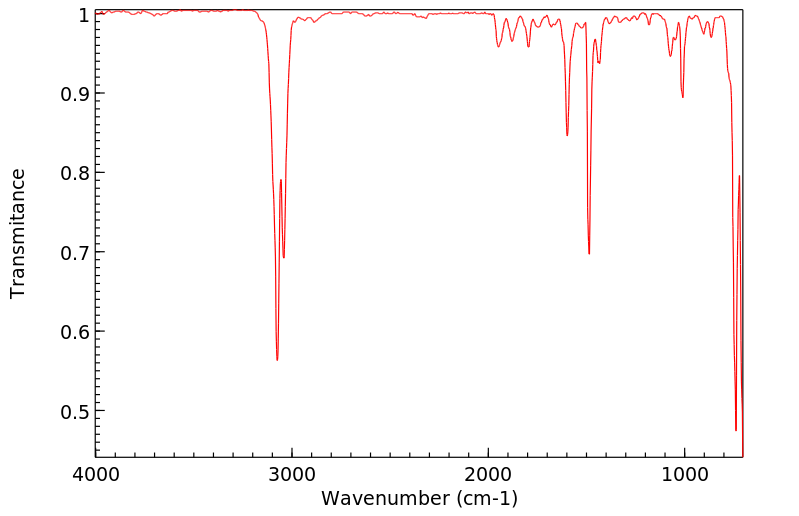
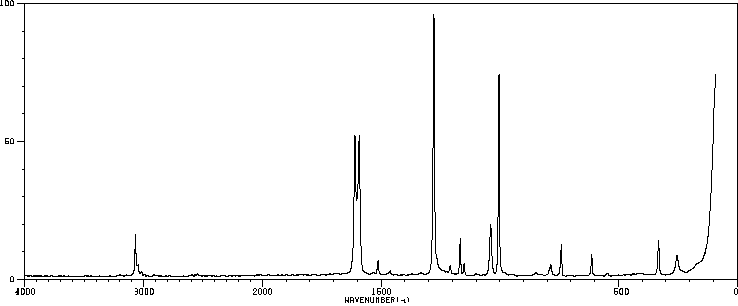
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息