苊 | 83-32-9
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:90-94 °C(lit.)
-
沸点:279 °C(lit.)
-
密度:1.06
-
蒸气密度:5.32 (vs air)
-
闪点:135 °C
-
溶解度:在氯仿的溶解度为50 mg/mL,透明
-
介电常数:3.0
-
LogP:4.04 at 30℃ and pH5-8
-
物理描述:Acenaphthene appears as white needles. Melting point 93.6°C. Soluble in hot alcohol. Denser than water and insoluble in water. Hence sinks in water. May irritate skin and mucous membranes. Emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes when heated to decomposition. Derived from coal tar and used to make dyes, pharmaceuticals, insecticides, fungicides, and plastics.
-
颜色/状态:White needles
-
蒸汽密度:5.32 (NTP, 1992) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:0.0022 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
亨利常数:1.84e-04 atm-m3/mole
-
大气OH速率常数:5.80e-11 cm3/molecule*sec
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
易燃,对眼睛、呼吸系统和皮肤有刺激性。大量使用时应穿适当的防护服,避免接触眼睛及皮肤。如不慎接触到眼睛,应立即用大量清水冲洗。
-
稳定性:稳定。
-
禁配物:强氧化剂。
-
应避免的条件:受热。
-
聚合危害:不会发生聚合反应。
-
-
自燃温度:>450 °C
-
分解:Hazardous decomposition products formed under fire conditions - Carbon oxides.
-
燃烧热:-4.033X10+7 J/kg
-
汽化热:3.48X10+5 J/kg at 40 °C
-
气味阈值:Odor detection in air, 8.0X10-2 ppm (chemically pure)
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.6048 at 95 °C
-
碰撞截面:127.7 Ų [M*]+
-
保留指数:1455.06;1439;1450;1445.3;1445.5;1472;1472;1475;1486;1463.9;1475;1463;1460;1455;1458;1464;1437;1463.2;1522;1466;251.3;253.3;253.5;247.8
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):3.9
-
重原子数:12
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:3.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.166
-
拓扑面积:0
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:0
ADMET
安全信息
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:9
-
危险品标志:N,T,Xn,F,Xi
-
安全说明:S16,S26,S36,S36/37,S36/37/39,S37/39,S45,S60,S61,S62,S7
-
危险类别码:R36/37/38
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:29029080
-
危险品运输编号:UN 3077 9/PG 3
-
危险类别:9
-
RTECS号:AB1000000
-
包装等级:III
-
储存条件:储存注意事项: - 储存于阴凉、通风的库房。 - 远离火种、热源,库温不宜超过35℃。 - 包装密封,并与氧化剂分开存放,切忌混储。 - 采用防爆型照明和通风设施,禁止使用易产生火花的机械设备和工具。 - 储区应备有合适的材料收容泄漏物。
SDS
| 国标编号: | 41515 |
| CAS: | 83-32-9 |
| 中文名称: | 苊 |
| 英文名称: | Acenaphthene;1,2-dihydroacenph |
| 别 名: | 萘己环 |
| 分子式: | C 12 H 10 |
| 分子量: | 154.21 |
| 熔 点: | 95℃ 沸点:277.5℃ |
| 密 度: | 相对密度(水=1)1.02(2 |
| 蒸汽压: | 1.33kPa(131.2℃) |
| 溶解性: | 不溶于水,溶于热苯、醚、醇 |
| 稳定性: | 稳定 |
| 外观与性状: | 白色针状结晶 |
| 危险标记: | 8(易燃固体) |
| 用 途: | 用作染料中间体,也可用作杀虫剂、杀菌剂等 |
2.对环境的影响:
一、健康危害
侵入途径:吸入、食入。 健康危害:本品对眼睛、皮肤、粘膜和上呼吸道有刺激性。
二、毒理学资料及环境行为
毒性:属微毒类。 急性毒性:LD5010g/kg(大鼠经口);2.1g/kg(小鼠经口)
危险特性:遇明火、高热与氧化剂接触,有引起燃烧爆炸的危险。受热分解产生有毒的烟气。 燃烧(分解)产物:一氧化碳、二氧化碳。
3.现场应急监测方法:
4.实验室监测方法:
气相色谱法《固体废弃物试验分析评价手册》中国环境监测总站等译高效液相色谱法《城市和工业废水中有机化合物分析》王克欧等译色谱-质谱法《水和废水标准检验法》19版译文,江苏省环境监测中心
5.环境标准:
前苏联(1975)水体中有害物质最高允许浓度 0.2mg/L
6.应急处理处置方法:
一、泄漏应急处理
隔离泄漏污染区,限制出入。切断火源。建议应急处理人员戴自给式呼吸器,穿一般作业工作服。小量泄漏:用洁净的铲子收集于干燥、洁净、有盖的容器中。大量泄漏:用塑料布、帆布覆盖,减少飞散。使用无火花工具收集回收或运至废物处理场所处置。
二、防护措施
呼吸系统防护:空气中粉尘浓度超标时,应该佩戴自吸过滤式防尘口罩。 眼睛防护:戴安全防护眼镜。 身体防护:穿防毒物渗透工作服。手防护:戴一般作业防护手套。 其它:工作现场禁止吸烟、进食和饮水。工作毕,淋浴更衣。保持良好的卫生习惯。
三、急救措施
皮肤接触:脱去被污染的衣着,用肥皂水和清水彻底冲洗皮肤。 眼睛接触:提起眼睑,用流动清水或生理盐水冲洗。就医。 吸入:迅速脱离现场至空气新鲜处。保持呼吸道通畅。如呼吸困难,给输氧。如呼吸停止,立即进行人工呼吸。就医。 食入:饮足量温水,催吐,就医。
制备方法与用途
苊(又称萘己环)是一种缩合环式芳香烃,通常为无色结晶。它不溶于水,可溶于酒精,并且是萘的重要衍生产品。一般从煤焦油中提取的苊,在氧化后会形成1,8-萘二甲酸酐和萘醌。
毒性- 急性毒性:大鼠腹腔LD50为600毫克/千克。
-
致突变性
- 微生物致突变:鼠伤寒沙门菌属,0.5纳米克/皿(48小时)。
- 细胞遗传学分析:仓鼠肺细胞10毫摩尔/升(6小时)。
苊为白色或略带黄色斜方针状结晶。不溶于水,微溶于乙醇,并能溶解在热醚、热苯、甲苯、冰醋酸、氯仿和石油醚中。
用途- 是生产1,8-萘二甲酸酐的原料。
- 可经脱氢后制得苊烯树脂,用于制染料、植物生长激素、杀虫杀菌剂等。
- 作为有机合成原料,硝化可制硝基苊;进一步氧化可制1,8-萘二甲酸酐和苊醌,可用于合成染料、聚酯树脂、聚酯纤维以及荧光颜料、药品、杀虫剂等。
- 芰脱氢得苊烯,可以制成苊烯树脂。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— 3-tert-Butyl-acenaphthen 35210-35-6 C16H18 210.319 5-溴苊 5-bromoacenaphthene 2051-98-1 C12H9Br 233.107 1-苊酮 1(2H)-acenaphthylenone 2235-15-6 C12H8O 168.195 3-溴苊 3-bromoacenaphthene 5209-31-4 C12H9Br 233.107 —— 1,2-dibromoacenaphthene 14209-08-6 C12H8Br2 312.004 —— cis-acenaphthene-1,2-diol 2963-86-2 C12H10O2 186.21 苊醌 acenaphthene quinone 82-86-0 C12H6O2 182.178 —— 1(2H)-acenaphthylenone oxime 5088-53-9 C12H9NO 183.21 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— 1,2,7,8-tetrahydrodicyclopenta[cd,lm]perylene 80475-20-3 C24H16 304.391 —— 5-Methyl-acenaphthen 17057-80-6 C13H12 168.238 —— pyracene 567-79-3 C14H12 180.249 5-乙基-1,2-二氢苊烯 5-ethylacenaphthene 13936-05-5 C14H14 182.265 —— 4-ethyl-acenaphthene 17190-46-4 C14H14 182.265 —— acenaphthen-5-yl-acetonitrile 37977-51-8 C14H11N 193.248 —— 2-acenaphthen-5-yl-ethanol 140616-47-3 C14H14O 198.265 —— 5-Isopropyl-acenaphthen 13936-12-4 C15H16 196.292 —— 3-tert-Butyl-acenaphthen 35210-35-6 C16H18 210.319 —— 5-hydroxymethylacenaphthene 50773-22-3 C13H12O 184.238 —— 4-isopropylacenaphthene 35738-13-7 C15H16 196.292 5-苊醛 acenaphthene-5-carbaldehyde 5345-46-0 C13H10O 182.222 —— 5-ethynylacenaphthene 33918-41-1 C14H10 178.233 5-(氯甲基)-1,2-二氢苊 5-chloromethylacenaphthene 62456-13-7 C13H11Cl 202.683 —— 5-cyanoacenaphthene 71235-81-9 C13H9N 179.221 —— 4,7-di-tert-butyl-1,2-dihydroacenaphthylene 10239-86-8 C20H26 266.426 —— 4-tert-butyl-acenaphthene 55939-14-5 C16H18 210.319 5-溴苊 5-bromoacenaphthene 2051-98-1 C12H9Br 233.107 5-氯苊 5-chloroacenaphthene 5209-33-6 C12H9Cl 188.656 1,2-二氢苊-5-胺 5-aminoacenaphthene 4657-93-6 C12H11N 169.226 —— 5,6-bis(hydroxymethyl)acenaphthene 4599-97-7 C14H14O2 214.264 1,2-二氢乙酰萘-5-醇 acenaphthen-5-ol 6373-33-7 C12H10O 170.211 1-乙基萘 1-ethylnapthelene 1127-76-0 C12H12 156.227 5-碘-1,2-二氢苊烯 5-iodoacenaphthene 6861-64-9 C12H9I 280.108 —— 4-Brom-acenaphthen 4657-98-1 C12H9Br 233.107 —— Acenaphthen-5-yl-essigsaeure 10556-23-7 C14H12O2 212.248 —— 5-(1-hydroxyethyl)acenaphthene 2346-72-7 C14H14O 198.265 —— 5,6-bis(bromomethyl)acenaphthene 4599-95-5 C14H12Br2 340.057 —— 5-Fluor-acenaphthen 6861-63-8 C12H9F 172.202 —— 4-acenaphthen-5-yl-butyric acid 38036-08-7 C16H16O2 240.302 5-苄基-1,2-二氢苊 5-benzyl-acenaphthene 4657-91-4 C19H16 244.336 5-乙酰-1,2-二氢苊烯 5-acetylacenaphthene 10047-18-4 C14H12O 196.249 —— 5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocyclohepta-acenaphthene 518-02-5 C16H16 208.303 5,6-二溴苊 5,6-dibromoacenaphthene 19190-91-1 C12H8Br2 312.004 —— 1,2-dihydropyracylene 23357-60-0 C14H10 178.233 —— 4,5-dideuterioacenaphthene 195992-00-8 C12H10 156.196 5,6-二氯苊 5,6-dichloroacenaphthene 4208-97-3 C12H8Cl2 223.102 —— 5,6-diaminoacenaphthene 3176-86-1 C12H12N2 184.241 —— 5,6-difluoroacenaphthene 24737-17-5 C12H8F2 190.192 —— 1-bromoacenaphthene 24171-73-1 C12H9Br 233.107 —— 1-acenaphthen-5-yl-propan-1-ol 55720-24-6 C15H16O 212.291 1-羟基二氢苊 1-acenaphthenol 6306-07-6 C12H10O 170.211 —— 1-acenaphthol —— C12H10O 170.211 (S)-1,2-二氢乙酰萘-1-醇 (S)-1-acenaphthenol 121961-98-6 C12H10O 170.211 5-苊甲酸 acenaphthene-5-carboxylic acid 55720-22-4 C13H10O2 198.221 —— 5-Acetyl-acenaphthen-oxim 92199-16-1 C14H13NO 211.263 —— 5(bromoacetyl)acenaphthene 34585-58-5 C14H11BrO 275.145 1-苊酮 1(2H)-acenaphthylenone 2235-15-6 C12H8O 168.195 1-氯苊 1-chloro-1,2-dihydroacenaphthylene 40745-49-1 C12H9Cl 188.656 —— 5-propionylacenaphthene 55720-25-7 C15H14O 210.276 3-氨基苊 1,2-dihydro-acenaphthylene-3-amine 55939-13-4 C12H11N 169.226 —— 1,2-dihydroacenaphthylene-3-carbaldehyde 92378-92-2 C13H10O 182.222 —— 5-(1-chloroethenyl)acenaphthene 177205-97-9 C14H11Cl 214.694 —— 3-iodoacenaphthene 24737-48-2 C12H9I 280.108 3-溴苊 3-bromoacenaphthene 5209-31-4 C12H9Br 233.107 —— acenaphthene-5-carboxamide —— C13H11NO 197.236 —— 1,2-dihydroacenaphthylen-3-ylmethanol 135510-01-9 C13H12O 184.238 —— 5-(chloroacetyl)acenaphthene 80262-61-9 C14H11ClO 230.694 3-氟苊 3-Fluor-acenaphthen 3798-80-9 C12H9F 172.202 —— 1-acenaphthen-5-yl-2-phenyl-ethanol 102077-51-0 C20H18O 274.362 1-叔-丁基萘 1-(tert-butyl)naphthalene 17085-91-5 C14H16 184.281 —— 1-benzyl-1,2-dihydroacenaphthylene 94257-40-6 C19H16 244.336 —— 1-(1,2-dihydroacenaphthylen-5-yl)-2-phenylethanone 116423-22-4 C20H16O 272.346 —— 5-phenylacenaphthene 56252-14-3 C18H14 230.309 —— 1,1',2,2'-tetrahydro-5,5'-biacenaphthylene 41908-42-3 C24H18 306.407 —— 4-acenaphthen-5-yl-valeric acid 16294-57-8 C17H18O2 254.329 —— 5-Butyryl-acenaphthen 93433-44-4 C16H16O 224.302 —— 1,2-dibromoacenaphthene 14209-08-6 C12H8Br2 312.004 —— 3-acenaphthen-5-yl-3-oxo-propionitrile —— C15H11NO 221.258 —— trans-1,2-dibromoacenaphthene 25226-58-8 C12H8Br2 312.004 —— trans-1,2-acenaphthalenediol 2963-87-3 C12H10O2 186.21 —— cis-acenaphthene-1,2-diol 2963-86-2 C12H10O2 186.21 —— 5-isobutyrylacenaphthene 87969-65-1 C16H16O 224.302 —— 5,6-diacetylnaphthylene 80475-26-9 C16H14O2 238.286 —— 1-acenaphthen-5-yl-3-chloro-propan-1-one 22336-45-4 C15H13ClO 244.721 苊醌 acenaphthene quinone 82-86-0 C12H6O2 182.178 —— 5-(1-phenyl-1-propyl)acenaphthene 92669-84-6 C21H20 272.39 1,2-二氢乙酰萘-5-基(苯基)甲酮 5-benzoylacenaphthene 4657-89-0 C19H14O 258.32 —— 5-(p-Toluyl)acenaphthene 87969-72-0 C20H16O 272.346 —— acenaphthen-5-yl-[1]naphthyl ketone —— C23H16O 308.379 —— 5-ethylacenaphthylene 223518-16-9 C14H12 180.249 —— 5-(α-oxy-benzyl)-acenaphthene 4657-90-3 C19H16O 260.335 —— acenaphthen-5-yl-phenyl-ethanedione 681463-31-0 C20H14O2 286.33 —— 2,4-diiodoacenaphthene 55143-90-3 C12H8I2 406.005 —— 5-decanoylacenaphthene 87969-71-9 C22H28O 308.464 —— 1(2H)-acenaphthylenone oxime 5088-53-9 C12H9NO 183.21 1-(1,2-二氢-3-苊)乙酮 1-acenaphthen-3-yl-ethanone 7434-96-0 C14H12O 196.249 —— 1,1,-dibromo-2-(1',2'-dihydroacenaphthylen-3'-yl)ethene 135509-95-4 C14H10Br2 338.041 —— 7,7a-dihydro-6bH-acenaphth[1,2-b]azirine 7156-07-2 C12H9N 167.21 —— 3-benzyl-acenaphthene —— C19H16 244.336 N-(1,2-dihydroacenaphthylen-5-基)乙酰胺 5-acetamidoacenaphthene 4657-94-7 C14H13NO 211.263 苊-5,6-二甲酸 5,6-acenaphthenedicarboxylic acid 5698-99-7 C14H10O4 242.231 —— acenaphthen-5-yl-glyoxylic acid 25178-59-0 C14H10O3 226.232 5-硝基苊 4-nitroacenaphthene 602-87-9 C12H9NO2 199.209 —— 4-acenaphthen-5-yl-4-oxo-trans-crotonic acid 92964-72-2 C16H12O3 252.269 —— Acenaphthoylacrylsaeure 92964-72-2 C16H12O3 252.269 —— (+/-)-1-Methoxy-acenaphthen 21857-35-2 C13H12O 184.238 (3-苊并基)丙酸 4-acenaphthen-5-yl-4-oxo-butyric acid 16294-60-3 C16H14O3 254.285 —— 5-acenaphthen-5-yl-5-oxo-valeric acid —— C17H16O3 268.312 - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:Stereospecificity in Brominations of Bibenzyl and Acenaphthene with N-Bromosuccinimide摘要:DOI:10.1021/ja01563a039
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:v. Braun; Bayer, Chemische Berichte, 1926, vol. 59, p. 922摘要:DOI:
-
作为试剂:描述:2-甲基-3-丁炔-2-醇 、 苯甲酸 在 Ru(CO)2(P[p-C6H4-CF3]3)2(O2CPh)2 、 苊 作用下, 以 甲苯 为溶剂, 反应 6.0h, 以75%的产率得到3-羟基-3-甲基-2-丁酮苯甲酸酯参考文献:名称:原子经济钌催化大体积β-氧代酯的合成摘要:钌配合物,分子式为Ru(CO)2(PR 3)2(O 2 CPh)2 [ 6a – h ; R =n- Bu,p -MeO-C 6 H 4,p -Me-C 6 H 4,Ph,p -Cl-C 6 H 4,m -Cl-C 6 H 4,p -CF 3 -C 6 H 4,m,m' -(CF 3)2 C 6 H 3 ]的制备方法是用膦和苯甲酸分别处理十二碳三钌[Ru 3(CO)12 ]或将Ru(CO)3(PR 3)2(8e - h)转化为苯甲酸。在制备8的过程中,可以分离出Ru(CO)(PR 3)3(H)2(9g,h)类型的氢化钌配合物作为副产物。讨论了新合成的固态配合物的分子结构。化合物发现6a - h是将羧酸添加到炔丙醇中以生成有价值的β-氧代酯的高效催化剂。催化剂筛选显示出膦的电子性质对所得活性的显着影响。使用具有吸电子膦配体的配合物6g和6h获得了最佳性能。另外,催化剂6g在空间上需要的底物的DOI:10.1002/adsc.201500712
文献信息
-
Synthesis of Aromatic Carboxylic Acids by Carbonylation of Aryl Halides in the Presence of Epoxide-Modified Cobalt Carbonyls as Catalysts作者:V. P. Boyarskii、T. E. Zhesko、S. A. LaninaDOI:10.1007/s11167-005-0619-y日期:2005.11A new procedure was developed for synthesis of aromatic and heteroaromatic acids and their derivatives (esters, salts) by carbonylation of the corresponding aryl halides. The acids are selectively formed in a high yield under very mild conditions. Highly active catalytic systems, base-containing alcoholic solutions of cobalt carbonyl modified with epoxides, were used to activate aryl halides.
-
Synthesis of aromatic aldehydes via 2-aryl-n,n'-diacyl-4-imidazolines作者:Jan Bergman、Lars Renström、Birger SjöbergDOI:10.1016/0040-4020(80)80230-4日期:1980.1Diacylimidazolium ions yield adducts with aromatic compounds. Thus the N,N'-diacetylimidazolium ion and indole gives 1,3-diacetyl-2-(3-indolyl)-4-imidazoline. Less reactive substrates such as thiophene, anisole and 1,3-dimethylbenzene fail to react with this reagent but do form adducts (e.g. 1,3-bis-(trifluoroacetyl)-2-(2-thienyl)-4-imidazoline) with an imidazole/trifluoroacetic anhydride reagent.
-
Ap-benzyne tom-benzyne conversion through a 1,2-shift of a phenyl group. Completion of the benzyne cascade作者:Alexei L. Polishchuk、Kevin L. Bartlett、Lee A. Friedman、Maitland JonesDOI:10.1002/poc.797日期:2004.95-diyne-cis-3-ene at 800–1000°C leads to a mixture of 1- and 2-phenylbiphenylene, along with triphenylene. Formation of the two biphenylenes is taken as strong evidence of the rearrangement of a p-benzyne into a m-benzyne through a shift of one of the phenyl groups. Copyright © 2004 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.1,6- diphenylhexa -1,5- diyne-热解顺式-3-烯在800-1000℃通入1-和2- phenylbiphenylene的混合物,用菲沿。两个亚联的形成被取为一个的重新安排的强有力的证据p -benzyne成米通过苯基基团中的一个的移位-benzyne。版权所有©2004 John Wiley&Sons,Ltd.
-
Photochemical Reactions of Hydroarenes with<i>N</i>-Bromosuccinimide作者:Zhi-Min Zong、Wei-Hong Zhang、Qun Jiang、Jin Lu、Xian-Yong WeiDOI:10.1246/bcsj.75.769日期:2002.4The photochemical reactions of 1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalene (THN), 9,10-dihydrophenanthrene (DHP), 9,10-dihydroanthracene (DHA), and acenaphthene (AN) with N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) were investigated under N2 atmosphere at room temperature. The results show that the relative reactivities of the hydroarenes toward a photochemical reaction with NBS are THN < DHP < AN << DHA, which is consistent with the stabilities of the radicals produced by benzylic hydrogen abstraction from the hydroarenes. Photochemical reactions of THN and DHP mainly afforded dehydrogenated products, while the photobrominations of the dehydrogenated products from AN and DHA with NBS proceeded readily.
-
一种新型电子盐体系以及不饱和烃类化合物 的还原方法
表征谱图
-
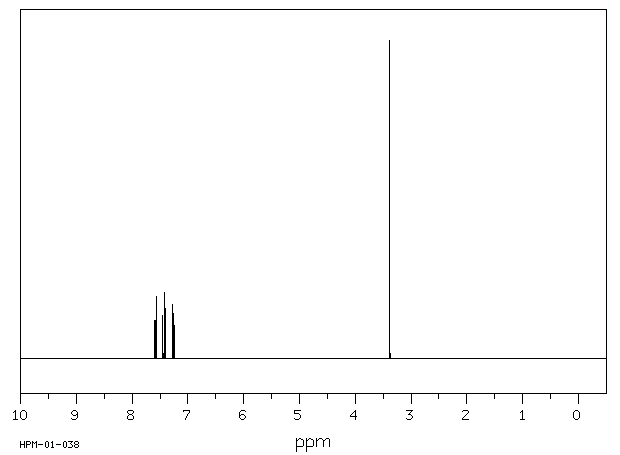
氢谱1HNMR
-
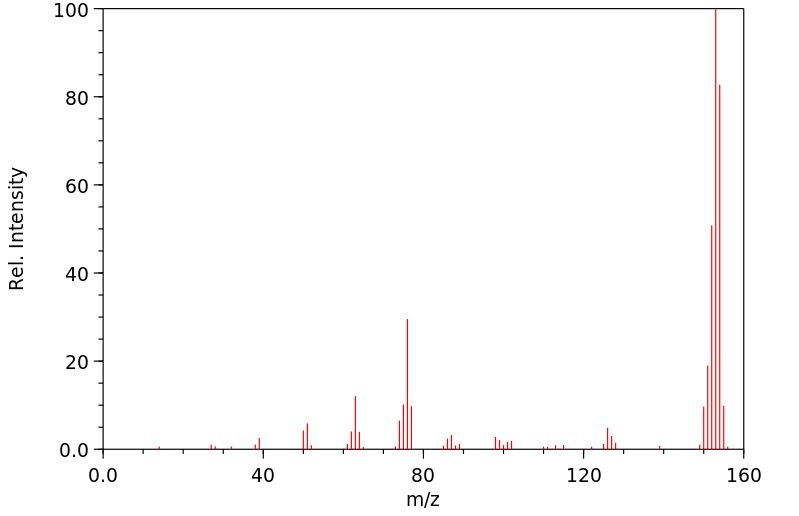
质谱MS
-
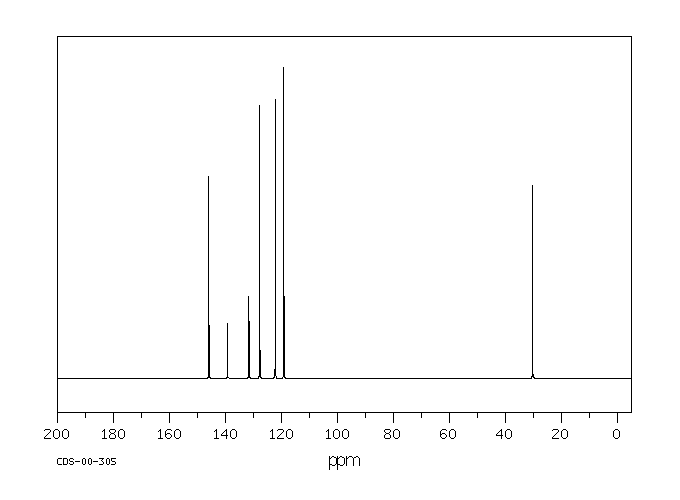
碳谱13CNMR
-
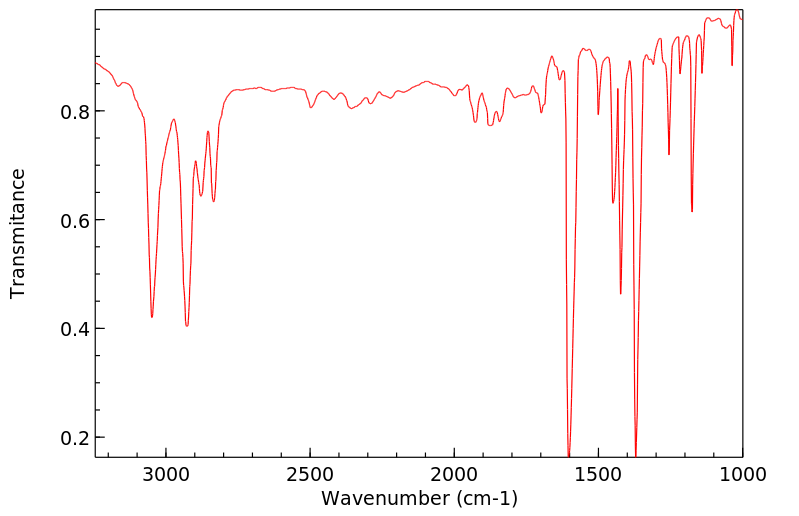
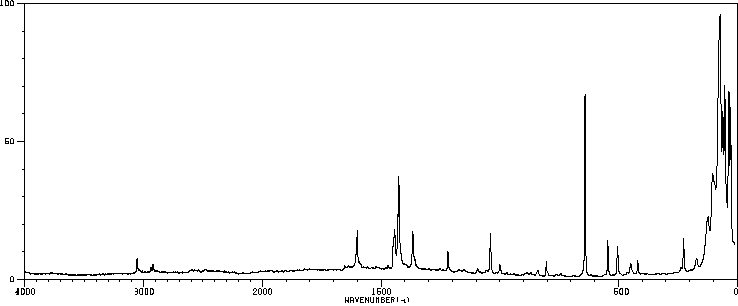
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息