氯苯 | 108-90-7
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:-45 °C (lit.)
-
沸点:132 °C (lit.)
-
密度:1.106 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
-
蒸气密度:3.86 (vs air)
-
闪点:75 °F
-
溶解度:水:20°C 时可溶 0.207 g/L
-
最大波长(λmax):λ: 288 nm Amax: 1.0λ: 290 nm Amax: 0.40λ: 300 nm Amax: 0.05λ: 325 nm Amax: 0.04λ: 360-400 nm Amax: 0.01
-
介电常数:5.6(25℃)
-
暴露限值:TLV-TWA 75 ppm (~345 mg/m3) (ACGIH, MSHA, OSHA, and NIOSH); IDLH 2400 ppm.
-
LogP:3 at 20℃
-
物理描述:Chlorobenzene appears as a colorless to clear, yellowish liquid with a sweet almond-like odor. Flash point 84°F. Practically insoluble in water and somewhat denser than water (9.2 lb / gal). Vapors heavier than air. Used to make pesticides, dyes, and other chemicals.
-
颜色/状态:Colorless liquid
-
气味:Faint, not unpleasant odor
-
蒸汽密度:3.88 (NTP, 1992) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:12.0 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
亨利常数:0.00 atm-m3/mole
-
大气OH速率常数:7.70e-13 cm3/molecule*sec
-
自燃温度:1099 °F (593 °C)
-
粘度:0.806 mPa.s at 20 °C
-
腐蚀性:Liquid chlorobenzene will attack some forms of plastics, rubber, and coatings
-
燃烧热:-3100 kJ/mol at 25 °C
-
汽化热:40.97 kJ/mol at 25 deg
-
表面张力:33.5 dynes/cm at 20 °C
-
电离电位:9.07 eV
-
气味阈值:Odor recognition in air: 2.10x10-1 ppm.
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.5241 at 20 °C/D
-
相对蒸发率:1 (Butyl acetate = 1)
-
保留指数:831.2;821.2;826.5;825.3;830;833;825;839;839;859.3;833;830.32;834;836;838.8;842;850;827;815;850.3;832;840;875;875;860;832;836;840;844;850;834;839;844;835;842;849;856;850;839;838.9;828;829.4;855;837;831.4;834.9;844;839;824;829;841;842;846;850;844;860;834;839;836;820;827;839;844;860;850
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
化学性质:性质稳定,在常温常压下不受空气、水分和光的作用,长时间煮沸也不发生分解。常温下与水蒸气、碱、盐酸、稀硫酸等均不反应。氯苯蒸气通过红热的铂丝或铁管时生成4,4’-二氯联苯、联苯、4-氯联苯等。在高温高压下与氢氧化钠溶液作用,或在常压和催化剂存在下与水蒸气作用则水解为苯酚。与氨气不反应,但在高温高压和铜催化剂存在下,能与浓氨水反应生成苯胺。与浓硝酸和浓硫酸的混合物在0℃时发生硝化反应,以7:3的比例生成对氯硝基苯和邻氯硝基苯。与热浓硫酸易发生磺化反应,生成对氯苯磺酸。用镍作催化剂加氢还原可生成苯和联苯,在沸腾的醇存在下与钠或钠汞齐反应也生成联苯。以三氯化铁为催化剂进行氯化反应,生成邻二氯苯和对二氯苯的混合物。与溴加热主要生成对溴氯苯。与熔融的三溴化铝反应生成溴苯。与碘的反应缓慢。与一般的氟化剂不生成氟苯。在发烟硫酸存在下与三氯乙醛缩合,生成二氯二苯基三氯乙烷(DDT)。
-
稳定性 [24]:稳定
-
聚合危害 [26]:不聚合
-
分解产物 [27]:氯化物
-
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):2.9
-
重原子数:7
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:0
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:0
ADMET
安全信息
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:3
-
立即威胁生命和健康浓度:1,000 ppm
-
危险品标志:Xn,F,T,N
-
安全说明:S24/25,S36/37,S45,S61
-
危险类别码:R23/24/25,R40,R10,R11,R51/53,R39/23/24/25,R20
-
WGK Germany:2
-
海关编码:2903919090
-
危险品运输编号:UN 1134 3/PG 3
-
危险类别:3
-
RTECS号:CZ0175000
-
包装等级:III
-
危险标志:GHS02,GHS07,GHS09
-
危险性描述:H226,H315,H332,H411
-
危险性防范说明:P210,P261,P370 + P378
-
储存条件:储存注意事项: - 储存在阴凉、通风良好的库房中。 - 远离火源和热源,库温不宜超过37℃。 - 保持容器密封。 - 应与氧化剂分开存放,切忌混储。 - 使用防爆型照明和通风设施。 - 禁止使用易产生火花的机械设备和工具。 - 储区应备有泄漏应急处理设备和合适的收容材料。
制备方法与用途
氯苯,又名氯代苯,是一种无色透明的液体,具有挥发性和轻微麻醉性。它能与空气形成爆炸混合物,爆炸极限为1.83%~9.23%(体积分数)。在适当的条件下,氯苯可以水解成苯酚或苯胺。
应用氯苯广泛应用于染料、医药、农药以及有机合成的中间体;它还可以用于生产苯酚、硝基氯苯和苯胺,并可用于制造杀虫剂DDT,溶剂,橡胶助剂,油漆,快干墨水及干洗剂等。
化学性质该物质为无色透明液体,易挥发并带有杏仁味。它可以溶解于大多数有机溶剂中,但不溶于水中。
用途氯苯用作分析试剂和有机溶剂,也广泛用于有机合成生产农药品种如三氯杀螨砜、滴滴涕等;它还用于合成染料、医药及其他有机化工产品,并作为乙基纤维素和多种树脂的溶剂,以及合成对二氯苯、对氯苯磺酸、2,4-二硝基氯苯、邻硝基氯苯、对硝基氯苯、硝基酚等中间体。
用途(续)作为一种溶剂,它被用于制造酚、苯胺、滴滴涕及染料,并用作传热介质。
生产方法氯苯主要由苯直接氯化制得。英国于1909年首次进行工业化生产的方法至今仍沿用此工艺。
气相法气相法中,反应温度在400~500℃之间,成本较高且已被淘汰;液相法又分间歇法和连续法两种。
间歇法干燥的苯装入氯化反应器中,并加入相当于苯量1%的铁屑作为催化剂。控制氯气加入速度以维持40~60℃的温度,防止多氯苯生产过多。至物料相对密度达到1.280(15℃)时结束反应。随后通过蒸馏分离出产品。
连续法在苯沸腾温度下进行液相氯化。使用催化剂(铁屑或无水氯化铁),反应热由苯和少量氯苯气化带出。经过干燥的苯经计量后加入氯化器底部,与计量的干燥氯气顺流进入氯化器反应。
液相法采用连续法时,酸性氯化液经水洗、碱洗、中和并用食盐干燥后进入初馏塔脱苯脱焦油。粗氯代苯进入精馏塔,分离出一氯苯成品。多氯苯回收得对二氯苯及邻二氯苯。
分类- 类别:易燃液体
- 毒性分级:中毒
-
急性毒性:
- 大鼠 LD50: 1100 毫克/公斤
- 小鼠 LD50: 2300 毫克/公斤
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 1,4-二氯苯 1,4-Dichlorobenzene 106-46-7 C6H4Cl2 147.004 1,3-二氯苯 1,3-Dichlorobenzene 541-73-1 C6H4Cl2 147.004 1,3,5-三氯苯 1,3,5-trichlorobenzene 108-70-3 C6H3Cl3 181.449 邻二氯苯 1,2-dichloro-benzene 95-50-1 C6H4Cl2 147.004 对氯甲苯 4-chlorotoluene 106-43-4 C7H7Cl 126.586 对氯碘苯 1-Chloro-4-iodobenzene 637-87-6 C6H4ClI 238.455 4-溴氯苯 bromochlorobenzene 106-39-8 C6H4BrCl 191.455 对氯苯酚 4-chloro-phenol 106-48-9 C6H5ClO 128.558 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 1,4-二氯苯 1,4-Dichlorobenzene 106-46-7 C6H4Cl2 147.004 1,3-二氯苯 1,3-Dichlorobenzene 541-73-1 C6H4Cl2 147.004 1,3,5-三氯苯 1,3,5-trichlorobenzene 108-70-3 C6H3Cl3 181.449 邻二氯苯 1,2-dichloro-benzene 95-50-1 C6H4Cl2 147.004 对氯甲苯 4-chlorotoluene 106-43-4 C7H7Cl 126.586 对氯碘苯 1-Chloro-4-iodobenzene 637-87-6 C6H4ClI 238.455 4-溴氯苯 bromochlorobenzene 106-39-8 C6H4BrCl 191.455 对氯苯酚 4-chloro-phenol 106-48-9 C6H5ClO 128.558 1-氯-4-氟苯 1-Chloro-4-fluorobenzene 352-33-0 C6H4ClF 130.549 —— (4-Chlor-phenyl)-phosphin 4538-32-3 C6H6ClP 144.54
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Estimation of dioxin emission from fires in chemicals摘要:The formation of the 17 toxic 2,3,7,8-substituted PCDDs and PCDFs during combustion of selected chemicals were measured by high-resolution GC/MS. The 16 chemicals studied were commonly used chlorinated pesticides, industrial chemicals, and PVC. In a series of experiments carried out in a DIN 53,436 furnace, 2.5 g of these compounds were burned at 500 degrees C and 900 degrees C, respectively. The resultant yields ranged from 740 ng ITEQ/g for pentachlorophenol, to below 0.01 ng ITEQ/g for PVC and dichlobenil. The results show that some chemicals generate PCDD/F in very high possibly dangerous - amounts during burning, whereas others generate insignificant amounts. The influence of scale were studied for chlorobenzene and 4-chloro-3-nitro-benzoic acid in additional experiments, carried out in a cone calorimeter burning 20 g substance, and in ISO 9705 room test burning about 50 kg. A good agreement between the results for large and small scale indicated that formation of PCCD/F during a fire may be estimated from laboratory experiments. This suggest laboratory test may be used to screen for chemicals posing a hazard for release of PCDD/F during fires. (C) 1999 Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved.DOI:10.1016/s0045-6535(99)00231-3
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:Aromatization of cyclohexenes and cyclohexadienes with selenium dioxide-trimethylsilyl polyphosphate摘要:Selenium dioxide is depolymerized and activated by trimethylsilyl polyphosphate in carbon tetrachloride. The reagent effectively aromatizes substituted cyclohexenes and cyclohexadienes under mild reaction conditions.DOI:10.1016/s0040-4039(00)60974-7
-
作为试剂:描述:2,3-二氢苯并吡喃-4-酮 在 2,2,6,6-四甲基哌啶 、 正丁基锂 、 palladium 10% on activated carbon 、 potassium tert-butylate 、 氯苯 作用下, 以 四氢呋喃 、 甲醇 、 正己烷 为溶剂, 反应 10.25h, 生成 racemic-4,4’-bichromane 、 meso-4,4’-bichromane参考文献:名称:通过去质子金属化对色满进行官能化摘要:针对苯并二氢吡喃在4-或8-位的脱原金属化,合理优化了两组条件。随后的亲电捕获可以得到各种功能化的衍生物。DOI:10.1002/ejoc.202400566
文献信息
-
BENZOTHIOPHENE INHIBITORS OF RHO KINASE申请人:Kahraman Mehmet公开号:US20080021026A1公开(公告)日:2008-01-24The present invention relates to compounds and methods which may be useful as inhibitors of Rho kinase for the treatment or prevention of disease.本发明涉及化合物和方法,这些化合物和方法可能作为Rho激酶的抑制剂在治疗或预防疾病方面有用。
-
Novel processes for the preparation of adenosine compounds and intermediates thereto申请人:——公开号:US20030069423A1公开(公告)日:2003-04-10Novel processes for the preparation of adenosine compounds and intermediates thereto. The adenosine compounds prepared by the present processes may be useful as cardiovascular agents, more particularly as antihypertensive and anti-ischemic agents, as cardioprotective agents which ameliorate ischemic injury or myocardial infarct size consequent to myocardial ischemia, and as an antilipolytic agents which reduce plasma lipid levels, serum triglyceride levels, and plasma cholesterol levels. The present processes may offer improved yields, purity, ease of preparation and/or isolation of intermediates and final product, and more industrially useful reaction conditions and workability.
-
DISUBSTITUTED TRIFLUOROMETHYL PYRIMIDINONES AND THEIR USE申请人:BAYER PHARMA AKTIENGESELLSCHAFT公开号:US20160221965A1公开(公告)日:2016-08-04The present application relates to novel 2,5-disubstituted 6-(trifluoromethyl)pyrimidin-4(3H)-one derivatives, to processes for their preparation, to their use alone or in combinations for the treatment and/or prevention of diseases, and to their use for preparing medicaments for the treatment and/or prevention of diseases, in particular for treatment and/or prevention of cardiovascular, renal, inflammatory and fibrotic diseases.
-
[EN] IMIDAZOLE DERIVATIVES USEFUL AS INHIBITORS OF FAAH<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS IMIDAZOLE UTILES COMME INHIBITEURS DE LA FAAH申请人:MERCK & CO INC公开号:WO2009152025A1公开(公告)日:2009-12-17The present invention is directed to certain imidazole derivatives which are useful as inhibitors of Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase (FAAH). The invention is also concerned with pharmaceutical formulations comprising these compounds as active ingredients and the use of the compounds and their formulations in the treatment of certain disorders, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, skeletomuscular pain, and fibromyalgia, as well as acute pain, migraine, sleep disorder, Alzeimer Disease, and Parkinson's Disease.
-
[EN] 3-[(HYDRAZONO)METHYL]-N-(TETRAZOL-5-YL)-BENZAMIDE AND 3-[(HYDRAZONO)METHYL]-N-(1,3,4-OXADIAZOL-2-YL)-BENZAMIDE DERIVATIVES AS HERBICIDES<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS DE 3-[(HYDRAZONO))MÉTHYL]-N-(TÉTRAZOL-5-YL)-BENZAMIDE ET DE 3-[(HYDRAZONO)MÉTHYL]-N-(1,3,4-OXADIAZOL-2-YL)-BENZAMIDE UTILISÉS EN TANT QU'HERBICIDES申请人:SYNGENTA CROP PROTECTION AG公开号:WO2021013969A1公开(公告)日:2021-01-28The present invention related to compounds of Formula (I): or an agronomically acceptable salt thereof, wherein Q, R2, R3, R4, R5 and R6 are as described herein. The invention further relates to compositions comprising said compounds, to methods of controlling weeds using said compositions, and to the use of compounds of Formula (I) as a herbicide.本发明涉及以下式(I)的化合物或其农业上可接受的盐,其中Q、R2、R3、R4、R5和R6如本文所述。该发明还涉及包含所述化合物的组合物,使用这些组合物控制杂草的方法,以及将式(I)的化合物用作除草剂的用途。
表征谱图
-
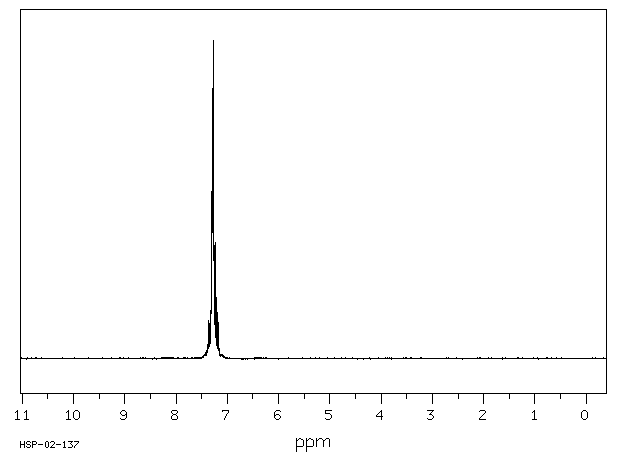
氢谱1HNMR
-
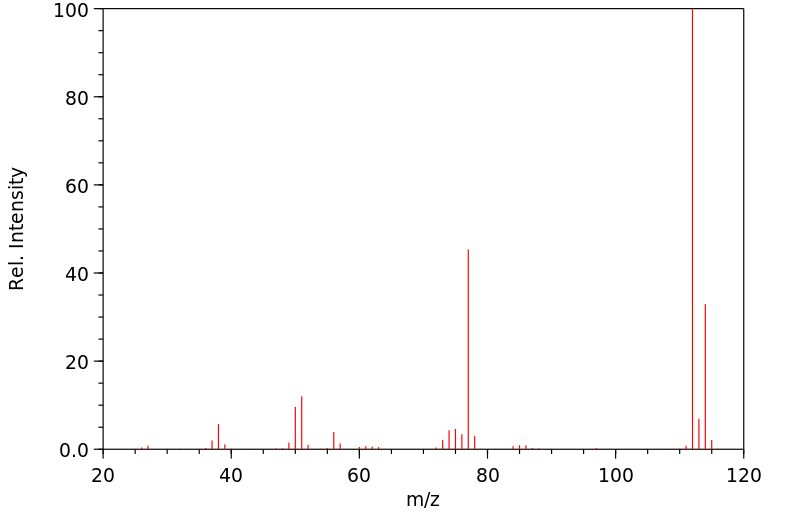
质谱MS
-
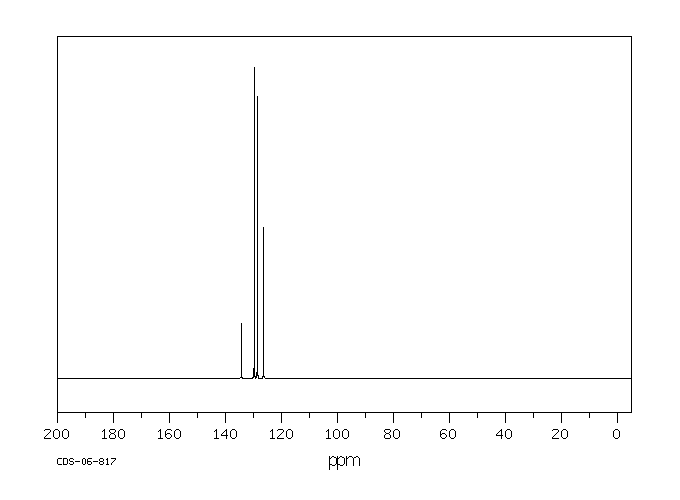
碳谱13CNMR
-
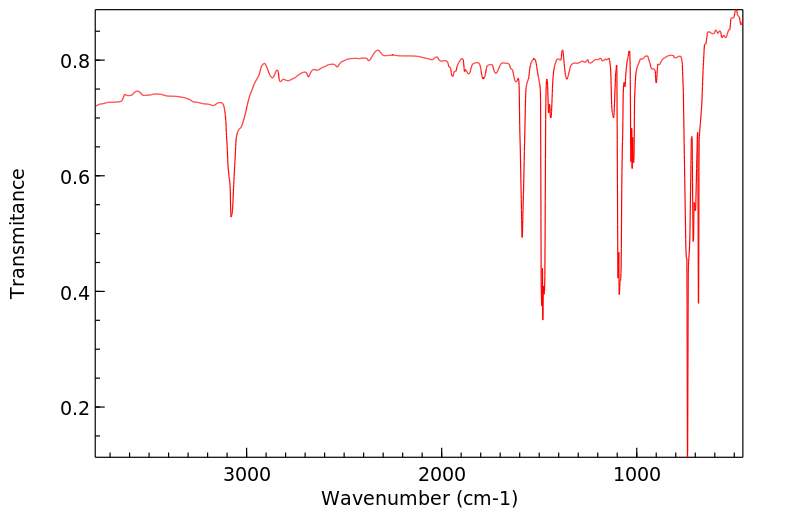
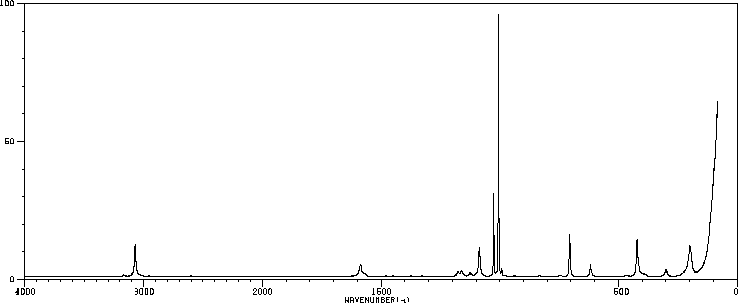
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息