壬醛 | 124-19-6
中文名称
壬醛
中文别名
九碳醛;天竺葵醛;天然壬醛;正壬醛;α-氢代壬烷
英文名称
Nonanal
英文别名
nonan-1-al;n-nonanal;1-nonanal;n-nonaldehyde;nonyl aldehyde
CAS
124-19-6
化学式
C9H18O
mdl
——
分子量
142.241
InChiKey
GYHFUZHODSMOHU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:-18°C
-
沸点:93 °C/23 mmHg (lit.)
-
密度:0.827 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
-
闪点:147 °F
-
溶解度:氯仿(微溶)、乙酸乙酯(微溶)
-
LogP:3.4 at 35℃
-
物理描述:Nonanal is a clear brown liquid characterized by a rose-orange odor. Insoluble in water. Found in at least 20 essential oils, including rose and citrus oils and several species of pine oil.
-
颜色/状态:Colorless liquid
-
气味:Orange-rose odor
-
蒸汽压力:3.7X10-1 mm Hg at 25 °C /Extrapolated/
-
亨利常数:7.34e-04 atm-m3/mole
-
稳定性/保质期:
- 存在于香料烟烟叶中。
- 自然存在于玫瑰油、柑橘油、白柠檬油及香紫苏油等精油中。
-
分解:When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke, and irritating fumes
-
折光率:Index of refraction = 1.4273 at 20 °C/D
-
保留指数:1081;1128;1079;1076;1076;1083;1082;1083;1081;1081;1079;1081;1067;1071;1074;1078;1082;1084;1084;1086;1083;1089;1101;1080.2;1085;1103;1082;1085;1098;1083;1084.8;1089;1130;1082;1082;1089;1089;1086;1088;1082;1088;1089.9;1084;1082;1081.4;1090;1092;1075;1082;1083;1082.5;1080;1085;1082;1084;1083;1089;1084;1085;1086;1082;1081;1091;1085;1091;1084;1084;1094;1104;1079.1;1080.7;1085.4;1084;1082;1087;1087.5;1093.3;1087;1084;1084;1086;1087;1095;1097;1086;1088;1087;1088;1093;1073;1104;1100;1074;1076;1084;1086;1073;1074;1093;1094;1076;1087;1073;1081;1104;1077;1085;1086;1073;1083;1100;1073;1081;1078;1078;1078;1081;1085;1085;1073;1082;1082;1094;1089;1083;1087;1102;1074;1092;1073;1099;1076;1078;1095;1095;1079;1079;1075;1084;1082;1092;1092;1080;1087;1088.2;1101;1075;1082;1082;1084;1082;1078;1081;1087;1088;1086;1097.2;1103;1084;1085;1085;1089;1085;1073;1081;1083.9;1082;1089.2;1084;1083;1083;1081;1080;1081;1084;1084;1084;1082;1073;1073;1082;1075;1102;1080;1085;1082;1082;1086;1083;1081;1083;1084;1085;1079;1086;1083;1082;1087;1082;1082;1082;1082;1087;1095;1083;1086;1081;1082;1082;1082;1084;1083;1083;1067;1087;1081;1083;1088;1082;1083;1078;1084;1081;1079;1083;1084;1089;1079.4;1069.1;1106
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):3.3
-
重原子数:10
-
可旋转键数:7
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.89
-
拓扑面积:17.1
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:1
ADMET
代谢
乙醛脱氢酶(ALDH)的特定活性在粗匀浆、线粒体后上清液、胞浆和微粒体组分中进行了测量,使用多种内源性和外源性乙醛以及NAD+和NADP+作为辅因子。在粗匀浆中发现的全部活性可以由胞浆和微粒体活性的总和来解释。在所有组分中,使用中链长度底物己醛和壬醛时发现最高的活性。不饱和乙醛(E,E)-2,4-壬二烯醛-1-醛和反式,反式-2,4-癸二烯醛也是两个组分的良好底物,而羟基化不饱和反式-4-羟基-2-壬醛仅是微粒体组分的良好底物。短链和芳香族外源性底物的代谢速率要低得多,只有微粒体组分对乙醛、丙烯醛和苯甲醛有效。两个组分都没有代谢2,5-二羟基苯甲醛。NAD+是大多数底物的首选辅因子。胞浆组分对己醛和壬醛的表观亲和力(Km)与在大鼠中发现的一致,但这些底物的理论最大速度(Vmax)以及其他底物的特定活性比哺乳动物中发现的要低得多。生化结果提示,鲑鱼很好地适应了内源性脂质过氧化产物的解毒,但适应外源性乙醛的解毒能力较差。
Aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) specific activity was measured in crude homogenates, post-mitochondrial supernatants, cytosolic and microsomal fractions of /Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss)/ liver, using a number of endogenous and xenobiotic aldehydes and both NAD+ and NADP+ as co-factors. All the activity found in the crude homogenate could be accounted for by the sum of the cytosolic and microsomal activities. Highest activities were found with the medium chain length substrates hexanal and nonanal in all fractions. The ,-unsaturated aldehydes, (E,E)-2,4-nonadienal-1-al, and trans, trans-2,4-decadienal, were also good substrates for both fractions, while the hydroxylated , unsaturated trans-4-hydroxy-2-nonenal was a good substrate only for the microsomal fraction. Short chain and aromatic xenobiotic substrates were metabolized at much lower rates, and only the microsomal fraction was effective against acetaldehyde, acrolein, and benzaldehyde. Neither fraction metabolized 2,5-dihydroxy benzaldehyde. NAD+ was the preferred co-factor for most substrates. Apparent affinity (Km) for hexanal and nonanal in the cytosolic fraction were comparable to that found in rats, but the theoretical maximal velocity (Vmax) for these substrates, and the specific activities for the other substrates, were much lower than found in mammals. The biochemical results suggest that trout are well adapted to detoxify products of endogenous lipid peroxidation, but are poorly adapted to detoxify xenobiotic aldehydes.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
Uremic toxins tend to accumulate in the blood either through dietary excess or through poor filtration by the kidneys. Most uremic toxins are metabolic waste products and are normally excreted in the urine or feces.
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
识别和使用:壬醛是一种无色液体。它目前在美国没有注册使用,但批准的农药使用可能会定期更改,因此必须咨询联邦、州和地方当局以获取当前批准的使用情况。它用于香水和作为调味剂。人类暴露和毒性:臭氧暴露导致人类呼吸道上皮细胞衬里液中壬醛显著早期增加。暴露后18小时,壬醛水平恢复到基线。通过脂质体臭氧化体外产生的壬醛导致人类红细胞溶血,壬醛和H2O2的联合使用比单独使用壬醛显著更具溶血性。在3-100 mM的成年人类肝细胞分析中,它对未计划的DNA合成呈阴性。动物研究:在3只皮肤完整的兔子和3只皮肤擦伤的兔子身上涂抹壬醛5克/千克的单一皮肤剂量,导致1只死亡以及涂抹部位严重水肿和烧伤。当怀孕雌性大鼠在怀孕的第6-15天给予1500毫克/千克体重的壬酸(壬醛的代谢物)时,没有出现胚胎毒性、胎儿毒性或致畸的迹象。在大鼠肝细胞姐妹染色单体交换分析中,它在0.1-100微摩尔呈阳性,在3-100 mM的成年大鼠肝细胞未计划DNA合成分析中呈阴性。在中国仓鼠肺细胞V79的前向突变分析中,它在0.1-0.3 mM呈阳性,在使用S. typhmiurium TA98、TA100和TA1535的修改的Ames测试(预孵化方法)中,在1-666微克/平板上呈阴性。在使用S. typhmiurium TA102和TA104的Ames测试中,它在高达1毫克/平板上呈阴性,在大鼠肝细胞染色体畸变测试中,在0.4微克/毫升上呈阴性。
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: Nonanal is a colorless liquid. It is not registered for current use in the U.S., but approved pesticide uses may change periodically and so federal, state and local authorities must be consulted for currently approved uses. It is used in perfume industry and as a flavoring agent. HUMAN EXPOSURE AND TOXICITY: Ozone exposure resulted in a significant early increase in nonanal in the airway epithelial lining fluid of humans. Nonanal levels returned to baseline by 18 hr after exposure. Nonanal produced in vitro by ozonation of liposomes induced hemolysis of human red blood cells, and combination of nonanal and H2O2 was significantly more hemolytic than nonanal alone. It was negative for unscheduled DNA synthesis in adult human hepatocytes assay at 3-100 mM. ANIMAL STUDIES: Single dermal dose of nonanal 5 g/kg applied on 3 rabbits with intact skin and 3 rabbits with abraded skin produced one death and severe edema and burns at site of application. There was no evidence of embryotoxicity, fetal toxicity, or teratogenesis when pregnant female rats were given 1500 mg/kg bw/day of nonanoic acid (metabolite of nonanal on days 6-15 of pregnancy. It was positive for sister chromatid exchange in rat hepatocytes at 0.1-100 uM, and negative for unscheduled DNA synthesis in adult rat hepatocytes assay at 3-100 mM. It was positive for forward mutation assay in V79 Chinese hamster lung cells at 0.1-0.3 mM and negative in modified Ames test (preincubation method) using S. typhmiurium TA98, TA100 and TA1535 at 1-666 ug/plate. It was also negative in Ames test using S. typhmiurium TA102 and TA104 at up to 1 mg/plate, and negative in the chromosomal aberration test using rat hepatocytes at 0.4 ug/mL.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
尿毒症毒素如壬醛通过有机离子转运体(特别是OAT3)被积极运输到肾脏中。尿毒症毒素水平的增加可以刺激活性氧种类的产生。这似乎是通过尿毒症毒素直接结合或抑制NADPH氧化酶(特别是肾脏和心脏中丰富的NOX4)来介导的(A7868)。活性氧种类可以诱导几种不同的DNA甲基转移酶(DNMTs),这些酶参与沉默一种被称为KLOTHO的蛋白质。KLOTHO已被确定在抗衰老、矿物质代谢和维生素D代谢中具有重要作用。许多研究表明,在急性或慢性肾脏疾病中,由于局部活性氧种类水平升高,KLOTHO mRNA和蛋白质水平会降低(A7869)。
Uremic toxins such as nonanal are actively transported into the kidneys via organic ion transporters (especially OAT3). Increased levels of uremic toxins can stimulate the production of reactive oxygen species. This seems to be mediated by the direct binding or inhibition by uremic toxins of the enzyme NADPH oxidase (especially NOX4 which is abundant in the kidneys and heart) (A7868). Reactive oxygen species can induce several different DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) which are involved in the silencing of a protein known as KLOTHO. KLOTHO has been identified as having important roles in anti-aging, mineral metabolism, and vitamin D metabolism. A number of studies have indicated that KLOTHO mRNA and protein levels are reduced during acute or chronic kidney diseases in response to high local levels of reactive oxygen species (A7869).
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
对人类不具有致癌性(未被国际癌症研究机构IARC列名)。
No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC).
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
长期暴露于尿毒症毒素可能会导致多种疾病,包括肾脏损伤、慢性肾病和心血管疾病。
Chronic exposure to uremic toxins can lead to a number of conditions including renal damage, chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular disease.
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
内源性的,摄入,皮肤(接触)
Endogenous, Ingestion, Dermal (contact)
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
安全信息
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:9
-
危险品标志:Xi
-
安全说明:S26,S37/39
-
危险类别码:R36/37/38
-
WGK Germany:2
-
海关编码:29121900
-
危险品运输编号:3082
-
危险类别:9
-
RTECS号:RA5700000
-
包装等级:III
-
危险性防范说明:P264,P273,P280,P302+P352,P332+P313,P362+P364
-
危险性描述:H315,H412
-
储存条件:贮存:在室温下密封保存,建议贮存温度为4°C。
SDS
模块 1. 化学品
1.1 产品标识符
: 壬醛
产品名称
1.2 鉴别的其他方法
Pelargonaldehyde
Nonyl aldehyde
Aldehyde C9
1.3 有关的确定了的物质或混合物的用途和建议不适合的用途
仅用于研发。不作为药品、家庭或其它用途。
模块 2. 危险性概述
2.1 GHS-分类
易燃液体 (类别 4)
皮肤刺激 (类别 2)
眼睛刺激 (类别 2A)
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触) (类别 3), 呼吸系统
2.2 GHS 标记要素,包括预防性的陈述
象形图
警示词 警告
危险申明
H227 可燃液体
H315 造成皮肤刺激。
H319 造成严重眼刺激。
H335 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
警告申明
预防措施
P210 远离热源、火花、明火和热表面。- 禁止吸烟。
P261 避免吸入粉尘/烟/气体/烟雾/蒸气/喷雾.
P264 操作后彻底清洁皮肤。
P271 只能在室外或通风良好之处使用。
P280 穿戴防护手套/ 眼保护罩/ 面部保护罩。
事故响应
P302 + P352 如接触皮肤:使用大量水冲洗。
P304 + P340 如果吸入:将受害人移至空气新鲜处并保持呼吸舒适的姿势休息。
P305 + P351 + P338 如与眼睛接触,用水缓慢温和地冲洗几分钟。如戴隐形眼镜并可方便地取
出,取出隐形眼镜,然后继续冲洗.
P312 如感觉不适,呼救中毒控制中心或医生.
P321 具体处置(见本标签上提供的急救指导)。
P332 + P313 如觉皮肤刺激:求医/就诊。
P337 + P313 如仍觉眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
P362 + P364 脱掉玷污的衣服,清洗后方可再用。
P370 + P378 在发生火灾时:用干砂,干粉或抗溶性泡沫扑灭。
安全储存
P403 + P233 存放于通风良的地方。 保持容器密闭。
P403 + P235 保持低温,存放于通风良好处。
P405 存放处须加锁。
废弃处置
P501 将内容物/ 容器处理到得到批准的废物处理厂。
2.3 其它危害物 - 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
3.1 物 质
: Pelargonaldehyde
别名
Nonyl aldehyde
Aldehyde C9
: C9H18O
分子式
: 142.24 g/mol
分子量
组分 浓度或浓度范围
Nonanal
50 - 100 %
化学文摘登记号(CAS 124-19-6
No.) 204-688-5
EC-编号
模块 4. 急救措施
4.1 必要的急救措施描述
一般的建议
请教医生。 向到现场的医生出示此安全技术说明书。
吸入
如果吸入,请将患者移到新鲜空气处。 如呼吸停止,进行人工呼吸。 请教医生。
皮肤接触
用肥皂和大量的水冲洗。 请教医生。
眼睛接触
用大量水彻底冲洗至少15分钟并请教医生。
食入
禁止催吐。 切勿给失去知觉者通过口喂任何东西。 用水漱口。 请教医生。
4.2 主要症状和影响,急性和迟发效应
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
4.3 及时的医疗处理和所需的特殊处理的说明和指示
无数据资料
模块 5. 消防措施
5.1 灭火介质
灭火方法及灭火剂
用水雾,抗乙醇泡沫,干粉或二氧化碳灭火。
5.2 源于此物质或混合物的特别的危害
碳氧化物
5.3 给消防员的建议
如必要的话,戴自给式呼吸器去救火。
5.4 进一步信息
用水喷雾冷却未打开的容器。
模块 6. 泄露应急处理
6.1 作业人员防护措施、防护装备和应急处置程序
使用个人防护用品。 避免吸入蒸气、烟雾或气体。 保证充分的通风。 移去所有火源。
人员疏散到安全区域。 谨防蒸气积累达到可爆炸的浓度。蒸气能在低洼处积聚。
6.2 环境保护措施
如能确保安全,可采取措施防止进一步的泄漏或溢出。 不要让产品进入下水道。
6.3 泄漏化学品的收容、清除方法及所使用的处置材料
围堵溢出,用防电真空清洁器或湿刷子将溢出物收集起来,并放置到容器中去,根据当地规定处理(见第13部
分)。 放入合适的封闭的容器中待处理。
6.4 参考其他部分
丢弃处理请参阅第13节。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
7.1 安全操作的注意事项
避免接触皮肤和眼睛。 避免吸入蒸气和烟雾。
切勿靠近火源。-严禁烟火。采取措施防止静电积聚。
7.2 安全储存的条件,包括任何不兼容性
贮存在阴凉处。 使容器保持密闭,储存在干燥通风处。
打开了的容器必须仔细重新封口并保持竖放位置以防止泄漏。
7.3 特定用途
无数据资料
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
8.1 容许浓度
最高容许浓度
没有已知的国家规定的暴露极限。
8.2 暴露控制
适当的技术控制
根据良好的工业卫生和安全规范进行操作。 休息前和工作结束时洗手。
个体防护设备
眼/面保护
带有防护边罩的安全眼镜符合 EN166要求请使用经官方标准如NIOSH (美国) 或 EN 166(欧盟)
检测与批准的设备防护眼部。
皮肤保护
戴手套取 手套在使用前必须受检查。
请使用合适的方法脱除手套(不要接触手套外部表面),避免任何皮肤部位接触此产品.
使用后请将被污染过的手套根据相关法律法规和有效的实验室规章程序谨慎处理. 请清洗并吹干双手
所选择的保护手套必须符合EU的89/686/EEC规定和从它衍生出来的EN 376标准。
身体保护
防渗透的衣服, 防护设备的类型必须根据特定工作场所中的危险物的浓度和数量来选择。
呼吸系统防护
如危险性评测显示需要使用空气净化的防毒面具,请使用全面罩式多功能防毒面具(US)或ABEK型
(EN
14387)防毒面具筒作为工程控制的候补。如果防毒面具是保护的唯一方式,则使用全面罩式送风防
毒面具。 呼吸器使用经过测试并通过政府标准如NIOSH(US)或CEN(EU)的呼吸器和零件。
模块 9. 理化特性
9.1 基本的理化特性的信息
a) 外观与性状
形状: 透明, 液体
颜色: 淡黄
b) 气味
无数据资料
c) 气味阈值
无数据资料
d) pH值
无数据资料
e) 熔点/凝固点
无数据资料
f) 沸点、初沸点和沸程
93 °C 在 31 hPa
g) 闪点
64 °C - 闭杯
h) 蒸发速率
无数据资料
i) 易燃性(固体,气体)
无数据资料
j) 高的/低的燃烧性或爆炸性限度 无数据资料
k) 蒸气压
0.35 hPa 在 25 °C
l) 蒸汽密度
无数据资料
m) 密度/相对密度
0.825 g/cm3
n) 水溶性
无数据资料
o) n-辛醇/水分配系数
无数据资料
p) 自燃温度
无数据资料
q) 分解温度
无数据资料
r) 粘度
无数据资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应活性
10.1 反应性
无数据资料
10.2 稳定性
无数据资料
含有下列稳定剂:
α-Tocopherol (>=0 - <=0.1 %)
10.3 危险反应
无数据资料
10.4 应避免的条件
热,火焰和火花。
10.5 不相容的物质
强氧化剂, 强还原剂, 强碱
10.6 危险的分解产物
其它分解产物 - 无数据资料
模块 11. 毒理学资料
11.1 毒理学影响的信息
急性毒性
半数致死剂量 (LD50) 经口 - 大鼠 - > 5,000 mg/kg
备注: 行为的:嗜睡(全面活力抑制)。 肾脏,输尿管,膀胱:尿液体积增多
皮肤刺激或腐蚀
皮肤 - 兔子 - 严重的皮肤刺激 - 24 h
眼睛刺激或腐蚀
眼睛 - 兔子 - 中度的眼睛刺激
呼吸道或皮肤过敏
无数据资料
生殖细胞致突变性
细胞突变性-体外试验 - 大鼠 - 肝
姐妹染色单体互换
细胞突变性-体外试验 - 仓鼠 - 肺
哺乳动物体细胞突变
致癌性
IARC:
此产品中没有大于或等于 0。1%含量的组分被 IARC鉴别为可能的或肯定的人类致癌物。
生殖毒性
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触)
吸入 - 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
特异性靶器官系统毒性(反复接触)
无数据资料
吸入危险
无数据资料
潜在的健康影响
吸入 吸入可能有害。 引起呼吸道刺激。
摄入 如服入是有害的。
皮肤 通过皮肤吸收可能有害。 造成皮肤刺激。
眼睛 造成严重眼刺激。
接触后的征兆和症状
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
附加说明
化学物质毒性作用登记: RA5700000
模块 12. 生态学资料
12.1 生态毒性
无数据资料
12.2 持久性和降解性
无数据资料
12.3 潜在的生物累积性
无数据资料
12.4 土壤中的迁移性
无数据资料
12.5 PBT 和 vPvB的结果评价
无数据资料
12.6 其它不良影响
无数据资料
模块 13. 废弃处置
13.1 废物处理方法
产品
此易爆炸产品可以在备有燃烧后处理和洗刷作用的化学焚化炉中燃烧
将剩余的和不可回收的溶液交给有许可证的公司处理。
受污染的容器和包装
按未用产品处置。
模块 14. 运输信息
14.1 联合国危险货物编号
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.2 联合国运输名称
欧洲陆运危规: 非危险货物
国际海运危规: 非危险货物
国际空运危规: 非危险货物
14.3 运输危险类别
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.4 包裹组
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.5 环境危险
欧洲陆运危规: 否 国际海运危规 国际空运危规: 否
海洋污染物(是/否): 否
14.6 对使用者的特别提醒
无数据资料
模块 15 - 法规信息
N/A
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
制备方法与用途
含量分析
按醛测定法(OT-6)测定。所取试样量为1.5 g,计算中的当量因子(e)取71.12。或按气相色谱法(GT-10-4)中非极性柱方法测定。
毒性LD₅₀ orally in Rabbit: > 5000 mg/kg
使用限量FEMA(mg/kg): 软饮料1.3;冷饮1.3;糖果4.1;焙烤食品2.3;布丁类6.0;胶姆糖0.20~38。适度为限(FDA§172.515,2000)。
食品添加剂最大允许使用量及最大允许残留量标准添加剂中文名称:壬醛
允许使用该种添加剂的食品中文名称:食品
添加剂功能:食品用香料
最大允许使用量(g/kg):用于配制香精的各香料成分不得超过在GB 2760中的最大允许使用量和最大允许残留量
壬醛是一种无色油状液体,冷时固化。沸点191-192℃,熔点5-7℃,相对密度0.820-0.830,折射率1.422-1.429,闪点71℃,溶于3体积70%乙醇与油类。酸值<10,有青而微甜、尖锐的蜜蜡花香气息,留香力一般。浓度低于0.0005%时香味新鲜,带有柑橘和醋味。
用途广泛用于香精配方,用量常应少于0.1%。可用于玫瑰、橙花、铃兰、牡丹、鸢尾、葵花香叶、甜橙、柠檬、茉莉、晚香玉、防风根和许多其他香型。也常作为醛香基的头香。还可极微量用于食用香精中,如柑橘类的配方,特别是柠檬和橘子。
GB 2760-1996 规定壬醛规定为暂时允许使用的食用香料,主要用于配制橙子、柠檬和白柠檬等型香精,用量极微。
化学性质(补充)壬醛具有强烈的油脂气味和甜橙气息。其稀乙醇溶液有类似香草醛和香调的特性,可用作食品添加剂,也可用于调制玫瑰、橙花、香紫罗兰、香味等香精。
生产方法天然存在于德国玫瑰、橙花油、锡兰桂皮油等精油中。工业上由壬醇脱氢来制取,或通过将壬酸和甲酸的钙盐或钡盐混合,在减压下加热蒸馏而得;也可在甲酸在一氧化锰上还原而成。
另外一种生产方法是正壬醇催化氧化得到。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 正辛醛 Octanal 124-13-0 C8H16O 128.214 庚醛 heptanal 111-71-7 C7H14O 114.188 壬酸 nonanoic acid 112-05-0 C9H18O2 158.241 壬酰氯 Nonanoyl chloride 764-85-2 C9H17ClO 176.686 正癸酸 1-decanoic acid 334-48-5 C10H20O2 172.268 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 正辛醛 Octanal 124-13-0 C8H16O 128.214 庚醛 heptanal 111-71-7 C7H14O 114.188 正己醛 hexanal 66-25-1 C6H12O 100.161 2-壬酮 2-Nonanone 821-55-6 C9H18O 142.241 2-癸酮 2-Decanone 693-54-9 C10H20O 156.268 7-甲基辛醛 7-methyloctanal 49824-43-3 C9H18O 142.241 9-十七酮 heptadecan-9-one 540-08-9 C17H34O 254.456 5-十三烷酮 5-tridecanone 30692-16-1 C13H26O 198.349 3-十一酮 undecan-3-one 2216-87-7 C11H22O 170.295 —— racemic trans-1-decalone 16979-02-5 C10H18O2 170.252 —— 2-oxo-nonanal 2363-87-3 C9H16O2 156.225 —— 4-oxo-dodecanal 56268-03-2 C12H22O2 198.305 —— (R)-3-methylundecanal 1147745-69-4 C12H24O 184.322 二十三烷-9,12,15-三酮 tricosane-9,12,15-trione 62619-55-0 C23H42O3 366.585 —— 2,5-tridecanedione 32781-67-2 C13H24O2 212.332 壬醯胺 nonanamide 1120-07-6 C9H19NO 157.256 壬酸 nonanoic acid 112-05-0 C9H18O2 158.241 壬酰氯 Nonanoyl chloride 764-85-2 C9H17ClO 176.686 十三烷二酸 brassylic acid 505-52-2 C13H24O4 244.331 —— octanoyl fluoride 463-14-9 C9H17FO 160.232 —— 9,11-nonadecanedione 94433-63-3 C19H36O2 296.494 —— 2-butylnonanal 65899-14-1 C13H26O 198.349 —— 2-heptyl-1-undecanal 64935-44-0 C18H36O 268.483 - 1
- 2
- 3
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Uemura, Sakae; Ohe, Kouichi; Sugita, Nobuyuki, Journal of the Chemical Society. Perkin transactions I, 1990, # 6, p. 1697 - 1703摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:负载在氧化铝上的氟铬酸喹啉 (QFC) 作为醇的选择性氧化剂摘要:摘要 通过新方法制备的氧化铝(中性)负载氟铬酸喹啉(QFC)可选择性地将脂肪族伯醇和仲醇、取代苄醇和脂环醇氧化成相应的羰基化合物,收率良好。DOI:10.1080/00397919908086204
-
作为试剂:描述:2-乙基-己酸稀土盐 在 壬醛 、 samarium diiodide 、 samarium(III) trifluoromethanesulfonate 作用下, 以 四氢呋喃 、 甲醇 、 氢氧化钾 为溶剂, 反应 0.13h, 以93%的产率得到2-乙基己醇参考文献:名称:Novel and facile selective reduction of carboxylic acid with a samarium diiodide–lanthanide triflate–methanol–base system摘要:The facile selective reduction of carboxylic acids in the presence of an aldehyde or that bearing a formyl group proceeded smoothly with a samarium diiodide-lanthanide triflate-methanol-base system at room temperature to give the corresponding alcohols in good to almost quantitative yield. (C) 2000 Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved.DOI:10.1016/s0040-4039(99)02051-1
文献信息
-
Water Accelerated Allylation of Aldehydes by Using Water Tolerant Grignard-Type Allylating Agents from Allylmagnesium Chloride and Various Metallic Salts作者:Tomohiro Fukuma、Sandra Lock、Norikazu Miyoshi、Makoto WadaDOI:10.1246/cl.2002.376日期:2002.3allylating agents prepared in situ from allylmagnesium chloride and bismuth trichloride, tin tetrachloride, tin dichloride, antimony trichloride, indium trichloride, or nickel dichloride reacted with aldehydes in THF–H2O to afford the desired homoallylic alcohols in good yields. The present reaction proceeded more smoothly than that under non-aqueous media.
-
A Convenient and Selective Palladium-Catalyzed Aerobic Oxidation of Alcohols作者:Saravanan Gowrisankar、Helfried Neumann、Dirk Gördes、Kerstin Thurow、Haijun Jiao、Matthias BellerDOI:10.1002/chem.201302526日期:2013.11.18An efficient procedure for the oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols to aldehydes and ketones, respectively, with molecular oxygen under ambient conditions has been achieved. By applying catalytic amounts of Pd(OAc)2 in the presence of tertiary phosphine oxides (OPR3) as ligands, a variety of substrates are selectively oxidized without formation of ester byproducts. Spectroscopic investigations
-
The oxidation of alcohols with O-iodoxybenzoic acid (IBX) in aqueous nanomicelles at room temperature作者:Aming Xie、Xiangxiang Zhou、Liandong Feng、Xinyu Hu、Wei DongDOI:10.1016/j.tet.2014.03.047日期:2014.5GMPGS-2000, a nonionic amphiphile composed of Guerbet alcohol (2-octyldodecan-1-ol), MPEG-2000 and succinic acid, has been prepared as an effective nanomicelle forming species for the oxidation of alcohols with 2-iodoxybenzoic acid (IBX) in water at room temperature.
-
Structure–Activity Relationships of 6- and 8-Gingerol Analogs as Anti-Biofilm Agents作者:Hyunsuk Choi、So-Young Ham、Eunji Cha、Yujin Shin、Han-Shin Kim、Jeong Kyu Bang、Sang-Hyun Son、Hee-Deung Park、Youngjoo ByunDOI:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b01426日期:2017.12.14attractive strategy for treating diseases associated with P. aeruginosa infection. In this study, we designed and synthesized a series of gingerol analogs targeting LasR, a master regulator of quorum sensing networks in P. aeruginosa. Structure–activity relationship studies showed that a hydrogen-bonding interaction in the head section, stereochemistry and rotational rigidity in the middle section, and optimal铜绿假单胞菌是免疫功能低下患者慢性感染的病原体。仲裁感应电路的中断是一种有吸引力的策略,用于治疗与铜绿假单胞菌感染相关的疾病。在这项研究中,我们设计和合成了一系列针对LasR的姜醇类似物,LasR是铜绿假单胞菌群体感应网络的主要调节剂。结构-活性关系研究表明,头部的氢键相互作用,中部的立体化学和旋转刚度以及尾部的最佳烷基链长度是增强LasR结合亲和力和抑制作用的重要因素。生物膜形成的过程。最有效的化合物41,类似物为(与已知的LasR拮抗剂(S)-6-姜油醇相比,R)-8-姜油醇旋转受限,显示出更强的LasR结合亲和力和生物膜形成抑制作用。这种新的LasR拮抗剂可以用作开发抗生物膜药物以治疗铜绿假单胞菌感染的早期先导化合物。
-
A Mild One-Pot Conversion of Alkenes into Amines through Tandem Ozonolysis and Reductive Amination作者:Patrick Dussault、ShivaKumar Kyasa、Thomas FisherDOI:10.1055/s-0030-1260244日期:2011.11The selective reduction of hydroperoxyacetals to aldehydes by sodium triacetoxyborohydride provides the basis for a mild one-pot synthesis of amines from alkenes. ozonolysis - hydroperoxyacetal - reductive amination - amine - sodium triacetoxyborohydride
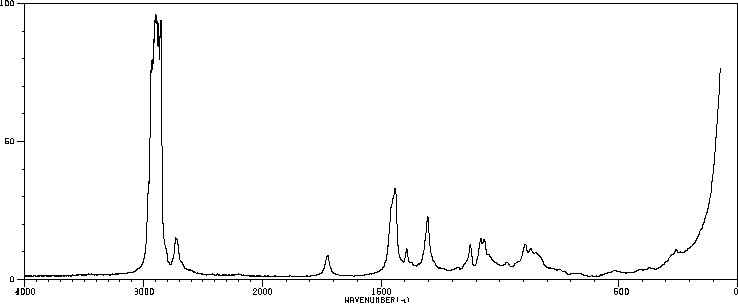
表征谱图
-
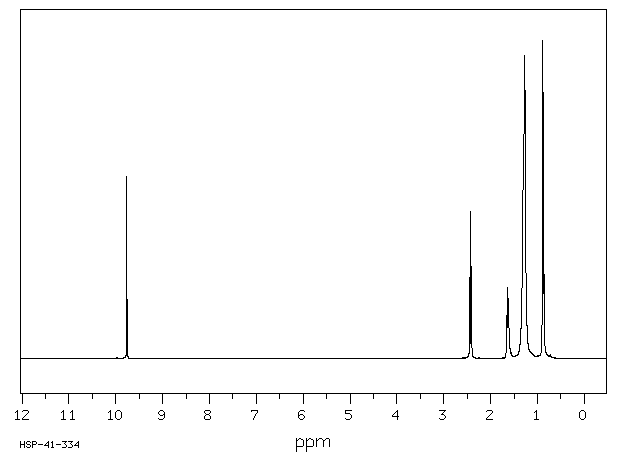
氢谱1HNMR
-
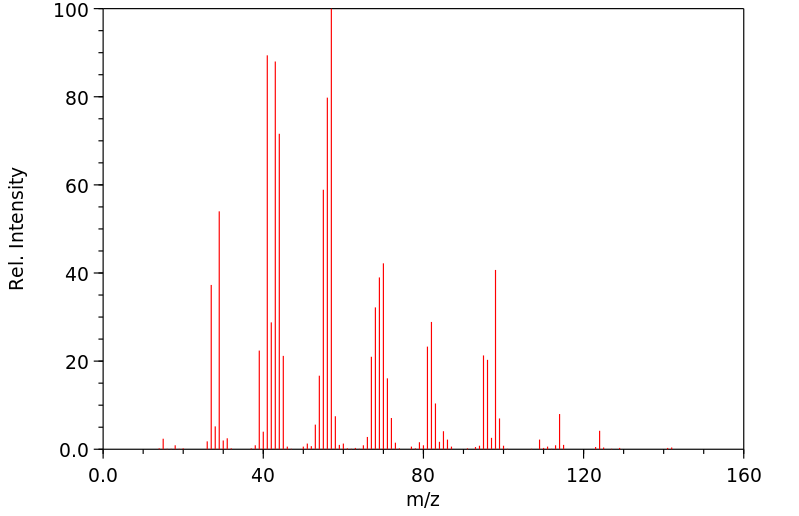
质谱MS
-
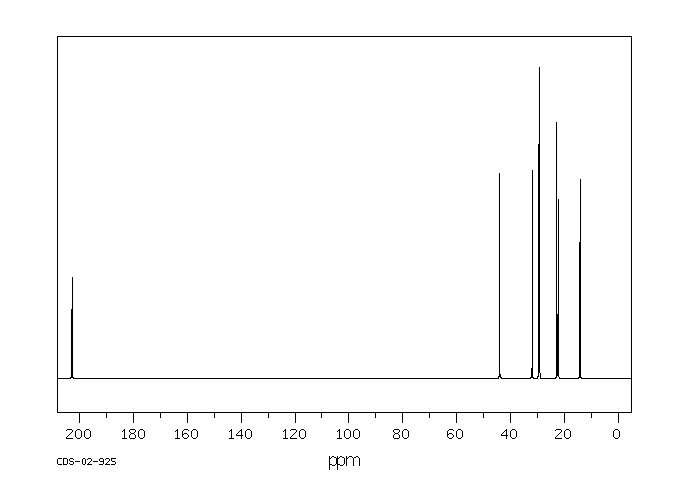
碳谱13CNMR
-
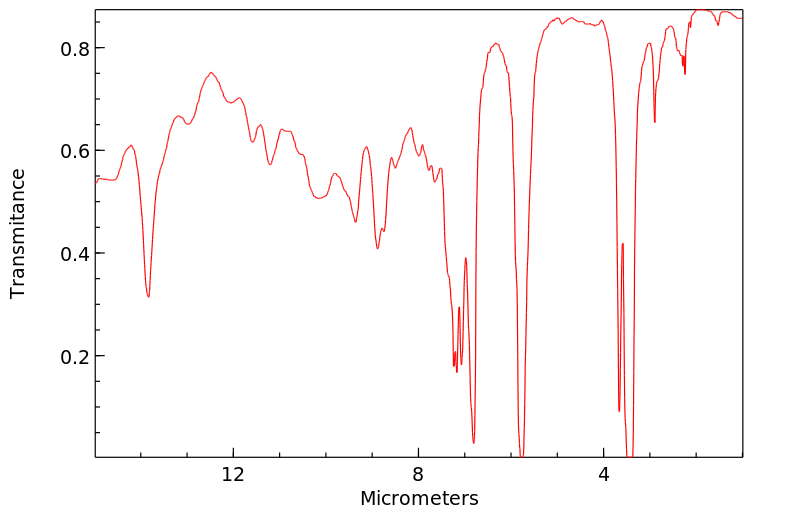
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(反式)-4-壬烯醛
(s)-2,3-二羟基丙酸甲酯
([1-(甲氧基甲基)-1H-1,2,4-三唑-5-基](苯基)甲酮)
(Z)-4-辛烯醛
(S)-氨基甲酸酯β-D-O-葡糖醛酸
(S)-3-(((2,2-二氟-1-羟基-7-(甲基磺酰基)-2,3-二氢-1H-茚满-4-基)氧基)-5-氟苄腈
(R)-氨基甲酸酯β-D-O-葡糖醛酸
(5,5-二甲基-2-(哌啶-2-基)环己烷-1,3-二酮)
(2,5-二氟苯基)-4-哌啶基-甲酮
龙胆苦苷
龙胆二糖甲乙酮氰醇(P)
龙胆二糖丙酮氰醇(P)
龙胆三糖
龙涎酮
齐罗硅酮
齐留通beta-D-葡糖苷酸
鼠李糖
黑芥子苷单钾盐
黑海棉酸钠盐
黑木金合欢素
黑曲霉三糖
黑介子苷
黄尿酸8-O-葡糖苷
麻西那霉素II
麦迪霉素
麦芽糖脎
麦芽糖基海藻糖
麦芽糖1-磷酸酯
麦芽糖
麦芽四糖醇
麦芽四糖
麦芽十糖
麦芽六糖
麦芽五糖水合物
麦芽五糖
麦芽五糖
麦芽五糖
麦芽三糖醇
麦芽三糖
麦芽三糖
麦芽三塘水合
麦芽七糖水合物
麦芽七糖
麦法朵
麦可酚酸-酰基-Β-D-葡糖苷酸
麦利查咪
麝香酮
鹤草酚
鸢尾酚酮 3-C-beta-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷
鸡矢藤苷