2,4'-二羟基二苯甲烷 | 2467-03-0
物质功能分类
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:119 °C
-
沸点:204-208 °C(Press: 6 Torr)
-
密度:1.208±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted)
-
溶解度:可溶于乙腈(少许)、DMSO(少许)
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):3.2
-
重原子数:15
-
可旋转键数:2
-
环数:2.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.076
-
拓扑面积:40.5
-
氢给体数:2
-
氢受体数:2
安全信息
-
安全说明:S26,S36/37/39
-
危险类别码:R36/37/38
-
海关编码:2907299090
-
WGK Germany:3
-
储存条件:室温
SDS
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: 2,4'-Dihydroxydiphenylmethane
修改号码: 5
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害 未分类
健康危害
皮肤腐蚀/刺激 第2级
严重损伤/刺激眼睛 2A类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志
信号词 警告
危险描述 造成皮肤刺激
造成严重眼刺激
防范说明
[预防] 处理后要彻底清洗双手。
穿戴防护手套/护目镜/防护面具。
[急救措施] 眼睛接触:用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续冲洗。
眼睛接触:求医/就诊
皮肤接触:用大量肥皂和水轻轻洗。
若皮肤刺激:求医/就诊。
脱掉被污染的衣物,清洗后方可重新使用。
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 2,4'-二羟基二苯甲烷
百分比: >98.0%(GC)
CAS编码: 2467-03-0
分子式: C13H12O2
2,4'-二羟基二苯甲烷 修改号码:5
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用大量肥皂和水轻轻洗。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,雾状水,二氧化碳
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 清扫收集粉尘,封入密闭容器。注意切勿分散。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的
法律法规处置。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止粉尘扩散。处理后彻底清洗双手
和脸。
注意事项: 如果粉尘或浮质产生,使用局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗处。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防尘面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
固体
外形(20°C):
外观: 晶体-粉末
颜色: 白色-微浅黄色
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
2,4'-二羟基二苯甲烷 修改号码:5
模块 9. 理化特性
熔点:
119°C
沸点/沸程 无资料
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 无资料
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂]
溶于: 甲醇
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在可燃溶剂中溶解混合,在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中
焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
2,4'-二羟基二苯甲烷 修改号码:5
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
制备方法与用途
溶解性于甲醇:轻微浑浊
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 亚甲基二苯酚 Bis(2-hydroxyphenyl)methane 2467-02-9 C13H12O2 200.237 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— 1-Hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-4-(2-hydroxybenzyl)benzene 34826-62-5 C20H18O3 306.361 1-甲氧基-2-[(4-甲氧基苯基)甲基]-苯 2,4'-dimethoxydiphenylmethane 30567-87-4 C15H16O2 228.291 —— 2,4'-dihydroxybenzyl-6,6'-methylenediphenol 197805-65-5 C27H24O4 412.485 —— 5-(hydroxymethyl)-2,4'-dihydroxydiphenylmethane 21243-72-1 C14H14O3 230.263 2,4'-二羟基二苯甲酮 4-[(2-hydroxyphenyl)carbonyl]phenol 606-12-2 C13H10O3 214.221 —— (2-ethoxy-phenyl)-(4-ethoxy-phenyl)methane 33451-13-7 C17H20O2 256.345 —— 2-hydroxy-5-salicyl-benzyl alcohol 21243-73-2 C14H14O3 230.263 —— 2-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-benzyl)-benzyl alcohol 21243-71-0 C14H14O3 230.263 1,3-苯二甲醇,2-羟基-5-[[2-羟基-3,5-二(羟甲基)苯基]甲基]- (2-hydroxy-3,5-bis-hydroxymethyl-phenyl)-(4-hydroxy-3,5-bis-hydroxymethyl-phenyl)-methane 103603-77-6 C17H20O6 320.342 —— 2-[[4-[tert-butyl(dimethyl)silyl]oxyphenyl]methyl]phenol 197805-63-3 C19H26O2Si 314.5 —— 2,4'-Diacetoxy-diphenylmethan 959033-36-4 C17H16O4 284.312 —— 3,3',5,5'-Tetrabrom-2,4'-dihydroxy-diphenylmethan 91261-00-6 C13H8Br4O2 515.821 2,4'-二甲氧基二苯甲酮 2,4'-dimethoxybenzophenone 5449-69-4 C15H14O3 242.274 [[2-[4-(环氧乙烷基甲氧基)苄基]苯氧基]甲基]环氧乙烷 ortho,para-bisphenol F diglycidyl ether 57469-07-5 C19H20O4 312.365 - 1
- 2
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:2,4'-二羟基二苯甲烷 在 咪唑 、 三氟化硼乙醚 作用下, 以 氯仿 、 N,N-二甲基甲酰胺 为溶剂, 反应 42.0h, 生成 4-[[2-[Tert-butyl(diphenyl)silyl]oxyphenyl]methyl]phenol参考文献:名称:The chemistry of novolac resins. Part 4. The strategic synthesis of model compounds摘要:An ion assisted ortho-specific phenol-formaldehyde condensation process, incorporating selective protecting-deprotecting methodology has been adapted to prepare a range of model novolac compounds which are ideal for studying crosslinking with hexamethylenetetramine. (C) 1997 Elsevier Science Ltd.DOI:10.1016/s0040-4020(97)00903-4
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:Finn et al., Journal of Applied Chemistry, 1954, vol. 4, p. 497,502摘要:DOI:
文献信息
-
Method for the preparation of aromatic chloroformates申请人:Davis Charles Gary公开号:US20060293535A1公开(公告)日:2006-12-28A method for preparing an aromatic chloroformate comprising, introducing a mixture of at least one aromatic hydroxyl compound, phosgene, at least one solvent, and at least one organic base into a flow reactor to obtain a unidirectionally flowing reaction mixture. The unidirectionally flowing reaction mixture is maintained at a temperature between about 0° C. and about 60° C. to produce a single product stream comprising an aromatic chloroformate.
-
Bioinspired Honokiol Analogs and Their Evaluation for Activity on the Norepinephrine Transporter作者:Kristen Stout、Marketa Bernaskova、Gary Miller、Antje Hufner、Wolfgang SchuehlyDOI:10.3390/molecules23102536日期:——
In traditional Asian medicinal systems, preparations of the root and stem bark of Magnolia species are widely used to treat anxiety and other nervous disturbances. The biphenyl-type neolignans honokiol and magnolol are the main constituents of Magnolia bark extracts. In the central nervous system, Magnolia bark preparations that contain honokiol are thought to primarily interact with γ-aminobutyric acid A (GABAA) receptors. However, stress responses inherently involve the noradrenergic system, which has not been investigated in the pharmacological mechanism of honokiol. We present here interactions of honokiol and other synthesized biphenyl-type neolignans and diphenylmethane analogs with the norepinephrine transporter (NET), which is responsible for the synaptic clearance of norepinephrine and the target of many anxiolytics. Of the synthesized compounds, 16 are new chemical entities, which are fully characterized. The 52 compounds tested show mild, non-potent interactions with NET (IC50 > 100 µM). It is thus likely that the observed anxiolytic effects of, e.g., Magnolia preparations, are not due to direct interaction with the noradrenergic system.
在传统的亚洲药物系统中,玉兰属植物的根和茎皮制剂被广泛用于治疗焦虑和其他神经紊乱。双苯型新木兰醇和木兰醇是玉兰树皮提取物的主要成分。在中枢神经系统中,含有新木兰醇的玉兰树皮制剂被认为主要与γ-氨基丁酸A(GABAA)受体相互作用。然而,应激反应本质上涉及未在新木兰醇的药理机制中进行研究的去甲肾上腺素系统。我们在这里介绍了新木兰醇和其他合成的双苯型新木兰醇和二苯甲烷类似物与去甲肾上腺素转运蛋白(NET)的相互作用,该蛋白负责去甲肾上腺素的突触清除,是许多抗焦虑药物的靶点。在合成的化合物中,有16种是新的化学实体,已经完全表征。测试的52种化合物与NET显示出轻微、非强效的相互作用(IC50 > 100 µM)。因此,例如玉兰制剂的观察到的抗焦虑效果可能不是由于与去甲肾上腺素系统的直接相互作用。 -
Highly efficient and recyclable alkylammonium hydrosulfate catalyst for formation of bisphenol F by condensation of phenol with formaldehyde作者:Jiafu Xiao、Hua Huang、Weijian Xiang、Wei Liao、Junyi Liu、Xichun She、Qiong Xu、Zaihui Fu、Steven Robert Kirk、Dulin YinDOI:10.1039/c6ra07385a日期:——spectroscopy with a basic indicator 4-nitroaniline. The catalytic performance of these hydrosulfates for the condensation of phenol with formaldehyde to bisphenol F (BPF) was evaluated in detail on a batch reactor. The results indicated that the proposed catalysts are very active for such condensation due to its homogeneous catalysis characteristics in reaction conditions. Among the catalysts examined,几种C 1 – C 4烷基硫酸氢盐[R 3 NH] [HSO 4 ]可以方便地从廉价的原料硫酸和烷基胺中制备。通过化学滴定法测量其酸度,并使用紫外-可见光谱法和碱性指示剂4-硝基苯胺进行测定。在间歇反应器上详细评估了这些硫酸氢盐对苯酚与甲醛缩合为双酚F(BPF)的催化性能。结果表明,所提出的催化剂由于在反应条件下的均相催化特性而对这种缩合反应非常有效。在所研究的催化剂中,[H 3 NCH 2 CH 2 NH 3] [HSO 4 ] 2显示出最佳的催化性能,并且可以实现甲醛的完全转化,在最佳条件下对BPF的选择性高于90%。此外,可以通过与环己烷的共沸蒸馏从反应混合物中回收催化剂以除去水,然后过滤,并重复使用六次,几乎没有活性损失,显示出优异的可重复使用性。建议本催化方法结合了均质反应和异质回收的特点,因此可能为合成双酚F提供高效,环保和低成本的途径。
-
Method for the preparation of aliphatic chloroformates申请人:Davis Charles Gary公开号:US20060084822A1公开(公告)日:2006-04-20A method for preparing an aliphatic chloroformate comprising, introducing a mixture of at least one aliphatic hydroxyl compound, phosgene, at least one solvent, and optionally at least one organic base into a flow reactor to obtain a unidirectional flowing reaction mixture. The at least one aliphatic hydroxyl compound comprises at least one aliphatic hydroxyl group. The unidirectional flowing reaction mixture is maintained at a temperature between about 0° C. and about 60° C. to produce a single product stream comprising an aliphatic chloroformate.
-
Optically active compound and photosensitive resin composition申请人:——公开号:US20030211421A1公开(公告)日:2003-11-13A photoactive compound is used in combination with a photosensitizer, represented by the following formula (1): A −[( J ) m −( X-Pro )] n (1) wherein A represents a hydrophobic unit comprising at least one kind of hydrophobic groups selected from a hydrocarbon group and a heterocyclic group, J represents a connecting group, X-Pro represents a hydrophilic group protected by a protective group Pro which is removable by light exposure, m represents 0 or 1, and n represents an integer of not less than 1. The protective group Pro may be removable by light exposure in association with the photosensitizer (especially, a photo acid generator), or may be a hydrophobic protective group. The hydrophilic group may be a hydroxyl group or a carboxyl group. The photoactive compound has high sensitivity to a light source of short wavelength beams, for resist application, therefore, the photoactive compound is advantageously used for forming a pattern with high resolution.
表征谱图
-
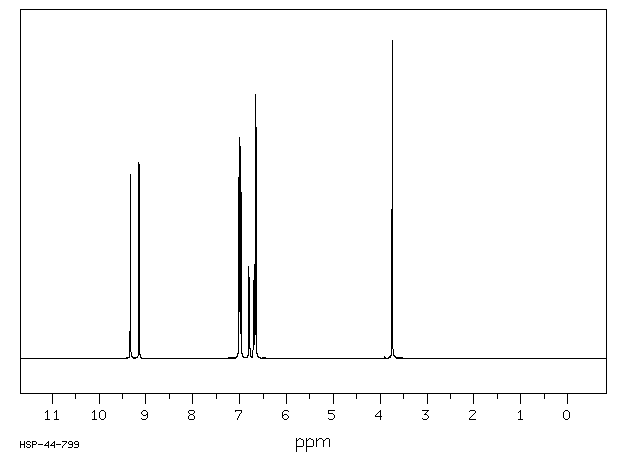
氢谱1HNMR
-
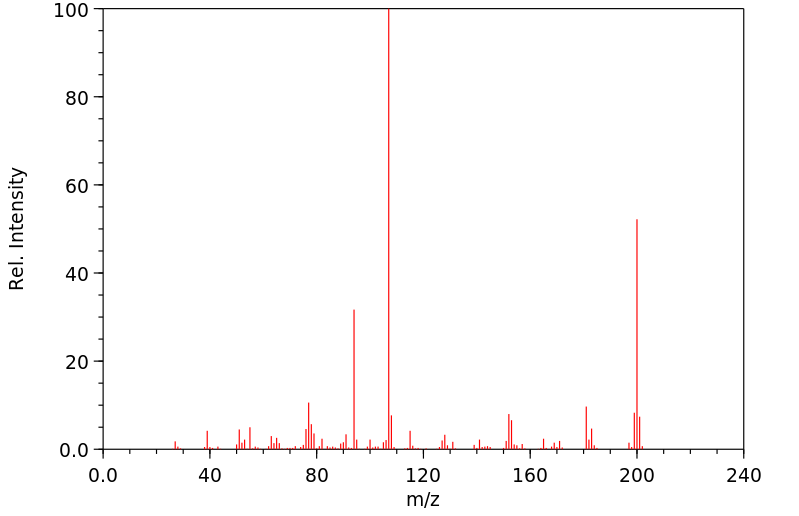
质谱MS
-
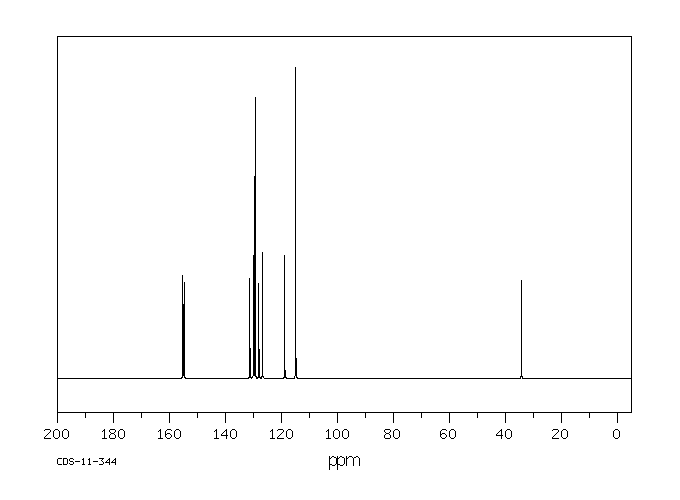
碳谱13CNMR
-
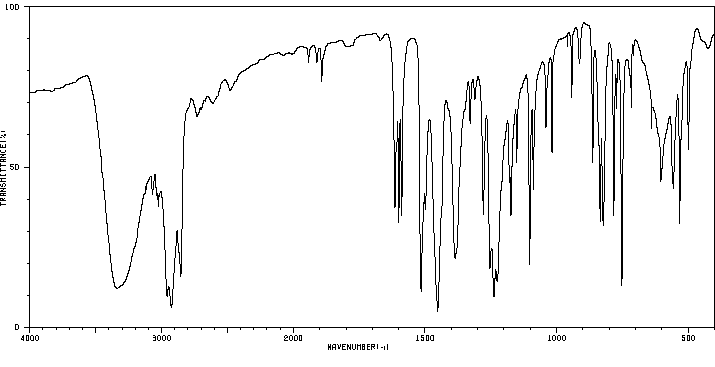
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息