醋酸 | 64-19-7
中文名称
醋酸
中文别名
冰醋酸;乙酸;乙酸,无水;冰乙酸
英文名称
acetic acid
英文别名
ethanoic acid;acoh;glacial acetic acid;HOAc;acetic;acetol;aqueous acetic acid;CH3COOH;acetate
CAS
64-19-7
化学式
C2H4O2
mdl
——
分子量
60.0526
InChiKey
QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:16.2 °C(lit.)
-
沸点:117-118 °C(lit.)
-
密度:1.049 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
-
蒸气密度:2.07 (vs air)
-
闪点:104 °F
-
溶解度:酒精:混溶(lit.)
-
最大波长(λmax):λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.05λ: 270 nm Amax: 0.02λ: 300 nm Amax: 0.01λ: 500 nm Amax: 0.01
-
介电常数:4.1(2℃)
-
暴露限值:TLV-TWA 10 ppm ~25 mg/m3) (ACGIH, OSHA, and MSHA); TLV-STEL 15 ppm (37.5 mg/m3) (ACGIH).
-
LogP:-0.170
-
物理描述:Liquid
-
颜色/状态:Clear, colorless liquid
-
气味:Pungent
-
味道:Burning taste
-
蒸汽密度:2.07 (NTP, 1992) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:15.7 mm Hg at 25 °C /Extrapolated/
-
水溶性:1.22
-
亨利常数:Henry's Law constant = 1.43X10-7 atm-cu m/mol at 25 °C in dilute aqueous solution
-
大气OH速率常数:7.40e-13 cm3/molecule*sec
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
纯乙酸在16℃以下时会结成冰状固体,因此被称为冰醋酸。当水加入到乙酸中后,混合物的总体积会减小,密度增加;分子比为1:1。进一步稀释则不会出现类似体积变化。它具有刺激性气味。
-
从化学性质来看,乙酸呈弱酸性(Ka=1.75×10^-5, 25℃),能够与碳酸氢钠、碳酸钠和氢氧化钠反应生成盐类;与三氯化磷、五氯化磷或亚硫酰氯作用时形成酰氯;与脱水剂共热可生成乙酸酐;在浓硫酸催化下,它还能与醇类发生酯化反应;与氨、碳酸铵或胺类化合物结合会生成酰胺。此外,其钠盐与碱石灰加热能释放出甲烷气体;钙、钡、锰及铅的乙酸盐强热时可产生丙酮;而α-氢原子较为活泼,容易被卤素取代生成α-卤代乙酸。
-
低浓度的乙酸无毒,但当其水溶液或在溶剂中的浓度超过50%时,对皮肤有强烈腐蚀性,且对眼睛、呼吸道、食道及胃产生强烈刺激作用,可能导致呕吐、腹泻、神经麻痹和尿中毒,甚至危及生命。小鼠和家兔的口服半数致死量分别为3310mg/kg和1200mg/kg,在工作场所,乙酸的最大允许浓度为10×10^-6。吸入被污染空气的人应立即移至新鲜空气中;若皮肤接触到乙酸,应使用大量清水或2%碳酸氢钠溶液冲洗;误服时,应用温水或2.5%氧化镁溶液洗胃(禁止用碳酸氢钠)。对于重度中毒者,应及时送医救治。
-
稳定性:稳定
-
避免接触碱类和强氧化剂
-
不会发生聚合反应
-
-
自燃温度:867 °F (463 °C)
-
分解:When heated to decomposition it emits irritating fumes.
-
粘度:1.056 mPa-s at 25 °C
-
腐蚀性:Corrosive organic acid
-
燃烧热:874.2 kJ/mol
-
汽化热:23.36 at 25 °C; 23.70 kJ/mol at 117.9 °C;
-
表面张力:27.10 mN/m at 25 °C
-
电离电位:10.66 eV
-
聚合:A drum contaminated with acetic acid was filled with acetaldehyde. The ensuing exothermic polymerization reaction caused a mild eruption lasting for several hours.
-
气味阈值:Odor Threshold Low: 0.03 [mmHg]; Odor Threshold High: 0.15 [mmHg]; Detection odor threshold from AIHA (mean = 0.074 ppm)
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.3720 @ °C/D
-
解离常数:4.76 (at 25 °C)
-
相对蒸发率:Evaporation rate ... at 25 °C and a wind speed of 4.5 m/sec (16.1 kg/hr) is 0.24 g/sq m/sec ... evaporation rates of 0.077 g/sq m/sec at 0 °C and 0.42 g/sq m/sec at 30 °C ... for wind speed of 4.5 m/sec.
-
保留指数:594 ;660.4 ;625 ;642 ;642 ;590 ;600 ;638 ;630 ;617 ;617 ;584 ;580 ;620.77 ;650 ;650 ;634 ;648 ;600 ;611 ;622 ;648 ;646 ;621
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-0.2
-
重原子数:4
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.5
-
拓扑面积:37.3
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:2
ADMET
代谢
醋酸...能被大多数组织轻易代谢,并可能作为中间产物产生酮体。在体外,醋酸盐被并入磷脂、中性脂质、类固醇、甾醇以及多种人和动物组织准备中的饱和和不饱和脂肪酸中。...在小鼠中代谢14(C)醋酸导致与血浆蛋白部分和大多数主要组织的放射性相关联。
Acetic acid ... is readily metabolized by most tissues and may give rise to the production of ketone bodies as intermediates. In vitro, acetate is incorporated into phospholipids, neutral lipids, steroids, sterols, and saturated and unsaturated fatty acids in a variety of human and animal tissue preparations. ...Metabolism of 14(C) acetate in mice results in radioactivity associated with the protein fractions of plasma and most major tissues.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
In the body, acetic acid is partially converted into formic acid.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
When dogs were administered large doses (1-2 g/kg ip or sc) of sodium acetate, only small amounts appeared in the urine, which is evidence of the rapid utilization of acetic acid.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
Acetic Acid is a known human metabolite of acetaldehyde.
来源:NORMAN Suspect List Exchange
代谢
铅通过吸入、口服和皮肤接触被吸收,然后主要分布到骨骼和红细胞中。在血液中,铅可能被发现与血清白蛋白或金属结合蛋白金属lothionein结合。有机铅通过细胞色素P-450酶代谢,而无机铅与δ-氨基酮酸脱氢酶形成复合物。铅主要通过尿液和粪便排出。
Lead is absorbed following inhalation, oral, and dermal exposure. It is then distributed mainly to the bones and red blood cells. In the blood lead may be found bound to serum albumin or the metal-binding protein metallothionein. Organic lead is metabolized by cytochrome P-450 enzymes, whereas inorganic lead forms complexes with delta-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase. Lead is excreted mainly in the urine and faeces. (L136)
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
识别和使用:醋酸是一种无色液体或固体,具有刺鼻的特征性气味,稀释在水中具有酸味。冰醋酸是一种99%活性的化学品。它被用作酸化剂、调味剂,用于防止烘焙中的绳索形成,以及作为溶剂。醋酸在化学和生物化学分析中用作实验室试剂,在铅烟雾的现场测试、氯乙烯测定、尿液中的尿酸、苯胺蒸气以及气体的分离中。此外,醋酸还用于农药配方中,作为一种除草剂,用于控制水果、蔬菜、观赏植物和草坪上的杂草。它也是液压破裂流体的组成部分,防止金属氧化物(铁控制)的沉淀。在美国注册使用,但批准的农药用途可能会定期更改,因此必须咨询联邦、州和地方当局以获取当前批准的用途。3%至5%的醋酸在妇科学领域常用于宫颈的阴道镜检查。它产生一种“醋白”效果,可能帮助临床医生识别肿瘤区域。人类暴露和毒性:醋酸从胃肠道、通过肺部吸收,几乎完全被组织氧化。这些代谢途径相当了解,涉及酮体形成。仅1.0毫升的冰醋酸就可能导致食道穿孔。在醋酸透析期间,患者频繁出现突然的低血压和心律不齐,并伴有所谓的失衡综合症的症状。在超过25 ppm的浓度下,眼睛和鼻腔极度刺激,并且在低于10 ppm的浓度下报告了结膜炎。冰醋酸导致了永久性角膜混浊。摄入200毫升80%的醋酸溶液导致反复心梗休克和大量肠道出血,导致有机脑综合症。通过使用血液透析和强化治疗,患者存活了中毒。在曾经接触过醋酸和醋酐的前化学工厂工人中,观察到了过多的前列腺癌。动物研究:醋酸的毒性作用是由于其刺激性质以及对中枢神经系统和肾脏的影响。大鼠和小鼠口服大剂量会导致中枢神经系统抑制和死亡。吸入16,000 ppm的醋酸导致6只暴露大鼠中有1只死亡。将3-6只大鼠分成一组,在饮水中给予醋酸,持续9-15周。所有处理组的液体摄取量相同,在高剂量组中,体重增加逐渐减少,食欲减退和食物消耗量下降。将4组各2只幼猪每天喂食连续30天的饮食,总共150天。对照组和试验组在生长速度、体重增加、早晨尿氨和终末血pH方面存在差异。在妊娠第6-19天通过灌胃给予大鼠、小鼠或家兔醋酸,剂量高达1600 mg/kg/天,醋酸对植入或母体或胎儿存活没有影响。测试组软组织或骨骼组织中异常的数量与对照组发生的数量没有差异。醋酸在使用或不使用代谢激活的情况下,对几种沙门氏菌属的菌株没有显示出致突变活性。在中性pH下,醋酸对培养的中国仓鼠卵巢K1细胞没有表现出裂变作用,但在pH 5.2至6.0时,无论是否进行代谢激活,都表现出裂变作用。生态毒性研究:醋酸对水生生物有害。高浓度产生的pH水平对氧化细菌有毒,抑制了氧气需求。对蚊子鱼是致命的:在320 ppm及更高浓度下,所有鱼在24小时内死亡。
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: Acetic acid is a colorless liquid or solid, having a pungent characteristic odor, and when diluted in water an acidic taste. Glacial acetic acid is a 99% active chemical. It is used as an acidifier, flavoring agent, for the prevention of rope in baking, and as a solvent. Acetic acid is used as a laboratory reagent in chemical and biochemical analysis, in field testing of lead fumes, vinyl chloride determination, uric acid in urine, aniline vapors, and separation of gases. In addition, acetic acid is used in pesticide formulations as a herbicide to controls weeds on fruits, vegetables, ornamentals and turf. It is also a component of the hydraulic fracturing fluids preventing precipitation of metal oxides (iron control). Registered for use in the U.S., but approved pesticide uses may change periodically, so federal, state and local authorities must be consulted for currently approved uses. Three to 5% acetic acid is commonly used in the field of gynecology for colposcopic examinations of the cervix. It gives an 'acetowhite' effect that may assist clinicians in identifying neoplastic areas. HUMAN EXPOSURE AND TOXICITY: Acetic acid is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and through the lungs and almost completely oxidized by tissues. The metabolic pathways are reasonably well known and involve the formation of ketone bodies. As little as 1.0 mL of glacial acetic acid has resulted in perforation of the esophagus. During acetic acid dialysis, patients showed a frequent onset of sudden hypotension and arrhythmia with concomitant symptoms of the so-called disequilibrium syndrome. Extreme eye and nasal irritation has occurred at concentrations in excess of 25 ppm and conjunctivitis from concentrations below 10 ppm has been reported. Glacial acetic acid has caused permanent corneal opacification. Ingestion of 200 mL of an 80% solution of acetic acid caused repeated shock due to myocardial infarction and massive intestinal bleeding led to an organic brain psychosyndrome. The patient survived the intoxication by use of hemodialysis and intensive care therapy. An excess of prostate cancer was observed among former chemical plant workers, some of whom had been exposed to both acetic acid and acetic anhydride. ANIMAL STUDIES: Toxic effects of acetic acid are due to irritant properties as well as its effect on the central nervous system and kidneys. Large oral doses cause CNS depression and death in rats and mice. Inhalation of 16,000 ppm killed 1 of 6 exposed rats. Groups of 3-6 rats were given acetic acid in drinking water for periods from 9-15 weeks. Fluid uptake was the same in all treatment groups, at the high dose group there was a progressive reduction in body weight gain, loss of appetite and fall in food consumption. Four groups of two young pigs were fed daily diets for successive 30 day periods for a total of 150 days. There were differences in growth rate, weight gain, early morning urinary ammonia and terminal blood pH between controls and test groups. Acetic acid had no effects on implantation or on maternal or fetal survival in rats, mice or rabbits dosed via gavage during gestation days 6-19 at doses up to 1600 mg/kg/day. The number of abnormalities seen in either soft or skeletal tissues of the test groups did not differ from the number occurring in the controls. Acetic acid has shown no evidence of mutagenic activity with or without metabolic activation using several strains of Salmonella typhimurium. Acetic acid did not show clastogenicity on cultured Chinese hamster ovary K1 cells at neutral pH, but it was clastogenic at pH 5.2 to 6.0 with or without metabolic activation. ECOTOXICITY STUDIES: Acetic acid was harmful to aquatic life. High concentrations produced pH levels toxic to oxidizing bacteria, inhibiting oxygen demand. It was lethal to Mosquito fish: at 320 ppm and higher all fish were dead at 24 hours.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
铅模仿其他生物学上重要的金属,如锌、钙和铁,作为许多相应酶促反应的辅因子与之竞争。例如,铅已被证明能竞争性地抑制钙与钙调蛋白的结合,干扰神经递质的释放。它在对NMDA受体和蛋白激酶C上也表现出类似的竞争性抑制作用,这损害了大脑微血管的形成和功能,并改变了血脑屏障。铅还通过影响多巴胺合成的调节和阻止乙酰胆碱的诱发释放来影响神经系统。然而,其主要作用机制是通过抑制delta-aminolevulinic酸脱氢酶,该酶在血红素生物合成中至关重要,而血红素是血红蛋白必不可少的辅因子。(T4, A20, A22, L136)
Lead mimics other biologically important metals, such as zinc, calcium, and iron, competing as cofactors for many of their respective enzymatic reactions. For example, lead has been shown to competitively inhibit calcium's binding of calmodulin, interferring with neurotransmitter release. It exhibits similar competitive inhibition at the NMDA receptor and protein kinase C, which impairs brain microvascular formation and function, as well as alters the blood-brain barrier. Lead also affects the nervous system by impairing regulation of dopamine synthesis and blocking evoked release of acetylcholine. However, it's main mechanism of action occurs by inhibiting delta-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase, an enzyme vital in the biosynthesis of heme, which is a necesssary cofactor of hemoglobin. (T4, A20, A22, L136)
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
醋酸因其腐蚀性而有毒。除了会导致皮肤灼伤和粘膜刺激外,摄入还可能导致消化系统严重损伤和血液酸度可能致命的变化。
Acetic acid is toxic due to its corrosive nature. In addition to causing skin burns and irritation to the mucous membranes, ingestion can result in severe damage to the digestive system and a potentially lethal change in the acidity of the blood. (L1885)
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
Organic lead compounds are not classifiable as to their carcinogenicity to humans (Group 3). To the extent that organic lead compounds are metabolized in part to ionic lead, they are expected to exert the toxicities associated with inorganic lead (Group 2A, probably carcinogenic to humans). (L135)
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
对人类无致癌性(未列入国际癌症研究机构IARC清单)。
No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC).
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
吸收、分配和排泄
醋酸从胃肠道和通过肺部被吸收。
Acetic acid is absorbed from the GI tract and through the lung.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
安全信息
-
职业暴露等级:A
-
职业暴露限值:TWA: 10 ppm (25 mg/m3), STEL: 15 ppm (37 mg/m3)
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:8
-
立即威胁生命和健康浓度:50 ppm
-
危险品标志:C
-
安全说明:S23,S24/25,S26,S36/37/39,S45
-
危险类别码:R35,R10
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:29152100
-
危险品运输编号:UN 1792 8/PG 2
-
危险类别:8
-
RTECS号:NN1650000
-
包装等级:II
-
危险标志:GHS02,GHS05
-
危险性描述:H226,H314
-
危险性防范说明:P210,P260,P280,P303 + P361 + P353,P305 + P351 + P338 + P310,P370 + P378
-
储存条件:1. 使用铝合金桶或塑料桶进行包装。大量运输通常通过铁路槽车完成,有时也会采用驳船运输乙酸。在贮运过程中,应远离火种、热源,并避免与氧化剂和碱类物品共存混运。存储容器需密封,注意防火防爆。 2. 储存注意事项 - 存储于阴凉通风的库房。 - 远离火种及热源。 - 冬季保持库温高于16℃以防凝固。 - 容器应密封保存。 - 与氧化剂和碱类分开存放,切忌混存。 - 使用防爆型照明和通风设施。 - 禁止使用易产生火花的机械设备和工具。 - 储区需配备泄漏应急处理设备及合适的收容材料。
制备方法与用途
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 羟基乙酸 Glycolic Acid 79-14-1 C2H4O3 76.052 乙酸甲酯 Methyl acetate 79-20-9 C3H6O2 74.0794 丙酸 propionic acid 79-09-4 C3H6O2 74.0794 丙酸-1-13C <1-(13)C>-Propionic acid 6212-69-7 C3H6O2 75.0684 羟乙醛 Glycolaldehyde 141-46-8 C2H4O2 60.0526 丙烯酸 acrylic acid 59913-86-9 C3H4O2 72.0636 巯基乙酸 mercaptoacetic acid 68-11-1 C2H4O2S 92.1186 聚甘氨酸 glycine 25718-94-9 C2H5NO2 75.0672 碘乙酸 Iodoacetic acid 64-69-7 C2H3IO2 185.949 乙酸-D1 deuteroacetic acid 758-12-3 C2H4O2 61.0446 氯乙酸 chloroacetic acid 79-11-8 C2H3ClO2 94.4976 过氧乙酸 peracetic acid 79-21-0 C2H4O3 76.052 溴乙酸 bromoacetic acid 79-08-3 C2H3BrO2 138.949 草酸 oxalic acid 144-62-7 C2H2O4 90.0355 - 1
- 2
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 乙酸-18O2 [18O]-acetic acid 17217-83-3 C2H4O2 64.0538 羟基乙酸 Glycolic Acid 79-14-1 C2H4O3 76.052 乙醛酸 Glyoxilic acid 298-12-4 C2H2O3 74.0361 丙酸 propionic acid 79-09-4 C3H6O2 74.0794 乙酸甲酯 Methyl acetate 79-20-9 C3H6O2 74.0794 羟乙醛 Glycolaldehyde 141-46-8 C2H4O2 60.0526 氯乙酸 chloroacetic acid 79-11-8 C2H3ClO2 94.4976 碘乙酸 Iodoacetic acid 64-69-7 C2H3IO2 185.949 聚甘氨酸 glycine 25718-94-9 C2H5NO2 75.0672 乙酰基次氟酸酯 acetyl hypofluorite 78948-09-1 C2H3FO2 78.043 溴乙酸 bromoacetic acid 79-08-3 C2H3BrO2 138.949 丙烯酸 acrylic acid 59913-86-9 C3H4O2 72.0636 乙酸-D1 deuteroacetic acid 758-12-3 C2H4O2 61.0446 过氧乙酸 peracetic acid 79-21-0 C2H4O3 76.052 —— acetyl hypobromite 4254-22-2 C2H3BrO2 138.949 —— acetyl hypochlorite 758-11-2 C2H3ClO2 94.4976 —— 18F-acetyl hypofluorite 84243-94-7 C2H3FO2 77.0446 —— acetyl hypoiodite 6540-76-7 C2H3IO2 185.949 丙炔酸 Propiolic acid 471-25-0 C3H2O2 70.0477 草酸 oxalic acid 144-62-7 C2H2O4 90.0355 - 1
- 2
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:[EN] METHODS AND COMPOUNDS FOR RESTORING MUTANT p53 FUNCTION
[FR] MÉTHODES ET COMPOSÉS POUR LA RESTAURATION DE LA FONCTION DU P53 MUTANT摘要:公开号:WO2021231474A9 -
作为产物:参考文献:名称:烯酮在水溶液中水解的速率和机理摘要:DOI:10.1021/j100461a027
-
作为试剂:描述:5-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenoxy)-6-methoxy-4-methyl-8-nitroquinoline 在 盐酸 、 tin(II) chloride dihdyrate 、 溶剂黄146 作用下, 以 水 为溶剂, 反应 5.0h, 生成 2-(5-((5-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenoxy)-6-methoxy-4-methylquinolin-8-yl)amino)hexyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione参考文献:名称:探索未开发的化学空间:合理鉴定具有抗疟特性的新型他非诺喹类似物摘要:专利倾向于定义由马库什结构的组合性质描述的巨大化学空间。然而,新主要活性成分的优化通常是由简单的 Free Wilson 方法驱动的。这一过程导致对命中化合物附近的化学空间进行高度集中的研究,留下许多可能存在高度生物活性储层的未探索区域。这项研究旨在证明,这种公开的化学空间可以隐藏具有值得研究的有趣潜在生物活性的化合物。这强调了拓宽传统策略之外的方法的价值和必要性。因此,我们主张采用一种在早期药物发现阶段可能更有效的替代方法。我们选择2018年FDA批准的单剂量根治疟疾药物他非诺喹的案例来说明这一过程。通过对他非诺喹化学空间的深入探索,合理鉴定并合成了七种具有潜在抗疟活性的化合物。这一小组代表了迄今为止报道的 58 种类似物尚未探索的化学多样性。经过生物学评估,结果证明我们的合理设计方法已被证明是一种非常有效的探索性方法,适合早期药物发现阶段。DOI:10.1016/j.bioorg.2024.107472
文献信息
-
BENZOTHIOPHENE INHIBITORS OF RHO KINASE申请人:Kahraman Mehmet公开号:US20080021026A1公开(公告)日:2008-01-24The present invention relates to compounds and methods which may be useful as inhibitors of Rho kinase for the treatment or prevention of disease.本发明涉及化合物和方法,这些化合物和方法可能作为Rho激酶的抑制剂在治疗或预防疾病方面有用。
-
Synthesis and Biological Activity of Peptide α-Ketoamide Derivatives as Proteasome Inhibitors作者:Salvatore Pacifico、Valeria Ferretti、Valentina Albanese、Anna Fantinati、Eleonora Gallerani、Francesco Nicoli、Riccardo Gavioli、Francesco Zamberlan、Delia Preti、Mauro MarastoniDOI:10.1021/acsmedchemlett.9b00233日期:2019.7.11Proteasome activity affects cell cycle progression as well as the immune response, and it is largely recognized as an attractive pharmacological target for potential therapies against several diseases. Herein we present the synthesis of a series of pseudodi/tripeptides bearing at the C-terminal position different α-ketoamide moieties as pharmacophoric units for the interaction with the catalytic threonine
-
Air-Tolerant Direct Thiol Esterification with Carboxylic Acids Using Hydrosilane via Simple Inorganic Base Catalysis作者:Maojie Xuan、Chunlei Lu、Meina Liu、Bo-Lin LinDOI:10.1021/acs.joc.9b00500日期:2019.6.21thioesterification of carboxylic acids with thiols using nontoxic activation agents is highly desirable. Herein, an efficient and practical protocol using safe and inexpensive industrial waste polymethylhydrosiloxane as the activation agent and K3PO4 with 18-crown-6 as a catalyst is described. Various functional groups on carboxylic acid and thiol substituents can be tolerated by the present system to afford thioesters
-
Synthesis and Properties of Aminoacylamido-AMP: Chemical Optimization for the Construction of an <i>N</i>-Acyl Phosphoramidate Linkage作者:Tomohisa Moriguchi、Terukazu Yanagi、Masao Kunimori、Takeshi Wada、Mitsuo SekineDOI:10.1021/jo0008338日期:2000.12.1This paper describes the design and synthesis of a new type of aminoacyl-adenylate analogue (aa-AMPN) having an N-acyl phosphoramidate linkage where the oxygen atom of the mixed anhydride bond of aminoacyl-adenylate (aa-AMP) is replaced by an amino group. This new type of aa-AMP analogue is expected to be useful as material for studies on the recognition mechanism of the aminoacylation of tRNA and本文介绍了具有N-酰基氨基磷酸酯键的新型氨基酰基-腺苷酸类似物(aa-AMPN)的设计和合成,其中氨基酰基-腺苷酸(aa-AMP)的混合酸酐键的氧原子被氨基。这种新型的aa-AMP类似物有望用作研究tRNA氨基酰化和其他生化反应识别机制的材料。羧酰胺的亚磷酰胺衍生物与核苷衍生物的缩合失败,因为活化的亚磷酰胺衍生物不仅与羟基反应,而且与另一种反应性物质反应。通过5'-O-亚磷酰胺基腺苷衍生物与羧酰胺衍生物的反应研究了另一种方法。选择TBTr和TSE基团分别用于保护氨基酸酰胺的氨基和磷酸基。详细研究表明,使用5-(3,5-二硝基苯基)-1H-四唑作为亚磷酰胺的活化催化剂可在10分钟内迅速缩合,从而得到完全保护的aa-AMPN衍生物。没有发生副反应。通过两步程序对这些产物进行脱保护,得到高产率的aa-AMPN衍生物。还证明由此获得的aa-AMPN在酸性和碱性条件下均是稳定的,例如0.1M HCl(pH
-
Electrophilic Sulfonium-Promoted Peptide and Protein Amidation in Aqueous Media作者:Chuan Wan、Yuan Feng、Zhanfeng Hou、Chenshan Lian、Liang Zhang、Yuhao An、Jinming Sun、Dongyan Yang、Chenran Jiang、Feng Yin、Rui Wang、Zigang LiDOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.1c04017日期:2022.1.21A novel amidation strategy using electrophilic sulfonium, which is soluble and stable in aqueous conditions, was developed. The sulfoniums could activate thioacid and carboxyl acid to efficiently react with amines to afford amides. This method enables applications in amidation in both aqueous media and solid-phase peptide synthesis, peptide/protein modifications, and reactive lysines of a proteome
表征谱图
-
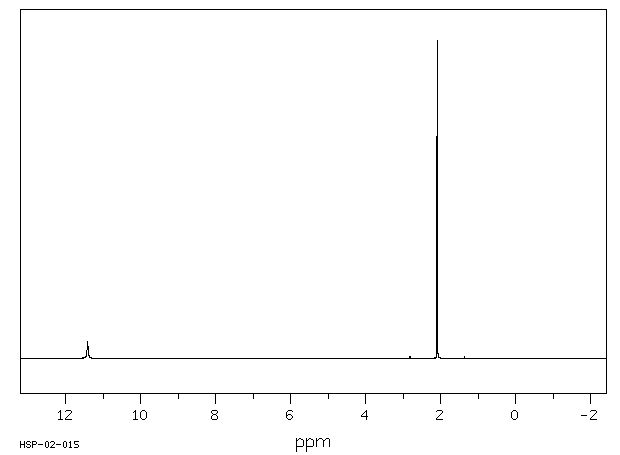
氢谱1HNMR
-
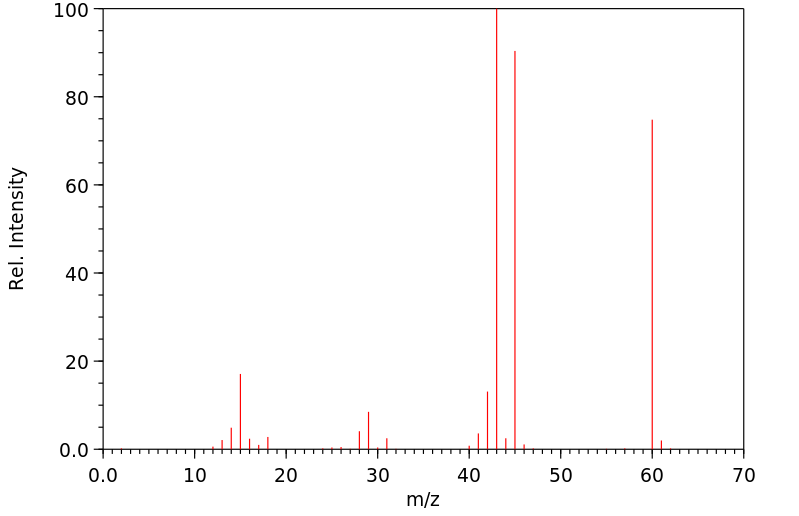
质谱MS
-
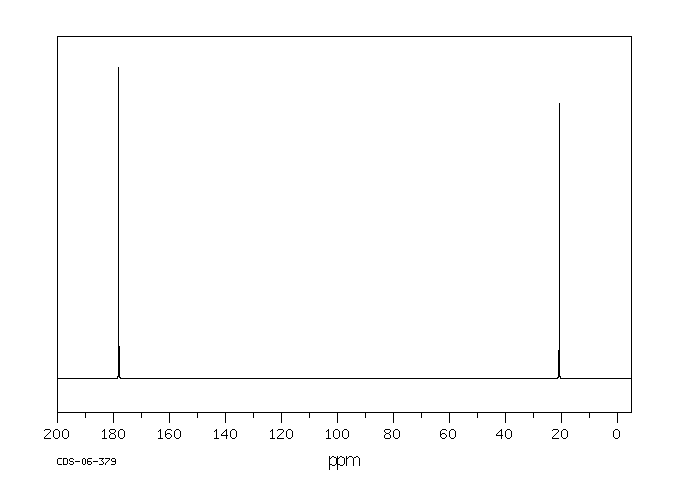
碳谱13CNMR
-
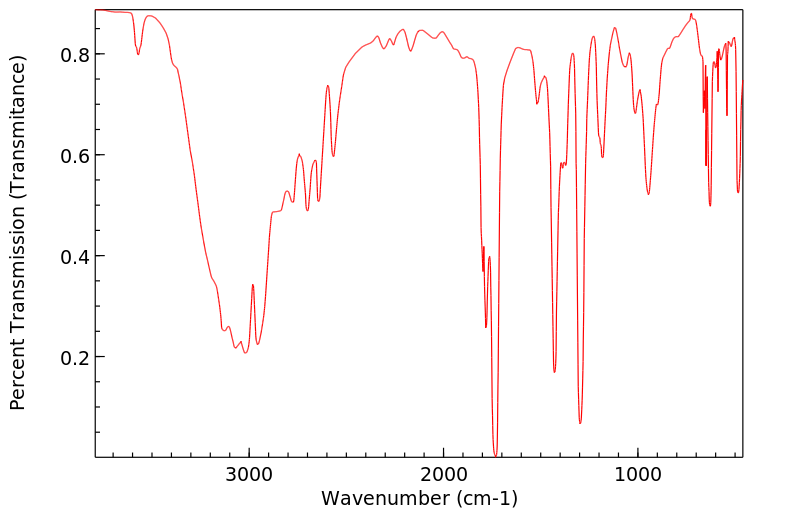
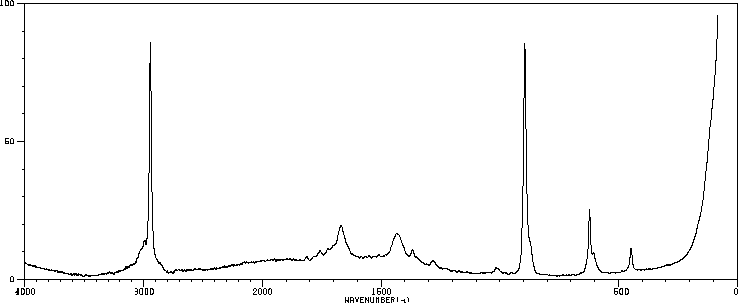
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(甲基3-(二甲基氨基)-2-苯基-2H-azirene-2-羧酸乙酯)
(±)-盐酸氯吡格雷
(±)-丙酰肉碱氯化物
(d(CH2)51,Tyr(Me)2,Arg8)-血管加压素
(S)-(+)-α-氨基-4-羧基-2-甲基苯乙酸
(S)-阿拉考特盐酸盐
(S)-赖诺普利-d5钠
(S)-2-氨基-5-氧代己酸,氢溴酸盐
(S)-2-[[[(1R,2R)-2-[[[3,5-双(叔丁基)-2-羟基苯基]亚甲基]氨基]环己基]硫脲基]-N-苄基-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(S)-2-[3-[(1R,2R)-2-(二丙基氨基)环己基]硫脲基]-N-异丙基-3,3-二甲基丁酰胺
(S)-1-(4-氨基氧基乙酰胺基苄基)乙二胺四乙酸
(S)-1-[N-[3-苯基-1-[(苯基甲氧基)羰基]丙基]-L-丙氨酰基]-L-脯氨酸
(R)-乙基N-甲酰基-N-(1-苯乙基)甘氨酸
(R)-丙酰肉碱-d3氯化物
(R)-4-N-Cbz-哌嗪-2-甲酸甲酯
(R)-3-氨基-2-苄基丙酸盐酸盐
(R)-1-(3-溴-2-甲基-1-氧丙基)-L-脯氨酸
(N-[(苄氧基)羰基]丙氨酰-N〜5〜-(diaminomethylidene)鸟氨酸)
(6-氯-2-吲哚基甲基)乙酰氨基丙二酸二乙酯
(4R)-N-亚硝基噻唑烷-4-羧酸
(3R)-1-噻-4-氮杂螺[4.4]壬烷-3-羧酸
(3-硝基-1H-1,2,4-三唑-1-基)乙酸乙酯
(2S,4R)-Boc-4-环己基-吡咯烷-2-羧酸
(2S,3S,5S)-2-氨基-3-羟基-1,6-二苯己烷-5-N-氨基甲酰基-L-缬氨酸
(2S,3S)-3-((S)-1-((1-(4-氟苯基)-1H-1,2,3-三唑-4-基)-甲基氨基)-1-氧-3-(噻唑-4-基)丙-2-基氨基甲酰基)-环氧乙烷-2-羧酸
(2S)-2,6-二氨基-N-[4-(5-氟-1,3-苯并噻唑-2-基)-2-甲基苯基]己酰胺二盐酸盐
(2S)-2-氨基-N,3,3-三甲基-N-(苯甲基)丁酰胺
(2S)-2-氨基-3-甲基-N-2-吡啶基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基-N-(苯基甲基)丁酰胺,
(2S)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基-N-2-吡啶基丁酰胺
(2S,4R)-1-((S)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基丁酰基)-4-羟基-N-(4-(4-甲基噻唑-5-基)苄基)吡咯烷-2-甲酰胺盐酸盐
(2R,3'S)苯那普利叔丁基酯d5
(2R)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基-N-(苯甲基)丁酰胺
(2-氯丙烯基)草酰氯
(1S,3S,5S)-2-Boc-2-氮杂双环[3.1.0]己烷-3-羧酸
(1R,5R,6R)-5-(1-乙基丙氧基)-7-氧杂双环[4.1.0]庚-3-烯-3-羧酸乙基酯
(1R,4R,5S,6R)-4-氨基-2-氧杂双环[3.1.0]己烷-4,6-二羧酸
齐特巴坦
齐德巴坦钠盐
齐墩果-12-烯-28-酸,2,3-二羟基-,苯基甲基酯,(2a,3a)-
齐墩果-12-烯-28-酸,2,3-二羟基-,羧基甲基酯,(2a,3b)-(9CI)
黄酮-8-乙酸二甲氨基乙基酯
黄荧菌素
黄体生成激素释放激素(1-6)
黄体生成激素释放激素 (1-5) 酰肼
黄体瑞林
麦醇溶蛋白
麦角硫因
麦芽聚糖六乙酸酯
麦根酸