巯基乙酸 | 68-11-1
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:−16 °C(lit.)
-
沸点:96 °C5 mm Hg(lit.)
-
密度:1.326 g/mL at 20 °C(lit.)
-
蒸气密度:3.2 (vs air)
-
闪点:126 °C
-
溶解度:可溶于氯仿(少量)、甲醇(少量)
-
暴露限值:TLV-TWA 1 ppm (~3.8 mg/m3) (ACGIH).
-
LogP:0.090
-
物理描述:Thioglycolic acid appears as a colorless liquid with an unpleasant odor. Density 1.325 g / cm3. Used to make permanent wave solutions and depilatories. Corrosive to metals and tissue.
-
颜色/状态:Colorless liquid
-
气味:Strong, unpleasant odor
-
蒸汽密度:3.18 (Air = 1)
-
蒸汽压力:8.68X10-2 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
自燃温度:350 °C
-
分解:When heated to decomp it emits toxic fumes of /sulfur oxides/.
-
粘度:6.55 mPa.s (= cP) at 20 °C
-
腐蚀性:Corrosive
-
燃烧热:1450 kJ/mol
-
汽化热:627.2 J/g
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.5080 at 20 °C/D
-
解离常数:pKa = 3.55
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):0.1
-
重原子数:5
-
可旋转键数:1
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.5
-
拓扑面积:38.3
-
氢给体数:2
-
氢受体数:3
ADMET
安全信息
-
职业暴露等级:B
-
职业暴露限值:TWA: 1 ppm (4 mg/m3) [skin]
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:8
-
危险品标志:T+
-
安全说明:S23,S25,S27,S28,S28C,S36/37,S45
-
危险类别码:R26,R34,R24/25
-
WGK Germany:1
-
海关编码:2930909090
-
危险品运输编号:UN 1940 8/PG 2
-
危险类别:8
-
RTECS号:AI5950000
-
包装等级:II
-
危险标志:GHS05,GHS06
-
危险性描述:H301 + H311 + H331,H314
-
危险性防范说明:P280,P301 + P310 + P330,P303 + P361 + P353,P304 + P340 + P310,P305 + P351 + P338,P403 + P233
-
储存条件:储存注意事项: - 储存于阴凉、通风的库房。 - 远离火种、热源,保持容器密封。 - 应与氧化剂分开存放,切忌混储。 - 配备相应品种和数量的消防器材。 - 储区应备有泄漏应急处理设备和合适的收容材料。
SDS
| 国标编号: | 81611 |
| CAS: | 68-11-1 |
| 中文名称: | 巯基乙酸 |
| 英文名称: | thioglycolic acid;mercaptoacetic acid |
| 别 名: | 硫氢基乙酸;硫代乙醇酸 |
| 分子式: | C 2 H 4 O 2 S;HSCH 2 COOH |
| 分子量: | 92.12 |
| 熔 点: | -16.5℃ 沸点:123℃/ |
| 密 度: | 相对密度(水=1)1.33 |
| 蒸汽压: | >110℃ |
| 溶解性: | 与水混溶,可混溶于乙醇、乙醚,溶于普通溶剂 |
| 稳定性: | 稳定 |
| 外观与性状: | 无色透明液体,有强烈令人不愉快的气味 |
| 危险标记: | 20(酸性腐蚀品) |
| 用 途: | 用作测定铁的试剂及稳定剂,用于药水、烫发水制造等 |
2.对环境的影响:
一、健康危害
侵入途径:吸入、食入、经皮吸收。
健康危害:本品的毒作用,可能是其与某些酶的巯基的特殊作用有关,本品有强烈的刺激性。眼接触可致严重损害,导致永久性失明。可致皮肤灼伤;对皮肤有致敏性,引起过敏性皮炎。能经皮肤吸收引起中毒,动物皮肤贴敷本品10%溶液<5mL/kg即引起死亡。
二、毒理学资料及环境行为
毒性:属高毒类。其毒作用可能是与某些酶的巯基特殊作用有关。
急性毒性:LD50<50mg/kg(大鼠经口);250mg/kg(小鼠经口)
危险特性:遇明火、高热或与氧化剂接触,有引起燃烧爆炸的危险。受热分解产生有毒的硫化物烟气。具有较强的腐蚀性。
燃烧(分解)产物:一氧化碳、二氧化碳、硫化物。
3.现场应急监测方法:
4.实验室监测方法:
用碘-聚乙烯吡咯烷酮容量测定有机化合物:I直接测定[刊,西班牙]/Hernandez Mendez J.;Gonzalez Perez C.,Espada Saenz-Torre M.//Stud.Chem.Univ.Salamanca.-1984,(9).-57~64 《分析化学文摘》1987.8
5.环境标准:
前苏联 车间空气中有害物质的最高容许浓度 0.1mg/m3[皮]
6.应急处理处置方法:
一、泄漏应急处理
迅速撤离泄漏污染区人员至安全区,并进行隔离,严格限制出入。切断火源。建议应急处理人员戴自给正压式呼吸器,穿防酸碱工作服。不要直接接触泄漏物,尽可能切断泄漏源,防止进入下水道、排洪沟等限制性空间。小量泄漏:用砂土或其它不燃材料吸附或吸收。也可以用大量水冲洗,洗水稀释后放入废水系统。大量泄漏:构筑围堤或挖坑收容;用泡沫覆盖,降低蒸气灾害。用泵转移至槽车或专用收集器内,回收或运至废物处理场所处置。
二、防护措施
呼吸系统防护:可能接触其蒸气时,应该佩戴自吸过滤式防毒面具(半面罩)。紧急事态抢救或撤离时,建议佩戴自给式呼吸器。
眼睛防护:戴化学安全防护眼镜。
防护服:穿防酸碱工作服。
手防护:戴橡胶耐酸碱手套。
其它:工作场所禁止吸烟、进食和饮水,饭前要洗手。工作毕,淋浴更衣。单独存放被毒物污染的衣服,洗后备用。保持良好的卫生习惯。
三、急救措施
皮肤接触:脱去被污染的衣着,用大量流动清水冲洗,至少15分钟。就医。
眼睛接触:立即提起眼睑,用大量流动清水或生理盐水彻底冲洗至少15分钟。就医。
吸入:迅速脱离现场至空气新鲜处。保持呼吸道通畅。如呼吸困难,给输氧。如呼吸停止,立即进行人工呼吸。就医。
食入:误服者用水漱口,洗胃。给饮牛奶或蛋清。就医。
灭火方法:灭火剂:雾状水、泡沫、砂土。
制备方法与用途
巯基乙酸工业生产的方法有硫氢化钠法、硫代硫酸钠法、多硫化钠法等。这些方法均需要从巯基乙酸的水溶液中分离提取巯基乙酸。巯基乙酸的水溶液主要成分有9.0%~11.0%的巯基乙酸、20%~24.0%氯化钠和水。具体的分离步骤如下:
- 将巯基乙酸水溶液进行第一次浓缩减压蒸馏脱水;
- 对步骤(1)得到的浓缩液进行压滤,分离出固体氯化钠;
- 将步骤(2)所得的滤液进行第二次浓缩,浓缩液进行压滤;
- 将步骤(2)和(3)所得的固体氯化钠合并后进行洗涤,回收夹带的巯基乙酸;
- 将步骤(3)所得巯基乙酸的浓缩液加入稳定剂后减压精馏分离出巯基乙酸成品。
纯品巯基乙酸为无色透明液体,工业品为微黄色至无色,具有强烈刺激性气味。它能与水、乙醇和乙醚混溶。烫发类产品利用巯基乙酸断裂头发中的部分二硫化键来改变头发的弯曲程度,以达到烫发、美发效果。但是,巯基乙酸具有毒性,易经皮肤和呼吸道吸收,造成皮肤损伤过敏等症状,甚至影响机体代谢,长期接触会引起多种组织器官损伤,并具有较强的致突变性和生殖毒性。因此,需要对其进行严格的控制。
用途巯基乙酸(TGA)主要用作毛毯整理剂及冷烫液的原料。它既具羟酸的反应特征,又具巯基的反应特征,其中最重要的反应是与二硫化物之间的反应。特别是在碱性条件下与头发中的胱氨酸反应,切断胱氨酸的(-S-S-)键,生成易于卷曲的半胱氨酸。主要用作卷发剂、脱毛剂、聚氯乙烯低毒或无毒稳定剂、聚合反应的引发剂、加速剂及链转移剂、金属表面处理剂。此外,巯基乙酸是检定铁、钼、铝、锡等的敏感试剂;也可作为聚丙烯加工成型时的结晶成核剂以及涂料、纤维的改性剂、毛毯速理剂。
用途巯基乙酸除用作头孢维曲(Cefivitril)的中间体,还广泛用作卷发剂、脱毛剂、PVC低毒或无毒稳定剂、金属表面处理剂和聚合反应的引发剂、加速剂及链转移剂。
用途铁、钼、银、锡的灵敏试剂。其铵盐及钠盐用作卷发冷烫剂,钙盐为脱毛剂。
生产方法由有机或无机含硫化合物与一氯乙酸的钠、钾盐反应得到巯基乙酸。例如,一氯乙酸与硫化钠、硫磺反应生成二硫二乙酸,然后用锌和酸还原;或者硫代氨基甲酸酯与一氯乙酸反应,其产物经水解而得;再如一氯乙酸与硫脲反应,生成异硫脲代乙酸,然后用氢氧化钡转化沉淀,再用硫酸酸化制成巯基乙酸水溶液,经蒸发可制得60%-70%溶液,收率70%以上。
类别腐蚀物品
毒性分级高毒
急性毒性口服- 大鼠 LD50: 114毫克/公斤;口服- 小鼠 LD50: 242毫克/公斤
刺激数据皮肤- 人 3%
可燃性危险特性可燃;燃烧产生有毒硫氧化物烟雾
储运特性库房通风低温干燥; 与氧化剂、碱类分开存放。
灭火剂砂土、泡沫、雾状水
职业标准TLV-TWA 1 PPM (4毫克/立方米); STEL 3 PPM (15毫克/立方米)
上下游信息
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 (甲硫基)乙酸 methylsulfanyl-acetic acid 2444-37-3 C3H6O2S 106.145 巯基乙酸甲酯 Methyl thioglycolate 2365-48-2 C3H6O2S 106.145 溶剂黄146 acetic acid 64-19-7 C2H4O2 60.0526 (乙基硫代)乙酸 S-ethylthioglycolic acid 627-04-3 C4H8O2S 120.172 2-(甲基二硫烷基)乙酸 methyldisulfanyl-acetic acid 60033-23-0 C3H6O2S2 138.211 巯基乙酸乙酯 Ethyl mercaptoacetate 623-51-8 C4H8O2S 120.172 2-羟基乙基硫代乙酸酯 <(2-hydroxyethyl)thio>acetic acid 5512-65-2 C4H8O3S 136.172
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Winbladh, # 138, p. 29摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:Ginsburg; Bondzynski, Chemische Berichte, 1886, vol. 19, p. 114,117摘要:DOI:
-
作为试剂:描述:在 RuCl2(1,3-dimesityl-imidazolidin-2-yl)(PCy3)(=CHPh) 、 lithium aluminium tetrahydride 、 caesium carbonate 、 戴斯-马丁氧化剂 、 巯基乙酸 作用下, 以 四氢呋喃 、 甲醇 、 二氯甲烷 、 水 为溶剂, 反应 35.0h, 生成参考文献:名称:FUSED CYCLIC COMPOUNDS AND USE THEREOF摘要:The invention relates to fused cyclic compounds, a composition containing the same and the use thereof.公开号:WO2024120433A1
文献信息
-
Compositions for Treatment of Cystic Fibrosis and Other Chronic Diseases申请人:Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated公开号:US20150231142A1公开(公告)日:2015-08-20The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising an inhibitor of epithelial sodium channel activity in combination with at least one ABC Transporter modulator compound of Formula A, Formula B, Formula C, or Formula D. The invention also relates to pharmaceutical formulations thereof, and to methods of using such compositions in the treatment of CFTR mediated diseases, particularly cystic fibrosis using the pharmaceutical combination compositions.
-
腈及其相应胺的制造方法申请人:中国石油化工股份有限公司公开号:CN104557610B公开(公告)日:2018-04-27本发明涉及一种腈的制造方法,与现有技术相比,具有氨源用量显著降低、环境压力小、能耗低、生产成本低、腈产物的纯度和收率高等特点,并且能够获得结构更为复杂的腈。本发明还涉及由该腈制造相应胺的方法。
-
Synthesis of 5-hydroxy- and 5-sulfanyl-substituted [1,2,3]triazolo[4,5-е][1,4]diazepines作者:Sergiy V. Kemskiy、Natalia A. Syrota、Andriy V. Bol’but、Viktor I. Dorokhov、Mykhaylo V. VovkDOI:10.1007/s10593-018-2350-7日期:2018.85-Amino-N-(2,2-dimethoxyethyl)-1Н-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxamides in formic acid were subjected to intramolecular cyclization to 5-hydroxy[1,2,3]triazolo[4,5-е][1,4]diazepines, which were converted by treatment with S-nucleophiles to 5-thio-functionalized derivatives.
-
Fast Ruthenium-Catalysed Allylation of Thiols by Using Allyl Alcohols as Substrates作者:Alexey B. Zaitsev、Helen F. Caldwell、Paul S. Pregosin、Luis F. VeirosDOI:10.1002/chem.200900192日期:2009.6.22Green and fast: Allylation of aromatic and aliphatic thiols, by using allyl alcohols as substrates, requires only minutes at ambient temperature with a Ru catalyst (see scheme). Quantitative conversion is normal and the catalyst possesses high functional‐group tolerance.
-
[EN] SUBSTITUTED BENZYLAMINE COMPOUNDS, THEIR USE IN MEDICINE, AND IN PARTICULAR THE TREATMENT OF HEPATITIS C VIRUS (HCV) INFECTION<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS DE BENZYLAMINE SUBSTITUÉS, LEUR UTILISATION EN MÉDECINE, EN PARTICULIER DANS LE TRAITEMENT D'UNE INFECTION PAR LE VIRUS DE L'HÉPATITE C (VHC)申请人:ASTEX THERAPEUTICS LTD公开号:WO2013064538A1公开(公告)日:2013-05-10The invention provides compounds of the formula (I): or a salt, N-oxide or tautomer thereof, wherein A is CH, CF or nitrogen; E is CH, CF or nitrogen; and R0 is hydrogen or C1-2 alkyl; R1a is selected from CONH2; CO2H; an optionally substituted acyclic C1-8 hydrocarbon group; and an optionally substituted monocyclic carbocyclic or heterocyclic group of 3 to 7 ring members, of which 0, 1, 2, 3 or 4 are heteroatom ring members selected from O, N and S; R2 is selected from hydrogen and a group R2a; R2a is selected from an optionally substituted acyclic d-8 hydrocarbon group; an optionally substituted monocyclic carbocyclic or heterocyclic group of 3 to 7 ring members, of which 0, 1 or 2 ring members are heteroatom ring members selected from O, N and S; and an optionally substituted bicyclic heterocyclic group of 9 or 10 ring members, of which 1 or 2 ring members are nitrogen atoms; wherein at least one of R1 and R2 is other than hydrogen; R3 is an optionally substituted 3- to 10-membered monocyclic or bicyclic carbocyclic or heterocyclic ring containing 0, 1, 2 or 3 heteroatom ring members selected from N, O and S; R4a is selected from halogen; cyano; C1-4 alkyl optionally substituted with one or more fluorine atoms; C1-4 alkoxy optionally substituted with one or more fluorine atoms; hydroxy-C1-4 alkyl; and C1-2 alkoxy-C1-4 alkyl; R5 is selected from hydrogen and a substituent R5a; and R5a is selected from C1-2 alkyl optionally substituted with one or more fluorine atoms; C1-3 alkoxy optionally substituted with one or more fluorine atoms; halogen; cyclopropyl; cyano; and amino, The compounds have activity against hepatitis C virus and can be used in the prevention or treatment of hepatitis C viral infections.该发明提供了以下式(I)的化合物,或其盐、N-氧化物或互变异构体,其中A为CH、CF或氮;E为CH、CF或氮;R0为氢或C1-2烷基;R1a选自CONH2;CO2H;一个可选择取代的非环状C1-8碳氢化合物基团;以及一个可选择取代的含有3至7个环成员的单环碳环或杂环基团,其中0、1、2、3或4个是从O、N和S中选择的杂原子环成员;R2选自氢和一个基团R2a;R2a选自一个可选择取代的非环状d-8碳氢化合物基团;一个可选择取代的含有3至7个环成员的单环碳环或杂环基团,其中0、1或2个环成员是从O、N和S中选择的杂原子环成员;以及一个可选择取代的含有9或10个环成员的双环杂环基团,其中1或2个环成员是氮原子;其中R1和R2中至少一个不是氢;R3选自一个可选择取代的含有0、1、2或3个从N、O和S中选择的杂原子环成员的3至10个成员的单环或双环碳环或杂环环;R4a选自卤素;氰基;C1-4烷基,可选择取代一个或多个氟原子;C1-4烷氧基,可选择取代一个或多个氟原子;羟基-C1-4烷基;和C1-2烷氧基-C1-4烷基;R5选自氢和一个取代基R5a;R5a选自C1-2烷基,可选择取代一个或多个氟原子;C1-3烷氧基,可选择取代一个或多个氟原子;卤素;环丙基;氰基;和氨基。这些化合物对丙型肝炎病毒具有活性,并可用于预防或治疗丙型肝炎病毒感染。
表征谱图
-
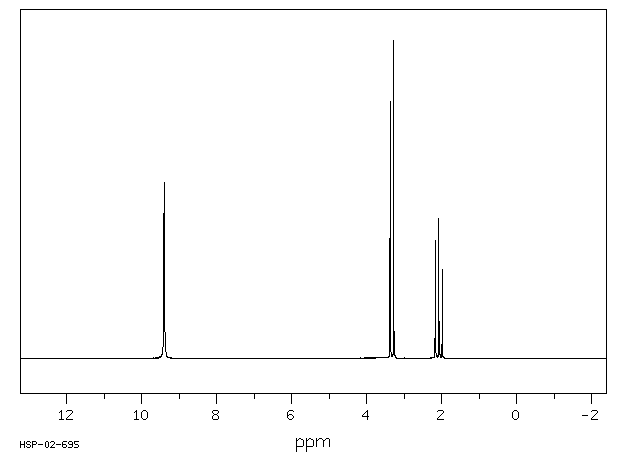
氢谱1HNMR
-
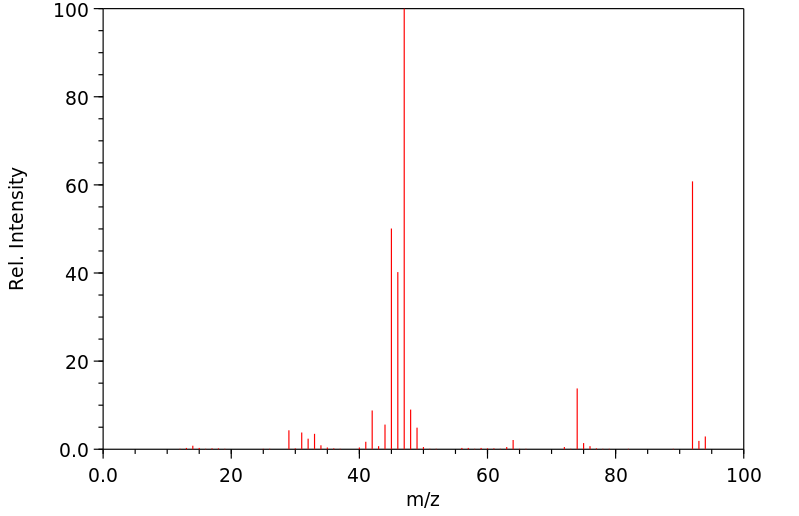
质谱MS
-
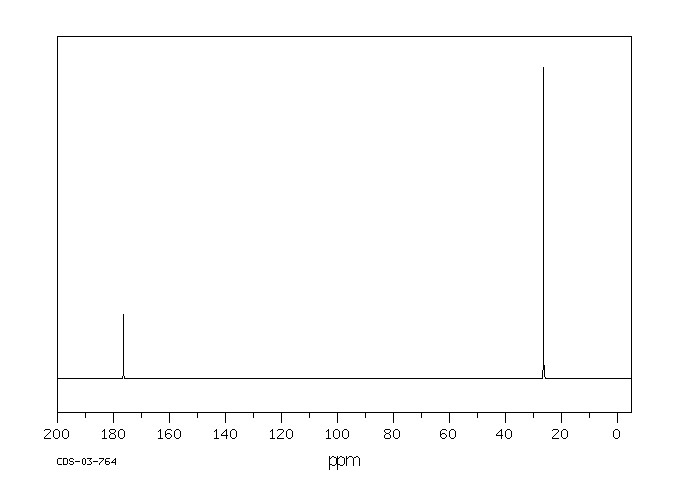
碳谱13CNMR
-
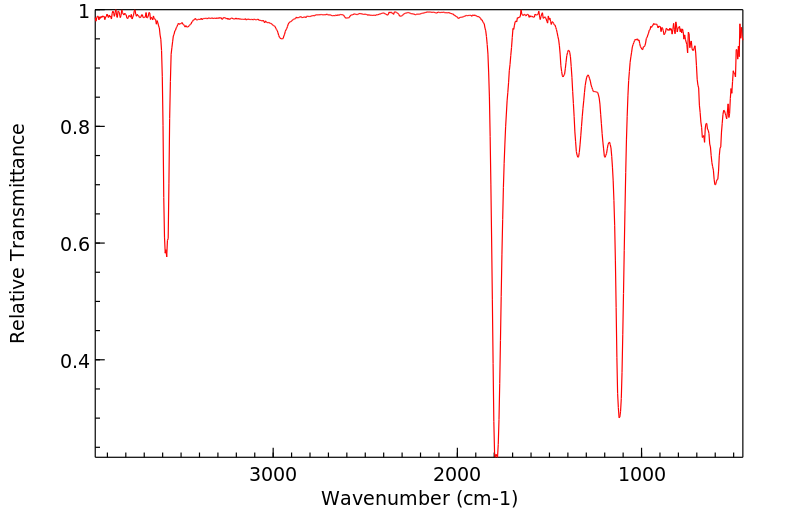
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息