代谢
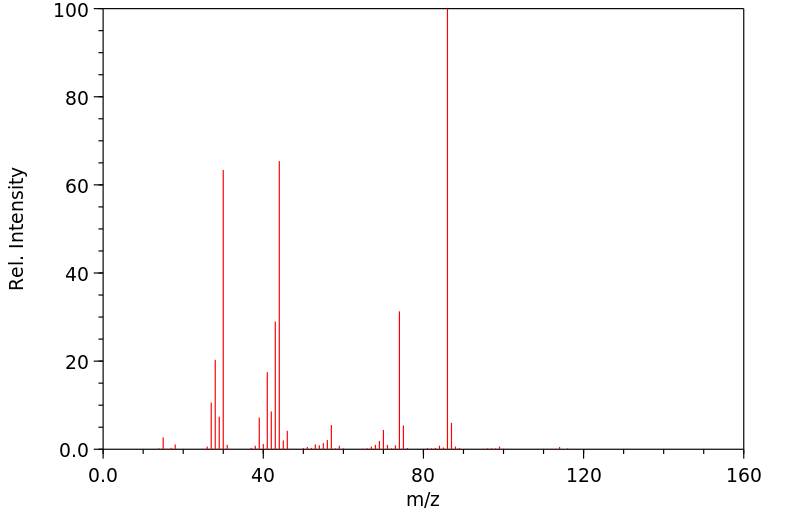
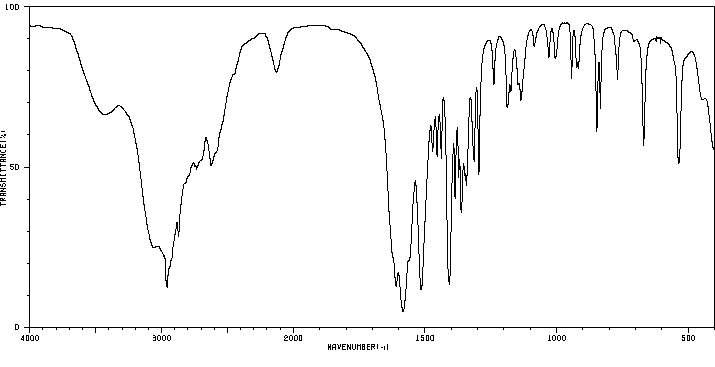
支链氨基酸(BCAA)——亮氨酸、异亮氨酸和缬氨酸——与大多数其他必需氨基酸的不同之处在于,最初负责它们分解的酶主要存在于肝外组织中。每一种氨基酸都会经历可逆的转氨作用,由支链氨基酸转移酶(BCAT)催化,并产生α-酮异己酸(KIC,来自亮氨酸)、α-酮-β-甲基戊酸(KMV,来自异亮氨酸)和α-酮异戊酸(KIV,来自缬氨酸)。这些酮酸然后经历不可逆的氧化脱羧作用,由支链酮酸脱氢酶(BCKAD)催化。后者是一个位于线粒体膜上的多酶系统。这些氧化反应的产物会进一步转化为乙酰辅酶A、丙酰辅酶A、乙酰乙酸和琥珀酰辅酶A;因此,BCAA是生酮和生糖的。
The branched-chain amino acids (BCAA) -- leucine, isoleucine, and valine -- differ from most other indispensable amino acids in that the enzymes initially responsible for their catabolism are found primarily in extrahepatic tissues. Each undergoes reversible transamination, catalyzed by a branched-chain aminotransferase (BCAT), and yields alpha-ketoisocaproate (KIC, from leucine), alpha-keto-beta-methylvalerate (KMV, from isoleucine), and alpha-ketoisovalerate (KIV, from valine). Each of these ketoacids then undergoes an irreversible, oxidative decarboxylation, catalyzed by a branchedchain ketoacid dehydrogenase (BCKAD). The latter is a multienzyme system located in mitochondrial membranes. The products of these oxidation reactions undergo further transformations to yield acetyl CoA, propionyl CoA, acetoacetate, and succinyl CoA; the BCAA are thus keto- and glucogenic.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)