L-缬氨酸 | 72-18-4
物质功能分类
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:295-300 °C (subl.) (lit.)
-
比旋光度:28 º (c=8, 6N HCl)
-
沸点:213.6±23.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:1.23
-
溶解度:在水中的溶解度25 mg/mL
-
最大波长(λmax):λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.15λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.1
-
LogP:0.29
-
物理描述:Solid
-
颜色/状态:Leaflets from water + alcohol
-
蒸汽压力:5.55X10-9 mm Hg at 25 °C (est)
-
旋光度:Specific optical rotation: +22.9 deg at 23 °C/D (c = 0.8 in 20% HCl). Molecular rotation: + 33.1 deg at at sodium line (5N HCl); + 72.6 deg at sodium line (glacial acetic acid)
-
分解:When heated to decomposition, it emits toxic fumes of /nitric oxides/.
-
解离常数:pKa = 2.30
-
碰撞截面:134.28 Ų [M+H]+ [CCS Type: DT, Method: stepped-field]
-
稳定性/保质期:
存在于烤烟和白肋烟烟叶以及烟气中。
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-2.3
-
重原子数:8
-
可旋转键数:2
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.8
-
拓扑面积:63.3
-
氢给体数:2
-
氢受体数:3
ADMET
这一组必需氨基酸被确定为支链氨基酸,即BCAAs。由于这种碳原子排列人类无法制造,这些氨基酸是饮食中的基本要素。这三种化合物的分解起始于肌肉,并产生NADH和FADH2,这些可以用于生成ATP。这三种氨基酸的分解在前两个步骤中使用相同的酶。每种情况的第一步是使用单一BCAA转氨酶进行转氨,以α-酮戊二酸作为氨基受体。结果,产生了三种不同的α-酮酸,并使用共同的支链α-酮酸脱氢酶进行氧化,产生了三种不同的辅酶A衍生物。随后,代谢途径发生分歧,产生了许多中间产物。
缬氨酸的主要产物是丙酰辅酶A,是琥珀酰辅酶A的糖原前体。异亮氨酸的分解以乙酰辅酶A和丙酰辅酶A的产生结束;因此,异亮氨酸既是糖原性的也是酮原性的。亮氨酸产生乙酰辅酶A和乙酰乙酰辅酶A,因此被归类为严格的酮原性。
存在一些与BCAAs错误分解相关的遗传疾病。最常见的缺陷是在支链α-酮酸脱氢酶中。由于这三种氨基酸只有一个脱氢酶酶,所有三种α-酮酸都会积累并从尿液中排出。这种疾病被称为枫糖尿症,因为受影响的个体的尿液具有特征性的气味。这些情况下的智力迟钝是严重的。不幸的是,由于这些是必需氨基酸,它们不能在饮食中大量限制;最终,受影响个体的寿命短暂,发育异常。主要的神经系统问题是由于中枢神经系统中髓鞘形成不良。
安全信息
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险品标志:Xn
-
安全说明:S24/25
-
危险类别码:R40
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:29224995
-
危险品运输编号:NONH for all modes of transport
-
RTECS号:YV9361000
-
危险性防范说明:P261,P305+P351+P338
-
危险性描述:H315,H319,H335
-
储存条件:本品应密封、置于阴凉干燥处并避免光照保存。
SDS
模块 1. 化学品
1.1 产品标识符
: L-缬氨酸
产品名称
1.2 鉴别的其他方法
(S)-α-Aminoisovaleric acid
L-2-Amino-3-methylbutanoic acid
1.3 有关的确定了的物质或混合物的用途和建议不适合的用途
仅用于研发。不作为药品、家庭或其它用途。
模块 2. 危险性概述
2.1 GHS-分类
非危险物质或混合物。
2.3 其它危害物 - 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
3.1 物 质
: (S)-α-Aminoisovaleric acid
别名
L-2-Amino-3-methylbutanoic acid
: C5H11NO2
分子式
: 117.15 g/mol
分子量
无
模块 4. 急救措施
4.1 必要的急救措施描述
吸入
如果吸入,请将患者移到新鲜空气处。 如呼吸停止,进行人工呼吸。
皮肤接触
用肥皂和大量的水冲洗。
眼睛接触
用水冲洗眼睛作为预防措施。
食入
切勿给失去知觉者通过口喂任何东西。 用水漱口。
4.2 主要症状和影响,急性和迟发效应
已发现左旋亮氨酸、异亮氨酸和缬氨酸能促进膀胱癌发生,
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
4.3 及时的医疗处理和所需的特殊处理的说明和指示
无数据资料
模块 5. 消防措施
5.1 灭火介质
灭火方法及灭火剂
用水雾,抗乙醇泡沫,干粉或二氧化碳灭火。
5.2 源于此物质或混合物的特别的危害
碳氧化物, 氮氧化物
5.3 给消防员的建议
如必要的话,戴自给式呼吸器去救火。
5.4 进一步信息
无数据资料
模块 6. 泄露应急处理
6.1 作业人员防护措施、防护装备和应急处置程序
避免粉尘生成。 避免吸入蒸气、烟雾或气体。
6.2 环境保护措施
不要让产品进入下水道。
6.3 泄漏化学品的收容、清除方法及所使用的处置材料
扫掉和铲掉。 放入合适的封闭的容器中待处理。
6.4 参考其他部分
丢弃处理请参阅第13节。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
7.1 安全操作的注意事项
在有粉尘生成的地方,提供合适的排风设备。
7.2 安全储存的条件,包括任何不兼容性
贮存在阴凉处。 使容器保持密闭,储存在干燥通风处。
7.3 特定用途
无数据资料
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
8.1 容许浓度
最高容许浓度
没有已知的国家规定的暴露极限。
8.2 暴露控制
适当的技术控制
常规的工业卫生操作。
个体防护设备
眼/面保护
请使用经官方标准如NIOSH (美国) 或 EN 166(欧盟) 检测与批准的设备防护眼部。
皮肤保护
戴手套取 手套在使用前必须受检查。
请使用合适的方法脱除手套(不要接触手套外部表面),避免任何皮肤部位接触此产品.
使用后请将被污染过的手套根据相关法律法规和有效的实验室规章程序谨慎处理. 请清洗并吹干双手
所选择的保护手套必须符合EU的89/686/EEC规定和从它衍生出来的EN 376标准。
完全接触
物料: 丁腈橡胶
最小的层厚度 0.11 mm
溶剂渗透时间: 480 min
测试过的物质Dermatril® (KCL 740 / Z677272, 规格 M)
飞溅保护
物料: 丁腈橡胶
最小的层厚度 0.11 mm
溶剂渗透时间: 480 min
测试过的物质Dermatril® (KCL 740 / Z677272, 规格 M)
, 测试方法 EN374
如果以溶剂形式应用或与其它物质混合应用,或在不同于EN
374规定的条件下应用,请与EC批准的手套的供应商联系。
这个推荐只是建议性的,并且务必让熟悉我们客户计划使用的特定情况的工业卫生学专家评估确认才可.
这不应该解释为在提供对任何特定使用情况方法的批准.
身体保护
根据危险物质的类型,浓度和量,以及特定的工作场所选择身体保护措施。,
防护设备的类型必须根据特定工作场所中的危险物的浓度和数量来选择。
呼吸系统防护
不需要保护呼吸。如需防护粉尘损害,请使用N95型(US)或P1型(EN 143)防尘面具。
呼吸器使用经过测试并通过政府标准如NIOSH(US)或CEN(EU)的呼吸器和零件。
模块 9. 理化特性
9.1 基本的理化特性的信息
a) 外观与性状
形状: 固体
颜色: 白色
b) 气味
无数据资料
c) 气味阈值
无数据资料
d) pH值
无数据资料
e) 熔点/凝固点
295 - 300 °C
f) 沸点、初沸点和沸程
无数据资料
g) 闪点
无数据资料
h) 蒸发速率
无数据资料
i) 易燃性(固体,气体)
无数据资料
j) 高的/低的燃烧性或爆炸性限度 无数据资料
k) 蒸气压
无数据资料
l) 蒸汽密度
无数据资料
m) 密度/相对密度
无数据资料
n) 水溶性
无数据资料
o) n-辛醇/水分配系数
无数据资料
p) 自燃温度
无数据资料
q) 分解温度
无数据资料
r) 粘度
无数据资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应活性
10.1 反应性
无数据资料
10.2 稳定性
无数据资料
10.3 危险反应
无数据资料
10.4 应避免的条件
无数据资料
10.5 不相容的物质
强氧化剂
10.6 危险的分解产物
其它分解产物 - 无数据资料
模块 11. 毒理学资料
11.1 毒理学影响的信息
急性毒性
半数致死剂量 (LD50) 腹膜内的 - 大鼠 - 5,390 mg/kg
备注: 行为的:肌肉收缩或痉挛 肺,胸,或者呼吸系统:呼吸困难 营养与总代谢:变化:体温降低。
皮肤刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
眼睛刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
呼吸道或皮肤过敏
无数据资料
生殖细胞致突变性
无数据资料
致癌性
IARC:
此产品中没有大于或等于 0。1%含量的组分被 IARC鉴别为可能的或肯定的人类致癌物。
生殖毒性
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触)
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(反复接触)
无数据资料
吸入危险
无数据资料
潜在的健康影响
吸入 吸入可能有害。 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
摄入 如服入是有害的。
皮肤 通过皮肤吸收可能有害。 可能引起皮肤刺激。
眼睛 可能引起眼睛刺激。
接触后的征兆和症状
已发现左旋亮氨酸、异亮氨酸和缬氨酸能促进膀胱癌发生,
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
附加说明
化学物质毒性作用登记: YV9361000
模块 12. 生态学资料
12.1 生态毒性
无数据资料
12.2 持久性和降解性
无数据资料
12.3 潜在的生物累积性
无数据资料
12.4 土壤中的迁移性
无数据资料
12.5 PBT 和 vPvB的结果评价
无数据资料
12.6 其它不良影响
无数据资料
模块 13. 废弃处置
13.1 废物处理方法
产品
将剩余的和不可回收的溶液交给有许可证的公司处理。
受污染的容器和包装
按未用产品处置。
模块 14. 运输信息
14.1 联合国危险货物编号
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.2 联合国运输名称
欧洲陆运危规: 非危险货物
国际海运危规: 非危险货物
国际空运危规: 非危险货物
14.3 运输危险类别
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.4 包裹组
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.5 环境危险
欧洲陆运危规: 否 国际海运危规 国际空运危规: 否
海洋污染物(是/否): 否
14.6 对使用者的特别提醒
无数据资料
模块 15 - 法规信息
N/A
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
制备方法与用途
L-缬氨酸又称2-氨基-3-甲基丁酸,化学式C5H11NO2。它是一种白色单斜晶系晶体或结晶性粉末,使用乙醇水溶液重洁净时可获得无色板状或鳞片状结晶。无臭,味苦。L-缬氨酸在水中溶解度为8.85%,而在乙醇、乙醚和丙酮中几乎不溶。其熔点(分解点)为315℃,等电点为5.96,[α]D25^+ = 28.3(C=1-2 g/ml,在5 mol/L HCl中)。
化学性质L-缬氨酸可溶于水,在25°C时的溶解度为8.85%。其在乙醇、乙醚和丙酮中的溶解性极低,熔点为315℃,等电点为5.96,旋光度为[α]D25^+ = 28.3(C=1-2 g/ml,在5 mol/L HCl中)。
用途L-缬氨酸是一种人体必需氨基酸,广泛应用于生化研究、组织培养基的制备以及氨基酸类药物。它也是营养增补剂的重要组成部分,可用于氨基酸输液和综合氨基酸制剂的配制,并治疗肝功能衰竭及中枢神经系统功能紊乱。
作为食品添加剂时,在米制糕饼中添加1g/kg L-缬氨酸可赋予产品芝麻香风味;在面包中使用亦能改善其口感。此外,L-缬氨酸还是三种支链氨基酸之一,属于必需氨基酸,成人男子每日的需要量约为10mg/(kg·d)。
生产方法 合成法L-缬氨酸的主要生产方法有蛋白质水解法、化学合成法、酶法和生物发酵法。由于生物发酵法原料易得、成本低廉且易于大规模生产,几乎所有厂家都采用此法生产L-缬氨酸。
化学合成法- 由异丁醛与氨生成氨基异丁醇,再与氰化氢反应生成氨基异丁腈,随后水解成L-缬氨酸。
- 以异丁醛为原料,通过斯特克(Steyer)反应与氨及氢氰酸作用生成α氨基异丁腈,然后进行水解得到DL-缬氨酸,并使用拆分剂得L-缬氨酸。此外,也可由异丁醛与氰化钠和氯化铵直接合成氨基异丁腈,再经过水解过程获得所需的产物。
- 通过异丁醛、氰化钠及碳酸铵合成己内酰脲后进行水解步骤,得到的得率大约为49%。
使用产谷氨酸微球菌(Micrococcus glutamicus.Paracolabacterum coliforme)、产氨短杆菌(Brevibacterium ammoniagenes)、大肠杆菌(Escherichia coli)和产气气杆菌(Aerobacter aerogenes),在含有葡萄糖、尿素及无机盐的培养基中生成L-型缬氨酸,且无需进行旋光拆分。
酰化酶处理法通过以乙酰-DL-缬氨酸为原料,在弱碱性条件下用酰化酶精制而得。
毒性和使用限量LD50值为5390 mg/kg(大鼠,腹腔注射),可安全用于食品。其在食品中占总蛋白质重量的7.4%为FDA许可的最大使用限量。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 DL-缬氨酸 L-valine 516-06-3 C5H11NO2 117.148 D-缬氨酸 D-Val-OH 640-68-6 C5H11NO2 117.148 L-缬氨酸甲酯 H-L-Val-OMe 4070-48-8 C6H13NO2 131.175 —— D,L-Val-OMe 4070-48-8 C6H13NO2 131.175 (S)-(+)-2-氨基-3-羟基-3-甲基丁酸 (S)-2-amino-3-hydroxy-3-methylbutanoic acid 2280-27-5 C5H11NO3 133.147 D-青霉胺 3,3-dimethyl-D-cysteine 771431-20-0 C5H11NO2S 149.214 乙基缬氨酸酯 L-valine ethyl ester 17431-03-7 C7H15NO2 145.202 L-亮氨酸 L-leucine 61-90-5 C6H13NO2 131.175 N-甲酰基-DL-缬氨酸 N-formylvaline 4289-96-7 C6H11NO3 145.158 (2S)-2-叠氮基-3-甲基丁酸 azidovaline 40224-47-3 C5H9N3O2 143.145 L-丙氨酸 L-alanin 56-41-7 C3H7NO2 89.0941 - 1
- 2
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 D-缬氨酸 D-Val-OH 640-68-6 C5H11NO2 117.148 DL-缬氨酸 L-valine 516-06-3 C5H11NO2 117.148 L-缬氨酸甲酯 H-L-Val-OMe 4070-48-8 C6H13NO2 131.175 L-异亮氨酸 L-isoleucine 73-32-5 C6H13NO2 131.175 N-甲基-L-缬氨酸 N-methyl-L-valine 2480-23-1 C6H13NO2 131.175 —— N-chloro-L-valine 52316-70-8 C5H10ClNO2 151.593 —— N-Br-Valine —— C5H10BrNO2 196.044 —— 4-chloro-L-valine 925686-25-5 C5H10ClNO2 151.593 (S)-(+)-2-氨基-3-羟基-3-甲基丁酸 (S)-2-amino-3-hydroxy-3-methylbutanoic acid 2280-27-5 C5H11NO3 133.147 乙基缬氨酸酯 L-valine ethyl ester 17431-03-7 C7H15NO2 145.202 (2S)-2-(乙胺基)-3-甲基丁酸 N-ethyl-L-Val 90600-06-9 C7H15NO2 145.202 L-亮氨酸 L-leucine 61-90-5 C6H13NO2 131.175 —— L-valinal 98137-41-8 C5H11NO 101.148 N,N-二甲基-L-缬氨酸 N,N-dimethyl-L-valine 2812-32-0 C7H15NO2 145.202 N,N-二甲基缬氨酸 N,N-dimethylvaline 15206-52-7 C7H15NO2 145.202 Formyl-L-缬氨酸 N-formyl-L-valine 4289-97-8 C6H11NO3 145.158 N-甲酰基-DL-缬氨酸 N-formylvaline 4289-96-7 C6H11NO3 145.158 L-缬氨醇 (S)-valinol 2026-48-4 C5H13NO 103.164 DL-2-氨基-3-甲基-1-丁醇 valinol 16369-05-4 C5H13NO 103.164 (2S)-2-叠氮基-3-甲基丁酸 azidovaline 40224-47-3 C5H9N3O2 143.145 —— Valol —— C5H11NO3 133.147 —— D-<2-2H>valine 77257-02-4 C5H11NO2 118.14 —— ValOPr —— C8H17NO2 159.228 —— pleurocybellaziridine 1275621-85-6 C5H9NO2 115.132 L-丙氨酸 L-alanin 56-41-7 C3H7NO2 89.0941 —— (2S,3RS)-3-methylaspartic acid 31571-69-4 C5H9NO4 147.131 - 1
- 2
- 3
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:肽中色氨酸向天冬氨酸的转化摘要:色氨酸侧链通过原位生成的钌(VIII)以高收率转化为天冬氨酸。根据四氢咔唑向己二酸,缬氨酸向异丁酸,苯丙氨酸向苯乙酸的转化,提出了多步降解顺序。DOI:10.1039/c39870001085
-
作为产物:描述:N-苯甲酰-N-缬氨酸 生成 L-缬氨酸参考文献:名称:Kameda et al., Yakugaku Zasshi/Journal of the Pharmaceutical Society of Japan, 1958, vol. 78, p. 767摘要:DOI:
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:通过醇与亚磺酰胺或磺酰胺的氧化级联反应,Fe(III)/l-缬氨酸催化一锅法合成 N-亚磺酰基-和 N-磺酰亚胺摘要:发现了一种有效的 Fe(III)、l-缬氨酸和 4-OH-TEMPO 催化体系,用于醇的氧化,然后在一个锅中与亚磺酰胺或磺酰胺缩合,合成 N-亚磺酰基-和 N-磺酰亚胺化合物。条件温和。这种转变适用于各种底物,显示出高官能团耐受性,并以良好到优异的产率提供相应的产品。DOI:10.1055/s-0037-1609320
文献信息
-
Properties and Reactions of Substituted 1,2-Thiazetidine 1,1-Dioxides: Chiral Mono- and Bicyclic 1,2-Thiazetidine 1,1-Dioxides fromα-Amino Acids作者:Alexandra Meinzer、Andrea Breckel、Bassam Abu Thaher、Nico Manicone、Hans-Hartwig OttoDOI:10.1002/hlca.200490021日期:2004.1New chiral mono- and bicyclic β-sultams, valuable building blocks for drug synthesis, have been prepared from L-Ala, L-Val, L-Leu, L-Ile, L-Phe, L-Cys, L-Ser, L-Thr, and D-penicillamine by transformation of the COOH group into a methylsulfonyl chloride function, followed by cyclization under basic conditions. Selected properties, derivatives, and reactions of the β-sultams are described.
-
Fmoc-Amox, A Suitable Reagent for the Introduction of Fmoc作者:Ashish Kumar、Anamika Sharma、Elvira Haimov、Ayman El-Faham、Beatriz G. de la Torre、Fernando AlbericioDOI:10.1021/acs.oprd.7b00199日期:2017.10.20Synthesis of most peptides is achieved using solid-phase peptide synthesis employing the Fmoc/tert-butyl strategy. However, the introduction of Fmoc in N-unprotected amino acids seems to be challenging due to the formation of dipeptides and sometimes tripeptides as impurities and β-alanyl impurities when Fmoc-OSu is used as well. Herein, we report an efficient and successful method using Fmoc-Amox
-
5-Norbornene-2,3-dicarboximido Carbonochloridate. A New Stable Reagent for the Introduction of Amino-Protecting Groups作者:Peter Henklein、Hans-Ulrich Heyne、Wolf-Rainer Halatsch、Hartmut NiedrichDOI:10.1055/s-1987-27873日期:——The synthesis of activated carbonates, based on a new carbonochloridate derived from N-hydroxy-5-norbornene-2,3-dicarboximide, is reported. These activated carbonic esters are excellent reagents for the introduction of all currently used urethane protecting groups.
-
Alkyl 1-Chloroalkyl Carbonates: Reagents for the Synthesis of Carbamates and Protection of Amino Groups作者:Gérard Barcelo、Jean-Pierre Senet、Gérard Sennyey、Jean Bensoam、Albert LoffetDOI:10.1055/s-1986-31724日期:——The synthesis of 1-chloroalkyl carbonates and their reaction with various type of amines are described. This reaction is useful for the synthesis of carbamate pesticides and for the protection of various amino groups, including amino acids.
-
Determination of Chemical and Enantiomeric Purity of α‐Amino Acids and their Methyl Esters as N‐Fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl Derivatives Using Amylose‐derived Chiral Stationary Phases作者:Md. Fokhrul Islam、Suraj Adhikari、Man‐Jeong Paik、Wonjae LeeDOI:10.1002/bkcs.11694日期:2019.4were observed to be 0.49–17.50%. Enantiomeric impurities of several commercially available L‐amino acid methyl esters were found to be 0.03–0.58%, whereas chemical impurities as the corresponding racemic acids present in the same analytes were found to be 0.13–13.62%. This developed analytical method will be useful for the determination of chemical and enantiomeric purity of α‐amino acids and/or esters
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
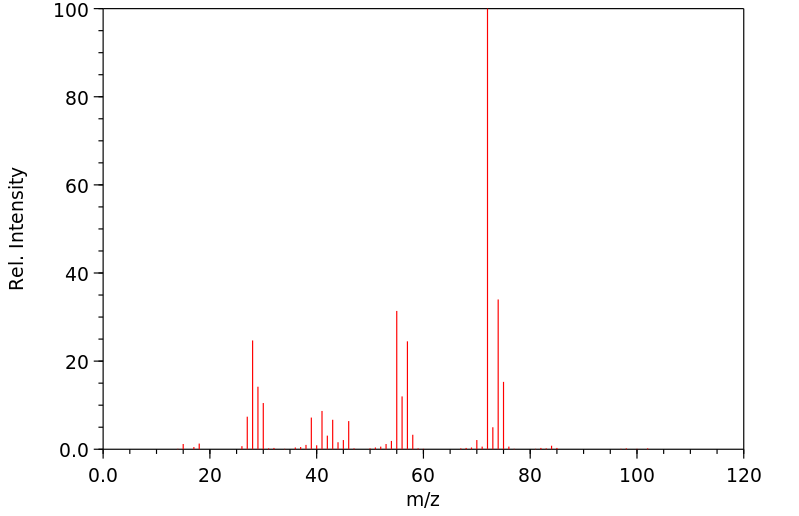
质谱MS
-
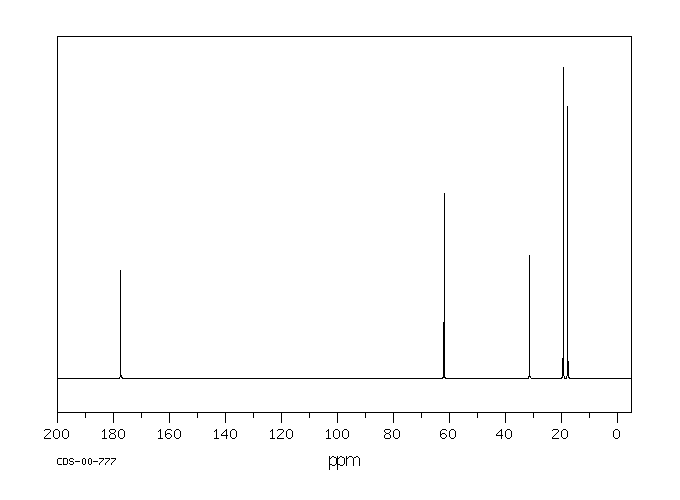
碳谱13CNMR
-
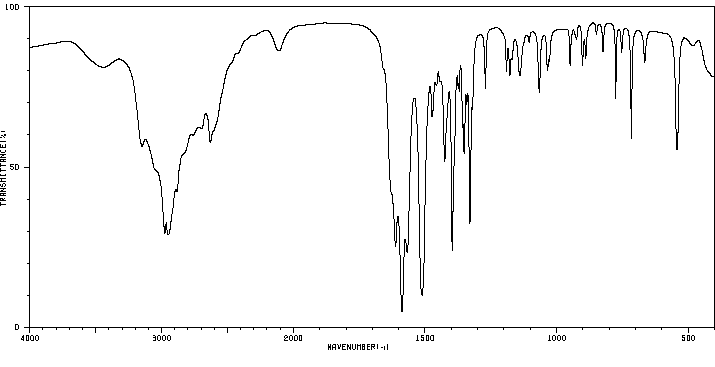
红外IR
-
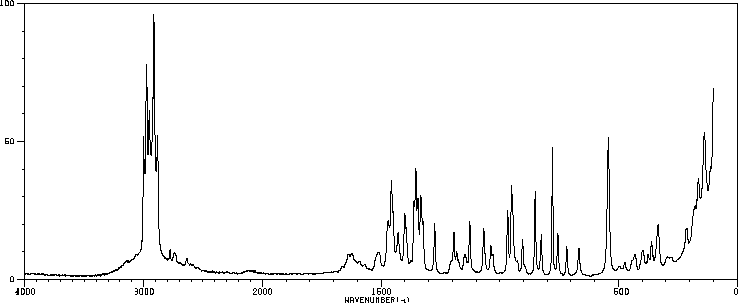
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息