利多卡因 | 137-58-6
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:66-69°C
-
沸点:bp4 180-182°; bp2 159-160°
-
密度:0.9944 (rough estimate)
-
闪点:9℃
-
溶解度:乙醇:4 mg/mL
-
LogP:2.440
-
物理描述:Solid
-
颜色/状态:Needles from benzene or alcohol
-
气味:Characteristic odor
-
蒸汽压力:6.76X10-6 mm Hg at 25 °C (est)
-
水溶性:-1.76
-
稳定性/保质期:
Commercially available solutions of lidocaine hydrochloride in 5% dextrose usually are stable for 18 months after the date of manufacture. Commercially available solutions of lidocaine hydrochloride in 5% dextrose may be provided in plastic containers.
-
分解:When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of /nitrogen oxides/.
-
Caco2细胞的药物渗透性:-4.21
-
解离常数:pKa = 7.86
-
碰撞截面:157.7 Ų [M+H]+ [CCS Type: TW, Method: Major Mix IMS/Tof Calibration Kit (Waters)]
-
保留指数:1870;1881;1884;1838;1857;1865;1875;1875;1875;1875;1875;1880;1880;1880;1880;1880;1880;1880;1881;1882;1882;1882;1882;1882;1885;1885;1885;1885;1885;1885;1885;1885;1890;1890;1890;1890;1890;1892;1893;1895;1895;1895;1854;1852;1848;1854;1860;1863;1842;1865;1875;1875;1882;1875;1850;1900;1869;1859;1866;1860;1885;1875;1876.9;1841;1842;1870;1856;1844;1842;1852;1854;1856;1857;1857;1858;1858;1860;1860;1870;1865;1865
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):2.3
-
重原子数:17
-
可旋转键数:5
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.5
-
拓扑面积:32.3
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:2
ADMET
安全信息
-
危险等级:6.1(b)
-
危险品标志:Xn
-
安全说明:S22,S26,S36
-
危险类别码:R22
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:2924299090
-
危险品运输编号:3249
-
危险类别:6.1(b)
-
RTECS号:AN7525000
-
包装等级:III
-
储存条件:本品应密封保存在阴凉干燥的地方。
SDS
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: Lidocaine
修改号码: 5
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害 未分类
健康危害
急性毒性(经口) 第4级
特异性靶器官毒性 心血管系统, 中枢神经系统
- 单一接触 [第1级]
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志
信号词 危险
危险描述 吞咽有害。
对器官引起损害: 心血管系统 中枢神经系统
防范说明
[预防] 切勿吸入。
使用本产品时切勿吃东西,喝水或吸烟。
处理后要彻底清洗双手。
[急救措施] 食入:若感不适,呼叫解毒中心/医生。漱口。
如接触到:呼叫解毒中心/医生。
[储存] 存放处须加锁。
[废弃处置] 根据当地政府规定把物品/容器交与工业废弃处理机构。
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 利多卡因
百分比: >99.0%(LC)(T)
CAS编码: 137-58-6
俗名: 2-Diethylamino-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)acetamide
利多卡因 修改号码:5
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
分子式: C14H22N2O
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。立即呼叫解毒中心/医生。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用大量肥皂和水轻轻洗。
呼叫解毒中心/医生。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。
立即呼叫解毒中心/医生。
食入: 呼叫解毒中心/医生。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,雾状水,二氧化碳
特殊危险性: 小心,燃烧或高温下可能分解产生毒烟。
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用特殊的个人防护用品(针对有毒颗粒的P3过滤式空气呼吸器)。远离溢出物/泄露
紧急措施: 处并处在上风处。
泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 清扫收集粉尘,封入密闭容器。注意切勿分散。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的
法律法规处置。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止粉尘扩散。处理后彻底清洗双手
和脸。
注意事项: 如果可能,使用封闭系统。如果粉尘或浮质产生,使用局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗处。
存放处须加锁。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统。同时安装淋浴器和洗眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防尘面具,自携式呼吸器(SCBA),供气呼吸器等。使用通过政府标准的呼吸器。依
据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防渗手套。
眼睛防护: 护目镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防渗防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
利多卡因 修改号码:5
模块 9. 理化特性
固体
外形(20°C):
外观: 晶体-粉末
颜色: 白色类白色
气味: 特殊味
pH: 无数据资料
熔点: 69°C
沸点/沸程 182 °C/0.5kPa
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 无资料
溶解度:
[水] 不溶于(410mg/L, 30°C)
[其他溶剂]
溶于: 醚, 酒精, 苯, 氯仿
log水分配系数 = 2.06
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳, 氮氧化物 (NOx)
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: scu-rat LD50:335 mg/kg
orl-rat LD50:317 mg/kg
ipr-rat LD50:133 mg/kg
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: mmo-sat 50 umol/plate (-S9)
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: par-wmn TDLo:540 ug/kgimp-rat TDLo:7500 mg/kg
imp-rat TDLo:7500 mg/kg(3-17D preg)
ims-rat TDLo:6 mg/kg(11D preg)
par-rat TDLo:6 mg/kg(11D preg)
RTECS 号码: AN7525000
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 2.06
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
利多卡因 修改号码:5
模块 12. 生态学信息
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在可燃溶剂中溶解混合,在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中
焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
制备方法与用途
利多卡因通过可逆性地封闭钠通道,阻断动作电位在神经纤维上的传递来发挥局部麻醉的作用。感觉神经纤维比运动神经纤维更早被阻断,因此低剂量的利多卡因即可产生选择性的感觉阻滞作用。此外,利多卡因也有抗心律失常作用,属于Ⅰb类抗心律失常药。它能够降低心室率、缩短动作电位时间和绝对不应期,并延长相对不应期。利多卡因起效快,持续时间短。在利多卡因中加入肾上腺素可以延长其麻醉效果,减少副作用。
局部麻醉作用利多卡因是一种局部麻醉药,又称赛罗卡因,因其脂溶性、蛋白结合率均高于普鲁卡因,穿透细胞能力强,起效快,作用时间长。其效力是普鲁卡因的四倍,常用于美容整形手术中的局部浸润麻醉。
临床应用利多卡因适用于浸润麻醉、硬膜外麻醉和表面麻醉(包括胸腔镜检查或腹腔手术时的黏膜麻醉)。为了延长麻醉时间并减少副作用,在麻醉药中加入肾上腺素是常用的做法。它也被用于治疗急性心肌梗死后的心律失常,如室性早搏、室性心动过速及室颤。对于其他抗惊厥药物无效的癫痫持续状态,利多卡因也是一个选择。不过,对室上性心律失常通常无效。
化学性质利多卡因为白色针状结晶,熔点为68-69℃,沸点180-182℃(0.53kPa),159-160℃(0.267kPa)。它溶于乙醇、乙醚、苯和氯仿等有机溶剂中,而不溶于水中。利多卡因的盐酸盐是一种白色结晶性粉末,熔点为127-129℃,一水合物的熔点为77-78℃。它极易溶解于水中,0.5%水溶液pH值在4.0-5.5之间,无臭,有苦麻味。
生产方法-
酰化:将2,6-二甲基苯胺溶解于无水苯中,在冷却至28℃以下的条件下,搅拌下缓缓滴加氯乙酰氯。保持温度在30℃以下反应1小时后回流8小时。冷却结晶、过滤并干燥,得到2,6-二甲基氯乙酰苯胺,收率为75%。
-
胺化:将上述2,6-二甲基氯乙酰苯胺加入苯中,再加入二乙胺搅拌加热回流7小时后回收大部分苯。冷却结晶、过滤并用苯洗涤结晶。合并苯液,用10%盐酸萃取,提取液加活性炭脱色然后过滤。滤液用10%氢氧化钠溶液调节pH至10,析出结晶后甩滤并用水洗至中性,最终得到利多卡因。重结晶之后将其与盐酸成盐即为利多卡因盐酸盐。此过程的胺化反应收率为76%。
利多卡因是一种广泛应用于表面麻醉、浸润麻醉和传导麻醉及硬膜外麻醉的酰胺类局部麻醉药。其盐酸盐对小鼠口服的LD50为290mg/kg,可用作局部麻醉药物。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 去乙基利多卡因 N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-2-ethylaminoacetamide 7728-40-7 C12H18N2O 206.288 —— 2-(N-ethylacetamido)2',6'-dimethylacetanilide —— C14H20N2O2 248.325 2,6-二甲基氯代乙酰苯胺 2-chloro-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)acetamide 1131-01-7 C10H12ClNO 197.664 N-(2,6-二甲苯基)-2-羟基乙酰胺 N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-2-hydroxyacetamide 29183-14-0 C10H13NO2 179.219 N-(2,6-二甲基苯)甲酰胺 2,6-dimethylformanilide 607-92-1 C9H11NO 149.192 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 去乙基利多卡因 N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-2-ethylaminoacetamide 7728-40-7 C12H18N2O 206.288 —— N-(4-amino-2,6-dimethylphenyl)-2-(diethylamino)acetamide 27951-88-8 C14H23N3O 249.356 —— 2-(N-ethylacetamido)2',6'-dimethylacetanilide —— C14H20N2O2 248.325 利多卡因 N-氧化物 lidocaine N-oxide 2903-45-9 C14H22N2O2 250.341 —— 2-(diethylamino)-N-(4-bromo-2,6-dimethylphenyl)acetamide 17060-81-0 C14H21BrN2O 313.238 —— [18F]2-(diethylamino)-N-(4-fluoro-2,6-dimethylphenyl)acetamide —— C14H21FN2O 251.334 4-羟基利多卡因 4-hydroxylidocaine 39942-41-1 C14H22N2O2 250.341 2-氨基-N-(2,6-二甲基苯基)乙酰胺 Glycine xylidide 18865-38-8 C10H14N2O 178.234 3-氨基利多卡因 N-(3-amino-2,6-dimethylphenyl)-2-(diethylamino)acetamide 39942-50-2 C14H23N3O 249.356 2-二乙氨基-2'-羟甲基-6'-甲基乙酰苯胺 2-diethylamino-2'-hydroxymethyl-6'-methyl acetanilide 64585-18-8 C14H22N2O2 250.341 —— 2-(diethylamino)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-N-methylacetamide 31058-85-2 C15H24N2O 248.368 3-羟基利多卡因 3-Hydroxylidocaine 34604-55-2 C14H22N2O2 250.341 —— 2-diethylamine-N-(3-formyl-2,6-dimethyl-phenyl)-acetamide 1044658-04-9 C15H22N2O2 262.352 —— 2-(diethylamino)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-N-ethylacetamide 75889-30-4 C16H26N2O 262.395 N-(3-溴-2,6-二甲基苯基)-2-(二乙基氨基)乙酰胺 N-(3-bromo-2,6-dimethyl-phenyl)-2-diethylamine-acetamide 1044658-01-6 C14H21BrN2O 313.238 —— 2-diethylamino-N-[2,6-dimethyl-3-tridecylamino-phenyl]-acetamide 848441-64-5 C27H49N3O 431.706 —— 2-(diethylamino)-N-[2-(diethylamino)ethyl]-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)acetamide 75889-37-1 C20H35N3O 333.517 2-乙基氨基-N-(3-羟基-2,6-二甲基苯基)乙酰胺 3-Hydroxy-monoethylglycinexylidide 34604-56-3 C12H18N2O2 222.287 —— N,N-diethyl-glycine-(N-acetyl-2,6-dimethyl-anilide) —— C16H24N2O2 276.379 —— 2-(diethylamino)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-N-propylacetamide 75889-32-6 C17H28N2O 276.422 —— tetradecanoic acid [3-(2-diethylamino-acetylamino)-2,4-dimethyl-phenyl]-amide 848441-46-3 C28H49N3O2 459.716 —— 2-diethylamine-N-(2,6-dimethyl-3-phenethyl-phenyl)-acetamide 1044658-24-3 C22H30N2O 338.493 —— 2-diethylamino-N-[2,6-dimethyl-3-(4-phenyl-butylamino)-phenyl]-acetamide 848441-68-9 C24H35N3O 381.561 —— 2-(diethylamino)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-N-(2-hydroxyethyl)acetamide 75889-33-7 C16H26N2O2 278.395 —— 2-diethylamine-N-(2,6-dimethyl-3-styryl-phenyl)-acetamide 1044658-47-0 C22H28N2O 336.477 —— 2-diethylamine-N-(2,6-dimethyl-3-phenylethynyl-phenyl)-acetamide 1044658-46-9 C22H26N2O 334.461 —— 2-diethylamino-N-[2,6-dimethyl-3-(3,7,11-trimethyl-dodeca-2,6,10-trienylamino)-phenyl]-acetamide —— C29H47N3O 453.712 —— 2-diethylamine-N-(2,6-dimethyl-3-phenylaminomethyl-phenyl)-acetamide 1044658-20-9 C21H29N3O 339.481 —— 2-(diethylamino)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-N-(2-ethoxyethyl)acetamide 75889-35-9 C18H30N2O2 306.448 —— N,N-diethyl-thioglycine-(2,6-dimethyl-anilide) 109366-65-6 C14H22N2S 250.408 —— 2-diethylamine-N-(2,6-dimethyl-biphenyl-3-yl)-acetamide 1044658-25-4 C20H26N2O 310.439 3-硝基利多卡因 2-diethylamino-N-(2,6-dimethyl-3-nitro-phenyl)-acetamide 39942-49-9 C14H21N3O3 279.339 —— N-[3-(3-benzyl-ureido)-2,6-dimethyl-phenyl]-2-diethylamino-acetamide 848441-58-7 C22H30N4O2 382.506 —— N-(3-benzyloxy-2,6-dimethyl-phenyl)-2-diethylamine-acetamide 313371-48-1 C21H28N2O2 340.466 - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:利多卡因盐酸盐一水合物的分子结构和振动,(1)H和(13)C NMR光谱。摘要:通过B3LYP / 6-311G(*∗)计算研究了局部麻醉药利多卡因盐酸盐一水合物盐的结构,振动和NMR光谱。利多卡因·HCl·H2O盐预计在室温下具有主要形式的薄纱状结构,NCCN和CNCC扭转角分别为110°和-123°,而基础利多卡因分别为10°和-64°。两个NH键之间的排斥相互作用破坏了利多卡因·HCl·H2O盐的gauche结构的稳定性。所观察到的振动光谱的分析与室温下仅一种乳脂状构象中利多卡因盐的存在是一致的。利多卡因·HCl·H2O的(1)H和(13)C NMR光谱通过实验和DFT计算得出的利多卡因盐的化学位移进行了解释。DOI:10.1016/j.saa.2015.07.060
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:1,3,5-三嗪酮类药物在Ugi反应中作为福尔马胺替代品摘要:1,3,5-三嗪酮被用作Ugi反应中易于操作,稳定的福尔马胺替代物,用于快速组装具有多样性的三种多样性的甘氨酰胺衍生物,收率接近定量。该方案适用于利多卡因和几种不对称取代的二酮哌嗪的一锅两步合成法。DOI:10.1002/ejoc.202000569
文献信息
-
[EN] SUBSTITUTED N-HETEROCYCLIC CARBOXAMIDES AS ACID CERAMIDASE INHIBITORS AND THEIR USE AS MEDICAMENTS<br/>[FR] CARBOXAMIDES N-HÉTÉROCYCLIQUES SUBSTITUÉS UTILISÉS EN TANT QU'INHIBITEURS DE LA CÉRAMIDASE ACIDE ET LEUR UTILISATION EN TANT QUE MÉDICAMENTS申请人:BIAL BIOTECH INVEST INC公开号:WO2021055627A1公开(公告)日:2021-03-25The invention provides substituted N-heterocyclic carboxamides and related compounds, compositions containing such compounds, medical kits, and methods for using such compounds and compositions to treat a medical disorder, e.g., cancer, lysosomal storage disorder, neurodegenerative disorder, inflammatory disorder, in a patient.这项发明提供了替代的N-杂环羧酰胺和相关化合物,含有这些化合物的组合物,医疗工具包,以及使用这些化合物和组合物治疗患者的医疗疾病(例如癌症、溶酶体贮积症、神经退行性疾病、炎症性疾病)的方法。
-
Eflornithine Prodrugs, Conjugates and Salts, and Methods of Use Thereof申请人:Xu Feng公开号:US20100120727A1公开(公告)日:2010-05-13In one aspect, the present invention provides a composition of a covalent conjugate of an eflornithine analog with an anti-inflammatory drug. In another aspect, the present invention provides a composition of an eflornithine prodrug. In another aspect, the present invention provides a composition of an eflornithine or its derivatives aspirin salt. In another aspect, the present invention provides methods for treating or preventing cancer using the conjugates or salts of eflornithine analogs or eflornithine prodrugs.
-
[EN] THIENOPYRIDONE DERIVATIVES AS AMP-ACTIVATED PROTEIN KINASE (AMPK) ACTIVATORS<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS DE THÉNOPYRIDONE COMME ACTIVATEURS DE LA PROTÉINE KINASE DÉPENDANTE DE L'AMP (AMPK)申请人:MERCK PATENT GMBH公开号:WO2009124636A1公开(公告)日:2009-10-15The present invention relates to compounds of formula (I) wherein R1, R2 and R3 are as defined in claim 1, including pharmaceutical compositions thereof and for their use in the treatment and/or prevention of diseases and disorders modulated by AMP agonists. The invention is also directed to intermediates and to a method of preparation of compounds of formula (I).本发明涉及式(I)的化合物,其中R1、R2和R3如权利要求1所定义,包括其药物组合物以及用于治疗和/或预防由AMP激动剂调节的疾病和紊乱的用途。该发明还涉及中间体和式(I)化合物的制备方法。
-
THIENOPYRIDONE DERIVATIVES AS AMP-ACTIVATED PROTEIN KINASE (AMPK) ACTIVATORS申请人:Cravo Daniel公开号:US20110034505A1公开(公告)日:2011-02-10The present invention relates to compounds of formula (I) wherein R1, R2 and R3 are as defined in claim 1 , including pharmaceutical compositions thereof and for their use in the treatment and/or prevention of diseases and disorders modulated by AMP agonists. The invention is also directed to intermediates and to a method of preparation of compounds of formula (I).本发明涉及式(I)化合物,其中R1、R2和R3如权利要求1所定义,包括其药物组合物以及用于治疗和/或预防由AMP激动剂调节的疾病和紊乱的用途。该发明还涉及中间体和式(I)化合物的制备方法。
-
[EN] ARYL ETHER-BASE KINASE INHIBITORS<br/>[FR] INHIBITEURS DE KINASES DE TYPE ARYLÉTHER-BASE申请人:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO公开号:WO2015038112A1公开(公告)日:2015-03-19The present disclosure is generally directed to compounds which can inhibit AAK1 (adaptor associated kinase 1), compositions comprising such compounds, and methods for inhibiting AAK1.
表征谱图
-
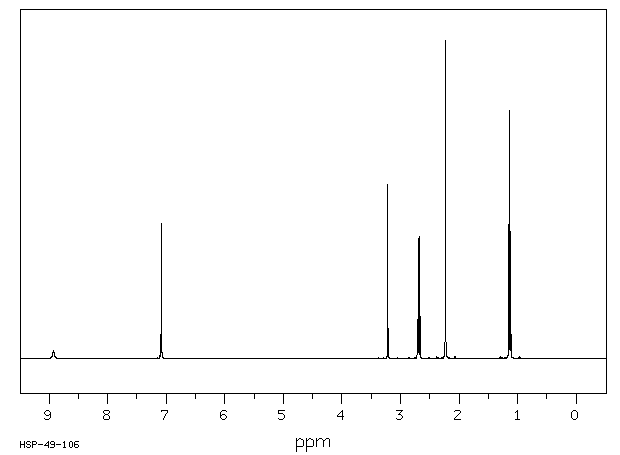
氢谱1HNMR
-
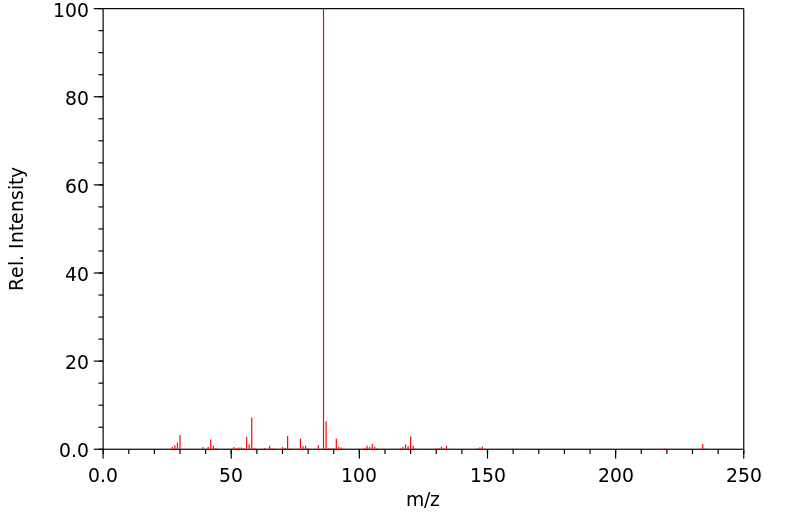
质谱MS
-
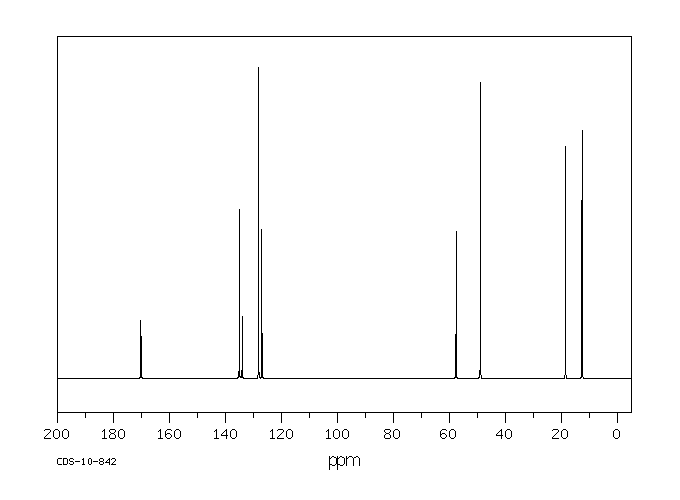
碳谱13CNMR
-
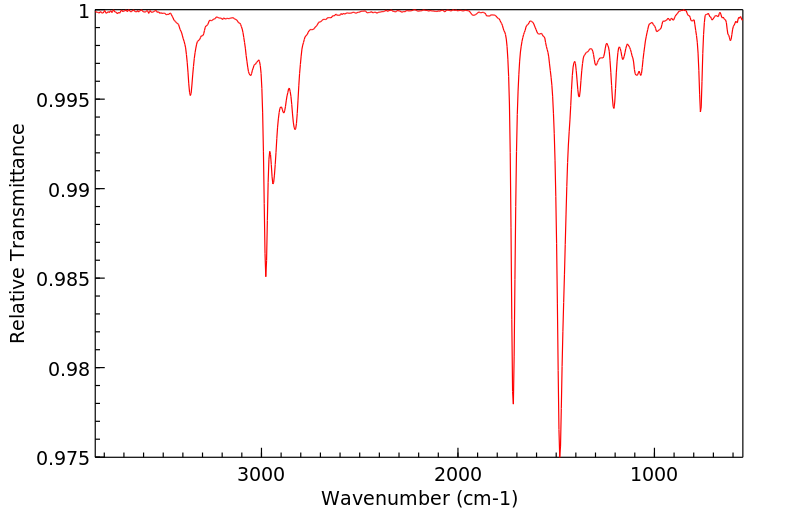
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息