1-己烯-3-醇 | 4798-44-1
物质功能分类
中文名称
1-己烯-3-醇
中文别名
丙基乙烯基甲醇;3-羟基己-1-烯
英文名称
1-hexene-3-ol
英文别名
1-hexen-3-ol;hex-1-en-3-ol
CAS
4798-44-1
化学式
C6H12O
mdl
——
分子量
100.161
InChiKey
BVOSSZSHBZQJOI-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:22.55°C (estimate)
-
沸点:134-135 °C (lit.)
-
密度:0.834 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
-
闪点:95 °F
-
LogP:1.58
-
物理描述:Clear, colourless liquid; meat-like
-
溶解度:25.2 mg/mL at 25 °C
-
折光率:1.425-1.431
-
保留指数:776;772;756;769;767;770;771;771;771;770;764
-
稳定性/保质期:
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):1.5
-
重原子数:7
-
可旋转键数:3
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.67
-
拓扑面积:20.2
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:1
安全信息
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:3
-
安全说明:S16,S29,S33
-
危险类别码:R10
-
WGK Germany:3
-
危险品运输编号:UN 1987 3/PG 3
-
包装等级:III
-
危险类别:3
-
危险性防范说明:P305+P351+P338
-
危险性描述:H225,H302
-
储存条件:请将药品存放在避光、阴凉且干燥的地方,并密封保存。
SDS
模块 1. 化学品
1.1 产品标识符
: 1-己烯-3-醇
产品名称
1.2 鉴别的其他方法
无数据资料
1.3 有关的确定了的物质或混合物的用途和建议不适合的用途
仅用于研发。不作为药品、家庭或其它用途。
模块 2. 危险性概述
2.1 GHS-分类
易燃液体 (类别 3)
急性水生毒性 (类别 3)
2.2 GHS 标记要素,包括预防性的陈述
象形图
警示词 警告
危险申明
H226 易燃液体和蒸气
H402 对水生生物有害。
警告申明
预防措施
P210 远离热源、火花、明火和热表面。- 禁止吸烟。
P233 保持容器密闭。
P240 容器和接收设备接地。
P241 使用防爆的电气/ 通风/ 照明 设备。
P242 只能使用不产生火花的工具。
P243 采取措施,防止静电放电。
P273 避免释放到环境中。
P280 戴防护手套/穿防护服/戴护目镜/戴面罩.
事故响应
P303 + P361 + P353 如果皮肤(或头发)接触:立即除去/脱掉所有沾污的衣物,用水清洗皮肤/淋
浴。
P370 + P378 火灾时: 用干的砂子,干的化学品或耐醇性的泡沫来灭火。
安全储存
P403 + P235 保持低温,存放于通风良好处。
废弃处置
P501 将内容物/ 容器处理到得到批准的废物处理厂。
2.3 其它危害物 - 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
3.1 物 质
: C6H12O
分子式
: 100.16 g/mol
分子量
组分 浓度或浓度范围
Hex-1-en-3-ol
<=100%
化学文摘登记号(CAS 4798-44-1
No.) 225-355-0
EC-编号
模块 4. 急救措施
4.1 必要的急救措施描述
一般的建议
请教医生。 向到现场的医生出示此安全技术说明书。
吸入
如果吸入,请将患者移到新鲜空气处。 如呼吸停止,进行人工呼吸。 请教医生。
皮肤接触
用肥皂和大量的水冲洗。 请教医生。
眼睛接触
用水冲洗眼睛作为预防措施。
食入
禁止催吐。 切勿给失去知觉者通过口喂任何东西。 用水漱口。 请教医生。
4.2 主要症状和影响,急性和迟发效应
4.3 及时的医疗处理和所需的特殊处理的说明和指示
无数据资料
模块 5. 消防措施
5.1 灭火介质
灭火方法及灭火剂
小(起始)火时,使用媒介物如“乙醇”泡沫、干化学品或二氧化碳。大火时,尽可能使用水灭火。使用大量(
洪水般的)水以喷雾状应用;水柱可能是无效的。用大量水降温所有受影响的容器。
5.2 源于此物质或混合物的特别的危害
碳氧化物
5.3 给消防员的建议
如必要的话,戴自给式呼吸器去救火。
5.4 进一步信息
用水喷雾冷却未打开的容器。
模块 6. 泄露应急处理
6.1 作业人员防护措施、防护装备和应急处置程序
避免吸入蒸气、烟雾或气体。 保证充分的通风。 移去所有火源。
谨防蒸气积累达到可爆炸的浓度。蒸气能在低洼处积聚。
6.2 环境保护措施
如能确保安全,可采取措施防止进一步的泄漏或溢出。 不要让产品进入下水道。
一定要避免排放到周围环境中。
6.3 泄漏化学品的收容、清除方法及所使用的处置材料
围堵溢出,用防电真空清洁器或湿刷子将溢出物收集起来,并放置到容器中去,根据当地规定处理(见第13部
分)。
6.4 参考其他部分
丢弃处理请参阅第13节。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
7.1 安全操作的注意事项
避免吸入蒸气和烟雾。
切勿靠近火源。-严禁烟火。采取措施防止静电积聚。
7.2 安全储存的条件,包括任何不兼容性
贮存在阴凉处。 使容器保持密闭,储存在干燥通风处。
打开了的容器必须仔细重新封口并保持竖放位置以防止泄漏。
充气保存
7.3 特定用途
无数据资料
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
8.1 容许浓度
最高容许浓度
没有已知的国家规定的暴露极限。
8.2 暴露控制
适当的技术控制
根据良好的工业卫生和安全规范进行操作。 休息前和工作结束时洗手。
个体防护设备
眼/面保护
面罩與安全眼鏡请使用经官方标准如NIOSH (美国) 或 EN 166(欧盟) 检测与批准的设备防护眼部。
皮肤保护
戴手套取 手套在使用前必须受检查。
请使用合适的方法脱除手套(不要接触手套外部表面),避免任何皮肤部位接触此产品.
使用后请将被污染过的手套根据相关法律法规和有效的实验室规章程序谨慎处理. 请清洗并吹干双手
所选择的保护手套必须符合EU的89/686/EEC规定和从它衍生出来的EN 376标准。
身体保护
防渗透的衣服, 阻燃防静电防护服,
防护设备的类型必须根据特定工作场所中的危险物的浓度和数量来选择。
呼吸系统防护
如危险性评测显示需要使用空气净化的防毒面具,请使用全面罩式多功能防毒面具(US)或ABEK型
(EN
14387)防毒面具筒作为工程控制的候补。如果防毒面具是保护的唯一方式,则使用全面罩式送风防
毒面具。 呼吸器使用经过测试并通过政府标准如NIOSH(US)或CEN(EU)的呼吸器和零件。
模块 9. 理化特性
9.1 基本的理化特性的信息
a) 外观与性状
形状: 液体
颜色: 无色
b) 气味
无数据资料
c) 气味阈值
无数据资料
d) pH值
无数据资料
e) 熔点/凝固点
无数据资料
f) 沸点、初沸点和沸程
134 - 135 °C - lit.
g) 闪点
35 °C - 闭杯
h) 蒸发速率
无数据资料
i) 易燃性(固体,气体)
无数据资料
j) 高的/低的燃烧性或爆炸性限度 无数据资料
k) 蒸气压
无数据资料
l) 蒸汽密度
无数据资料
m) 密度/相对密度
0.834 g/cm3 在 25 °C
n) 水溶性
无数据资料
o) n-辛醇/水分配系数
无数据资料
p) 自燃温度
无数据资料
q) 分解温度
无数据资料
r) 粘度
无数据资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应活性
10.1 反应性
无数据资料
10.2 稳定性
无数据资料
10.3 危险反应
无数据资料
10.4 应避免的条件
热,火焰和火花。
10.5 不相容的物质
强氧化剂, 强酸
10.6 危险的分解产物
其它分解产物 - 无数据资料
模块 11. 毒理学资料
11.1 毒理学影响的信息
急性毒性
无数据资料
皮肤刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
眼睛刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
呼吸道或皮肤过敏
无数据资料
生殖细胞致突变性
无数据资料
致癌性
IARC:
此产品中没有大于或等于 0。1%含量的组分被 IARC鉴别为可能的或肯定的人类致癌物。
生殖毒性
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触)
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(反复接触)
无数据资料
吸入危险
无数据资料
潜在的健康影响
吸入 吸入可能有害。 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
摄入 如服入是有害的。
皮肤 通过皮肤吸收可能有害。 可能引起皮肤刺激。
眼睛 可能引起眼睛刺激。
附加说明
化学物质毒性作用登记: 无数据资料
模块 12. 生态学资料
12.1 生态毒性
对鱼类的毒性 半数致死浓度(LC50) - 肥头鲦鱼 (黑头软口鲦鱼) - 30.4 mg/l - 96 h
12.2 持久性和降解性
无数据资料
12.3 潜在的生物累积性
无数据资料
12.4 土壤中的迁移性
无数据资料
12.5 PBT 和 vPvB的结果评价
无数据资料
12.6 其它不良影响
对水生生物有害。
无数据资料
模块 13. 废弃处置
13.1 废物处理方法
产品
在装备有加力燃烧室和洗刷设备的化学焚烧炉内燃烧处理,特别在点燃的时候要注意,因为此物质是高度易燃
性物质 将剩余的和不可回收的溶液交给有许可证的公司处理。
联系专业的拥有废弃物处理执照的机构来处理此物质。
受污染的容器和包装
按未用产品处置。
模块 14. 运输信息
14.1 联合国危险货物编号
欧洲陆运危规: 1987 国际海运危规: 1987 国际空运危规: 1987
14.2 联合国运输名称
欧洲陆运危规: ALCOHOLS, N.O.S. (Hex-1-en-3-ol)
国际海运危规: ALCOHOLS, N.O.S. (Hex-1-en-3-ol)
国际空运危规: Alcohols, n.o.s. (Hex-1-en-3-ol)
14.3 运输危险类别
欧洲陆运危规: 3 国际海运危规: 3 国际空运危规: 3
14.4 包裹组
欧洲陆运危规: III 国际海运危规: III 国际空运危规: III
14.5 环境危险
欧洲陆运危规: 否 国际海运危规 国际空运危规: 否
海洋污染物(是/否): 否
14.6 对使用者的特别提醒
无数据资料
上述信息视为正确,但不包含所有的信息,仅作为指引使用。本文件中的信息是基于我们目前所知,就正
确的安全提示来说适用于本品。该信息不代表对此产品性质的保证。
参见发票或包装条的反面。
模块 15 - 法规信息
N/A
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
制备方法与用途
上下游信息
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:One-Pot Synthesis of Homoallylic Alcohols via a Facile Conversion of Allylic Alcohols into Allylic Iodides摘要:烯丙醇在温和条件下通过氯三甲基硅烷/碘化钠和水或醇现场生成的氢碘酸,可以方便地转化为烯丙基碘化物。具有末端双键的烯丙醇的取代反应会产生伴随烯丙基重排的烯丙基碘化物。这一方法已成功扩展为通过连续的巴比耶型反应,实现高烯丙醇的一锅法合成。DOI:10.1055/s-1989-27223
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:An efficient didehydroxylation method for the biomass-derived polyols glycerol and erythritol. Mechanistic studies of a formic acid-mediated deoxygenation摘要:发现了一种高效的1,2-脱氧方法,涉及一种意外的机理,适用于简单二醇和生物质衍生多元醇(甘油和赤藓糖醇),能够将1,2-二羟基转化为碳-碳双键。DOI:10.1039/b907746d
文献信息
-
Regiospezifische Herstellung von primären Allylacetaten (2-Alkenyl-acetaten)作者:Antonio García Martínez、Angeles Cruces Villalobos、Manuel Oliver RuizDOI:10.1055/s-1988-27464日期:——Regiospecific Preparation of Primary Allyl Acetates (2-Alkenyl Acetates) The reaction of primary, secondary and tertiary allyl alcohols 1 with anhydrous magnesium iodide in benzene gives regiospecifically the primary allyl iodides 2. The corresponding primary allyl acetates 3 are obtained regiospecifically by reaction of 2 with anhydrous sodium acetate in dimethylformamide.
-
A 1,4‐Palladium Migration/Heck Sequence with Unactivated Alkenes: Stereoselective Synthesis of Trisubstituted 1,3‐Dienes作者:Ze‐Jian Xue、Meng‐Yao Li、Bin‐Bin Zhu、Zhi‐Tao He、Chen‐Guo Feng、Guo‐Qiang LinDOI:10.1002/adsc.202001589日期:2021.4.13The palladium‐catalyzed cross‐coupling of ortho‐vinyl aromatic bromides and olefins was achieved through a controllable 1,4‐palladium migration/Heck cascade protocol. The reaction represents a mild, efficient and highly stereoselective method for the synthesis of trisubstituted 1,3‐dienes, especially for triaryl‐substituted ones.
-
The Effects of Lewis Acid on the 1,3-Dipolar Cycloaddition Reaction of C-Arylaldonitrones with Alkenes.作者:Tomio Shimizu、Masaya Ishizaki、Nobuo NitadaDOI:10.1248/cpb.50.908日期:——The regio- and stereoselectivity of the 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition reactions of C-aryl-N-alkylaldonitrones (1a-e) with some alkenes were found to be affected significantly by the addition of Lewis acid. The rate of the reaction was also affected by adding the Lewis acid. In the reactions using allyl alcohol as a dipolarophile an addition of Lewis acid caused a remarkable acceleration of the reaction
-
The reaction between acyl halides and alcohols: Alkyl halide vs. Ester formation作者:Paolo Strazzolini、Angelo G. Giumanini、Giancarlo VerardoDOI:10.1016/s0040-4020(01)80747-x日期:1994.4therefore, ester formation practically confined to a triggering role. But, in those cases where the cation is less easily formed, ester formation was favoured and, consequently, became the necessary elementary step towards alkyl halide formation. This final product, on the other hand, might be extremely slow to form in an SN2 reaction between the protonated ester function and the halide ion. In these hnstances在酰基卤和醇之间的反应中,热力学上有利的产物是游离羧酸和烷基卤。最初的反应通常是形成酯和HHal。当该醇非常容易被HHal质子化时产生烷基阳离子时,形成的H 2 O表现出超活性,并且与该醇成功竞争了酰基卤的制备,因此,酯的形成实际上局限于触发作用。但是,在那些阳离子不易形成的情况下,有利于酯的形成,因此成为形成卤代烷的必要的基本步骤。另一方面,最终产品在S N中的形成速度可能非常慢2质子化的酯官能团与卤离子之间的反应。因此,在这些情况下,以及在碱性溶剂竞争HHal质子的情况下,酯都是最终产物。α-羟基,α-苯基苯乙酸(2y)给出了上述虚线所示的一个显着例外,它似乎通过季中间体(E)进行了直接的氯-羟基交换,最后塌陷为α-氯- α-苯基苯乙酸(4y)。在严格相似的条件下,使用CH 2 Cl 2作为溶剂比较了不同的系统。测试了约28种不同的底物与AcCl(1a)的反应,而八种酰基卤(1)对(R
-
Activation of Alcohols with Carbon Dioxide: Intermolecular Allylation of Weakly Acidic Pronucleophiles作者:Simon B. Lang、Theresa M. Locascio、Jon A. TungeDOI:10.1021/ol502023d日期:2014.8.15coupling of allyl alcohols with nitroalkanes, nitriles, and aldehydes using catalytic Pd(PPh3)4 has been accomplished via activation of C–OH bonds with CO2. The in situ formation of carbonates from alcohols and CO2 facilitates oxidative addition to Pd to form reactive π-allylpalladium intermediates. In addition, the formation of a strong base activates nucleophiles toward the reaction with the π-allylpalladium
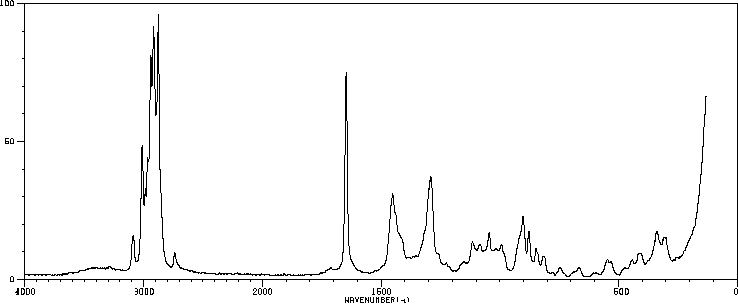
表征谱图
-
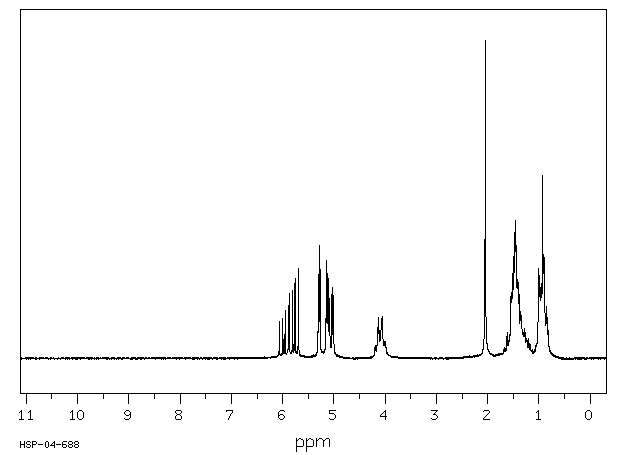
氢谱1HNMR
-
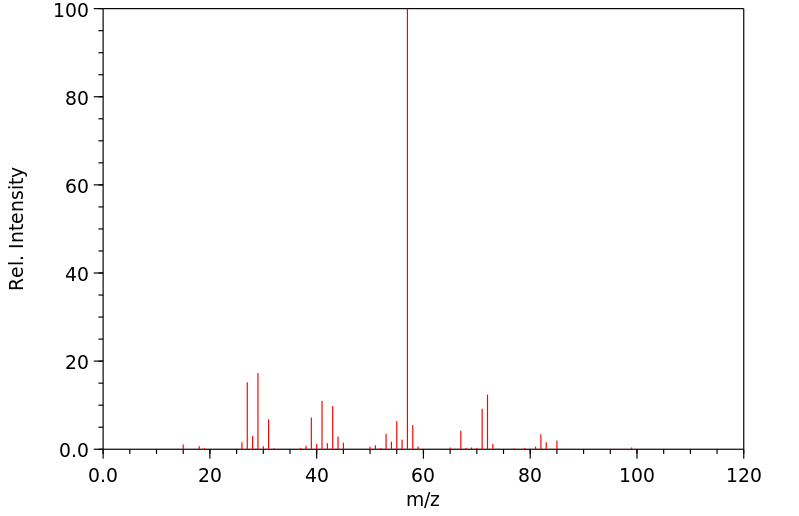
质谱MS
-
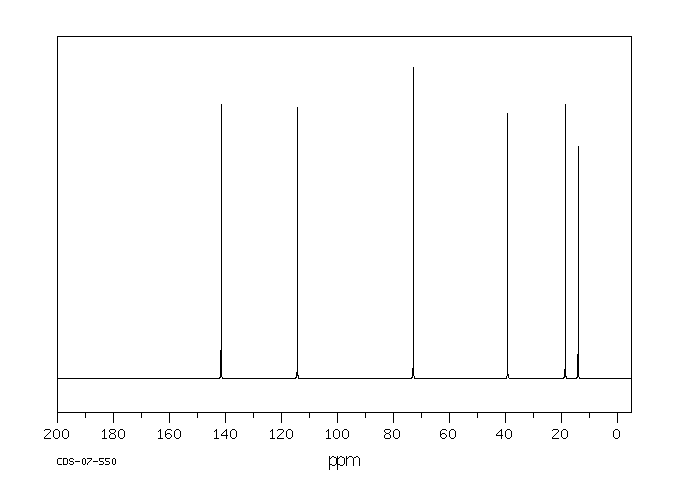
碳谱13CNMR
-
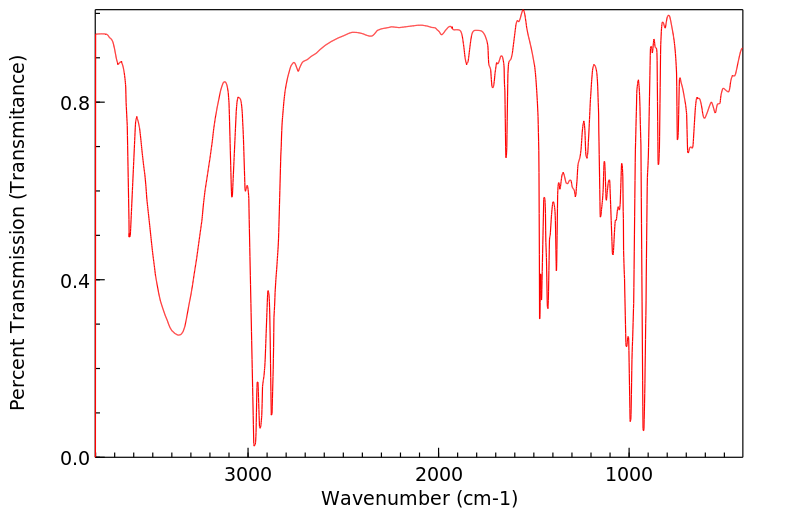
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(反式)-4-壬烯醛
(s)-2,3-二羟基丙酸甲酯
([1-(甲氧基甲基)-1H-1,2,4-三唑-5-基](苯基)甲酮)
(Z)-4-辛烯醛
(S)-氨基甲酸酯β-D-O-葡糖醛酸
(S)-3-(((2,2-二氟-1-羟基-7-(甲基磺酰基)-2,3-二氢-1H-茚满-4-基)氧基)-5-氟苄腈
(R)-氨基甲酸酯β-D-O-葡糖醛酸
(5,5-二甲基-2-(哌啶-2-基)环己烷-1,3-二酮)
(2,5-二氟苯基)-4-哌啶基-甲酮
龙胆苦苷
龙胆二糖甲乙酮氰醇(P)
龙胆二糖丙酮氰醇(P)
龙胆三糖
龙涎酮
齐罗硅酮
齐留通beta-D-葡糖苷酸
鼠李糖
黑芥子苷单钾盐
黑海棉酸钠盐
黑木金合欢素
黑曲霉三糖
黑介子苷
黄尿酸8-O-葡糖苷
麻西那霉素II
麦迪霉素
麦芽糖脎
麦芽糖基海藻糖
麦芽糖1-磷酸酯
麦芽糖
麦芽四糖醇
麦芽四糖
麦芽十糖
麦芽六糖
麦芽五糖水合物
麦芽五糖
麦芽五糖
麦芽五糖
麦芽三糖醇
麦芽三糖
麦芽三糖
麦芽三塘水合
麦芽七糖水合物
麦芽七糖
麦法朵
麦可酚酸-酰基-Β-D-葡糖苷酸
麦利查咪
麝香酮
鹤草酚
鸢尾酚酮 3-C-beta-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷
鸡矢藤苷