2-溴蒽醌 | 572-83-8
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:208 °C
-
沸点:443.4±34.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:1.5425 (rough estimate)
-
溶解度:在热甲苯中几乎完全溶解
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):4.1
-
重原子数:17
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:3.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:34.1
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:2
安全信息
-
海关编码:2914700090
-
RTECS号:CB5950000
-
危险性防范说明:P261,P305+P351+P338
-
危险性描述:H302,H315,H319
-
储存条件:| 室温 |
SDS
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: 2-BromoaNThraquinone
修改号码: 5
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害 未分类
健康危害 未分类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志 无
信号词 无信号词
危险描述 无
防范说明 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 2-溴蒽醌
百分比: >96.0%(GC)
CAS编码: 572-83-8
分子式: C14H7BrO2
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用水清洗皮肤/淋浴。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,雾状水,二氧化碳
特殊危险性: 小心,燃烧或高温下可能分解产生毒烟。
2-溴蒽醌 修改号码:5
模块 5. 消防措施
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 清扫收集粉尘,封入密闭容器。注意切勿分散。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的
法律法规处置。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止粉尘扩散。处理后彻底清洗双手
和脸。
注意事项: 如果粉尘或浮质产生,使用局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗处。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防尘面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
固体
外形(20°C):
外观: 晶体-粉末
颜色: 浅黄色-灰红黄色
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点:
208°C
沸点/沸程 无资料
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 无资料
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂] 无资料
2-溴蒽醌 修改号码:5
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳, 溴化氢
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
RTECS 号码: CB5950000
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在可燃溶剂中溶解混合,在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中
焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
2-溴蒽醌 修改号码:5
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
制备方法与用途
2-溴蒽醌以9,10-二蒽酮为母核,通过不同程度的还原可转化为氧化蒽酚、蒽酮和蒽酚结构。其侧位基团可以被羟基、甲氧基、甲基、羟甲基、卤素或糖苷等取代基团所取代。由于母核中含有大量生色团和助色团,蒽醌类化合物呈现出较深的颜色,并具有荧光特性。
制备在25毫升单颈圆底烧瓶中混合邻苯二甲酸酐(1毫摩尔)、取代苯(1.1毫摩尔)和水(5毫升),并加入25%的催化剂。将反应混合物在室温下搅拌适当时间(参见表2,条目3a-j)。通过薄层色谱(TLC)监测反应进程。反应完成后,使用乙酸乙酯(2-10毫升)萃取混合物。合并有机相,并在无水硫酸钠上干燥。然后在减压下蒸发以除去溶剂;粗产物通过硅胶柱层析纯化,最终得到2-溴蒽醌,产率为80%,熔点为205-206°C。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 2-氨基-3-溴蒽醌 2-amino-3-bromoanthraquinone 6337-00-4 C14H8BrNO2 302.127 2-苯甲酰基-4-溴苯甲酸 2-benzoyl-4-bromobenzoic acid 412299-83-3 C14H9BrO3 305.128 1-溴蒽醌 1-Bromoanthraquinone 632-83-7 C14H7BrO2 287.112 蒽醌 9,10-phenanthrenequinone 84-65-1 C14H8O2 208.216 2-(3-溴苯甲酰基)苯甲酸 2-(3-bromobenzoyl)benzoic acid 65565-11-9 C14H9BrO3 305.128 2(4-溴苯甲酰基)苯甲酸 2-(4-bromobenzoyl)benzoic acid 2159-40-2 C14H9BrO3 305.128 2-氨基蒽醌 2-aminoanthraquinone 117-79-3 C14H9NO2 223.231 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— 2-bromoanthrone 76656-50-3 C14H9BrO 273.129 蒽醌 9,10-phenanthrenequinone 84-65-1 C14H8O2 208.216 —— 9,10-dioxo-9,10-dihydroanthracene-2-carbonitrile 37649-98-2 C15H7NO2 233.226 2-乙烯基蒽醌 2-Vinyl-anthrachinon 13388-33-5 C16H10O2 234.254 2-羟基蒽醌 2-hydroxy-9,10-anthraquinone 605-32-3 C14H8O3 224.216 2-氨基蒽醌 2-aminoanthraquinone 117-79-3 C14H9NO2 223.231 —— 2-ethynylanthraquinone 78053-65-3 C16H8O2 232.238 2-(三氟甲基)蒽-9,10-二酮 2-trifluoromethyl-anthraquinone 362-21-0 C15H7F3O2 276.215 2-(4-甲基戊-3-烯基)蒽-9,10-二酮 2-(4-methyl-3-pentenyl)-anthraquinone 71308-16-2 C20H18O2 290.362 —— 2,2'-Dianthrachinonyl 809-63-2 C28H14O4 414.417 2-苯基蒽醌 2-Phenyl-anthrachinon 6485-97-8 C20H12O2 284.314 —— 2,2'-sulfanediyl-di-anthraquinone 749250-55-3 C28H14O4S 446.483 —— 2-(4-aminophenyl)anthracene-9,10-dione 856357-68-1 C20H13NO2 299.329 - 1
- 2
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:Graebe; Liebermann, Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie, 1870, vol. Suppl.7, p. 277摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:描述:2-(3-溴苯甲酰基)苯甲酸 在 硫酸 作用下, 反应 1.0h, 以89%的产率得到2-溴蒽醌参考文献:名称:Popov, S.I.; Kopylova, T.M.; Andrievskii, A.M., Russian Journal of Organic Chemistry, 1994, vol. 30, # 2, p. 279 - 285摘要:DOI:
-
作为试剂:描述:参考文献:名称:2-溴蒽醌作为仲芳香醇氧化的高效光催化剂:实验和DFT研究摘要:蒽醌被认为是高效光催化剂,可以在水相或有机相中进行各种氧化还原反应。我们通过实验证明2-BrAQ可以在光照条件下与α-芳香醇进行氢转移,从而有效地将芳香醇氧化成相应的产物。 1-苯乙醇制苯乙酮的收率可达96%以上。在后续的催化剂筛选实验中,发现蒽醌环2位取代基的电负性和溶剂的酸性影响蒽醌类化合物的光催化活性。使用各种芳香醇底物后,2-BrAQ对大多数芳香醇表现出良好的转化率和选择性,但对非α位芳香醇表现出C-C键断裂和低选择性。为了探索2-BrAQ在乙腈溶液中的氧化还原反应机理,提出了相应的自由基反应路径,并通过密度泛函理论(DFT)进行了验证。重点关注2-BrAQ反应过程中的计算以及2-BrAQ三重态分子与1-苯基乙醇分子之间的第一步氢转移反应,我们认识到反应过程中发生的变化,从而对氧化还原有了更深入的了解有机体系中蒽醌化合物的反应。DOI:10.1039/d0ra06414a
文献信息
-
Efficient one-pot transformation of aminoarenes to haloarenes using halodimethylisulfonium halides generated in situ作者:Woonphil Baik、Wanqiang Luan、Hyun Joo Lee、Cheol Hun Yoon、Sangho Koo、Byeong Hyo KimDOI:10.1139/v05-026日期:2005.3.1
Halodimethylsulfonium halide 1, which is readily formed in situ from hydrohaloic acid and DMSO, is a good nucleophilic halide. This activated nucleophilic halide rapidly converts aryldiazonium salt prepared in situ by the same hydrohaloic acid and nitrite ion to aryl chlorides, bromides, or iodides in good yield. The combined action of nitrite ion and hydrohaloic acid in DMSO is required for the direct transformation of aromatic amines, which results in the production of aryl halides within 1 h. Substituted compounds with electron-donating or -withdrawing groups or sterically hindered aromatic amines are also smoothly transformed to the corresponding aromatic halides. The only observed by-product is the deaminated arene (usually <7%). The isolated aryldiazonium salts can also be converted to the corresponding aryl halides using 1. The present method offers a facile, one-step procedure for transforming aminoarenes to haloarenes and lacks the environmental pollutants that usually accompany the Sandmeyer reaction using copper halides. Key words: aminoarenes, haloarenes, halodimethylsulfonium halide, halogenation, amination.
卤二甲基亚砜卤化物1是一种良好的亲核卤化物,可在现场由氢卤酸和二甲亚砜形成。这种活化的亲核卤化物迅速将由相同的氢卤酸和亚硝酸根在现场制备的芳基重氮盐转化为芳基氯化物、溴化物或碘化物,收率较高。在DMSO中,亚硝酸根和氢卤酸的联合作用是直接转化芳香胺的必要条件,从而在1小时内产生芳基卤化物。带有电子给体或吸引基团或有立体位阻的芳香胺的取代化合物也可顺利转化为相应的芳香卤化物。观察到的唯一副产物是去氨基芳烃(通常<7%)。孤立的芳基重氮盐也可以使用1转化为相应的芳基卤化物。该方法提供了一种简便的、一步法的程序,用于将氨基芳烃转化为卤代芳烃,并且不伴随通常伴随使用铜卤化物进行桑迈尔反应的环境污染物。关键词:氨基芳烃,卤代芳烃,卤二甲基亚砜卤化物,卤化,胺化。 -
ORGANIC COMPOUND AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE USING THE SAME申请人:Kim Kong Kyeom公开号:US20140077166A1公开(公告)日:2014-03-20The present invention provides an organic light emitting device comprising a first electrode, at least one organic layer and a second electrode, laminated successively, in which at least one layer of the organic layer has a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon as a core and comprises at least one of a derivative in which a substituted or unsubstituted C 2-30 cycloalkane, or a substituted or unsubstituted C 5-50 polycycloalkane is directly fused to the core or fused to a substituent of the core: and a new organic compound usable in the organic light emitting device. Furthermore, the present invention provides a charge carrier extracting, injecting or transporting material which has a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon as a core and comprises a derivative in which a substituted or unsubstituted C 2-30 cycloalkane, or a substituted or unsubstituted C 5-50 polycycloalkane is directly fused to the core or fused to a substituent of the core.
-
Direct Route to 1,3-Diketones by Palladium-Catalyzed Carbonylative Coupling of Aryl Halides with Acetylacetone作者:Signe Korsager、Dennis U. Nielsen、Rolf H. Taaning、Anders T. Lindhardt、Troels SkrydstrupDOI:10.1002/chem.201303872日期:2013.12.23Man up your magnesium! By employing a MgCl2/Et3N system, aryl diketones can be generated from the Pd‐catalyzed carbonylative α‐arylation of acetylacetone with aryl bromides (see scheme). The method is ideal for the introduction of carbon isotopes into more complex structures, since only stoichiometric amounts of carbon monoxide are employed.
-
발광 화합물 및 이를 포함하는 유기전계발광소자申请人:SFC CO., LTD. 에스에프씨 주식회사(120060087061) Corp. No ▼ 135511-0105889BRN ▼134-81-54429公开号:KR101553561B1公开(公告)日:2015-09-17본 발명은 하기 식 (1)로 표시되는 발광 화합물 및 이를 포함하는 유기전계발광소자에 관한 것으로서, 본 발명에 따른 발광 화합물은 휘도가 우수하고, 장수명을 갖는 유기전계발광소자를 제공할 수 있다. (1)这项发明涉及标记为式(1)的发光化合物及包含该化合物的有机电致发光器件,根据本发明,所述发光化合物可以提供具有优异亮度和长寿命的有机电致发光器件。 (1)
-
신규한 질소 함유 헤테로환 화합물 및 이를 이용한 유기 전자 소자申请人:LG CHEM, LTD. 주식회사 엘지화학(120010134563) Corp. No ▼ 110111-2207995BRN ▼107-81-98139公开号:KR101567610B1公开(公告)日:2015-11-09본 발명은 신규한 질소 함유 헤테로환 화합물 및 이를 이용한 유기 전자 소자를 제공한다. 본 발명에 따른 유기 전자 소자는 효율, 구동전압 및 수명 면에서 우수한 특성을 나타낸다.这项发明提供了一种新型的含氮杂环化合物以及利用它们制造的有机电子器件。根据这项发明,有机电子器件表现出优异的效率、驱动电压和寿命特性。
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
质谱MS
-
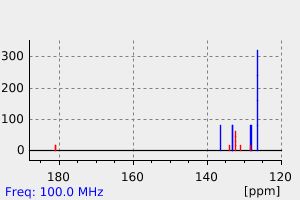
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息