苯胺 | 62-53-3
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:-6 °C (lit.)
-
沸点:184 °C (lit.)
-
密度:1.022 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
-
蒸气密度:3.22 (185 °C, vs air)
-
闪点:76 °C
-
溶解度:可溶于水
-
介电常数:7.8(0℃)
-
暴露限值:TLV-TWA skin 2 ppm (~8 mg/m3) (ACGIH), 5 ppm (~19 mg/m3) (MSHA, OSHA, and NIOSH); IDLH 100 ppm (NIOSH).
-
LogP:0.900
-
物理描述:Aniline appears as a yellowish to brownish oily liquid with a musty fishy odor. Melting point -6°C; boiling point 184°C; flash point 158°F. Denser than water (8.5 lb / gal) and slightly soluble in water. Vapors heavier than air. Toxic by skin absorption and inhalation. Produces toxic oxides of nitrogen during combustion. Used to manufacture other chemicals, especially dyes, photographic chemicals, agricultural chemicals and others.
-
颜色/状态:Colorless to brown, oily liquid [Note: A solid below 21 °F]
-
气味:Hedonic tone; pungent
-
味道:Burning taste
-
蒸汽密度:3.22 (EPA, 1998) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:6.67X10-1 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
亨利常数:Henry's Law constant = 2.02X10-6 atm-cu m/mol at 25 °C
-
大气OH速率常数:1.11e-10 cm3/molecule*sec
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
无色油状易燃液体,具有强烈气味。它稍溶于水,并能与乙醇、乙醚、氯仿及其他大多数有机溶剂混溶。苯胺呈碱性,可以生成盐酸盐。在空气中或光照下会逐渐变为棕色。易燃的蒸气与空气可形成爆炸混合物,其爆炸极限为1.2%-8.3%(体积分数)。高毒性的苯胺化学性质活泼,能进行烷基化、磺化等反应,并特别容易氧化,根据条件不同可能生成硝基苯或对苯。暴露在空气中和光照下颜色会加深,还能随水蒸气挥发。
-
化学性质上,苯胺相较于脂肪族胺的碱性较弱。它与亚硝酸作用时会发生重氮化反应形成重氮盐,随后经偶合反应生成偶氮化合物。苯胺可以与无机酸发生中和反应产生可溶于水的盐类,或与氯化锌、铜、氯化钙等形成复盐。在酸性溶液中与醇发生烷基化反应,得到N-烷基化合物;同时也能与烯烃、卤代烷进行同样的反应。苯胺可以与羧酸、酸酐、酰氯及酯类物质发生反应生成酰替苯胺。由于含有氨基,苯胺使芳核容易参与取代反应,在邻位或对位上发生烷基化、卤化、磺化、硝化、亚硝化等反应。此外,它还容易被氧化成对苯醌、硝基苯、偶氮苯、氧化偶氮苯等。在特定条件下,苯胺可以氢化生成环己胺,并与醛类物质反应生成树脂状缩合物。
-
苯胺可通过口服、吸入蒸气或皮肤吸收而引起中毒,其中皮肤接触液体和蒸气通常是导致中毒的主要途径之一。苯胺对血液和神经系统具有强烈的毒性作用,可形成高铁血红蛋白。急性中毒症状可能包括头痛及发绀,严重时甚至可能导致死亡。根据相关标准,当空气中苯胺浓度达到406~619毫克/立方米时,在少于一小时内吸入不会对人体健康产生损害;而车间空气中最高容许浓度规定为5毫克/立方米。
-
苯胺相对稳定。
-
禁忌物包括强氧化剂、酸类及酰基氯、酸酐等。
-
苯胺不具有聚合性。
-
-
自燃温度:1139 °F (615 °C)
-
分解:Decomposes above 190 °C . This produces toxic and corrosive fumes of nitrogen oxides and ammonia and flammable vapors.
-
粘度:4.35 cP at 20 °C; 1.62 cP at 60 °C
-
燃烧热:-3392.8 KJ/mol
-
汽化热:55.83 kJ/mol
-
表面张力:42.12 dynes/cm at 25 °C in contact with air; 39.41 dynes/cm at 50 °C in contact with air; 36.69 dynes/cm at 75 °C in contact with air.
-
电离电位:7.70 eV
-
聚合:Unless inhibited (usually methanol), aniline is readily able to polymerize.
-
气味阈值:Odor Threshold Low: 0.58 [mmHg]; Odor Threshold High: 10.0 [mmHg]; Detection odor threshold from AIHA (mean = 2.4 ppm)
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.5863 at 20 °C/D
-
解离常数:4.6 (at 25 °C; aniline conjugate acid)
-
相对蒸发率:< 1 (Butyl acetate = 1)
-
保留指数:939.2 ;945.6 ;955 ;955 ;939.1 ;952.6 ;966 ;967 ;968 ;968 ;983 ;995 ;995 ;946 ;945 ;946 ;947 ;950 ;954 ;947 ;952 ;958 ;964 ;963 ;953.3
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):0.9
-
重原子数:7
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:26
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:1
ADMET
安全信息
-
职业暴露限值:TWA: None ppm
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:6.1
-
立即威胁生命和健康浓度:100 ppm
-
危险品标志:T
-
安全说明:S26,S27,S36/37,S36/37/39,S45,S46,S61,S63
-
危险类别码:R40,R43,R68,R48/23/24/25,R23/24/25,R50,R41
-
WGK Germany:2
-
海关编码:2921411000
-
危险品运输编号:UN 1547 6.1/PG 2
-
危险类别:6.1
-
RTECS号:BW6650000
-
包装等级:II
-
危险标志:GHS05,GHS06,GHS08,GHS09
-
危险性描述:H301 + H311 + H331,H317,H318,H341,H351,H372,H410
-
危险性防范说明:P260,P280,P302 + P352 + P312,P304 + P340 + P312,P305 + P351 + P338 + P310
-
储存条件:储存于阴凉、通风的库房中。远离火种与热源,库温不宜超过32℃,相对湿度保持在80%以下。避免阳光直射并确保密封包装,防止与空气接触。应将储存物与氧化剂、酸类及食用化学品分开存放,并禁止混合储存。配备相应的消防器材,并在储区备有泄漏应急处理设备和合适的收容材料。
SDS
| 国标编号: | 61746 |
| CAS: | 62-53-3 |
| 中文名称: | 苯胺 |
| 英文名称: | Aniline;Aminobenzene |
| 别 名: | 氨基苯 |
| 分子式: | C 6 H 7 N;C 6 H 5 NH 2 |
| 分子量: | 93.12 |
| 熔 点: | -6.2℃ 沸点:184.4℃ |
| 密 度: | 相对密度(水=1)1.02; |
| 蒸汽压: | 70℃ |
| 溶解性: | 微溶于水,溶于乙醇、乙醚、苯 |
| 稳定性: | 稳定 |
| 外观与性状: | 无色或微黄色油状液体,有强烈气味 |
| 危险标记: | 14(毒害品) |
| 用 途: | 用于染料、医药、橡胶、树脂、香料等的合成 |
2.对环境的影响:
一、健康危害
侵入途径:吸入、食入、经皮吸收。
健康危害:苯胺的毒作用,主要因形成的高铁血红蛋白所致,造成组织缺氧,引起中枢神经系统、心血管系统和其它脏器损害。
急性中毒:中毒者的口唇、指端、耳廓发绀,病人有恶心、呕吐、手指发麻、精神恍惚等;重度中毒进,皮肤、粘膜严重青紫,出现心悸、呼吸困难、抽搐甚至昏迷、休克;重笃者可出现溶血性黄疸、中毒性肝炎、中毒性肾损伤。
慢性中毒:患者有神经衰弱综合征表现,伴有轻度发绀、贫血和肝、脾肿大。皮肤接触可发生湿疹。
二、毒理学资料及环境行为
毒性:中等毒性。
急性毒性:LD 50 442mg/kg(大鼠经口);820mg/kg(兔经皮);LC 50 175ppm,7小时(小鼠吸入)
亚急性和慢性毒性:大鼠吸入19mg/m 3 ,6小时/天,23周时高铁血蛋白升高至600mg/mL。
致突变性:微粒体诱变试验:鼠伤寒沙门氏菌100ug/皿。姊妹染色单体交换:小鼠腹腔内210mg/kg。
生产苯胺的有机化工厂、焦化厂及石油冶炼厂等企业,使用苯胺的染料合成,制药业,印染工业,橡胶促凝剂和防老化剂、打印油墨、2,4,6-三硝基苯甲硝胺、光学白涂剂、照相显影剂、树脂、假漆、香料、轮胎抛光剂及许多其他有机化学品的制造。在这些生产和使用苯胺的行业中以及在贮运过程中的意外事故均会造成对环境的污染、对人体危害。
危险特性:遇高热、明火或与氧化剂接触,有引起燃烧的危险。
燃烧(分解)产物:一氧化碳、二氧化碳、氧化氮。
3.现场应急监测方法:
气体检测管法;直接进水样气相色谱法
快速检测管法;便携式气相色谱法《突发性环境污染事故应急监测与处理处置技术》万本太主编
气体速测管(北京劳保所产品、德国德尔格公司产品)
4.实验室监测方法:
| 监测方法 | 来源 | 类别 |
| 盐酸乙二胺分光光度法 | GB/T15502 | 空气 |
| 溶剂解吸气相色谱法 | WS/T142-1999 | 作业场所空气 |
| 溶剂解吸高效液相色谱法 | WS/T170-1999 | 作业场所空气 |
| N-(1-萘基)-乙二胺偶氮分光光度法 | GB11889-89 | 水质 |
| 气相色谱法 | 《水质分析大全》张宏陶等主编 | 水质 |
5.环境标准:
| 中国(TJ36-79) | 车间空气中有害物质的最高容许浓度 | 5mg/m 3 [皮] |
| 中国(TJ36-79) | 居住区大气中有害物质的最高容许浓度 | 0.10mg/m 3 (一次值) 0.03mg/m 3 (日均值) |
| 中国(GB16297-1996) | 大气污染物综合排放标准 | ①最高允许排放浓度(mg/m 3 ): 20(表2);25(表1) ②最高允许排放速率(kg/h): 二级0.52~11(表2);0.61~13(表1) 三级0.78~17(表2);0.92~20(表1) ③无组织排放监控浓度限值(mg/m 3 ): 0.40(表2);0.50(表1) |
| 中国(待颁布) | 饮用水源水中有害物质的最高容许浓度 | 0.1mg/L |
| 中国(GB8978-1996) | 污水综合排放标准 | 一级:1.0mg/L 二级:2.0mg/L 三级:5.0mg/L |
| 嗅觉阈浓度 | 0.37~4.15mg/m 3 |
6.应急处理处置方法:
一、泄漏应急处理
疏散泄漏污染区人员至安全区,禁止无关人员进入污染区,切断火源。建议应急处理人员戴自给式呼吸器,穿化学防护服,不要直接接触泄漏物,在确保安全情况下堵漏。用沙土混合,逐渐倒入稀盐酸中(1体积浓盐酸加2体积水稀释),放置24小时,然后废弃。如大量泄漏,收集回收或无害处理后废弃。
⑴土壤污染。在大多数情况下,发生事故时最先受到污染的就是土壤。由于苯胺是油状液体,故土壤对其有很好的吸收作用。道德用土训将污染区作覆盖处理,或者筑坝将其拦住,以防污染进一步扩大,特别是应采取措施不能让其污染附近的水体。当污染区域被控制住,并用土壤将其完全吸收后,应对受污染土壤进行处理:
①进行永久性密封处理:在大面积污染情况下,使用密封材料将受污染区域进行密封,这实际上使化学品泄漏地区变成了一个永久处理场,可以使用不同的密封材料,如粘土、沥青和有机密封剂。
②暂时保存法:将受污染的土壤清除剥离后,装在可密封的容器中保存,待有条件时再做处理。
③焚烧法:将受到苯胺污染的土壤挖掘起来在现场进行焚烧处理,这各处理方法要求焚烧炉带有气体回收装置。
④自然降解法:由于苯胺溶于水,故可采用开沟淋洗土壤的方法,收集洗涤水或让苯胺随水蒸气一同挥发,也可采用不断地翻耕土壤,让苯胺随土壤中的水分一同逸散。
⑵水体污染。如果发生在地面上的苯胺污染事故由于处理不当,已使污染物进入水体;或者水体沿岸的污染源超标准排放的苯胺废水进入水体,则可对受污染水体作以下处理:
①在小溪、小河、水渠或其它流速缓慢的地表水体受到苯胺污染时,可设法在污染区域下方筑一水坝,将受污染水体与其它水体隔离。如果是非点源污染事故,则在污染区域上方也应拦住未受污染的水继续进入污染区。
②将受污染的水体泵到可接纳的水体中,如排污渠中,以使进入市政或其它污水处理厂进行处理,也可就地进行曝气等处理,让苯胺随水蒸气一同挥发。
③在大江大河或水量大的河流受到苯胺污染后,没有有效的处理方法。在这种情况下,唯一可做的就是迅速通知下游有关单位,特别是下游沿岸的自来水厂,加强监测,希望通过天然净化和稀释过程来减轻受污染的程度。
二、防护措施
呼吸系统防护:可能接触其蒸气时,佩带防毒面具。紧急事态抢救或逃生时,佩带正压自给式呼吸器。
眼睛防护:戴安全防护眼镜。
防护服:穿紧袖工作服,长统胶鞋。
手防护:戴橡皮手套。
其它:工作现场禁止吸烟、进食和饮水。及时换洗工作服。工作前后不饮酒,用温水洗澡。监测毒物,进行就业前和定期的体检。
三、急救措施
皮肤接触:立即脱去污染的衣着,用5%醋酸清洗污染的皮肤,再用肥皂水和清水冲洗。注意手、足和指甲等部位。
眼睛接触:立即提起眼睑,用大量流动清水或生理盐水冲洗医。
吸入:迅速脱离现场至空气新鲜处。呼吸困难时给输氧。呼吸停止时,立即进行人工呼吸。就医。
食入:误服者给漱口,饮水,洗胃后口服活性炭,再给以导泻。就医。
灭火方法:雾状水、泡沫、二氧化碳、干粉、砂土。
制备方法与用途
这段文本主要介绍了苯胺的生产方法、用途、性质及相关安全信息。
生产方法 用途-
作为弱碱使用:
-
显微晶分析:用于检验能生成硫氰酸络合阴离子或其他阴离子(如Cu、Mg、Ni、Co、Zn、Cd、Mo、W、V)的元素。
-
其他用途:
- 毒性分级:高毒
-
急性毒性:
- 大鼠口服LD50: 250 毫克/ 公斤;
- 小鼠口服LD50: 464 毫克/ 公斤。
-
刺激数据:
- 皮肤接触:兔子 20 毫克/ 24小时 中度
- 眼睛接触:兔子 20 毫克/ 24小时 中度
-
爆炸和燃烧特性:
- 与空气混合可爆。
- 与氧化剂反应剧烈。
- 明火、高温或强氧化剂下易燃,高热分解会产生有毒氮氧化物气体。
- 库房应通风、低温干燥。
- 需要与其他危险化学品(尤其是氧化剂)分开存放。
- 可使用泡沫灭火器、二氧化碳灭火器或干粉灭火器进行灭火。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 对苯二胺 1,4-Diaminobenzene 106-50-3 C6H8N2 108.143 间苯二胺 m-phenylenediamine 108-45-2 C6H8N2 108.143 邻苯二胺 1,2-diamino-benzene 95-54-5 C6H8N2 108.143 苯肼 phenylhydrazine 100-63-0 C6H8N2 108.143 苯基羟胺 N-Phenylhydroxylamine 100-65-2 C6H7NO 109.128 N-苯基甲亚胺 N-methylenebenzenamine 100-62-9 C7H7N 105.139 亚硝基苯 Nitrosobenzene 586-96-9 C6H5NO 107.112 N-甲基苯胺 N-methylaniline 100-61-8 C7H9N 107.155 对碘苯胺 4-Iodoaniline 540-37-4 C6H6IN 219.025 乙烷,三氯氟- p-toluidine 106-49-0 C7H9N 107.155 4-氨基苯硫酚 4-aminotiophenol 1193-02-8 C6H7NS 125.194 - 1
- 2
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 对苯二胺 1,4-Diaminobenzene 106-50-3 C6H8N2 108.143 间苯二胺 m-phenylenediamine 108-45-2 C6H8N2 108.143 邻苯二胺 1,2-diamino-benzene 95-54-5 C6H8N2 108.143 苯基羟胺 N-Phenylhydroxylamine 100-65-2 C6H7NO 109.128 苯肼 phenylhydrazine 100-63-0 C6H8N2 108.143 N-苯基甲亚胺 N-methylenebenzenamine 100-62-9 C7H7N 105.139 N-氯苯胺 2-chloroaminobenzene 24613-03-4 C6H6ClN 127.573 N-甲基苯胺 N-methylaniline 100-61-8 C7H9N 107.155 —— (anilino)dihydroborane 37479-90-6 C6H8BN 104.947 亚硝基苯 Nitrosobenzene 586-96-9 C6H5NO 107.112 —— aniline-D1 2987-37-3 C6H7N 94.1203 对碘苯胺 4-Iodoaniline 540-37-4 C6H6IN 219.025 乙烷,三氯氟- p-toluidine 106-49-0 C7H9N 107.155 4-氨基苯硫酚 4-aminotiophenol 1193-02-8 C6H7NS 125.194 - 1
- 2
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:铜催化 Ullmann 型偶联和芳基卤化物与丙二酸酯的脱羧级联以获得 α-芳基酯摘要:我们开发了一种高效实用的铜催化交叉偶联,通过利用容易获得的芳基溴化物(或氯化物)和丙二酸盐直接构建多功能的 α-芳基酯。这些克级方法的周转率高达 1560,并且通过使用低催化剂负载、新的可用配体和绿色溶剂顺利进行。可以耐受多种官能团,并且使用 α-芳基酯来获得克级的非甾体抗炎药 (NSAID)。DOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.1c03688
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:以H2CO3为分子催化配体的环己酮合成新途径以促进Pd纳米催化剂上硝基芳烃的彻底加氢摘要:二氧化碳在绿色化学中特别是在催化和化学工程应用中一直很重要。在探索CO 2来生产尼龙或尼龙66的环己酮(目前使用苛刻的催化方法低收率生产)时,我们做出了令人振奋的发现,将溶于水中的CO 2产生的碳酸用作分子催化配体来生产环己酮通过使用Pd催化剂的水溶液中硝基苯的加氢,总收率高于90%。重要的是,催化配体H 2 CO 3的气态与液态或固态催化剂不同,它极大地简化了催化后的净化过程。这种新的绿色催化策略证明了芳族化合物(如苯胺和N-甲基苯胺)的加氢反应的普遍性,可广泛应用于其他催化领域,如人工光合作用和电催化有机合成。DOI:10.1002/cctc.201900389
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:未受保护的碳水化合物支架硝酮的应变促进炔烃-硝酮环加成 (SPANC) 动力学摘要:研究了使用未受保护的碳水化合物衍生的硝酮作为菌株促进的炔-硝酮环加成反应中的伙伴作为生物共轭的新工具。观察到的二级反应显示速率常数为 3.4 × 10 –4 –5.8 × 10 –2 M –1 s –1 ,这是其他简单脂肪族或芳香族硝酮反应动力学的常见数量级。通过执行一锅方案证明了该方法对水性介质的适用性,该方案结合了硝酮的顺序形成以及与水中的环辛炔的环加成。DOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.4c01098
文献信息
-
Alkyl 1-Chloroalkyl Carbonates: Reagents for the Synthesis of Carbamates and Protection of Amino Groups作者:Gérard Barcelo、Jean-Pierre Senet、Gérard Sennyey、Jean Bensoam、Albert LoffetDOI:10.1055/s-1986-31724日期:——The synthesis of 1-chloroalkyl carbonates and their reaction with various type of amines are described. This reaction is useful for the synthesis of carbamate pesticides and for the protection of various amino groups, including amino acids.
-
1,3,5-Triazapentadienes by Nucleophilic Addition to 1,3- and 1,4-Dinitriles—Sterically Constrained Examples by Incorporation into Cyclic Peripheries: Synthesis, Aggregation, and Photophysical Properties作者:Agnes Johanna Wrobel、Ralph Lucchesi、Birgit Wibbeling、Constantin-Gabriel Daniliuc、Roland Fröhlich、Ernst-Ulrich WürthweinDOI:10.1021/acs.joc.6b00126日期:2016.4.1with the two cyano groups in 1,3 or 1,4 distance. These novel compounds show very strong tendency for aggregation due to hydrogen bonding, especially to form homodimers as seen from X-ray data in the solid state. Additional hydrogen bonding generates also linear chains in the crystal. Several of the new compounds show fluorescence in solution. Quantum chemical DFT calculations were used for evaluation由于主要的n /π*相互作用,1,3,5-三氮杂戊二烯通常在N–C–N–C–N骨架上呈U形或扭曲的S形构象。但是,如果1,3,5-三氮杂戊二烯单元是环的一部分,则其W构象可能仅限于平面。在这里,我们描述了13个新的1,3,5- triazapentadienes合成10 - 12,它们在空间上通过掺入抑制成六元或七元环系统,通过加入锂化的伯胺或肼的5到二腈7,8或9两个氰基的距离为1,3或1,4。这些新型化合物由于氢键而显示出非常强的聚集趋势,尤其是从固态X射线数据可以看出,它们形成同二聚体。额外的氢键还在晶体中产生线性链。几种新化合物在溶液中显示荧光。量子化学DFT计算用于评估二聚能和光物理性质的解释。
-
Racemization free longer N-terminal peptide hydroxamate synthesis on solid support using ethyl 2-(tert-butoxycarbonyloxyimino)-2-cyanoacetate作者:Srinivasa Rao Manne、Kishore Thalluri、Rajat Subhra Giri、Ashim Paul、Bhubaneswar MandalDOI:10.1016/j.tetlet.2015.09.084日期:2015.10protocol for the synthesis of peptide hydroxamic acids directly from carboxylic/amino acids by ethyl 2-(tert-butoxycarbonyloxyimino)-2-cyanoacetate in the presence of DIPEA/DMAP at room temperature is described. The compatibility of this method with Fmoc based solid phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) is also demonstrated by synthesizing three relatively large N-terminal peptide hydroxamic acids on resin. Also
-
Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation of Ketimines with Trichlorosilane: Structural Studies作者:Peter Schreiner、Zhiguo Zhang、Parham Rooshenas、Heike HausmannDOI:10.1055/s-0028-1088045日期:——structural and mechanistic studies on the organocatalytic asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of ketimines with trichlorosilane. Amines were obtained in good yields and moderate enantioselectivities. Both experiment and computation were utilized to provide an improved understanding of the mechanism. amines - Lewis bases - organocatalysis - transfer hydrogenation - trichlorosilane
-
Long-chain phenols. Part 18. Conversion of anacardic acid into urushiol作者:Lam Soot Kiong、John H. P. TymanDOI:10.1039/p19810001942日期:——(15 : 0)-Anacardic acid (6-pentadecylsalicylic acid), prepared by reduction of unsaturated anacardic acid from Anacardium occidentale, has been converted into anacardic alcohol (6-pentadecylsalicyl alcohol) and thence by oxidation at carbon into anacardaldehyde. Phenolic oxidation of anacardic alcoholled to 8-pentadecyl-1-oxaspiro-[2.5]octa-5,7-dien-4-one, itself readily convertible photochemically(15:0)-通过将西洋参Anacardium的不饱和的熊果酸还原而制得的Anacardic酸(6-pentadecylsalicylic acid),已被转化为anacardic醇(6-pentadecylsalicyl alcohol),然后在碳上被氧化为anacardaldehyde。拟南芥醇的苯酚氧化可生成8-十五烷基-1-氧杂螺-[2.5] octa-5,7-dien-4-one,其本身很容易光化学转化,但在热方面却不太容易转化为仲醛。亚硫酰氯与熊果酸的反应主要产生酸酐,通过氢化物还原,酸酐令人满意地降低了茴香醛。anacardaldehyde的达金反应提供(15:0)-urushiol(3- pentadecylcatechol)相同化学和从argentation TLC与来自氢化天然产物漆树。在氢化漆酚中检测到(15:0)-腰果酚(3-十五烷基苯酚)。漆酚的由不饱和组分的组合
表征谱图
-
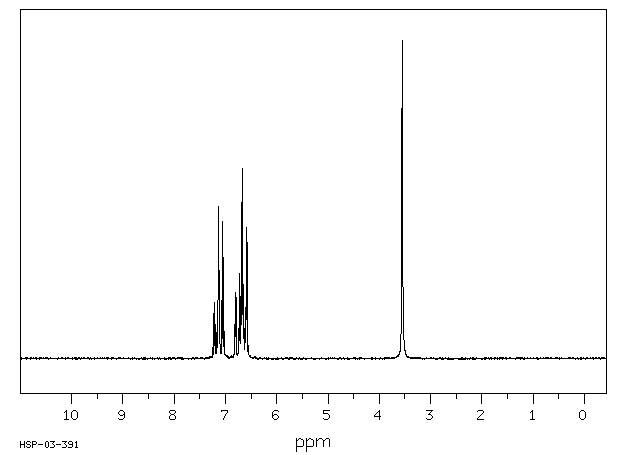
氢谱1HNMR
-
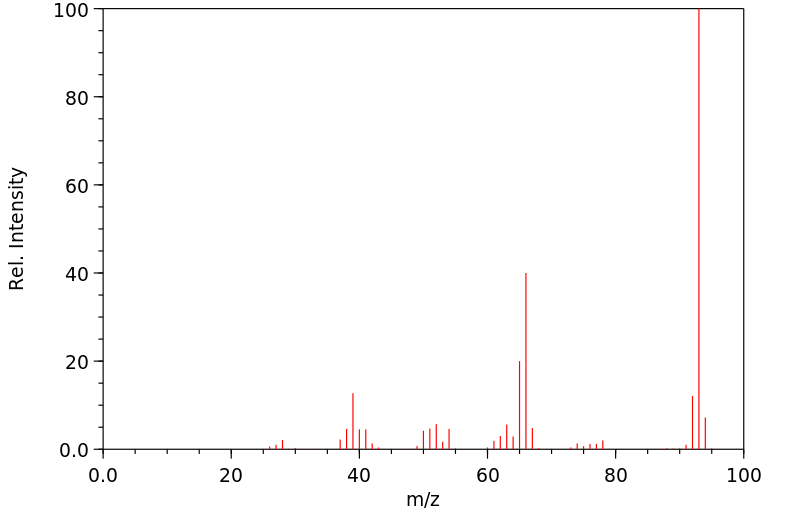
质谱MS
-
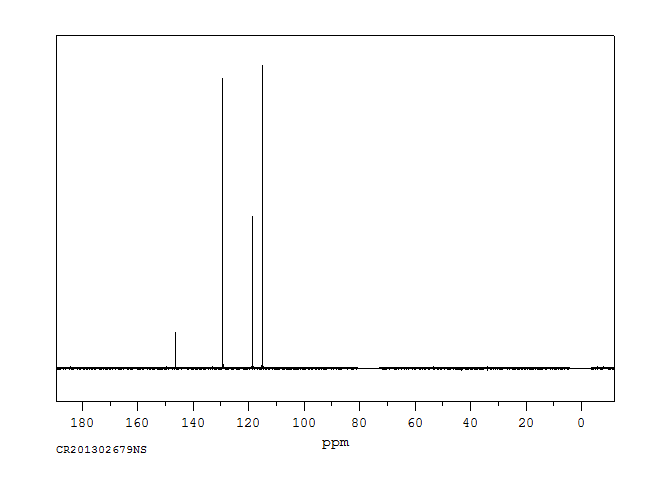
碳谱13CNMR
-
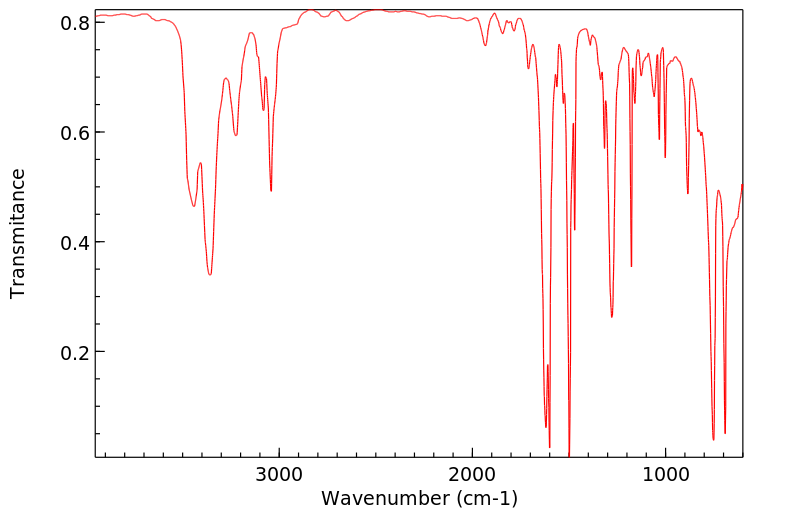
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息