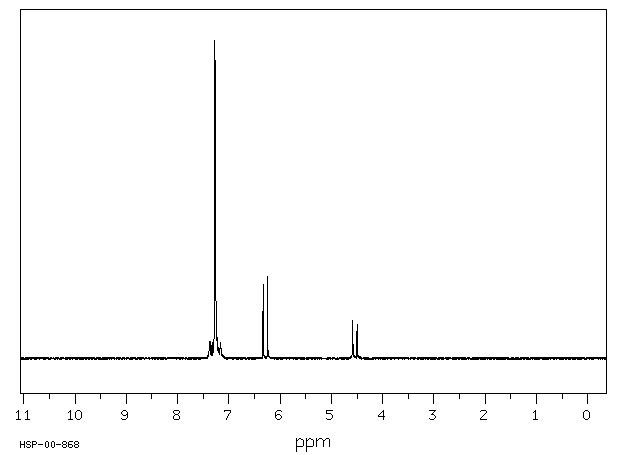
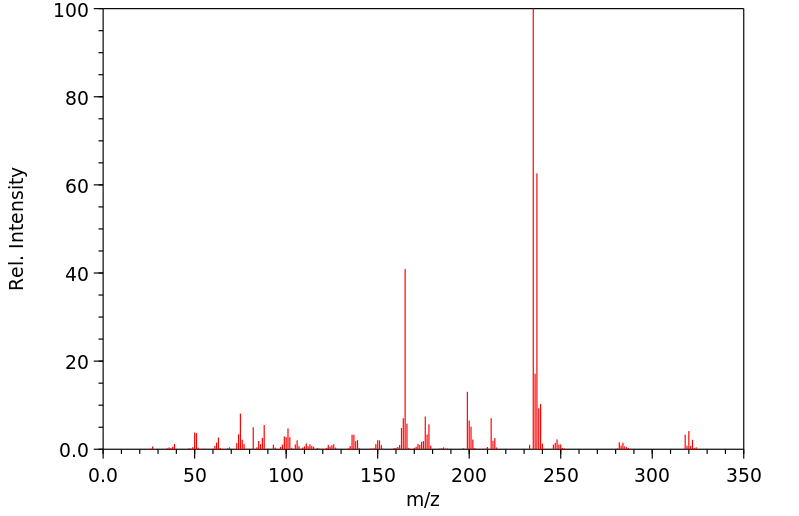
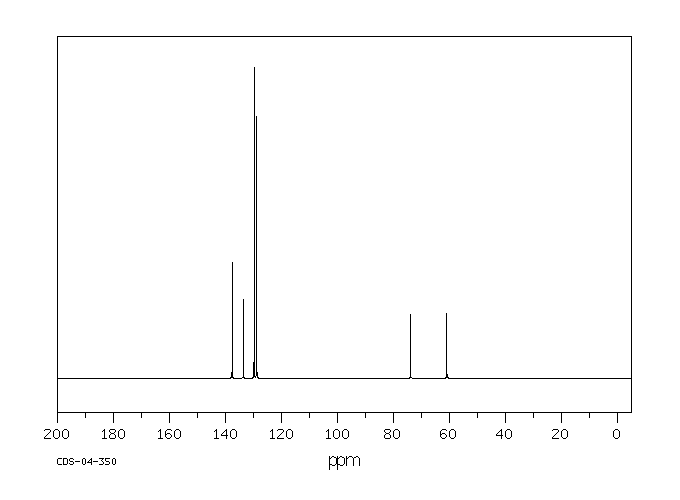
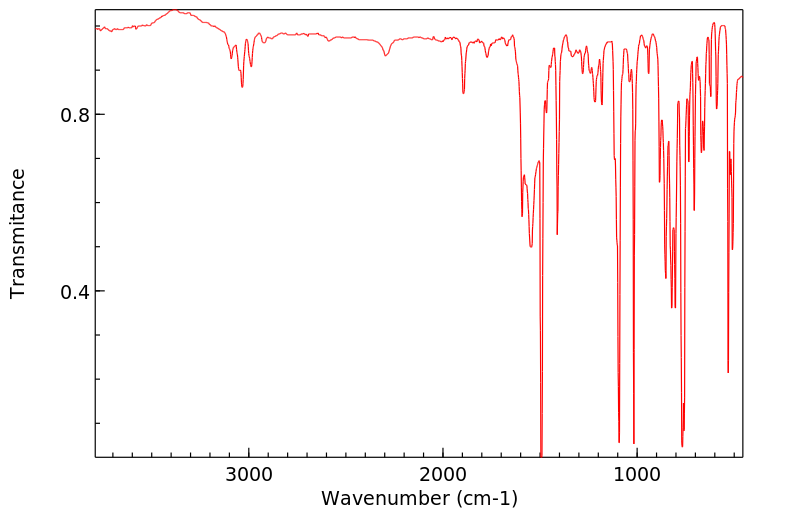
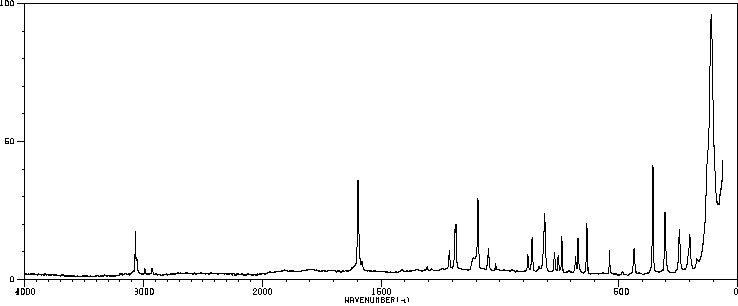
代谢
In pigeons (Columba liva) ... feeding of DDD ... /gave/ rise to small residues of DDE. The DDD was rapidly metabolized exclusively to 2,2-bis(p-chlorophenyl-1-chloroethylene.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)