(E)-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-phenylprop-2-en-1-one | 2657-25-2
分子结构分类
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:174-178 °C
-
沸点:419.6±45.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:1.191±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted)
-
溶解度:DMF:30mg/mL; DMSO:30mg/mL;乙醇:30mg/mL;乙醇:PBS (pH 7.2) (1:4): 0.2 mg/mL
-
LogP:3.650 (est)
-
碰撞截面:150.8 Ų [M+H]+ [CCS Type: TW, Method: calibrated with polyalanine and drug standards]
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):2.7
-
重原子数:17
-
可旋转键数:3
-
环数:2.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:37.3
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:2
ADMET
安全信息
-
安全说明:S26,S37/39
-
危险品标志:Xi
-
危险类别码:R36/37/38
-
海关编码:29145090
-
危险性防范说明:P261,P305+P351+P338
-
危险性描述:H315,H319,H335
SDS
制备方法与用途
4'-Hydroxychalcone(P-肉桂酰苯酚)存在于草药、香料和茶叶中,是一种刺甘草查尔酮。它具有多种生物活性,能够抑制TNF-α诱导的NF-κB通路激活,并激活BMP信号通路。
靶点| Target | Value |
|---|---|
| NF-κB |
4'-Hydroxychalcone (20-40 μM,2小时) 在剂量依赖性方式下抑制TNFα(20 ng/mL,6小时)诱导的NF-kB途径激活。
4'-Hydroxychalcone (0.1-25 μM,8小时) 以剂量依赖性方式抑制蛋白酶体活性,但不影响IKK活性。
4'-Hydroxychalcone 抑制TNFα引起的IkBα降解,并阻止p50/p65核转运,从而抑制NF-kB靶基因的表达。
4'-Hydroxychalcone 影响癌细胞活力,但对非转化细胞无显著影响。
| 操作参数 | 值 |
|---|---|
| 细胞系 | K562细胞、Jurkat细胞、U937细胞、PBMCs |
| 浓度 | 5 μM, 10 μM, 20 μM, 24 μM, 28 μM, 32 μM, 40 μM, 60 μM |
| 孵育时间 | 24小时 |
| 结果 | 影响癌细胞活力,但对非转化细胞无显著影响。 |
| 操作参数 | 值 |
|---|---|
| 细胞系 | Jurkat细胞 |
| 浓度 | 60 μM(随后加入TNFα 20 ng/mL) |
| 孵育时间 | 2小时 |
| 结果 | 抑制TNFα引起的IkBα降解,并阻止p50/p65核转运。 |
4'-Hydroxychalcone 在小鼠中表现出抗肝损伤活性,用于对乙酰氨基酚诱导的肝脏毒性。
动物模型| 操作参数 | 值 |
|---|---|
| 动物模型 | 雄性白化小鼠(5-30 g) |
| 剂量 | 25 mg/kg, 50 mg/kg, 100 mg/kg |
| 给药方式 | 口服给药,每12小时一次,4次剂量 |
| 结果 | 显著降低了由对乙酰氨基酚(1 g/kg)引起的死亡率。 |
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 (2E)-1-(4-甲氧基苯基)-3-苯基-2-丙烯-1-酮 trans-4'-methoxychalcone 22966-19-4 C16H14O2 238.286 —— 4'-isopropyloxy-trans-chalcone 99259-75-3 C18H18O2 266.34 对羟基苯乙酮 4-Hydroxyacetophenone 99-93-4 C8H8O2 136.15 —— 4-(tetrahydropyran-2-yloxy)chalcone 468060-22-2 C20H20O3 308.377 对甲氧基苯乙酮 1-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethanone 100-06-1 C9H10O2 150.177 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— (Z)-4'-hydroxychalcone 102692-58-0 C15H12O2 224.259 反式-查耳酮 1,3-diphenyl-propen-3-one 614-47-1 C15H12O 208.26 —— 4'-(2-hydroxy-ethoxy)-trans-chalcone 36452-09-2 C17H16O3 268.312 —— (E)-3-phenyl-1-(4-(prop-2-yn-1-yloxy)phenyl)prop-2-en-1-one 1196532-71-4 C18H14O2 262.308 —— (2E,2'E)-1,1'-((propane-1,3-diylbis(oxy))bis(4,1-phenylene))bis(3-phenylprop-2-en-1-one) 252006-47-6 C33H28O4 488.583 —— (E)-1-(4-(3-bromopropyloxy)phenyl)-3-phenylprop-2-en-1-one —— C18H17BrO2 345.236 —— (2E)-3-phenyl-1-[4-(3-methylbut-2-enyloxy)phenyl]propenone —— C20H20O2 292.378 —— (E)-1-(4-(2-(dimethylamino)ethoxy)phenyl)-3-phenylprop-2-en-1-one 94310-97-1 C19H21NO2 295.381 —— (E)-1-(4-(4-bromobutyloxy)phenyl)-3-phenylprop-2-en-1-one 1262136-39-9 C19H19BrO2 359.263 2-(4-肉桂基苯氧基)乙酸 {4-[(2E)-3-phenylprop-2-enoyl]phenoxy}acetic acid 136068-42-3 C17H14O4 282.296 —— (E)-1-(4-(2-(diethylamino)ethoxy)phenyl)-3-phenylprop-2-en-1-one 25960-41-2 C21H25NO2 323.435 —— (E)-1-(4-(6-bromohexyloxy)phenyl)-3-phenylprop-2-en-1-one 1262136-42-4 C21H23BrO2 387.316 —— (E)-1-(4-(3-(dipropylamino)propoxy)phenyl)-3-phenylprop-2-en-1-one 114277-97-3 C24H31NO2 365.516 —— (E)-1-(4-(6-(dimethylamino)hexyloxy)phenyl)-3-phenylprop-2-en-1-one 134994-58-4 C23H29NO2 351.489 —— (E)-1-(4-(3-(dibutylamino)propoxy)phenyl)-3-phenylprop-2-en-1-one —— C26H35NO2 393.569 —— (E)-1-(4-(2-(dipropylamino)ethoxy)phenyl)-3-phenylprop-2-en-1-one —— C23H29NO2 351.489 —— ethyl {4-[(2E)-3-phenylprop-2-enoyl]phenoxy}acetate 370590-07-1 C19H18O4 310.35 —— (E)-1-(4-(4-(dipropylamino)butoxy)phenyl)-3-phenylprop-2-en-1-one —— C25H33NO2 379.543 —— (E)-1-(4-(4-(dibutylamino)butoxy)phenyl)-3-phenylprop-2-en-1-one —— C27H37NO2 407.596 —— 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-phenylprop-1-ene 21148-30-1 C15H14O 210.276 —— (E)-1-(4-(5-(dipropylamino)pentyloxy)phenyl)-3-phenylprop-2-en-1-one —— C26H35NO2 393.569 —— (E)-1-(4-(5-(dibutylamino)pentyloxy)phenyl)-3-phenylprop-2-en-1-one —— C28H39NO2 421.623 —— (E)-1-(4-(2-(dibutylamino)ethoxy)phenyl)-3-phenylprop-2-en-1-one —— C25H33NO2 379.543 —— (E)-1-(4-(6-(dipropylamino)hexyloxy)phenyl)-3-phenylprop-2-en-1-one —— C27H37NO2 407.596 —— (E)-1-(4-((tert-butyldimethylsilyl)oxy)phenyl)-3-phenylprop-2-en-1-one —— C21H26O2Si 338.522 对羟基苯乙酮 4-Hydroxyacetophenone 99-93-4 C8H8O2 136.15 —— 4-(4-((E)-3-Phenylprop-2-enoyl)phenoxy)azetidin-2-one 119005-18-4 C18H15NO3 293.3 —— ethyl 2-methyl-2-{4-[(2E)-3-phenylprop-2-enoyl]phenoxy}propanoate 1609180-21-3 C21H22O4 338.403 —— (E)-1-[3-[(dibenzylamino)methyl]-4-hydroxyphenyl]-3-phenylprop-2-en-1-one 1137686-75-9 C30H27NO2 433.55 —— ethyl 2-methyl-2-[4-(2-{4-[(2E)-3-phenylprop-2-enoyl]phenoxy}ethyl)phenoxy]propanoate 1415608-82-0 C29H30O5 458.554 —— ethyl 2-methyl-2-[4-(3-{4-[(2E)-3-phenylprop-2-enoyl]phenoxy}propyl)phenoxy]propanoate 1415608-83-1 C30H32O5 472.581 - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:(E)-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-phenylprop-2-en-1-one 在 双氧水 、 potassium carbonate 作用下, 以 乙腈 为溶剂, 反应 6.0h, 以87%的产率得到肉桂酸参考文献:名称:Solvent-Dependent Regioselective Oxidation oftrans-Chalcones using Aqueous Hydrogen Peroxide摘要:A novel method for regioselective oxidation of trans-chalcones with hydrogen peroxide in acetonitrile to afford cinnamic acids is reported. Only trans-beta-arylacrylic acids were observed. A wide range of functionalized products can be effectively produced from various chalcones in good to excellent yields.DOI:10.5935/0103-5053.20130063
-
作为产物:描述:对羟基苯乙酮 在 barium hydroxide octahydrate 、 4-甲基苯磺酸吡啶 作用下, 以 甲醇 、 二氯甲烷 为溶剂, 反应 16.5h, 生成 (E)-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-phenylprop-2-en-1-one参考文献:名称:2′,5′-Dihydroxychalcone as a Potent Chemical Mediator and Cyclooxygenase Inhibitor摘要:摘要:对十一种查尔酮衍生物进行了测试,以评估它们对兔血小板悬液中血小板聚集、肥大细胞和中性粒细胞激活的抑制作用。花生四烯酸诱导的血小板聚集几乎被所有化合物强烈抑制,有些化合物对胶原诱导的血小板聚集和环氧化酶也有强烈的抑制作用。一些羟基查尔酮衍生物显示出对β-葡萄糖苷酸酶和溶菌酶释放,以及对受到fMet-Leu-Phe(fMLP)肽激活的大鼠中性粒细胞产生的超氧化物的强烈抑制作用。我们发现,2′,5′-二羟基查尔酮的抗炎效果大于三氟她嗪。即使在低浓度(50 μm)下,在人体富含血小板的血浆中,2′,5′-二羟基和2′,3,4,4′-四羟基查尔酮几乎完全抑制了由肾上腺素诱导的继发性聚集。这些结果表明,查尔酮的抗血小板作用主要是通过抑制血栓素形成实现的。DOI:10.1111/j.2042-7158.1997.tb06837.x
文献信息
-
Small Multitarget Molecules Incorporating the Enone Moiety作者:Thalia Liargkova、Nikolaos Eleftheriadis、Frank Dekker、Efstathia Voulgari、Constantinos Avgoustakis、Marina Sagnou、Barbara Mavroidi、Maria Pelecanou、Dimitra Hadjipavlou-LitinaDOI:10.3390/molecules24010199日期:——
Chalcones represent a class of small drug/druglike molecules with different and multitarget biological activities. Small multi-target drugs have attracted considerable interest in the last decade due their advantages in the treatment of complex and multifactorial diseases, since “one drug-one target” therapies have failed in many cases to demonstrate clinical efficacy. In this context, we designed and synthesized potential new small multi-target agents with lipoxygenase (LOX), acetyl cholinesterase (AChE) and lipid peroxidation inhibitory activities, as well as antioxidant activity based on 2-/4- hydroxy-chalcones and the bis-etherified bis-chalcone skeleton. Furthermore, the synthesized molecules were evaluated for their cytotoxicity. Simple chalcone b4 presents significant inhibitory activity against the 15-human LOX with an IC50 value 9.5 µM, interesting anti-AChE activity, and anti-lipid peroxidation behavior. Bis-etherified chalcone c12 is the most potent inhibitor of AChE within the bis-etherified bis-chalcones followed by c11. Bis-chalcones c11 and c12 were found to combine anti-LOX, anti-AchE, and anti-lipid peroxidation activities. It seems that the anti-lipid peroxidation activity supports the anti-LOX activity for the significantly active bis-chalcones. Our circular dichroism (CD) study identified two structures capable of interfering with the aggregation process of Aβ. Compounds c2 and c4 display additional protective actions against Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and add to the pleiotropic profile of the chalcone derivatives. Predicted results indicate that the majority of the compounds with the exception of c11 (144 Å) can cross the Blood Brain Barrier (BBB) and act in CNS. The results led us to propose new leads and to conclude that the presence of a double enone group supports better biological activities.
查耳酮类药物代表了一类具有多种和多重靶点生物活性的小分子药物或类药分子。在过去的十年里,小型多靶点药物因其能够治疗复杂和多因素疾病的优点而引起了相当大的兴趣,因为“一种药物一个靶点”的治疗方法在许多情况下未能显示出临床疗效。在这种情况下,我们设计并合成了具有潜在的新小型多靶点药物,具有脂氧合酶(LOX)、乙酰胆碱酯酶(AChE)和脂质过氧化抑制活性,以及基于2-/4-羟基查耳酮和双醚化双查耳酮骨架的抗氧化活性。此外,合成的分子还对其细胞毒性进行了评估。简单的查耳酮b4对15-人LOX具有显著的抑制活性,IC50值为9.5 µM,具有有趣的抗AChE活性和抗脂质过氧化行为。双醚化查耳酮c12是双醚化双查耳酮中对AChE最有效的抑制剂,其次是c11。发现双查耳酮c11和c12具有抗LOX、抗AchE和抗脂质过氧化活性。看来抗脂质过氧化活性支持显著活性的双查耳酮的抗LOX活性。我们的圆二色性(CD)研究发现两种结构能够干扰Aβ的聚集过程。化合物c2和c4显示了额外的保护作用,防止阿尔茨海默病(AD)的发生,并增加了查耳酮衍生物的多效性特征。预测结果表明,除了c11(144 Å)之外,大多数化合物能够穿越血脑屏障(BBB)并在中枢神经系统发挥作用。这些结果使我们提出了新的线索,并得出结论,存在一个双烯酮基团可以支持更好的生物活性。 -
Mosquito larvicidal studies of some chalcone analogues and their derived products: structure–activity relationship analysis作者:Naznin A. Begum、Nayan Roy、Rajibul A. Laskar、Kunal RoyDOI:10.1007/s00044-010-9305-6日期:2011.3A series of chalcone analogues and some of their derivatives were synthesized and subjected to the mosquito larvicidal study. Chalcones having electron releasing group(s) on either ring A or ring B showed high toxicity. Electron withdrawing group(s), especially at ring B, reduced the activity of chalcones. The activity was abruptly decreased due to replacement of ring A by CH3, extension of conjugation
-
Pentamethylphenyl (Ph*) and Related Derivatives as Useful Acyl Protecting Groups for Organic Synthesis: A Preliminary Study作者:Timothy J. Donohoe、Choon Boon Cheong、James R. FrostDOI:10.1055/s-0040-1707289日期:2020.11A study of acyl protecting groups derived from the Ph* motif is reported. While initial studies indicated that a variety of functional groups were not compatible with the Br2-mediated cleavage conditions required to release the Ph* group, strategies involving the use of different reagents or a modification of Ph* itself (Ph*OH) were investigated to solve this problem.报道了对衍生自 Ph* 基序的酰基保护基团的研究。虽然最初的研究表明各种官能团与释放 Ph* 基团所需的 Br2 介导的裂解条件不相容,但研究了涉及使用不同试剂或修饰 Ph* 本身 (Ph*OH) 的策略以解决这个问题。
-
[EN] FLUORESCENT NEAR INFRA-RED (NIR) DYES<br/>[FR] COLORANTS FLUORESCENTS DANS LE PROCHE INFRAROUGE (NIR)申请人:HAE THERAPEUTICS公开号:WO2011048217A1公开(公告)日:2011-04-28A compound of formula (I) is described in which each A, which may be the same or different, is a halide selected from fluoride, chloride, bromide and iodide, or is O-Y, wherein Y is a substituted or unsubstituted, saturated or unsaturated, straight or branched chain alkyl moiety. R1, R2, R3, R6, R7, and R8 are each independently H, OH, NO2 or O-L-X, wherein L is a spacer group, and X is a conjugation group or a water- solubilizing group. At least one of R1, R2, R3 is OH or O-L-X and at least one of R6, R7, and R8 is OH or O-L-X. R4 and R5, which may be the same or different, are each independently H; or are a substituted or unsubstituted, saturated or unsaturated, cyclic moiety; a substituted or unsubstituted, saturated or unsaturated heterocyclic moiety; or a substituted or unsubstituted, saturated or unsaturated, straight or branched chain alkyl moiety. Also described are dye conjugates comprising a compound of the invention.化合物的结构式(I)中描述了每个A,它可以相同也可以不同,是从氟化物、氯化物、溴化物和碘化物中选择的卤素,或者是O-Y,其中Y是取代或未取代的、饱和或不饱和的、直链或支链烷基基团。R1、R2、R3、R6、R7和R8各自独立地是H、OH、NO2或O-L-X,其中L是一个间隔基团,X是一个共轭基团或水溶性基团。R1、R2、R3中至少有一个是OH或O-L-X,R6、R7和R8中至少有一个是OH或O-L-X。R4和R5,它们可以相同也可以不同,各自独立地是H;或者是一个取代或未取代的、饱和或不饱和的、环状基团;一个取代或未取代的、饱和或不饱和的杂环基团;或者是一个取代或未取代的、饱和或不饱和的、直链或支链烷基基团。还描述了包含本发明化合物的染料结合物。
-
Screening of Biological Activities of a Series of Chalcone Derivatives against Human Pathogenic Microorganisms作者:İsa Karaman、Hayreddin Gezegen、M. Burcu Gürdere、Alparslan Dingil、Mustafa CeylanDOI:10.1002/cbdv.200900027日期:2010.2In an effort to develop new antimicrobial agents, a series of chalcone derivatives, 3-60, were prepared by Claisen-Schmidt condensation of appropriate acetophenones and 2-furyl methyl ketones with appropriate aromatic aldehydes, furfural, and thiophene-2-carbaldehyde in an aqueous solution of NaOH and EtOH at room temperature. The synthesized compounds were characterized by means of their IR- and NMR-spectral
表征谱图
-
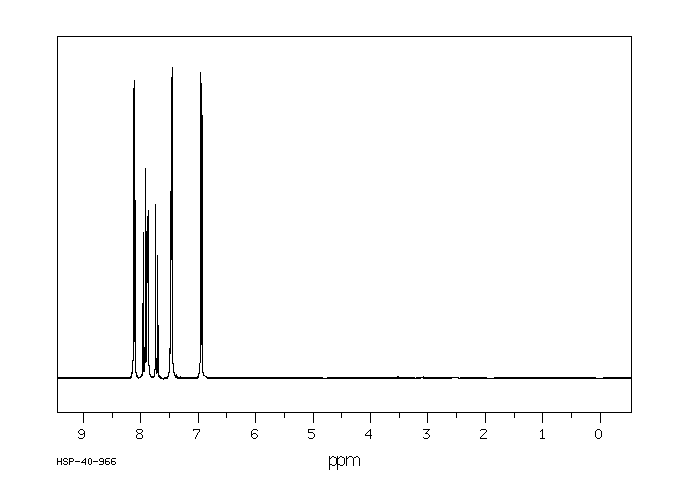
氢谱1HNMR
-
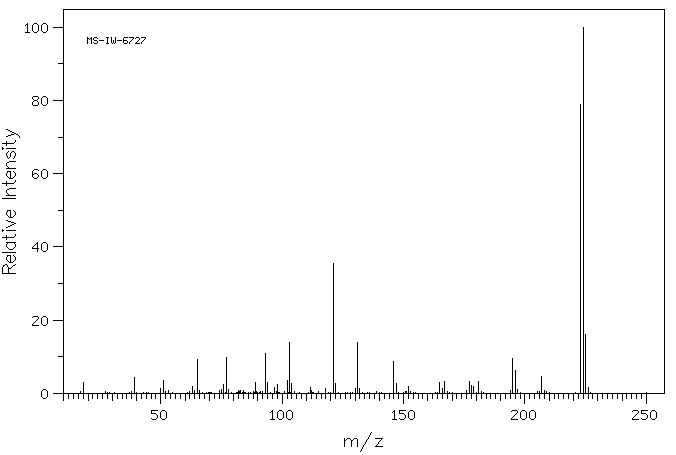
质谱MS
-
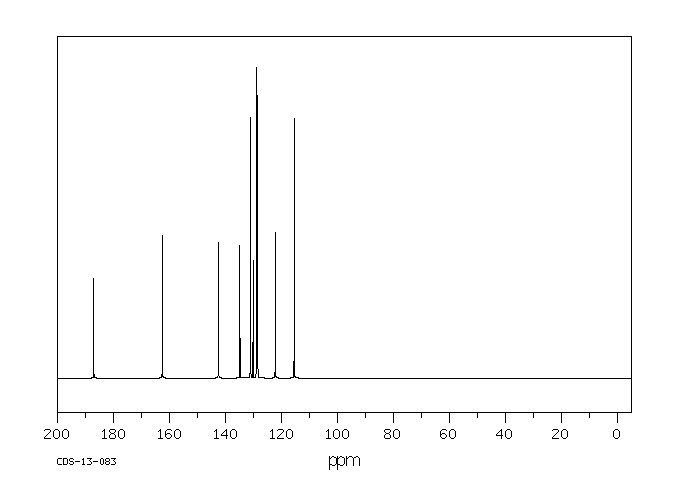
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息