2,3-丁二醇 | 513-85-9
物质功能分类
中文名称
2,3-丁二醇
中文别名
2,3-丁烯二醇;2,3-二羟基丁烷;2,3,4-三甲氧基-6-甲基苯酚;丁二仲醇
英文名称
2,3-butandiol
英文别名
2.3-butanediol;butane-2,3-diol;2,3‐butanediol;2,3-Butanediol
CAS
513-85-9
化学式
C4H10O2
mdl
MFCD00004523
分子量
90.1222
InChiKey
OWBTYPJTUOEWEK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:25 °C (lit.)
-
沸点:183-184 °C (lit.)
-
密度:1.002 g/mL at 20 °C (lit.)
-
闪点:185 °F
-
溶解度:可溶于氯仿、甲醇
-
LogP:-0.92 at 25℃
-
物理描述:Liquid
-
颜色/状态:Nearly colorless, crystalline solid or liquid
-
气味:Odorless
-
味道:Sweet taste
-
蒸汽密度:3.1 (Air = 1)
-
蒸汽压力:0.243 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
按照规定使用和贮存,不会发生分解,避免与氧化物接触。这是一种可燃性的液体,并且具有吸湿性,但不会腐蚀金属。
-
应避免吸入,同时要防止其接触眼睛、皮肤和衣物。由于对空气敏感,应将其储存在干燥阴凉处并用氮气保护。
-
-
自燃温度:756 °F (402 °C)
-
分解:Hazardous decomposition products formed under fire conditions - Carbon oxides.
-
粘度:0.121 sq m/sec at 25 °C
-
燃烧热:-2461 kJ/mol at 20 °C
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.438 at 20 °C
-
解离常数:pKa = 14.9 at 25 °C; Kb = 0.33 at 25 °C, aqueous HCl
-
保留指数:747.5;824;762.8;756;768;746;750;749
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-0.9
-
重原子数:6
-
可旋转键数:1
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:1.0
-
拓扑面积:40.5
-
氢给体数:2
-
氢受体数:2
ADMET
代谢
2-Butanol, 3-hydroxy-2-butanone, and 2,3-butanediol were identified as metabolies in the serum of guinea pigs injected ip with methyl ethyl ketone.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
... Glucuronides of 2,3-butanediol /were found/ in the urine of rabbits equivalent to about 20% of the dose given.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
在受控实验中,19名严重酗酒男性中有15人(79%)在饮用蒸馏烈酒后,血清中2,3-丁二醇的浓度大于或等于5微摩尔/升,而22名对照者中只有1人。另一种二醇,1,2-丙二醇,在所有患者在饮酒后的标本中的浓度都大于或等于5微摩尔/升;但它也在大多数患者的参考标本中以较低浓度存在。这些数据与实验证据一致,即乙醇可以在大鼠中被代谢产生2,3-丁二醇,并且与流行病学假设一致,即严重酗酒男性通过不同于对照受试者的途径代谢乙醇。
In a controlled experiment 15 (79%) of 19 severely alcoholic men but only 1 of 22 controls had a serum concentration of greater than or equal to 5 umol/L 2,3-butanediol after ingestion of distilled spirits. Another diol, 1,2-propanediol, was found in a concentration of greater than or equal to 5 umol/L in all patients' specimens after drinking; but it was also present in lower concentrations in the reference specimens of most of the patients. These data are consistent with the experimental evidence that ethanol can be metabolized in rats to produce 2,3-butanediol and with the epidemiological hypothesis that severely alcoholic men metabolize ethanol by a different pathway than do control subjects.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
理解Paenibacillus polymyxa DSM 365对不断增加的2,3-丁二醇(2,3-BD)浓度的耐受能力对于工程化一个过量生产2,3-BD的菌株至关重要。因此,我们研究了P. polymyxa对高浓度2,3-BD的反应。在分批补料培养中(6-L生物反应器),尽管培养基中仍有残留的13克/升葡萄糖,2,3-BD还是积累到了47克/升的最大浓度。同时,随着2,3-BD达到最大浓度,2,3-BD的前体物质乙偶姻的积累也增加了,这表明当2,3-BD的浓度超过了耐受阈值后,2,3-BD又被转化回了乙偶姻。接着,将P. polymyxa培养物在0小时时用左旋-2,3-BD(20、40和60克/升)进行挑战,在葡萄糖培养基中观察到了与左旋-2,3-BD浓度相关的生长抑制反应。60克/升的左旋-2,3-BD完全抑制了P. polymyxa的生长。此外,P. polymyxa在12、24和36小时分别接受了递增的2,3-BD浓度(20、40和60克/升)的挑战,以模拟发酵过程中2,3-BD的积累。有趣的是,当2,3-BD的浓度达到60克/升时,它又被转化回了乙偶姻,可能是为了减轻2,3-BD的毒性。总的来说,我们的发现表明,2,3-BD介导的毒性是过量生产2,3-BD的主要代谢障碍,因此,这使得它成为理性设计一个过量生产2,3-BD菌株的重要代谢工程目标。
Understanding the capacity of Paenibacillus polymyxa DSM 365 to tolerate increasing concentrations of 2,3-butanediol (2,3-BD) is critical to engineering a 2,3-BD-overproducing strain. Hence, we investigated the response of P. polymyxa to high 2,3-BD concentrations. In fed-batch cultures (6-L bioreactor) 2,3-BD was accumulated to a maximum concentration of 47 g/L despite the presence of residual 13 g/L glucose in the medium. Concomitantly, accumulation of acetoin, the precursor of 2,3-BD increased after maximum 2,3-BD concentration was reached, suggesting that 2,3-BD was reconverted to acetoin after the concentration tolerance threshold of 2,3-BD was exceeded. Cultures of P. polymyxa were then challenged with levo-2,3-BD (20, 40 and 60 g/L) at 0h in a glucose medium, and a concentration dependent growth inhibition response to levo-2,3-BD was observed. The growth of P. polymyxa was completely inhibited by 60 g/L levo-2,3-BD. Furthermore, P. polymyxa was challenged with incremental 2,3-BD concentrations (20, 40 and 60 g/L at 12, 24 and 36 hr, respectively) to mimic 2,3-BD accumulation during fermentation. Interestingly, 2,3-BD was reconverted to acetoin when its concentration reached 60 g/L, possibly to alleviate 2,3-BD toxicity. Collectively, our findings indicate that 2,3-BD-mediated toxicity is a major metabolic impediment to 2,3-BD overproduction, thus, making it an important metabolic engineering target towards rational design of a 2,3-BD-overproducing strain.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
二乙酰(2,3-丁二酮)、乙偶姻(3-羟基-2-丁酮)和2,3-丁二醇是乙醛的代谢物,本研究利用大鼠肝脏匀浆、肝脏灌注和体内实验对这些物质的代谢进行了定量研究。在这些实验中,二乙酰和乙偶姻被还原为2,3-丁二醇,但乙偶姻和2,3-丁二醇几乎不被氧化为二乙酰,这表明从二乙酰还原为2,3-丁二醇的反应在大鼠肝脏中活跃进行。从二乙酰形成乙偶姻需要NADH或NADPH作为还原剂,而从乙偶姻还原为2,3-丁二醇则需要NADH。在大脑组织中,乙偶姻和2,3-丁二醇比二乙酰更容易积累。
The metabolism of diacetyl (2,3-butanedione), acetoin (3-hydroxy-2-butanone), and 2,3-butanediol, which are metabolites of acetaldehyde, was quantitatively investigated using rat liver homogenate, liver perfusion, and in vivo experiments. Diacetyl and acetoin were reduced to 2,3-butanediol in these experiments, but acetoin and 2,3-butanediol were scarcely oxidized to diacetyl, indicating that the reduction reaction to 2,3-butanediol from diacetyl occurs actively in rat liver. The formation of acetoin from diacetyl required either NADH or NADPH as a reductant, while the reduction of acetoin to 2,3-butanediol required NADH. Acetoin and 2,3-butanediol were more readily accumulated than diacetyl in brain tissue.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
识别和使用:2,3-丁二醇是一种几乎无色的结晶固体或液体。2,3-丁二醇用作特定硬橡胶产品生产中萘-1,5-二异氰酸酯的交联剂。2,3-丁二醇的衍生物在制药工业中作为中间体非常重要。2,3-丁二醇作为保湿剂以及在聚合物和塑化剂合成中具有一定的兴趣。人体研究:对于红细胞,30%的2,3-丁二醇溶液显示出相对较低的毒性。5小时后溶血仅为2%,但21小时后增加到6%,46小时后达到60%。动物研究:通过分析大鼠前额皮质记录的脑电图(EEG)频谱功率来研究2,3-丁二醇对中枢神经系统(CNS)的影响。发现2,3-丁二醇处理通过口服和静脉给药在相对较低剂量下增加了EEG频谱功率。从这些发现可以得出结论,2,3-丁二醇具有强大的CNS抑制作用。在培养的10天大鼠胚胎中检查时,2,3-丁二醇不具有胚胎毒性。2,3-丁二醇对大鼠先天免疫反应具有负调节作用。
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: 2,3-Butanediol is nearly colorless, crystalline solid or liquid. 2,3-Butanediol is used as a crosslinking agent for naphthalene-1,5-diisocyanate in the production of specific hard-rubber products. Derivatives of 2,3-butanediol are important as intermediates in the pharmaceutical industry. 2,3-Butanediols have some interest as humectants and in the synthesis of polymers and plasticizers. HUMAN STUDIES: For erythrocytes a solution of 30% 2,3-butanediol showed relatively low toxicity. Hemolysis was only 2% after 5 hr, but increased to 6% after 21 hr and reached 60% after 46 hr. ANIMAL STUDIES: Effects of 2,3-butanediol on the central nervous system (CNS) were investigated by using the analysis of EEG (electroencephalogram) spectral powers recorded at the frontal cortex in rats. It was found that 2,3-butanediol treatment led to increase in EEG spectral powers by oral and intravenous administrations at relatively low doses. From these findings it can be concluded that 2,3-butanediol has a potent CNS depressant effect. 2,3-Butanediol was not embryotoxic when examined in cultured 10-day rat embryo. 2,3-Butanediol has a negative regulatory effect on rats innate immunity response.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
神经毒素 - 急性溶剂综合症
Neurotoxin - Acute solvent syndrome
来源:Haz-Map, Information on Hazardous Chemicals and Occupational Diseases
毒理性
红细胞被储存在4摄氏度的磷酸盐缓冲盐水中,溶液中含有2,3-丁二醇和4%(w/w)的海藻糖、蔗糖、山梨醇或甘露醇。2,3-丁二醇中含有96.7%(w/w)的左旋和右旋异构体的外消旋混合物,只有3.1%(w/w)的meso异构体(2,3-丁二醇97% dl)。2,3-丁二醇的浓度分别为30%和35%(w/w)。含有30% 2,3-丁二醇的溶液显示出相对较低的毒性。5小时后溶血率仅为2%,但在21小时后增加到6%,在46小时后达到60%。添加4%(w/w)的上述任何一种化合物都会显著降低毒性。其中最有效的是海藻糖和蔗糖。在30% 2,3-丁二醇和4%的任何四种化合物的情况下,储存2天后溶血率约为0.6%。此外,使用海藻糖或蔗糖,溶血率在1个月内保持在3%以下。使用山梨醇或甘露醇时,溶血率在7天后缓慢增加到2%,然后迅速增加。即使在35% 2,3-丁二醇的情况下,含有海藻糖或蔗糖的溶液也显示出低毒性。还测量了在不含2,3-丁二醇和添加剂的缓冲溶液中重新稀释后的溶血情况,以模拟用冷冻保护剂灌注器官和清洗的过程。在储存几天后观察到最低的溶血率。目前的溶液也具有高成玻倾向。它们对于器官的玻璃化可能有很大兴趣。
Erythrocytes were stored at 4 degrees C in solutions of phosphate-buffered saline containing 2,3-butanediol and 4% (w/w) trehalose, sucrose, sorbitol, or mannitol. The 2,3-butanediol contained 96.7% (w/w) racemic mixture of the levo and dextro isomers and only 3.1% (w/w) of the meso isomer (2,3-butanediol 97% dl). The concentrations of 2,3-butanediol were 30 and 35% (w/w). A solution of 30% 2,3-butanediol showed relatively low toxicity. Hemolysis was only 2% after 5 hr, but increased to 6% after 21 hr and reached 60% after 46 hr. Adding 4% (w/w) of one of the above compounds drastically decreased the toxicity. The two most efficient were the sugars trehalose and sucrose. With 30% 2,3-butanediol and 4% of any of the four compounds, hemolysis was about 0.6% after 2 days of storage. Furthermore, with trehalose or sucrose, hemolysis remained below 3% for 1 month. With sorbitol or mannitol, hemolysis slowly increased to 2% after 7 days and then increased rapidly. Even with 35% 2,3-butanediol, solutions containing trehalose or sucrose showed low toxicity. Hemolysis was also measured after redilution to buffered solution without 2,3-butanediol and without the additive, to mimic perfusion of organs with cryoprotectants and washing. Minima of hemolysis were observed after a few days of storage. The present solutions also have high glass-forming tendencies. They could be of great interest for organ vitrification.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
在四氯化碳(0.1 mL/kg,腹腔注射)诱导的肝毒性反应中,经过16小时的预处理,使用2-丁酮(2.1 mL/kg,口服)或2,3-丁二醇(2.12 mL/kg,口服)均可显著增强反应,这一结果是通过血清谷氨酸丙酮酸转氨酶活性和肝脏甘油三酯含量来测量的。在体内,经过这一剂量的2,3-丁二醇处理后,仅有限地形成了3-羟基-2-丁酮。
... A 16 hr pretreatment with either 2-butanone (2.1 mL/kg, orally) or 2,3-butanediol (2.12 mL/kg, orally) markedly enhanced the hepatotoxic response to CCl4 (0.1 mL/kg, ip), as measured by serum glutamic pyruvic transaminase activity and hepatic triglyceride content. In vivo, limited formation of 3-hydroxy-2-butanone occurred after this dose of 2,3-butanediol.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
/SRP:/ 紧急急救:确保已经进行了充分的中毒物清除。如果患者停止呼吸,开始人工呼吸,最好使用需求阀复苏器、袋阀面罩装置或口袋面罩,按训练操作。根据需要执行心肺复苏。立即用缓慢流动的水冲洗受污染的眼睛。不要催吐。如果发生呕吐,让患者前倾或将其置于左侧卧位(如果可能的话,头部向下)以保持呼吸道畅通,防止窒息。保持患者安静,维持正常体温。寻求医疗救助。/高级醇(大于3个碳原子)及相关化合物/
/SRP:/ Immediate first aid: Ensure that adequate decontamination has been carried out. If patient is not breathing, start artificial respiration, preferably with a demand-valve resuscitator, bag-valve-mask device, or pocket mask, as trained. Perform CPR as necessary. Immediately flush contaminated eyes with gently flowing water. Do not induce vomiting. If vomiting occurs, lean patient forward or place on left side (head-down position, if possible) to maintain an open airway and prevent aspiration. Keep patient quiet and maintain normal body temperature. Obtain medical attention. /Higher alcohols (>3 carbons) and related compounds/
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
在受控实验中,19名严重酗酒者中有15人(79%)的血清浓度在摄入蒸馏酒后大于或等于5微摩尔/升的2,3-丁二醇,而22名对照组中只有1人。
In a controlled experiment 15 (79%) of 19 severely alcoholic men but only 1 of 22 controls had a serum concentration of greater than or equal to 5 umol/l 2,3-butanediol after ingestion of distilled spirits.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
安全信息
-
TSCA:Yes
-
安全说明:S24/25
-
WGK Germany:1
-
海关编码:29053980
-
危险品运输编号:NONH for all modes of transport
-
RTECS号:EK0532000
-
危险性防范说明:P210,P280,P370+P378,P403+P235,P501
-
危险性描述:H227,H315,H319,H335
-
储存条件:本品应密封保存于阴凉干燥处。需储存于阴凉、干燥、通风良好的库房中,并远离火种和热源,避免阳光直射。包装须密封完好。应与酸类及食用化学品分开存放,切忌混储。存储区域应备有适当的材料以收集泄漏物。
SDS
| 第一部分:化学品名称 |
| 化学品中文名称: | 2,3-丁二醇;丁二仲醇 |
| 化学品英文名称: | 2,3-Butylene glycol;2,3-Butanediol |
| 中文俗名或商品名: | |
| Synonyms: | |
| CAS No.: | 513-85-9 |
| 分子式: | C 4 H 10 O 2 |
| 分子量: | 90.12 |
| 第二部分:成分/组成信息 |
| 纯化学品 混合物 | ||||||
| 化学品名称:2,3-丁二醇;丁二仲醇 | ||||||
|
| 第三部分:危险性概述 |
| 危险性类别: | |
| 侵入途径: | 吸入 食入 |
| 健康危害: | 在生产环境中,本品蒸气对人没有危险,未见其对人有损害的报道。 |
| 环境危害: | |
| 燃爆危险: | 本品可燃。 |
| 第四部分:急救措施 |
| 皮肤接触: | 脱去污染的衣着,用流动清水冲洗。 |
| 眼睛接触: | 立即翻开上下眼睑,用流动清水冲洗。 |
| 吸入: | 脱离现场至空气新鲜处。 |
| 食入: | 误服者给饮足量温水,催吐,就医。 |
| 第五部分:消防措施 |
| 危险特性: | 遇高热、明火或与氧化剂接触,有引起燃烧的危险。若遇高热,容器内压增大,有开裂和爆炸的危险。 |
| 有害燃烧产物: | 一氧化碳、二氧化碳 |
| 灭火方法及灭火剂: | 水、雾状水、抗溶性泡沫、干粉、二氧化碳、砂土。 |
| 消防员的个体防护: | |
| 禁止使用的灭火剂: | |
| 闪点(℃): | 85 |
| 自燃温度(℃): | 引燃温度(℃):402.2 |
| 爆炸下限[%(V/V)]: | 无资料 |
| 爆炸上限[%(V/V)]: | 无资料 |
| 最小点火能(mJ): | |
| 爆燃点: | |
| 爆速: | |
| 最大燃爆压力(MPa): | |
| 建规火险分级: |
| 第六部分:泄漏应急处理 |
| 应急处理: | 切断火源。戴自给式呼吸器,穿一般消防防护服。在确保安全情况下堵漏。用大量水冲洗,经稀释的洗液放入废水系统。如大量泄漏,利用围堤收容,然后收集、转移、回收或无害处理后废弃。 |
| 第七部分:操作处置与储存 |
| 操作注意事项: | 密闭操作,提供良好的自然通风条件。操作人员必须经过专门培训,严格遵守操作规程。远离火种、热源,工作场所严禁吸烟。使用防爆型的通风系统和设备。防止蒸气泄漏到工作场所空气中。避免与氧化剂、还原剂接触。搬运时轻装轻卸,保持包装完整,防止洒漏。配备相应品种和数量的消防器材及泄漏应急处理设备。倒空的容器可能残留有害物。 |
| 储存注意事项: | 储存于阴凉、通风的库房。远离火种、热源。应与氧化剂、还原剂等分开存放,切忌混储。配备相应品种和数量的消防器材。储区应备有泄漏应急处理设备和合适的收容材料 |
| 第八部分:接触控制/个体防护 |
| 最高容许浓度: | 中 国 MAC:未制订标准前苏联MAC:未制订标准美国TLV—TWA:未制订标准美国 |
| 监测方法: | |
| 工程控制: | 提供良好的自然通风条件。 |
| 呼吸系统防护: | 一般不需要特殊防护,高浓度接触时可佩带自给式呼吸器。 |
| 眼睛防护: | 必要时戴安全防护眼镜。 |
| 身体防护: | 穿工作服。 |
| 手防护: | 必要时戴防化学品手套。 |
| 其他防护: | 工作后,淋浴更衣。避免长期反复接触。定期体检。 |
| 第九部分:理化特性 |
| 外观与性状: | 无色、液体。 |
| pH: | |
| 熔点(℃): | 23~27 |
| 沸点(℃): | 179~182 |
| 相对密度(水=1): | 1.05 |
| 相对蒸气密度(空气=1): | 3.1 |
| 饱和蒸气压(kPa): | 0.02(20℃) |
| 燃烧热(kJ/mol): | |
| 临界温度(℃): | |
| 临界压力(MPa): | |
| 辛醇/水分配系数的对数值: | |
| 闪点(℃): | 85 |
| 引燃温度(℃): | 引燃温度(℃):402.2 |
| 爆炸上限%(V/V): | 无资料 |
| 爆炸下限%(V/V): | 无资料 |
| 分子式: | C 4 H 10 O 2 |
| 分子量: | 90.12 |
| 蒸发速率: | |
| 粘性: | |
| 溶解性: | 与水混溶,溶于乙醇,微溶于乙醚。 |
| 主要用途: | 用于制备树脂和用作溶剂等。 |
| 第十部分:稳定性和反应活性 |
| 稳定性: | 在常温常压下 稳定 |
| 禁配物: | 强氧化剂、酰基氯、酸酐、氯仿、强还原剂。 |
| 避免接触的条件: | |
| 聚合危害: | 不能出现 |
| 分解产物: | 一氧化碳、二氧化碳。 |
| 第十一部分:毒理学资料 |
| 急性毒性: | 属低毒类 LD50:小鼠经口:9.1g/kg LC50: |
| 急性中毒: | |
| 慢性中毒: | |
| 亚急性和慢性毒性: | |
| 刺激性: | |
| 致敏性: | |
| 致突变性: | |
| 致畸性: | |
| 致癌性: |
| 第十二部分:生态学资料 |
| 生态毒理毒性: | |
| 生物降解性: | |
| 非生物降解性: | |
| 生物富集或生物积累性: |
| 第十三部分:废弃处置 |
| 废弃物性质: | |
| 废弃处置方法: | 处置前应参阅国家和地方有关法规。建议用焚烧法处置。 |
| 废弃注意事项: |
| 第十四部分:运输信息 |
| |
| 危险货物编号: | |
| UN编号: | |
| 包装标志: | |
| 包装类别: | |
| 包装方法: | |
| 运输注意事项: | 储存于阴凉、通风仓间内。远离火种、热源。防止阳光直射。保持容器密封。应与氧化剂、酸类分开存放。搬运时轻装轻卸,保持包装完整,防止洒漏。 |
| RETCS号: | |
| IMDG规则页码: |
| 第十五部分:法规信息 |
| 国内化学品安全管理法规: | 化学危险物品安全管理条例 (1987年2月17日国务院发布),化学危险物品安全管理条例实施细则 (化劳发[1992] 677号),工作场所安全使用化学品规定 ([1996]劳部发423号)等法规,针对化学危险品的安全使用、生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应规定。 |
| 国际化学品安全管理法规: |
| 第十六部分:其他信息 |
| 参考文献: | 1.周国泰,化学危险品安全技术全书,化学工业出版社,1997 2.国家环保局有毒化学品管理办公室、北京化工研究院合编,化学品毒性法规环境数据手册,中国环境科学出版社.1992 3.Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety,CHEMINFO Database.1998 4.Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety, RTECS Database, 1989 |
| 填表时间: | 年月日 |
| 填表部门: | |
| 数据审核单位: | |
| 修改说明: | |
| 其他信息: | 3 |
| MSDS修改日期: | 年月日 |
制备方法与用途
2,3-丁二醇简介
2,3-丁二醇是一种有机化合物,以三种立体异构体——手性对和内消旋异构体的形式存在。它常作为试剂使用,是无色液体且微溶于水、乙醇、乙醚和丙酮。该物质广泛应用于塑料和农药的制备过程中。
注意事项:在处理时应避免吸入;切勿接触眼睛、皮肤或衣服。此试剂具有吸湿性,并对空气敏感,需在干燥阴凉处并用氮气保护储存。
应用2,3-丁二醇可用于多种反应中,如对映体拆分、不对称间醇醛反应、手性缩醛的不对称断裂、手性炔基缩醛不对称β-消去、不对称烯丙基化、手性二烯缩醛环化以及对映选择性环氧化等。
化学性质2,3-丁二醇为无色结晶固体或粘稠液体,熔点在23至27℃之间,沸点179至182℃,相对密度1.045(20/20℃),折射率1.438。其闪点为85℃,能与水混溶,并溶解于醇和醚中。此物质具有吸湿性。
用途在生产过程中,可以通过硫酸作催化剂,在140至150℃条件下反应2小时生成2,3-丁二醇二乙酸酯,可作为奶油添加剂、吸湿剂、增塑剂及偶联剂使用。此外,也可用作溶剂和合成树脂的原料。
生产方法通过生物发酵法将糖类、糖蜜、麦芽浆或酵母液等为原料生产2,3-丁二醇,在酒精制备过程中副产乙醛可被酵母菌转化为此物质。
安全信息 类别易燃液体
毒性分级低毒
急性毒性口服 - 大鼠LD50:5462毫克/公斤
可燃性危险特性遇明火、高温或强氧化剂可燃;燃烧时会排放刺激烟雾。
储运特性库房应通风干燥并低温保存
灭火剂上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 (2R,3R)-(-)-2,3-丁二醇 (R,R)-2,3-butandiol 24347-58-8 C4H10O2 90.1222 1,2-丙二醇 1,2-Propanediol 57-55-6 C3H8O2 76.0953 1,2,3-丁三醇 butane-1,2,3-triol 4435-50-1 C4H10O3 106.122 甘油 glycerol 56-81-5 C3H8O3 92.0947 1,2,4-丁三醇 D,L-1,2,4-butanetriol 3068-00-6 C4H10O3 106.122 赤藓醇 1,2,3,4-butanetetrol 7541-59-5 C4H10O4 122.121 —— Erythritol 149-32-6 C4H10O4 122.121 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— (2R,3S)-2,3-butanediol 5341-95-7 C4H10O2 90.1222 (2S,3S)-(+)-2,3-丁二醇 (2S,3S)-2,3-butanediol 19132-06-0 C4H10O2 90.1222 仲丁醇 iso-butanol 78-92-2 C4H10O 74.1228 2-甲基丁烷-2,3-二醇 2-methyl-2,3-butanediol 5396-58-7 C5H12O2 104.149 —— (+)-(2R,3S)-3-methoxy-2-butanol 336620-64-5 C5H12O2 104.149
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:一系列N-未取代的氨基磺酸盐的男性合成和抗雄性评估。摘要:已经合成了一系列六种脂族和一个碳环N-未取代的氨基磺酸盐,并被评估为潜在的雄性抗生育剂。当对雄性大鼠口服给药时,脂族氨基磺酸盐中的三种,1,2-乙二氨基磺酸盐(1),1,3-丙二氨基磺酸盐(2)和1,4-丁二氨基磺酸盐(3)导致数量减少。怀孕的女性和/或植入,以及增加的胚胎和胎儿吸收。通过用氨磺酰氯处理适当的乙二醇盐或通过用三氟乙酸裂解氨基磺酸叔丁基酯来制备化合物。DOI:10.1021/jm00139a029
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:Harden; Norris, Chemisches Zentralblatt, 1912, vol. 83, # I, p. 1045,2051摘要:DOI:
-
作为试剂:描述:8-氨基喹啉 、 3-戊烯酸 在 吡啶 、 bis(η3-allyl-μ-chloropalladium(II)) 、 lithium acetate 、 水 、 N-[(dimethylamino)-3-oxo-1H-1,2,3-triazolo[4,5-b]pyridin-1-yl-methylene]-N-methylmethanaminium hexafluorophosphate 、 2-(二环己基膦酰基)-1-苯基-1H-吡咯 、 2,3-丁二醇 作用下, 以 二氯甲烷 为溶剂, 反应 18.0h, 生成 4-phenyl-N-(quinolin-8-yl)pentanamide参考文献:名称:未活化的脂肪族烯烃与有机卤化物的分子间还原性Heck反应。摘要:首先以高收率和完全的反马尔科夫尼科夫选择性实现了有机卤化物与末端和内部未活化的脂肪族烯烃的一般分子间还原性Heck反应。首先应用了具有挑战性的乙烯基溴化物,芳基氯和多取代的内部烯烃。从易于获得的起始原料中快速合成了100多种远程碳官能化的烷基羧酸衍生物。药物分子的合成进一步证明了这种可扩展策略的广泛合成效用。初步的机理研究与所提出的催化循环一致。DOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.9b04474
文献信息
-
Novel synthesis of 2H-1,5-benzoxathiepin-3(4H)-one and 5H-4,1-benzoxathiepin-3(2H)-one derivatives and chemical properties evaluation作者:Taras M. Tarasiuk、Olena O. Shyshkina、Yulian M. Volovenko、Volodymyr V. Medviediev、Tetiana A. Volovnenko、Oleg V. ShishkinDOI:10.1007/s00706-015-1500-1日期:2015.10for the synthesis of 2H-1,5-benzoxathiepin-3(4H)-one and 5H-4,1-benzoxathiepin-3(2H)-one derivatives have been developed. Carbonyl group of 2H-1,5-benzoxathiepin-3(4H)-one has been protected by cyclic and acyclic ketals. Interaction of 2H-1,5-benzoxathiepin-3(4H)-one with NaBH4, hydroxylamine, hydrazines, and Br2 has been investigated. Strecker reaction has been carried out for the synthesis of corresponding摘要已开发出合成2 H -1,5-苯并氧杂噻吩-3(4 H)-one和5 H -4,1-苯并氧杂噻吩-3(2 H)-one衍生物的新方法。2 H -1,5-benzoxathiepin-3(4 H)-one的羰基已被环状和非环状缩酮保护。研究了2 H -1,5-benzoxathiepin-3(4 H)-one与NaBH 4,羟胺,肼和Br 2的相互作用。进行了Strecker反应以合成相应的α-氨基酸。Horner-Wadsworth-Emmons和Michael反应的结合可以得到β-取代的羧酸的衍生物。另外,2 H -1,5-苯并噻吩-3(4 H)-1参与了Johnson-Corey-Chaykovsky反应。 图形概要
-
Substituted diether diols by ring-opening of carbocyclic and stannylene acetals作者:Rolando Martínez-Bernhardt、Peter P. Castro、Gayane Godjoian、Carlos G. GutiérrezDOI:10.1016/s0040-4020(98)00563-8日期:1998.7Reduction of malonaldehyde bis(ethylene and propylene acetals) with borane or monochloroborane produces diether diols 1 and 2 in high yield. Similar reduction of glyoxal bis(ethylene acetals) has only limited utility for the preparation of tetrasubstituted triethylene glycols 3. Organotin chemistry is complementary: stannylene acetals prepared from disubstituted vicinal diols can be alkylated with half
-
Total synthesis, antiprotozoal and cytotoxicity activities of rhuschalcone VI and analogs作者:Shetonde O. Mihigo、Wendimagegn Mammo、Merhatibeb Bezabih、Kerstin Andrae-Marobela、Berhanu M. AbegazDOI:10.1016/j.bmc.2010.02.055日期:2010.4The total synthesis of a potent antiplasmodial natural bichalcone, rhuschalcone VI, is described starting from simple and available resorcinol and 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde. Key steps include the solvent-free Aldol syntheses of chalcones, and the successful application of the Suzuki–Miyaura coupling reaction in the synthesis of bichalcones. The present work constitutes a general method for the rapid syntheses
-
Purification and Characterization of an NADH-Dependent Alcohol Dehydrogenase from<i>Candida maris</i>for the Synthesis of Optically Active 1-(Pyridyl)ethanol Derivatives作者:Shigeru KAWANO、Miho YANO、Junzo HASEGAWA、Yoshihiko YASOHARADOI:10.1271/bbb.100528日期:2011.6.23A novel (R)-specific alcohol dehydrogenase (AFPDH) produced by Candida maris IFO10003 was purified to homogeneity by ammonium sulfate fractionation, DEAE-Toyopearl, and Phenyl-Toyopearl, and characterized. The relative molecular mass of the native enzyme was found to be 59,900 by gel filtration, and that of the subunit was estimated to be 28,900 on SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. These results suggest that the enzyme is a homodimer. It required NADH as a cofactor and reduced various kinds of carbonyl compounds, including ketones and aldehydes. AFPDH reduced acetylpyridine derivatives, β-keto esters, and some ketone compounds with high enantioselectivity. This is the first report of an NADH-dependent, highly enantioselective (R)-specific alcohol dehydrogenase isolated from a yeast. AFPDH is a very useful enzyme for the preparation of various kinds of chiral alcohols.一种由Candida maris IFO10003产生的新型(R)-特异性醇脱氢酶(AFPDH)通过硫酸铵分级、DEAE-Toyopearl和Phenyl-Toyopearl纯化至均一,并进行了表征。通过凝胶过滤法测得该酶的原分子质量为59,900,而在SDS-聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳中亚基的估计分子质量为28,900。这些结果表明该酶为同源二聚体。它需要NADH作为辅因子,并能还原包括酮和醛在内的多种羰基化合物。AFPDH能高对映选择性地还原乙酰吡啶衍生物、β-酮酯和某些酮化合物。这是首例从酵母中分离出的依赖NADH的高对映选择性(R)-特异性醇脱氢酶的报道。AFPDH对于制备多种手性醇是非常有用的酶。
-
Biomass into chemicals: One-pot two- and three-step synthesis of quinoxalines from biomass-derived glycols and 1,2-dinitrobenzene derivatives using supported gold nanoparticles as catalysts作者:M.J. Climent、A. Corma、J.C. Hernández、A.B. Hungría、S. Iborra、S. Martínez-SilvestreDOI:10.1016/j.jcat.2012.05.002日期:2012.8one-pot two-step method, for the synthesis of quinoxalines by oxidative coupling of vicinal diols with 1,2-phenylenediamine derivatives, has been developed by using gold nanoparticles supported on nanoparticulated ceria (Au/CeO2) or hydrotalcite (Au/HT) as catalysts and air as oxidant, in the absence of any homogeneous base. Reaction kinetics shows that the reaction controlling step is the oxidation of
表征谱图
-
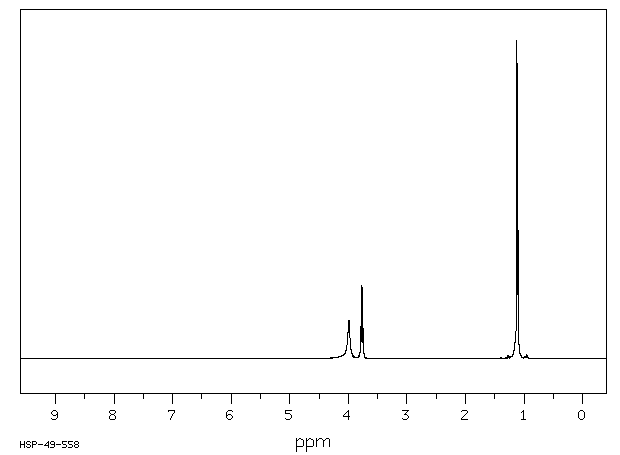
氢谱1HNMR
-
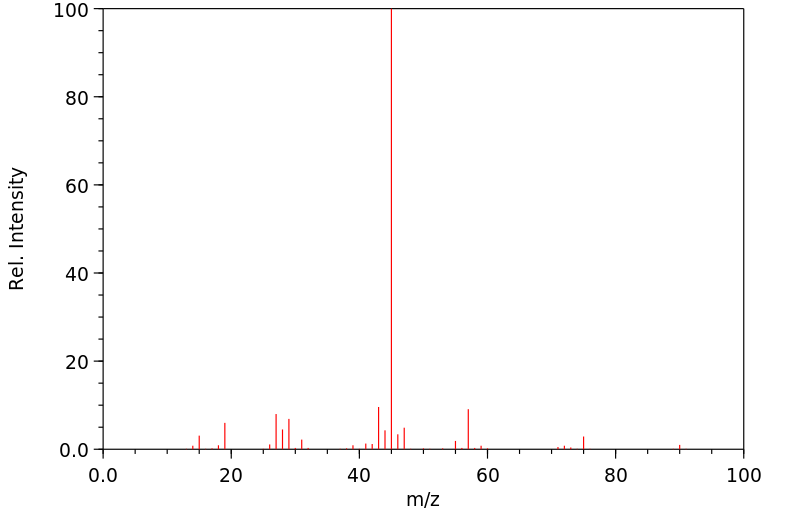
质谱MS
-
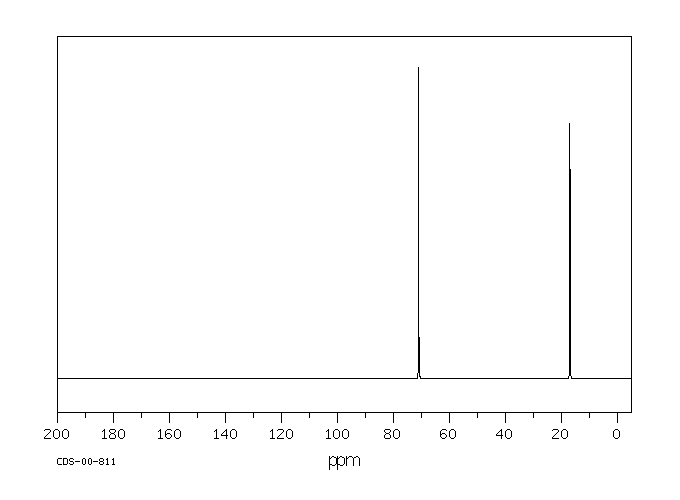
碳谱13CNMR
-
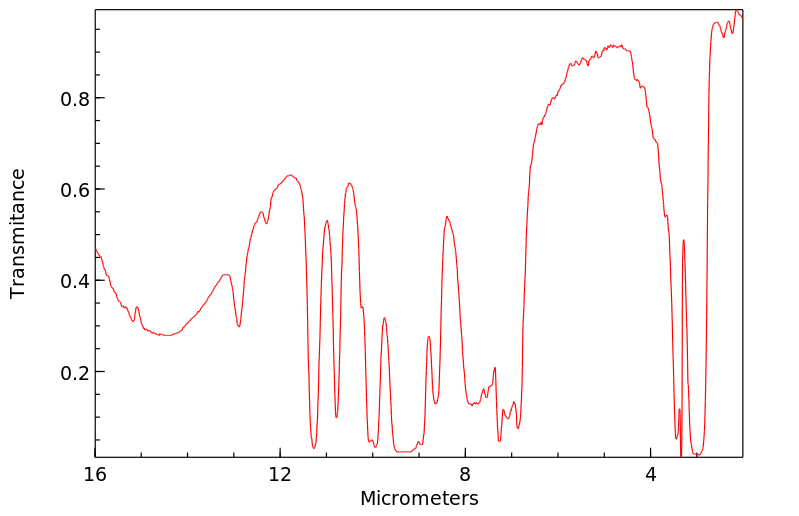
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(反式)-4-壬烯醛
(s)-2,3-二羟基丙酸甲酯
([1-(甲氧基甲基)-1H-1,2,4-三唑-5-基](苯基)甲酮)
(Z)-4-辛烯醛
(S)-氨基甲酸酯β-D-O-葡糖醛酸
(S)-3-(((2,2-二氟-1-羟基-7-(甲基磺酰基)-2,3-二氢-1H-茚满-4-基)氧基)-5-氟苄腈
(R)-氨基甲酸酯β-D-O-葡糖醛酸
(5,5-二甲基-2-(哌啶-2-基)环己烷-1,3-二酮)
(2,5-二氟苯基)-4-哌啶基-甲酮
龙胆苦苷
龙胆二糖甲乙酮氰醇(P)
龙胆二糖丙酮氰醇(P)
龙胆三糖
龙涎酮
齐罗硅酮
齐留通beta-D-葡糖苷酸
鼠李糖
黑芥子苷单钾盐
黑海棉酸钠盐
黑木金合欢素
黑曲霉三糖
黑介子苷
黄尿酸8-O-葡糖苷
麻西那霉素II
麦迪霉素
麦芽糖脎
麦芽糖基海藻糖
麦芽糖1-磷酸酯
麦芽糖
麦芽四糖醇
麦芽四糖
麦芽十糖
麦芽六糖
麦芽五糖水合物
麦芽五糖
麦芽五糖
麦芽五糖
麦芽三糖醇
麦芽三糖
麦芽三糖
麦芽三塘水合
麦芽七糖水合物
麦芽七糖
麦法朵
麦可酚酸-酰基-Β-D-葡糖苷酸
麦利查咪
麝香酮
鹤草酚
鸢尾酚酮 3-C-beta-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷
鸡矢藤苷